External-Stimuli-Assisted Control over Assemblies of Plasmonic Metals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Control over the Assembly of Plasmonic NPs via External Stimuli
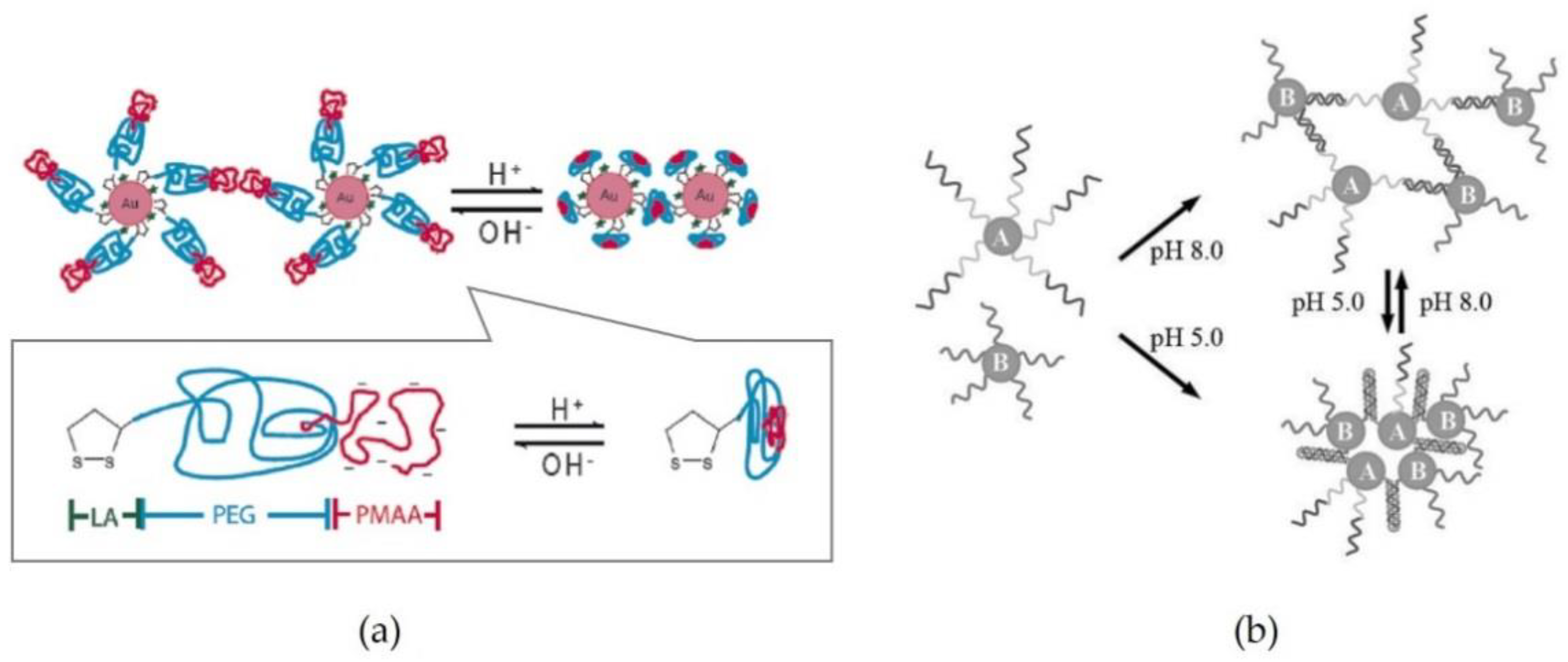
2.1. pH
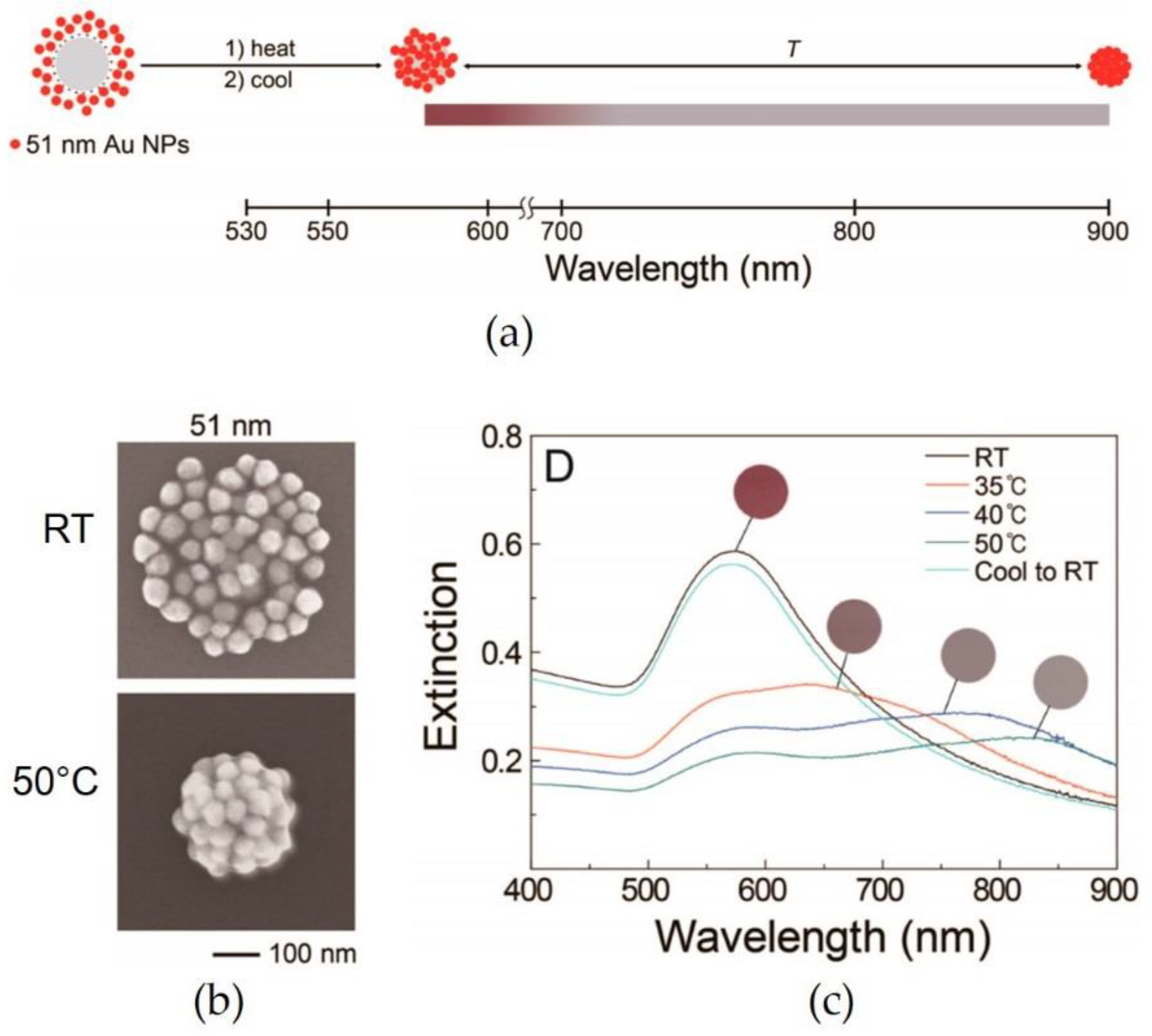
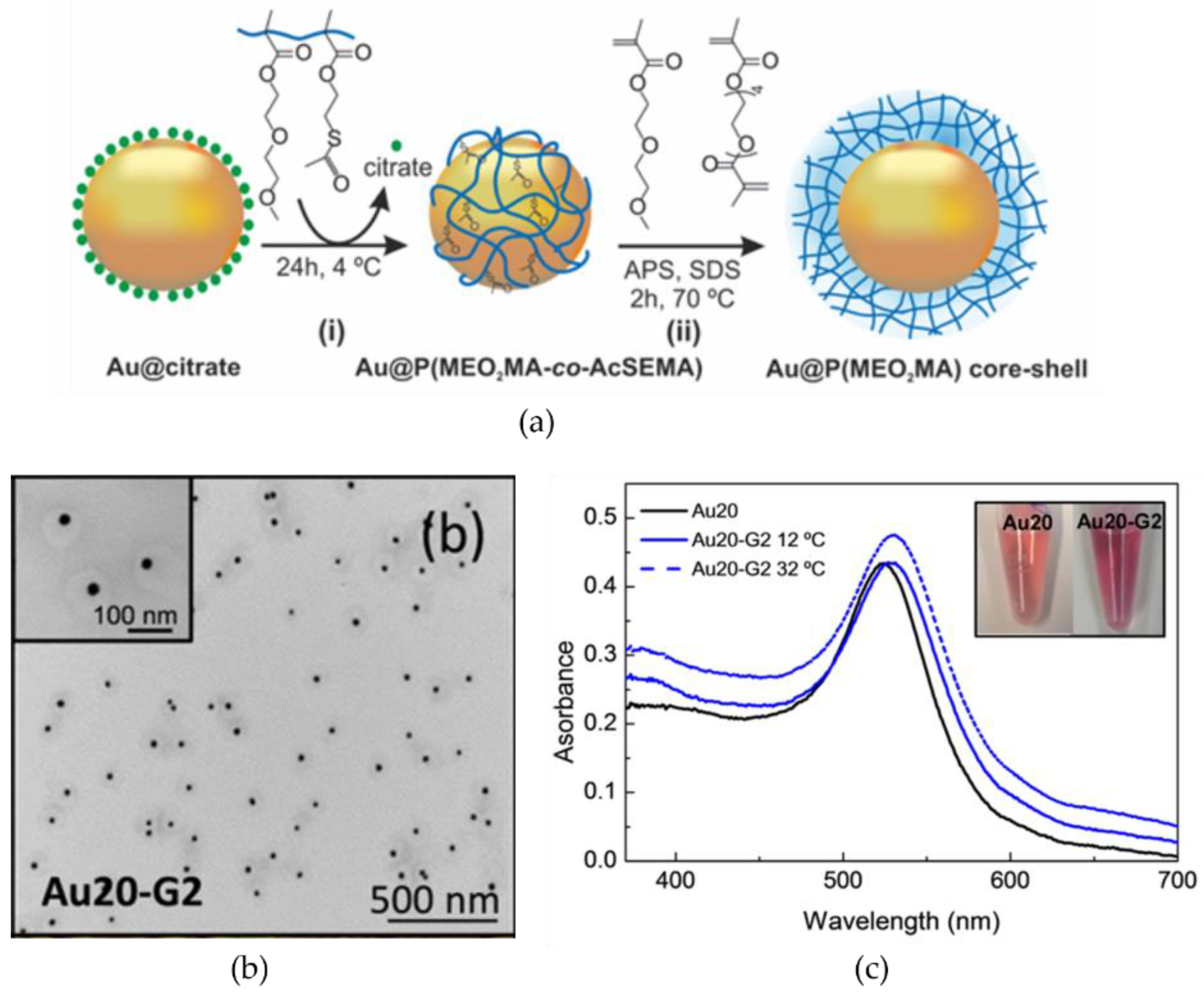
2.2. Temperature
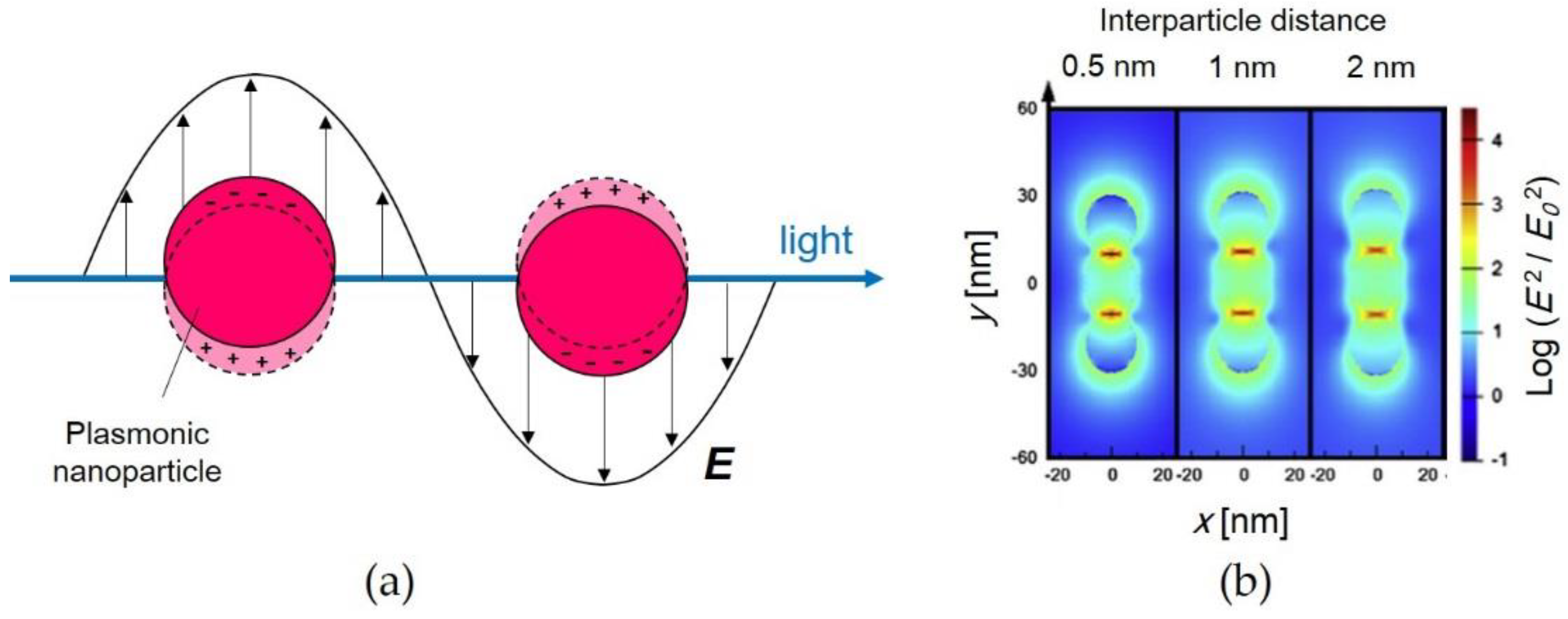
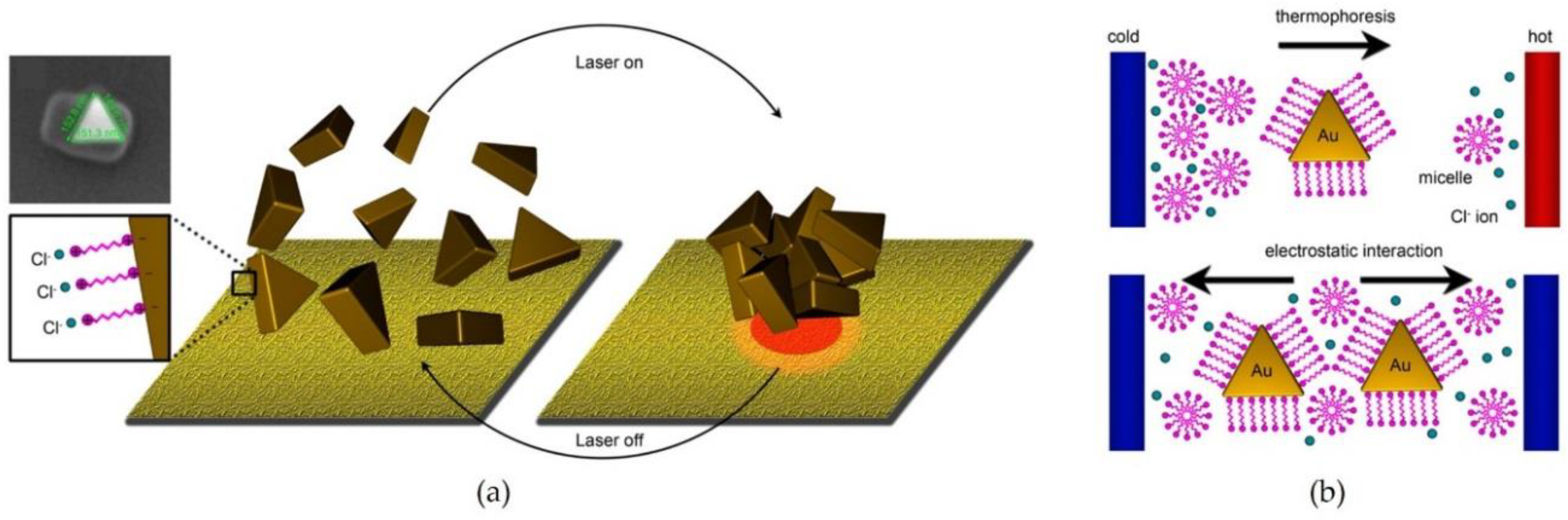
2.3. Light
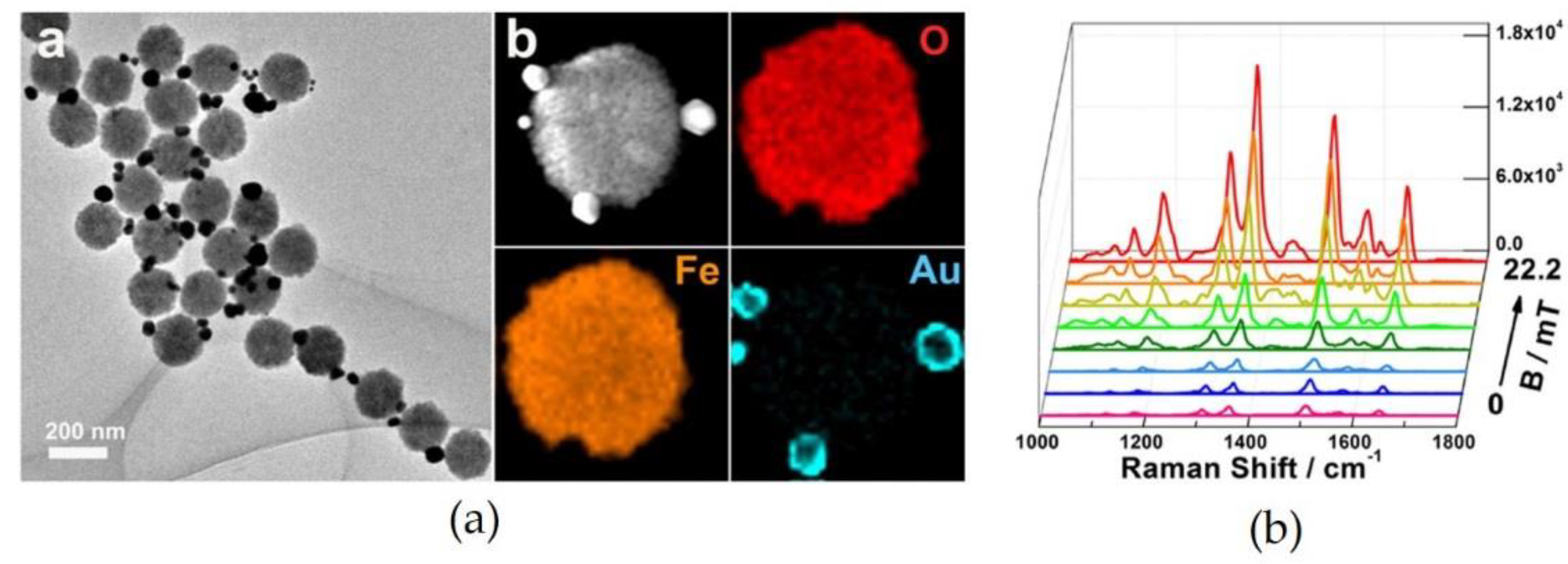
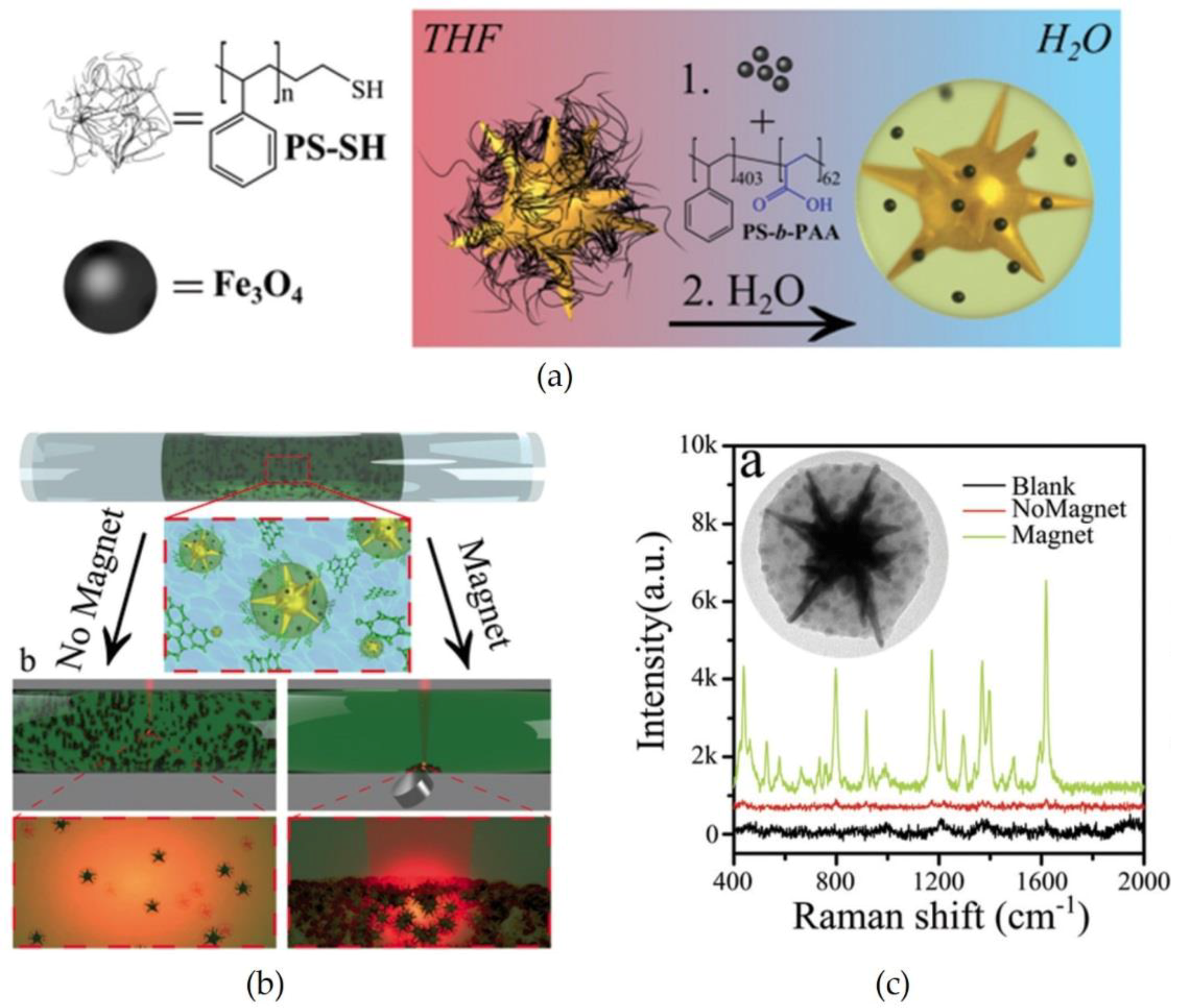
2.4. Magnetic Field
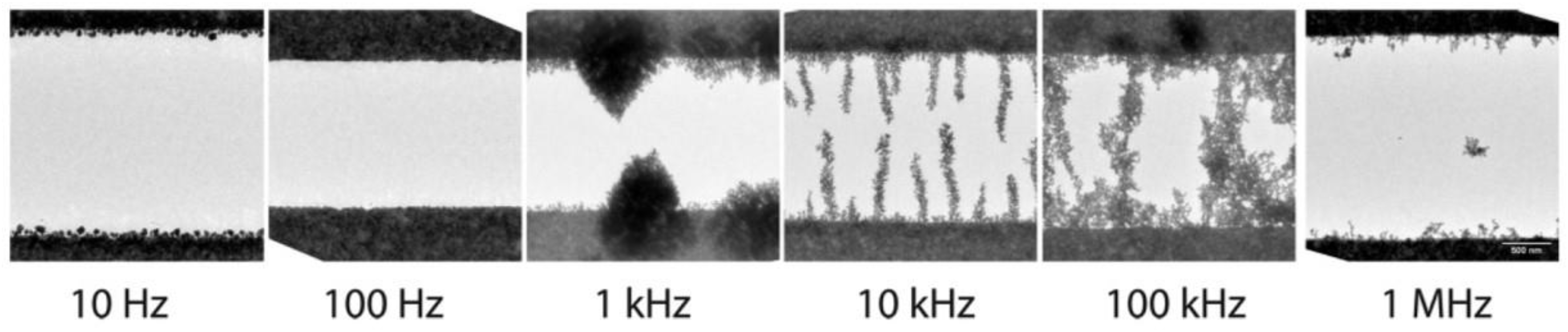
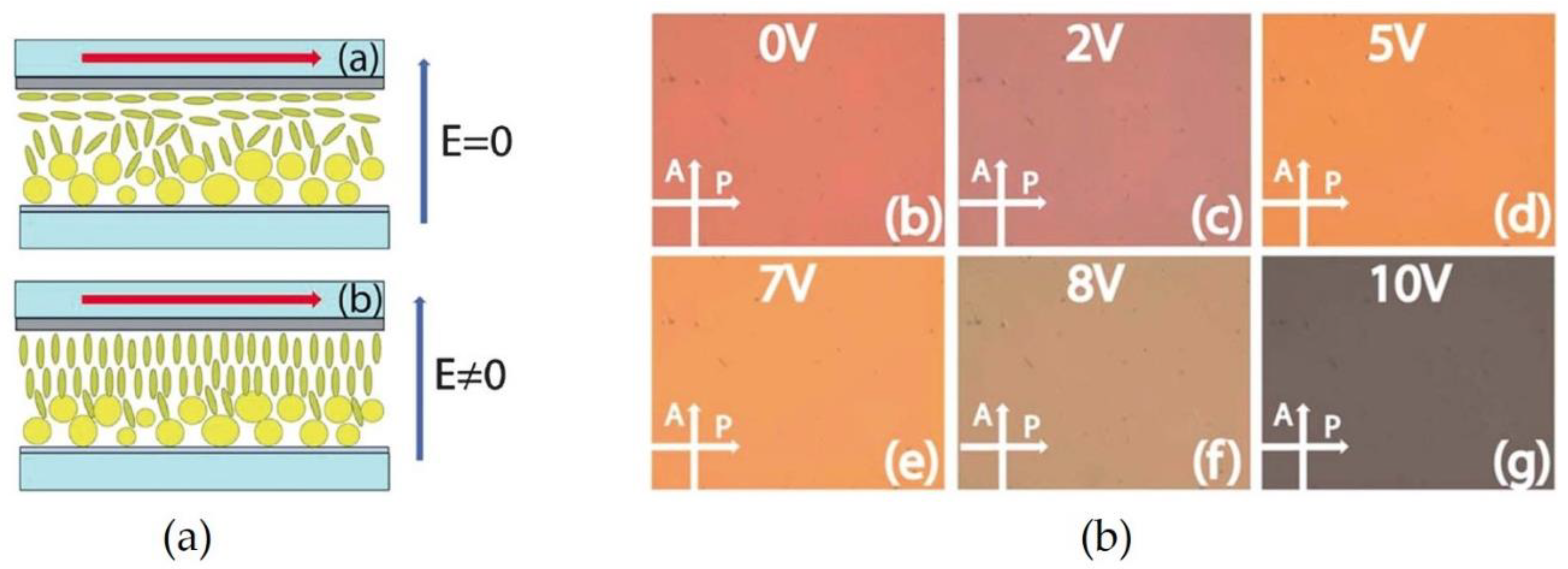
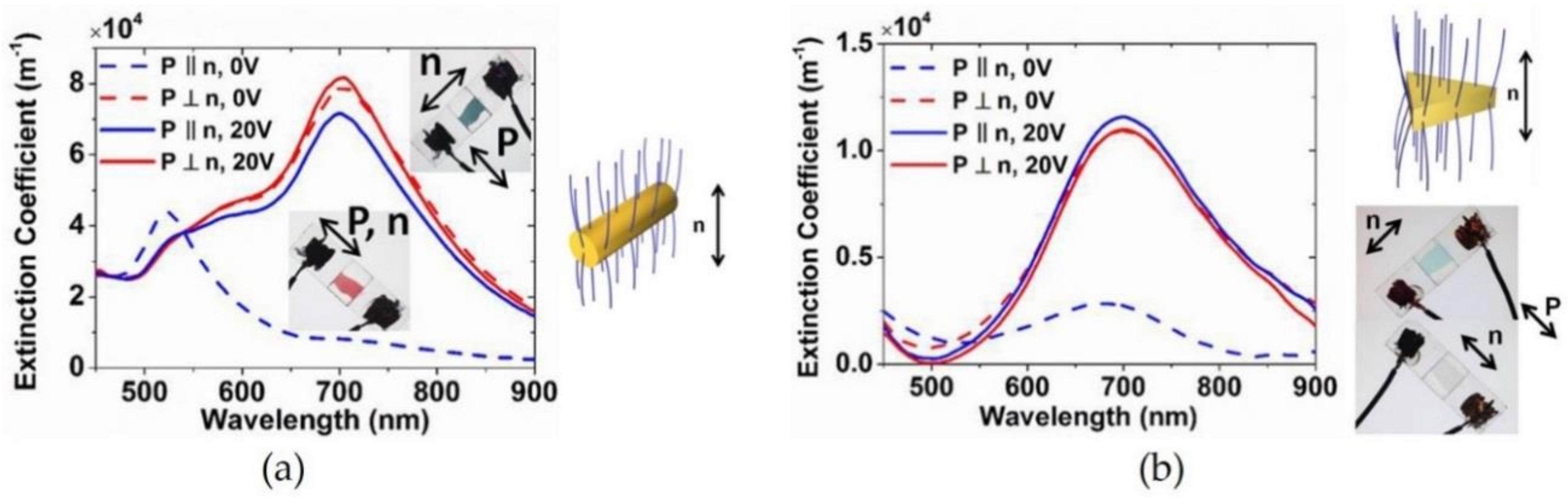
2.5. Electric Field
3. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutter, E.; Fendler, J.H. Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1685–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.M.; Hafner, J.H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, C.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Nanosphere lithography: A versatile nanofabrication tool for studies of size-dependent nanoparticle optics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5599–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Murphy, C.J. Shape-dependent plasmon-resonant gold nanoparticles. Small 2006, 2, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M. Nanometals: Formation and color. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoki, P.N.; Lim, I.-I.S.; Mott, D.; Park, H.-Y.; Khan, B.; Mishra, S.; Sujakumar, R.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C.-J. Size Correlation of Optical and Spectroscopic Properties for Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14664–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Gole, A.M.; Orendorff, C.J.; Gao, J.; Gou, L.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Li, T. Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: Synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13857–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, C.G.; Vo-Dinh, T. Gold Nanostars for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: Synthesis, Characterization and Optimization. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18849–18859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H.; Nordlander, P. Plasmon resonances of a gold nanostar. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.P.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; McLellan, J.M.; Chen, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Xia, Y. Kinetically controlled synthesis of triangular and hexagonal nanoplates of palladium and their SPR/SERS properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17118–17127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, E.; Schatz, G.C. Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoury, P.Z.; Khon, E.; Gong, Y.; Joly, A.G.; Abellan, P.; Evans, J.E.; Browning, N.D.; Hu, D.; Zamkov, M.; Hess, W.P. Electric field enhancement in a self-assembled 2D array of silver nanospheres. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 214308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechberger, W.; Hohenau, A.; Leitner, A.; Krenn, J.R.; Lamprecht, B.; Aussenegg, F.R. Optical properties of two interacting gold nanoparticles. Opt. Commun. 2003, 220, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Thomas, R.; Swathi, R.S.; Thomas, K.G. Au nanorod quartets and Raman signal enhancement: Towards the design of plasmonic platforms. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10454–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tira, C.; Tira, D.; Simon, T.; Astilean, S. Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) design of gold nanoparticle chains with specific surface plasmon resonance. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1072, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P.J.; McQuillan, A.J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmaire, D.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1977, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, A.; Kambhampati, P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.X.; Zhao, B.; Ozaki, Y. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering for protein detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.-M.; Nie, S.M. Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: From fundamental mechanisms to biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Noble Metals on the Nanoscale: Optical and Photothermal Properties and Some Applications in Imaging, Sensing, Biology, and Medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirumamilla, M.; Toma, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Das, G.; Zaccaria, R.P.; Krahne, R.; Rondanina, E.; Leoncini, M.; Liberale, C.; De Angelis, F.; et al. 3D nanostar dimers with a sub-10-nm gap for single-/few-molecule surface-enhanced raman scattering. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Meng, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z. Three-dimensional and time-ordered surface-enhanced raman scattering hotspot matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, M.; Patze, S.; Hidi, I.J.; Knipper, R.; Radu, A.I.; Mühlig, A.; Yüksel, S.; Peksa, V.; Weber, K.; Mayerhöfer, T.; et al. Plasmonic nanostructures for surface enhanced spectroscopic methods. Analyst 2016, 141, 756–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiohara, A.; Wang, Y.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Recent approaches toward creation of hot spots for SERS detection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2014, 21, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Boriskina, S.V.; Feng, N.N.; Reinhard, B.M.; Dal Negro, L. Photonic-plasmonic scattering resonances in deterministic aperiodic structures. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquale, A.J.; Reinhard, B.M.; Dal Negro, L. Engineering photonic-plasmonic coupling in metal nanoparticle necklaces. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6578–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camden, J.P.; Dieringer, J.A.; Zhao, J.; Van Duyne, R.P. Controlled plasmonic nanostructures for surface-enhanced spectroscopy and sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.; Tebbe, M.; Kuttner, C.; Schnepf, M.J.; König, T.A.F.; Fery, A. Template-assisted colloidal self-assembly of macroscopic magnetic metasurfaces. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 191, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, E.M.; Lyandres, O.; Paige Hall, W.; Zou, S.; Glucksberg, M.R.; Van Duyne, R.P. Plasmonic properties of anchored nanoparticles fabricated by reactive ion etching and nanosphere lithography. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4116–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Isa, L.; Wolf, H. Capillary assembly as a tool for the heterogeneous integration of micro- and nanoscale objects. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 2978–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flauraud, V.; Mastrangeli, M.; Bernasconi, G.D.; Butet, J.; Alexander, D.T.L.; Shahrabi, E.; Martin, O.J.F.; Brugger, J. Nanoscale topographical control of capillary assembly of nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.J.; Campolongo, M.J.; Luo, D.; Cheng, W. Building plasmonic nanostructures with DNA. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Kim, H.S.; Aldeanueva-Potel, P.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Kotov, N.A. SERS-active gold lace nanoshells with built-in hotspots. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4013–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Qian, Z.; Ginger, D.S. Reversibly Reconfigurable Colloidal Plasmonic Nanomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5266–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Panigrahi, S.; Praharaj, S.; Kumar Ghosh, S.; Pande, S.; Jana, S.; Pal, T. Dipole-dipole plasmon interactions in self-assembly of gold organosol induced by glutathione. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ni, W.; Yang, Z.; Kou, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J. pH-controlled reversible assembly and disassembly of gold nanorods. Small 2008, 4, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Li, J.; Nie, S. Stimuli-responsive SERS nanoparticles: Conformational control of plasmonic coupling and surface Raman enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7540–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kanyo, I.; Kuo, C.-H.; Thanneeru, S.; He, J. pH-programmable self-assembly of plasmonic nanoparticles: Hydrophobic interaction versus electrostatic repulsion. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, Y.; Sugimura, N.; Mitomo, H.; Niikura, K.; Ijiro, K. PH-Responsive Coassembly of Oligo(ethylene glycol)-Coated Gold Nanoparticles with External Anionic Polymers via Hydrogen Bonding. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5537–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Controllable synthesis of P(NIPAM-co-MPTMS)/PAA–Au composite materials with tunable LSPR performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9584–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, C. pH-induced reversible expansion/contraction of gold nanoparticle aggregates. Small 2008, 4, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganta, S.; Devalapally, H.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.; La, W.G.; Hwang, S.; Ha, Y.S.; Park, N.; Won, N.; Jung, S.; Bhang, S.H.; Ma, Y.J.; Cho, Y.M.; et al. PH-responsive assembly of gold nanoparticles and “spatiotemporally concerted” Drug release for synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3388–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggard, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle-protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time evolution of nanoparticle protein corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillaud, L.; Chehimi, M.M.; Aubard, J.; Hohenau, A.; Felidj, N. Thermo-induced Electromagnetic Coupling in Gold/Polymer Hybrid Plasmonic Structures Probed by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6491–6500. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Rudrum, A.W.; Herrmann, L.O.; Turek, V.; Baumberg, J.J. Polymer-assisted self-assembly of gold nanoparticle monolayers and their dynamical switching. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15864–15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; An, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L. Thermosensitive mixed shell polymeric micelles decorated with gold nanoparticles at the outmost surface: Tunable surface plasmon resonance and enhanced catalytic properties with excellent colloidal stability. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47458–47465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Song, J.E.; La, J.A.; Cho, E.C. Gold nanospheres assembled on hydrogel colloids display a wide range of thermoreversible changes in optical bandwidth for various plasmonic-based color switches. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.F.; Akdemir, Ö.; Hoth, A. Point by point comparison of two thermosensitive polymers exhibiting a similar LCST: Is the age of poly(NIPAM) over? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13046–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarrotxena, N.; Quijada-Garrido, I. Optical and Swelling Stimuli-Response of Functional Hybrid Nanogels: Feasible Route to Achieve Tunable Smart Core@Shell Plasmonic@Polymer Nanomaterials. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, L.; Rong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tong, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T. Light-triggered reversible self-assembly of gold nanoparticle oligomers for tunable SERS. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Hwang, S.; Im, K.; Hur, J.; Nam, J.; Hwang, S.; Ahn, G.-O.; Kim, S.; Park, N. Light-responsible DNA hydrogel–gold nanoparticle assembly for synergistic cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Sun, R.; Yin, L.; Chai, Z.; Shi, H.; Gao, M. Light-Triggered Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy and Photoacoustic Imaging of Tumors In Vivo. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, D.; Udayabhaskararao, T.; Zhao, H.; Klajn, R. Orthogonal light-induced self-assembly of nanoparticles using differently substituted azobenzenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12394–12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, D.; Rossner, C.; Vana, P. Light-induced self-assembly of gold nanoparticles with a photoresponsive polymer shell. Polymer 2016, 107, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.K.; Das, S.; Ahrens, J.; Klajn, R. Controlling the lifetimes of dynamic nanoparticle aggregates by spiropyran functionalization. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19280–19286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, C.; Shinmori, H. Light-triggered Assembly of Gold Nanorods based on Photoisomerization of Spiropyrans. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, M.; Scarabelli, L.; Mao, Z.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Becker, M.F.; Zheng, Y. Light-Directed Reversible Assembly of Plasmonic Nanoparticles Using Plasmon-Enhanced Thermophoresis. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9659–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Y.; Gunawan, H.; Tsai, S.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Yen, T.C.; Liaw, J.W. Single-crystalline gold nanowires synthesized from light-driven oriented attachment and plasmon-mediated self-assembly of gold nanorods or nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Wei, C.; Xu, M.M.; Yuan, Y.X.; Gu, R.A.; Yao, J.L. Controlling dynamic SERS hot spots on a monolayer film of Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles by a magnetic field. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 152, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Irudayaraj, J. Multifunctional magnetic-optical nanoparticle probes for simultaneous detection, separation, and thermal ablation of multiple pathogens. Small 2010, 6, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Liu, K.; Furlani, E.P. Theoretical Study of the Self-Assembly and Optical Properties of 1D Chains of Magnetic-Plasmonic Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9489–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, F.; Shao, M.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Smart liquid SERS substrates based on Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles with reversibly tunable enhancement factor for practical quantitative detection. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Porta, A.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Altantzis, T.; Bals, S.; Grzelczak, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Multifunctional self-assembled composite colloids and their application to SERS detection. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10377–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, K.D.; Lumsdon, S.O.; Williams, J.P.; Kaler, E.W.; Velev, O.D. Dielectrophoretic assembly of electrically functional microwires from nanoparticle suspensions. Science 2001, 294, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, K.H.; Velev, O.D. Control and Modeling of the Dielectrophoretic Assembly of On-Chip Nanoparticle Wires. Langmuir 2004, 20, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierhart, B.C.; Howitt, D.G.; Chen, S.J.; Smith, R.L.; Collins, S.D. Frequency dependence of gold nanoparticle superassembly by dielectrophoresis. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12450–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G.; Castellanos, A. Ac electrokinetics: A review of forces in microelectrode structures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 2338–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Morgan, H.; Green, G.N.; Castellanos, A. AC Electric-Field-Induced Fluid Flow in Microelectrodes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 422, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.S. Limiting laws and counterion condensation in polyelectroyte solutions. I. Colligative properties. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutukuri, H.R.; Badaire, S.; De Winter, D.A.M.; Imhof, A.; Van Blaaderen, A. Directed Self-Assembly of Micron-Sized Gold Nanoplatelets into Oriented Flexible Stacks with Tunable Interplate Distance. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sio, L.; Cunningham, A.; Verrina, V.; Tone, C.M.; Caputo, R.; Bürgi, T.; Umeton, C. Double active control of the plasmonic resonance of a gold nanoparticle array. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7619–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Mundoor, H.; Yuan, Y.; Smalyukh, I.I. Metal Nanoparticle Dispersion, Alignment, and Assembly in Nematic Liquid Crystals for Applications in Switchable Plasmonic Color Filters and E-Polarizers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, K.; Kuroda, K.; Nagao, D. External-Stimuli-Assisted Control over Assemblies of Plasmonic Metals. Materials 2018, 11, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050794
Watanabe K, Kuroda K, Nagao D. External-Stimuli-Assisted Control over Assemblies of Plasmonic Metals. Materials. 2018; 11(5):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050794
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Kanako, Kotaro Kuroda, and Daisuke Nagao. 2018. "External-Stimuli-Assisted Control over Assemblies of Plasmonic Metals" Materials 11, no. 5: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050794
APA StyleWatanabe, K., Kuroda, K., & Nagao, D. (2018). External-Stimuli-Assisted Control over Assemblies of Plasmonic Metals. Materials, 11(5), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050794




