Study of Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Multiphase Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials Preparation and Experimental Procedure
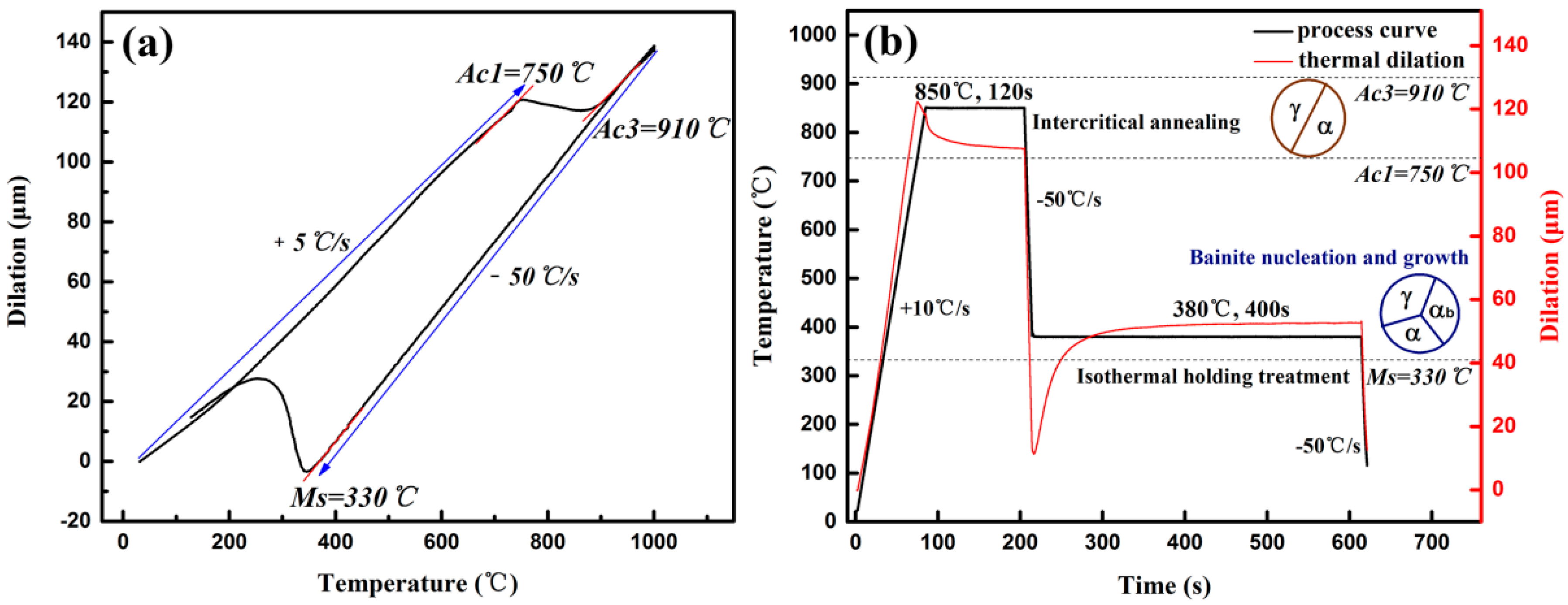
2.1. Materials Production and Heat Treatment
2.2. Tensile Tests and Microscopy Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microscopy and Mechanical Properties after Heat Treatment
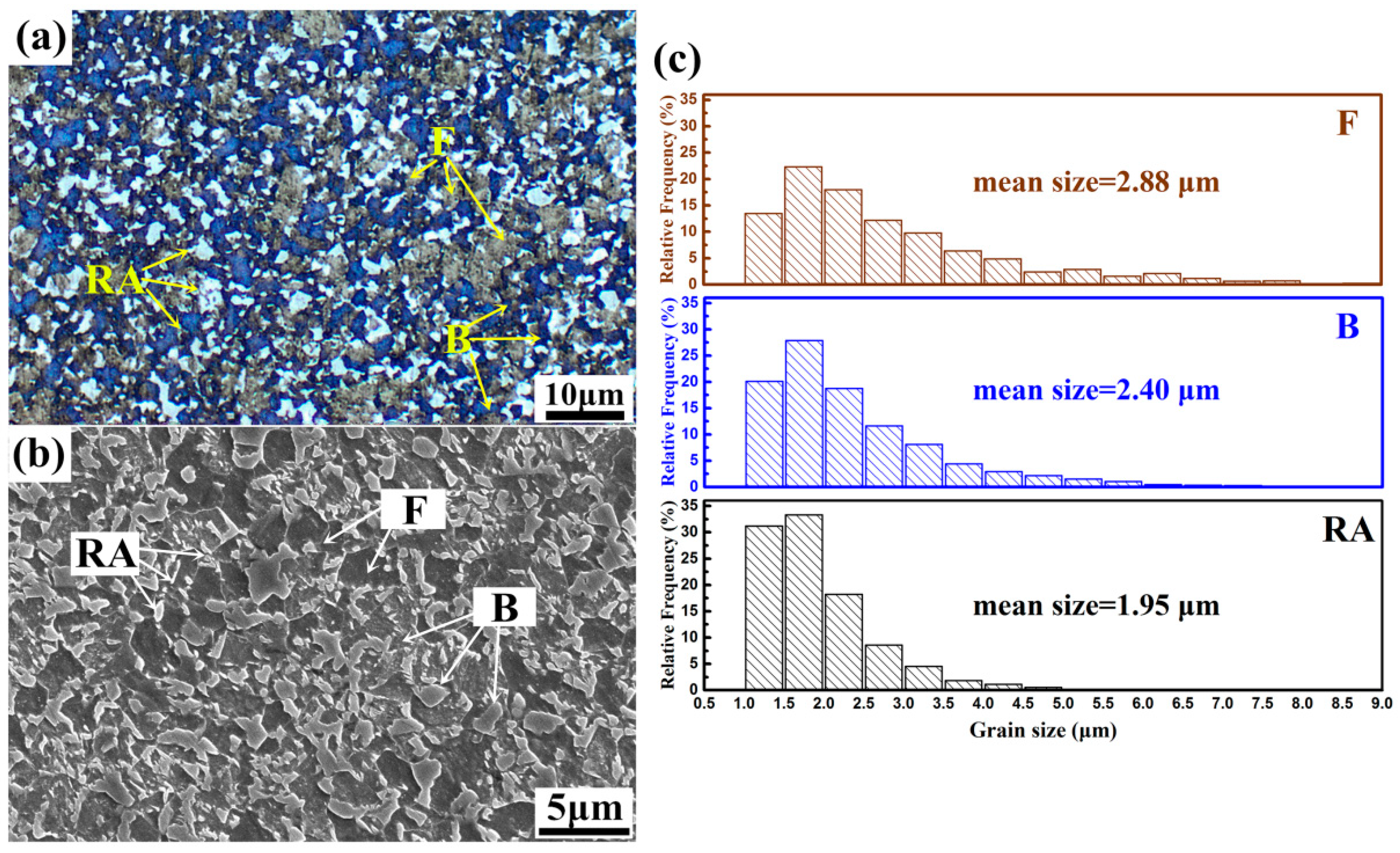
3.1.1. Microstructure Components and Tensile Properties
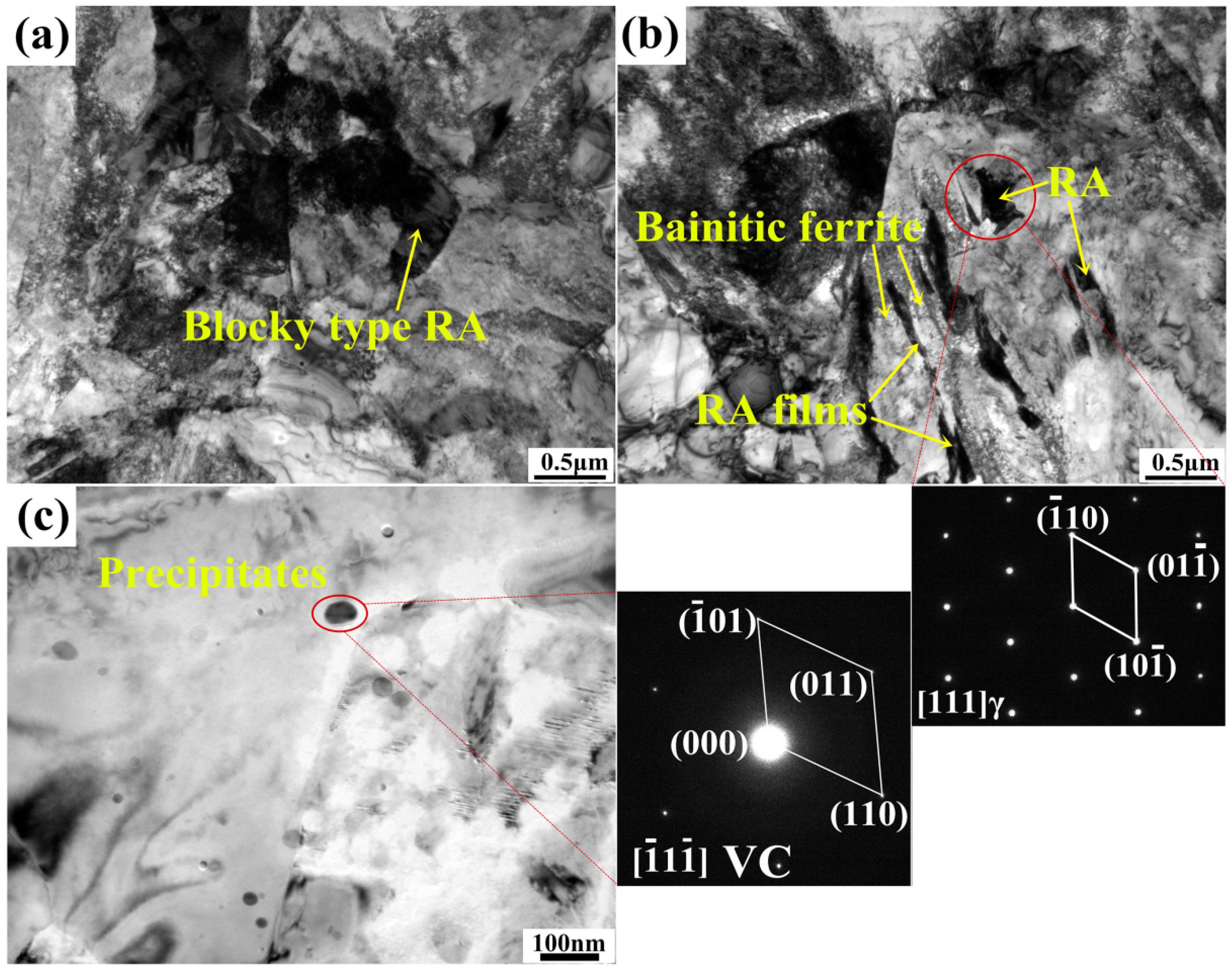
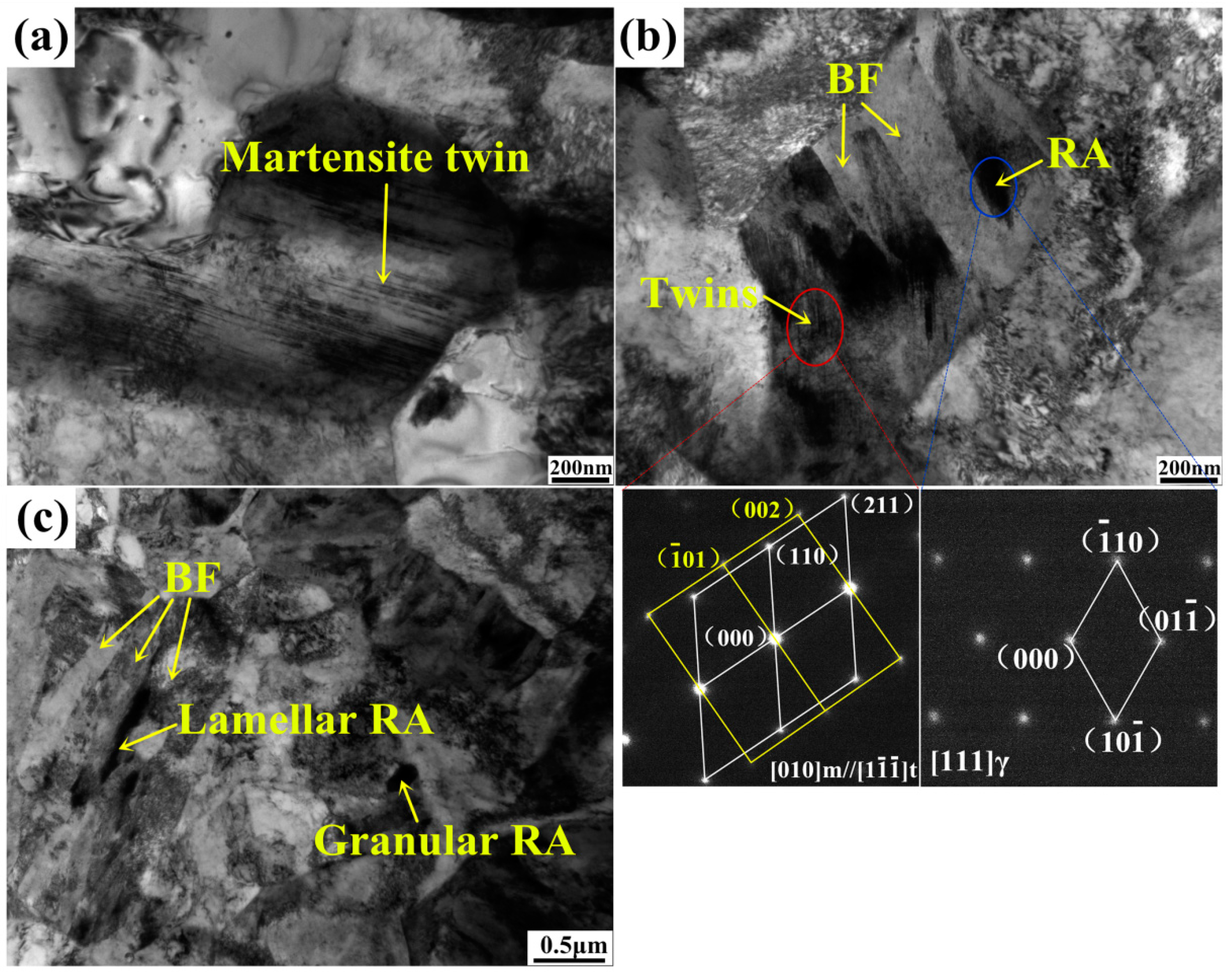
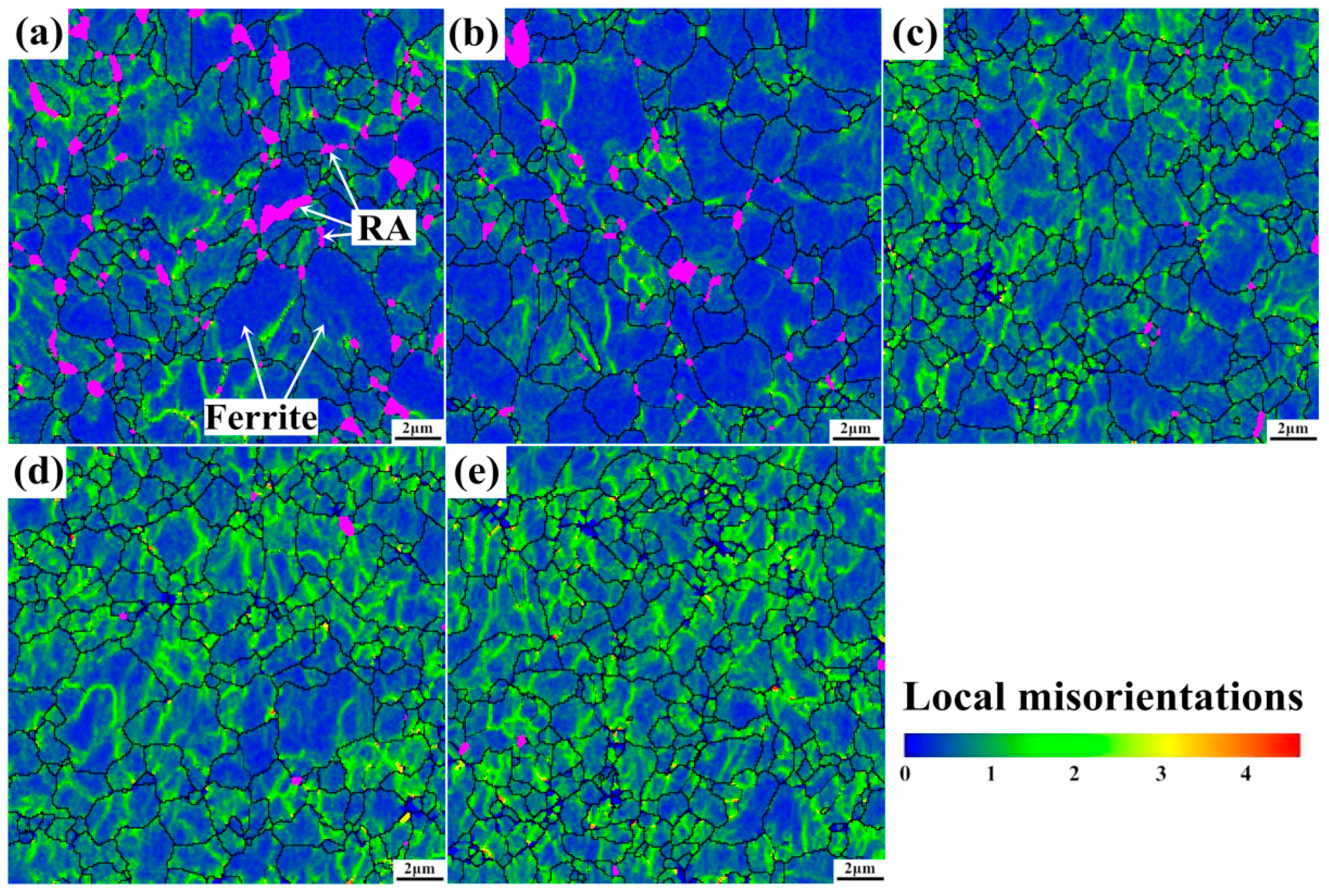
3.1.2. RA Morphology and Distribution
3.2. RA Transformation during Deformation
3.2.1. RA Transformation during Deformation
3.2.2. Relationship between RA Volume Fraction and Strain Hardening Rate
3.3. Substructure Formation and Ferrite Grain Subdivision under Strain
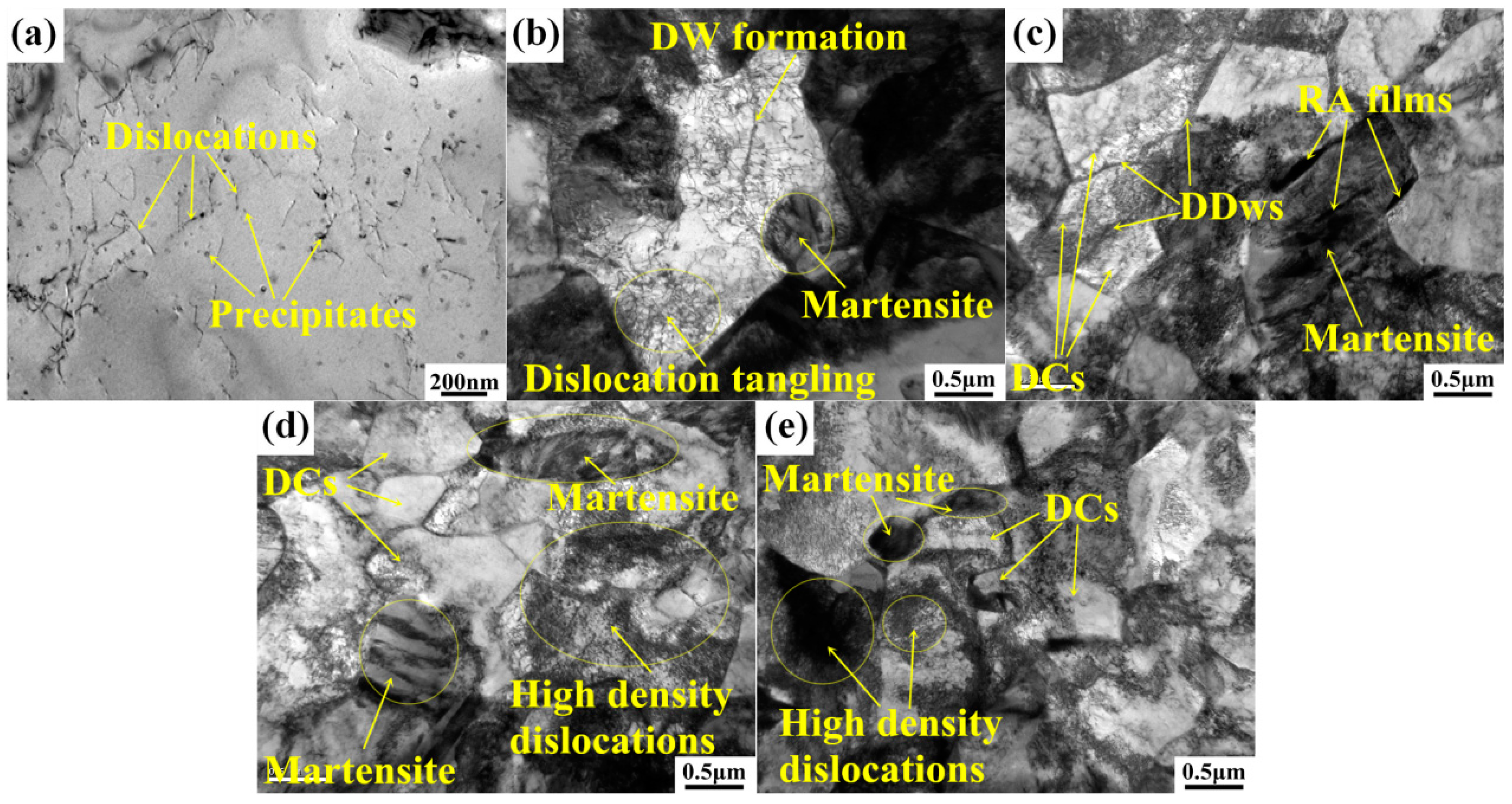
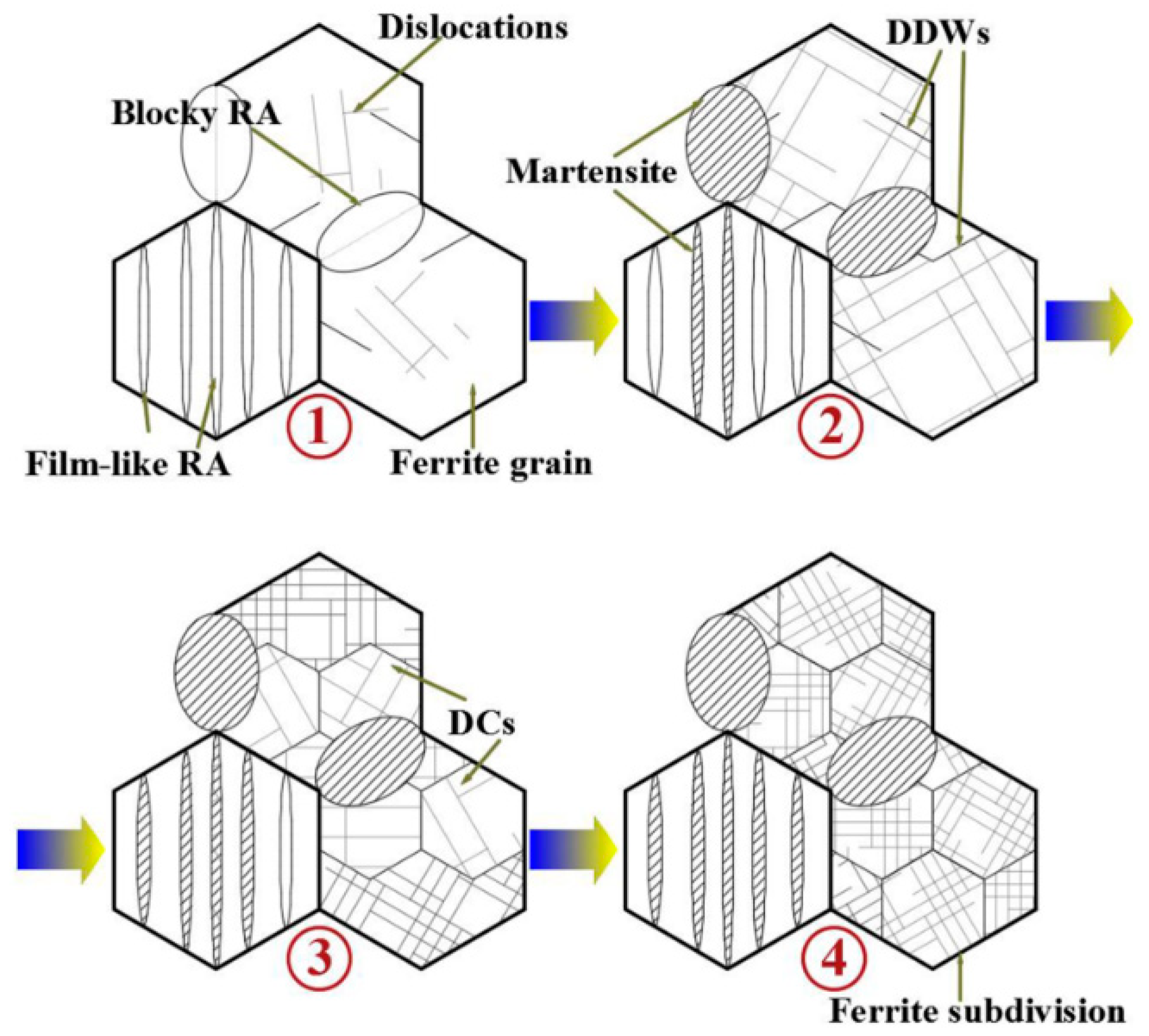
3.3.1. TEM Observation of Dislocation Evolution and Ferrite Subdivision
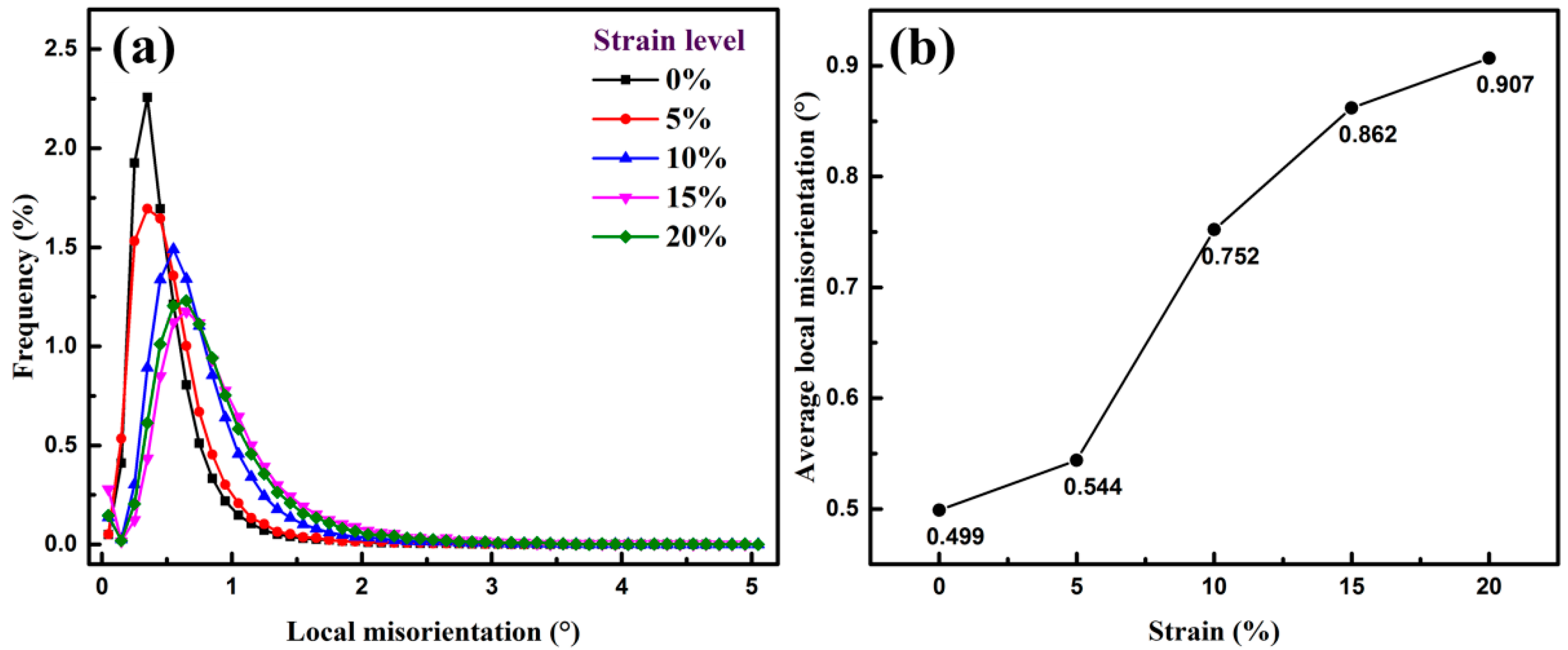
3.3.2. EBSD Investigation of Local Misorientations in Ferrite
3.4. Microstructural Development during Deformation in the Multiphase Steel
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The multiphase steel exhibits a mixture of soft ferrite matrix, a strong bainitic phase, a suitable proportion of 14.4 vol% RA and numerous vanadium precipitates. The steel exhibits fine-grains (<5 μm) with high UTS 1106 ± 10 MPa and TEL 27.7 ± 0.8%, and the PSE 30.6 GPa·%.
- (2)
- RA transformation is mainly controlled by its morphology and distribution. RA in this steel is mostly blocky-type that distributes on ferrite grain boundaries and will easily transform at the beginning of straining because of its low stability. Film-like RA that distributes between BF plates exhibits gradual transformation tendency owing to its higher carbon content, smaller grain size and surrounding BF structures, which lead to higher mechanical stability of the film-like RA.
- (3)
- The change of retained austenite volume fraction can be described as Vγ = Ae−Rε in exponential relationship, which indicates the fast transformation rate at the early deformation stage and rather gentle variation tendency at higher strain level. The fast transformation of blocky-type RA contributes to relatively high strain hardening rate during early deformation and the gradual transformation of film-like RA contributes to continuous strain hardening throughout uniform plastic deformation.
- (4)
- Continuous dislocation configuration in ferrite begins with randomly distributed dislocations and ends up with DCs through the whole plastic deformation, leading to grain subdivision and refinement strengthening of ferrite phase. Ferrite subdivision caused by dislocation substructure evolution associated with precipitating strengthening plays vital roles for further improving strength of the steel, which is effective to suppress onset of necking to achieve lager uniform elongation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christodoulou, P.I.; Kermanidis, A.T.; Krizan, D. Fatigue behavior and retained austenite transformation of Al-containing TRIP steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 91, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.P.; Kostryzhev, A.G.; Chen, L.; Pereloma, E.V. Microstructure and mechanical properties of strip cast TRIP steel subjected to thermo-mechanical simulation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 677, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.H.; Ding, H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Ying, Z.Y. Austenite stability and deformation behavior in a cold-rolled transformation-induced plasticity steel with medium manganese content. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, H.R.; Tarazkouhi, M.F. Significant enhancement of tensile properties through combination of severe plastic deformation and reverse transformation in an ultrafine/nano grain lath martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 686, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, H.R. Characteristics of nano/ultrafine-grained austenitic TRIP steel fabricated by accumulative roll bonding and subsequent annealing. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, K.I.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Cho, K.M.; Oh, K.H. Control of retained austenite morphology through double bainitic transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 673, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.; Matlock, D.K.; De Cooman, B.C.; Schroth, J.G. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, R.; Karaman, I.; Arróyave, R. Development of a kinetic model for bainitic isothermal transformation in transformation-induced plasticity steels. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2884–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Beladi, H.; Singh, S.B.; Hodgson, P.D. Thermo-mechanical processing of TRIP-aided steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3232–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondé, R.; Jimenez-Melero, E.; Zhao, L.; Schell, N.; Brück, E.; Van Der Zwaagf, S.; Van Dijk, N.H. The mechanical stability of retained austenite in low-alloyed TRIP steel under shear loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 594, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Qiu, L.N.; Sun, X.; Zuo, L.; Liaw, P.K.; Raabe, D. Effects of retained austenite volume fraction, morphology, and carbon content on strength and ductility of nanostructured TRIP-assisted steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abedi, H.R.; Hanzaki, A.Z.; Ou, K.L.; Yu, C.H. Substructure hardening in duplex low density steel. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yoo, J.; Sohn, S.S.; Koo, M.; Lee, S. Achievement of high yield strength and strain hardening rate by forming fine ferrite and dislocation substructures in duplex lightweight steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 704, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Song, R.B.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Work hardening behavior involving the substructural evolution of an austenite–ferrite Fe-Mn-Al-C steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 640, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Liu, W.N.; Sun, X.; Khaleel, M.A. Microstructure-based constitutive modeling of TRIP steel: Prediction of ductility and failure modes under different loading conditions. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2592–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, P.J.; Moor, E.D.; Merwin, M.J.; Clausen, B.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Austenite stability effects on tensile behavior of manganese-enriched-austenite transformation-induced plasticity steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, B.L.; Jimenez-Melero, E.; Mostert, R.; Santillana, B.; Lee, P.D. The role of aluminium in chemical and phase segregation in a TRIP-assisted dual phase steel. Acta Mater. 2016, 115, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, E.; Rainforth, W.M. Microstructural evolution during bainite transformation in a vanadium microalloyed TRIP-assisted steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, C.G.; Choi, I.; Lee, S. Effects of heat treatment and alloying elements on the microstructures and mechanical properties of 0.15 wt.pct C transformation-induced plasticity-aided cold-rolled steel sheets. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, H. Microstructure development and mechanical properties of quenching and partitioning (Q & P) steel and an incorporation of hot-dipping galvanization during Q & P process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 586, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.S.; Song, H.; Suh, B.C.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, S. Novel ultra-high-strength (ferrite + austenite) duplex lightweight steels achieved by fine dislocation substructures (Taylor lattices), grain refinement, and partial recrystallization. Acta Mater. 2015, 96, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Han, J.C.; Lim, N.S.; Seol, J.B.; Park, C.G. Nano-scale observation on the transformation behavior and mechanical stability of individual retained austenite in C-Mn-Si-Al TRIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.C.; Chen, B.; Huang, M.X.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, L. The effect of morphology on the stability of retained austenite in a quenched and partitioned steel. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, B. Dislocation densities and strain hardening rate in some intermetallic compounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 349, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Dislocation configurations through austenite grain misorientations. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 70, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Cheng, C.; Gao, G.; Hui, W.; Misra, R.D.K.; Bai, B.; Weng, Y. The potential significance of microalloying with niobium in governing very high cycle fatigue behavior of bainite/martensite multiphase steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 650, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrard, F.; Scott, C. Vanadium precipitation during intercritical annealing in cold rolled TRIP steels. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Sivaprasad, S.; Tarafder, S.; Ray, K.K. Influence of asymmetric cyclic loading on substructure formation and ratcheting fatigue behaviour of AISI 304LN stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7571–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Kostka, A.; Choi, P.; Goto, S.; Ponge, D.; Kirchheim, R.; Raabe, D. Mechanisms of subgrain coarsening and its effect on the mechanical properties of carbon-supersaturated nanocrystalline hypereutectoid steel. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, S.S.; Chooi, Z.H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.W.; Srolovitz, D.J. The inverse hall-petch relation in nanocrystalline metals: A discrete dislocation dynamics analysis. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 88, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, T.; Lu, J.; Liu, X. The stability of retained austenite at different locations during straining of I & Q & P steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 670, 326–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, E.P.; Fujieda, S.; Shinoda, K.; Suzuki, S. Characterization of transformed and deformed microstructures in transformation induced plasticity steels using electron backscattering diffraction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5007–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillien, S.; Seefeldt, M.; Allain, S.; Bouaziz, O.; Van Houtte, P. EBSD study of the substructure development with cold deformation of dual phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Li, L.F.; Sun, Z.Q.; Ren, Y. Micromechanical behavior of TRIP-assisted multiphase steels studied with in situ high-energy X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muransky, O.; Sittner, P.; Zrnık, J.; Oliver, E.C. In situ neutron diffraction investigation of the collaborative deformation–transformation mechanism in TRIP-assisted steels at room and elevated temperatures. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 3367–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomota, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Adachi, Y.; Wakita, M.; Minakawa, N.; Moriai, A.; Morii, Y. Tensile behavior of TRIP-aided multi-phase steels studied by in situ neutron diffraction. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5737–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


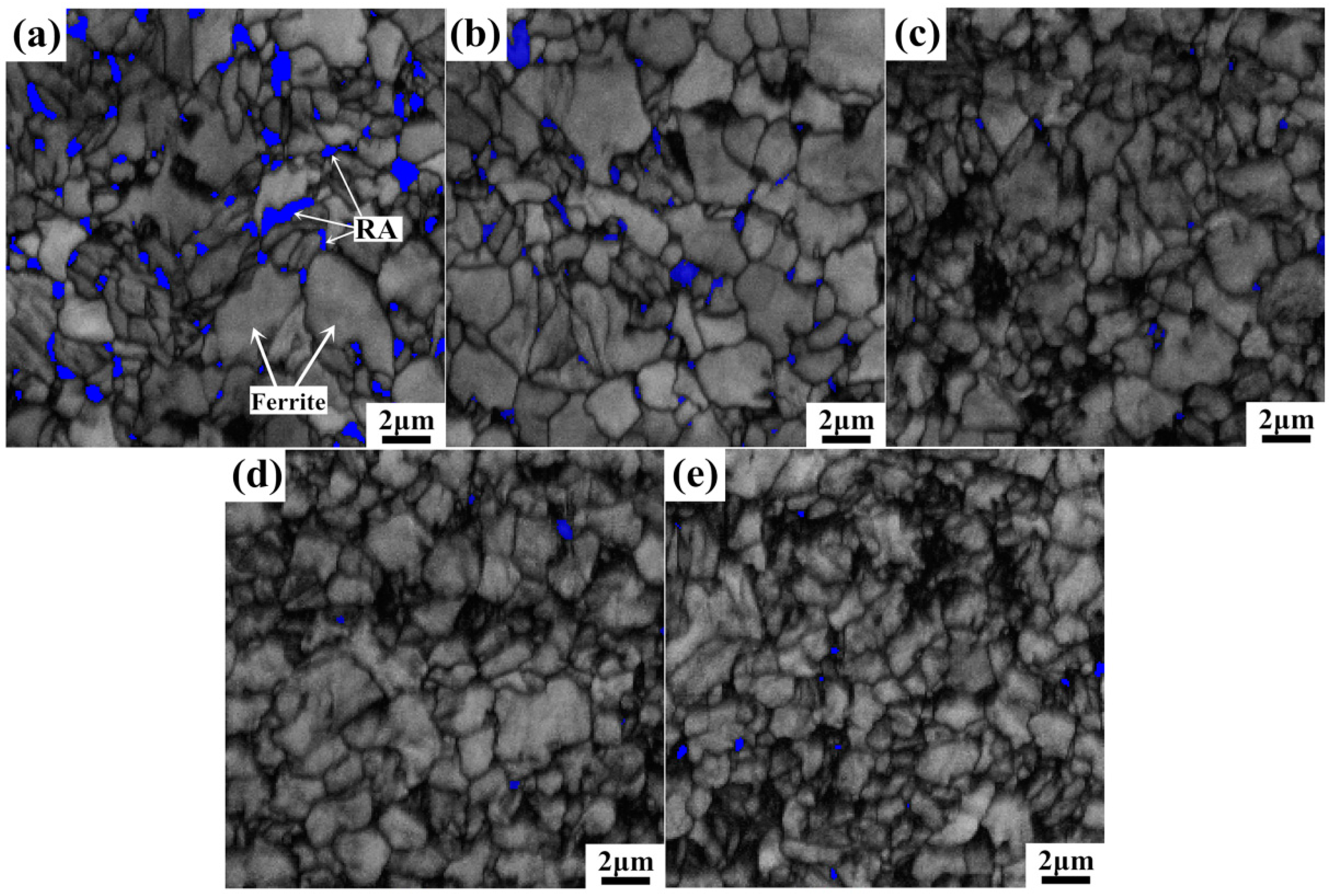
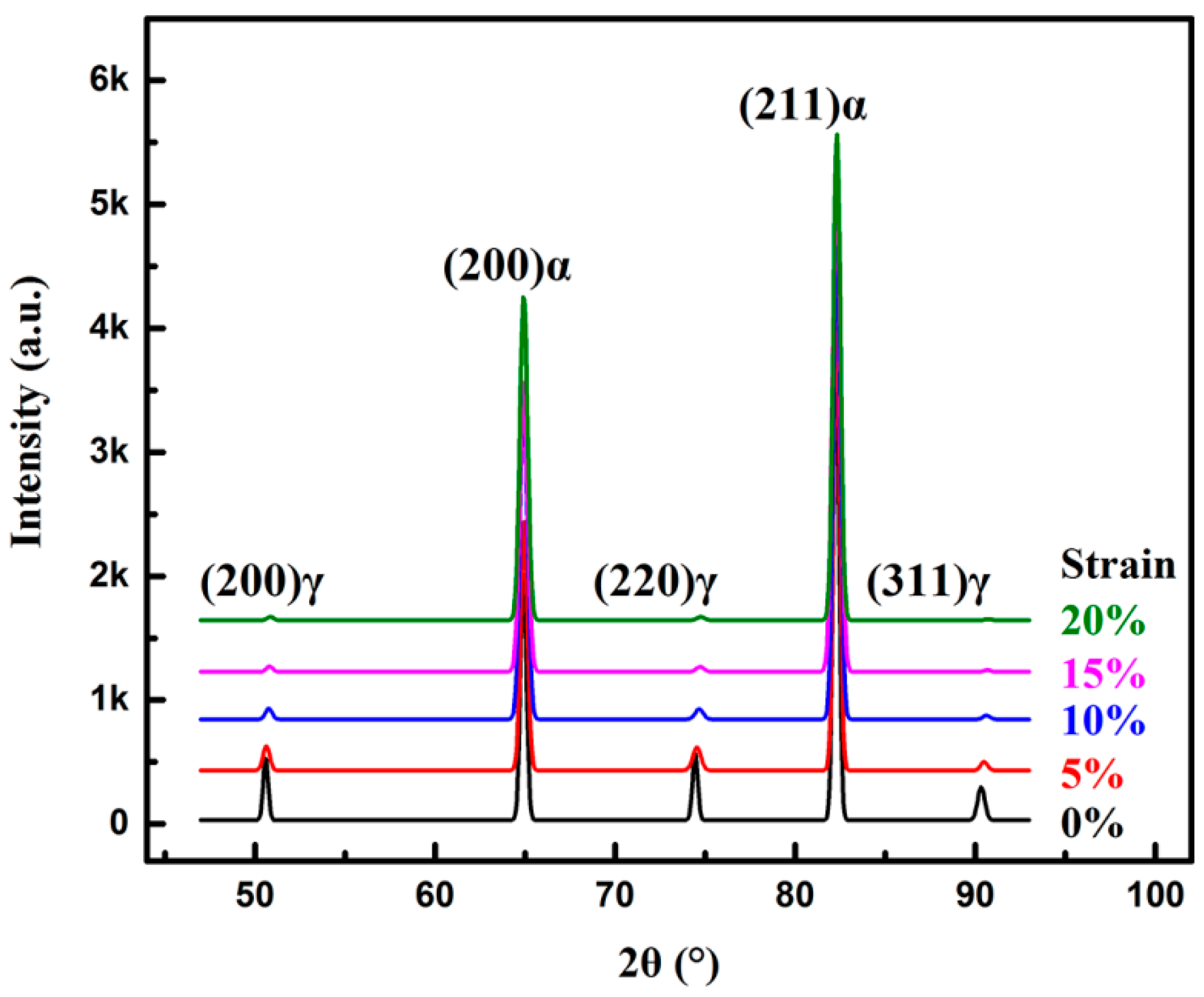
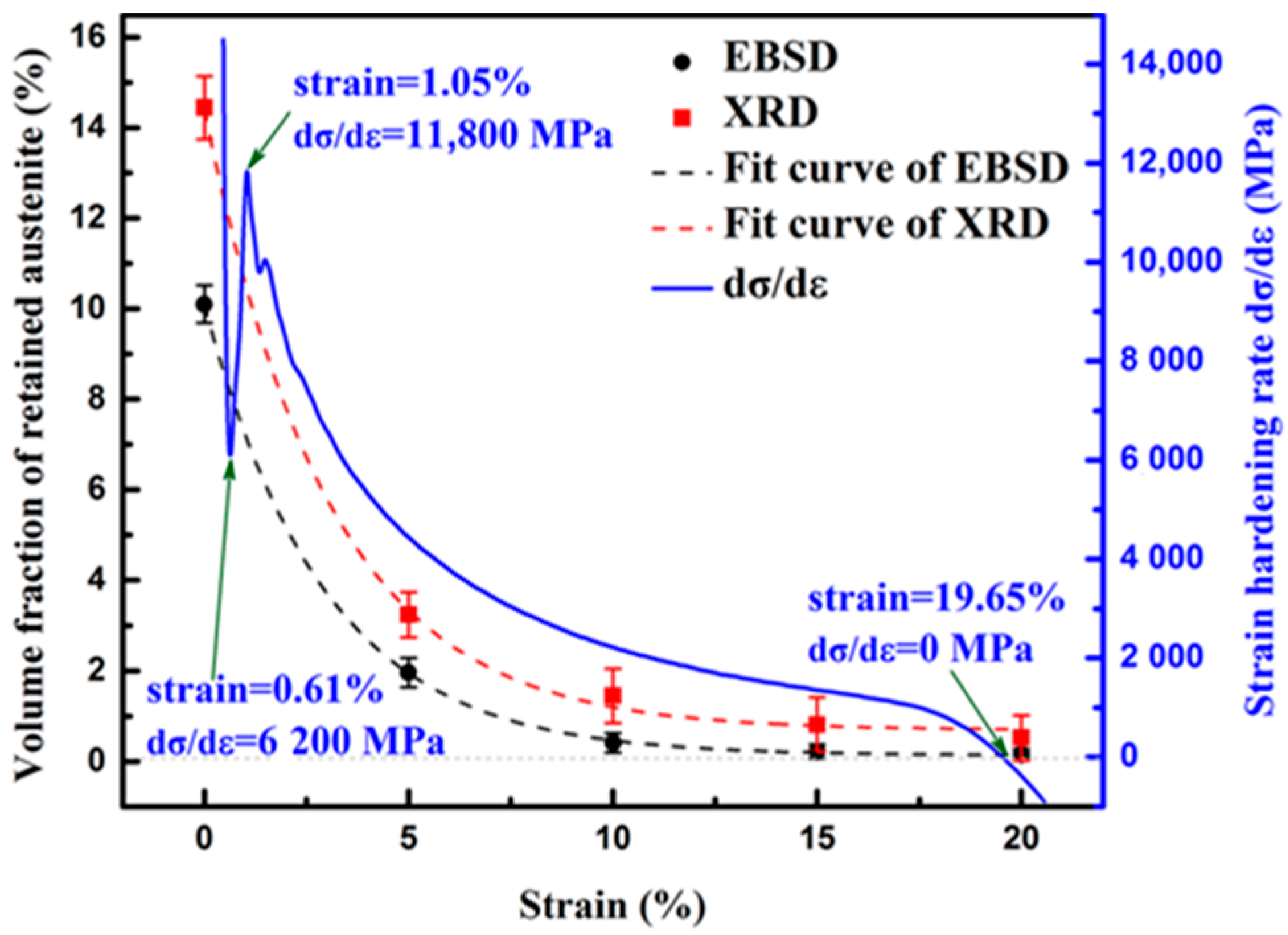

| Strain (%) | Volume Fraction of Retained Austenite (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| XRD Results | EBSD Results | |
| 0 | 14.4 ± 0.7 | 10.12 ± 0.42 |
| 5 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 1.96 ± 0.32 |
| 10 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 0.41 ± 0.21 |
| 15 | 0.8 ± 0.6 | 0.18 ± 0.15 |
| 20 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.15 ± 0.12 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Yu, H.; Duan, X.; Song, C. Study of Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Multiphase Steel. Materials 2018, 11, 2285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112285
Lu J, Yu H, Duan X, Song C. Study of Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Multiphase Steel. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112285
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jun, Hao Yu, Xiaoni Duan, and Chenghao Song. 2018. "Study of Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Multiphase Steel" Materials 11, no. 11: 2285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112285
APA StyleLu, J., Yu, H., Duan, X., & Song, C. (2018). Study of Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution in Multiphase Steel. Materials, 11(11), 2285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112285




