On the Phase Separation in n-Type Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
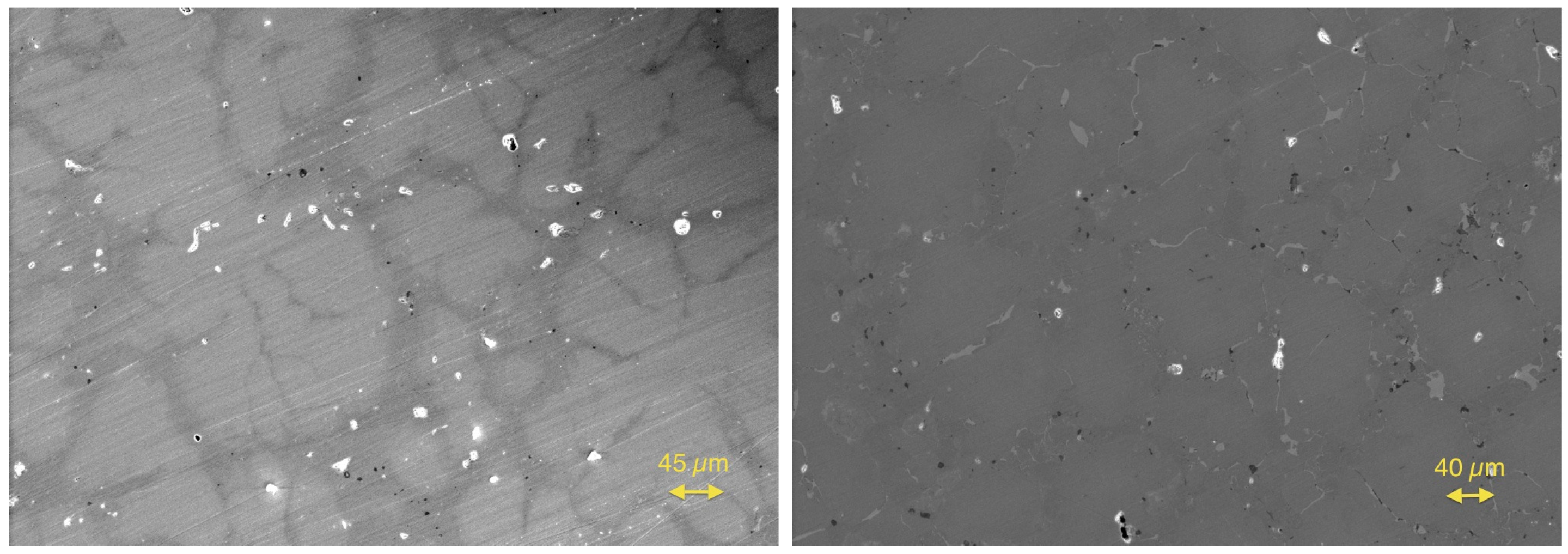
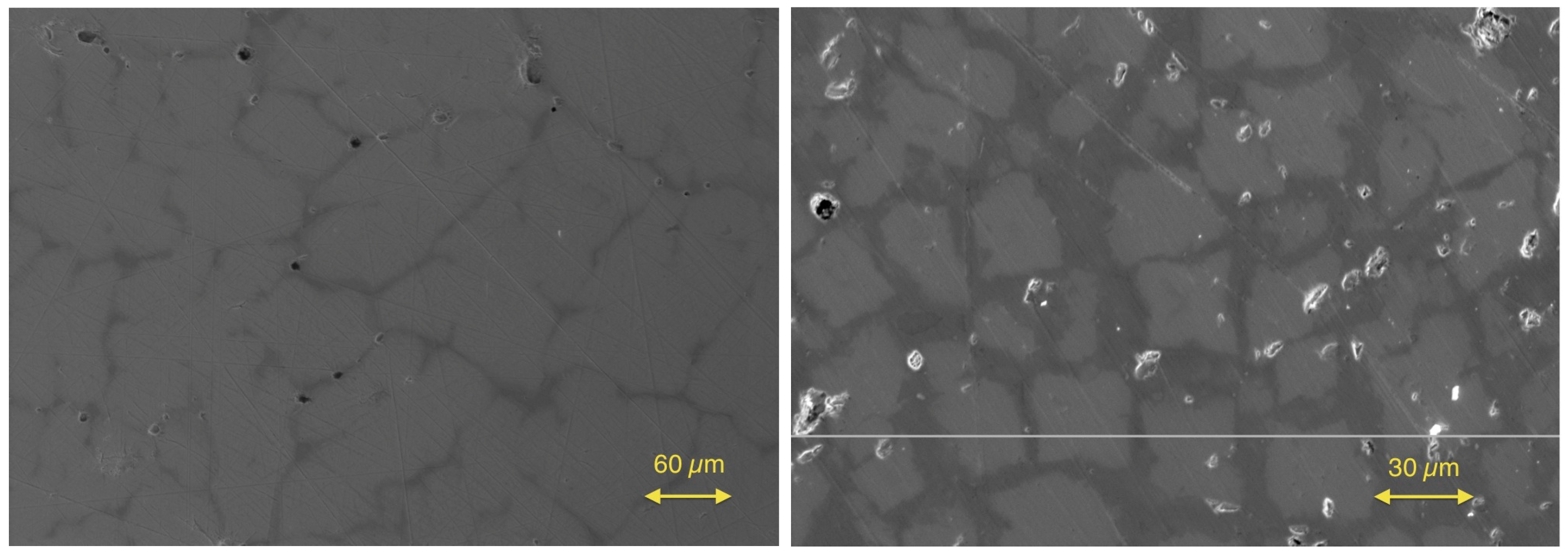
2.1. Understanding the Phase Separation in the n-Type HH Materials
2.2. The ZrHfNiSn Series
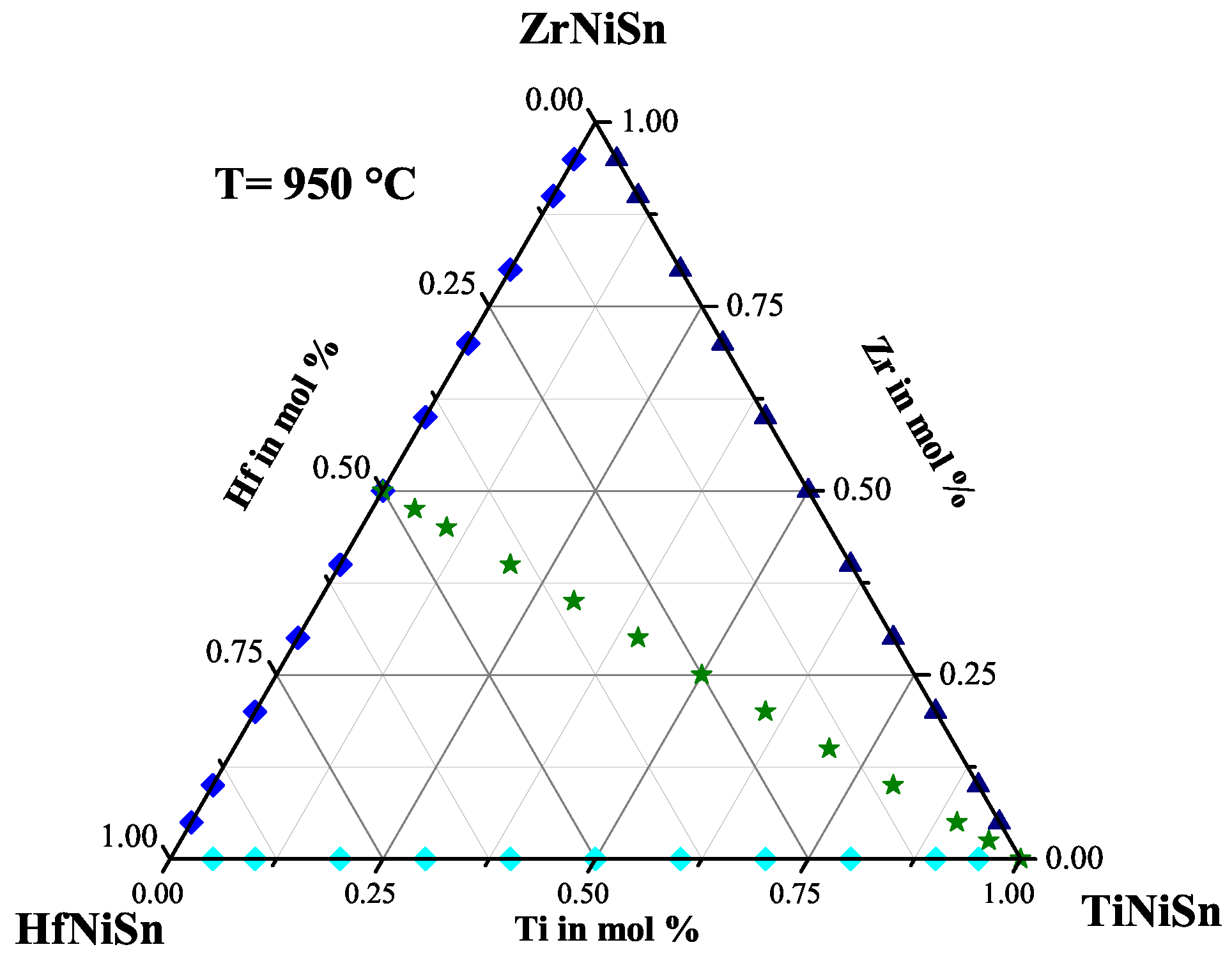
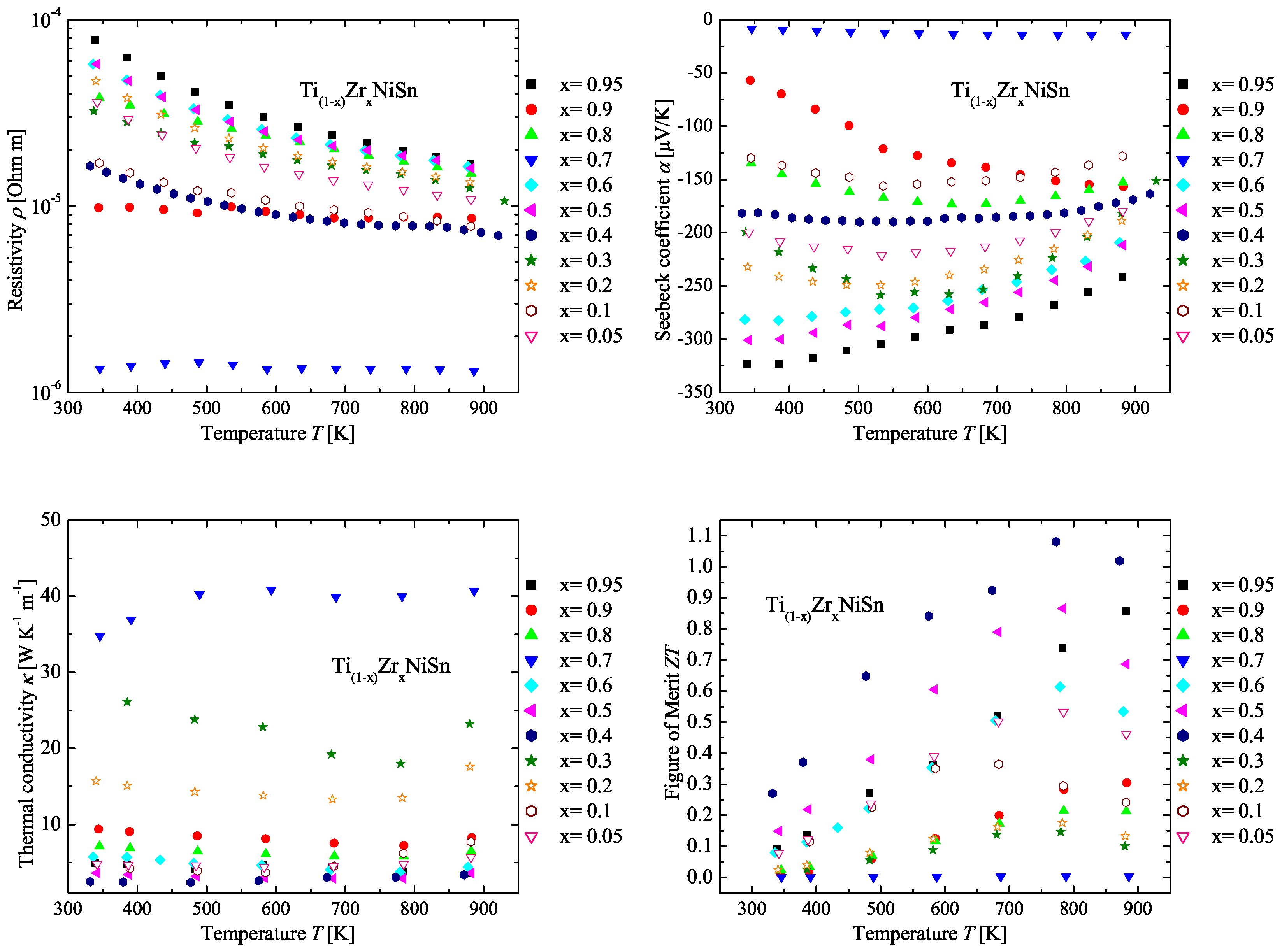
2.3. The TiZrNiSn Series
2.4. The TiHfNiSn Series
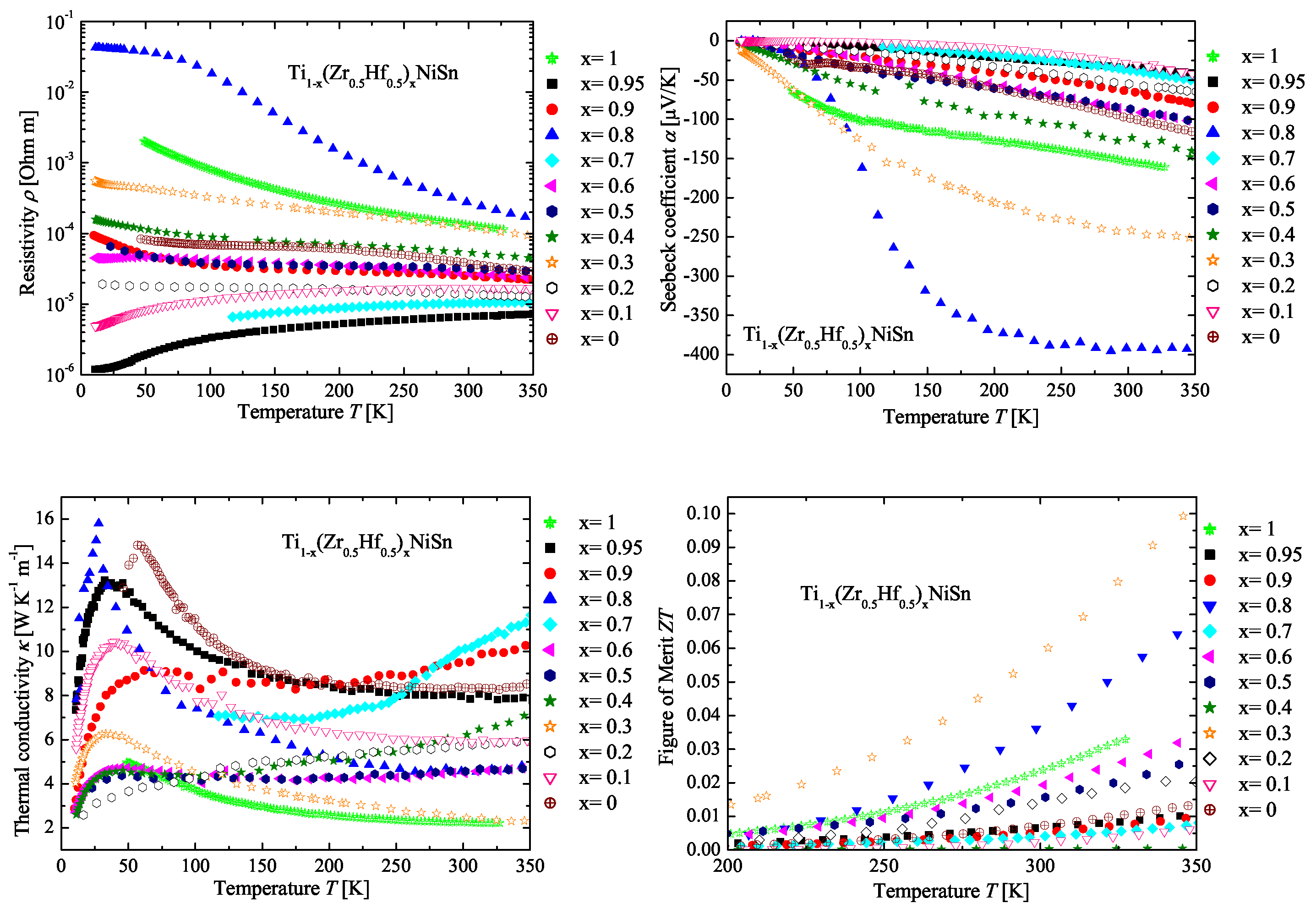
2.5. The Ti(ZrHf)NiSn Series
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laboratory, L.L.N. Energy Flow Charts of Primary Energy Resources and End Uses in the United States. Available online: https://flowcharts.llnl.gov/index.html (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Yang, J.; Stabler, F.R. Automotive applications of thermoelectric materials. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierle-Arndt, K.; Hermes, W. Thermoelektrik. Chem. Unserer Zeit 2013, 47, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritt, T.M. Thermoelectric phenomena, materials, and applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.J.; Toberer, E.S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, P.; Caillat, T. Energy Quarterly: Thermoelectric Heat Recovery could boots Auto Fule Economy. MRS Bull. Energy Q. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sales, B.C. Smaller is cooler. Science 2002, 295, 1248–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Caillat, T. Thermoelectric materials for space and automotive power generation. MRS Bull. 2006, 31, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, H.; Ramirez, A.; Kaefer, W.; Fess, K.; Thurner, C.; Kloc, C.; Bucher, E. A new class of materials with promising thermoelectric properties: MNiSn (M = Ti, Zr, Hf). Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1997, 478, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, H.; Ramirez, A.; Goldmann, C.; Ernst, G.; Wolfing, B.; Bucher, E. Efficient dopants for ZrNiSn-based thermoelectric materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1999, 11, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öğüt, S.; Rabe, K.M. Band gap and stability in the ternary intermetallic compounds NiSnM (M = Ti, Zr, Hf): A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, L.D.; Goto, T.; Hirai, T. Thermoelectric properties of ZrNiSn-based half-Heusler compounds by solid state reaction method. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 2197–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Chen, L.; Goto, T.; Hirai, T.; Yang, J.; Meisner, G.P.; Uher, C. Effects of partial substitution of Ni by Pd on the thermoelectric properties of ZrNiSn-based half-Heusler compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 4165–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clup, S.R.; Poon, S.J.; Hickman, N.; Tritt, T.M.; Blumm, J. Effect of substitutions on the thermoelectric figure of merit of half-Heusler phases at 800 ∘C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 042106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Dahal, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.Z.; Shiomi, J.; Chen, G.; Ren, Z.F. Enhancement of thermoelectric figure-of-merit at low temperatures by titanium substitution for hafnium in n-type half-Heuslers Hf0.75-xTixZr0.25NiSn0.99Sb0.01. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Ren, Z. Thermoelectric Property Study of Nanostructured p-Type Half-Heuslers (Hf, Zr, Ti) CoSb0.8Sn0.2. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, S.J.; Wu, D.; Zhu, S.; Xie, W.; Tritt, T.M.; Thomas, P.; Venkatasubramanian, R. Half-Heusler phases and nanocomposites as emerging high-ZT thermoelectric materials. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makongo, J.P.A.; Misra, D.K.; Zhou, X.; Pant, A.; Shabetai, M.R.; Su, X.; Uher, C.; Stokes, K.L.; Poudeu, P.F.P. Simultaneous large enhancements in thermopower and electrical conductivity of bulk nanostructured half-Heusler alloys. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18843–18852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurada, S.; Shutoh, N. Effect of Ti substitution on the thermoelectric properties of (Zr, Hf) NiSn half-Heusler compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Barth, J.; Blum, C.G.F.; Balke, B.; Felser, C.; Klaer, P.; Elmers, H.J. Phase-separation-induced changes in the magnetic and transport properties of the quaternary Heusler alloy Co2Mn1-xTixSn. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 194420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Klaer, P.; Barth, J.; Balke, B.; Elmers, H.J.; Felser, C. Phase separation in the quaternary Heusler compound CoTi(1-x)MnxSb—A reduction in the thermal conductivity for thermoelectric applications. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutoh, N.; Sakurada, S. Thermoelectric properties of the Tix(Zr0.5Hf0.5)1-xNiSn half-Heusler compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 389, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, S.; Zeng, X.; Dehkordi, A.M.; Tritt, T.M.; Poon, S.J. Uncovering high thermoelectric figure of merit in (Hf,Zr)NiSn half-Heusler alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Tritt, T.M.; Poon, S.J. High thermoelectric figure of merit by resonant dopant in half-Heusler alloys. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 065208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Bai, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, T. Realizing high figure of merit in heavy-band p-type half-Heusler thermoelectric materials. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwall, M.; Balke, B. Phase separation as a key to a thermoelectric high efficiency. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.; Entin-Wohlman, O.; Orbach, R. Phonon-fracton anharmonic interactions: The thermal conductivity of amorphous materials. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janot, C. Conductivity in quasicrystals via hierarchically variable-range hopping. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bai, S.; Chen, L.; Cuenat, A.; Joshi, G.; Kleinke, H.; König, J.; Lee, H.W.; Martin, J.; Oh, M.W.; et al. International round-robin study of the thermoelectric transport properties of an n-Type half-heusler compound from 300 K to 773 K. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 4482–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
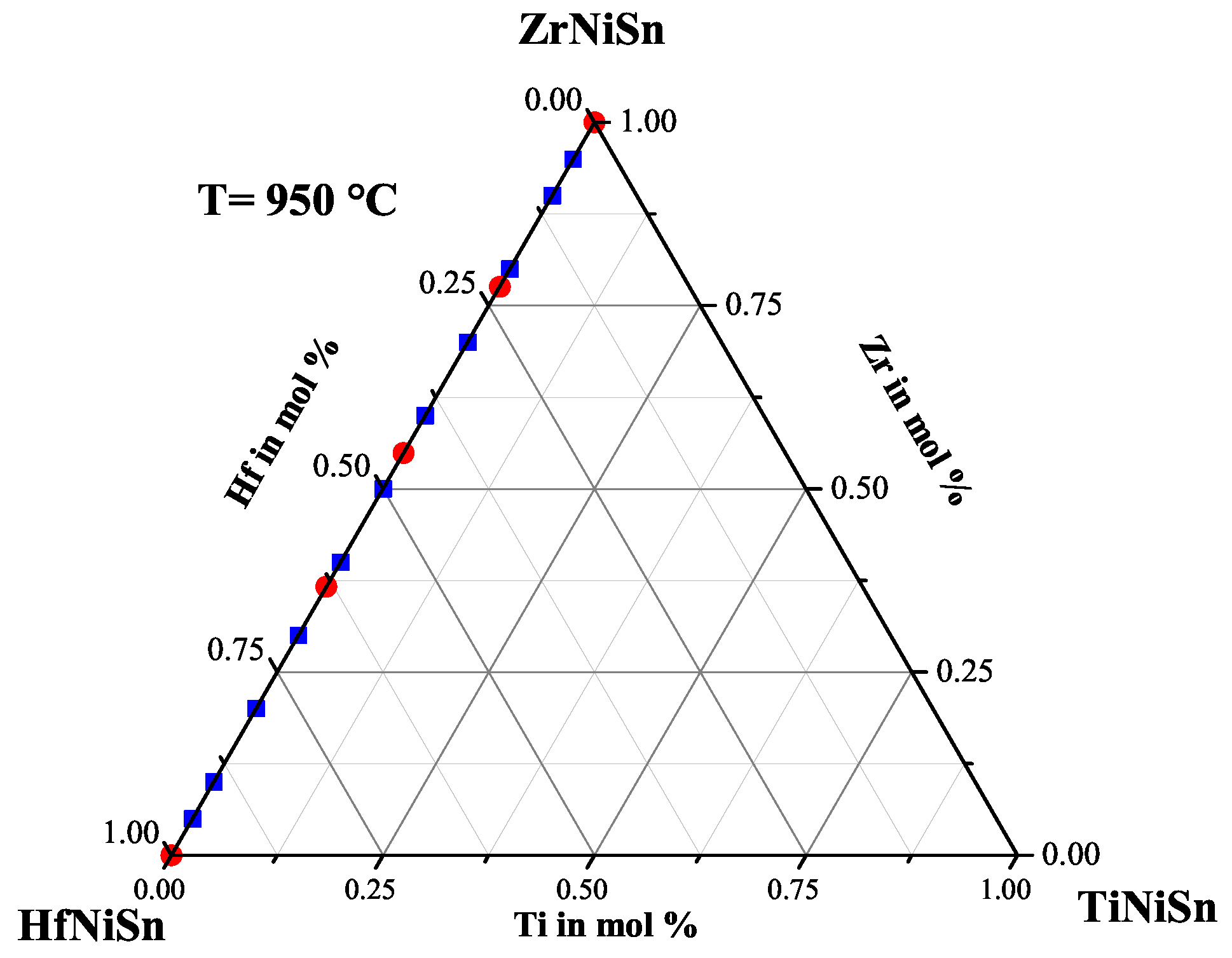

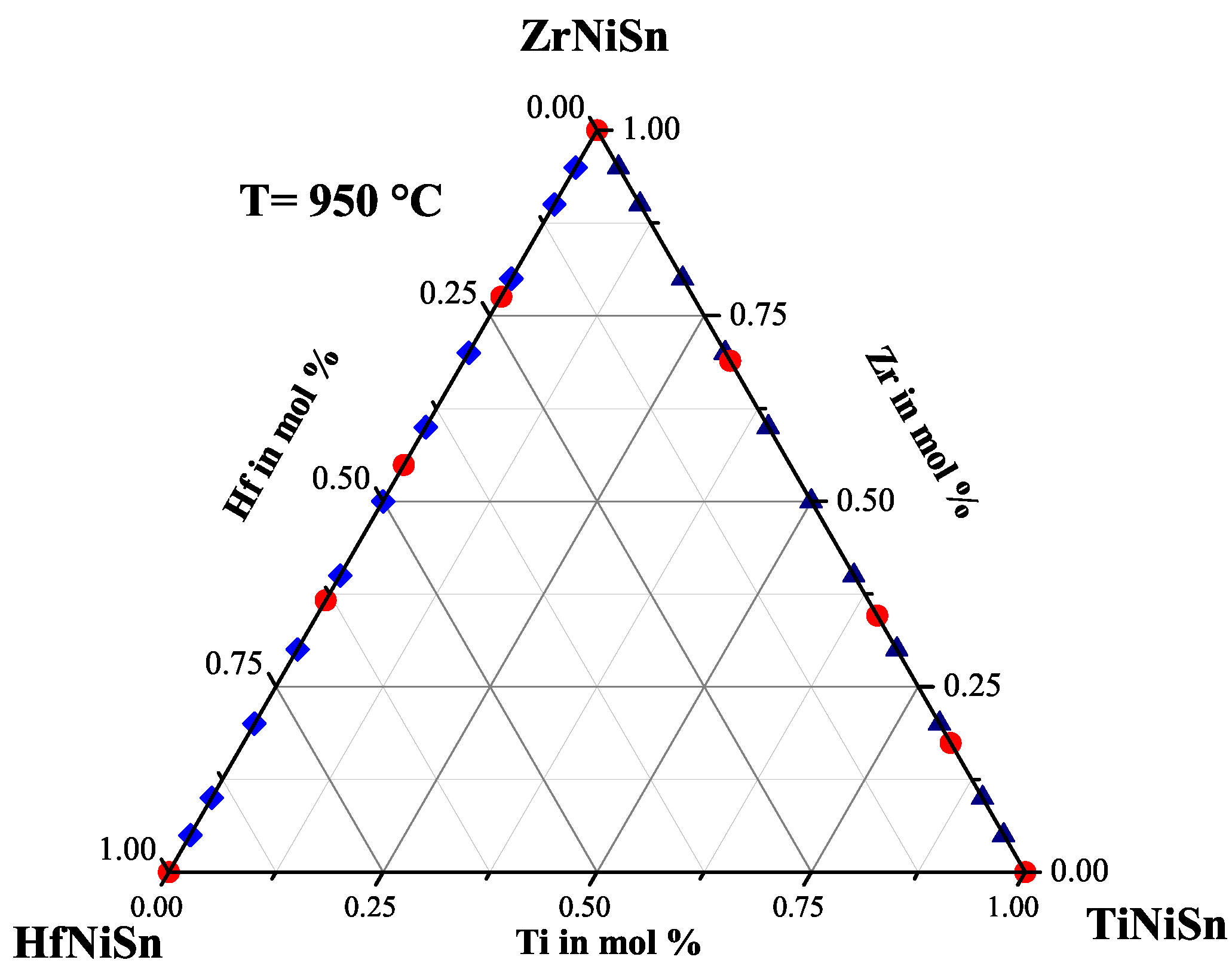
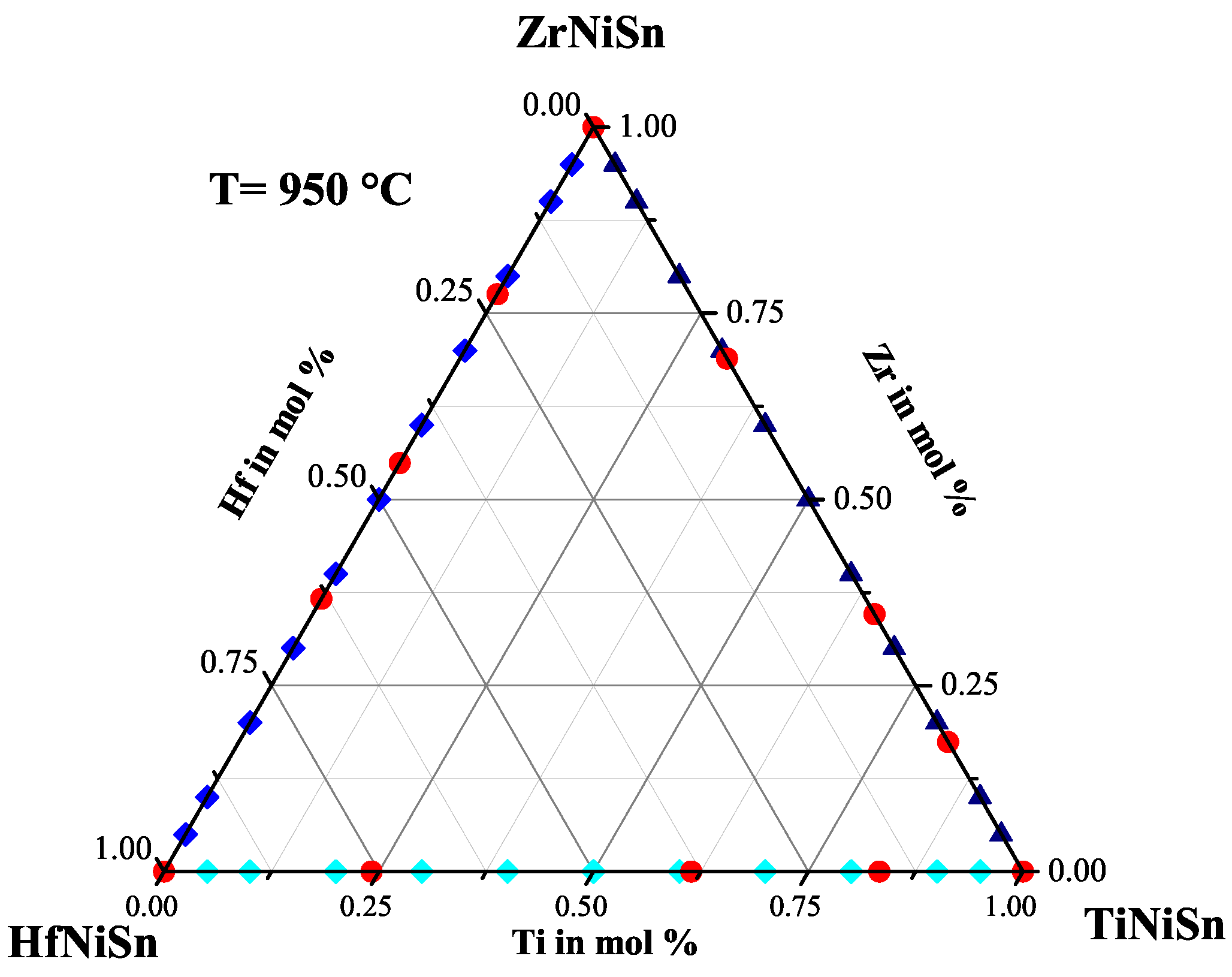


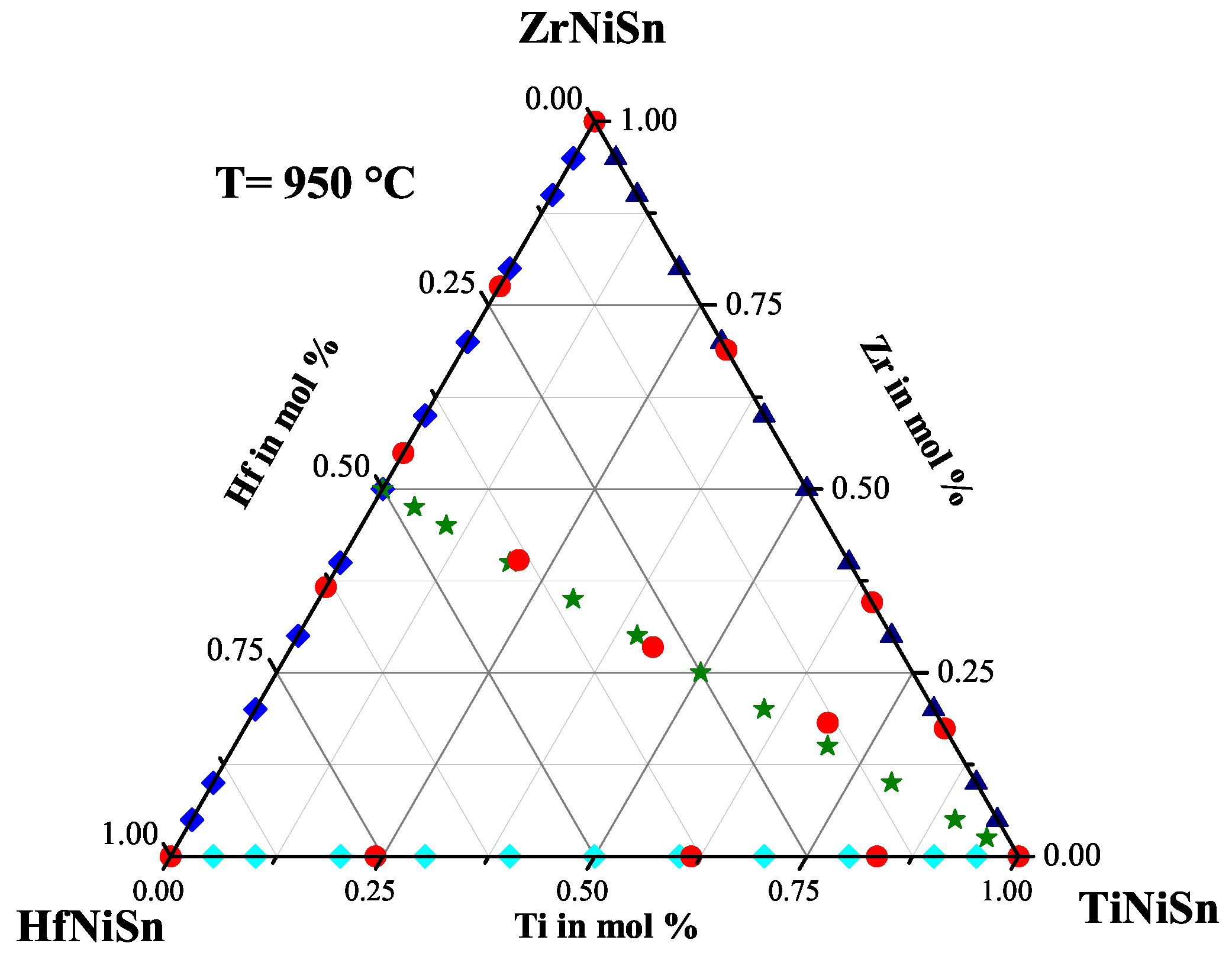

| Weighed Composition | Detected Phases | Ratio | a |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZrHfNiSn | (Å) | ||
| ZrNiSn | ZrNiSn, Sn | 97% ZrNiSn | 6.121 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrNiSn, Hf | inclusions | 6.114 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrNiSn, Hf | inclusions | 6.114 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XII), SnZr, HfNiSn | 95% (XII) | 6.112 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII), ZrHfNiSn(XII) | 6.105 | |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII), ZrSn | 95% (XIII) | 6.101 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII) | 95% (XIII) | 6.101 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIV), NiSn | 90% (XIV) | 6.098 |
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIV), ZrSn | 95% (XIV) | 6.094 |
| ZrHfNiSn | HfNiSn, ZrSn | 90% HfNiSn | 6.092 |
| ZrHfNiSn | HfNiSn, Zr | inclusions | 6.091 |
| ZrHfNiSn | HfNiSn, Zr | inclusions | 6.091 |
| HfNiSn | HfNiSn | 97% HfNiSn | 6.091 |
| Stable Compositions |
|---|
| ZrNiSn |
| ZrHfNiSn(XII) |
| ZrHfNiSn(XIII) |
| ZrHfNiSn(XIV) |
| HfNiSn |
| Weighed Composition | Detected Phases | Ratio | a |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiZrNiSn | (Å) | ||
| TiNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, TiSn, Sn | 85% TiNiSn | 5.939 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, TiSn, Zr | 85% TiNiSn | 5.961 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, Zr | 90% TiNiSn | 5.960 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), TiSn | 95% (IX) | 5.966 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), NiSn | 60% (IX) | 6.001 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(X), ZrSn | 90% (X) | 6.086 |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), TiZrNiSn(XI) | 6.005/6.067 | |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(X), TiZrNiSn(XI) | 6.075 | |
| TiZrNiSn | TiZrNiSn(XI) | 97% (XI) | 6.204 |
| TiZrNiSn | ZrNiSn, TiSn, Zr | 90% ZrNiSn | 6.101 |
| TiZrNiSn | ZrNiSn,TiSn | 95% ZrNiSn | 6.101 |
| TiZrNiSn | ZrNiSn, Ti | 95% ZrNiSn | 6.108 |
| ZrNiSn | ZrNiSn, Sn | 97% ZrNiSn | 6.121 |
| Stable Compositions |
|---|
| TiNiSn |
| TiZrNiSn(IX) |
| TiZrNiSn(X) |
| TiZrNiSn(XI) |
| ZrNiSn |
| Weighed Composition | Detected Phases | Ratio | a |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiHfNiSn | (Å) | ||
| TiNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, TiSn, Sn | 85% TiNiSn | 5.939 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, TiSn, Hf | 85% TiNiSn | 5.940 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VII), TiSn | 90% (VII) | 5.955 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VII) | 97% (VII) | 5.971 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VII), TiHfNiSn(VI) | 5.954/5.991 | |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VI), TiSn | 95% (VI) | 5.995 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VI), TiHfNiSn(V) | 6.038 | |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(VII), TiHfNiSn(V) | 6.043 | |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(V), TiSn | 85% (V) | 6.045 |
| TiHfNiSn | TiHfNiSn(V), TiSn | 95% (V) | 6.071 |
| TiHfNiSn | HfNiSn,TiSn | 90% HfNiSn | 6.090 |
| TiHfNiSn | HfNiSn, TiSn | 95% HfNiSn | 6.089 |
| HfNiSn | HfNiSn, Sn | 97% HfNiSn | 6.091 |
| Stable Compositions |
|---|
| TiNiSn |
| TiHfNiSn(VII) |
| TiHfNiSn(VI) |
| TiHfNiSn(V) |
| HfNiSn |
| Weighed Composition | Detected Phases | Ratio | a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | (Å) | ||
| ZrHfNiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII) | 95% (XIII) | 6.101 |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII), TiSn | 90% (XIII) | 6.109 |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | ZrHfNiSn(XIII), TiSn | 70% (XIII) | 6.117 |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(IV), TiZrHfNiSn(III) | 6.090 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(IV), TiZrHfNiSn(III), TiSn, Sn | 6.092/6.013 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(III), TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 6.020 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(III), TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 6.050/5.986 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(III), TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 6.045/5.983 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(III), TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 6.001 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 5.973 | |
| Ti(ZrHf)NiSn | TiHfNiSn(VII), TiSn, ZrSn | 70% (VII) | 5.957 |
| TiNiSn | TiNiSn, NiTiSn, TiSn, Sn | 85% TiNiSn | 5.939 |
| Stable Compositions |
|---|
| ZrHfNiSn(XIII) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(IV) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(III) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(I) |
| TiZrNiSn(IX) |
| TiHfNiSn(VII) |
| TiNiSn |
| Weighed Composition | Detected Phases | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| TiZrHfNiSn | ||
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrNiSn(X), TiZrNiSn(XI), Hf | |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrNiSn(X), TiZrNiSn(XI), Hf | |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), TiZrNiSn(XI), Hf | |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrNiSn(IX), TiZrNiSn(X), Hf | |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(I), ZrHfNiSn(XIV) | |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiNiSn, ZrHfNiSn(XIV) | 70% (XIV) |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiNiSn, ZrHfNiSn(XIV) | 80% (XIV) |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiNiSn, TiHfNiSn(VI), Zr | 70% (VI) |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(IV) | 97% (IV) |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(III) | 95% (III) |
| TiZrHfNiSn | TiZrHfNiSn(I) | 95% (I) |
| Stable Compositions |
|---|
| TiNiSn |
| ZrNiSn |
| HfNiSn |
| ZrHfNiSn(XII) |
| ZrHfNiSn(XIII) |
| ZrHfNiSn(XIV) |
| TiZrNiSn(IX) |
| TiZrNiSn(X) |
| TiZrNiSn(XI) |
| TiHfNiSn(VII) |
| TiHfNiSn(VI) |
| TiHfNiSn(V) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(IV) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(III) |
| TiZrHfNiSn(I) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwall, M.; Balke, B. On the Phase Separation in n-Type Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Materials. Materials 2018, 11, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040649
Schwall M, Balke B. On the Phase Separation in n-Type Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Materials. Materials. 2018; 11(4):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040649
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwall, Michael, and Benjamin Balke. 2018. "On the Phase Separation in n-Type Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Materials" Materials 11, no. 4: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040649
APA StyleSchwall, M., & Balke, B. (2018). On the Phase Separation in n-Type Thermoelectric Half-Heusler Materials. Materials, 11(4), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040649




