Further Theoretical Insight into the Mechanical Properties of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fillers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
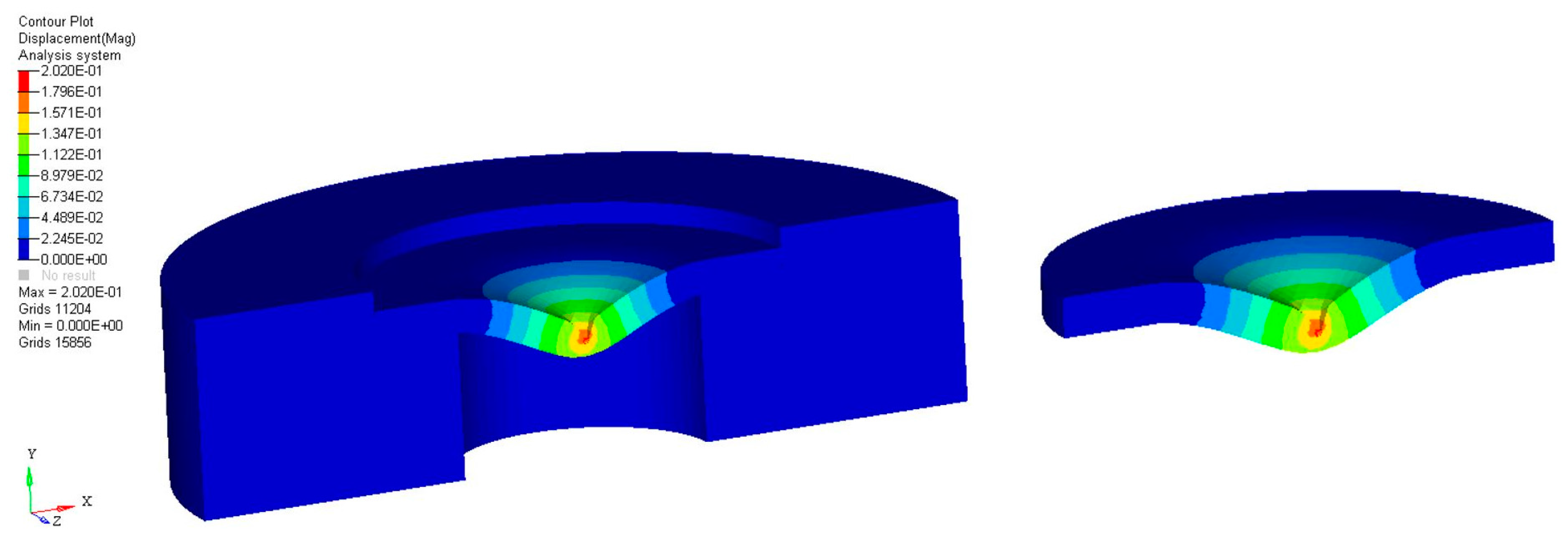
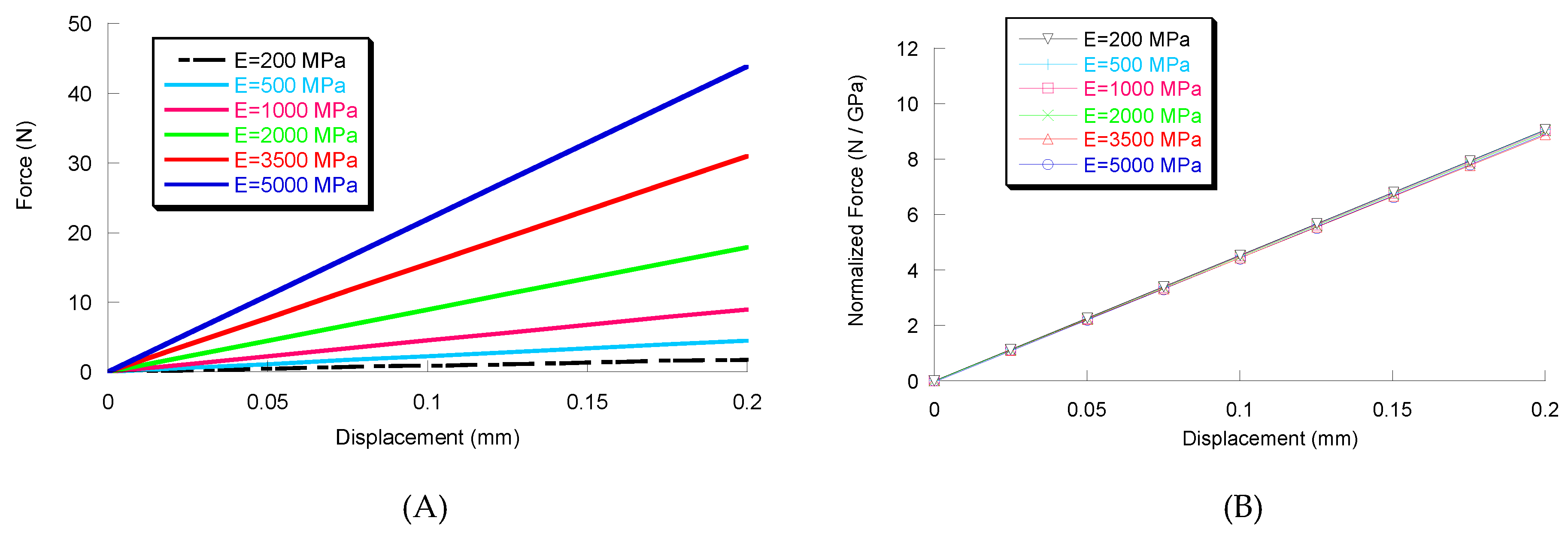
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
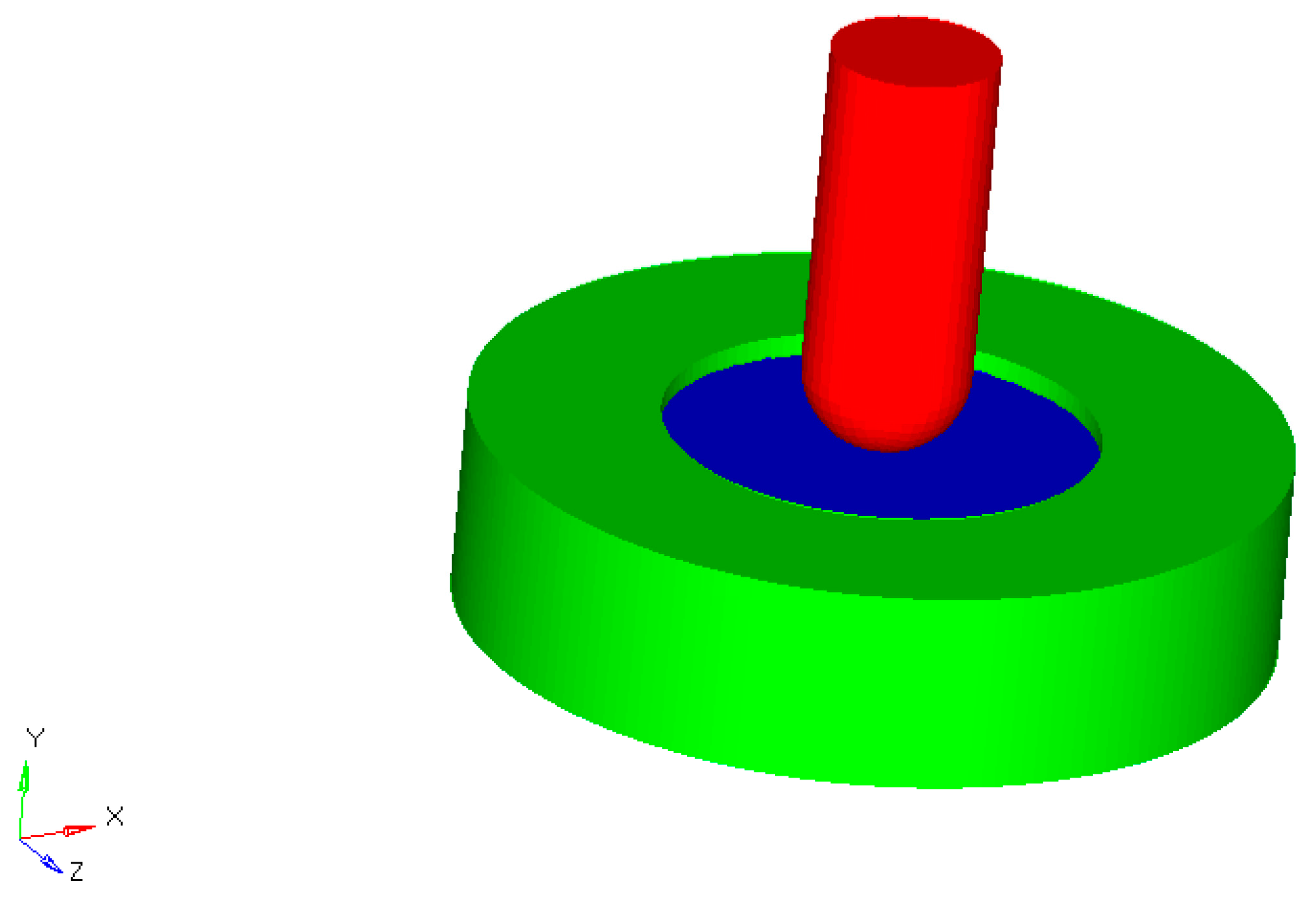
3.2. Generation of Solid Model and Numerical Simulation
4. Conclusions
- The results from the small punch test and Young’s modulus of PCL loaded with sol–gel-synthesized organic–inorganic hybrid fillers were newly correlated.
- The data were compared to those obtained from a previous theoretical modelling, suggesting a better approximation of the experimental Young’s modulus.
- The found correlation will be an important step in the evaluation of Young’s modulus starting from the small punch test data.
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, T.; Gloria, A.; D’Antò, V.; D’Amora, U.; Ametrano, G.; Bollino, F.; de Santis, R.; Ausanio, G.; Catauro, M.; Rengo, S. Poly(ε-caprolactone) reinforced with sol-gel synthesized organic-inorganic hybrid fillers as composite substrates for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2010, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gloria, A.; Russo, T.; D’Amora, U.; Zeppetelli, S.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Banobre-Lopez, M.; Pineiro-Redondo, Y.; Uhlarz, M.; Tampieri, A.; et al. Magnetic poly(ε-caprolactone)/iron-doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite substrates for advanced bone tissue engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzacchiello, A.; Gloria, A.; Mayol, L.; Dickinson, S.; Miot, S.; Martin, I.; Ambrosio, L. Natural/synthetic porous scaffold designs and properties for fibro-cartilaginous tissue engineering. J. Bioact. Compati. Polym. 2011, 26, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santis, R.; Gloria, A.; Russo, T.; D’Amora, U.; D’Antò, V.; Bollino, F.; Catauro, M.; Mollica, F.; Rengo, S.; Ambrosio, L. Advanced composites for hard-tissue engineering based on PCL/organic-inorganic hybrid fillers: From the design of 2D substrates to 3D rapid prototyped scaffolds. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, R.; Russo, A.; Gloria, A.; D’Amora, U.; Russo, T.; Panseri, S.; Sandri, M.; Tampieri, A.; Marcacci, M.; Dediu, V.A. Towards the design of 3D fiber-deposited poly(ε-caprolactone)/iron-doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite magnetic scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, M.; Gloria, A.; Coelho, J.; Bartolo, P.; Ciurana, J. Three-dimensional printed bone scaffolds: The role of nano/micro-hydroxyapatite particles on the adhesion and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2017, 231, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Raucci, M.G.; de Marco, D.; Ambrosio, L. Release kinetics of ampicillin, characterization and bioactivity of TiO2/PCL hybrid materials synthesized by sol-gel processing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 77, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Raucci, M.; Ausanio, G. Sol-gel processing of drug delivery zirconia/polycaprolactone hybrid materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Pacifico, S. Synthesis of bioactive chlorogenic acid-silica hybrid materials via the sol–gel route and evaluation of their biocompatibility. Materials 2017, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciprioti, S.V.; Bollino, F.; Tranquillo, E.; Catauro, M. Synthesis, thermal behavior and physicochemical characterization of ZrO2/PEG inorganic/organic hybrid materials via sol–gel technique. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Giovanardi, R.; Veronesi, P. Modification of Ti6Al4V implant surfaces by biocompatible TiO2/PCL hybrid layers prepared via sol-gel dip coating: Structural characterization, mechanical and corrosion behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 74, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Papale, F. Response of SAOS-2 cells to simulated microgravity and effect of biocompatible sol–gel hybrid coatings. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 122, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Papale, F.; Piccolella, S.; Pacifico, S. Sol–gel synthesis and characterization of SiO2/PCL hybrid materials containing quercetin as new materials for antioxidant implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Papale, F.; Marciano, S.; Pacifico, S. TiO2/PCL hybrid materials synthesized via sol–gel technique for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Bollino, F.; Mozzati, M.C.; Ferrara, C.; Mustarelli, P. Structure and magnetic properties of SiO2/PCL novel sol–gel organic–inorganic hybrid materials. J. Solid State Chem. 2013, 203, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Verardi, D.; Melisi, D.; Belotti, F.; Mustarelli, P. Novel sol-gel organic-inorganic hybrid materials for drug delivery. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2010, 8, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catauro, M.; Tranquillo, E.; Illiano, M.; Sapio, L.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. The Influence of the Polymer Amount on the Biological Properties of PCL/ZrO2 Hybrid Materials Synthesized via Sol-Gel Technique. Materials 2017, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, I.; Scherer, G. An organic/inorganic single-phase composite. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-J.; Kim, C.-H.; Park, J.-K. Synthesis and characterization of starch-g-polycaprolactone copolymer. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7402–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causa, F.; Battista, E.; Della Moglie, R.; Guarnieri, D.; Iannone, M.; Netti, P.A. Surface investigation on biomimetic materials to control cell adhesion: The case of RGDconjugation on PCL. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9875–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Sun, X.S. Properties of soy protein isolate/polycaprolactone blends compatibilized by methylene diphenyl diisocyanate. Polymer 2001, 42, 6961–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Schantz, T.; Zein, I.; Ng, K.W.; Teoh, S.H.; Tan, K.C. Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2001, 55, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, T.; Domingos, M.; Gloria, A.; D’Amora, U.; Coelho, J.; Bártolo, P. Fabrication and characterisation of PCL and PCL/PLA scaffolds for tissue engineering. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, W.; Lv, X.; Lei, Z.; Bian, Y.; Deng, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Li, X. Biomimetic LBL structured nanofibrous matrices assembled by chitosan/collagen for promoting wound healing. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, S.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Luo, W.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Deng, H.; Du, Y. Recyclable Saccharomyces cerevisiae loaded nanofibrous mats with sandwich structure constructing via bio-electrospraying for heavy metal removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, C.; Kokubo, T.; Yamamuro, T. Mechanism of apatite formation on CaO-SiO2-P2O5 glasses in a simulated body fluid. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 1992, 143, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Kim, H.-M.; Kawashita, M. Novel bioactive materials with different mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzetti, E.; Speranza, D.; Marcolin, F.; Fracastoro, G. Diagnosing cleft lip pathology in 3D ultrasound: A landmarking-based approach. Image Anal. Stereol. 2015, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, C.; Esposito, L.; Speranza, D.; Bonora, N. Firecracker eye exposure: Experimental study and simulation. Biomech. Modeling Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moos, S.; Marcolin, F.; Tornincasa, S.; Vezzetti, E.; Violante, M.G.; Fracastoro, G.; Speranza, D.; Padula, F. Cleft lip pathology diagnosis and foetal landmark extraction via 3D geometrical analysis. Int. J. Interac. Des. Manuf. 2017, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorelli, M.; Maietta, S.; Gloria, A.; de Santis, R.; Pei, E.; Lanzotti, A. Design and analysis of 3D customized models of a human mandible. Procedia CIRP 2016, 49, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.; De Luca, A.; Greco, A.; Maietta, S.; Marro, A.; Apicella, A. Investigation on the static and dynamic structural behaviours of a regional aircraft main landing gear by a new numerical methodology. Frattura Integr. Strutt. 2018, 12, 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Eshraghi, S.; Das, S. Mechanical and microstructural properties of polycaprolactone scaffolds with one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional orthogonally oriented porous architectures produced by selective laser sintering. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, R.; Gloria, A.; Russo, T.; D’Amora, U.; Zeppetelli, S.; Dionigi, C.; Sytcheva, A.; Herrmannsdörfer, T.; Dediu, V.; Ambrosio, L. A basic approach toward the development of nanocomposite magnetic scaffolds for advanced bone tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3599–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Displacement (mm) | Force (N) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 0.195 | 1.70 | 193 |
| PCL/Ti2 | 0.191 | 3.26 | 378 |
| PCL/Zr2 | 0.192 | 3.59 | 415 |
| Material | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Disk 1 | 200 | 0.40 |
| Disk 2 | 500 | 0.40 |
| Disk 3 | 1000 | 0.40 |
| Disk 4 | 2000 | 0.40 |
| Disk 5 | 3500 | 0.40 |
| Disk 6 | 5000 | 0.40 |
| Total # of Grids | Total # of Elements | Total # of Contact Elements | Total # of Degrees of Freedom |
|---|---|---|---|
| 55,559 | 267,342 | 1461 | 158,939 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maietta, S.; Russo, T.; De Santis, R.; Ronca, D.; Riccardi, F.; Catauro, M.; Martorelli, M.; Gloria, A. Further Theoretical Insight into the Mechanical Properties of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fillers. Materials 2018, 11, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020312
Maietta S, Russo T, De Santis R, Ronca D, Riccardi F, Catauro M, Martorelli M, Gloria A. Further Theoretical Insight into the Mechanical Properties of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fillers. Materials. 2018; 11(2):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020312
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaietta, Saverio, Teresa Russo, Roberto De Santis, Dante Ronca, Filomena Riccardi, Michelina Catauro, Massimo Martorelli, and Antonio Gloria. 2018. "Further Theoretical Insight into the Mechanical Properties of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fillers" Materials 11, no. 2: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020312
APA StyleMaietta, S., Russo, T., De Santis, R., Ronca, D., Riccardi, F., Catauro, M., Martorelli, M., & Gloria, A. (2018). Further Theoretical Insight into the Mechanical Properties of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Fillers. Materials, 11(2), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020312










