Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
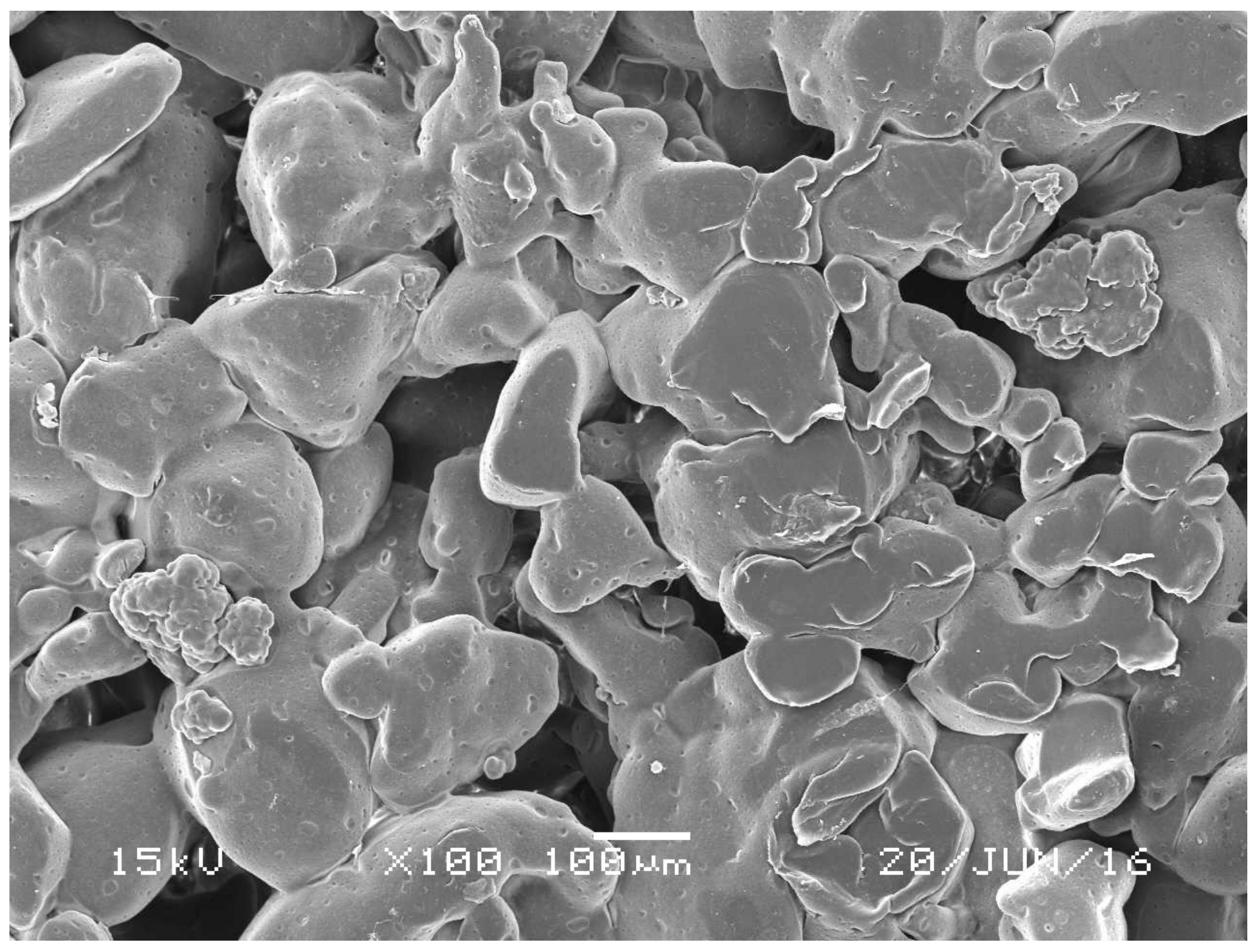
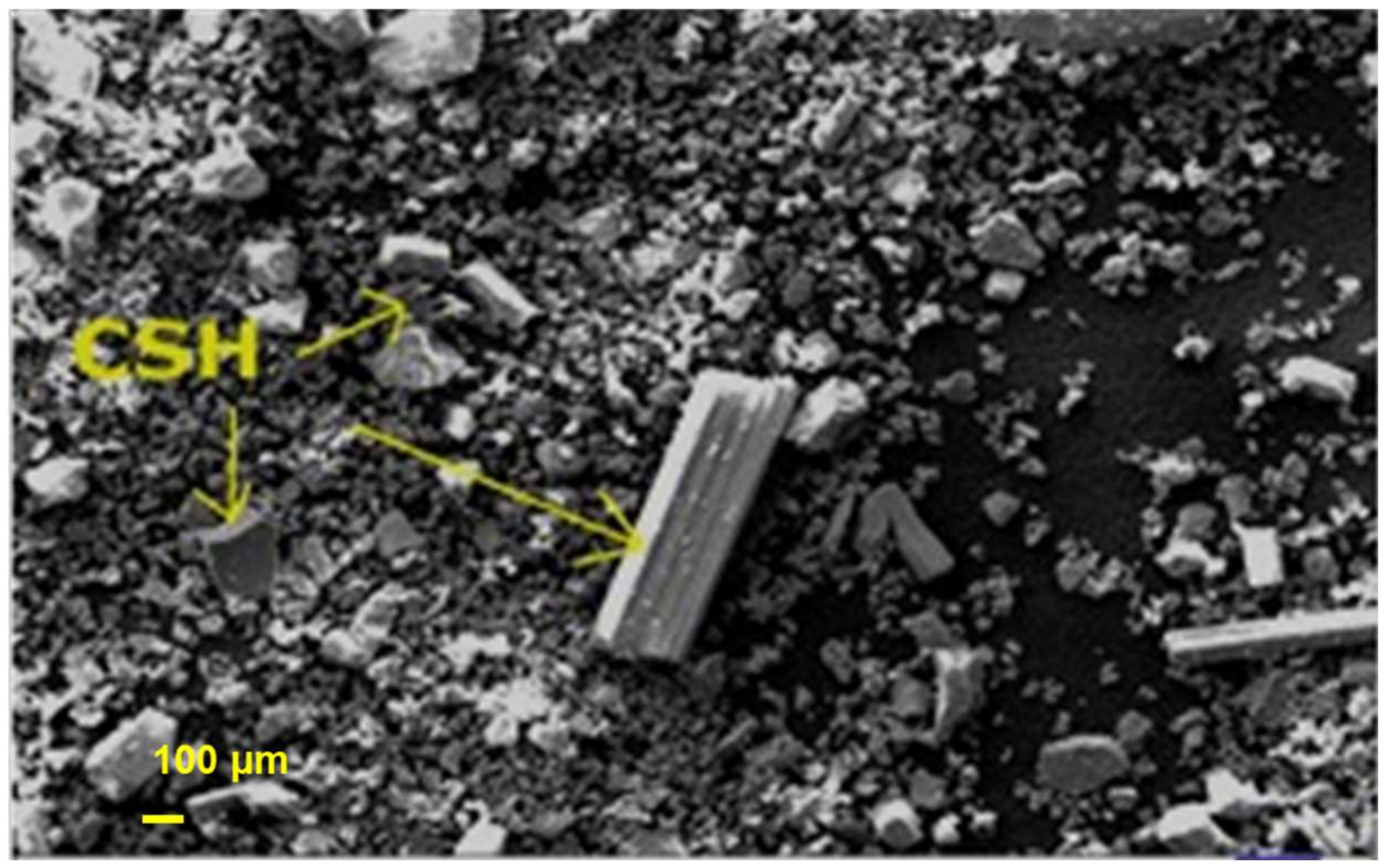
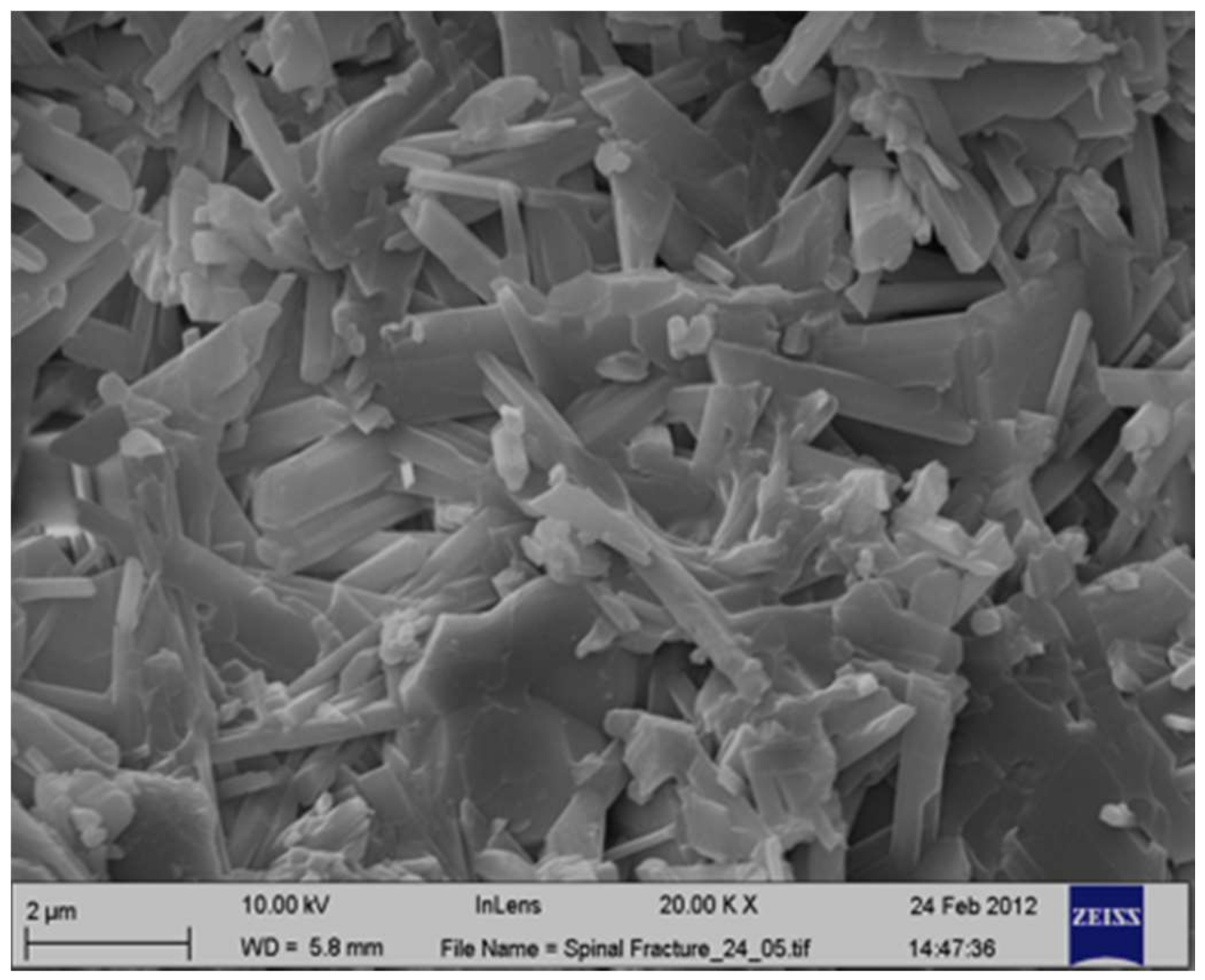
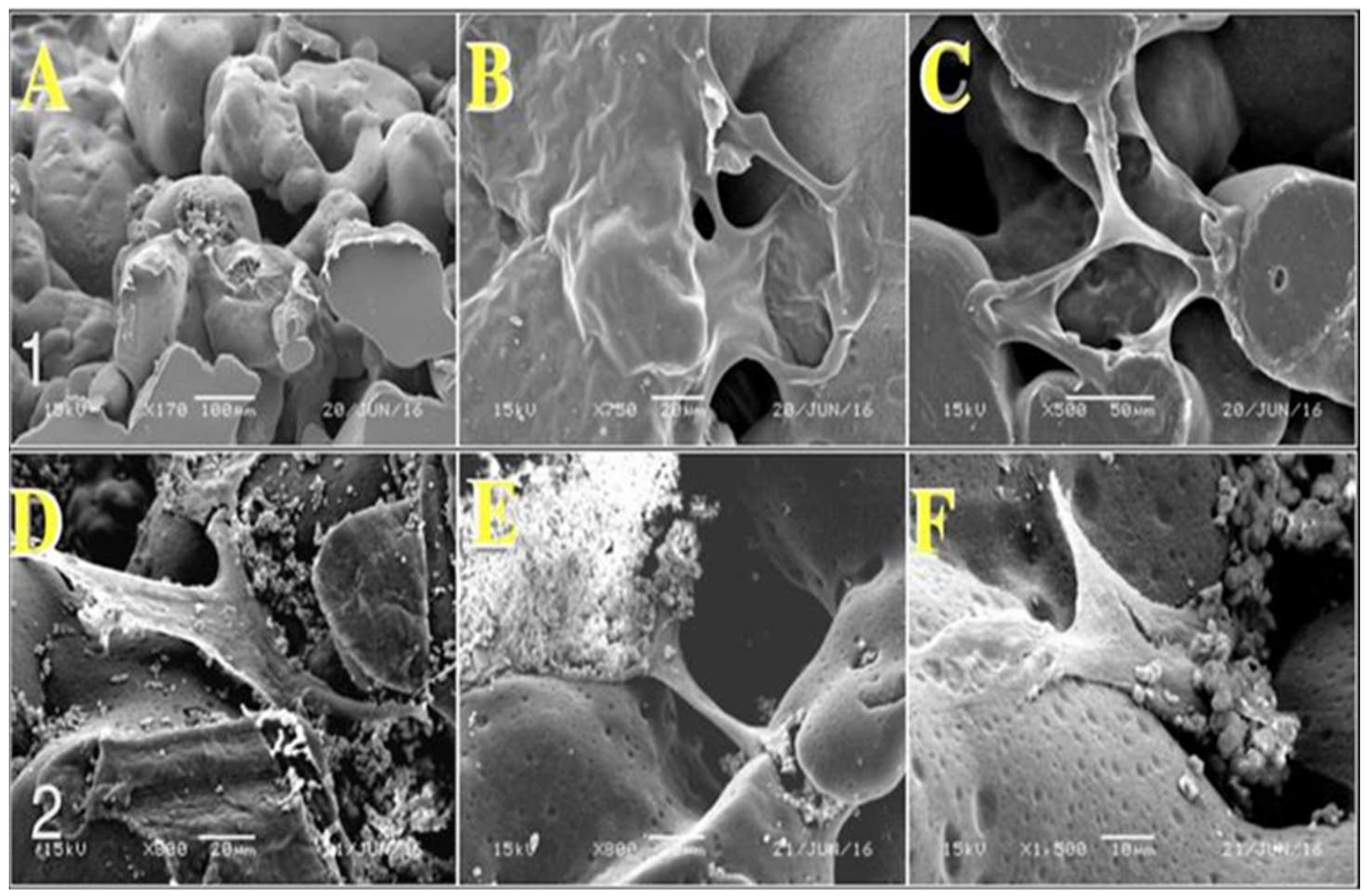
2.1. Morphological Analysis
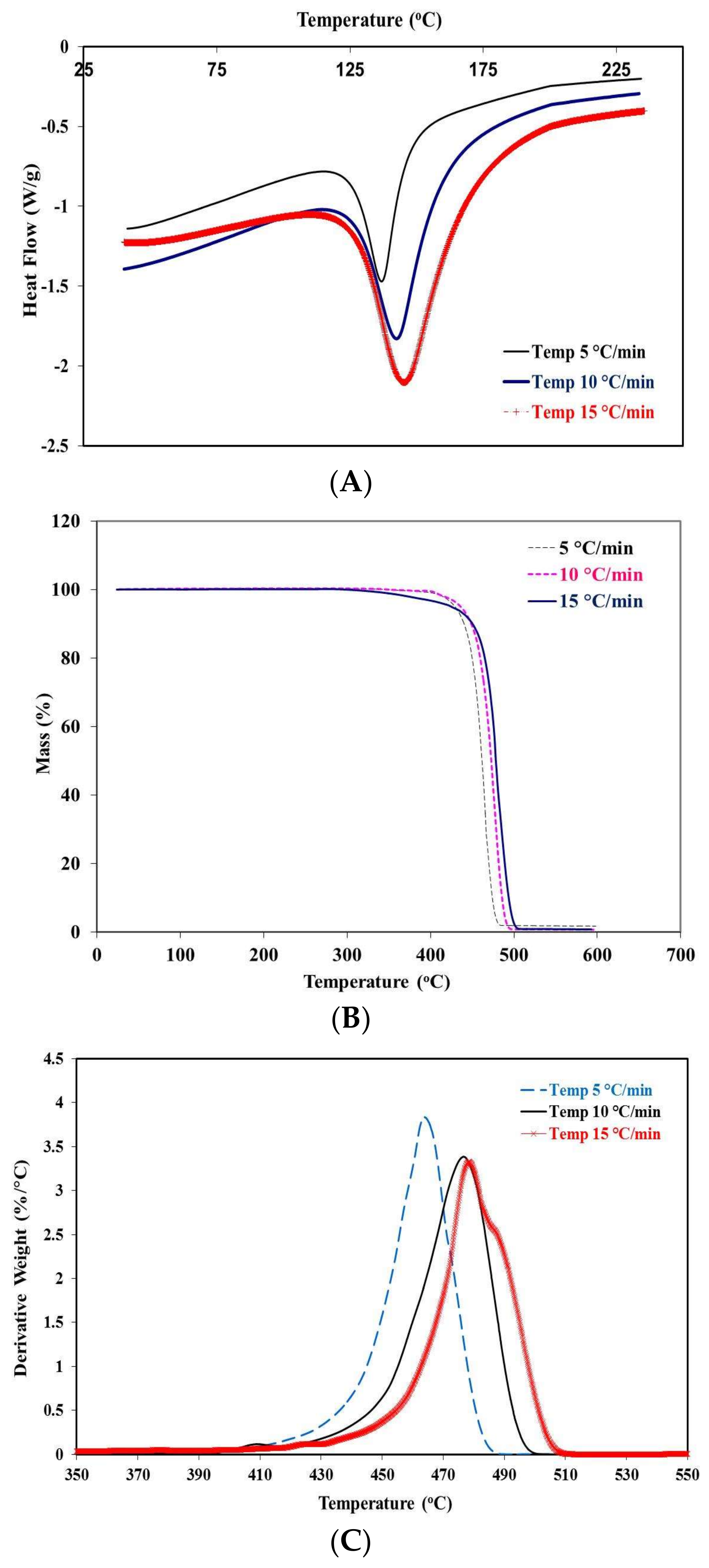
2.2. Thermographic Behavior at Different Rates of Heating
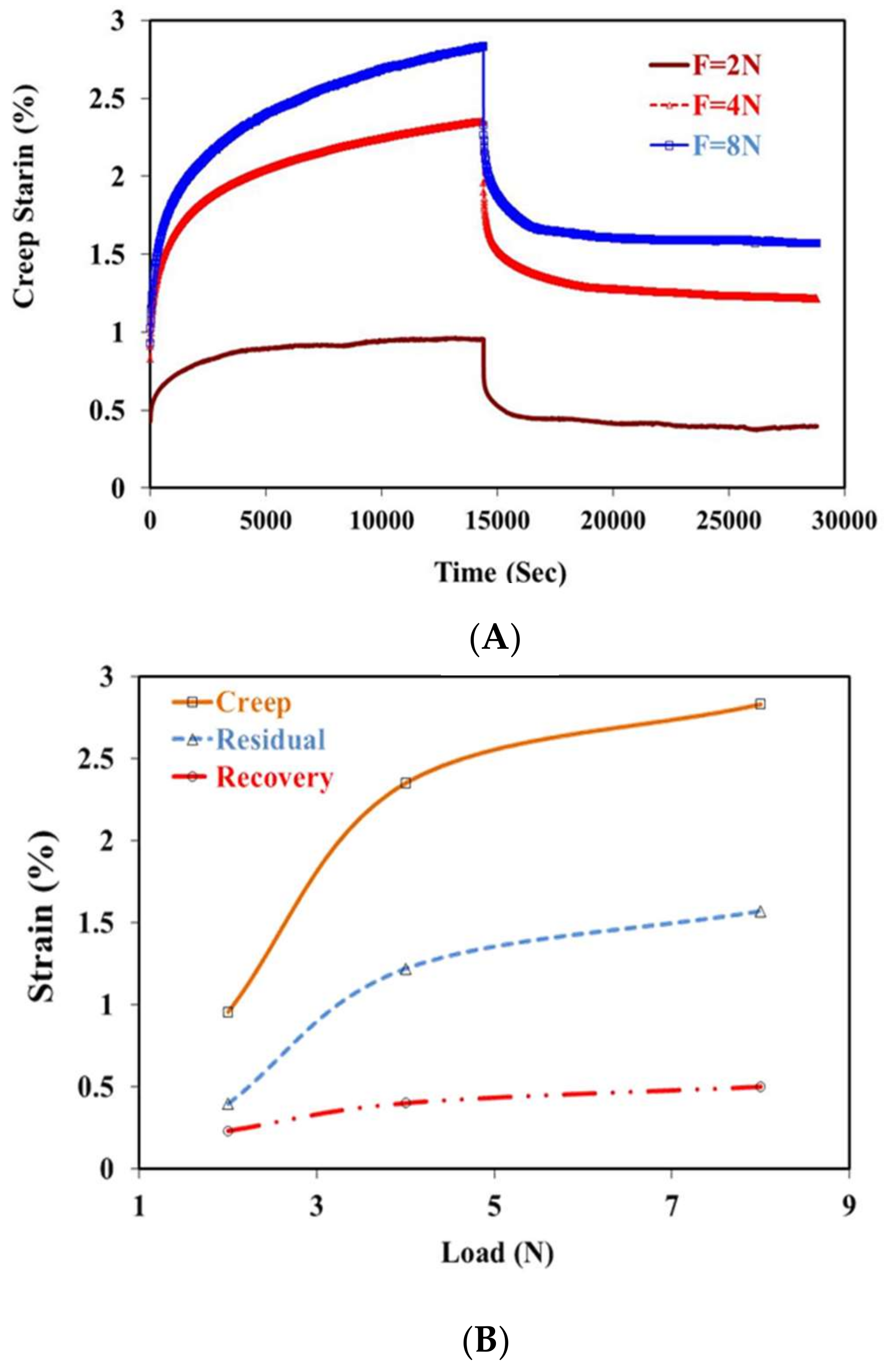
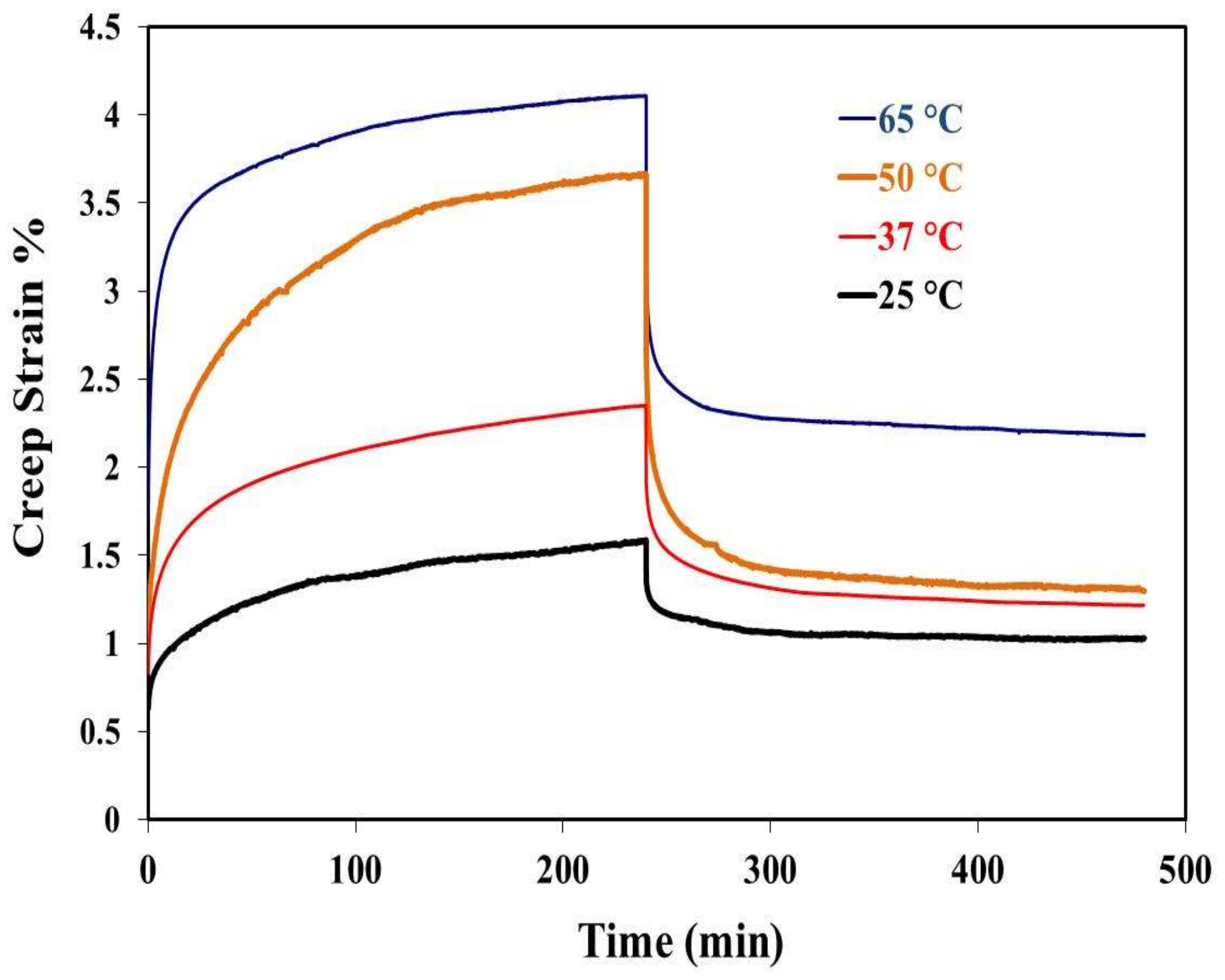
2.3. Creep Recovery Behavior
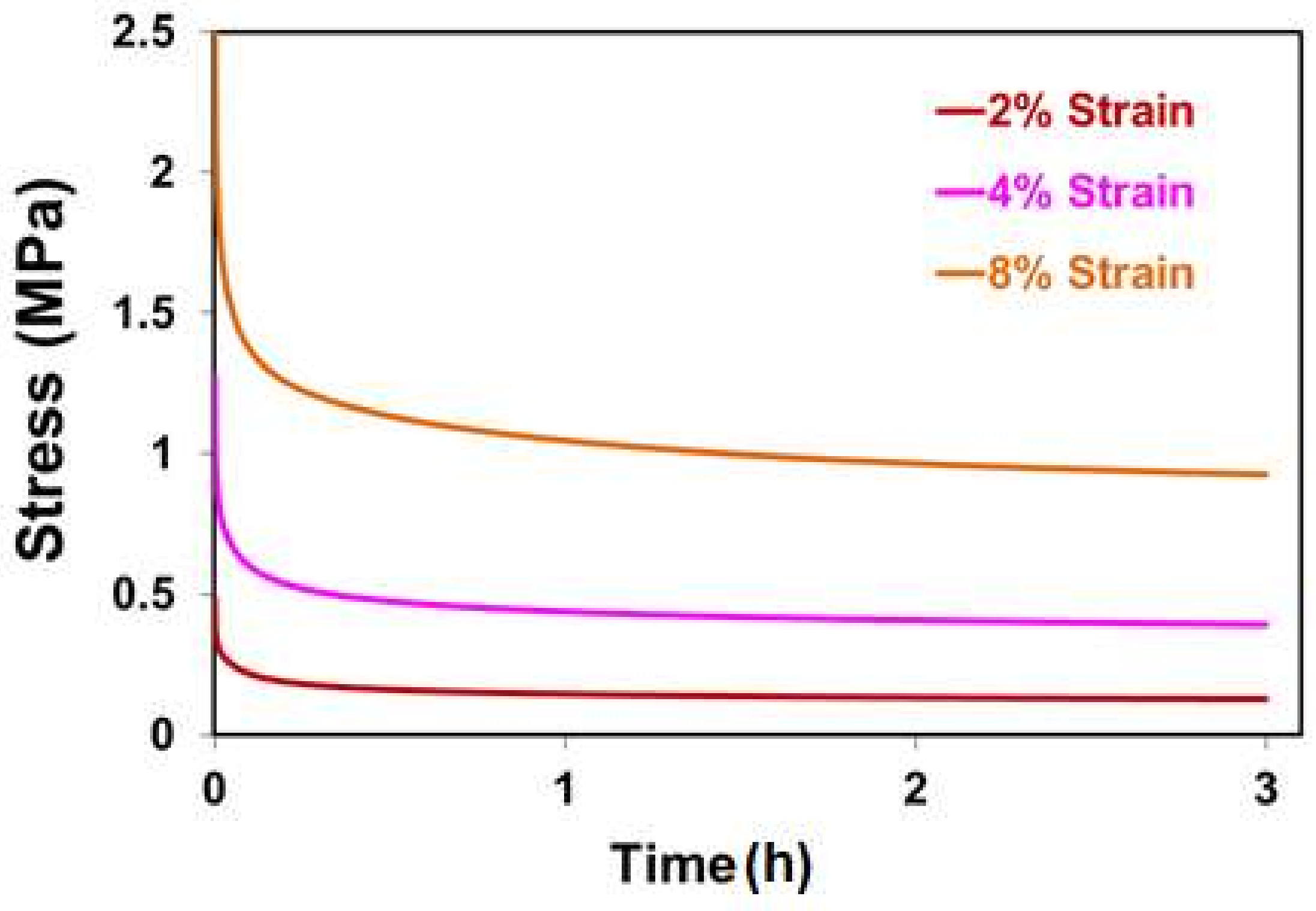
2.4. Relaxation Behavior
2.5. Tensile Test Results
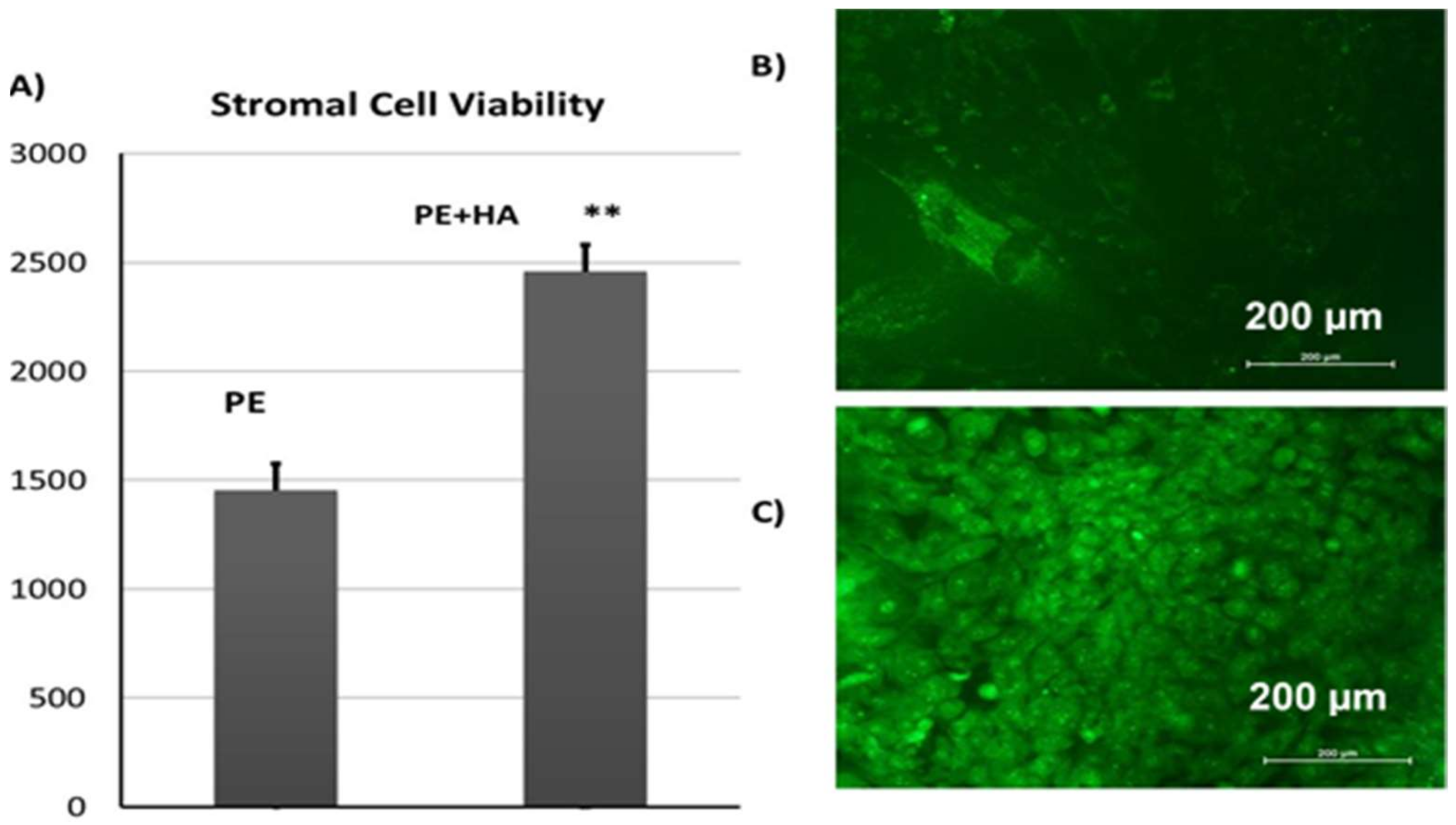
2.6. Cell Culture Results
2.6.1. Treatment of Porous PE Scaffolds: Composition of the Coating Material
2.6.2. Morphological Observation of Stromal Cell Attachment
2.6.3. Viability of CL1 Cells on Porous PE Scaffolds
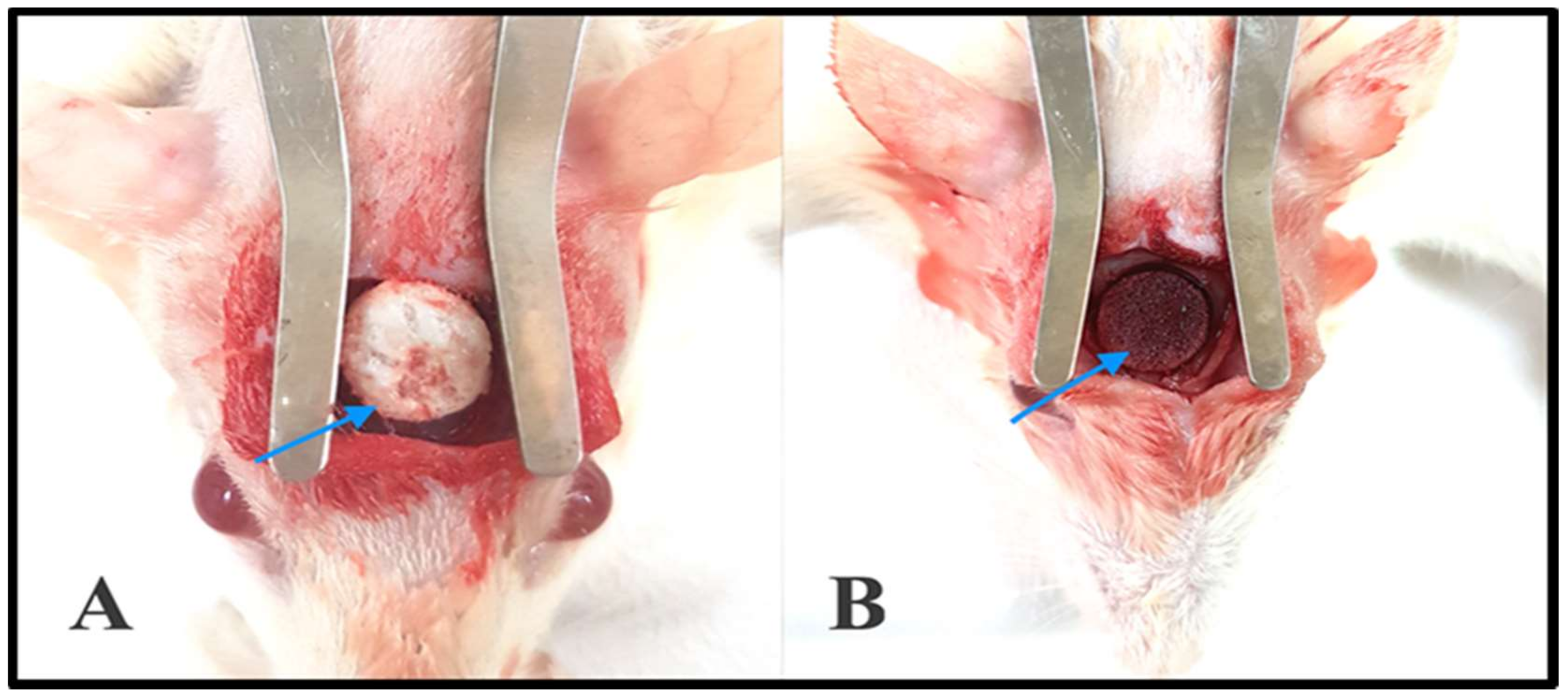
2.7. In Vivo Experiments
2.7.1. Gross Clinical Examination
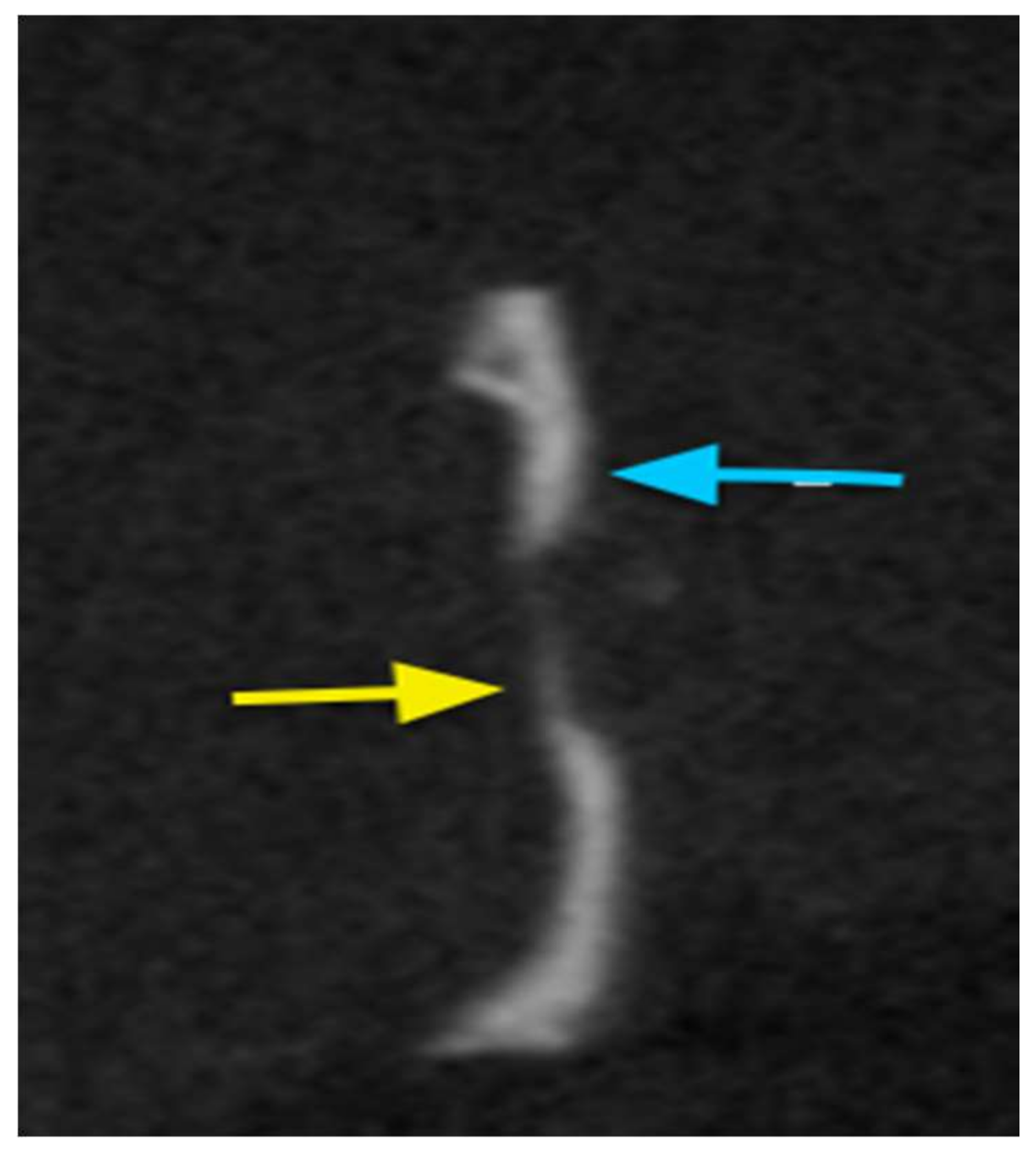
2.7.2. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
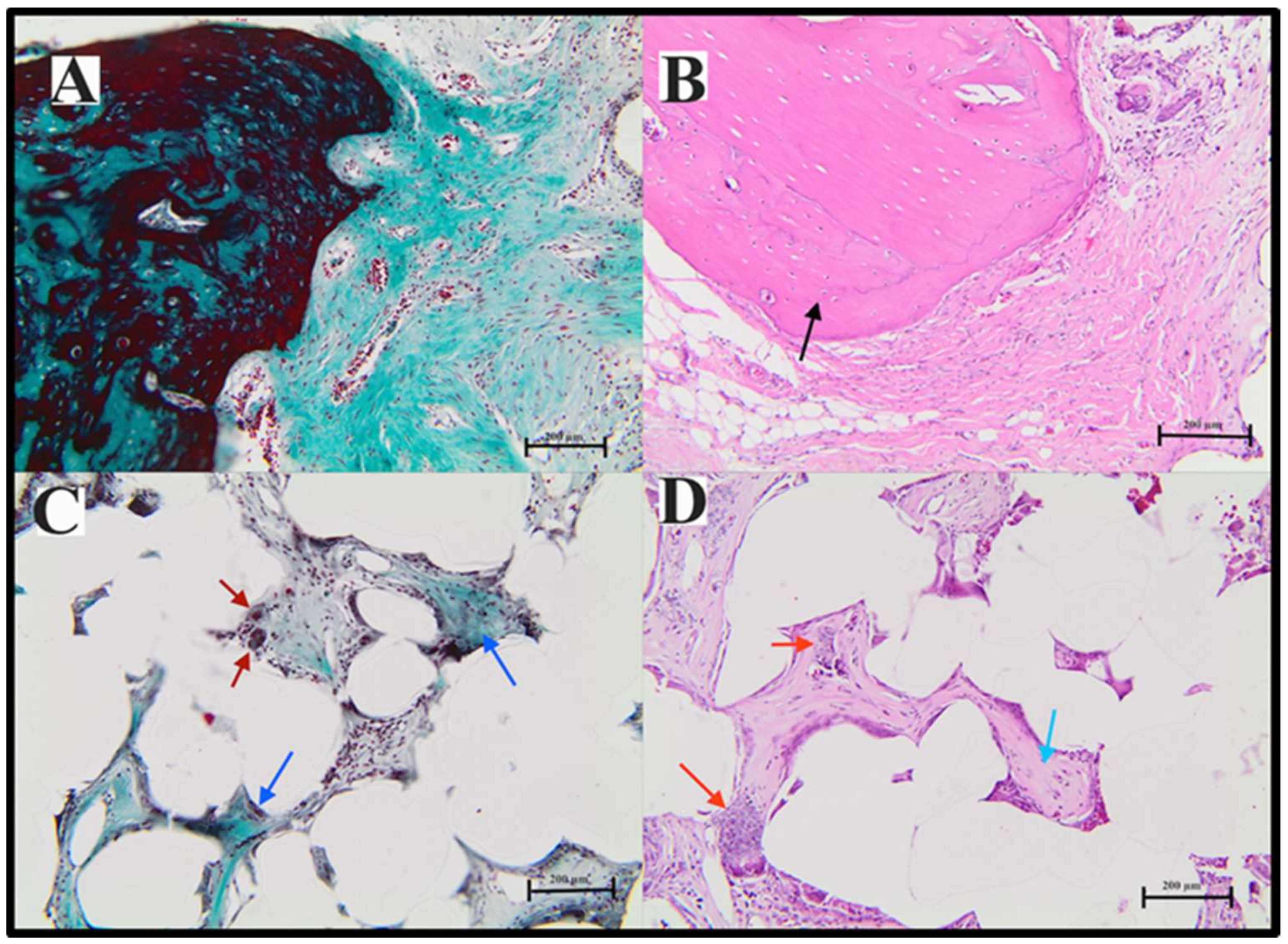
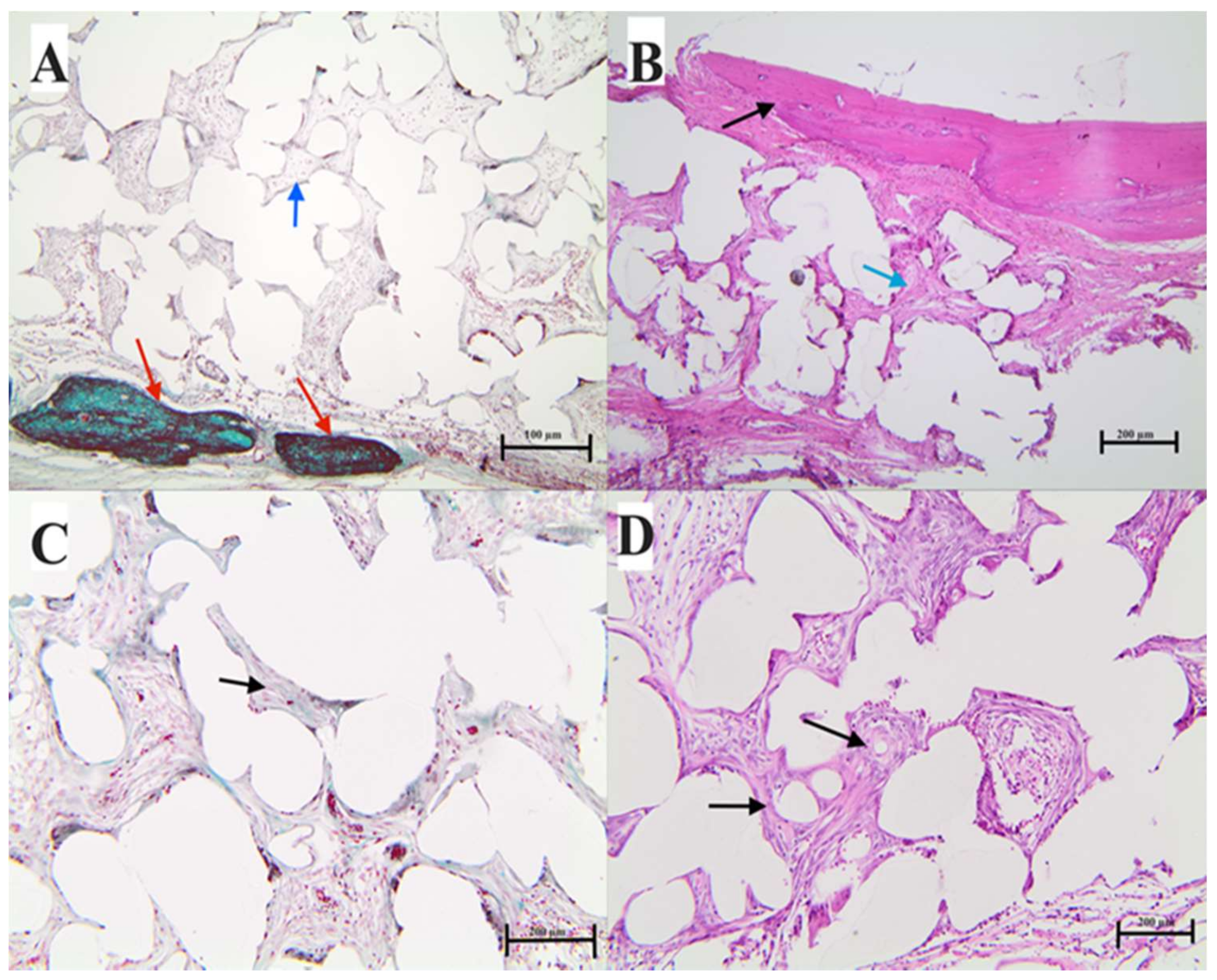
2.7.3. Histological Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Cell Study-Related Methods
3.4. Technique Used for Coating Experimental Samples
3.5. Stromal Cell Attachment and Morphology Assessment
3.6. Cell Viability Assay by alamarBlue®
3.7. In Vivo Bone Formation
3.8. Radiographic Assessment
Cone Beam Tomography
3.9. Histological Analysis
Slide Preparation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- Jeremy, M.H.; Peter, X.M. Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9622–9629. [Google Scholar]
- Behnaz, B.; Payam, Z.; Mohammad, O.O.; Farid, K.; Hamideh, F.; Sohrabi-Jahromi, S.; Zarrintaj, Z. Tissue engineering; strategies, tissues, and biomaterials. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2017, 33, 144–172. [Google Scholar]
- Schlickewei, W.; Schlickewei, S. The use of bone substitutes in the treatment of bone defects—The clinical view and history. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 253, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.M. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Hu, T.L.; Lai, J.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.R. Reconstruction of traumatic nasal deformity in Orientals. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curzio, P.D.; Carboni, A.; Perugini, M.; Matteini, C.; Saponaro, G.; Iannetti, G. Fifteen years of experience with porous polyethylene: A retrospective study. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2013, 36, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanf, H.; Deveci, M.; Uygur, F.; Şengezer, M. Reconstruction of contour and anterior wall defects of frontal bone with a porous polyethylene implant. J. Cranio maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 27, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Introducing an attractive method for total biomimetic creation of a synthetic biodegradable bioactive bone scaffold based on statistical experimental design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 86, 109–120.
- Wang, M. Developing bioactive composite materials for tissue replacement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2133–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, L.B.; Mawn, L.A.; Thompson, R.C. Reconstruction of the orbit after resection of spheno-orbital meningiomas: A novel technique. Skull Base 2011, 21, A107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, T.; Treiser, M.D.; Holmes, P.F.; Kohn, J.; Moghe, P.V.; Arinzeh, TL. Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on poly(ethylene glycol)-variant biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 15, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Mingming, D.; Fei, L.; Zhao, W.; Yiwen, L. “Click” chemistry in polymeric scaffolds: Bioactive materials for tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2018, 273, 160–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, S.; Park, H.J.; Ohk, S.H.; Oh, H.K. Evaluation of osseointegration ability of porous polyethylene implant (Medpor) treated with chitosan. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A.; Al-Fotawei, R. Biomaterials in the Reconstruction of the Oral and Maxillofacial Region. Front. Oral Biol. 2015, 17, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundáková, M.; Pazourková, L.; Kupková, J.; Samlíková, M.; Pazdziora, E. Preparation of antimicrobial polyethylene/inorgano-organo-vermiculite hybrid material. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 7783–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Vayvada, H.; Aydın, E.; Menderes, A.; Atabey, A. Repair of fractures of the orbital floor with porous polyethylene implants. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 45, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshzaban, A.; Mehrzad, S.; Tavakoli, V.; Keshel, S.H.; Behrouzi, G.R.; Bashtar, M. The comparative effectiveness of demineralized bone matrix; beta-tricalcium phosphate, and bovine-derived anorganic bone matrix on inflammation and bone formation using a paired calvarial defect model in rats. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2011, 29, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfotawei, R.; Alfayez, M.; Mahmood, A. In Situ tissue engineering using an induced muscle flap to reconstruct critical size bone defect. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2017, 11, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Deting, X.; Wenji, Y.; Wei, W.; Dan, S.; Xiangmin, T. Reconstruction of rat calvarial defects with human mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblast-like cells in poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid scaffolds. Eur. Cells Mater. 2010, 20, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agacayak, S.; Gulsun, B.; Ucan, M.; Karaoz, E.; Nergiz, Y. Effects of mesenchymal stem cells in critical size bone defect. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.J.; Kim, J.W. Surgical treatment of enophthalmos using an endoscope and T-shaped porous polyethylene fabricated with a mirror image. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Harrison, I.R. Polymer melting: Heating rate effects on DSC melting peaks. Thermochim. Acta 1994, 231, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strella, S.; Erhardt, P.F. Rate effects in the measurement of polymer transitions by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, A. Heating rate dependence of melting peak temperature examined by DSC of heat flux type. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Uhrich, K.E. Analysis of thermal properties of polymeric biomaterials. I. Ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 68, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, H. Effect of long-term natural aging on the thermal; mechanical; and viscoelastic behavior of biomedical grade of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, H.; Elleithy, R. High density polyethylene/graphite nano-composites for total hip joint replacements: Processing and in vitro characterization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, A.H.I.; Fouad, H.; Elleithy, R. Impact of some environmental conditions on the tensile; creep-recovery; relaxation; melting and crystallinity behaviour of UHMWPE-GUR 410-medical grade. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4112–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Wielanek, L.; Wang, J.-S.; Tanner, K.E.; Lidgren, L. Factors influencing the compressive strength of an injectable calcium sulfate-hydroxyapatite cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfotawi, R.; Naudi, K.; Dalby, M.J.; Tanner, K.E.; McMahon, J.D.; Ayoub, A. Assessment of cellular viability on calcium sulphate/hydroxyapatite injectable scaffolds. J. Tissue Eng. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strocchi, R.; Orsini, G.; Iezzi, G.; Scarano, A.; Rubini, C.; Pecora, G.; Piattelli, A. Bone regeneration with calcium sulfate: Evidence for increased angiogenesis in rabbits. J. Oral Implantol. 2002, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfotawi, R.; Ayoub, A.F.; Tanner, K.E.; Dalby, M.J.; Naudiand, K.B.; McMahon, J. A Novel Surgical Approach for the Reconstruction of Critical-Size Mandibular Defects Using Calcium Sulphate/Hydroxyapatite Cement, BMP-7 and Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Histological Assessment. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdallah, B.M.; Jafari, A.; Zaher, W.; Qiu, W.; Kassem, M. Skeletal (stromal) stem cells; an update on intracellular signaling pathways controlling osteoblast differentiation. Bone 2015, 70, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nbaheen, M.; Vishnubalaji, R.; Ali, D.; Bouslimi, A.; Al-Jassir, F.; Megges, M. Human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells from bone marrow: Adipose tissue and skin exhibit differences in molecular phenotype and differentiation potential. Stem Cell Rev. 2013, 9, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsafadi, M.; Manikandan, M.; Atteya, M.; Hashmi, J.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Aldahmash, A. Characterization of cellular and molecular heterogeneity of bone marrow stromal cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9378081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Tan, L.P.; Tan, L.S.; Huang, X. Porous calcium phosphate ceramics modified with PLGA-bioactive glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankaya, A.B.; Erdem, M.A.; Isler, S.C.; Demircan, S.; Soluk, M.; Kasapoglu, C.; Oral, C.K. Use of cone-beam computerized tomography for evaluation of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws in an experimental rat model. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 8, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.M.; Sophocleous, A. Quantitative analysis of bone and soft tissue by micro-computed tomography: Applications to ex vivo and in vivo studies. Bonekey Rep. 2014, 3, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Cross-Head Speed | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 mm/min | 480 ± 16 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 68 ± 3 |
| 1 mm/min | 560 ± 20 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 56 ± 2 |
| 2 mm/min | 580 ± 12 | 3.8 ± 0.13 | 50 ± 4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fouad, H.; AlFotawi, R.; Alothman, O.Y.; Alshammari, B.A.; Alfayez, M.; Hashem, M.; Mahmood, A. Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material. Materials 2018, 11, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040521
Fouad H, AlFotawi R, Alothman OY, Alshammari BA, Alfayez M, Hashem M, Mahmood A. Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material. Materials. 2018; 11(4):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040521
Chicago/Turabian StyleFouad, H., Randa AlFotawi, Othman Y. Alothman, Basheer A. Alshammari, Musaad Alfayez, Mohamed Hashem, and Amer Mahmood. 2018. "Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material" Materials 11, no. 4: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040521
APA StyleFouad, H., AlFotawi, R., Alothman, O. Y., Alshammari, B. A., Alfayez, M., Hashem, M., & Mahmood, A. (2018). Porous Polyethylene Coated with Functionalized Hydroxyapatite Particles as a Bone Reconstruction Material. Materials, 11(4), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040521







