Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
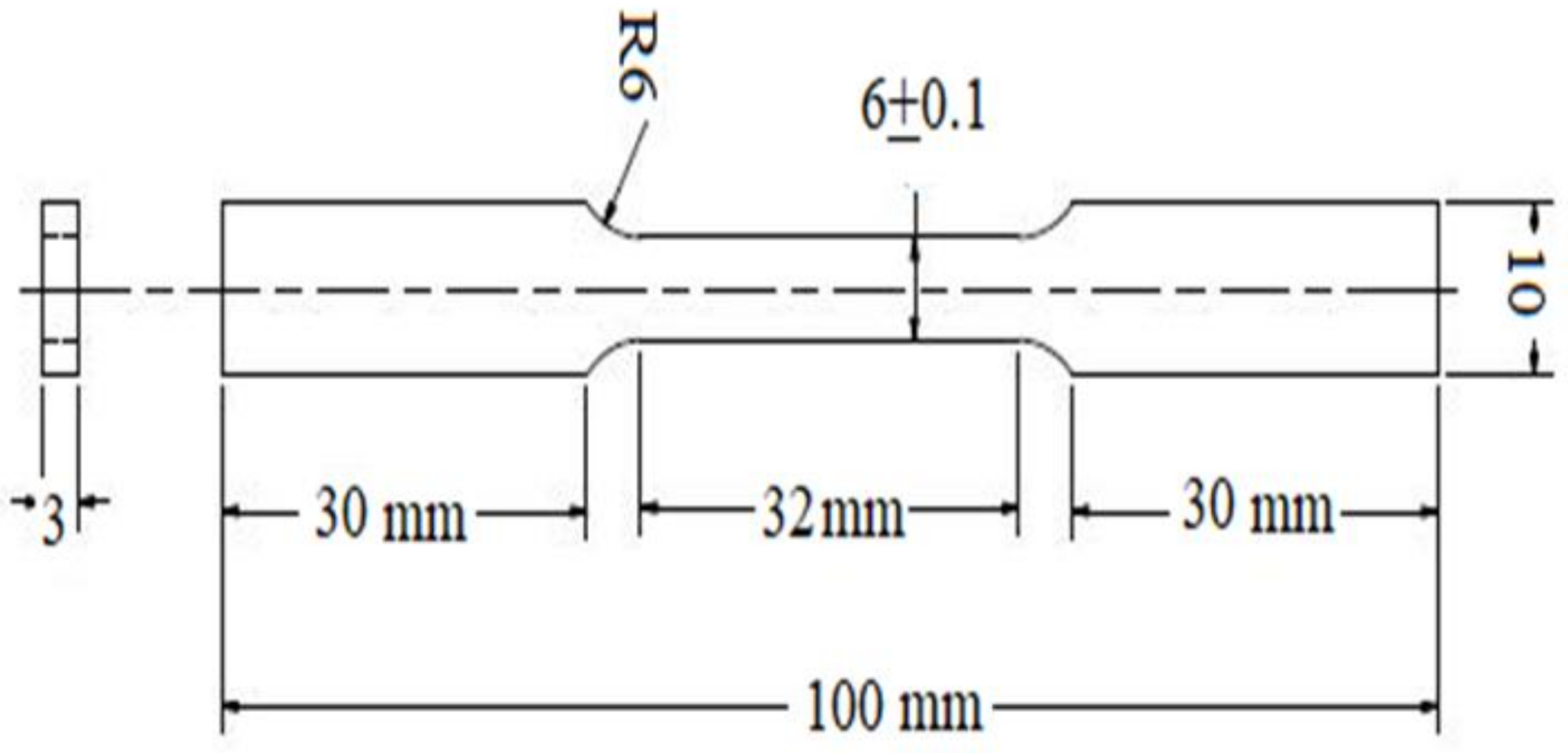
2.1. Sample Preparation
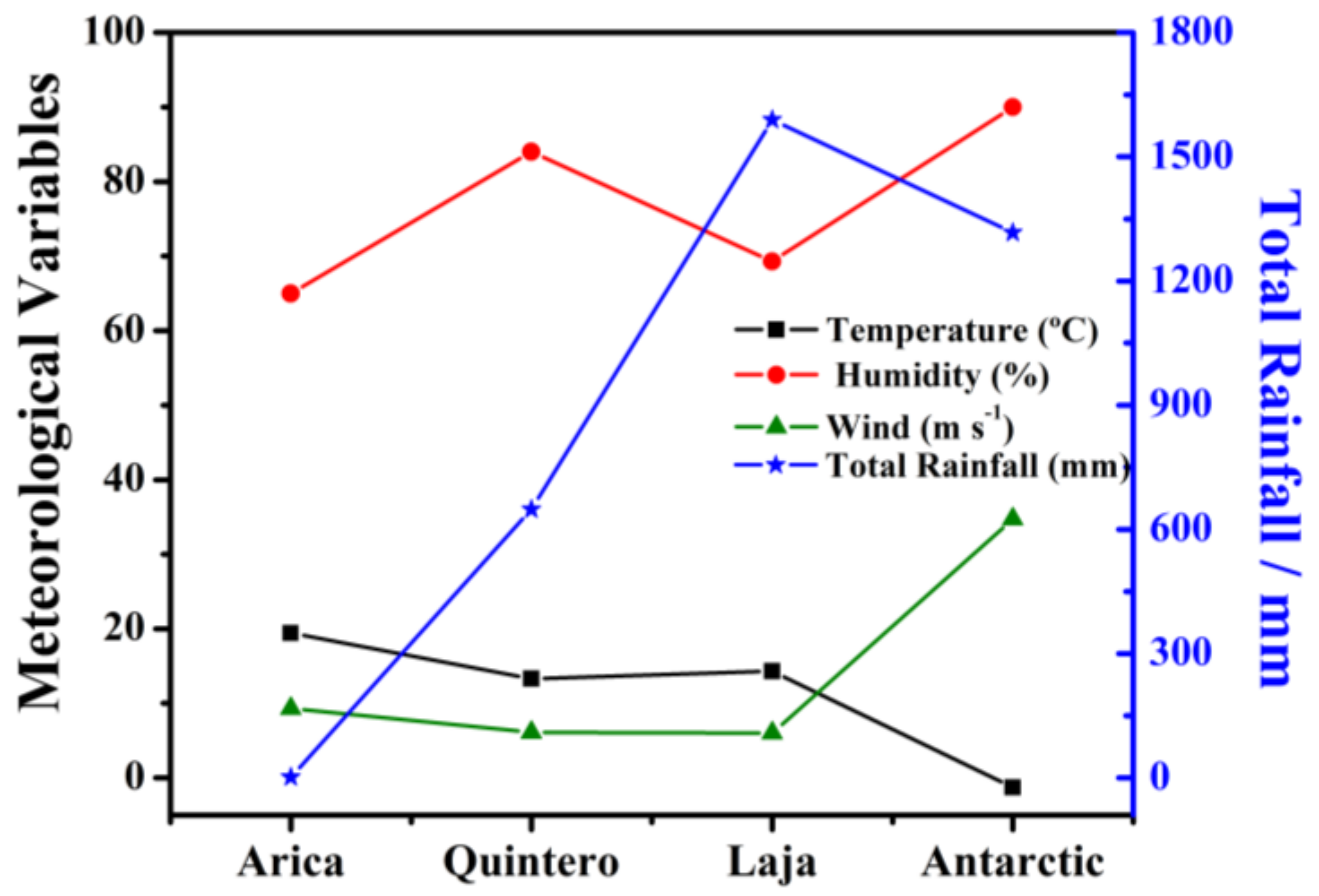
2.2. Environmental Conditions of Selected Locations
2.3. Methods of Characterization of Corrosion Products Formed on the Surface of SAE 1020 Steel
2.4. Methods Used for Determination of Electrochemical Behavior of SAE 1020 Steel
2.5. Mechanical Testing of SAE 1020 Steel
3. Results and Discussion
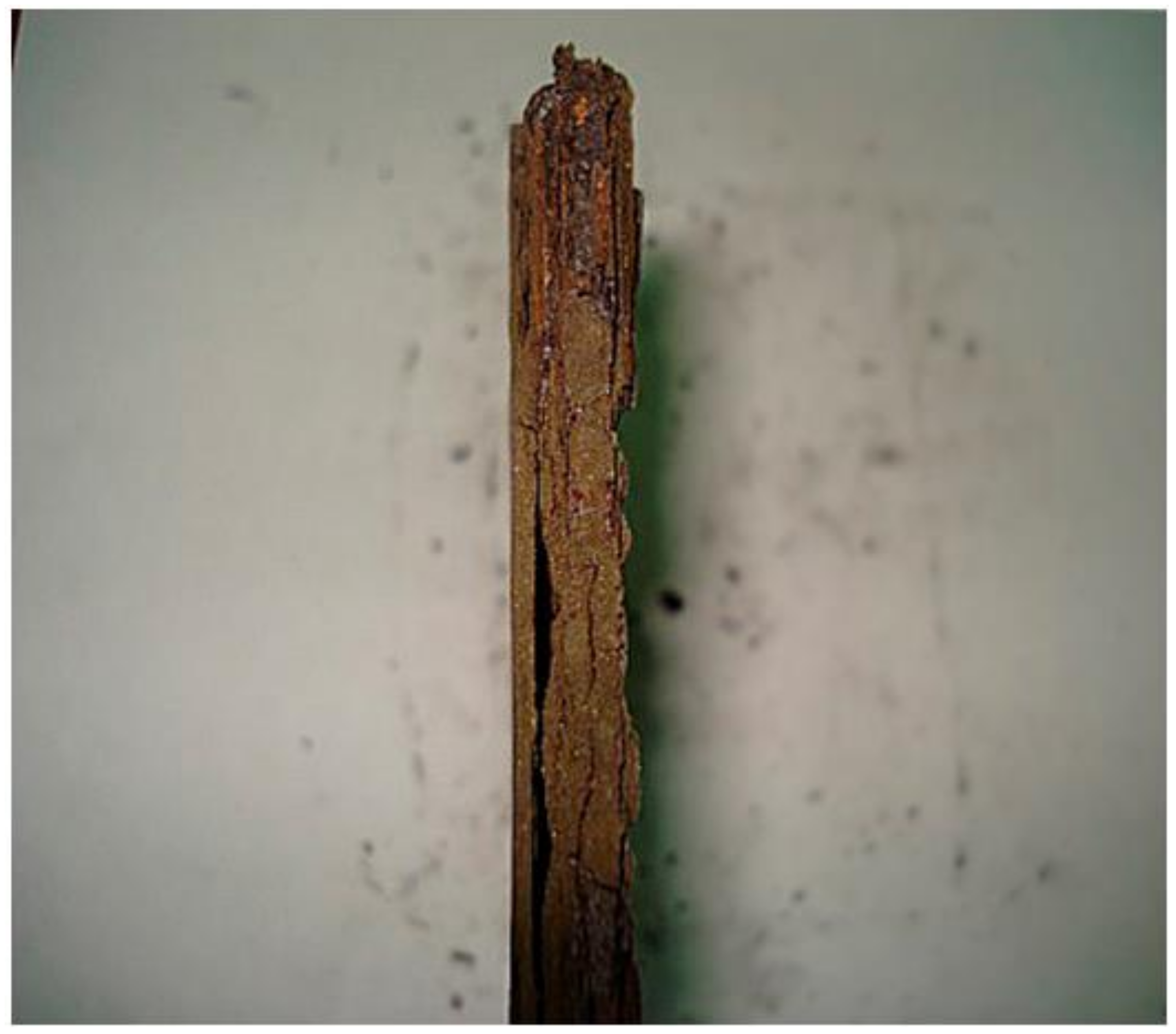
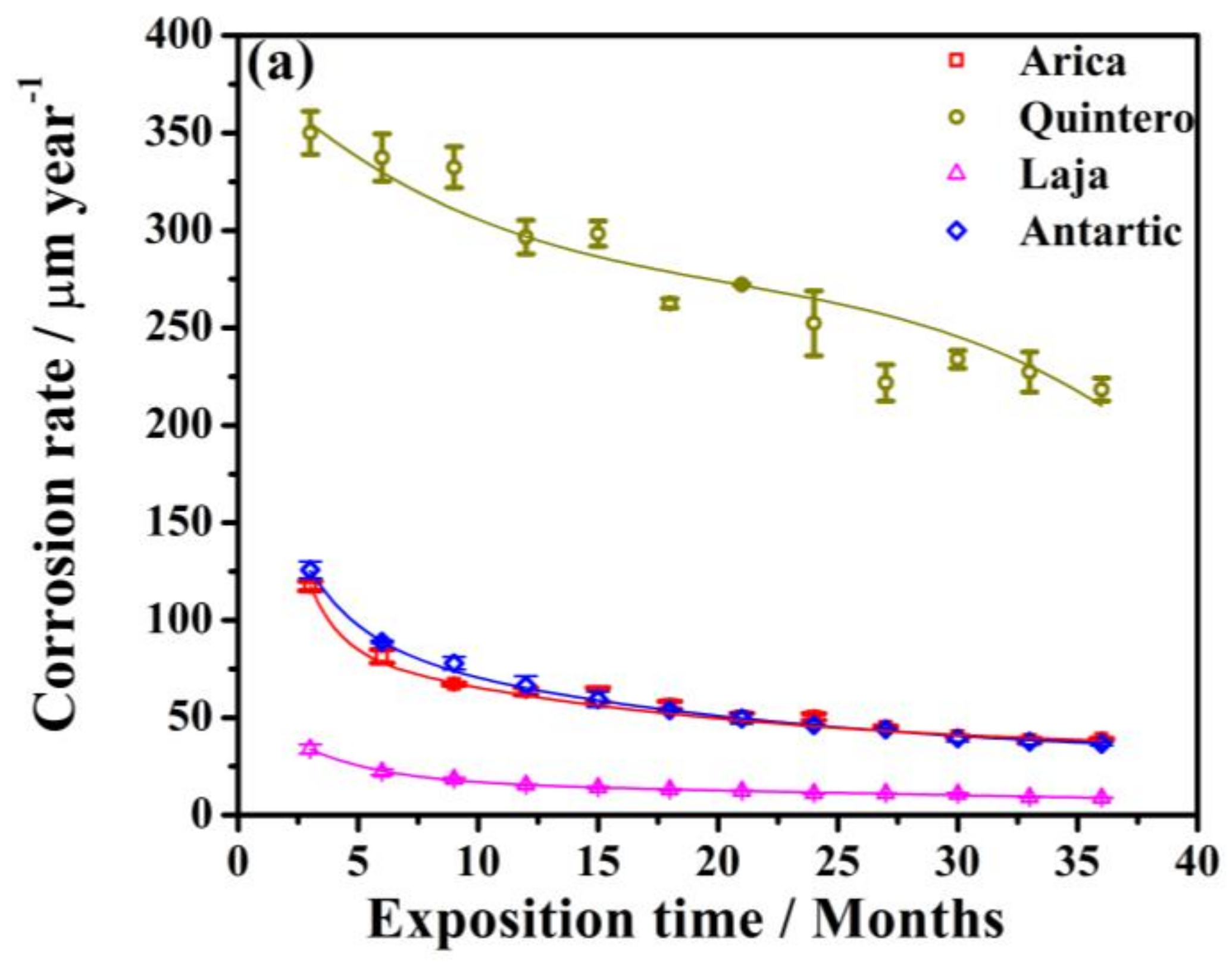
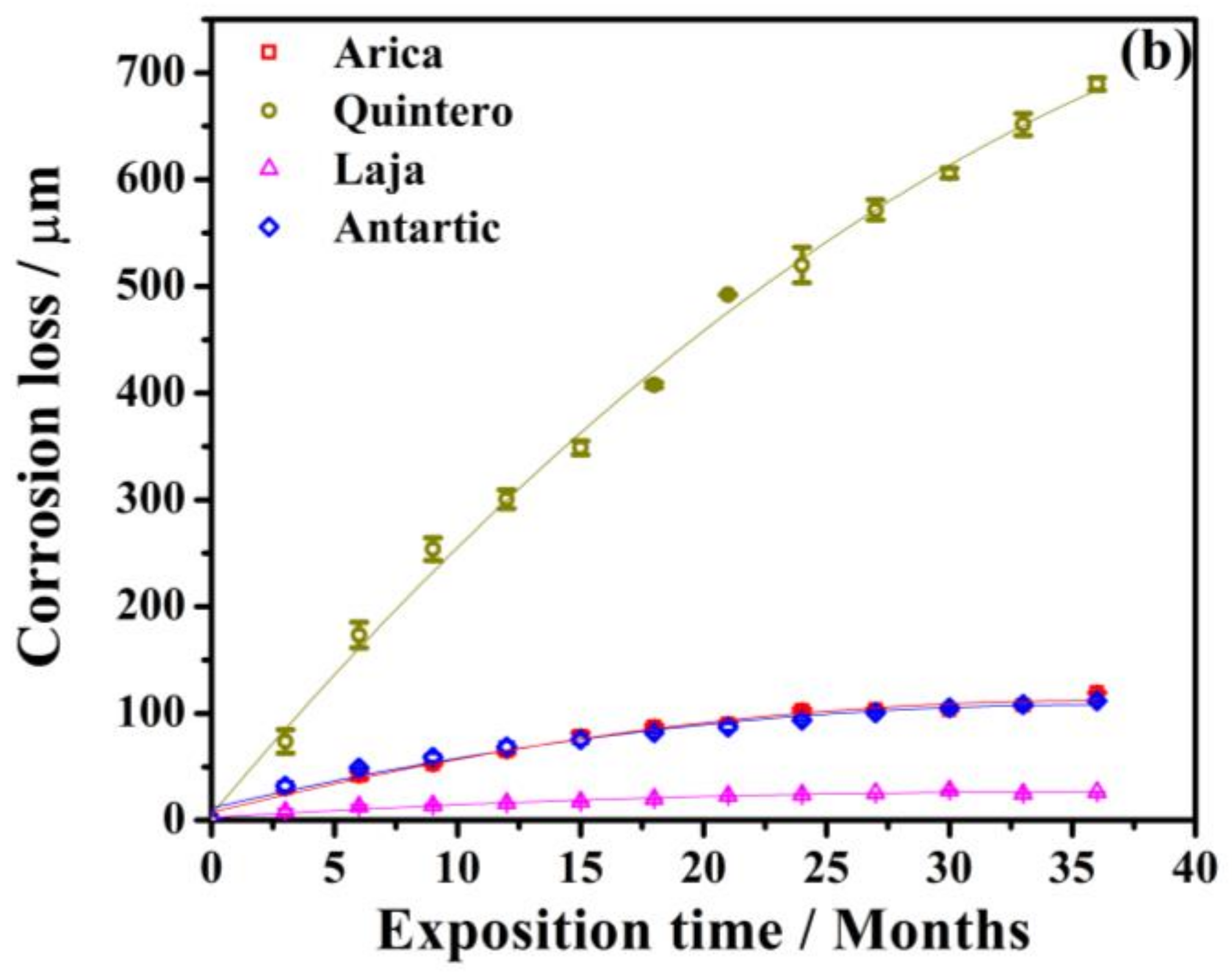
3.1. Process of Atmospheric Corrosion on SAE 1020 Steel
3.2. Corrosion Products Formed on the Surface of SAE 1020 Steel
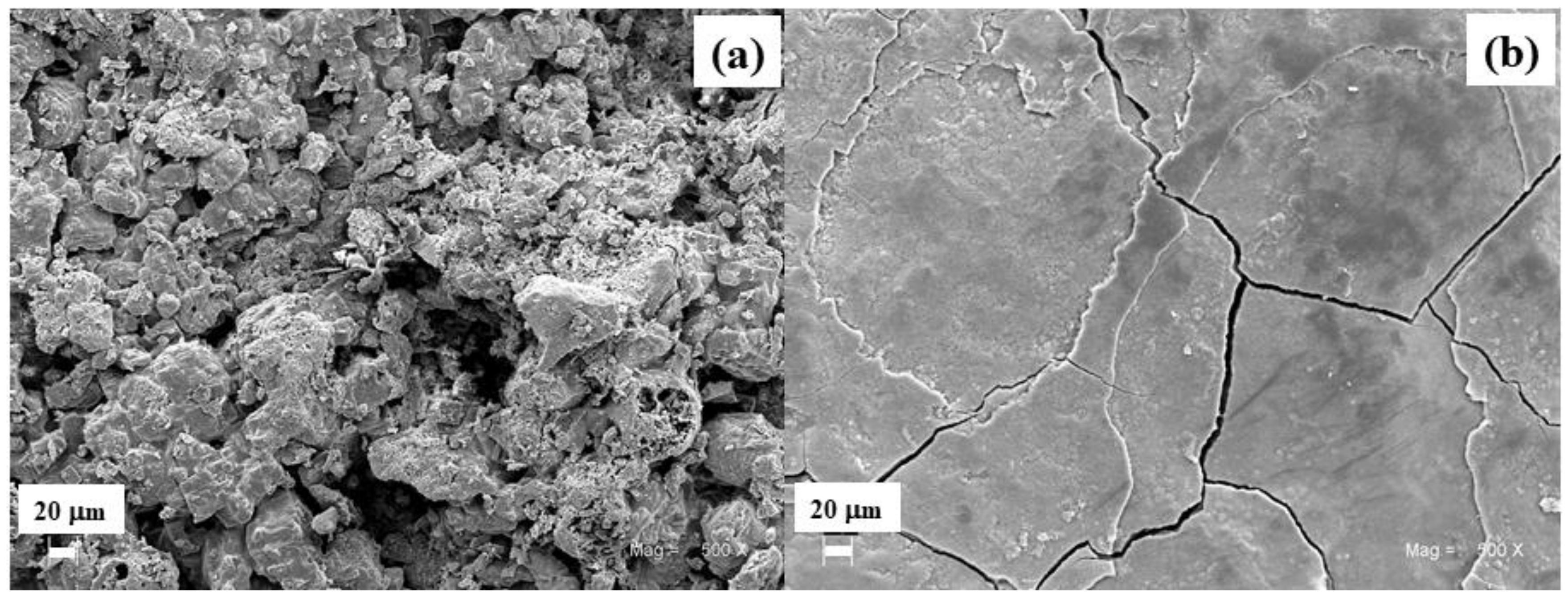
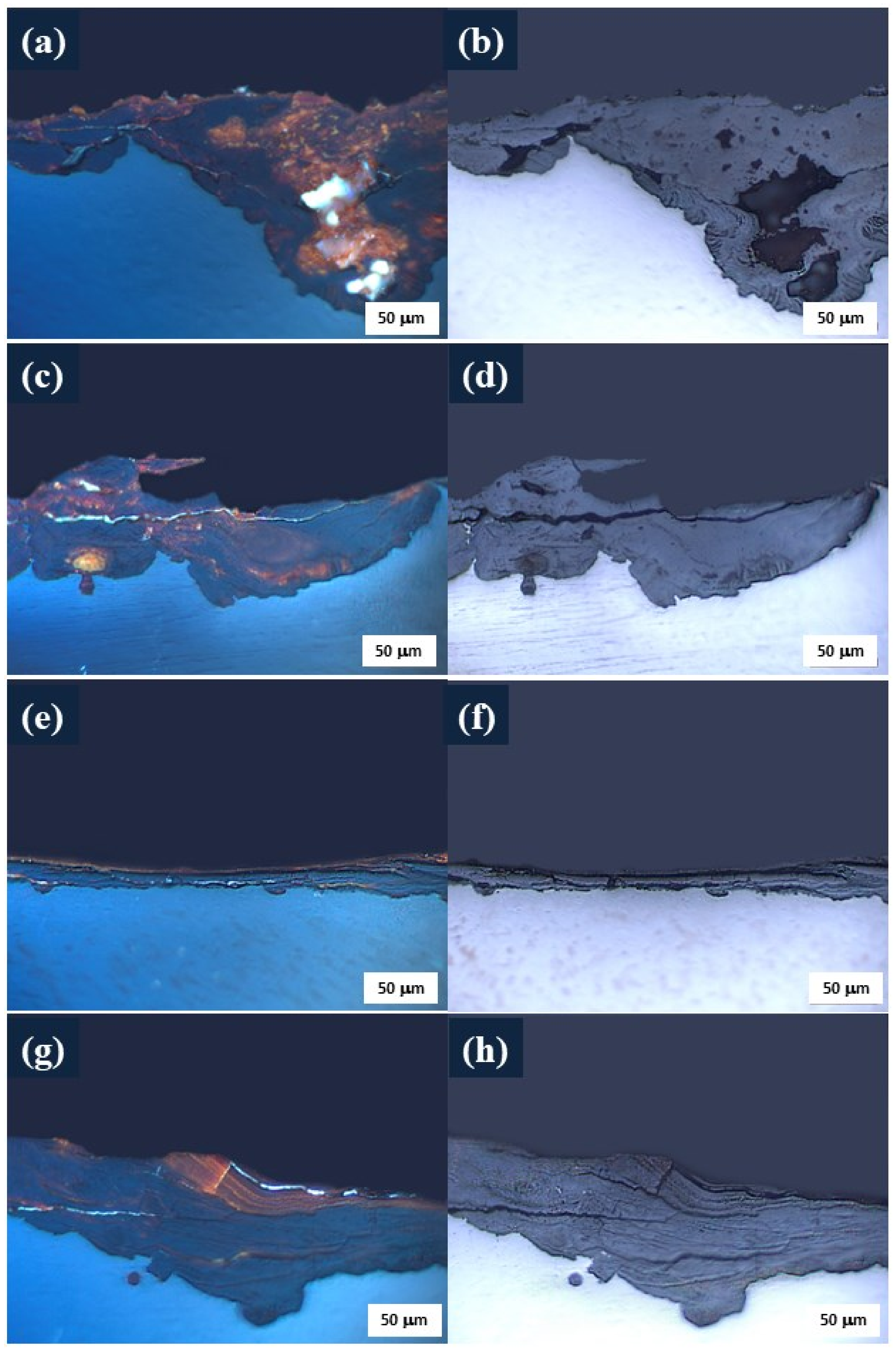
3.2.1. Morphology of Corrosion Products
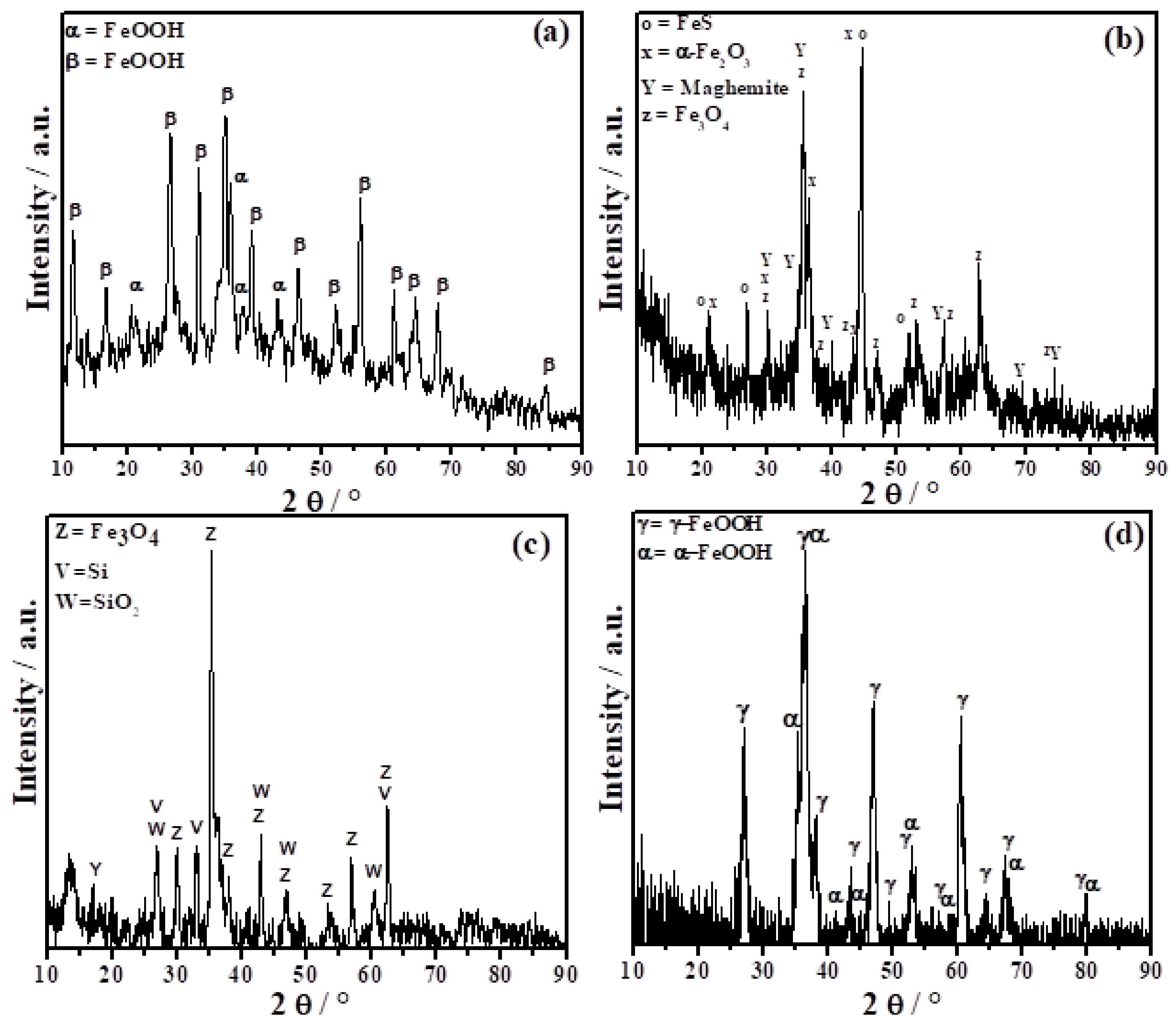
3.2.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
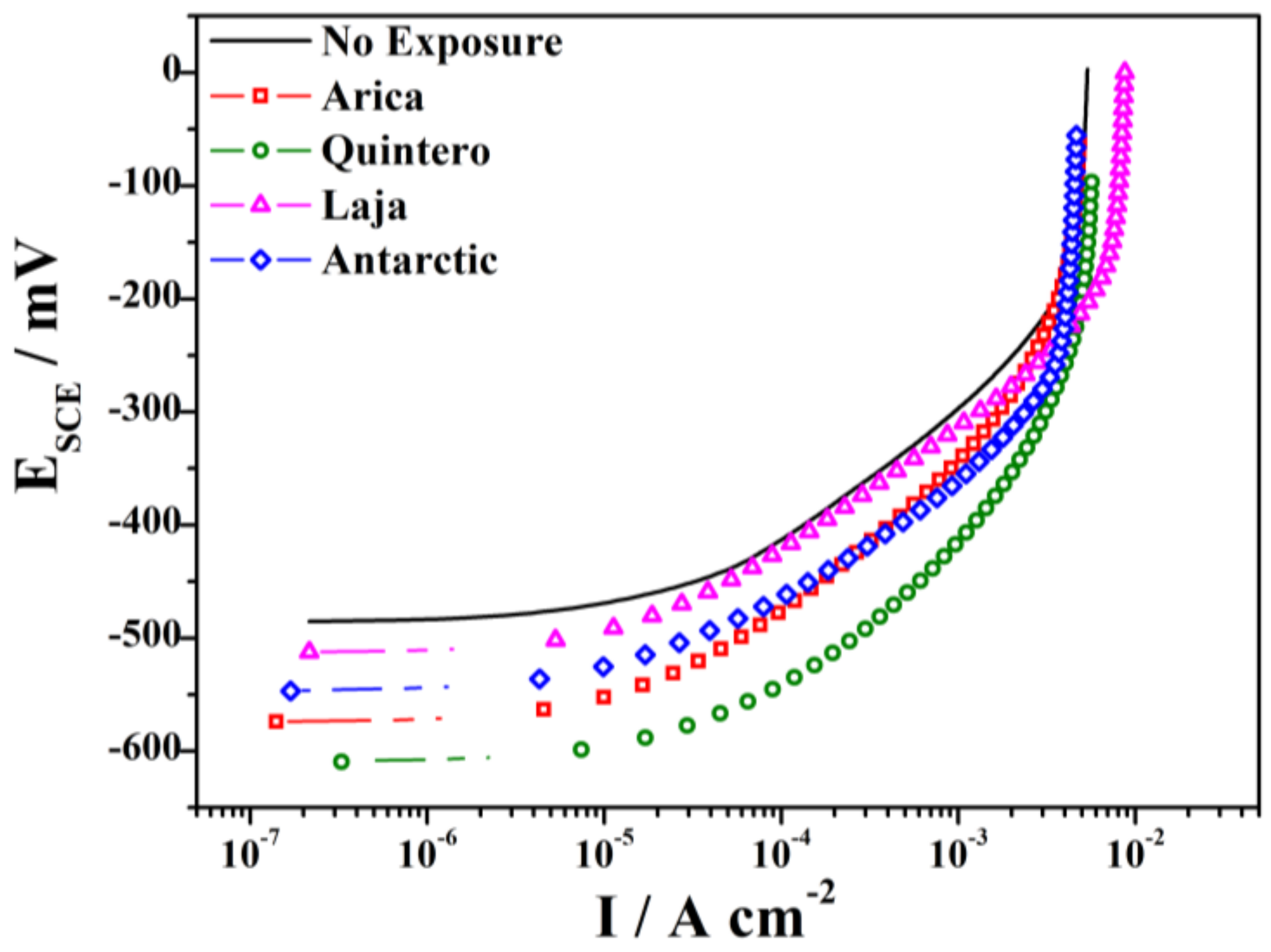
3.3. Electrochemical Behavior after 36 Months of Exposure
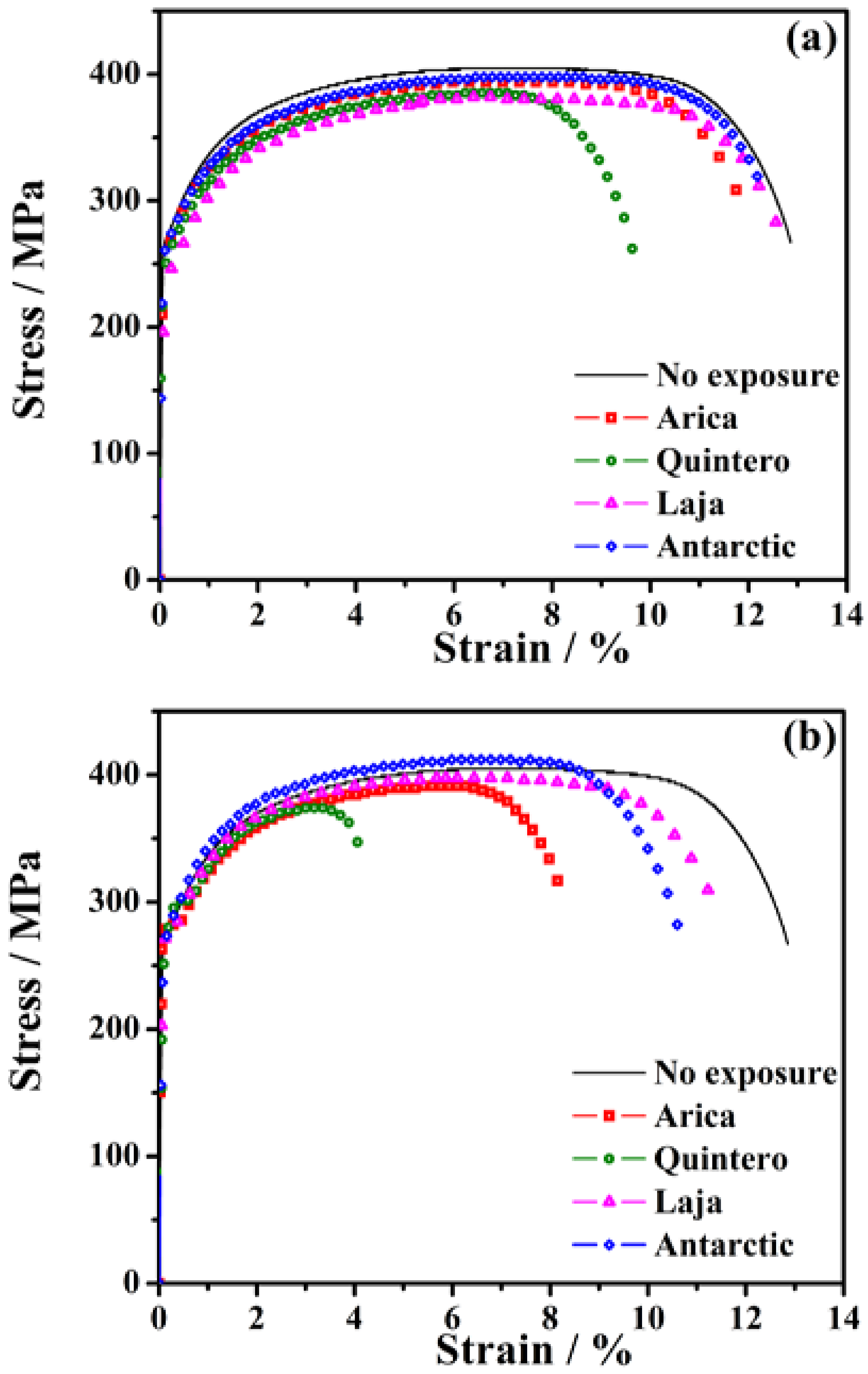
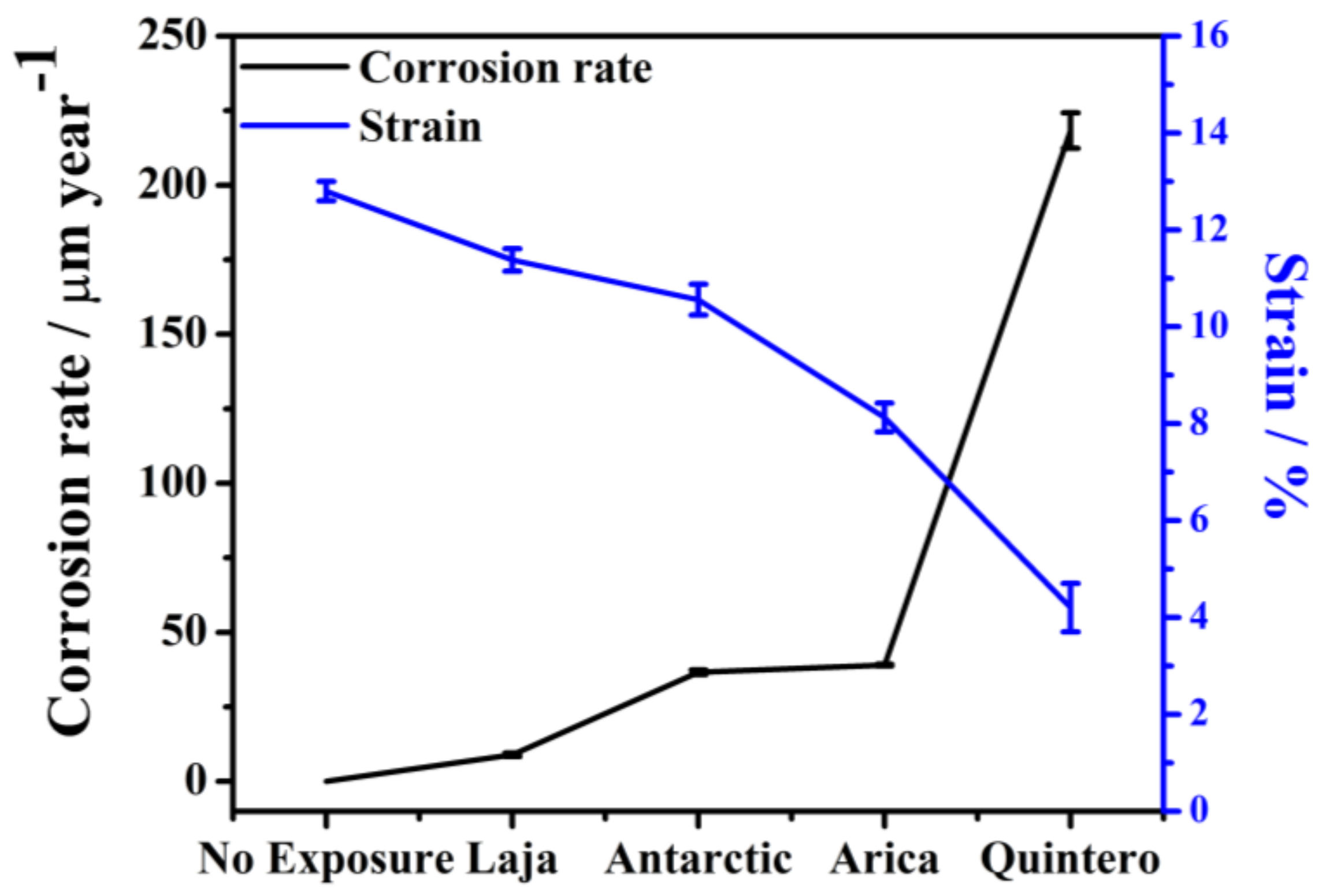
3.4. Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Steel Post-Exposure
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, N.G.; Yunovich, M.; Dunmire, D. Cost of corrosion and corrosion mainenance strategies. Corros. Rev. 2007, 25, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.J.S.; Hernández, F.J.S.; González, J.E.G. The effect of environmental and meteorological variables on atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel, copper, zinc and aluminium in a limited geographic zone with different types of environment. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyave, C.; Lopez, F.A.; Morcillo, M. The early atmospheric corrosion stages of carbon steel in acidic fogs. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Rosales, B.M.; Tapia, C. Effect of the exposure angle in the corrosion rate of plain carbon steel in a marine atmosphere. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.N.; Yadav, S.; Saha, J.K. Role of climatic conditions on corrosion characteristics of structural steels. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křivý, V.; Urban, V.; Kubzová, M. Thickness of corrosion layers on typical surfaces of weathering steel bridges. Procedia Eng. 2016, 142, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallinder, D.; Wallinder, I.O.; Leygraf, C. Influence of Surface Treatment of Type 304L Stainless Steel on Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance in Urban and Marine Environments. Corrosion 2003, 59, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivy, V.; Kubzova, M.; Kreislova, K.; Urban, V. Characterization of Corrosion Products on Weathering Steel Bridges Influenced by Chloride Deposition. Metals 2017, 7, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbatov, Y.; Soares, C.G.; Parunov, J.; Kodvanj, J. Tensile strength assessment of corroded small scale specimens. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.G.; Garbatov, Y.; Zayed, A.; Wang, G. Corrosion wastage model for ship crude oil tanks. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.; Alawi, H.; Sorein, K. Effect of atmospheric and marine corrosive environments on tensile, impact and hardness properties of some steels. Mech. Mater. 1994, 18, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocich, J.; Sevcikova, J.; Tuleja, S. Effect of atmospheric corrosion on the mechanical properties of the weathering steel Atmofix 52A. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, J.F.; Garcia, M.; Gancedo, J.R.; Martín-Luengo, M.A.; Joseph, G. Characterization of the corrosion products formed on caron steel after exposure ti the open atmosphere in the Antarctic and Easter Island. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Delgado, D.; Araya, R.; Puentes, M.; Guerrero, I.; Rojas, P.; Cabrera, G.; Erazo, S.; Carvajal, A.M. Construcción de mapas de corrosión atmosférica de chile. Result. Prelim. 2011, 32, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, R.; Puentes, M.; Araya, R.; Rojas, P.; Carvajal, A.M. Mapa de corrosión atmosférica de Chile: Resultados después de un año de exposición. Revista de la Construcción 2012, 11, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Guerrero, F.; Delgado, D.; Araya, R. Atmospheric corrosion of galvanized steel and precipitation runoff from zinc in a marine environment. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2013, 24, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.; Vera, R. Evaluation of the Atmospheric Corrosion Indices at Different Sites in Chile Using the (CLIMAT) Wire-on-Bolt Test. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 7687–7701. [Google Scholar]
- Del Angel, E.; Vera, R.; Corvo, F. Atmospheric Corrosion of Galvanised Steel in Different Environments in Chile and Mexico. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 7985–8004. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, R.; Araya, R.; Bagnara, M.; Díaz-Gómez, A.; Ossandón, S. Atmospheric corrosion of copper exposed to different environments in the region of Valparaiso, Chile. Mater. Corros. 2017, 68, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, P.; Martínez, C.; Vera, R.; Puentes, M. Toughness of SAE 1020 steel with and without galvanization exposed to different corrosive environments in Chile. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 2848–2858. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9223. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Classification of Corrosivity of Atmospheres; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9224. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys. Guiding Values for the Corrosivity Categories of Atmospheres; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9225. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys-Corrosivity of Atmospheres-Measurement of Environmental Parameters Affecting Corrosivity of Atmospheres; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9226. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Corrosivity of Atmospheres—Determination of Corrosion Rate of Standard Specimens for the Evaluation of Corrosivity; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 2011, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- ASTMG1-03. Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 90, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G50. Standard Practice for Conducting Atmospheric Corrosion Tests on Metals; American Society for Testing And Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelholz, E.; Kelly, R.G.; Cole, I.S.; Ganther, W.D.; Muster, T.H. Comparability and accuracy of time of wetness sensing methods relevant for atmospheric corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2013, 67, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials 1; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E92. Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004; Volume 82, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 09CN14-5879. 2010. 1. Available online: http://www.mapadecorrosionatmosfericadechile.cl/mapa/mapasGenerados (accessed on 30 January 2018).
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Corrosion of low carbon steel in atmospheric environments of different chloride content. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Han, R.; Sun, Y. Study of the corrosion behavior of weathering steels in atmospheric environments. Corros. Sci. 2013, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, I.; Cano, H.; de la Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Vega, J.M.; Morcillo, M. Atmospheric corrosion of Ni-advanced weathering steels in marine atmospheres of moderate salinity. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D.; Almeida, E.; Joseph, G.; Rivero, S.; Rosales, B. Atmospheric corrosion of reference metals in Antarctic sites. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2004, 40, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Alcántara, J.; Díaz, I.; Chico, B.; Simancas, J.; de la Fuente, D. Marine atmospheric corrosion of carbon steels. Rev. Met. 2015, 51, e045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, J.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; de la Fuente, D.; Morcillo, M. Airborne chloride deposit and its effect on marine atmospheric corrosion of mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 97, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Shimodaira, S. The mechanism of formation of iron oxide and oxyhydroxides in aqueous solutions at room temperature. Corros. Sci. 1974, 14, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillmann, P.; Mazaudier, F.; Hœrlé, S. Advances in understanding atmospheric corrosion of iron. I. Rust characterisation of ancient ferrous artefacts exposed to indoor atmospheric corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1401–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, T.; Hara, S.; Miyuki, H.; Yamashita, M.; Uchida, H. Composition and protective ability of rust layer formed on weathering steel exposed to various environments. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Díaz, I.; Simancas, J.; Chico, B.; Morcillo, M. Long-term atmospheric corrosion of mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidheiser, H.; Music, S. The atmospheric corrosion of Iron as studied by Mossbauer spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 1982, 22, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K. Corrosion behavior of steel with different microstructures under various elastic loading conditions. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathi, L.R.; Chaudhari, G.P.; Nath, S.K. Mechanical and corrosion behavior of plain low carbon dual-phase steels. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayasu, M.; Sato, K.; Okada, K.; Yoshifuji, S.; Mizuno, M. Effects of atmospheric corrosion on fatigue properties of a medium carbon steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novovic, D.; Dewes, R.C.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Voice, W.; Bowen, P. The effect of machined topography and integrity on fatigue life. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. The hardness and strength of metals. J. Inst. Met. 1951, 79, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.J.; Zhang, Z.L.; Su, Y.J.; Qiao, L.J.; Chu, W.Y. Influence of specimen thickness with rectangular cross-section on the tensile properties of structural steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | V | Ti | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.098 | 0.28 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Station | Latitude | Longitude | Sea Distance (m) | Sea Level (m a.s.l.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arica | 18.47775 LS | 70.320769 LO | 579 | 20 |
| Quintero | 32.752625 LS | 71.484508 LO | 70 | 14 |
| Laja | 37.189947 LS | 72.539644 LO | 78000 | 118 |
| Antarctic | 63.320833 LS | 57.899722 LO | 100 | 10 |
| Station | TOW (%) | τ | mg m−2 d−1 | Cl− | mg m−2 d−1 | SO2 | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arica | 6.3 | τ3 | 125.6 | S 2 | 5.0 | P 0 | 3–4 |
| Quintero | 79.3 | τ5 | 81.9 | S 2 | 26.5 | P 1 | 5 |
| Laja | 24.3 | τ3 | 3.6 | S 0 | 4.9 | P 0 | 2 |
| Antarctic | 9.3 | τ3 | 63.2 | S 2 | 7.2 | P 0 | 3–4 |
| Sample | Potential (mV) | Dissolution Current Density at −400 mV (A cm−2) |
|---|---|---|
| No Exposure | −486.5 | 1.3 × 10−4 |
| Arica | −574.7 | 4.0 × 10−4 |
| Quintero | −611.1 | 12 × 10−4 |
| Laja | −515.0 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| Antarctic | −548.7 | 4.6 × 10−4 |
| Sample | ε Rupture | UTS | Module of Toughness | Hardness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Time (Months) | (%) | (Mpa) | (Nm m−3) | (HV0.3) |
| No Exposure | 0 | 12.80 (100%) | 405 | 4846 (100%) | 148.7 (100%) |
| Arica | 6 | 11.71 (91%) | 394 | 4337 (89%) | 141.5 (95%) |
| 36 | 8.13 (64%) | 391 | 2951 (61%) | 132.4 (89%) | |
| Quintero | 6 | 9.62 (75%) | 385 | 3398 (70%) | 134.8 (91%) |
| 36 | 4.20 (33%) | 374 | 1385 (29%) | 124.0 (83%) | |
| Laja | 6 | 12.66 (99%) | 382 | 4499 (93%) | 132.6 (89%) |
| 36 | 11.38 (89%) | 397 | 4239 (87%) | 118.5 (80%) | |
| Antarctic | 6 | 12.31 (96%) | 398 | 4594 (95%) | 135.8 (91%) |
| 36 | 10.56 (82%) | 412 | 4039 (83%) | 135.2 (91%) | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, C.; Briones, F.; Villarroel, M.; Vera, R. Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel. Materials 2018, 11, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040591
Martínez C, Briones F, Villarroel M, Vera R. Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel. Materials. 2018; 11(4):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040591
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Carola, Francisco Briones, María Villarroel, and Rosa Vera. 2018. "Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel" Materials 11, no. 4: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040591
APA StyleMartínez, C., Briones, F., Villarroel, M., & Vera, R. (2018). Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel. Materials, 11(4), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040591





