Enhanced CO2 Adsorption by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Sheets (N-GOs) Prepared by Employing Polymeric Precursors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- W = volume of the pores that has been filled at p/po (cm3/g)
- Wo = total volume of the micropore system (cm3/g)
- β = structural constant related to the width of the Gaussian pore distribution (K−2)
- T = temperature at which the isotherm has been taken (K)
- B = similarity constant, depending solely on the adsorbate (-)
- po/p = inverse of the relative pressure of the adsorbate (-)
2.1. Experimental
2.1.1. Polymer Preparation
Polyaniline (PANI) and Polypyrrole (PPy)
Poly(Aniline-Co-Pyrrole) Copolymer
Carbonization/Activation of Prepared Polymers
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
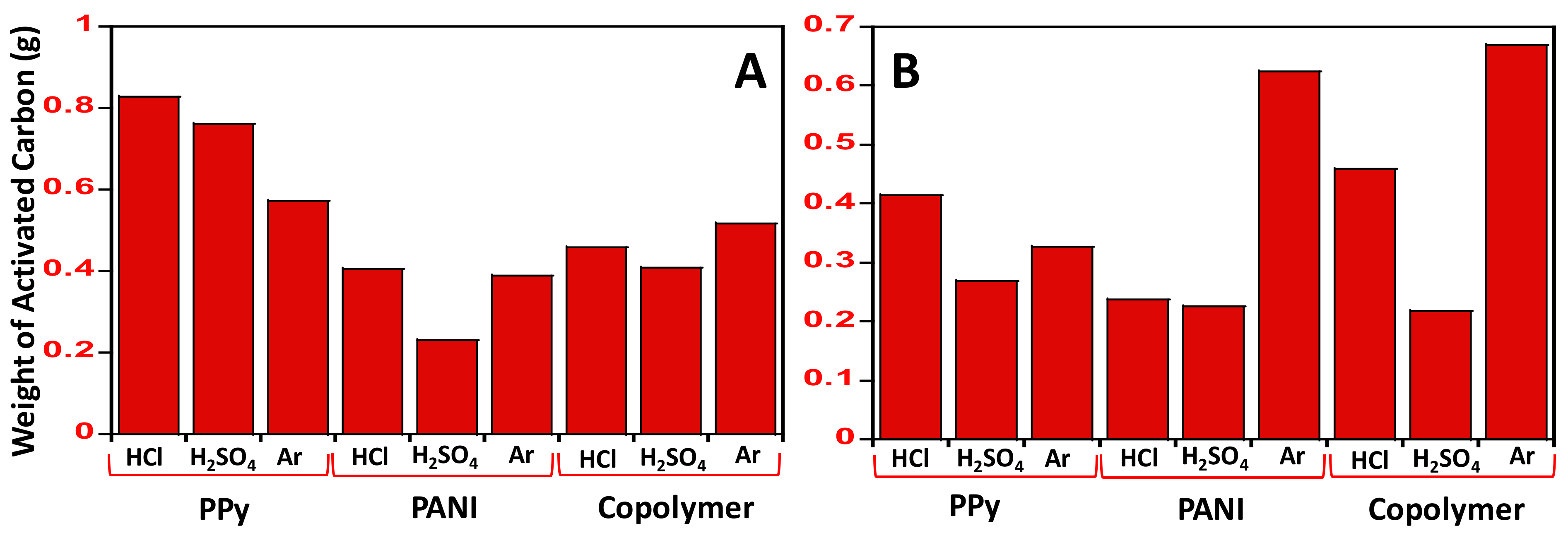
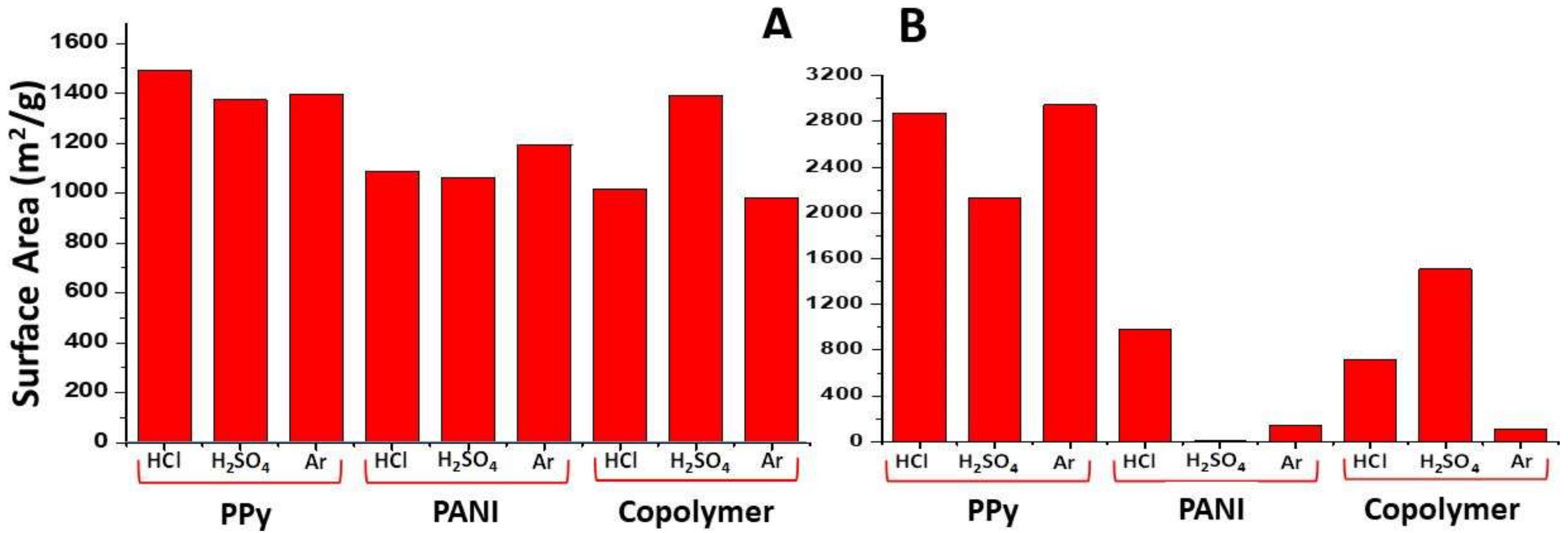
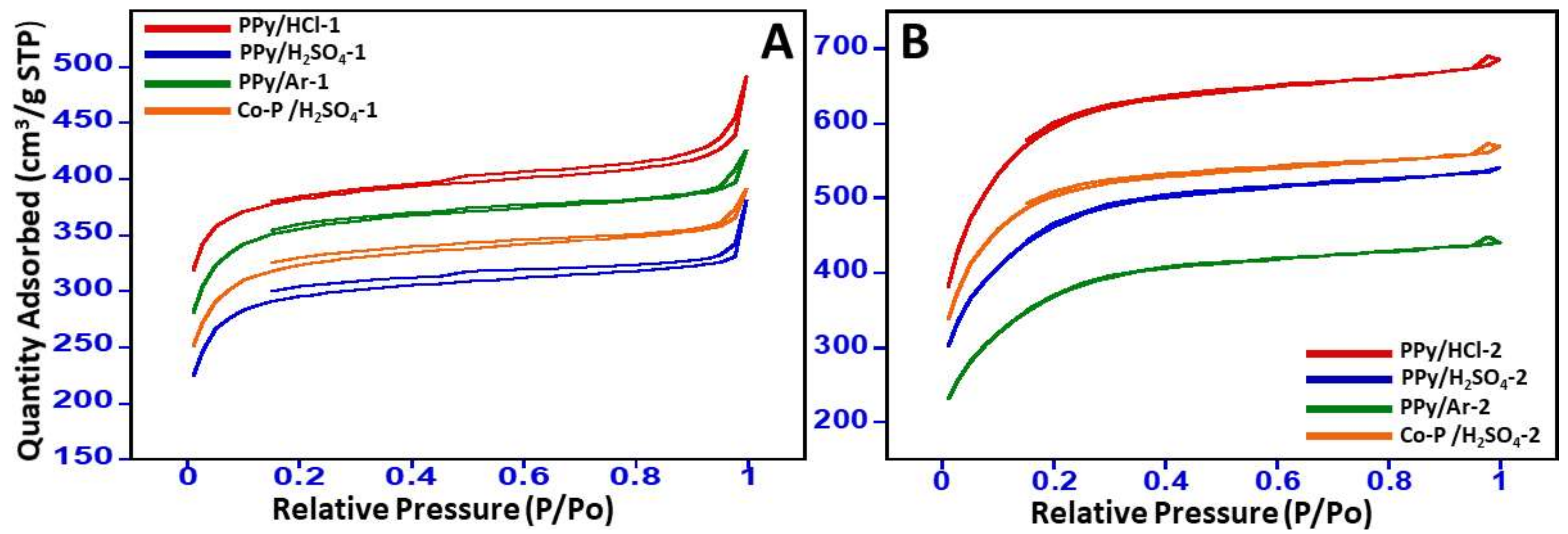
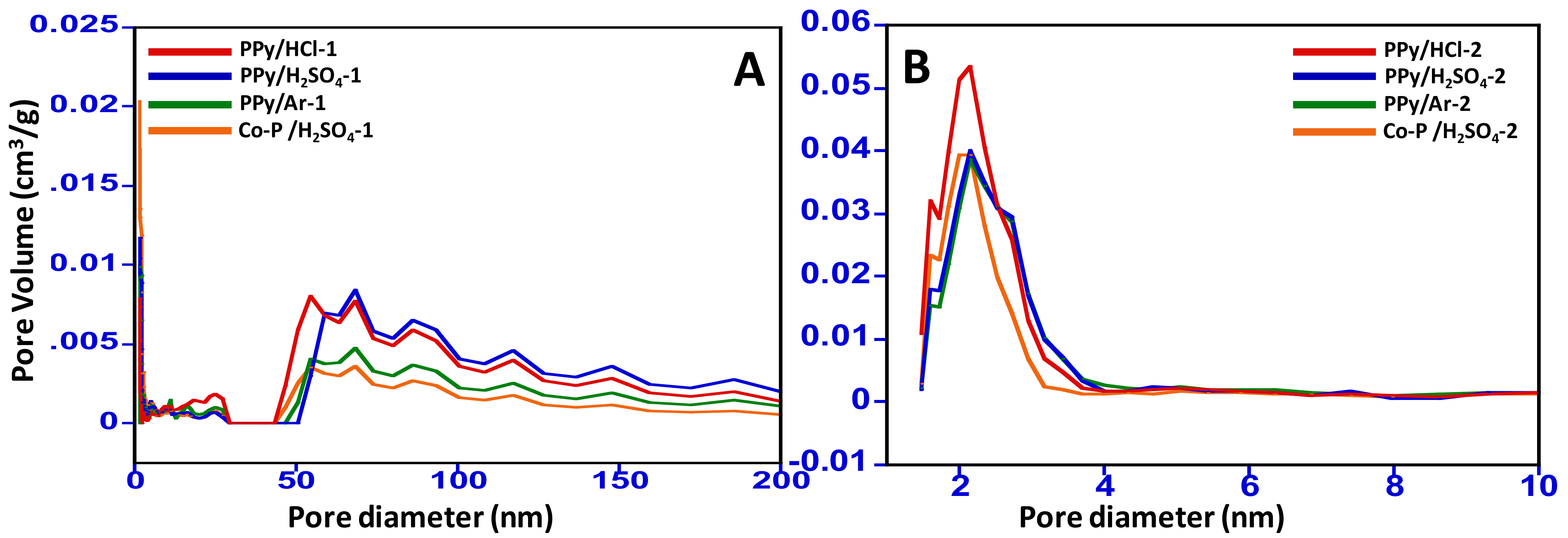
3.1. Textural Properties
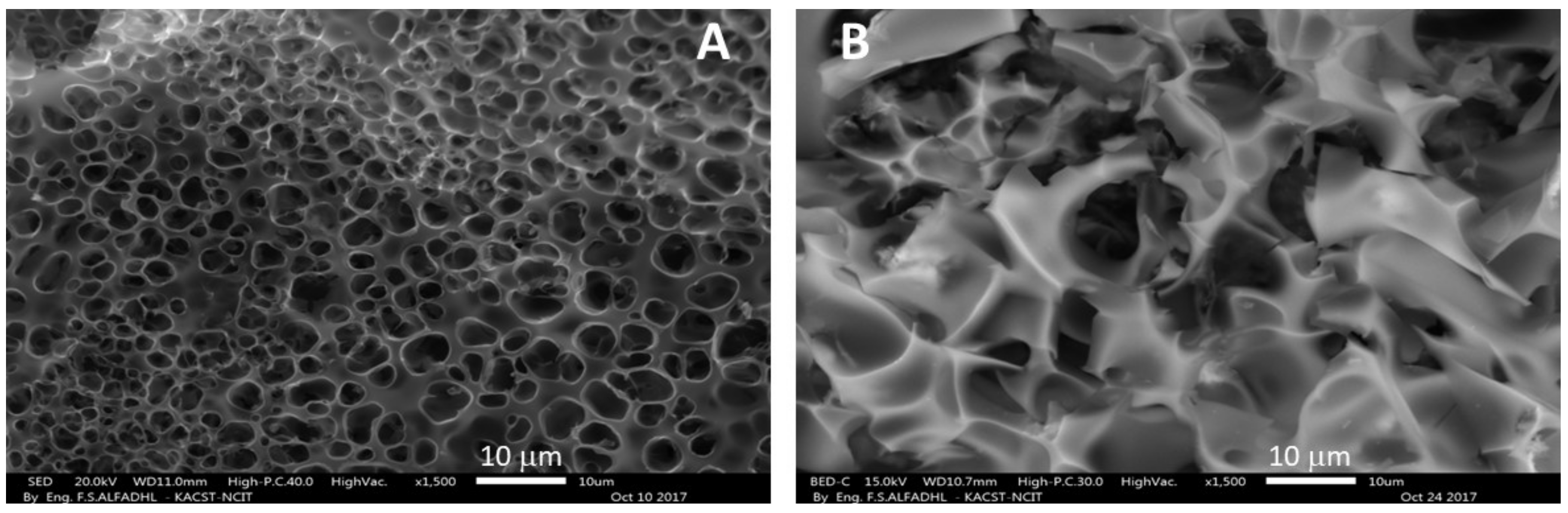
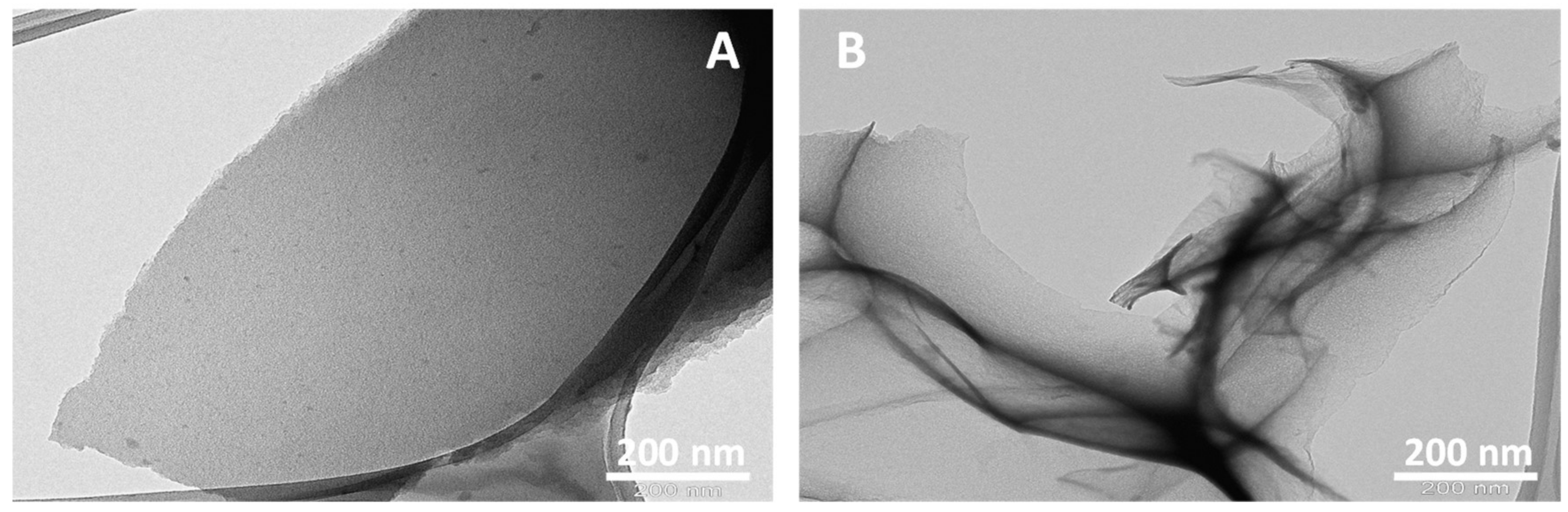
3.2. Morphological and Microscopic Analysis
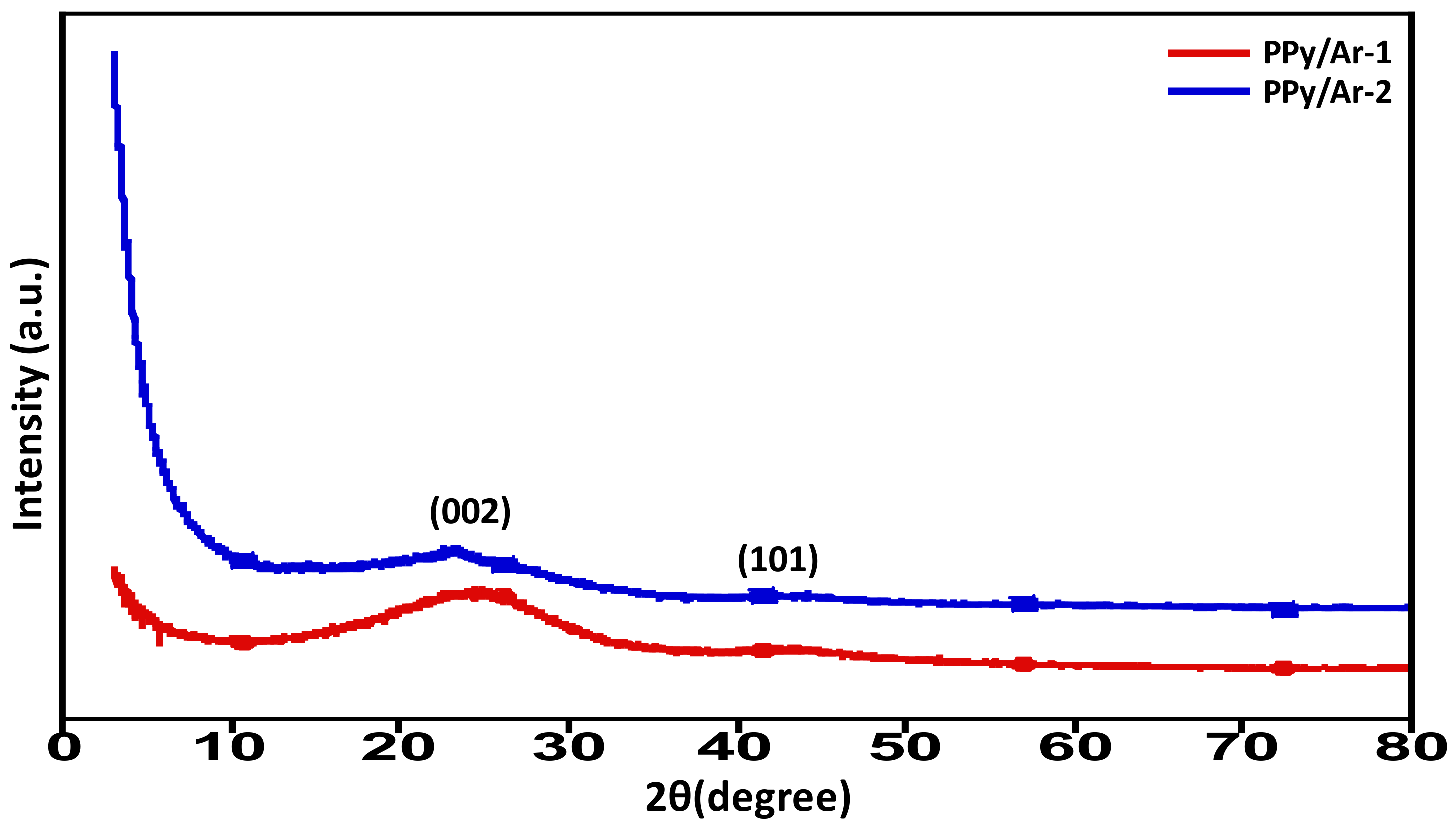
3.3. XRD Spectral Analysis
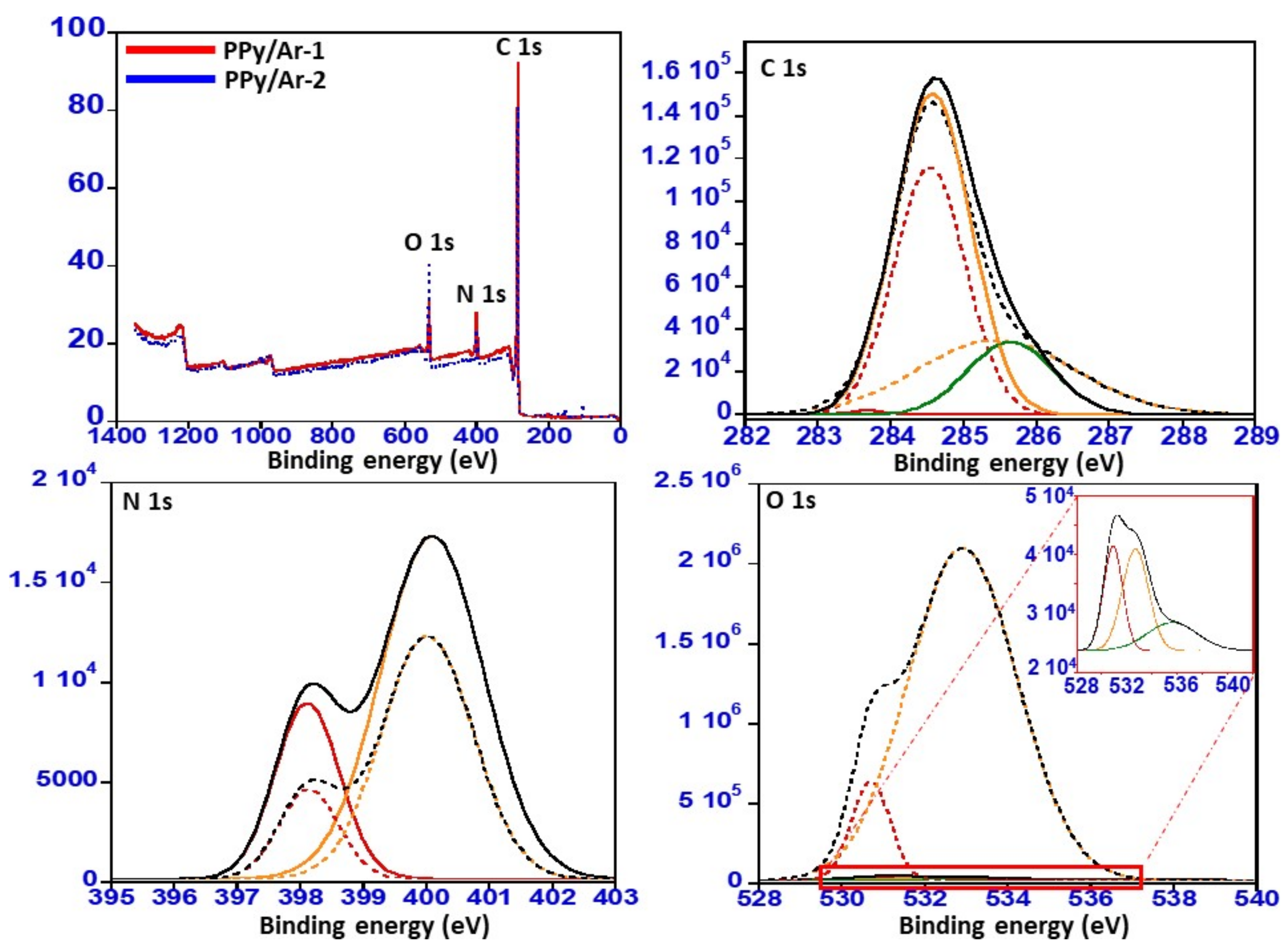
3.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
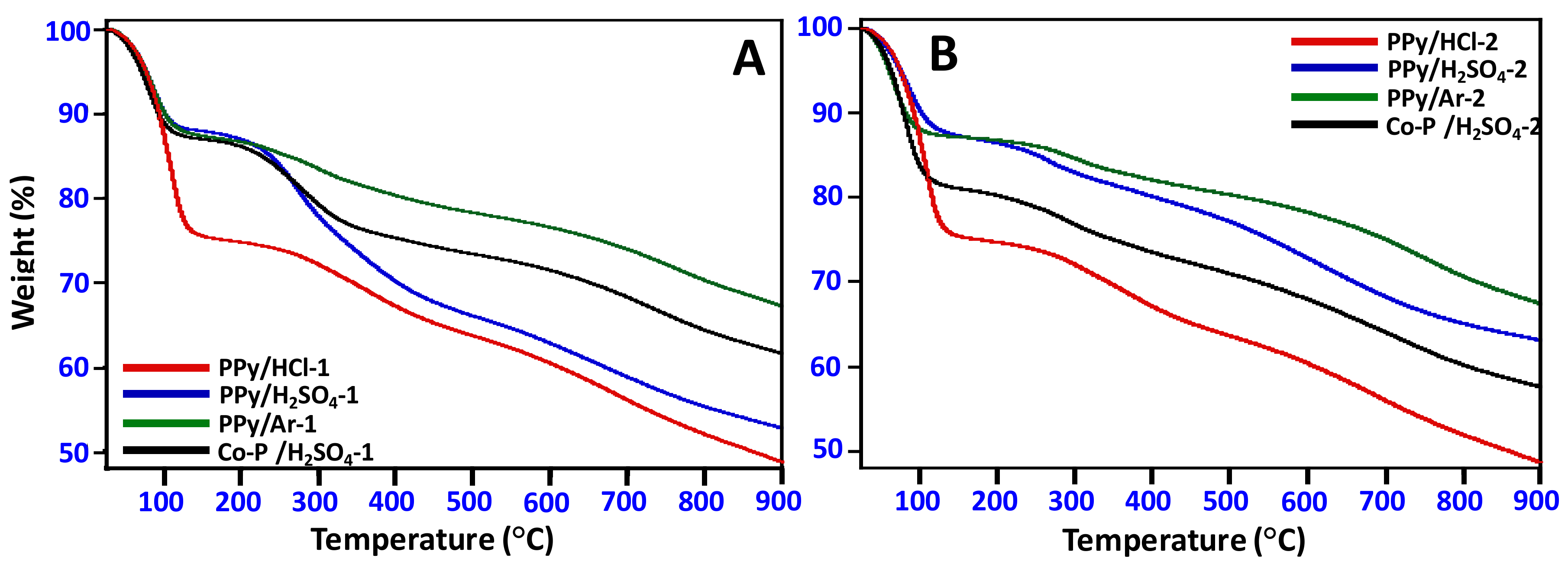
3.5. Thermal Stability
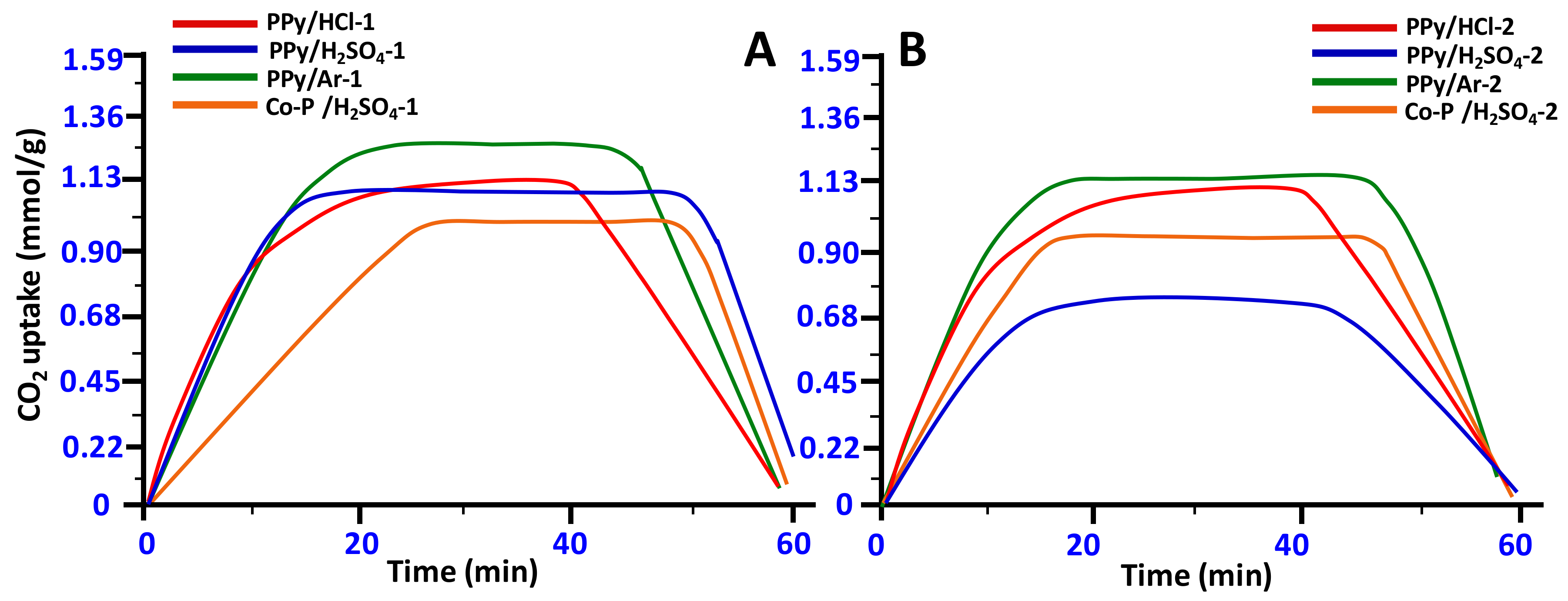
3.6. CO2 Adsorption Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitić, P.; Munitlak Ivanović, O.; Zdravković, A. A cointegration analysis of real GDP and CO2 emissions in transitional countries. Sustainability 2017, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vita, G.; Pilato, M.; Pecorino, B.; Brun, F.; D’Amico, M. A review of the role of vegetal ecosystems in CO2 capture. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Nicolini, A.; Palombo, M.; Castellani, B.; Morini, E.; Filipponi, M. An innovative configuration for CO2 capture by high temperature fuel cells. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6687–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, T.; Sorgenfrei, M.; Tsatsaronis, G. Design and assessment of an igcc concept with CO2 capture for the co-generation of electricity and substitute natural gas. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16213–16225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sadat, W.I.; Archer, L.A. The O2-assisted Al/CO2 electrochemical cell: A system for CO2 capture/conversion and electric power generation. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrens, A.D.; Gurgenci, H.; Rudolph, V. Electricity generation using a carbon-dioxide thermosiphon. Geothermics 2010, 39, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, J.B.; Saar, M.O.; Bielicki, J. Geothermal energy production at geologic CO2 sequestration sites: Impact of thermal drawdown on reservoir pressure. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 6625–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crake, A.; Christoforidis, K.C.; Kafizas, A.; Zafeiratos, S.; Petit, C. CO2 capture and photocatalytic reduction using bifunctional TiO2/MOF nanocomposites under UV-vis irradiation. App. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 210, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, V.; Shavi, R.; Seo, J.G. Mesoporous magnesium oxide nanoparticles derived via complexation-combustion for enhanced performance in carbon dioxide capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, A.; Kuang, M.; Yuan, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Yang, X. Acidic gases (CO2, NO2 and SO2) capture and dissociation on metal decorated phosphorene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minju, N.; Nair, B.N.; Mohamed, A.P.; Ananthakumar, S. Surface engineered silica mesospheres—A promising adsorbent for CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 181, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, R.; Wdowin, M.; Franus, W.; Czarna, D.; Stevens, L.; Deng, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, H.; Snape, C.E. Fly ash-derived MCM-41 as a low-cost silica support for polyethyleneimine in post-combustion CO2 capture. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 22, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.H. Hybrid membranes of nanostructrual copolymer and ionic liquid for carbon dioxide capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Singh, J.K.; Müller-Plathe, F. CO2 adsorption on charged carbon nanotube arrays: A possible functional material for electric swing adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 15232–15239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Hamamoto, Y.; Shiozawa, Y.; Tashima, K.; Fukidome, H.; Koitaya, T.; Mukai, K.; Yoshimoto, S.; Suemitsu, M.; et al. Adsorption of CO2 on graphene: A combined TPD, XPS, and vdW-DF study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramaratne, N.P.; Jaroniec, M. Activated carbon spheres for CO2 adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Alcaniz-Monge, J.; Linares-Solano, A. Characterization of activated carbon fibers by CO2 adsorption. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gallastegui, A.; Iruretagoyena, D.; Gouvea, V.; Mokhtar, M.; Asiri, A.M.; Basahel, S.N.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Alyoubi, A.O.; Chadwick, D.; Shaffer, M.S. Graphene oxide as support for layered double hydroxides: Enhancing the CO2 adsorption capacity. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4531–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, R.; Wu, H. Efficient CO2 capture by functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets as fillers to fabricate multi-permselective mixed matrix membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Ramaprabhu, S. Enhanced CO2 capture in Fe3O4-graphene nanocomposite by physicochemical adsorption. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 064306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, B. Graphene-manganese oxide hybrid porous material and its application in carbon dioxide adsorption. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.C.; Silva, R.; Voiry, D.; Asefa, T.; Chhowalla, M. Copper nanoparticles stabilized by reduced graphene oxide for CO2 reduction reaction. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla, C.; Shevlin, S.; Guo, Z. Calcium-based functionalization of carbon materials for CO2 capture: A first-principles computational study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 10990–10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhan, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ling, L.; Feng, X. Graphene-based porous silica sheets impregnated with polyethyleneimine for superior CO2 capture. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, K.C.; Chandra, V.; Saleh, M.; Kim, K.S. Reversible CO2 adsorption by an activated nitrogen doped graphene/polyaniline material. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 235703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Pan, X.; Yu, L.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, W.-X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, X.; Xue, Q. Toward N-doped graphene via solvothermal synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Yu, G. Synthesis of N-doped graphene by chemical vapor deposition and its electrical properties. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Shi, Z.; Gu, Z.; Xu, S. Large scale synthesis of N-doped multi-layered graphene sheets by simple arc-discharge method. Carbon 2010, 48, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G.; Xie, J. Toward N-doped graphene nanosheets via hydrazine steaming process. Mater. Lett. 2014, 131, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Tahir, M.N.; Adil, S.F.; Khan, H.U.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Al-warthan, A.A.; Tremel, W. Graphene based metal and metal oxide nanocomposites: Synthesis, properties and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18753–18808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Al-Marri, A.H.; Khan, M.; Shaik, M.R.; Mohri, N.; Adil, S.F.; Kuniyil, M.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Al-Warthan, A.; Tremel, W.; et al. Green approach for the effective reduction of graphene oxide using Salvadora persica L. Root (Miswak) extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Marri, A.H.; Khan, M.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F.; Al-Warthan, A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Tremel, W.; Labis, J.P.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Tahir, M.N. Pulicaria glutinosa extract: A toolbox to synthesize highly reduced graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-J.; Lee, H.-M.; Kim, H.-G.; An, K.-H.; Kang, H.-R. Comparative studies of porous carbon nanofibers by various activation methods. Carbon Lett. 2013, 14, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Hou, X. As-synthesized mesoporous silica MSU-1 modified with tetraethylenepentamine for CO2 adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniak, S.; Szymański, G.; Siedlewski, J.; Światkowski, A. The characterization of activated carbons with oxygen and nitrogen surface groups. Carbon 1997, 35, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Insight into highly efficient simultaneous photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) and 2, 4-diclorophenol under visible light irradiation by phosphorus doped porous ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheets from aqueous media: Performance and reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, L.K.; Ong, W.-J.; Chang, W.S.; Chai, S.-P. Heteroatom doped graphene in photocatalysis: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 358, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, D.; Cao, D.; Xiang, Z.; Yao, X.; Qiu, S. Selective adsorption of carbon dioxide by carbonized porous aromatic framework (PAF). Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8370–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, L.K.; Wickramaratne, N.P.; Ello, A.S.; Costa, M.J.; da Costa, C.E.; Jaroniec, M. Enhancement of CO2 adsorption on phenolic resin-based mesoporous carbons by KOH activation. Carbon 2013, 65, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, D.; Liu, J.; Ma, W. Electrospun phenolic resin-based carbon ultrafine fibers with abundant ultra-small micropores for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.-P.; Li, W.-C.; Qian, D.; Wang, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, A.-Q.; Schüth, F.; Bongard, H.-J.; Lu, A.-H. Structurally designed synthesis of mechanically stable poly (benzoxazine-co-resol)-based porous carbon monoliths and their application as high-performance CO2 capture sorbents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11378–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, G.-P.; Jin, Z.-Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-T.; Lu, A.-H. Porous carbon nanosheets with precisely tunable thickness and selective CO2 adsorption properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, B.; Başar, M.S.; Eropak, B.M.; Caglayan, B.S.; Aksoylu, A.E. CO2 adsorption over modified ac samples: A new methodology for determining selectivity. Catal Today 2018, 301, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Mahurin, S.M.; Mayes, R.T.; Williamson, B.; Teague, C.M.; Binder, A.J.; Baggetto, L.; Veith, G.M.; Dai, S. Preparation and CO2 adsorption properties of soft-templated mesoporous carbons derived from chestnut tannin precursors. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 222, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Phan, A.; Wang, B.; Knobler, C.; Furukawa, H.; O’keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. High-throughput synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and application to CO2 capture. Science 2008, 319, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himeno, S.; Komatsu, T.; Fujita, S. High-pressure adsorption equilibria of methane and carbon dioxide on several activated carbons. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Deng, S. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of CO2, CH4, N2O, and NH3 on ordered mesoporous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Effect of heat treatment on CO2 adsorption of KOH-activated graphite nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khdary, N.H.; Ghanem, M.A. Metal-organic-silica nanocomposites: Copper, silver nanoparticles-ethylenediamine-silica gel and their CO2 adsorption behaviour. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12032–12038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Polymers | Polymer:KOH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2 3 | 1:4 3 | |||||
| HCl 2 | H2SO4 2 | C6H5-SO3-K 2 | HCl 2 | H2SO4 2 | C6H5-SO3-K 2 | |
| ppy 1 | PPy/HCl-1 | PPy/H2SO4-1 | PPy/Ar-1 | PPy/HCl-2 | PPy/H2SO4-2 | PPy/Ar-2 |
| PANI 1 | PANI/HCl-1 | PANI/H2SO4-1 | PANI/Ar-1 | PANI/HCl-2 | PANI/H2SO4-2 | PANI/Ar-2 |
| Copolymer 1 | Co-P/HCl-1 | Co-P/H2SO4-1 | Co-P/Ar-1 | Co-P/HCl-2 | Co-P/H2SO4-2 | Co-P/Ar-2 |
| N-GOs | Elements | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | |
| PPy/Ar-1 | 80.80 | 8.08 | 11.11 |
| PPy/Ar-2 | 80.80 | 5.05 | 14.14 |
| Materials | Capacity (mmol g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonized porous aromatic framework (PAF) | 4.5 | [38] |
| Activated carbon-phloroglucinol-500 °C | 4.37 | [39] |
| Microporous carbon ultrafine fibers | 2.92 | [40] |
| N-containing porous carbon monoliths | 2.9 | [41] |
| Porous carbon nanosheets | 2.88 | [42] |
| Alkali-modified activated Carbon | 2.46 | [43] |
| Mesoporous carbons | 2.27 | [44] |
| Isoreticular zeolitic imidazolate frameworks | 2.2 | [45] |
| Mesoporous carbons | 2.14 | [44] |
| Commercially activated carbons including BPL, Maxsorb, and Norit R1 | <2.00 | [46] |
| Soft-templated mesoporous carbons | 1.49 | [47] |
| KOH-activated graphite nanofibers | 1.35 | [48] |
| PPy/Ar-1 | 1.28 | This work |
| PPy/Ar-2 | 1.18 | This work |
| Cu-propyl ethylenediamine-silica composites | 0.58 | [49] |
| Propyl ethylenediamine-silica composites | 0.45 | [49] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghamdi, A.A.; Alshahrani, A.F.; Khdary, N.H.; Alharthi, F.A.; Alattas, H.A.; Adil, S.F. Enhanced CO2 Adsorption by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Sheets (N-GOs) Prepared by Employing Polymeric Precursors. Materials 2018, 11, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040578
Alghamdi AA, Alshahrani AF, Khdary NH, Alharthi FA, Alattas HA, Adil SF. Enhanced CO2 Adsorption by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Sheets (N-GOs) Prepared by Employing Polymeric Precursors. Materials. 2018; 11(4):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040578
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghamdi, Abdulaziz Ali, Abdullah Fhead Alshahrani, Nezar H. Khdary, Fahad A. Alharthi, Hussain Ali Alattas, and Syed Farooq Adil. 2018. "Enhanced CO2 Adsorption by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Sheets (N-GOs) Prepared by Employing Polymeric Precursors" Materials 11, no. 4: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040578
APA StyleAlghamdi, A. A., Alshahrani, A. F., Khdary, N. H., Alharthi, F. A., Alattas, H. A., & Adil, S. F. (2018). Enhanced CO2 Adsorption by Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Sheets (N-GOs) Prepared by Employing Polymeric Precursors. Materials, 11(4), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040578








