Evaluation of Chemical Mechanical Polishing-Based Surface Modification on 3D Dental Implants Compared to Alternative Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
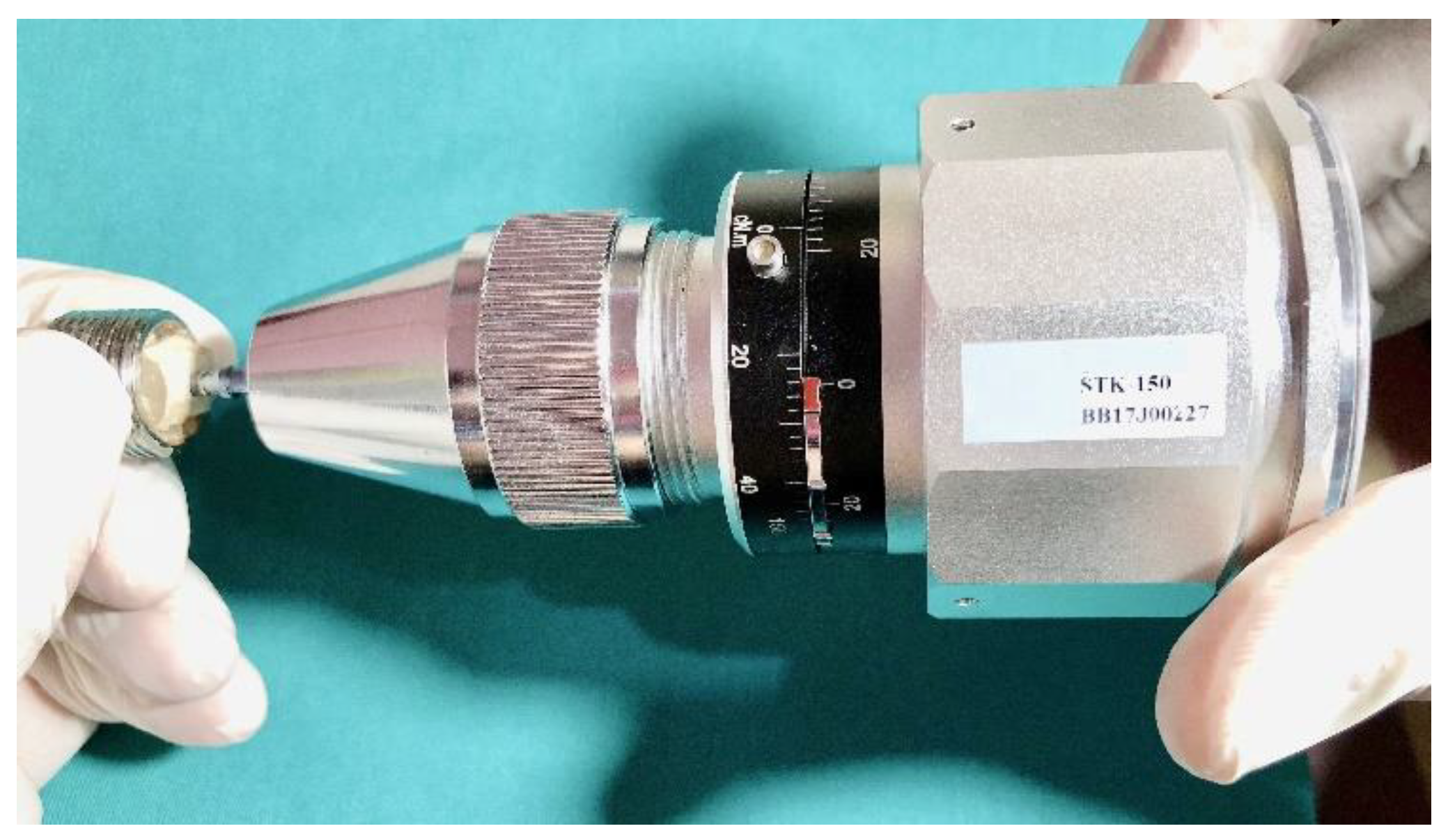
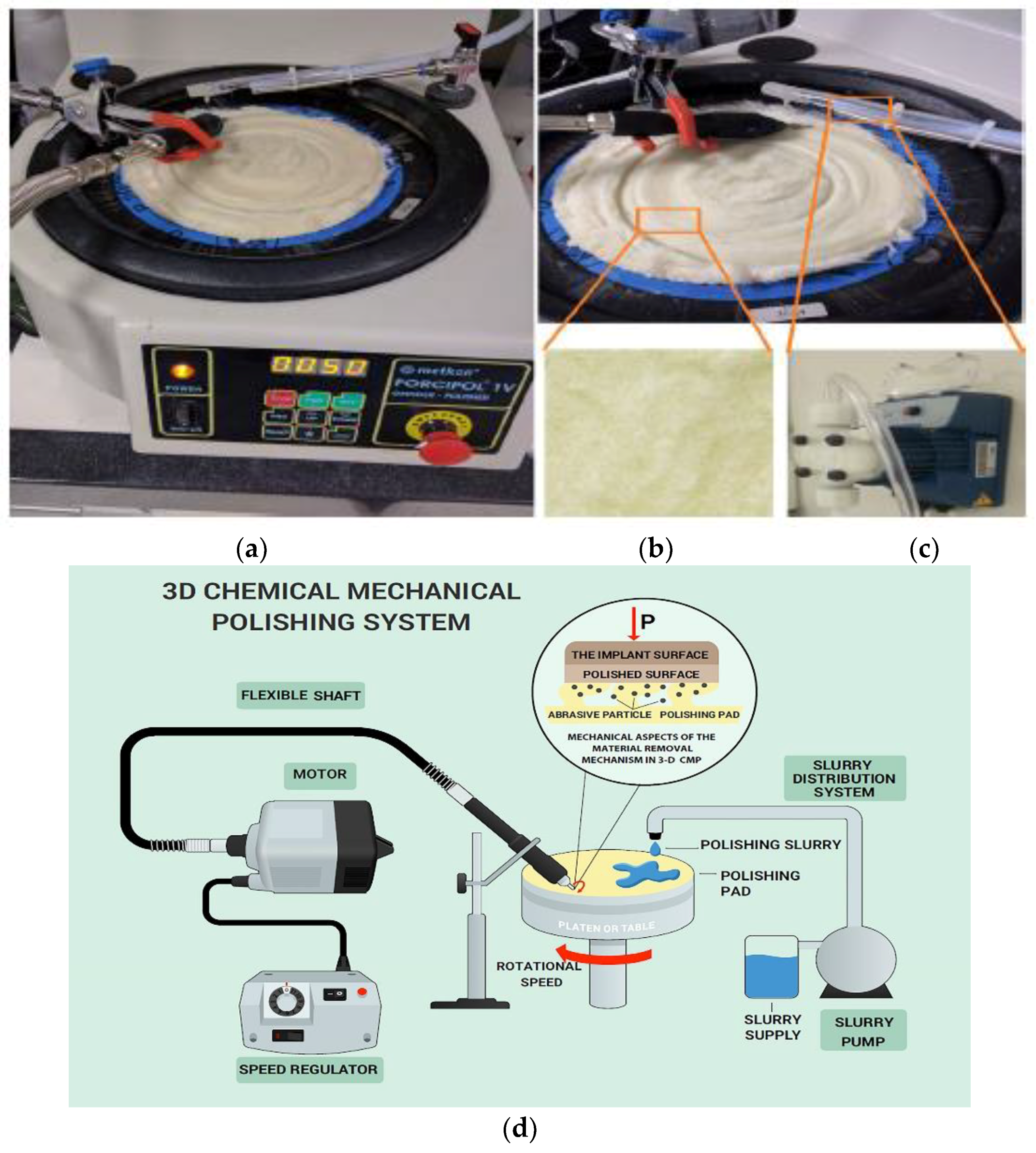
2.1. Dental Implant Treatment and CMP Equipment Set-Up
Presentation of the Lab-Scale Setup
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Chemical Mechanical Polishing Application
2.2.2. Material Removal Rate (MRR) Determination
2.2.3. Surface Roughness Evaluations
2.2.4. Wettability Characterization
2.2.5. Electrochemical Corrosion Assessment
2.2.6. Biomechanical Evaluations
Pull-Out Test
Removal Torque Test
Microhardness Test
3. Results and Discussion
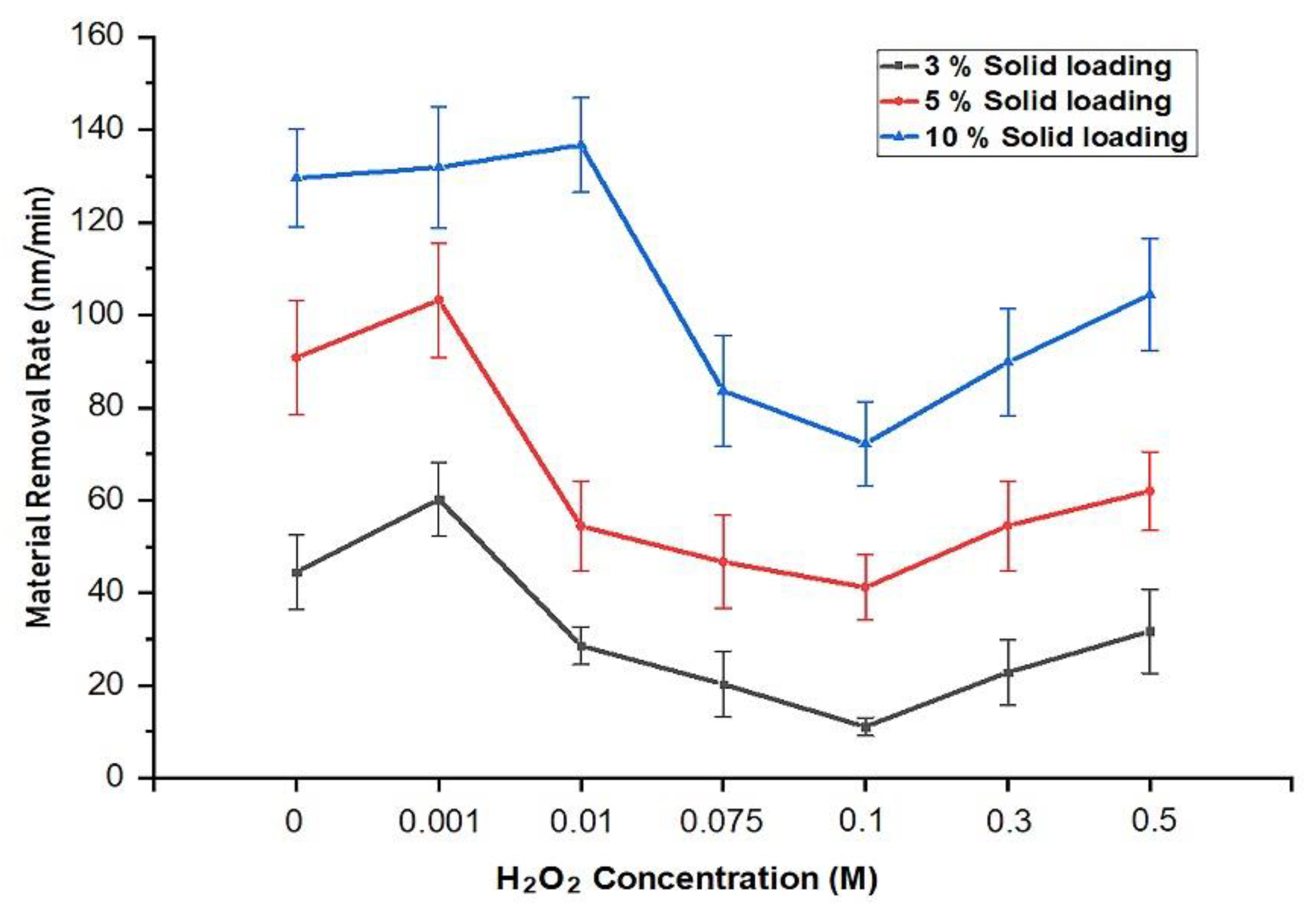
3.1. CMP Performance Evaluations
Effect of the H2O2 Concentration on the Material Removal Rate
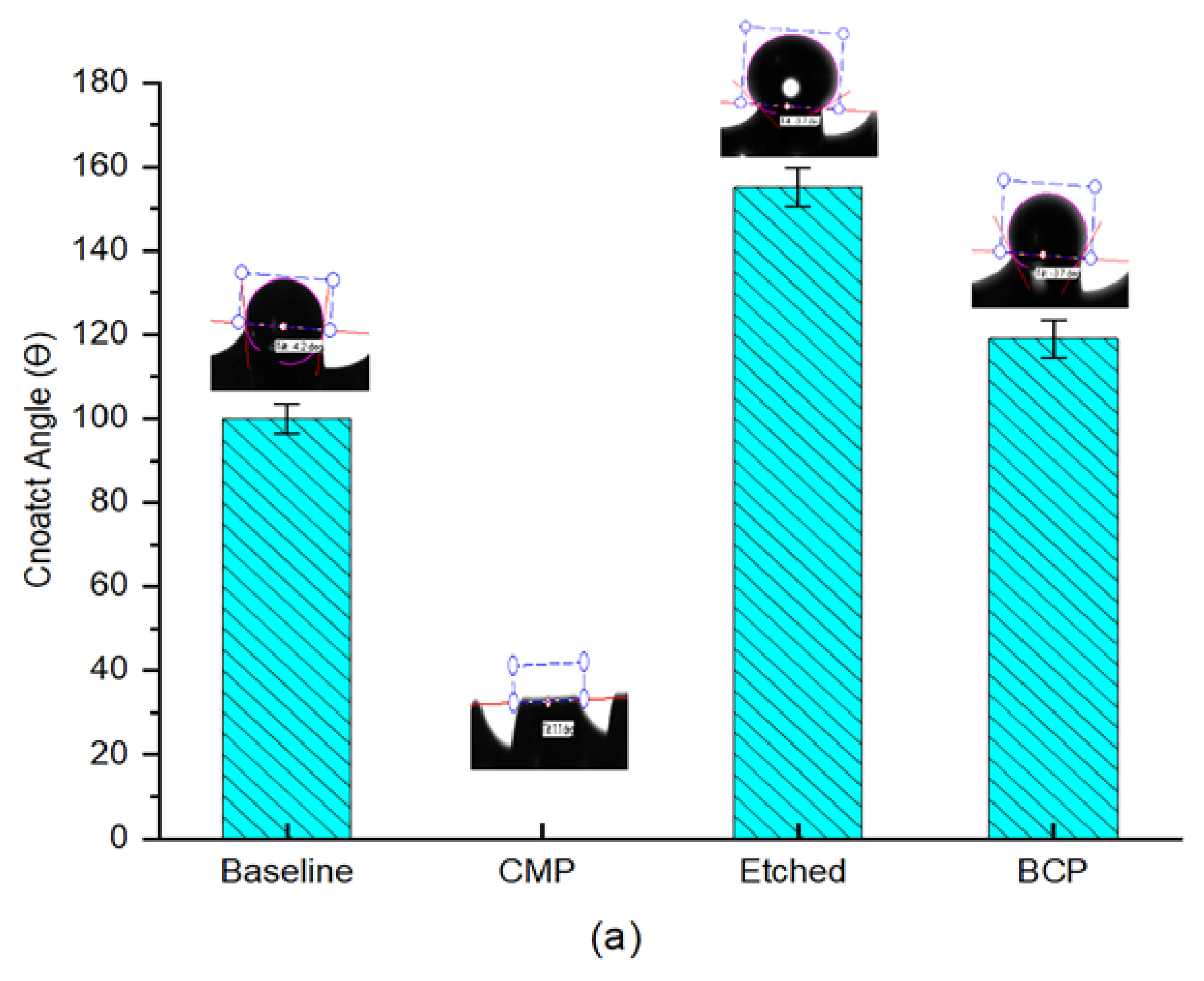
3.2. Wettability Evaluations
3.3. Effect of the Slurry Solid Loading on the Surface Roughness
- Osseointegration occurs more quickly,
- Higher percentages of bone are in direct contact with the implant, and
- The resistance to loosening is increased, since higher torques are required for extraction.
3.4. Potentiodynamic Polarization and Corrosion Rate Calculations
3.5. Microhardness Test
3.6. Effect of Surface Topography on the Pull-Out Strength
3.7. Removal Torque
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanawa, T.; Asami, K.; Asaoka, K. Repassivation of titanium and surface oxide film regenerated in simulated bioliquid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 40, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, P.; Quach-Vu, N.-C.; Gerber, I. Metallic medical implants: Electrochemical characterization of corrosion processes. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2008, 17, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Ozdemir, A.; Basim, G. Application of chemical mechanical polishing process on titanium based implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Taschieri, S.; Canciani, E.; Addis, A.; Musto, F.; Weinstein, R.; Dellavia, C. Osseointegration of titanium implants with different rough surfaces: A histologic and histomorphometric study in an adult minipig model. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubies, D.; Himmlová, L.; Riedel, T.; Chánová, E.; Balík, K.; Douderova, M.; Bártová, J.; Pesakova, V.J.P.R. The interaction of osteoblasts with bone-implant materials: 1. The effect of physicochemical surface properties of implant materials. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wirth, J.; Tahriri, M.; Khoshroo, K.; Rasoulianboroujeni, M.; Dentino, A.R.; Tayebi, L. Surface modification of dental implants. In Biomaterials for Oral and Dental Tissue Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nawas, B.; Wagner, W. 7.19 materials in dental implantology☆. In Comprehensive Biomaterials II; Ducheyne, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 341–377. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva Mello, A.S.; dos Santos, P.L.; Marquesi, A.; Queiroz, T.P.; Margonar, R.; de Souza Faloni, A.P. Some aspects of bone remodeling around dental implants. Revista Clínica de Periodoncia Implantología y Rehabilitación Oral 2018, 11, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.; Bazaka, O.; Chua, M.; Rochford, M.; Fedrick, L.; Spoor, J.; Symes, R.; Tieppo, M.; Collins, C.; Cao, A. Metallic biomaterials: Current challenges and opportunities. Materials 2017, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemat, A.; Ghazali, M.J.; Razali, M.; Otsuka, Y. Surface modifications and their effects on titanium dental implants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 791725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-A.; Park, K.-T. The removal torque of titanium screw inserted in rabbit tibia treated by dual acid etching. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3611–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Yi, Y.-J.; Yun, P.-Y. Prospective study of tapered resorbable blasting media surface implant stability in the maxillary posterior area. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, e19–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Lopez-Heredia, M.-A.; Enkel, B.; Weiss, P.; Amouriq, Y.; Layrolle, P. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattoni, D.; Ferrari, C.; Lebedev, L.; Pazos, L.; Svoboda, H. Effect of blasting on the fatigue life of ti-6al-7nb and stainless steel aisi 316 lvm. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canabarro, A.; Diniz, M.; Paciornik, S.; Carvalho, L.; Sampaio, E.; Beloti, M.; Rosa, A.; Fischer, R. High concentration of residual aluminum oxide on titanium surface inhibits extracellular matrix mineralization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 87, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, C.; Gil, F.J.; Fonseca, C.; Barbosa, M.; Planell, J.A. Corrosion behaviour of commercially pure titanium shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot particles for dental implant applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayganpour, A.; Rebaudi, A.; Cortella, P.; Diaspro, A.; Salerno, M. Electrochemical coating of dental implants with anodic porous titania for enhanced osteointegration. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandracci, P.; Mussano, F.; Rivolo, P.; Carossa, S.J.C. Surface treatments and functional coatings for biocompatibility improvement and bacterial adhesion reduction in dental implantology. Coatings 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabuda, C.; Sandalli, P.; Yalcin, S.; Steflik, D.E.; Parr, G.R. Histologic and histomorphometric comparison of immediately placed hydroxyapatite-coated and titanium plasma-sprayed implants: A pilot study in dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1999, 14, 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Medikal, M. Mode Medikal Offers New Generation Technological Solutions. Available online: http://modemedikal.com/en/ (accessed on 10 June 2018).
- Kim, S.; Saka, N.; Chun, J.-H.J. The role of pad topography in chemical-mechanical polishing. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2014, 27, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, M. Effect of process parameters on material removal rate in chemical mechanical polishing of si (1 0 0). Microelectron. Eng. 2005, 77, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunette, D.M.; Tengvall, P.; Textor, M.; Thomsen, P. Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kirmanidou, Y.; Sidira, M.; Drosou, M.-E.; Bennani, V.; Bakopoulou, A.; Tsouknidas, A.; Michailidis, N.; Michalakis, K. New ti-alloys and surface modifications to improve the mechanical properties and the biological response to orthopedic and dental implants: A review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2908570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMatteo, A.M. The myths and realities of immediately loaded dental implants. Inside Dent. 2008, 4, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman, M. Active Implants and Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, J.; Kundu, S.; Hazra, S. Role of metal ions of langmuir–blodgett film in hydrophobic to hydrophilic transition of hf-treated si surface. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenbil, N.; He, W.; Démery, V.; Dinsmore, A.D. Effect of interface shape on advancing and receding fluid-contact angles around spherical particles. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4999–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfro, R.; Bortoluzzi, M.C.; Fabris, V.; Elias, C.N.; de Araújo, V.C. Clinical evaluation of anodized surface implants submitted to a counter torque of 25 ncm after 60 days of osseointegration: Study in humans. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2015, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyan, B.D.; Dean, D.D.; Lohmann, C.H.; Cochran, D.L.; Sylvia, V.L.; Schwartz, Z. The titanium-bone cell interface in vitro: The role of the surface in promoting osteointegration. In Titanium in Medicine; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 561–585. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, L.; Jadwat, Y.; Khammissa, R.A.; Meyerov, R.; Schechter, I.; Lemmer, J. Cellular responses evoked by different surface characteristics of intraosseous titanium implants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 171945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, W.; Klein, D.; Karl, M. Micromotion of dental implants: Basic mechanical considerations. J. Med. Eng. 2013, 2013, 265412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, V.; Balaji, S.S. Surface topography of dental implants. Nitte Univ. J. Health Sci. 2014, 4, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Predcki, P.; Auslaender, B.; Stephan, J.; Mooney, V.L.; Stanitski, C. Attachment of bone to threaded implants by ingrowth and mechanical interlocking. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, 6, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svanborg, L.M.; Andersson, M.; Wennerberg, A. Surface characterization of commercial oral implants on the nanometer level. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2010, 92, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barfeie, A.; Wilson, J.; Rees, J. Implant surface characteristics and their effect on osseointegration. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 218, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, A. The Effect of Surface Roughness on the Fretting Corrosion of 316l Stainless Steel Biomaterial Surfaces. Master’s Thesis, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gamry Instruments. Getting Started with Electrochemical Corrosion Measurement; Gamry Instruments: Warminster, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.A. Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 168–198. [Google Scholar]
- Toloei, A.; Stoilov, V.; Northwood, D. The relationship between surface roughness and corrosion. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–21 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrini, M.; Cigada, A.; Rondell, G.; Vicentini, B. Effect of different surface finishing and of hydroxyapatite coatings on passive and corrosion current of ti6al4v alloy in simulated physiological solution. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Pettersson, J.; Molin Thorén, M.; Johansson, A. Release of titanium after insertion of dental implants with different surface characteristics—An ex vivo animal study. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Dcand. 2017, 3, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callister, W., Jr. Materials Science and Engineering, An Introduction; John Willey and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vuuren, D.J.; Laubscher, R. Surface friction behaviour of anodized commercially pure titanium screw assemblies. Procedia CIRP 2016, 45, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boquete-Castro, A.; Gómez-Moreno, G.; Aguilar-Salvatierra, A.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Romanos, G.E.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L. Retracted: Influence of the implant design on osseointegration and crestal bone resorption of immediate implants: A histomorphometric study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.-W.; Yang, J.-H.; Han, J.-S.; Lee, J.-B.; Kim, S.-H. Biomechanical evaluation of dental implants with different surfaces: Removal torque and resonance frequency analysis in rabbits. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2009, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Tafel Plot Variables | Baseline | CMP | Etched | BCP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Implant Tafel Data | ||||
| (μA) | 4.52 | 4.21 | 13.00 | 8.93 |
| (mV) | −266.0 | −284.0 | −381.0 | −212.0 |
| Corrosion Rate (mpy) | 2.068 | 1.930 | 5.933 | 4.089 |
| Corrosion Rate (mm/year) | 0.053 | 0.049 | 0.151 | 0.104 |
| V/decade | 5.435 | 6.594 | 7.006 | 5.974 |
| V/decade | 5.200 | 4.908 | 5.465 | 5.888 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaeedi, R.; Ozdemir, Z. Evaluation of Chemical Mechanical Polishing-Based Surface Modification on 3D Dental Implants Compared to Alternative Methods. Materials 2018, 11, 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112286
Alsaeedi R, Ozdemir Z. Evaluation of Chemical Mechanical Polishing-Based Surface Modification on 3D Dental Implants Compared to Alternative Methods. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112286
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaeedi, Riaid, and Z. Ozdemir. 2018. "Evaluation of Chemical Mechanical Polishing-Based Surface Modification on 3D Dental Implants Compared to Alternative Methods" Materials 11, no. 11: 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112286
APA StyleAlsaeedi, R., & Ozdemir, Z. (2018). Evaluation of Chemical Mechanical Polishing-Based Surface Modification on 3D Dental Implants Compared to Alternative Methods. Materials, 11(11), 2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112286




