Fatigue Performance of the CA Mortar Used in CRTS I Ballastless Slab Track under Simulated Servicing Condition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportions and Mechanical Properties of the CA Mortar
2.3. Fatigue Testing
2.3.1. Fatigue Testing Device
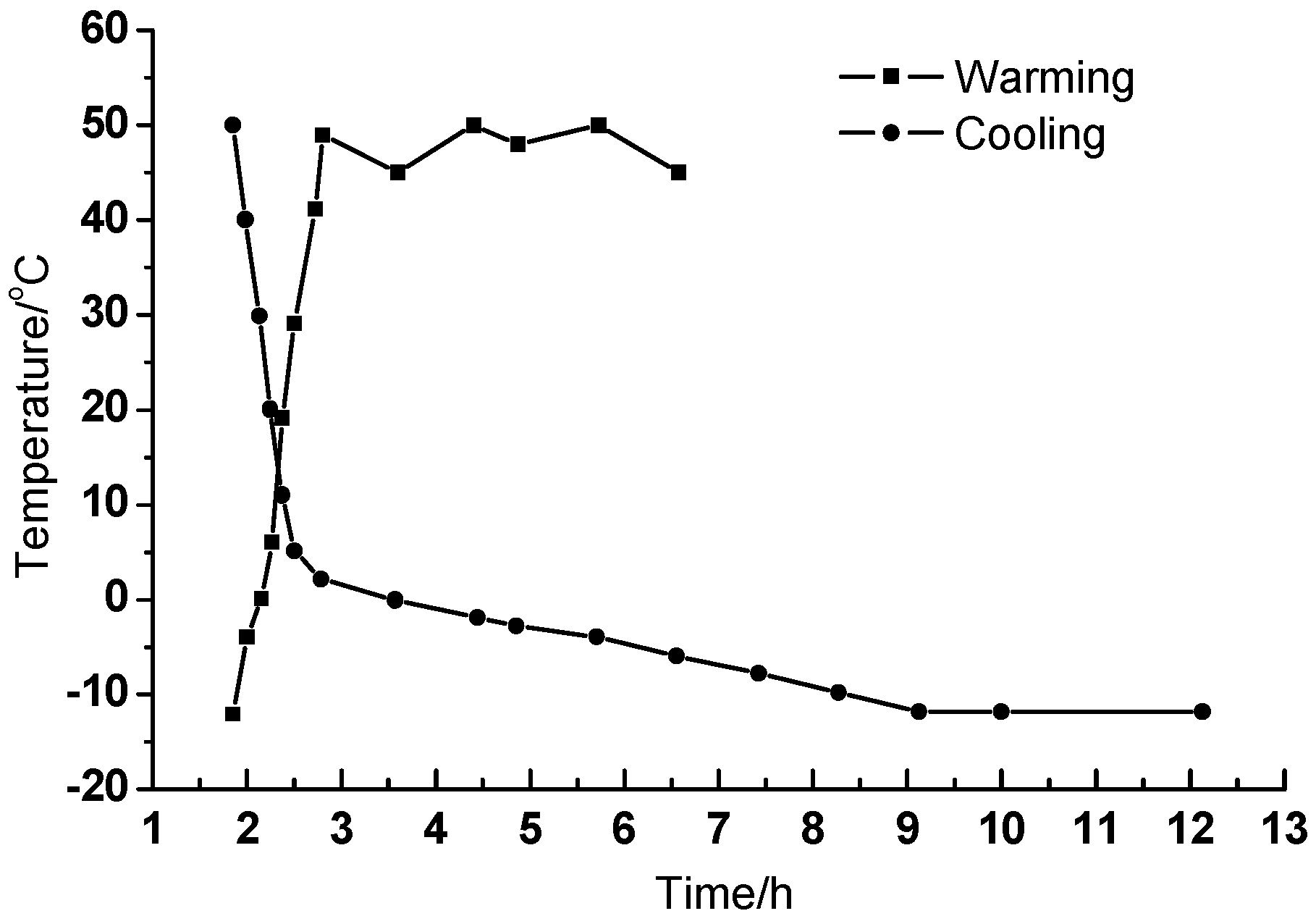
2.3.2. Temperature Range
2.3.3. Vibration Control
2.3.4. Load Control
2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Microstructure
3. Results and Discussion
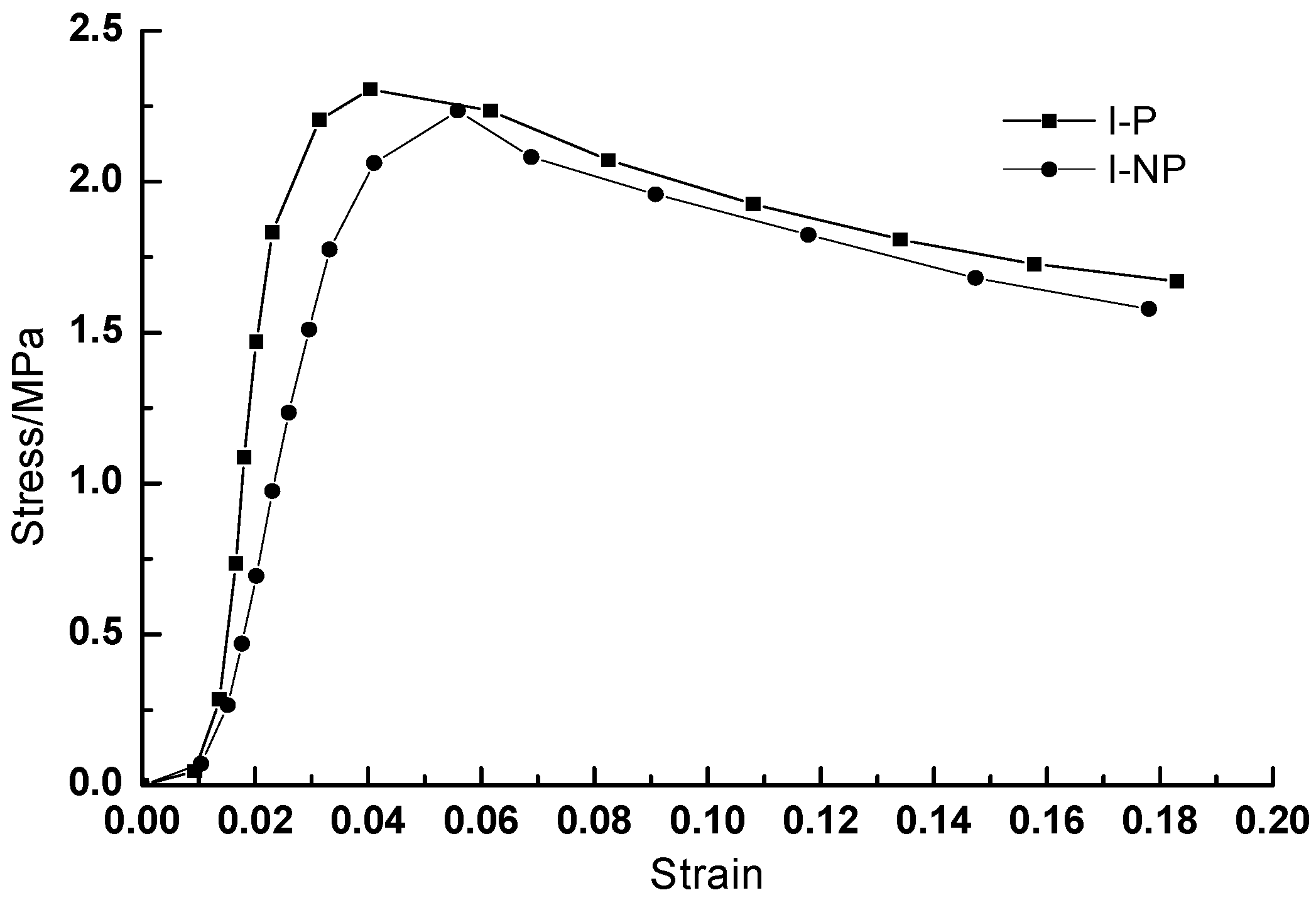
3.1. Stress-Strain Curves of the CA Mortar before and after Fatigue Test
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
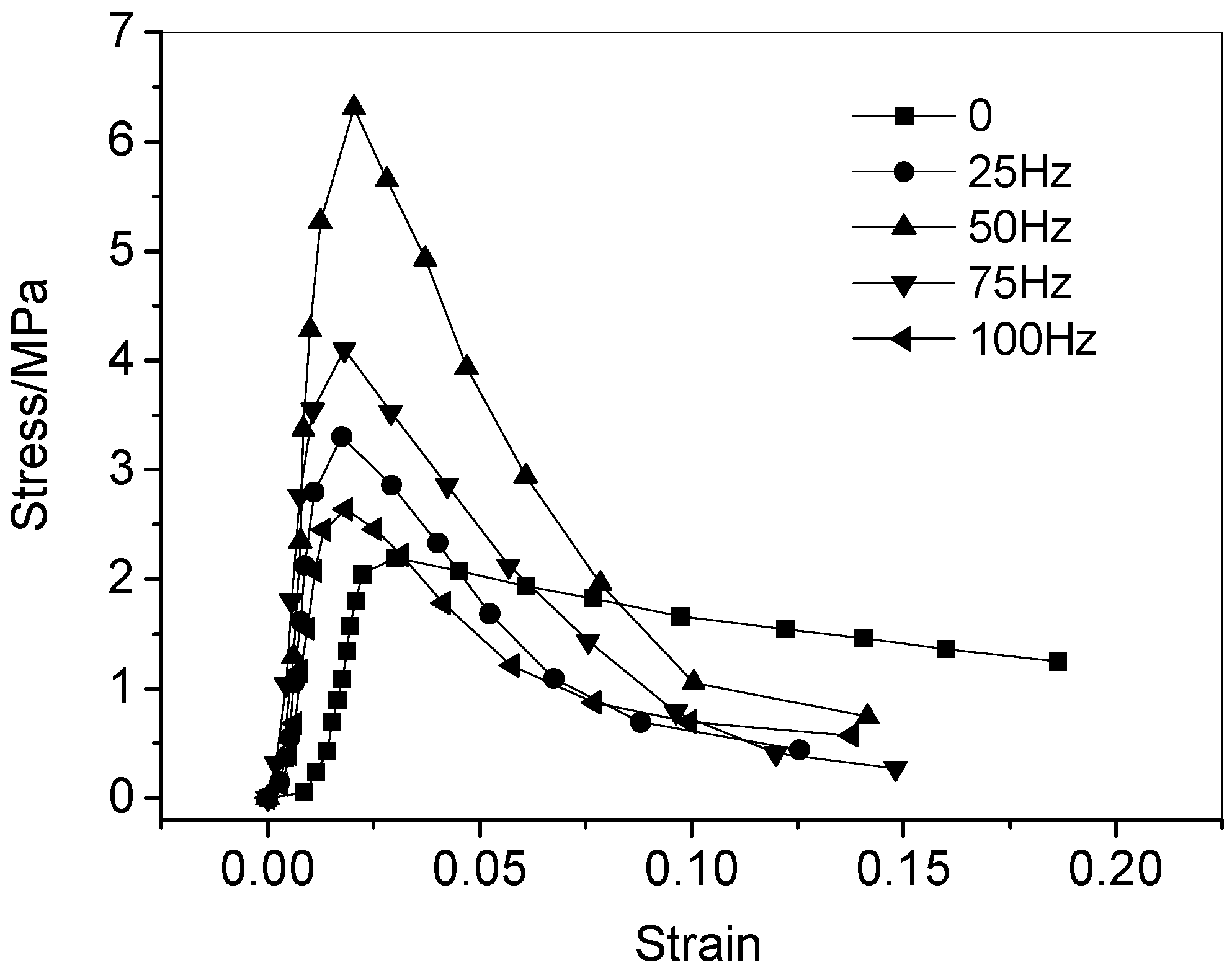
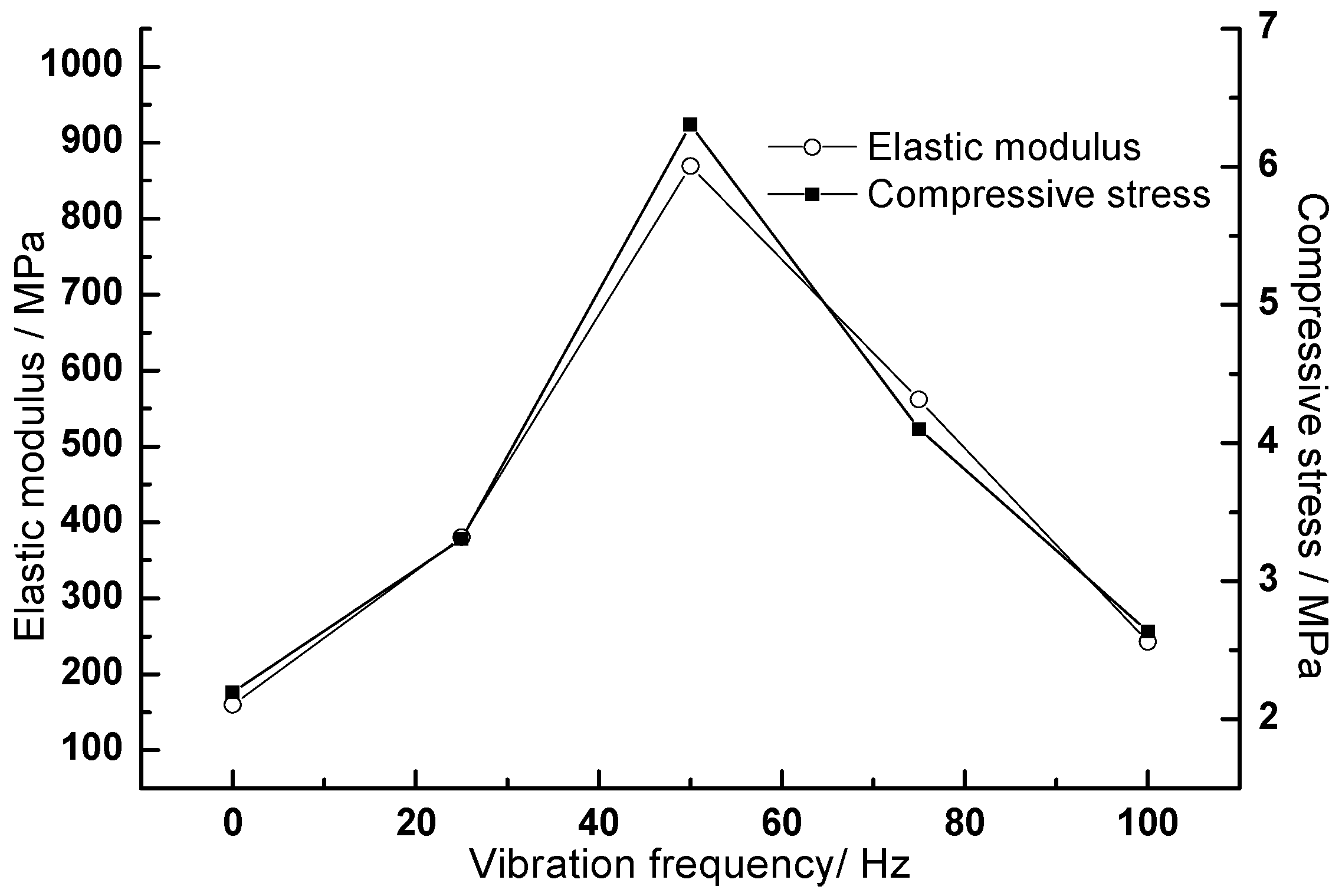
3.3. Effect of Vibration Frequency on the Properties of the CA Mortar after the Fatigue Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ando, K.; Sunaga, M.; Aoki, H.; Haga, O. Development of slab tracks for Hokuriku Shinkansen line. Q. Rep. RITI. 2001, 42, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esveld, C. Recent developments in slab track. Eur. Railw. Rev. 2003, 9, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, K.C.; Chen, H.S.; Ye, H.P.; Ji, X.; Hong, W.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Y. Thermo-mechanical coupling effect on fatigue behavior of cement asphalt mortar. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 51, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.H.; Xie, Y.J.; Deng, D.H. A study of the mixing of cement and emulsified asphalt mortar. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.Y.; Zhao, C.; Hu, H.G.; Qian, X.Q.; Yang, F.E.; Yang, L.J. Effect of silica sol addition on properties of the cement asphalt mortar for CRTS II Ballastless Slab Track. R. Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 572–575. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.Q.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Y.L. Factors influencing rheological properties of fresh cement asphalt emulsion paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.W.; Deng, D.H.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, Z.Q.; Fang, L. Study of the rheological behavior of fresh cement emulsified asphalt Paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.M.; Hou, S.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Han, S. Study on the rheological properties of fresh cement asphalt paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Tan, Y.Q.; Corr, D.J.; Shah, S.P. Viscosity prediction of fresh cement asphalt emulsion pastes. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, P.Y.; Ruhan, A.; Yang, J.B.; Kong, X.M. Strength mechanism of cement-asphalt mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.F.; Xu, R.Q.; Chen, Y.R. Effects of temperature and loading rate on the compressive behavior of CA mortar. Mag. Concr. Res. 2016, 68, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Wu, X.; Fan, X.L.; Chen, Y.R. Stress–strain model of cement asphalt mortar subjected to temperature and loading rate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xie, Y.J.; Long, G.C.; Meng, F.; Song, H. Temperature sensitivity and model of stress relaxation properties of cement and asphalt mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.-F. Compressive Behavior of Cement Asphalt Mortar Under Low Confinement. J. Test. Eval. 2018, 46, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Tan, Y.Q. Modeling mechanical properties of cement asphalt emulsion mortar with different asphalt to cement ratios and temperatures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Fu, Q.; Zheng, K.R.; Yuan, Q. Dynamic mechanical properties of cement and asphalt mortar based on SHPB test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Liu, W.T.; Pan, Y.R.; Deng, D.H.; Liu, Z.Q. Characterization of cement asphalt mortar for slab track by dynamic mechanical thermoanalysis. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 28, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.H.; Xie, Y.J.; Deng, D.H.; Wang, P.; Qu, F.L. A study of the dynamic mechanical properties of CRTS I type CA mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Fu, Q.; Long, G.C.; Zheng, K.R.; Song, H. Creep properties of cement and asphalt mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xie, Y.J.; Long, G.C.; Niu, D.T.; Song, H.; Liu, X.G. Impact characterization and modelling of cement and asphalt mortar based on SHPB experiments. Intern. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 106, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.V.; Dawson, A.R.; Heelis, M.E. Rail movement and ground waves caused by high speed trains approaching track-soil critical velocities. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2000, 214, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, L.C.; Hu, J.T. Application of EBP on Taiwan high-speed railway. Earthq. Resist. Eng. Retrofit. 2011, 33, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z. Study on the Damage of Slab Ballastless Track Structure and the Railway Maintenance System for High-Speed Railway; Southwest Jiaotong University: Chongqing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; He, D.; Zeng, Q.Y. Effect of cement asphalt mortar disease on dynamic performance of slab track. J. Cent. South Univ. 2009, 40, 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Z.; Liu, Z.C.; Hu, S.G. Influence of loading rate on compressive strength of CA mortar. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2008, 10, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Lin, Z.M.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, C. Damping technology applied to low vibration ballastless track in high speed railway. China Railw. Sci. 1998, 19, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.Y.; Mao, J.D.; Wu, Y.Z.; Yang, F.E.; Ye, S.; Yao, J.; Wei, S. Anti-Fatigue Experimental Device of CA Mortar for High Speed Railway Slab Ballastless Track. Chinese Patent ZL 201,010,600,106.7, 22 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Translational Editorial Committee of High-speed Trains Abroad. Translational Collection of High-Speed Trains Abroad; Academy of Railway Science: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.R. Thermal Stress of Slab Ballastless Track. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, January–February 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Yamada, M. Analysis of railway track vibration. J. Sound Vib. 1989, 130, 269–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Luo, H.; Sun, C.X. Simulation study on vibration load of high-speed railway. Acta Railw. J. 2006, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.T.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.L.; Tian, X.G. A viscoelastic fatigue constitutive model of asphalt mixture. J. Changsha Jiaotong Univ. 2006, 22, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.G.; Zheng, J.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Liu, G.F. Fatigue effect of asphalt mixture under low loading frequency. Chin. J. Highw. 2002, 15, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Gao, G.Y.; Feng, S.J.; Shi, G. Analysis of ground vibration caused by high-speed train operation. J. Tongji Univ. 2007, 35, 909–914. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.Y.; Luo, Q.; Wei, Y.X. Dynamic stress measurement and analysis of CA mortar layer near culvert of ballastless track of Sui-Yu Railway. J. Railw. Eng. 2008, 6, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, I.J. Damage Analysis in Asphalt Concrete Mixtures Based on Parameter Relationships. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]






| Engler’s viscosity (25 °C)/s | 7.8 | |
| Particle polarity | Positive | |
| Mixing stability with cement/% | 0.1 | |
| Residue on sieve (1.18 mm)/% | 0.00 | |
| Storage stability (1 d, 25 °C)/% | 0.1 | |
| Storage stability (5 d, 25 °C)/% | 2.3 | |
| Storage stability at −5 °C | Qualified | |
| Evaporation residue | Content of residue/% | 62.5 |
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g)/0.1 mm | 85.0 | |
| Ductility (15 °C)/cm | 118 | |
| Solubility (trichloroethylene)/% | 99.2 | |
| Expansion Ratio/% | Compressive Strength/MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 7 d | 28 d | |
| 2.52 | 11.7 | 35.9 | 60.2 |
| Serial Number | Asphalt Emulsion/mL | Dry-Mixed Mortar/g | Water/mL | Polymer Emulsion/mL | De-Foaming Agent/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-P | 442 | 1000 | 50 | 50 | 1 |
| I-NP | 442 | 1000 | 80 | 0 | 1 |
| Serial Number | Compressive Strength/MPa | Elastic Modulus/MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 7 d | 28 d | 28 d | |
| I-P | 0.26 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 160 |
| I-NP | 0.13 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 130 |
| CA Mortar | Frequency (Hz) | Stress Peak (MPa) | Strain at Peak Stress (%) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-P | Standard curing | 2.310 | 4.036 | 160.0 |
| I-NP | 2.234 | 5.586 | 130.0 | |
| I-P | 0 | 2.194 | 3.027 | 159.8 |
| 25 | 3.306 | 1.755 | 380.1 | |
| 50 | 6.306 | 2.048 | 868.9 | |
| 75 | 4.101 | 1.821 | 561.6 | |
| 100 | 2.636 | 1.838 | 242.6 | |
| I-NP | 100 | 4.083 | 1.087 | 745.7 |
| Serial Number | Total Intrusion Volume (mL/g) | Median Pore Diameter (Volume) (nm) | Median Pore Diameter (Area) (nm) | Average Pore Diameter (4 V/A) (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After fatigue test | 0.0971 | 1853.3 | 11.6 | 153.4 |
| Standard curing | 0.1641 | 2862.8 | 11.8 | 299.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W.; Mao, J.; Kong, D. Fatigue Performance of the CA Mortar Used in CRTS I Ballastless Slab Track under Simulated Servicing Condition. Materials 2018, 11, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112259
Shan Y, Zheng S, Zhang X, Luo W, Mao J, Kong D. Fatigue Performance of the CA Mortar Used in CRTS I Ballastless Slab Track under Simulated Servicing Condition. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112259
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yuchuan, Shuguang Zheng, Xuefeng Zhang, Wei Luo, Jingda Mao, and Deyu Kong. 2018. "Fatigue Performance of the CA Mortar Used in CRTS I Ballastless Slab Track under Simulated Servicing Condition" Materials 11, no. 11: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112259
APA StyleShan, Y., Zheng, S., Zhang, X., Luo, W., Mao, J., & Kong, D. (2018). Fatigue Performance of the CA Mortar Used in CRTS I Ballastless Slab Track under Simulated Servicing Condition. Materials, 11(11), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112259






