Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Superlight Mg-Li Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
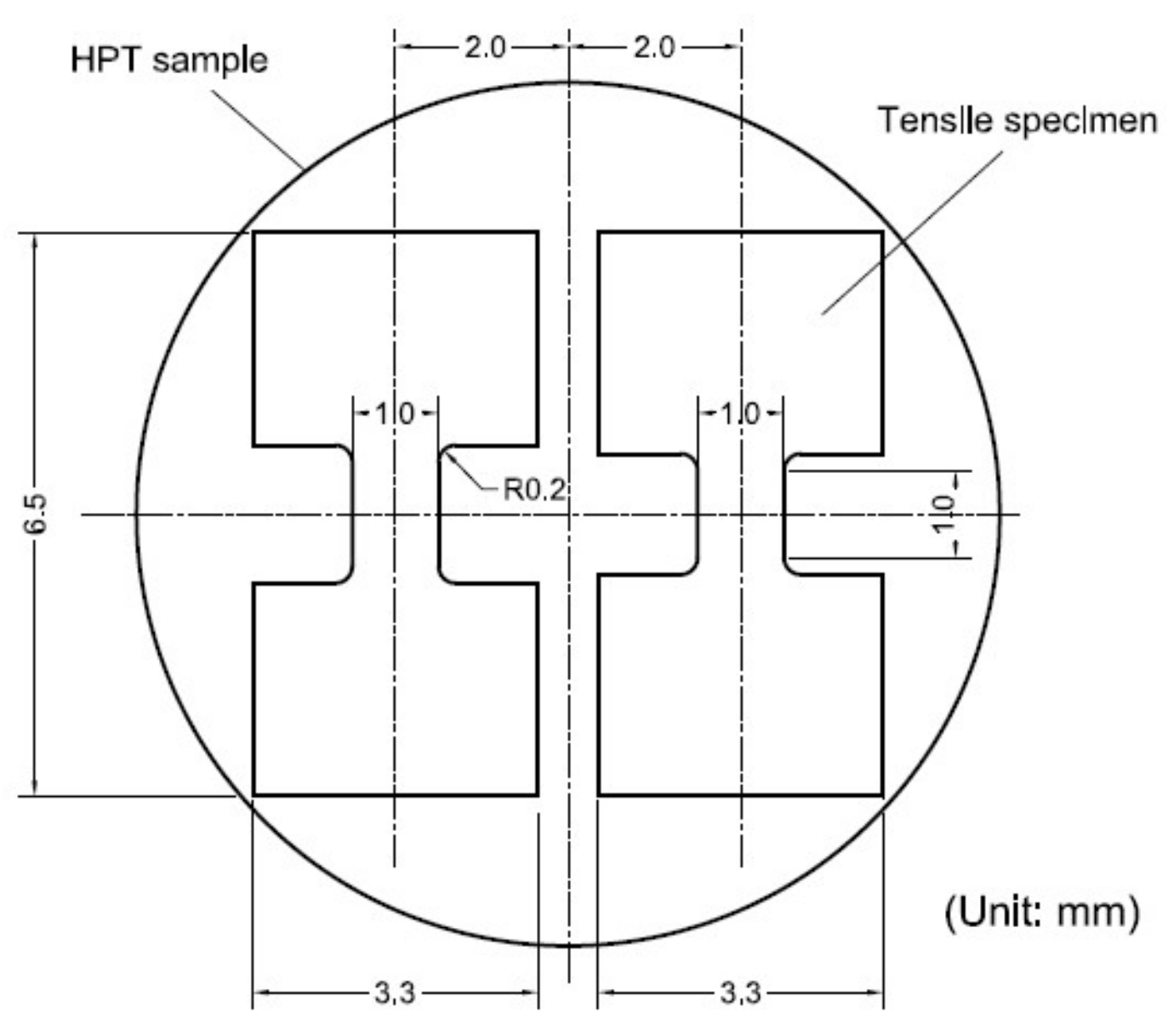
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
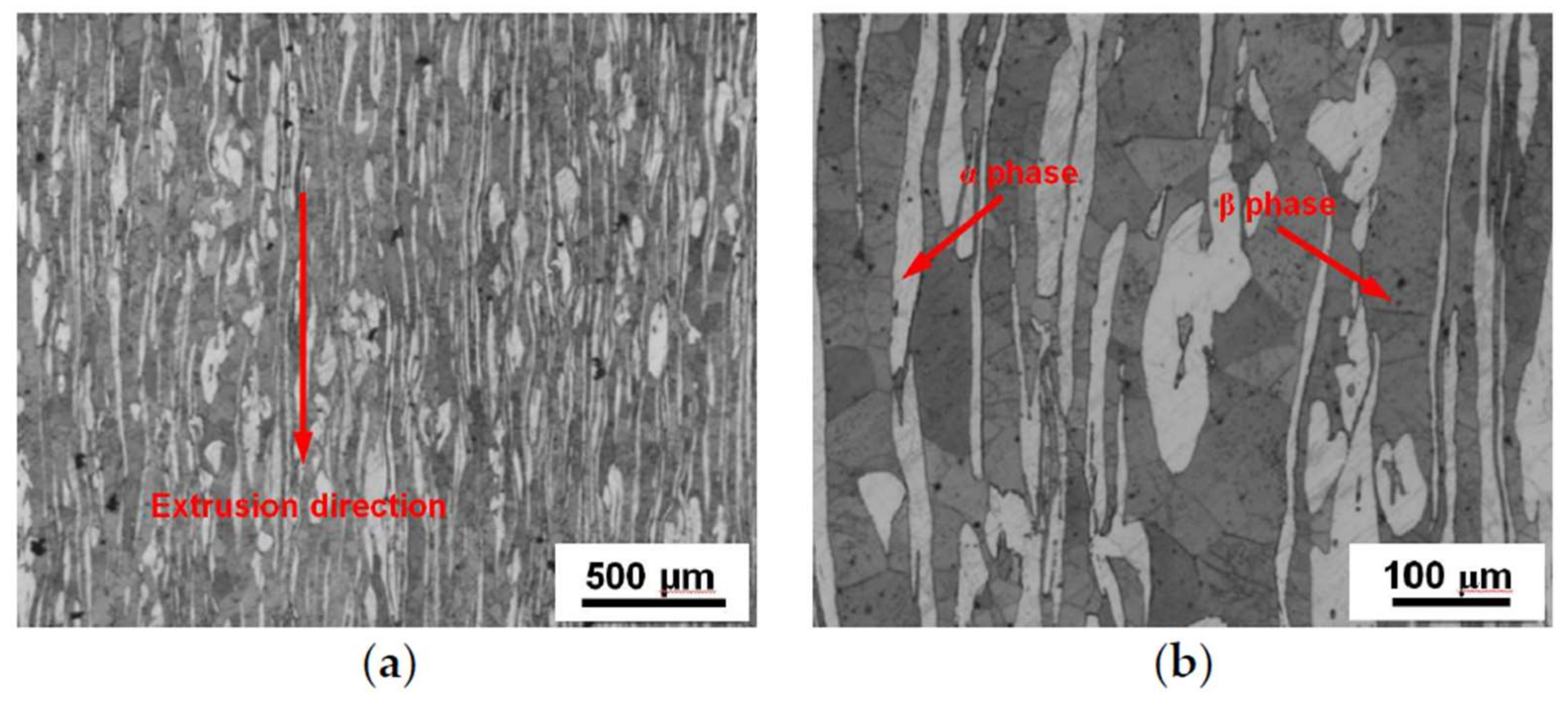
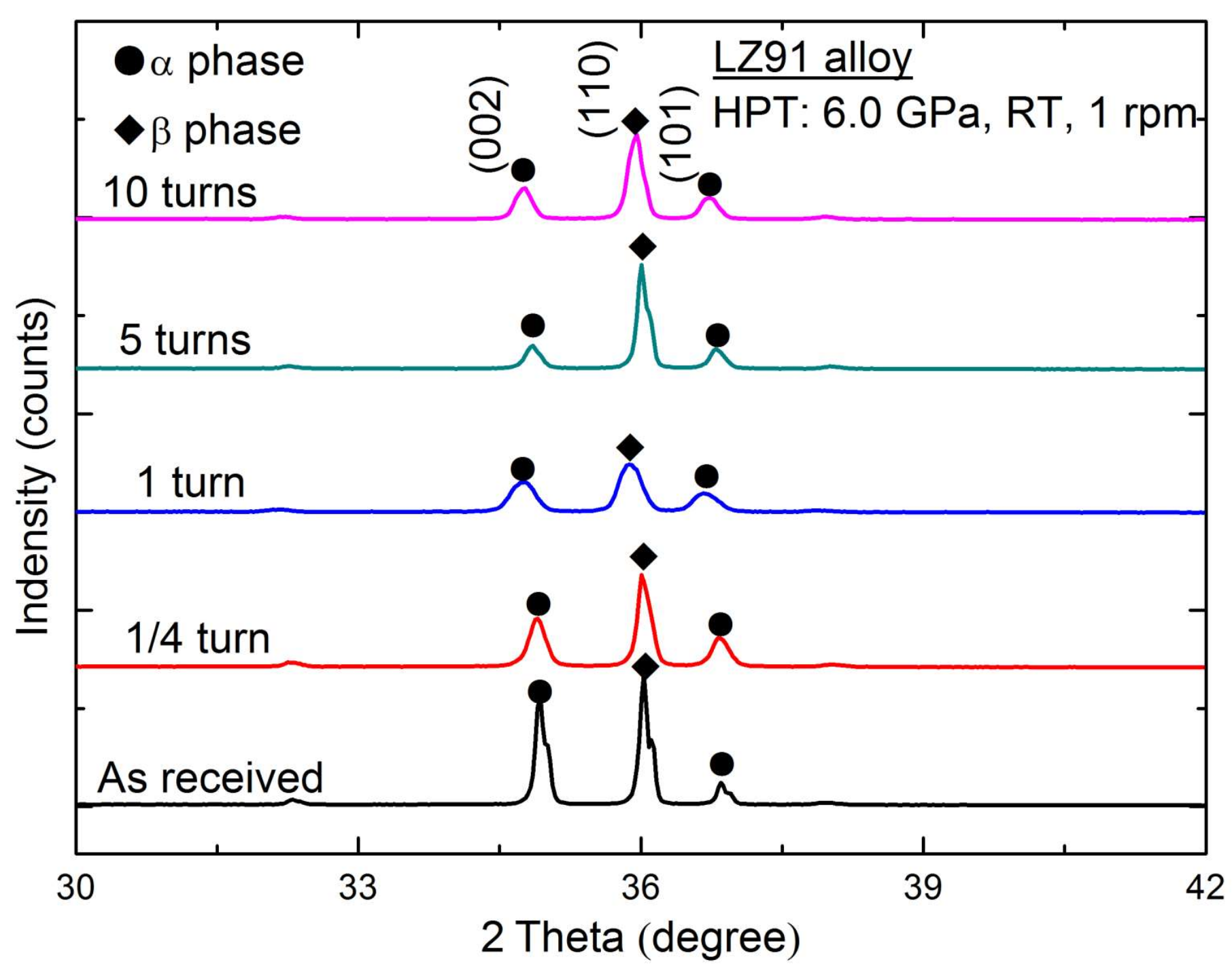
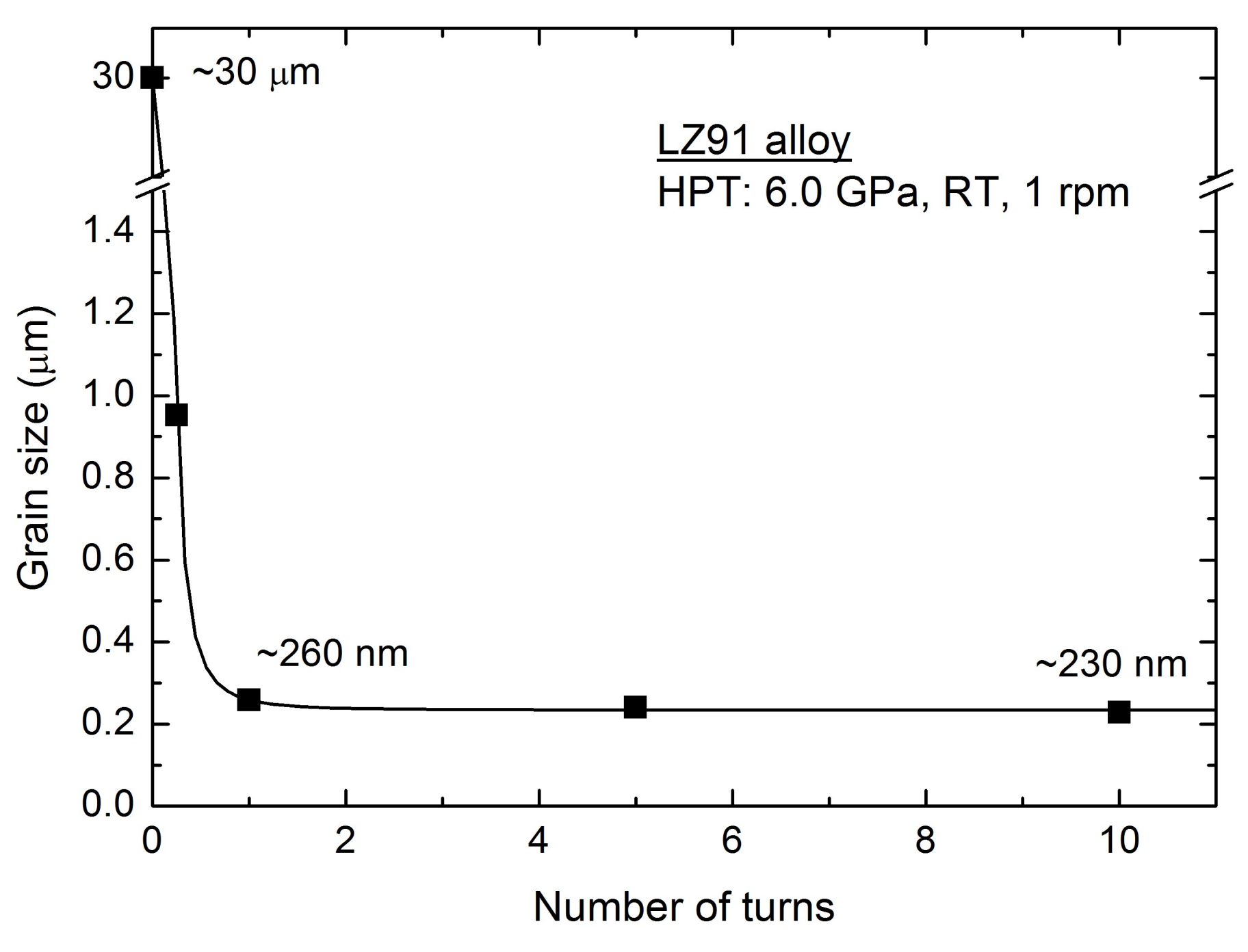
3.1. Microstructural Characteristics before and after HPT
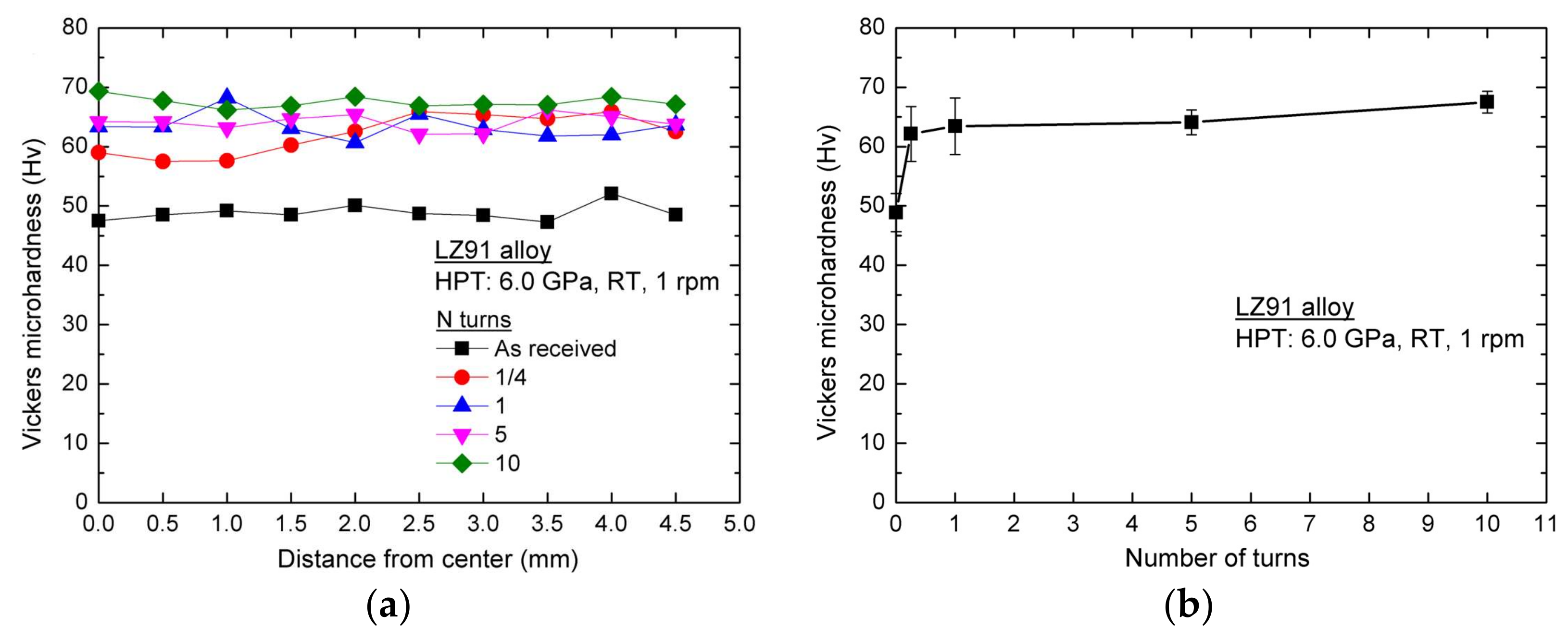
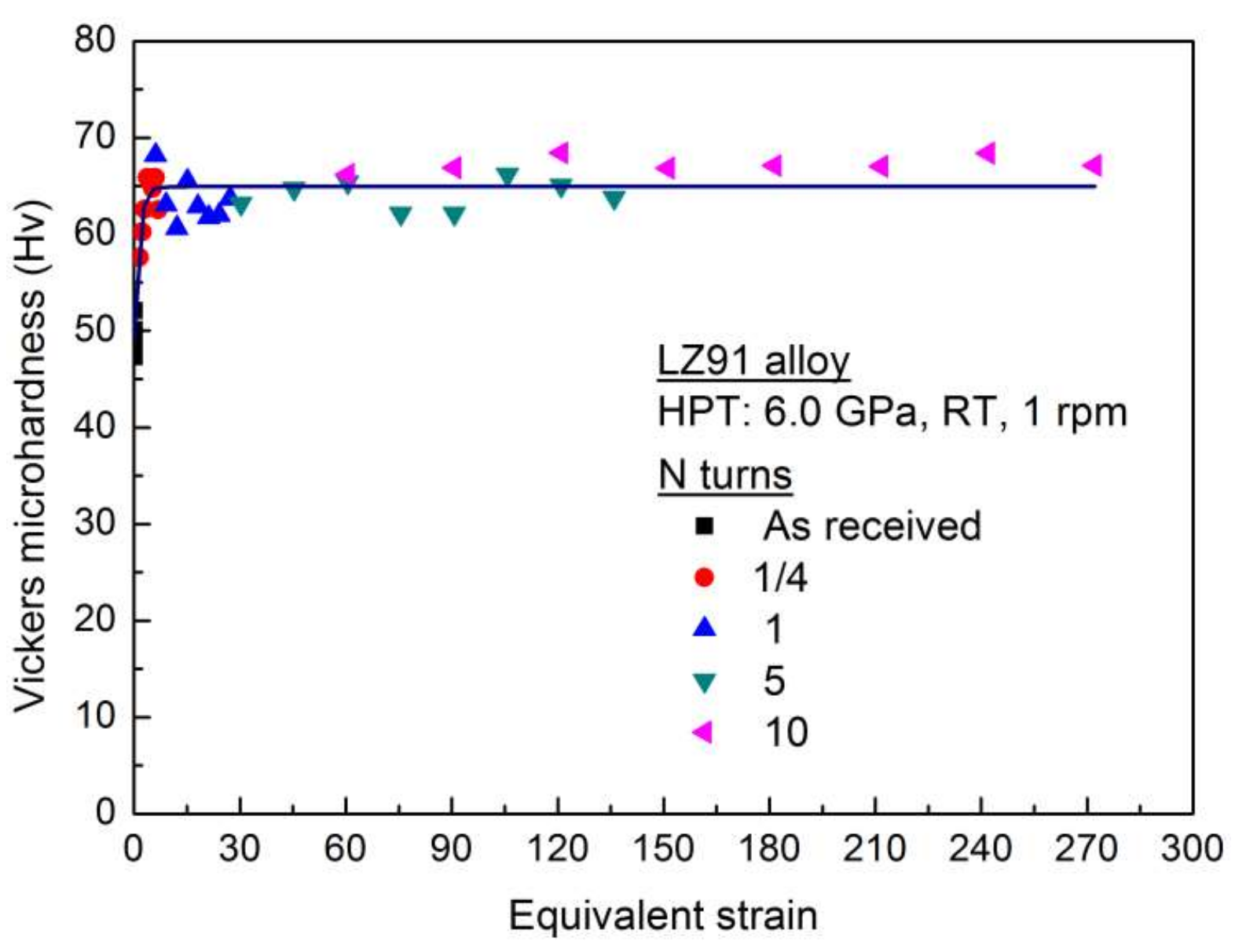
3.2. Microhardness Evaluation during HPT Processing
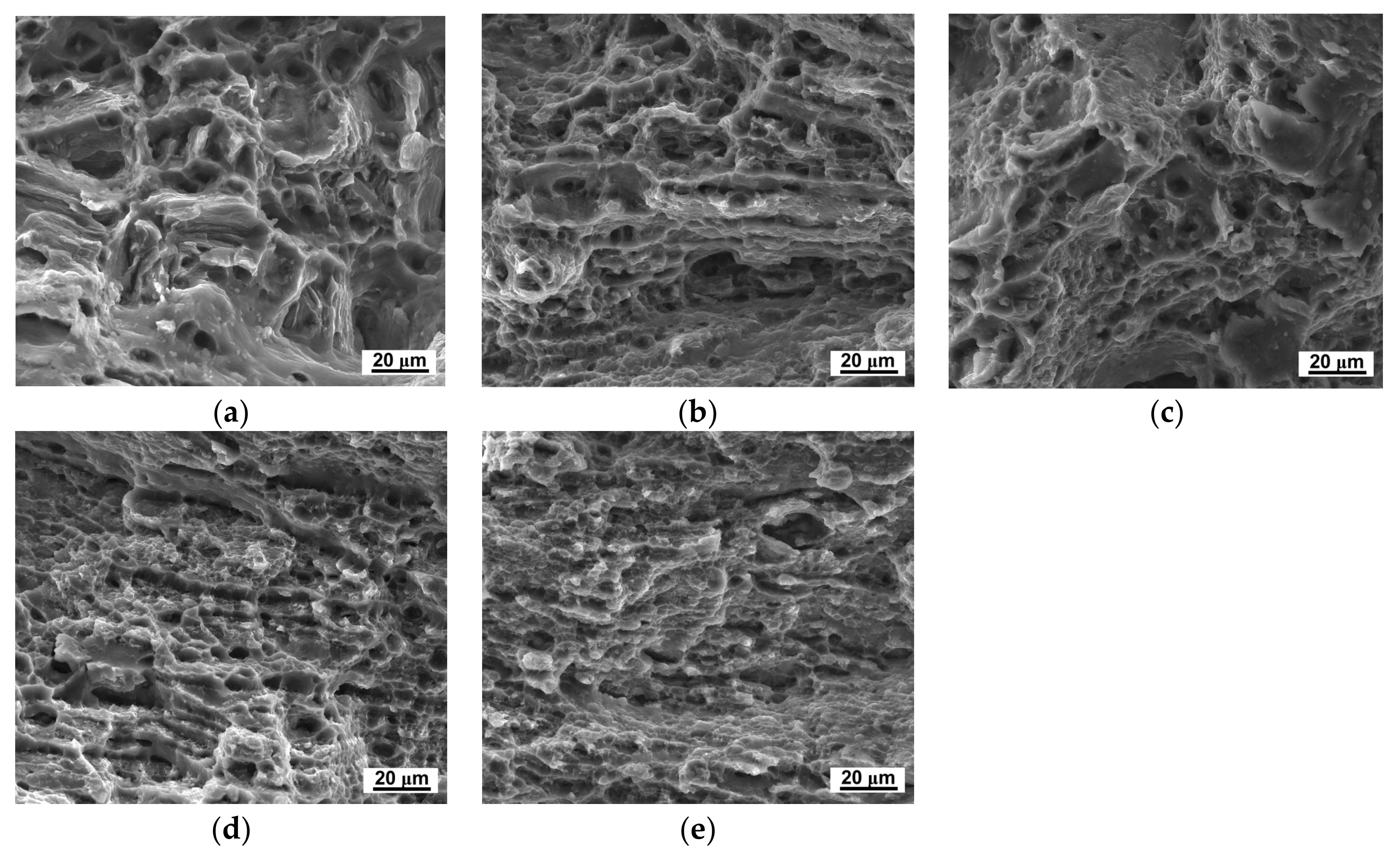
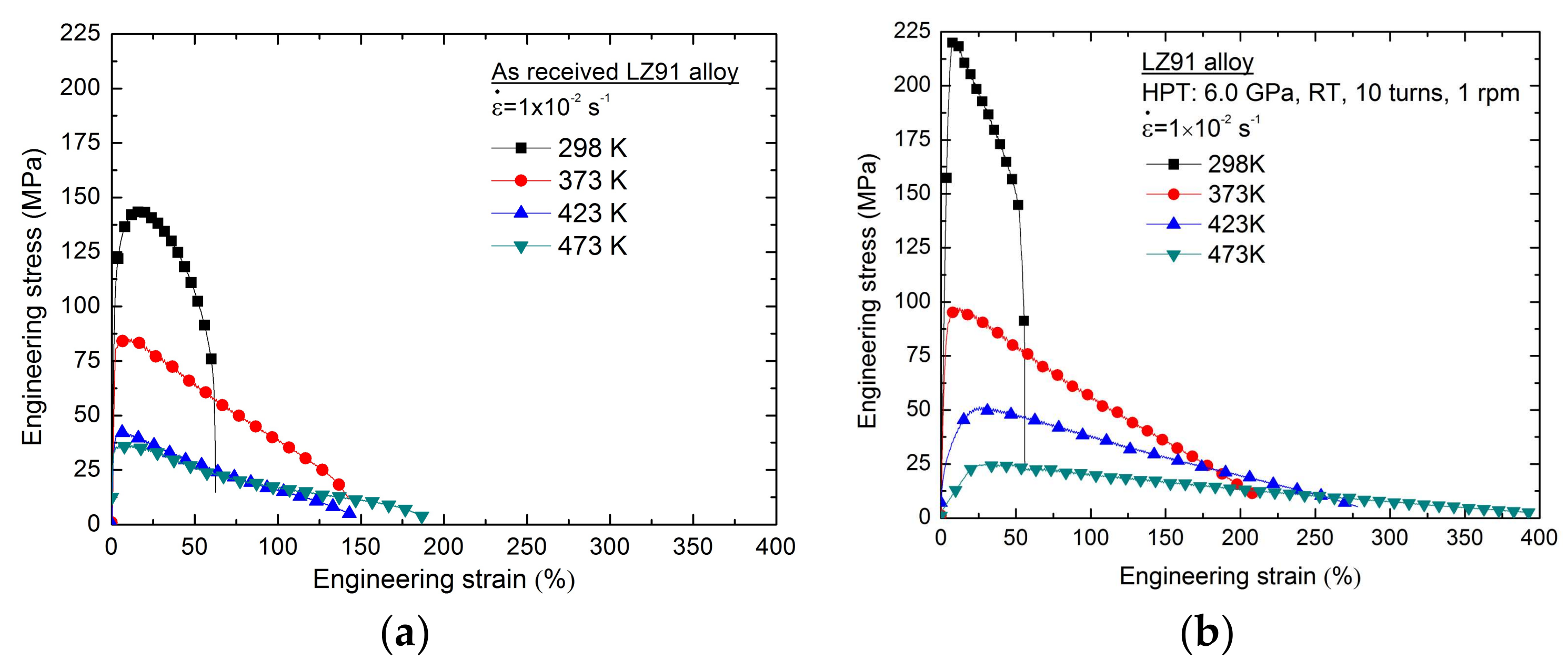
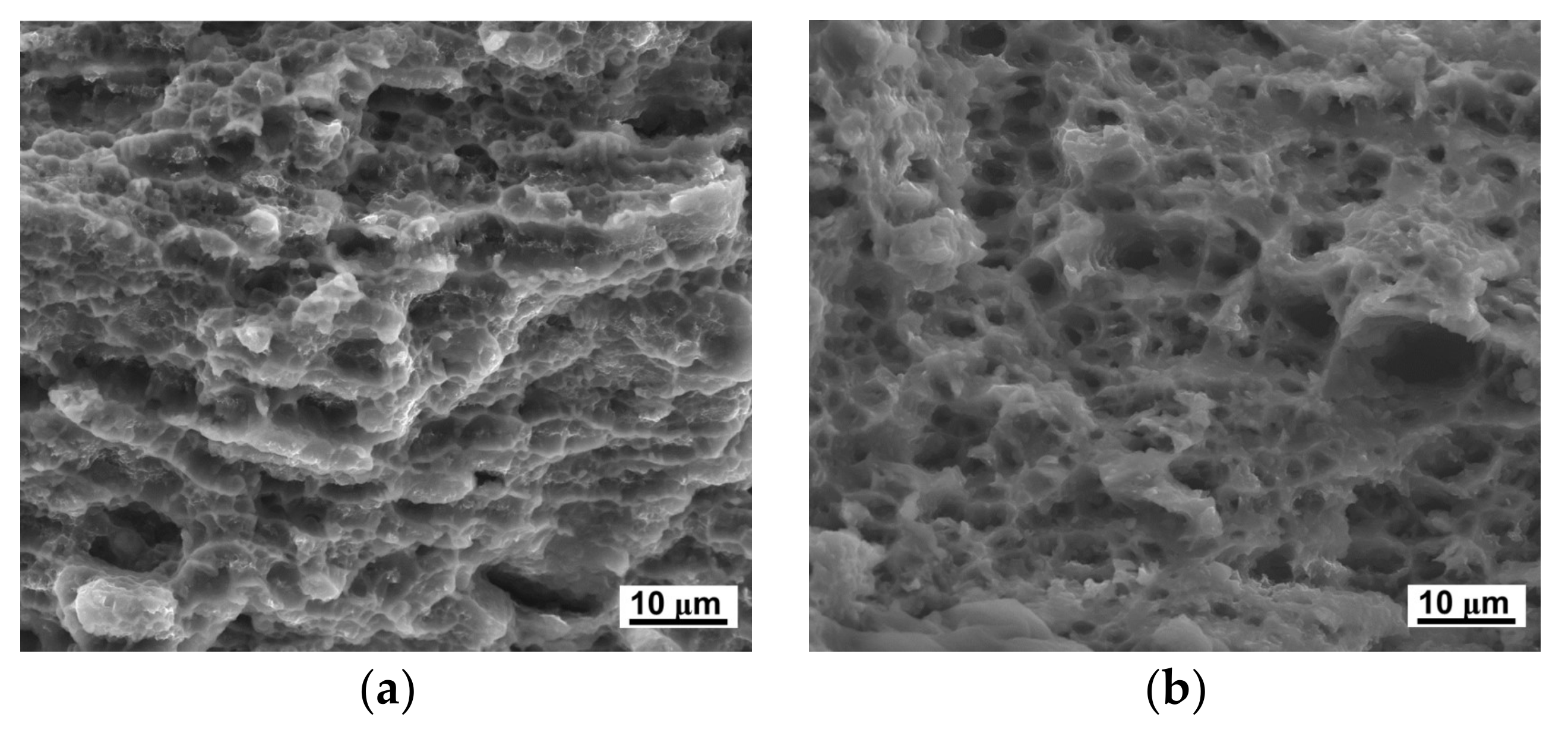
3.3. Tensile Behavior before and after HPT Processing
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructural Evolution in the Mg-Li Alloy after Processing by HPT
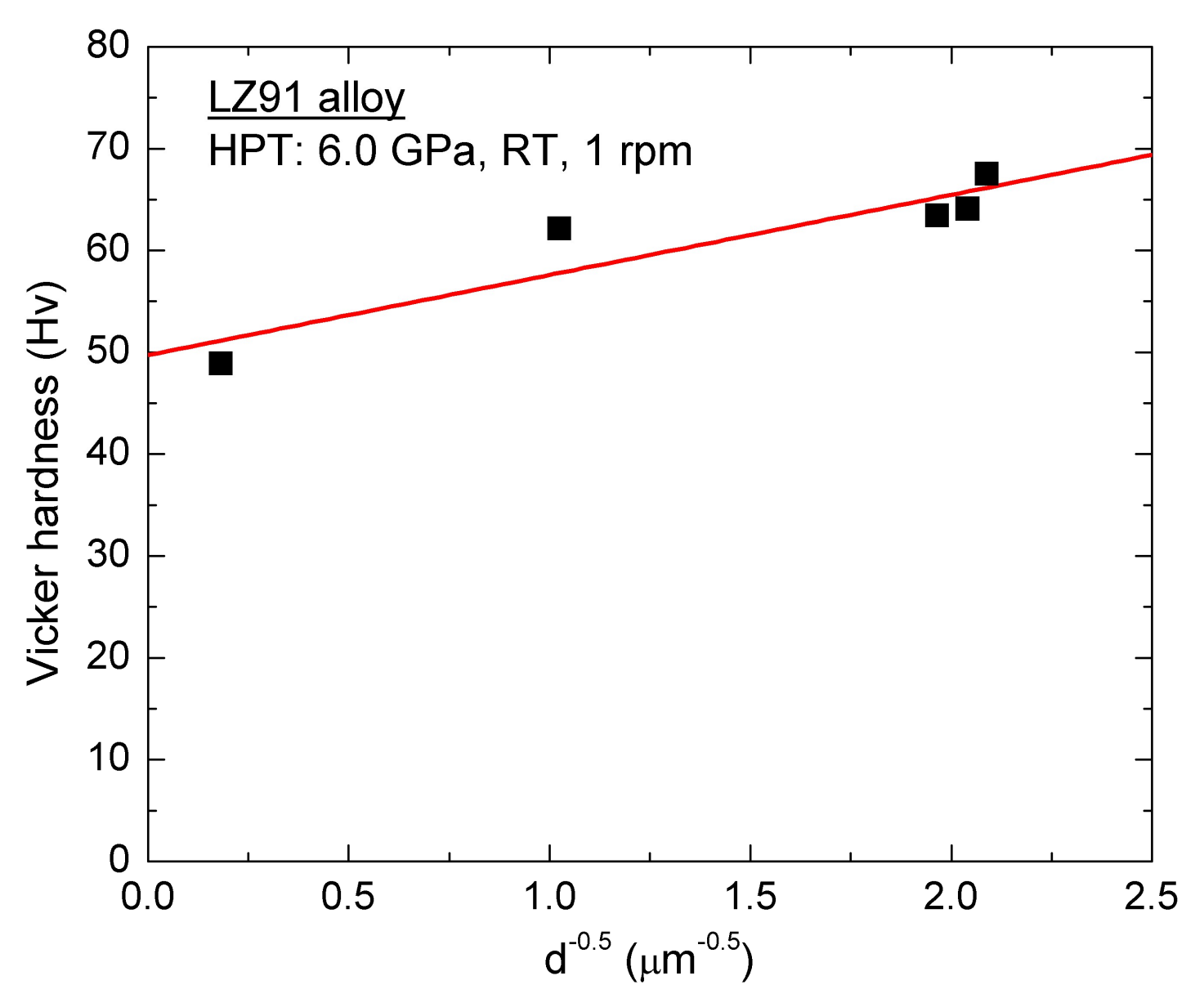
4.2. Microhardness Evolution in the Mg-Li Alloy after Processing by HPT
4.3. The Potential Application of the UFG Mg-Li Alloy on Micro-Forming Technology
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Mg-Li alloys were prepared via HPT processing with a pressure of 6.0 GPa up to 10 turns at ambient temperature. The average grain size diminished from ~30 μm (the original specimen) to ~230 nm (the HPT-processed specimen after 10 turns). The XRD results reveal the alloy was consist of hcp α-phase and bcc β-phase before and after HPT processing.
- (2)
- Vickers microhardness measurements indicate the average microhardness increases significantly with increasing number of HPT turns. Meanwhile, after five or more turns, the microhardness of HPT-processed LZ91 alloy is homogeneous. This significantly increased hardness can be explained by Hall-Petch strengthening. The variation of Vickers hardness along the radius of disk after HPT processing for LZ91 alloy is different from the previous reports which can be explained by the existing of two different phases.
- (3)
- The results from micro-tensile testing of the LZ91 alloy before and after HPT indicate that both the strength and ductility of LZ91 are improved with increasing number of HPT turns at both ambient and elevated temperatures. The maximum recorded tensile elongation is approximately 400% at 473 K with the initial strain rate of 1 × 10−2 s−1, indicating that after 10 turns HPT processing the ductility is improved significantly.
- (4)
- Based on the experimental results, it is confirmed that the UFG LZ91 Mg-Li alloy processed by HPT processing after 10 turns presents enormous potential application to micro-forming.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valiev, R.Z.; Islamgaliev, R.K.; Alexandrov, I.V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2000, 45, 103–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, T.G. Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: Achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 7035–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.G.; Ying, T.; Zheng, M.Y.; Wei, E.D.; Wu, K.; Hu, X.S.; Gan, W.M.; Brokmeier, H.G.; Golovin, I.S. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of nano-SiCp/AZ91 composite processed by extrusion and equal channel angular pressing (ECAP). Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnak, T.; Minarik, P.; Gubicza, J.; Mathis, K.; Kuzel, R.; Janecek, M. Influence of equal channel angular pressing routes on texture, microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded AX41 magnesium alloy. Mater. Charact. 2017, 123, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajeri, S.N.; Al-Fadhalah, K.J.; Almazrouee, A.I.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructure and microhardness of an Al-6061 metal matrix composite processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Charact. 2016, 118, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarzade, M.; Masoumi, A.; Faraji, G.; Mohammadpour, M.; Yan, X.S. A new designed incremental high pressure torsion process for producing long nanostructured rod samples. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Toroghinejad, M.R.; Dutldewicz, J. Nanostructure formation during accumulative roll bonding of commercial purity titanium. Mater. Charact. 2016, 122, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Gandarilla, F.; Maria Salcedo-Garrido, A.; Bolmaro, R.E.; Baudin, T.; De Vincentis, N.S.; Avalos, M.; Cabanas-Moreno, J.G.; Mendoza-Leon, H. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties on an ARB processed IF steel studied by X-ray diffraction and EBSD. Mater. Charact. 2016, 118, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavian, M.M.; Khatami-Hamedani, H.; Abedi, H.R. Macrostructure evolution and mechanical properties of accumulative roll bonded Al/Cu/Sn multilayer composite. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 703, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyaev, A.P.; Kim, B.K.; Nurislamova, G.V.; Baro, M.D.; Szpunar, J.A.; Langdon, T.G. Orientation imaging microscopy of ultrafine-grained nickel. Scripta Mater. 2002, 46, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyaev, A.P.; Nurislamova, G.V.; Kim, B.K.; Baro, M.D.; Szpunar, J.A.; Langdon, T.G. Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyaev, A.P.; Kim, B.K.; Szpunar, J.A.; Baro, M.D.; Langdon, T.G. The microstructural characteristics of ultratine-grained nickel. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2005, 391, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.C.; Kori, S.A.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Das, G.; Alhajeri, S.N.; Langdon, T.G. Using ball indentation to determine the mechanical properties of an Al-7475 alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polmear, I.J. Magnesium alloys and applications. Mater. Sci. Tech. Lond. 1994, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shirooyeh, M.; Wongsa-Ngam, J.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Langdon, T.G. Hardness homogeneity and micro-tensile behavior in a magnesium AZ31 alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2013, 586, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Song, X. Formability of AZ31 Mg alloy sheets within medium temperatures. J. Magnesium Alloy 2013, 1, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Qiu, D.; Taylor, J.A.; Easton, M.A.; Zhang, M.X. The role of Al2Y in grain refinement in Mg–Al–Y alloy system. J. Magnes. Alloy 2013, 1, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, X.; Wen, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, W.; Lavernia, E.J. Influence of Extrusion on the Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Mg-9Li-3Al-xSr Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44A, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Wang, J.; Chu, C.; Lee, S. Mechanical properties and microstructures of various Mg-Li alloys. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 3272–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.D.; Wu, S.D.; Peng, R.L.; Huang, C.X.; Jiang, C.B.; Li, S.X. Textures and mechanical behavior of Mg-3.3%Li alloy after ECAP. Scripta Mater. 2004, 51, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dong, Z.; Yu, C.; Tong, R. Microstructure and properties of Mg-5.21Li-3.44Zn-0.32Y-0.01Zr alloy. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2013, 559, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Aguilar, M.; Cetlin, P.R.; Langdon, T.G. Processing magnesium alloys by severe plastic deformation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 63, 12171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranachowski, Z.; Ranachowski, P.; Rejmund, F.; Pawelek, A.; Piatkowski, A.; Jasienski, Z. The study of influence of high pressure torsion process on acoustic emission activity of compressed Mg-Li alloys. Arch. Acoust. 2008, 33, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kudela, S.; Pawelek, A.; Ranachowski, Z.; Piatkowski, A.; Kudela, S., Jr.; Ranachowski, P. Effect of Al alloying on the Hall-Petch strengthening and AE in compressed Mg-Li-Al alloys before and after HPT processing. Kovove Mater. 2011, 49, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao, B.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Perez-Prado, M.T. Stabilization of metastable phases in Mg-Li alloys by high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater. 2013, 68, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisenko, Y.; Lojkowski, W.; Valiev, R.Z.; Fecht, H.J. The mechanism of formation of nanostructure and dissolution of cementite in a pearlitic steel during high pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5555–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, J.; Kruzik, M.; Sedlacek, R. A model of ultrafine microstructure evolution in materials deformed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Shirooyeh, M.; Xing, G.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Langdon, T.G. Microhardness, microstructure and tensile behavior of an AZ31 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7424–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhou, H.; Wan, Z. Microstructural evolution of AZ61-10 at. % Ti composite powders during mechanical milling. Mater. Design 2016, 104, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunoshita, H.; Edalati, K.; Furui, M.; Horita, Z. Ultrafine-grained magnesium-lithium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion: Low-temperature superplasticity and potential for hydroforming. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 640, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Masuda, T.; Arita, M.; Furui, M.; Sauvage, X.; Horita, Z.; Valiev, R.Z. Room-temperature superplasticity in an ultrafine-grained magnesium alloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Poggiali, F.S.J.; Silva, C.L.P.; Cetlin, P.R.; Langdon, T.G. The influence of grain size and strain rate on the mechanical behavior of pure magnesium. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Figueiredo, R.B.; Baudin, T.; Brisset, F.; Langdon, T.G. Evolution of Strength and Homogeneity in a Magnesium AZ31 Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion at Different Temperatures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straska, J.; Janecek, M.; Gubicza, J.; Krajnak, T.; Yoon, E.Y.; Kim, H.S. Evolution of microstructure and hardness in AZ31 alloy processed by high pressure torsion. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 625, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbati-Sarraf, S.A.; Langdon, T.G. Properties of a ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 613, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ahn, B.; Kawasaki, M.; Langdon, T.G. Evolution in hardness and microstructure of ZK60A magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubaie, S.A.; Bazarnik, P.; Lewandowska, M.; Huang, Y.; Langdon, T.G. Evolution of microstructure and hardness in an AZ80 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Rosalie, J.M.; Singh, A.; Somekawa, H.; Tsuchiya, K. Ultrafine grain formation in Mg-Zn alloy by in situ precipitation during high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater. 2014, 78–79, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.O. The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J. The cleavage strength of polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Ivanisenko, Y.V.; Rauch, E.F.; Baudelet, B. Structure and deformation behaviour of armco iron subjected to severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 4705–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetscher, F.; Vorhauer, A.; Stock, R.; Pippan, R. Structural refinement of low alloyed steels during severe plastic deformation. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2004, 387, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetscher, F.; Pippan, R.; Sturm, S.; Kauffmann, F.; Scheu, C.; Dehm, G. TEM investigations of the structural evolution in a pearlitic steel deformed by high-pressure torsion. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37A, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhauer, A.; Pippan, R. On the homogeneity of deformation by high pressure torsion. Scripta Mater. 2004, 51, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Han, J.; Janakiraman, S.; Ahn, B.; Kawasaki, M.; Langdon, T.G. Significance of grain refinement on microstructure and mechanical properties of an Al-3% Mg alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 686, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Microhardness measurements and the Hall-Petch relationship in an Al-Mg alloy with submicrometer grain size. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 4619–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Factors influencing the flow and hardness of materials with ultrafine grain sizes. Philos. Mag. A 1998, 78, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarnik, P.; Huang, Y.; Lewandowska, M.; Langdon, T.G. Structural impact on the Hall-Petch relationship in an Al-5Mg alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 626, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucif, A.; Figueiredo, R.B.; Baudin, T.; Brisset, F.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructural evolution in an Al-6061 alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2010, 527, 4864–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Alhajeri, S.N.; Xu, C.; Langdona, T.G. The development of hardness homogeneity in pure aluminum and aluminum alloy disks processed by high-pressure torsion. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2011, 529, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirooyeh, M.; Xu, J.; Langdon, T.G. Microhardness evolution and mechanical characteristics of commercial purity titanium processed by high-pressure torsion. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2014, 614, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollertsen, F.; Biermann, D.; Hansen, H.N.; Jawahir, I.S.; Kuzman, K. Size effects in manufacturing of metallic components. CIRP Ann. 2009, 58, 566–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.W.; Chan, W.L. A review on the state-of-the-art microforming technologies. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2013, 67, 2411–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Li | Zn | Mn | Else |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt %) | 8.92 | 0.97 | 0.1 | / |
| Material | HPT | Grain Size (nm) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turns | Pressure(GPa) | Temperature | |||
| Mg-8% Li | 5 | 3.0 | RT | ~500 | Matsunoshita et al. [32] |
| Mg-8% Li | 20 | 6.0 | RT | ~240 | Edalati et al. [33] |
| Pure Mg | 10 | 6.0 | RT | ~1000 | Figueiredo et al. [34] |
| AZ31 | 5 | 6.0 | RT | ~900–1200 | Huang et al. [35] |
| AZ31 | 10 | 6.0 | RT | ~110 | Xu et al. [30] |
| AZ31 | 15 | 2.5 | RT | ~150–200 | Stráská et al. [36] |
| ZK60 | 5 | 2.0 | RT | ~1000 | Torbati-Sarraf et al. [37] |
| ZK60A | 5 | 6.0 | RT | ~2000–5000 | Lee et al. [38] |
| AZ80 | 10 | 6.0 | RT | ~200 | Alsubaie et al. [39] |
| Mg-3.4 Zn | 20 | 5.0 | RT | ~140 | Meng et al. [40] |
| Mg-8.92% Li | 10 | 6.0 | RT | ~230 | Present paper |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Yoon, J.I.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Kim, H.S. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Superlight Mg-Li Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion. Materials 2018, 11, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040598
Su Q, Xu J, Li Y, Yoon JI, Shan D, Guo B, Kim HS. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Superlight Mg-Li Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion. Materials. 2018; 11(4):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040598
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Qian, Jie Xu, Yuqiao Li, Jae Ik Yoon, Debin Shan, Bin Guo, and Hyoung Seop Kim. 2018. "Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Superlight Mg-Li Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion" Materials 11, no. 4: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040598
APA StyleSu, Q., Xu, J., Li, Y., Yoon, J. I., Shan, D., Guo, B., & Kim, H. S. (2018). Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Superlight Mg-Li Alloy Processed by High-Pressure Torsion. Materials, 11(4), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040598






