Characterization of Luminescent Materials with 151Eu Mössbauer Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
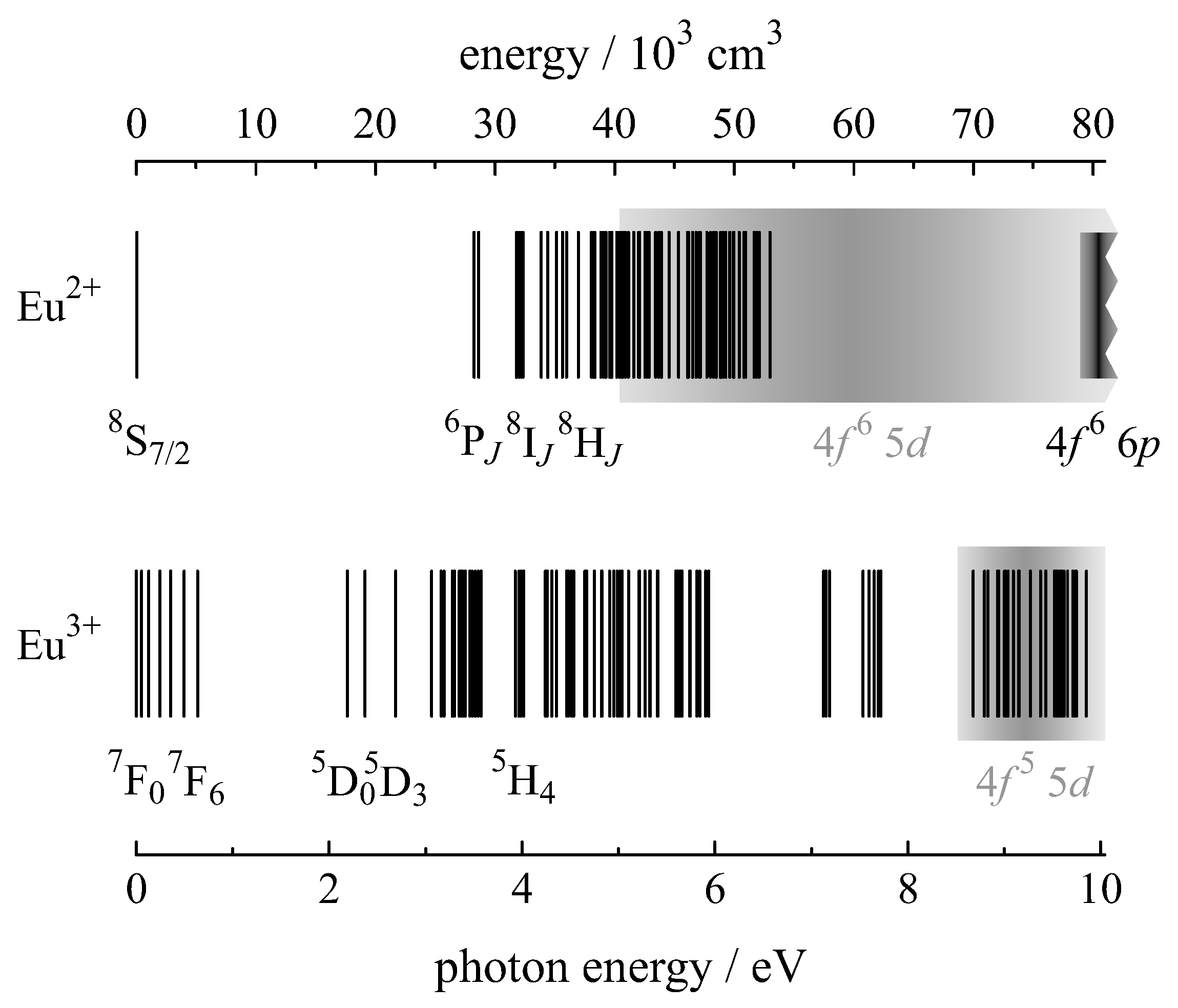
2. The Lanthanide Ions Eu/Eu and Their Optical Properties
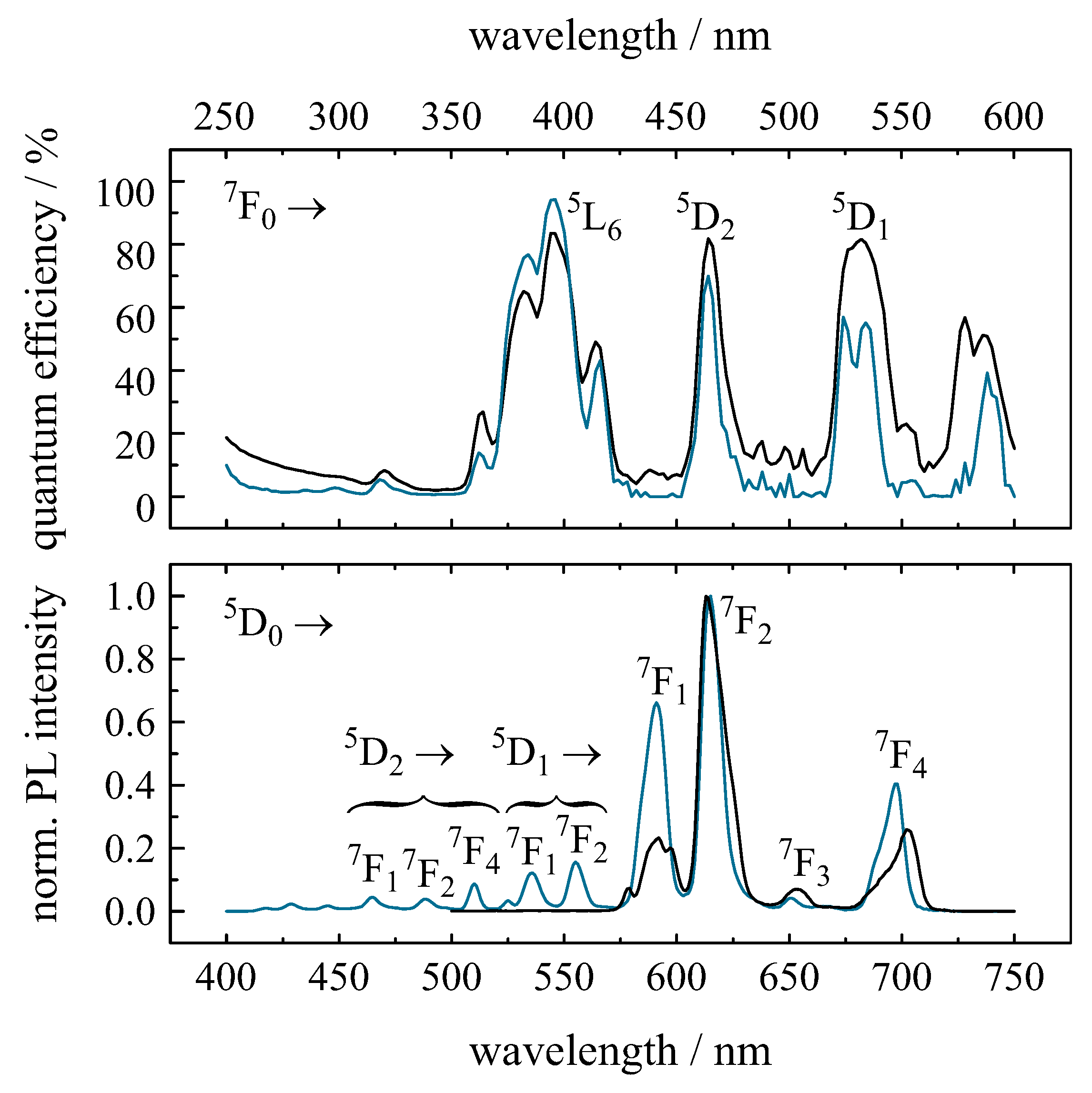
2.1. Optical Properties of Eu
2.1.1. Eu in Luminescent Fluoride and Oxide Glasses
2.1.2. Eu in (Persistent) Phosphors/Aluminates
2.1.3. Eu in Other Luminescent Materials
2.2. Optical Properties of Eu
2.2.1. Eu in Luminescent Glasses
2.2.2. Eu in Lanthanide Oxides
2.2.3. Eu in Other Luminescent Materials
3. Europium Mössbauer Spectroscopy
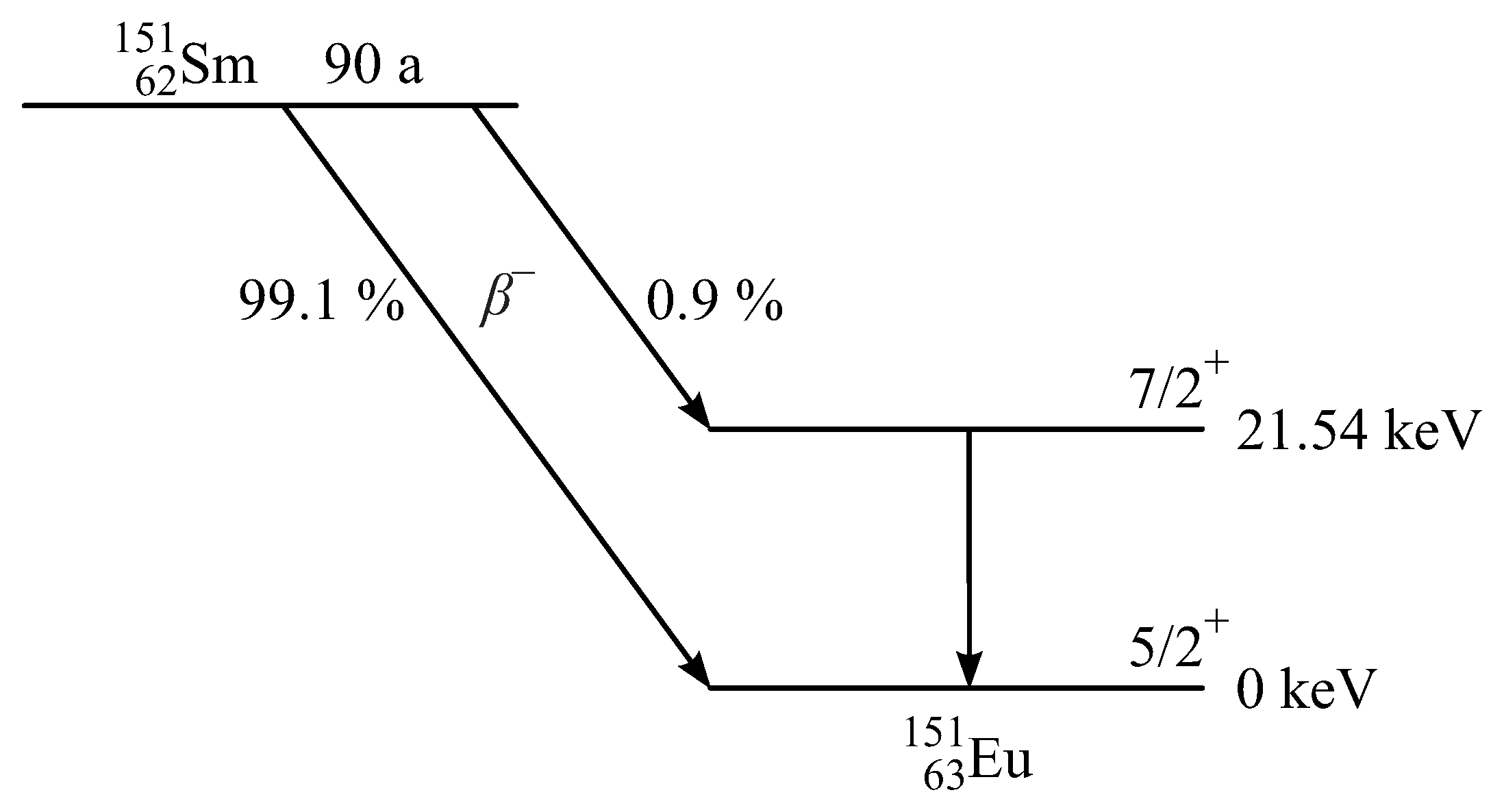
3.1. Mössbauer Isotope 151Eu
3.2. Isomer Shift
3.3. Quadrupole Interaction
3.4. Magnetic Hyperfine Interaction
3.5. Linewidth (FWHM)
4. Materials Overview
4.1. Fluorides
4.2. Fluorochlorozirconate (FCZ) Glasses
4.3. Aluminates
4.4. Oxide Glasses
4.5. Lanthanides and Related Compounds Sc2O3, Y2O3, In2O3
4.6. Vanadates
4.7. Titanates
4.8. Nitrides
4.9. Sulfides
4.10. ZrO2
4.11. Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG:Eu)
4.12. Discussion
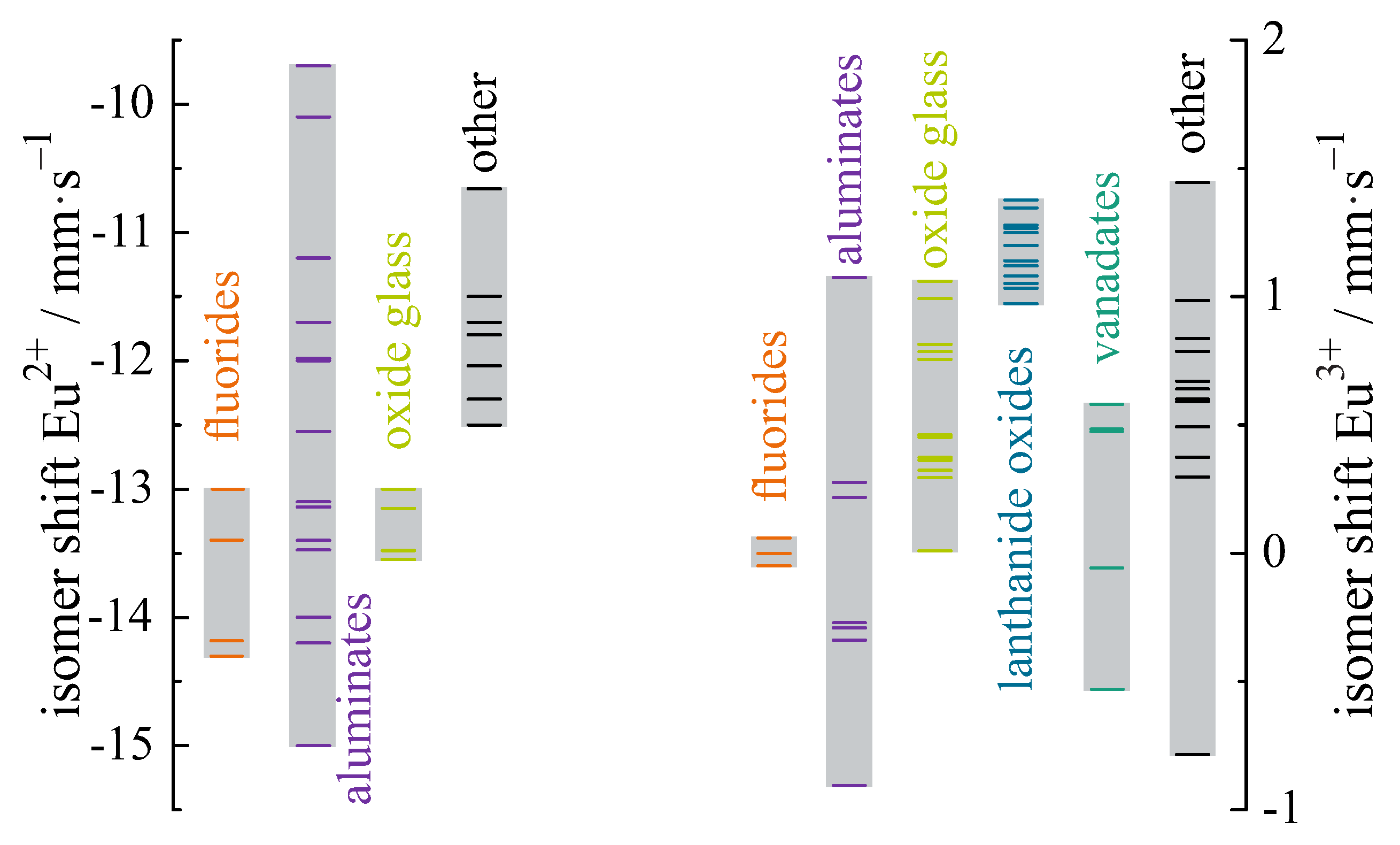
4.12.1. Correlation of Isomer Shift with Bond Length and Covalency
4.12.2. Determination of Site Occupancies
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blasse, G.; Grabmaier, B.C. Luminescent Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Cui, Q.; Yang, B. Eu3+-doped Bi4Si3O12 red phosphor for solid state lighting: Microwave synthesis, characterization, photoluminescence properties and thermal quenching mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradal, N.; Potdevin, A.; Chadeyron, G.; Bonville, P.; Caillier, B.; Mahiou, R. Spectroscopic study and enhanced thermostability of combustion-derived BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ blue phosphors for solid-state lighting. Opt. Mater. 2017, 64, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyver, J.F.; Meijerink, A. Europium safeguards the euro. Chemisch2Weekblad 2002, 98, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Furniss, D.; Harris, E.A.; Hollis, D.B. EPR of Gd3+ and Eu2+ in fluorozirconate glasses. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1987, 20, L147–L150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Newman, P.J.; Cashion, J.D.; Edgar, A. In situ generation of Eu2+ in glass-forming melts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 256–257, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthout, K.; Van den Eeckhout, K.; Botterman, J.; Nikitenko, S.; Poelman, D.; Smet, P.F. Luminescence and X-ray absorption measurements of persistent SrAl2O4:Eu,Dy powders: Evidence for valence state changes. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 085140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthout, K.; Parmentier, A.B.; Smet, P.F.; Poelman, D. A XAS study of the luminescent Eu centers in thiosilicate phosphors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 8678–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mössbauer, R.L. Kernresonanzfluoreszenz von Gammastrahlung in Ir191. Z. Phys. 1958, 151, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvius, M.; Kienle, P. (Eds.) The Rudolf Mössbauer Story—His Scientific Work and Its Impact on Science and History; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F.; Long, G.J. Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry. In Modern Inorganic Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; Chapter Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Europium-Containing Compounds; pp. 513–597. [Google Scholar]
- Mössbauer Effect Data Center. Available online: http://www.medc.dicp.ac.cn (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Gonser, U. Application of the Mössbauer effect in materials science. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1968, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woude, F.V.D.; Sawatzky, G. Mössbauer effect in iron and dilute iron based alloys. Phys. Rep. 1974, 12, 335–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkjian, C. Mössbauer spectroscopy in inorganic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1970, 3, 157–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Warmuth, W.; Eckert, H. Nuclear magnetic-resonance and Mössbauer spectroscopy of glasses. Phys. Rep. 1982, 88, 91–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Johnson, C.E. Mössbauer spectroscopy as a probe of silicate glasses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandelia, M.E.; Lanz, N.D.; Booker, S.J.; Krebs, C. Mössbauer spectroscopy of Fe/S proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boncher, W.; Dalafu, H.; Rosa, N.; Stoll, S. Europium chalcogenide magnetic semiconductor nanostructures. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289–290, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieke, G.H.; Crosswhite, H.M. The Spectra of the Doubly and Triply Ionized Rare Earths. Appl. Opt. 1963, 2, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.C.; Zalubas, R.; Hagan, L. Atomic Energy Levels—The Rare-Earth Elements: The Spectra of Lanthanum, Cerium, Praseodymium, Neodymium, Promethium, Samarium, Europium, Gadolinium, Terbium, Dysprosium, Holmium, Erbium, Thulium, Ytterbium, and Lutetitum; U.S. Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Liu, G. Advances in the theoretical understanding of photon upconversion in rare-earth activated nanophosphors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1635–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, M.; Poulain, M.; Lucas, J.; Brun, P. Verres fluores au tetrafluorure de zirconium proprietes optiques d’un verre dope au Nd3+. Mater. Res. Bull. 1975, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digonnet, M.J.F. (Ed.) Rare-Earth-Doped Fiber Lasers and Amplifiers, Revised and Expanded; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Peyghambarian, N. High-Power ZBLAN Glass Fiber Lasers: Review and Prospect. Adv. OptoElectron. 2010, 2010, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandrelli, E. Made in Space Plans to Create a Superior Optical Fiber in Microgravity. Available online: https://techcrunch.com/2016/07/13/made-in-space-plans-to-create-a-superior-optical-fiber-in-microgravity/ (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Schweizer, S.; Hobbs, L.W.; Secu, M.; Spaeth, J.M.; Edgar, A.; Williams, G.V.M. Photostimulated luminescence in Eu-doped fluorochlorozirconate glass ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.E.; Vu, M.; Johnson, J.A.; Brown, D.E.; Weber, J.K.R.; Paßlick, C.; Schweizer, S. Mössbauer spectroscopy of europium-containing glasses: optical activator study for X-ray image plates. Hyperfine Interact. 2014, 226, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, E.; Hesselink, L.; Ralston, J.; Macfarlane, R. A three-color, solid-state, three-dimensional display. Science 1996, 273, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupke, T.; Green, M.A.; Würfel, P. Improving solar cell efficiencies by up-conversion of sub-band-gab light. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, B.; Löper, P.; Goldschmidt, J.C.; Glunz, S.; Henke, B.; Miclea, P.T.; Schweizer, S. Neodymium-doped fluorochlorozirconate glasses as an upconversion model system for high efficiency solar cells. Phys. Status Solidi A 2008, 205, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Schweizer, S.; Henke, B.; Chen, G.; Woodford, J.; Newman, P.J.; MacFarlane, D.R. Eu-activated fluorochlorozirconate glass-ceramic scintillators. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Schweizer, S.; Lubinsky, A.R. A Glass-Ceramic Plate for Mammography. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, S.; Hobbs, L.W.; Secu, M.; Spaeth, J.M.; Edgar, A.; Williams, G.V.M.; Hamlin, J. Photostimulated luminescence from fluorochlorozirconate glass ceramics and the effect of crystallite size. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, M.W.; Suits, J.C. Preparation and Faraday Rotation of Divalent Europium Glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1966, 49, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tanaka, K.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Borate Glasses Containing Divalent Europium Ions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangleiter, T.; Koschnick, F.K.; Spaeth, J.M.; Nuttall, R.H.D.; Eachus, R.S. Temperature dependence of the photostimulated luminescence of X-irradiate BaFBr:Eu2+. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1990, 2, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gecevicius, M.; Qiu, J. Long persistent phosphors - from fundamentals to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2090–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Hernandez, R.E.; Rubio-Marcos, F.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Fernandez, J.F. Long lasting phosphors: SrAl2O4:Eu, Dy as the most studied material. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2759–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsinelis, S.; Kitsinelis, S. Light Sources, Second Edition: Basics of Lighting Technologies and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.S. (Ed.) Phosphors, up Conversion Nano Particles, Quantum Dots and Their Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hölsä, J.; Aitasalo, T.; Jungner, H.; Lastusaari, M.; Niittykoski, J.; Spano, G. Role of defect states in persistent luminescence materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 374, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitasalo, T.; Dereń, P.; Hölsä, J.; Jungner, H.; Krupa, J.C.; Lastusaari, M.; Legendziewicz, J.; Niittykoski, J.; Strȩk, W. Persistent luminescence phenomena in materials doped with rare earth ions. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 171, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.X.; Chang, C.K.; Mao, D.L.; Ying, W. Effect of composition on the luminescent properties of Sr4Al14O25: Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 377, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabau, F.; Garcia, A.; Bonville, P.; Gonbeau, D.; Mercier, T.L.; Deniard, P.; Jobic, S. Fluorescence and phosphorescence properties of the low temperature forms of the MAl2Si2O8:Eu2+ (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.K.; Kurchania, R. Synthesis and thermoluminescence properties of SrAl2O4 (EU) phosphor irradiated with cobalt-60, 6 MV and 16 MV photon beams. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 117, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.; Rennie, J. Thermoluminescence dosimetry using doped calcium sulphide. J. Cryst. Growth 1988, 86, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title, R.S. Paramagnetic Resonance Detection of the Optical Excitation of an Infrared Stimulable Phosphor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1959, 3, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, R.; Chen, I.W. (Eds.) Ceramics Science and Technology, Volume 1: Structures; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zeuner, M.; Pagano, S.; Matthes, P.; Bichler, D.; Johrendt, D.; Harmening, T.; Pöttgen, R.; Schnick, W. Mixed Valence Europium Nitridosilicate Eu2SiN3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11242–11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Kate, O.M.; Vranken, T.; van der Kolk, E.; Jansen, A.P.; Hintzen, H.T. Optical properties of Eu2+/Eu3+ mixed valence, silicon nitride based materials. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 213, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, F.; Oeckler, O.; Höppe, H.A.; Möller, M.H.; Pöttgen, R.; Mosel, B.D.; Schmidt, P.; Duppel, V.; Simon, A.; Schnick, W. Crystal Structure, Physical Properties and HRTEM Investigation of the New Oxonitridosilicate EuSi2O2N2. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 6984–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintzen, H.T.; Van Hal, H.A.M.; Langereis, C.; Denissen, C.J.M. Crystal chemistry of BaCa2Ln6O12 (Ln = In, Sc, Y, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) and luminescence of europium- and terbium-activated BaCa2Y6O12. J. Less Common Met. 1989, 155, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zych, E.; Meijerink, A.; de Mello Donegá, C. Quantum efficiency of europium emission from nanocrystalline powders of Lu2O3:Eu. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Chen, B.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Lu, S.; Lai, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Di, W.; et al. Fluorescence lifetime and quantum efficiency of Y2O3:Eu nanocrystals. In Proceedings of the ICO20: Display Devices and Systems, Changchun, China, 21–26 August 2005; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 6030, pp. 60300I-1–60300I-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, F.; Loos, S.; Ahrens, B.; Schweizer, S. Quantum efficiency and energy transfer processes in rare-earth doped borate glass for solid-state lighting. J. Lumin. 2016, 170, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, S.; Steudel, F.; Ahrens, B.; Leonard, R.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Schweizer, S. Temperature-dependent luminescence of Tb3+ and Eu3+ single-doped glasses for LED applications. Phys. Status Solidi C 2015, 12, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetenkamp, L.; West, G.; Többen, H. Co-doping effects in erbium3+- and holmium3+-doped ZBLAN glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 140, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmon, G.; Sato, H.; Ohya, J.; Fujita, T. Energy transfer in Tm:Eu codoped fluorozirconate fiber. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 1528–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, F.; Loos, S.; Ahrens, B.; Schweizer, S. Luminescent borate glass for efficiency enhancement of CdTe solar cells. J. Lumin. 2015, 164, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, P. Efficiency stokes shifting luminescent materials: Ce3+-Tb3+-Eu3+ toward solar energy applications. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 11417–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Rocha, A.; Lozada-Morales, R.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Caldiño, U. White light generation in Tb3+/Eu3+/Dy3+ triply-doped Zn(PO3)2 glass. Opt. Mater. 2016, 51, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, J.M.F.; Schuurmans, M.F.H. On the nonradiative and radiative decay rates and a modified exponential energy gap law for 4f–4f transitions in rare earth ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 78, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojiya, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kanno, R.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kadono, K. Optical transitions of Er3+ ions in ZnCl2-based glass. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 6259–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendow, B.; Banerjee, P.K.; Drexhage, M.G.; Goltman, J.; Mitra, S.S.; Moynihan, C.T. Comparative study of vibrational characteristics of fluorozirconate and fluorohafnate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1982, 65, C8–C9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, H.; van Noort, H. Investigation of luminescent Eu-doped sesquioxides Ln2O3 (Ln = In, Sc, Y, La, Gd, Lu) and some mixed oxides by 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1988, 49, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohus, G.; Hornok, V.; Oszkó, A.; Vértes, A.; Kuzmann, E.; Dékány, I. Structural and luminescence properties of Y2O3:Eu3+ core-shell nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2012, 405, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, R.; Lempicki, A.; Kappers, L.; Hamilton, D. Hole traps in Lu2O3:Eu ceramic scintillators. II. Radioluminescence and thermoluminescence. J. Lumin. 2004, 106, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zych, E.; Trojan-Piegza, J.; Kępiński, L. Homogeneously precipitated Lu2O3:Eu nanocrystalline phosphor for X-ray detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 109, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkoç, H. Handbook of Nitride Semiconductors and Devices: GaN-Based Optical and Electronic Devices; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, R.A.; Desai, S.K.; Allison, S.W.; Heyes, A.L.; Walker, D.G. Emission lifetimes of europium-doped pyrochlores for phosphor thermometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 016101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Cheng, K.; Weng, W.; Song, C.; Du, P.; Shen, G.; Xu, G.; Han, G. Enhanced Luminescence of Eu-Doped TiO2 Nanodots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frindell, K.L.; Bartl, M.H.; Popitsch, A.; Stucky, G.D. Sensitized Luminescence of Trivalent Europium by Three-Dimensionally Arranged Anatase Nanocrystals in Mesostructured Titania Thin Films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shionoya, S.; Yen, W.M.; Yamamoto, H. (Eds.) Phosphor Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shirmane, L.; Feldmann, C.; Pankratov, V. Comparing the luminescence processes of YVO4:Eu and core-shell YVO4@YF3 nanocrystals with bulk-YVO4:Eu. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 504, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaume, D.; Buissette, V.; Lahlil, K.; Gacoin, T.; Boilot, J.P.; Casanova, D.; Beaurepaire, E.; Sauviat, M.P.; Mercuri, A.; Alexandrou, A. New biological labels based on functionalized YVO4:Eu nanoparticles. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2004, 845, AA6.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shao, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of lanthanide orthovanadate: EuVO4 particles and their fluorescence application. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 8033–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, K.; Grigorjeva, L.; Millers, D.; Sarakovskis, A.; Opalinska, A.; Fidelus, J.D.; Lojkowski, W. Europium doped zirconia luminescence. Opt. Mater. 2010, 32, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, R.K.; Bisen, D.P.; Upadhyay, K. Photoluminescence behavior of ZrO2:Eu3+ with variable concentration of Eu3+ doped phosphor. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, S.; Georgescu, S.; Bibicu, I.; Chinie, A.A.; Stefan, A.S.; Toma, O. Mossbauer and optical investigation of Eu:YAG nanocrystals synthesized by a sol-gel method. Rom. J. Phys. 2007, 52, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Lv, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, S. Combination of translucent Eu:YAG glass ceramic with LED chip. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 62nd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2012; pp. 2145–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mössbauer Effect Data Center. 151Eu Isotope Properties. Available online: http://www.medc.dicp.ac.cn/Resources-isotopes/Resource-Eu.php (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Bibicu, I.; Cretu, C. Mössbauer backscattering measurements on Eu-151. Rom. J. Phys. 2009, 54, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Bibicu, I. Some comments on 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopy. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 62, 11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Congiu, F.; Spano, G.; Bettinelli, M.; Speghini, A. Mössbauer Investigation of Eu3+ Site Occupancy and Eu–O Covalency in Y2O3 and Gd2O3 Nanocrystals. Z. Naturforsch. 2001, 56, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.L.; Sleight, A.W. Mössbauer effect studies of europium pyrochlores. Phys. Rev. B 1978, 18, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.P.; Friedt, J.M.; Westerholt, K.; Bach, H. 151Eu Mössbauer study of the EuxLa1−xS solid solution. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 4514–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Nagy, S.; Nomura, K. Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; Chapter Mössbauer Spectroscopy; pp. 1379–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Congiu, F.; Spano, G.; Speghini, A.; Gatterer, K. Mössbauer investigation of rare earth sites in europium containing glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 232–234, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.K.R.; Vu, M.; Paßlick, C.; Schweizer, S.; Brown, D.E.; Johnson, C.E.; Johnson, J.A. The oxidation state of europium in halide glasses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 495402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selling, J.; Bielemeier, B.; Wortmann, G.; Johnson, J.A.; Alp, E.E.; Chen, T.; Brown, D.E.; Johnson, C.E.; Schweizer, S. Paramagnetic hyperfine splitting in the 151Eu Mössbauer spectra of CaF2:Eu2+. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 224442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coey, J.M.D.; McEvoy, A.; Shafer, M.W. Mössbauer study of europium in fluorozirconate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1981, 43, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, C.; Paßlick, C.; Gray, S.K.; Johnson, J.A.; Johnson, C.E.; Schweizer, S. Mössbauer spectroscopy of europium-doped fluorochlorozirconate glasses and glass ceramics: optimization of storage phosphors in computed radiography. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 205402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Nagata, N. Luminescence properties of A1−xEuxAl12O19S6 (A=Ca, Sr, Ba). J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408–412, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Fuchigami, H. Preparation and Europium-151 Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Ca1−xEuxAl12O19. Hyperfine Interactions (C); Thomas, M.F., Williams, J.M., Gibb, T.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, K.; Tokuhara, Y.; Wakeshima, M.; Shan, Y.J.; Imoto, H.; Hinatsu, Y. Crystal Structures and Properties of Europium Aluminum Oxynitride Eu2AlO3.75N0.1 and Europium Aluminum Oxide EuAl2O4. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 12972–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boolchand, P.; Mishra, K.C.; Raukas, M.; Ellens, A.; Schmidt, P.C. Occupancy and site distribution of europium in barium magnesium aluminate by 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 134429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronc, E.; Saber, D.; Lejus, A.M.; Vivien, D. 151Eu Mössbauer investigation of La1−xEuxMgAl11O19. J. Less Common Met. 1985, 111, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraknóy-Körös, V.; Gelencsér, P.; Nagy, I.C.; Vértes, A. Application of Mössbauer spectroscopy to investigate different europium(II) and (III)-activated phosphors. Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett. 1980, 44, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Hintzen, H.T.; Denissen, C.J.M.; van Noort, H.M. 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopic study of the phosphor SrAl12O19:Eu with the magnetoplumbite structure. Mater. Res. Bull. 1989, 24, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winterer, M.; Mörsen, E.; Mosel, B.D.; Müller-Warmuth, W. Paramagnetic hyperfine structure in 151Eu Mössbauer spectra of Eu2+ ions in borate glasses. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1987, 20, 5389–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Thi, M.; Ruelle, N.; Tronc, E.; Simons, D.; Vivien, D. Electron Spin Resonance and Mössbauer Studies of CaS:Eu Synthesized Using the Flux Method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 33, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.E.; Costa, L.; Johnson, J.A.; Brown, D.E.; Somarajan, S.; He, W.; Dickerson, J.H. Mössbauer spectra and superparamagnetism of europium sulfide nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnik, Z.M.; Stroink, G.; Arakawa, T. Quadrupole interactions at divalent and trivalent europium sites in several europium oxides. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 22, 12552–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningthoujam, R.; Sudarsan, V.; Vatsa, R.; Kadam, R.; Jagannath; Gupta, A. Photoluminescence studies on Eu doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 486, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. Local structure of rare-earth ions in fluorophosphate glasses by phonon sideband and mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 142, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, G. Mössbauer study of amorphous Al2O3:Eu3+. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1997, 16, 743–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, C.; Long, Y. Synthesis, characterization of an AlPO-CJ2 analogue containing heteroatomic Eu. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2064–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taragin, M.F.; Eisenstein, J.C. Mössbauer-Effect Study of Europium in Glass. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 2, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musić, S.; Bajs, Z.; Furić, K.; Mohac̆ek, V. Mössbauer and vibrational spectra of sodium borosilicate glasses containing europium or tin ions. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Hanada, T.; Ohyagi, T.; Soga, N. Correlation between 151Eu Mössbauer isomer shift and Judd-Ofelt Ω6 parameters of Nd3+ ions in phosphate and silicate laser glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 10591–10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, E.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Hening, A.; Vlad, V.I.; Tugulea, L.; Diamandescu, L.; Bibicu, I.; Chipara, M. Three-dimensional memory effect in fluorescent photosensitive glass activated by europium and cerium. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Hirao, K.; Soga, N. Mössbauer spectroscopy of 151Eu in oxide crystals and glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1989, 113, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Congiu, F.; Muntoni, C.; Bettinelli, M.; Speghini, A. Hyperfine interactions at europium sites in oxide glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 6197–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmann, E.; Vértes, A.; Bohus, G.; Hornok, V.; Oszkó, A.; Dékány, I. 151Eu Mössbauer study of luminescent Y2O3:Eu3+ core-shell nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 2013, 218, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Spano, G.; Bettinelli, M.; Speghini, A. Distribution of Eu3+ Dopant Ions in C3i and C2 Sites of the Nanocrystalline Sc2O3:Eu Phosphor. Z. Naturforsch. 2008, 63a, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Spano, G.; Zych, E.; Trojan-Piegzan, J. Nano- and microcrystalline Lu2O3:Eu phosphors: variations in occupancy of C2 and S6 sites by Eu3+ ions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, G.; Spano, G.; Bettinellia, M.; Speghinia, A. Investigation of Eu3+ Site Occupancy in Cubic Y2O3 and Lu2O3 Nanocrystals. Z. Naturforsch. 2003, 58, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibicu, I.; Constantinescu, S.; Diamandescu, L.; Voiculescu, A.M.; Cotoi, E. Mössbauer spectroscopy study on YVO4:Eu luminescent material. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2014, 66, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.P.; Li, G.S.; Xue, Y.F.; Inomatac, H. Structure, Luminescence, and Transport Properties of EuVO4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, J45–J49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwung, S.; Enseling, D.; Wesemann, V.; Rytz, D.; Heying, B.; Rodewald, U.C.; Gerke, B.; Niehaus, O.; Pöttgen, R.; Jüstel, T. KYW42O8:Eu3+—A closer look on its photoluminescence and structure. J. Lumin. 2015, 159, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noort, H.M.; Popma, T.J.A. Concentration-dependent site occupancy in europium-doped Y2WO6 as studied by 151Eu Mössbauer spectroscopy. Solid State Commun. 1985, 55, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, F.; Murakami, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Takahashi, M. Orange luminescence of Eu3+-doped CuLaO2 delafossite oxide. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ovenstone, J.; Titler, P.J.; Withnall, R.; Silver, J. A Study of the Effects of Europium Doping and Calcination on the Luminescence of Titania Phosphor Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 7170–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemov, S.A.; Marchenko, A.V.; Seregin, P.P. Parameters of luminescence and the local structure of Eu3+ centers in fluorogermanate glasses. Glass Phys. Chem. 2008, 34, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, P.; Nava, N.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; la Rosa, E.D.; Diaz-Torres, L.A. Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization of ZrO2:Eu3+ Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhopte, S.; Muthal, P.; Kondawar, V.; Moharil, S. Luminescence in CaF2:Eu. J. Lumin. 1992, 54, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, Y. The luminescence of Eu2+ in CaF2 crystal. J. Lumin. 1988, 40–41, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.C.; Raukas, M.; Marking, G.; Chen, P.; Boolchand, P. Investigation of Fluorescence Degradation Mechanism of Hydrated BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ Phosphor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, H183–H190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tanaka, K.; Yamashita, K.; Hirao, K. Room-temperature persistent spectral hole burning of Eu3+-doped sodium borate glasses. J. Lumin. 2000, 87–89, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauminger, E.R.; Kalvius, G.M.; Nowik, I. Mössbauer Isomer Shifts; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; Chapter 10; pp. 661–756. [Google Scholar]
- Large, N.; Bullock, R.; Glentworth, P.; Newton, D. Isomer shift of the Mössbauer spectrum of 151EuF3. Phys. Lett. A 1969, 29, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, A.F. Mössbauer Spectroscopy of the Rare Earths. In The Mössbauer Effect and Its Application in Chemistry; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Chapter 8; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezdrogina, M.M.; Danilovsky, E.Y.; Kuzmin, R.V. Emission sensitization and mechanisms of electron-excitation migration in structures based on III-nitrides doped with rare-earth elements (Eu, Er, Sm). Semiconductors 2010, 44, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilkin, M.; Must, M.; Pedak, E.; Pärnoja, E.; Ryasnyi, G.; Shpinkov, I.; Shpinkova, L.; Seeman, V. Different Eu-centres in CaS:Eu, Cl. Radiat. Meas. 1995, 24, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Fernández, A.; Menéndez, J.L.; Torrecillas, R. Transparent Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering of Lyophilized Gels. J. Nanomater. 2009, 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkooz, O. Isomer shifts of 151Eu in divalent europium compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1969, 30, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

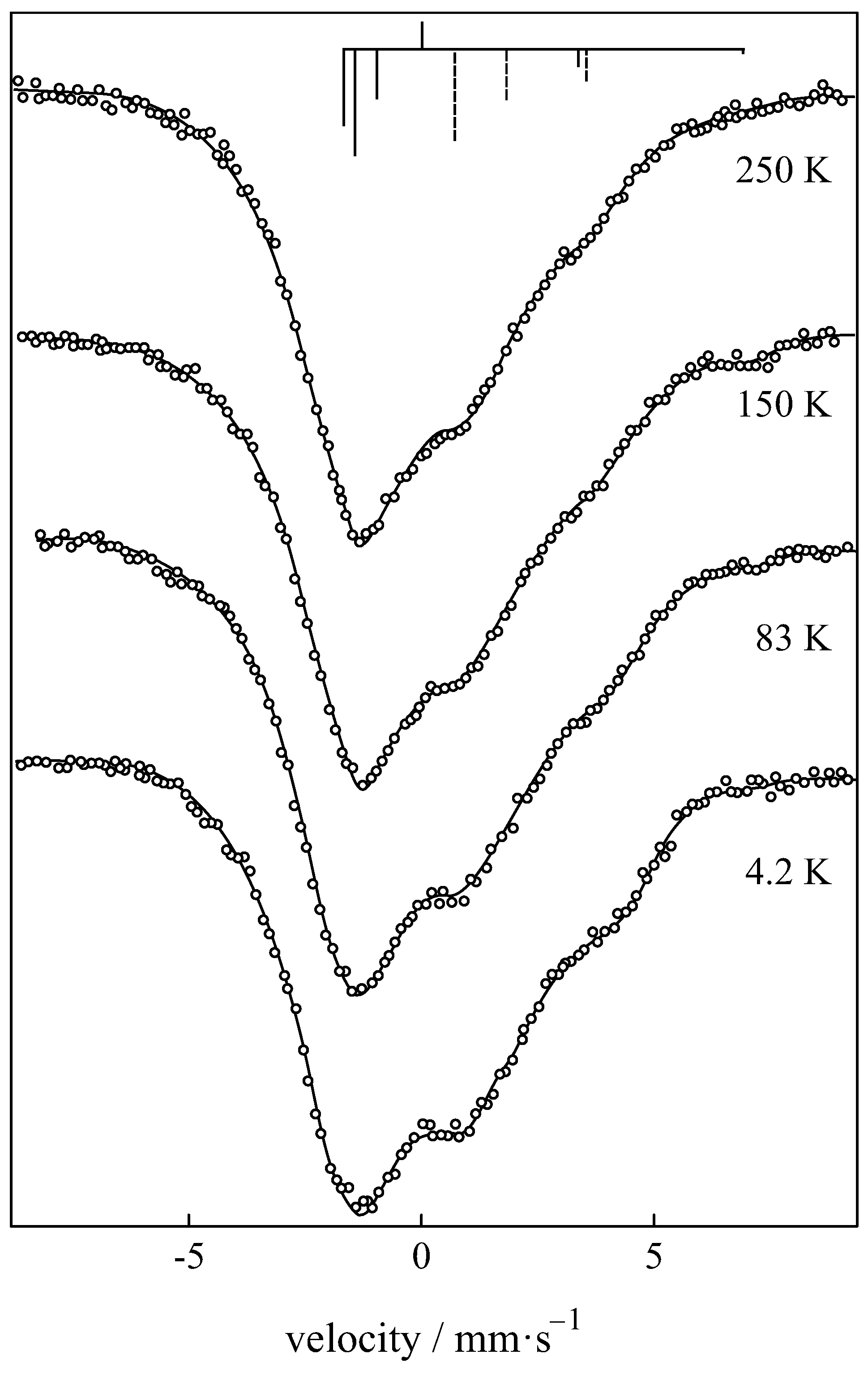
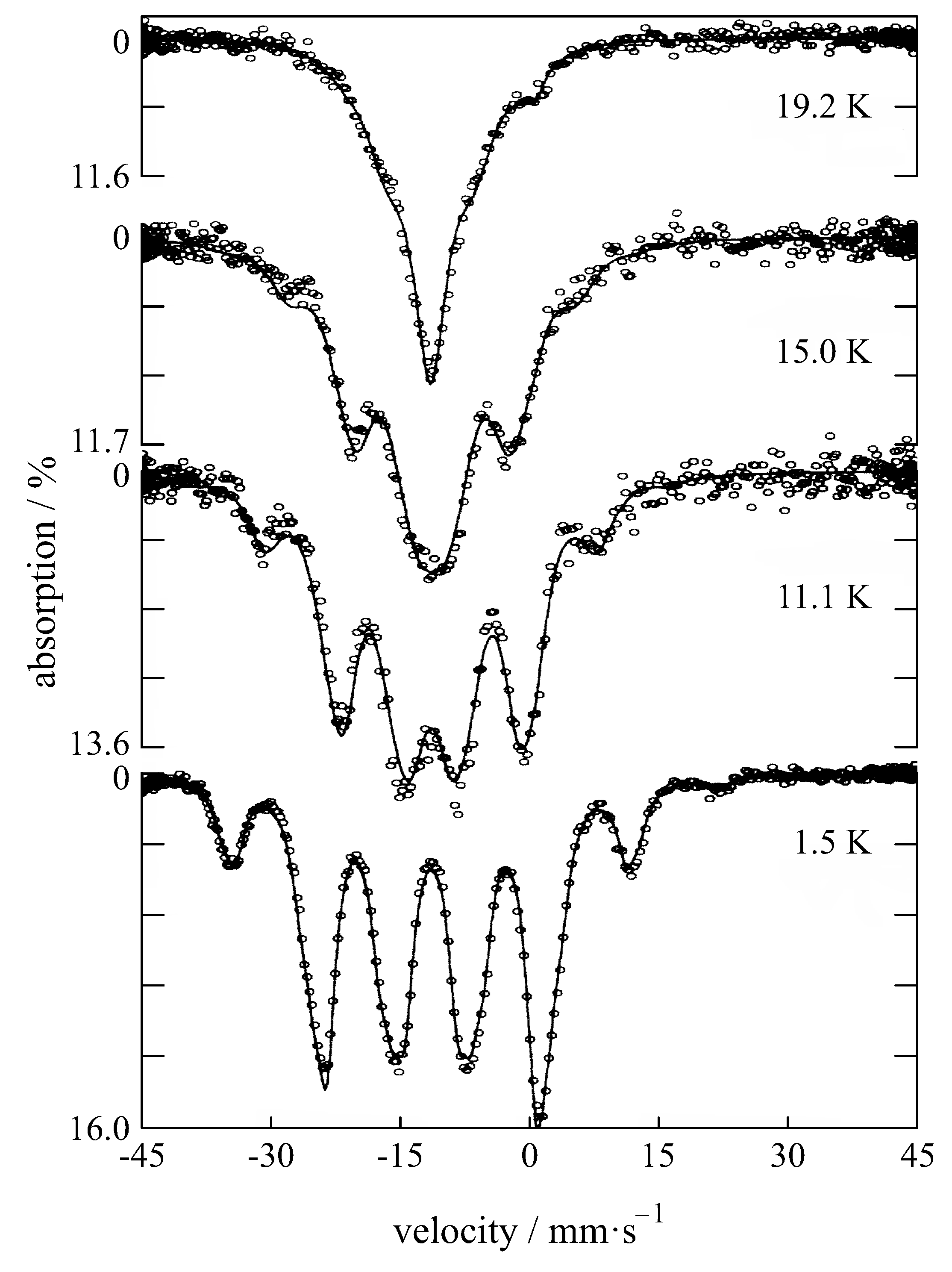
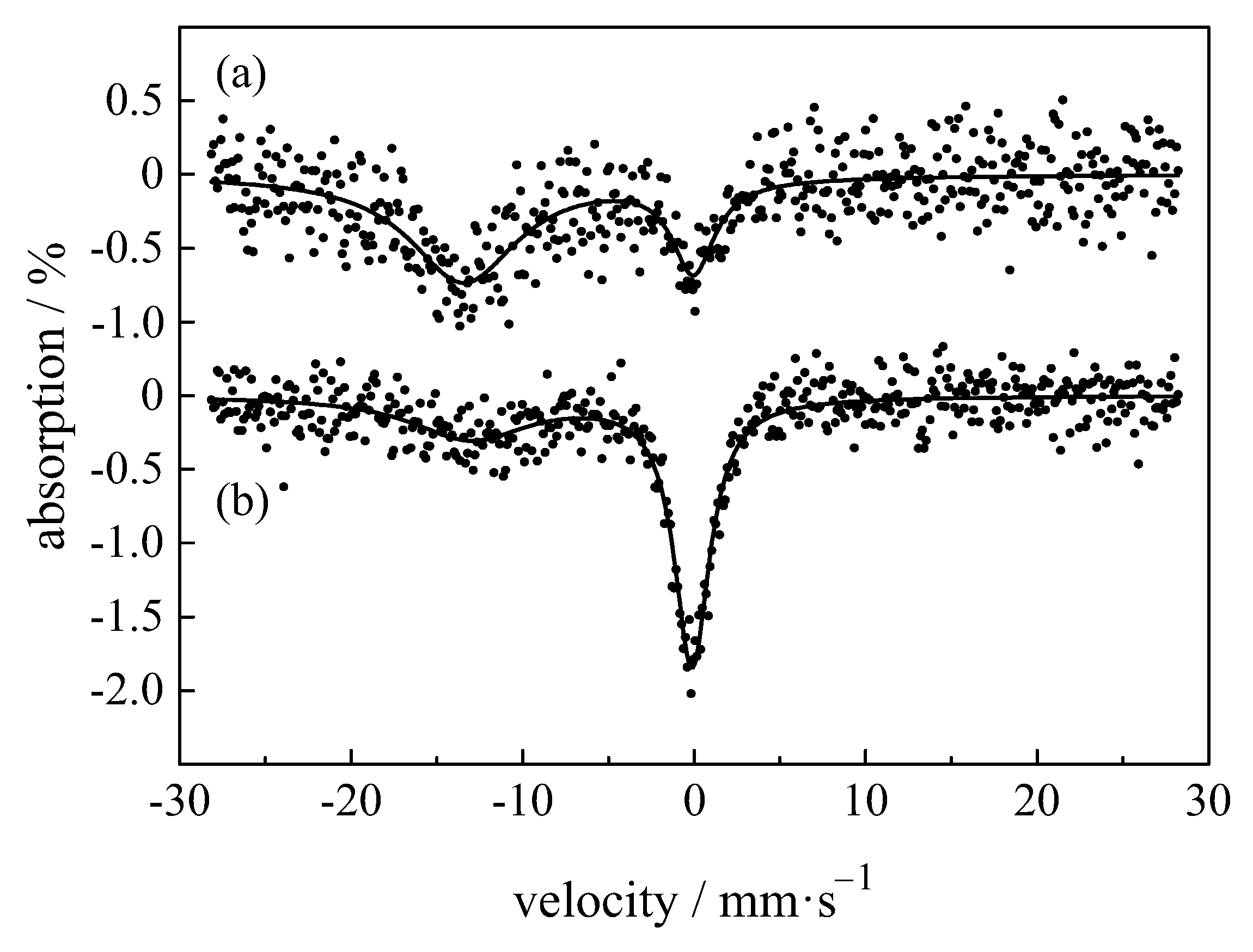
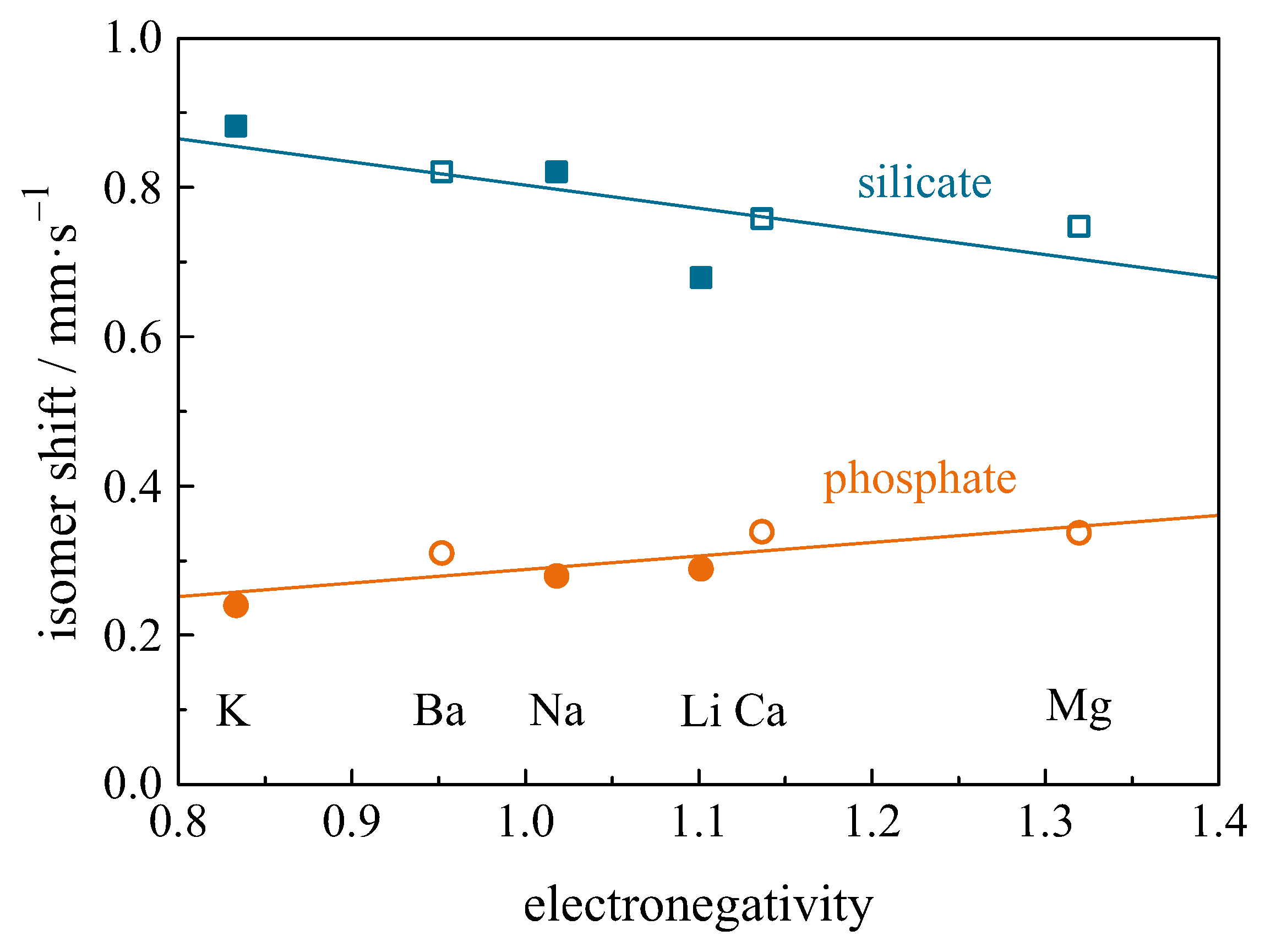
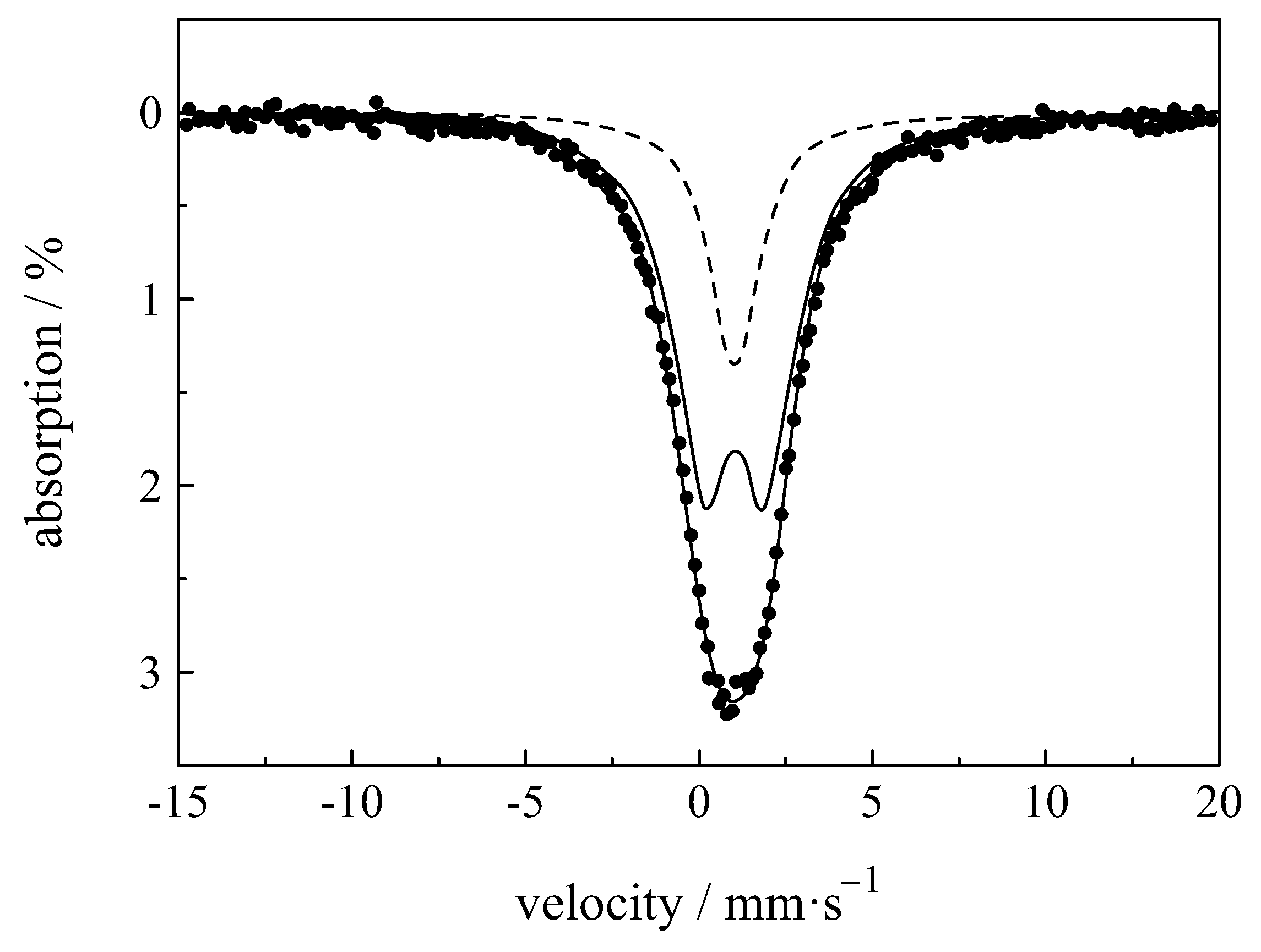
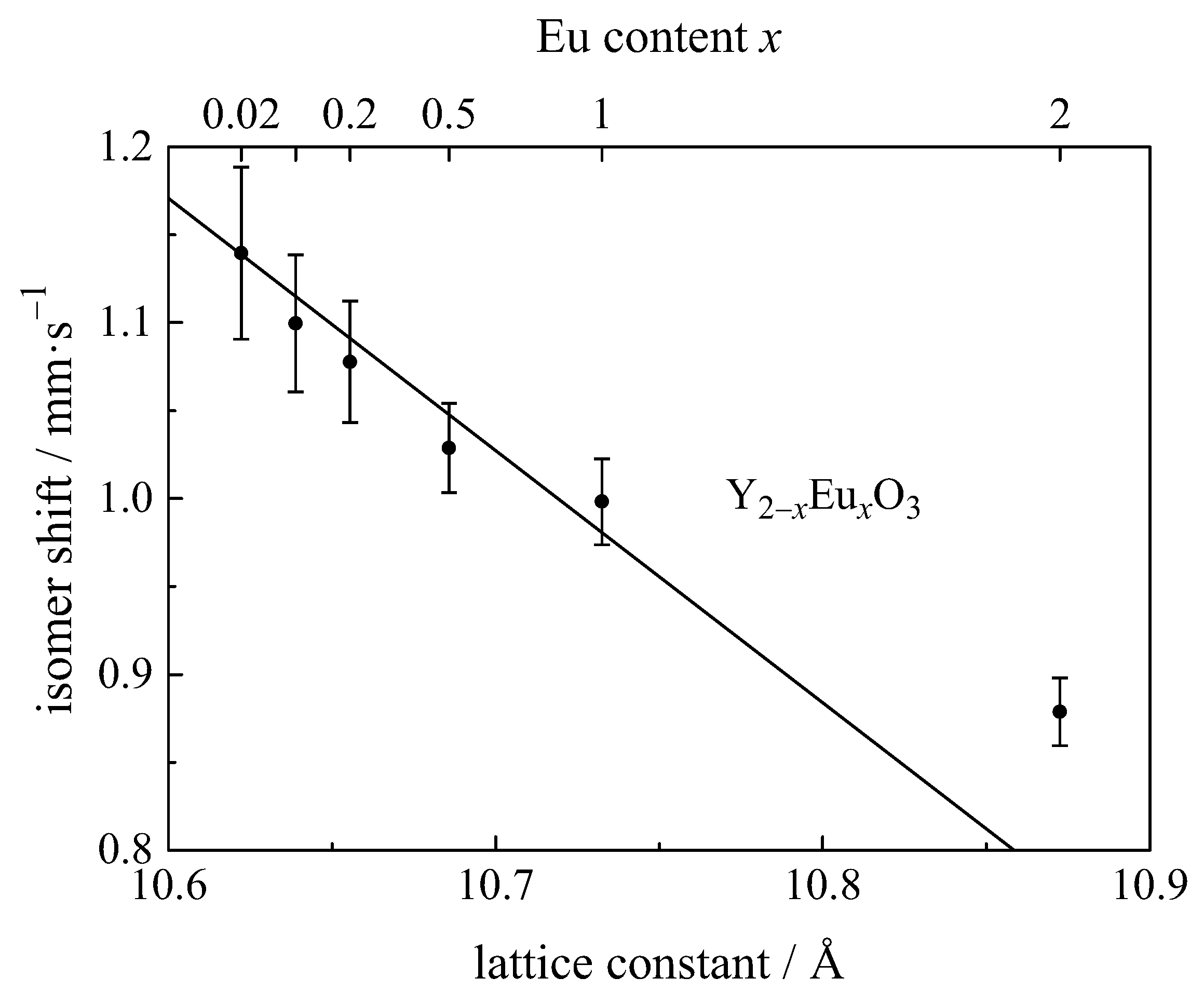
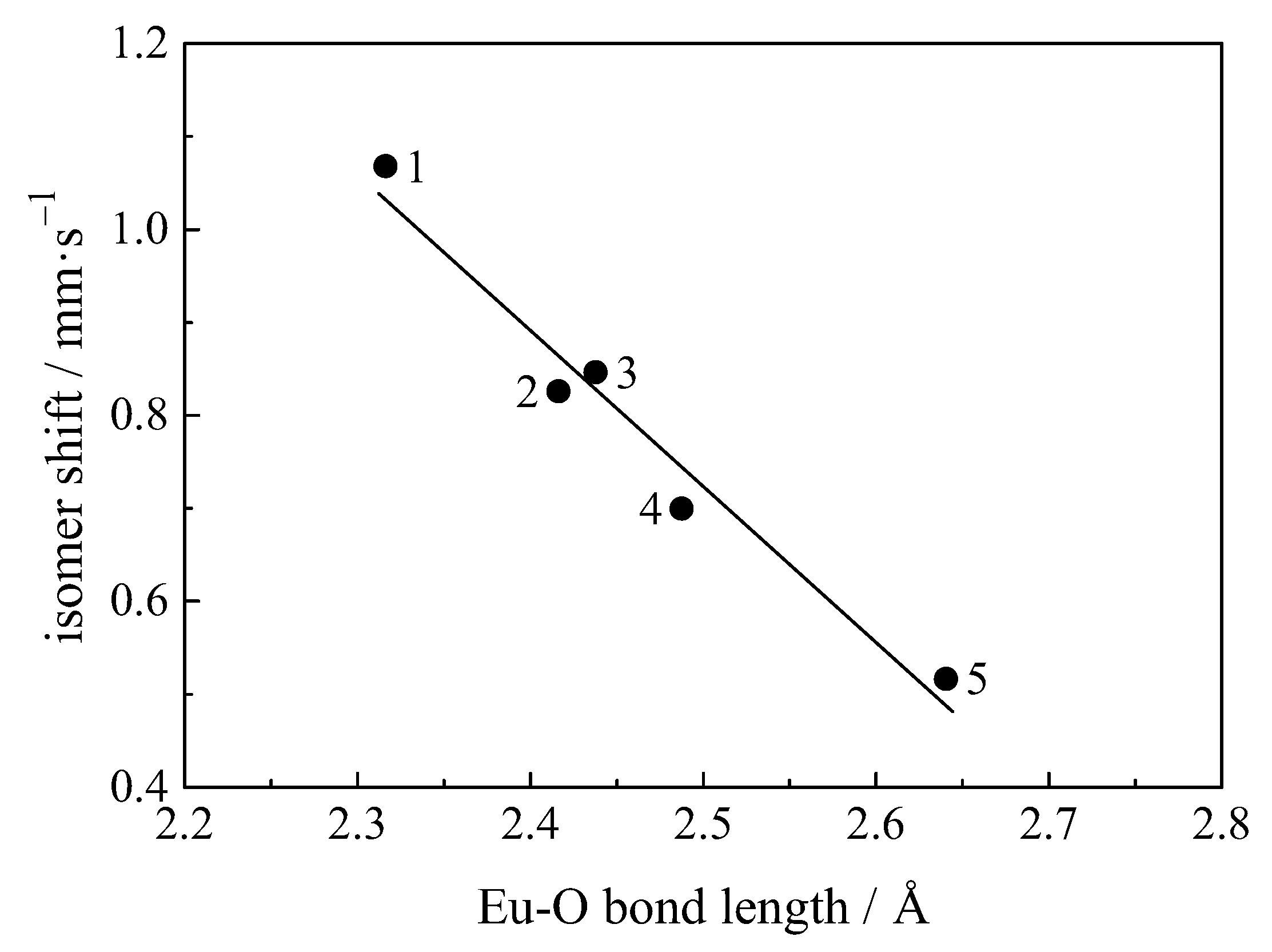
| Compound with Divalent Eu | Isomer Shift in mm/s | Compound with Trivalent Eu | Isomer Shift in mm/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| EuF | EuF | 0 (standard) | |
| EuBr | EuCl | 0.05 | |
| EuCl | EuBr | 0.17 | |
| EuI | EuI | 0.29 | |
| EuO | EuO | 1.01 |
| Host | Isomer Shift in mm/s | Hyperfine Structure for Diluted Eu | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZBLAN and Cl glasses | U | [91] | |
| CaF | hyperfine field of 34 T | [92] | |
| ZrF·BaF·EuF·ThF glass | U | [93] | |
| ZBLAN glass | U | [94] | |
| SrEuAlO | [95] | ||
| BaEuAlO | [95] | ||
| CaEuAlO | [95] | ||
| CaEuAlO | [95,96] | ||
| EuAlON | [97] | ||
| BaMgAlO:Eu | [3] | ||
| BaMgAlO:6%Eu | [98] | ||
| EuAlO | [97] | ||
| EuMgAlO | P | [99] | |
| BaEuMgAl | [100] | ||
| LuEuMgAlO | P | [99] | |
| BaAlSiO | U | [45] | |
| SrEuAlO | U | [101] | |
| BO glass | hyperfine field of 35 T | [102] | |
| (0.7BO·0.3NaO)·(EuO) glass | P | [36] | |
| (0.7BO·0.3NaO)·(EuO) glass | P | [36] | |
| (0.7BO·0.3NaO)·(EuO) glass | P | [36] | |
| (0.9BO·0.1NaO)·(EuO) glass | P | [36] | |
| EuSiN | U | [50] | |
| CaS:Eu | [103] | ||
| EuS | [104] | ||
| EuVO | [105] | ||
| TiO:Eu | [106] | ||
| EuSiON | [52] | ||
| EuVO | [105] |
| Host | Isomer Shift in mm/s | References |
|---|---|---|
| ZrF·BaF·EuF·ThF glass | 0.06 | [93] |
| ZBLAN glass | 0 | [94] |
| ZBLAN and Cl glasses | 0 | [91] |
| (45)AlF·xAlPO·5EuF·30CaF·20BaF | [107] | |
| AlEuO (mainly amorphous) | 1.11 | [108] |
| EuAlON | 0.28 | [97] |
| EuAlPO | 0.22 | [109] |
| LaEuMgAlO | [99] | |
| SrEuAlO | [101] | |
| LaMgAlO | [99] | |
| BaMgAlO | [98] | |
| SiO·NaO·BaO·ZnO·EuO | 1.07 | [110] |
| SiO·BO·NaO·EuO | 1 | [111] |
| BaO·SiO | 0.82 | [112] |
| 50NaO·44PO·3EuO·3CeO | 0.79 | [113] |
| CaO·SiO | 0.76 | [112] |
| 50SiO·25A10·25EuO | 0.46 | [114] |
| (4ZnO)·3BO·0.025EuO | 0.45 | [115] |
| 0.1Eu(PO)·0.9Zn(PO) | 0.37 | [115] |
| 0.1Eu(PO)·0.9Sr(PO) | 0.36 | [115] |
| CaO·PO | 0.36 | [112] |
| BaO·PO | 0.32 | [112] |
| 0.1Eu(PO)·0.9Pb(PO) | 0.29 | [115] |
| (0.7BO·0.3NaO)·(EuO) | 0 | [36] |
| InEuO | 1.38 | [66] |
| LuEuO | 1.35 | [66] |
| YO:Eu (nanoparticle) | 1.28 | [67,116] |
| ScEuO | 1.28 | [117] |
| ScEuO | 1.27 | [66] |
| LuEuO | 1.25 /1.23 | [117,118] |
| LaEuO | 1.2 | [66] |
| YEuO | 1.2 | [100] |
| YEuO | 1.14 | [117] |
| YEuO | 1.12 | [66] |
| GdEuO (monoclinic) | 1.08 | [66] |
| GdEuO (cubic) | 1.05 | [66] |
| YO@Eu (core-shell) | 1.03 | [67,116] |
| GdEuO (nanocrystalline) | 0.97 | [86,119] |
| EuVO | 0.6 | [105] |
| YVO (nanoparticle) | 0.5 | [120] |
| EuVO | 0.5 | [105] |
| YEuVO | 0.49 | [100] |
| EuVO (zircon) | [121] | |
| EuVO (scheelite) | [121] | |
| YAG:Eu nanocrystal | 1.47 | [81] |
| BaCaYO:Eu | 1.0 | [53] |
| EuSiN | 0.85 | [50] |
| EuTiO | 0.8 | [87] |
| KYEuWO | 0.68 | [122] |
| YEuWO | 0.65 | [123] |
| CuLaEuO | 0.61 | [124] |
| 6 TiO:Eu | 0.6 | [125] |
| (BaGeO)·(AlO)·(0.45CaF·0.55MgF) | 0.48 | [126] |
| TiO:Eu | 0.38 | [106] |
| ZrO:Eu | 0.3 | [127] |
| CaS:Eu | [103] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steudel, F.; Johnson, J.A.; Johnson, C.E.; Schweizer, S. Characterization of Luminescent Materials with 151Eu Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Materials 2018, 11, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050828
Steudel F, Johnson JA, Johnson CE, Schweizer S. Characterization of Luminescent Materials with 151Eu Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Materials. 2018; 11(5):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050828
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteudel, Franziska, Jacqueline A. Johnson, Charles E. Johnson, and Stefan Schweizer. 2018. "Characterization of Luminescent Materials with 151Eu Mössbauer Spectroscopy" Materials 11, no. 5: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050828
APA StyleSteudel, F., Johnson, J. A., Johnson, C. E., & Schweizer, S. (2018). Characterization of Luminescent Materials with 151Eu Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Materials, 11(5), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050828