Silk as a Natural Reinforcement: Processing and Properties of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
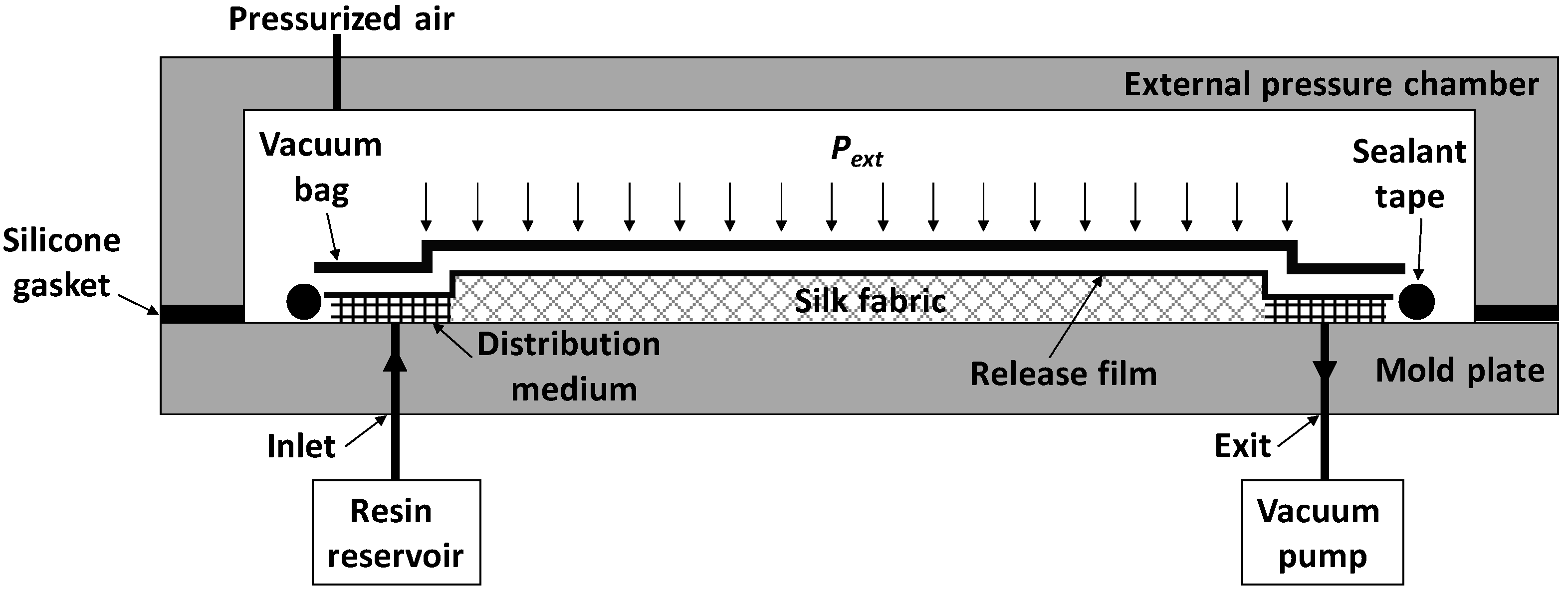
2.2. Manufacturing Procedure
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Density Measurement and Volume Fraction Determinations
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.6. Mechanical Testing
2.7. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
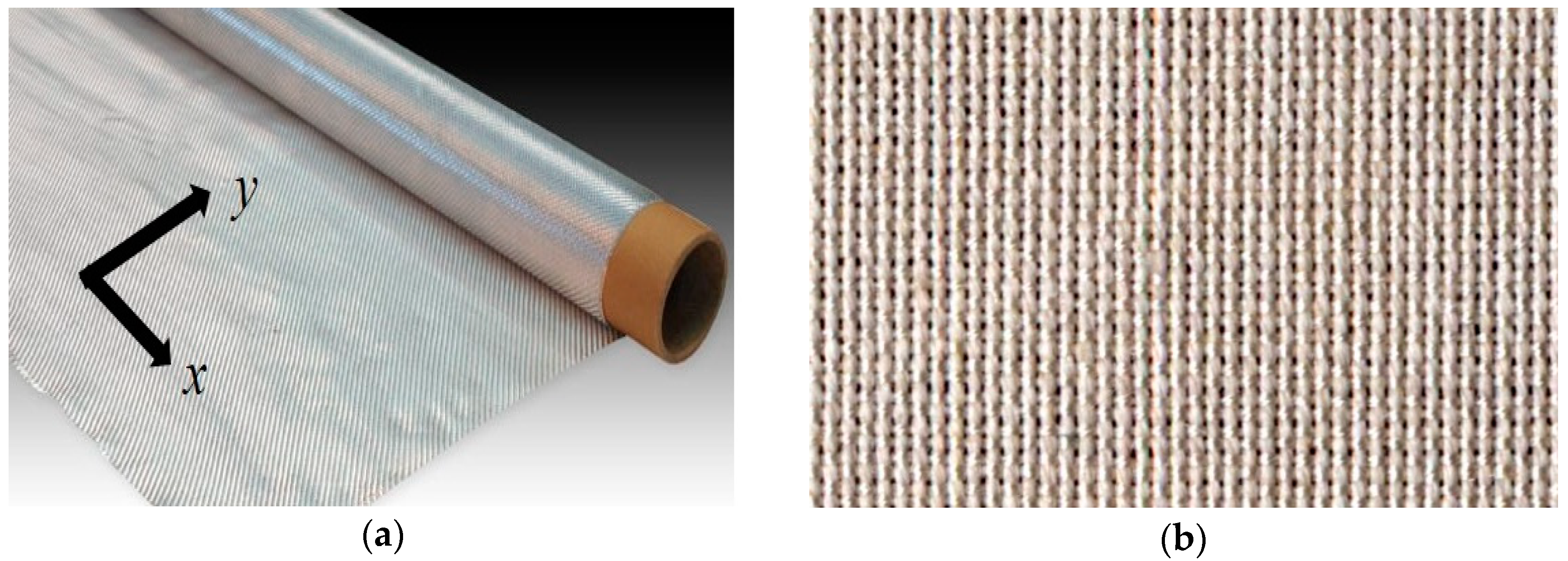
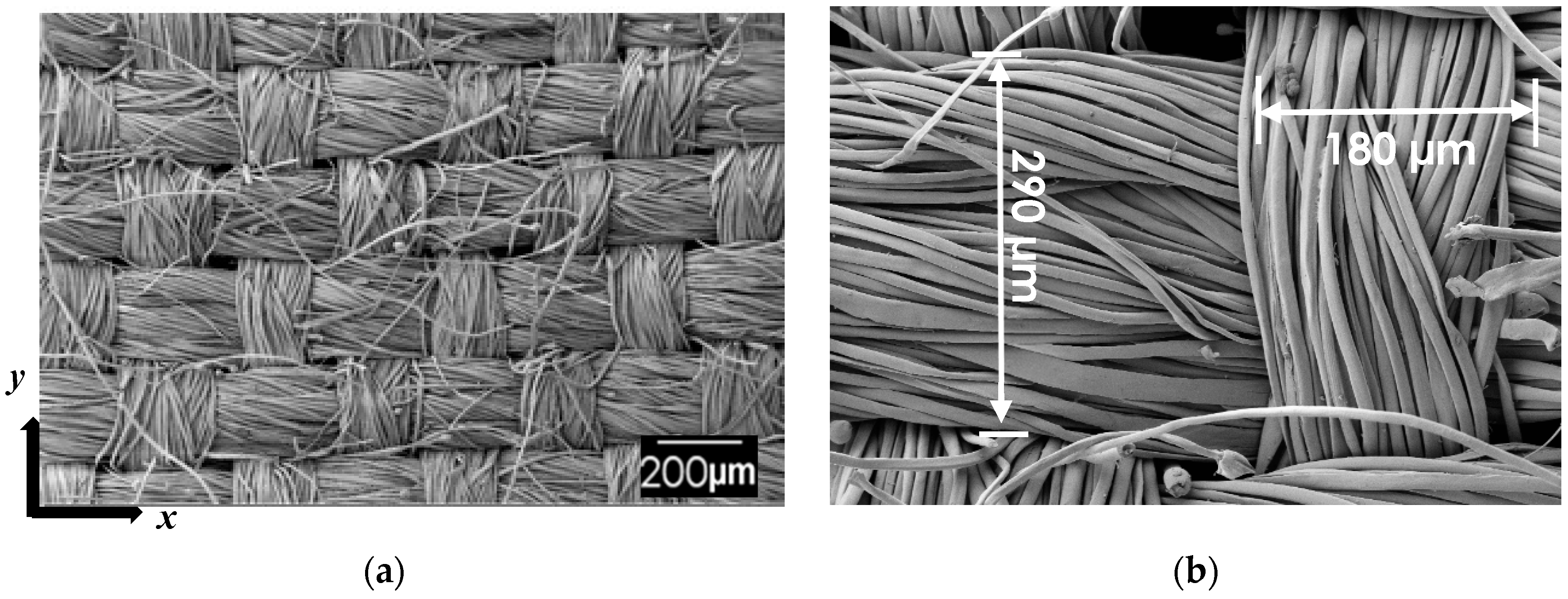
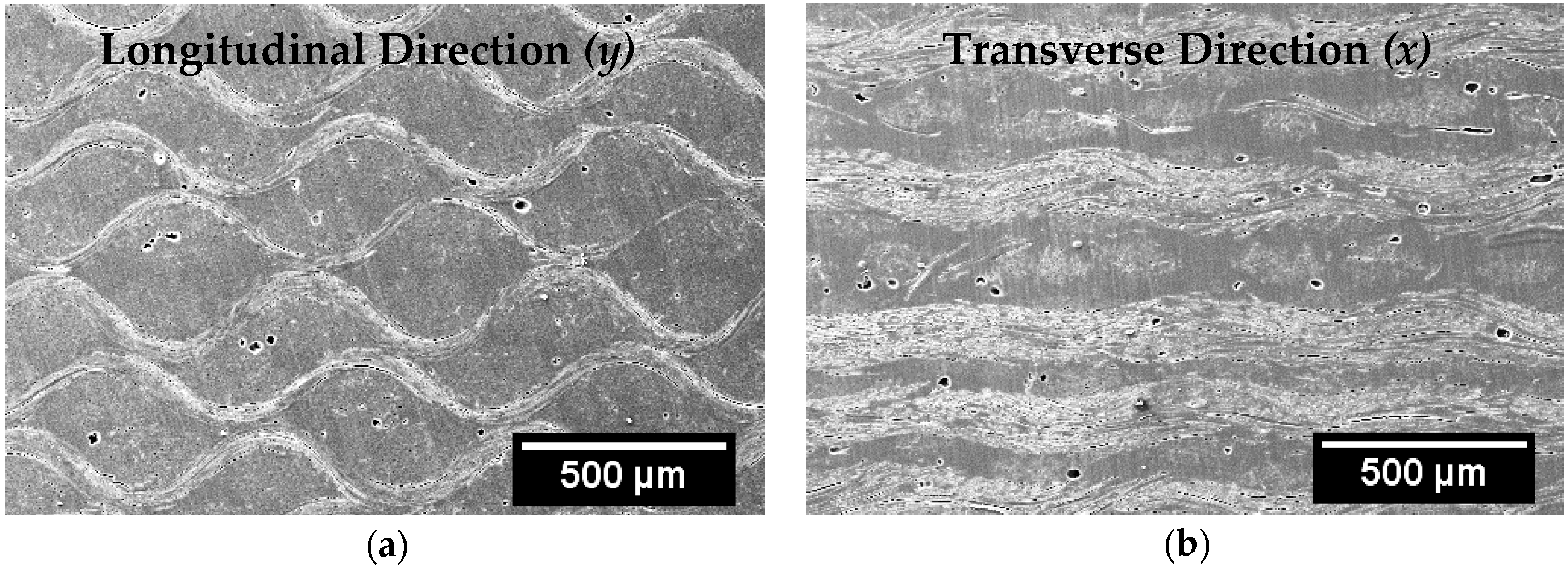
3.1. Morphology and Microstructure of Silk Fabric
3.2. Morphology and Microstructure of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates
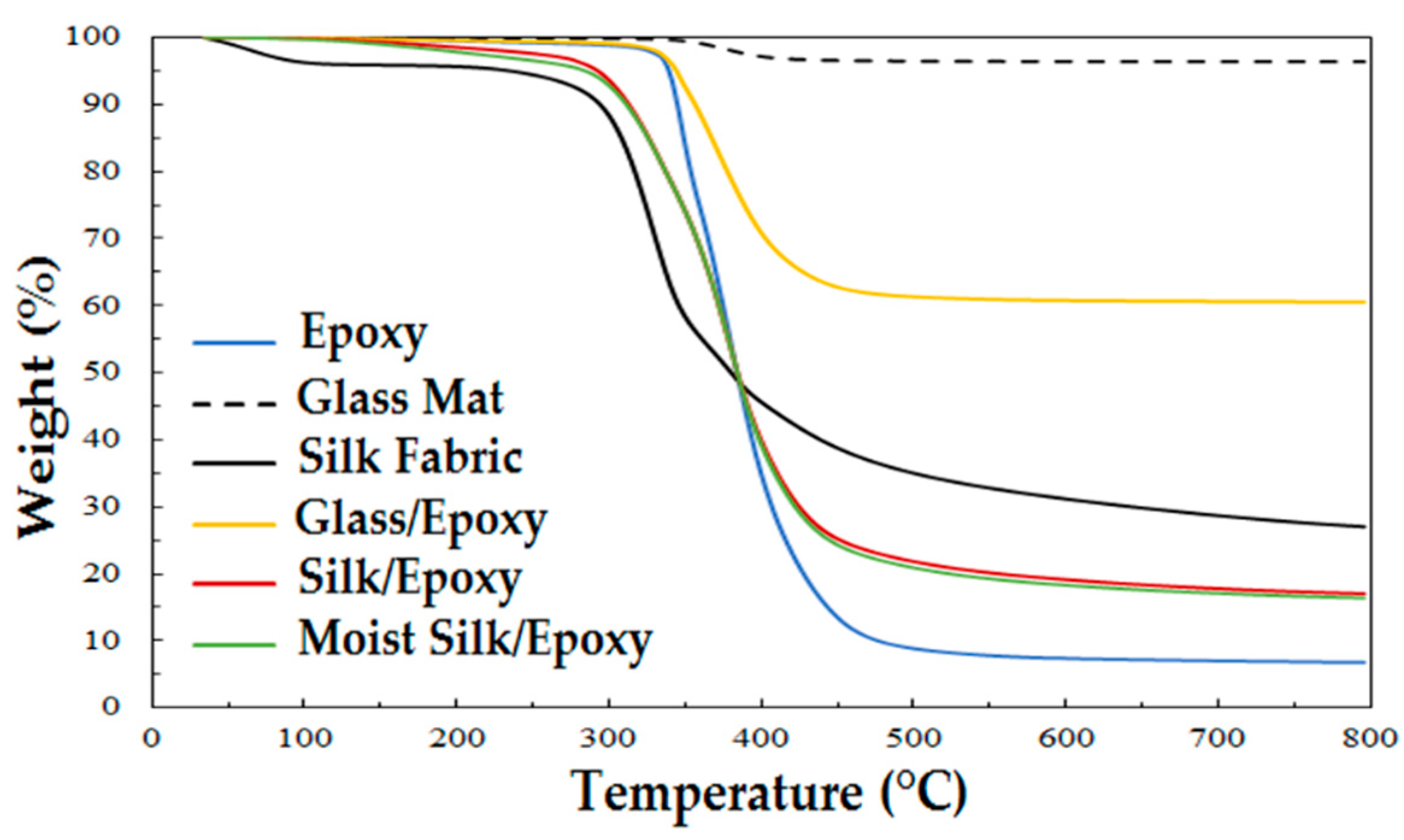
3.3. Thermal Stability of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates
3.4. Fabric Anisotropy Effects on Fiber Wetting
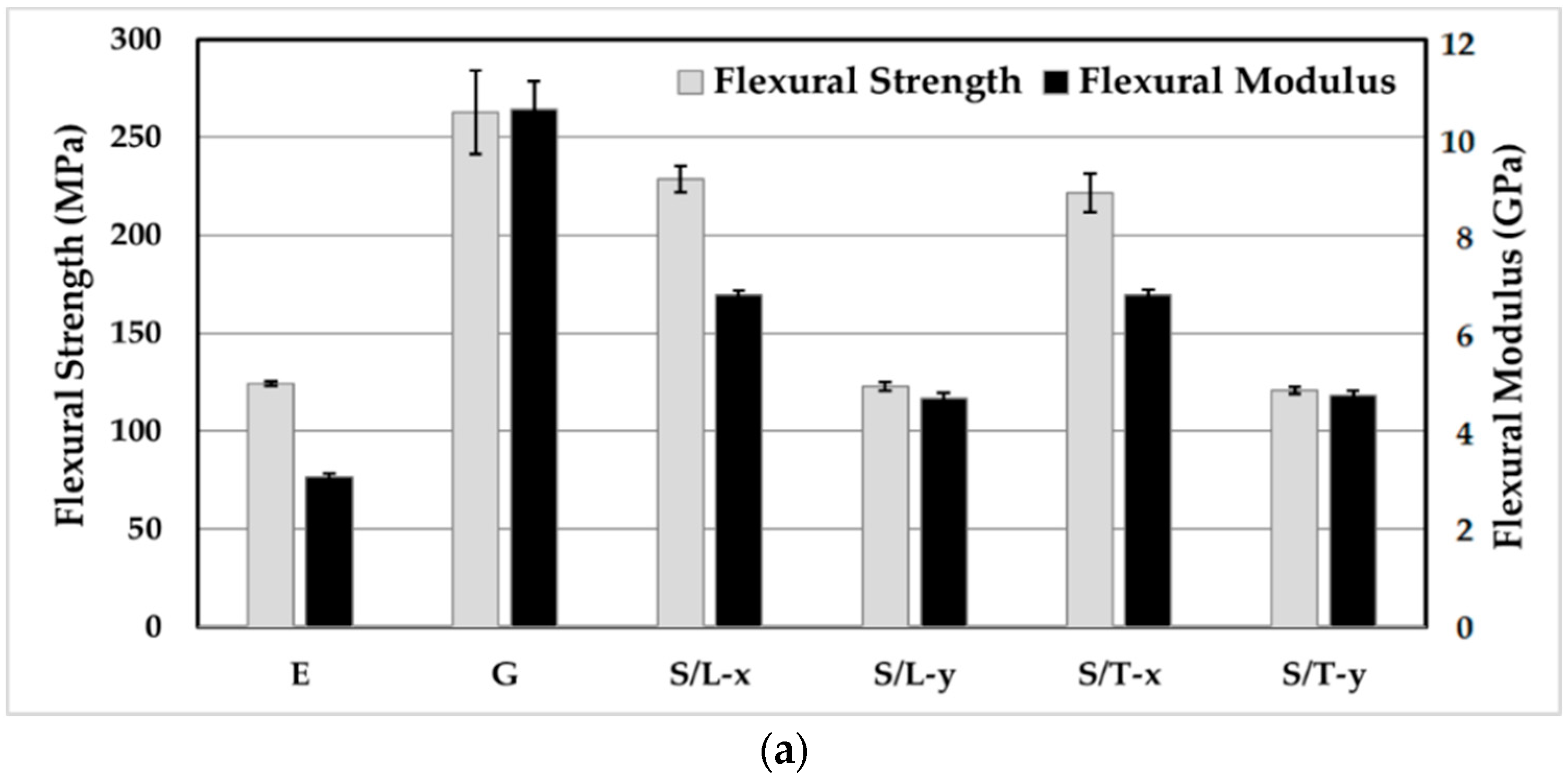
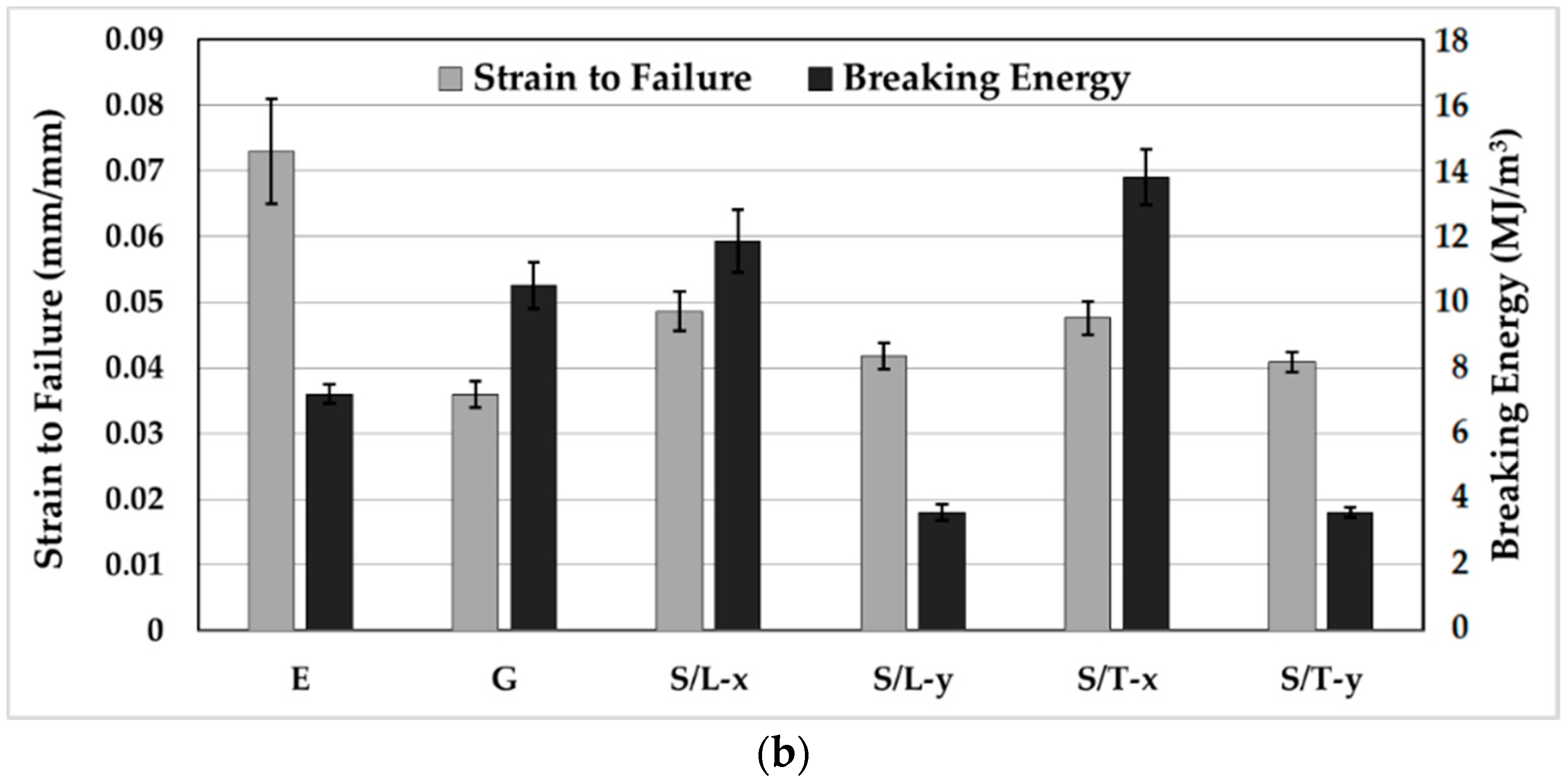
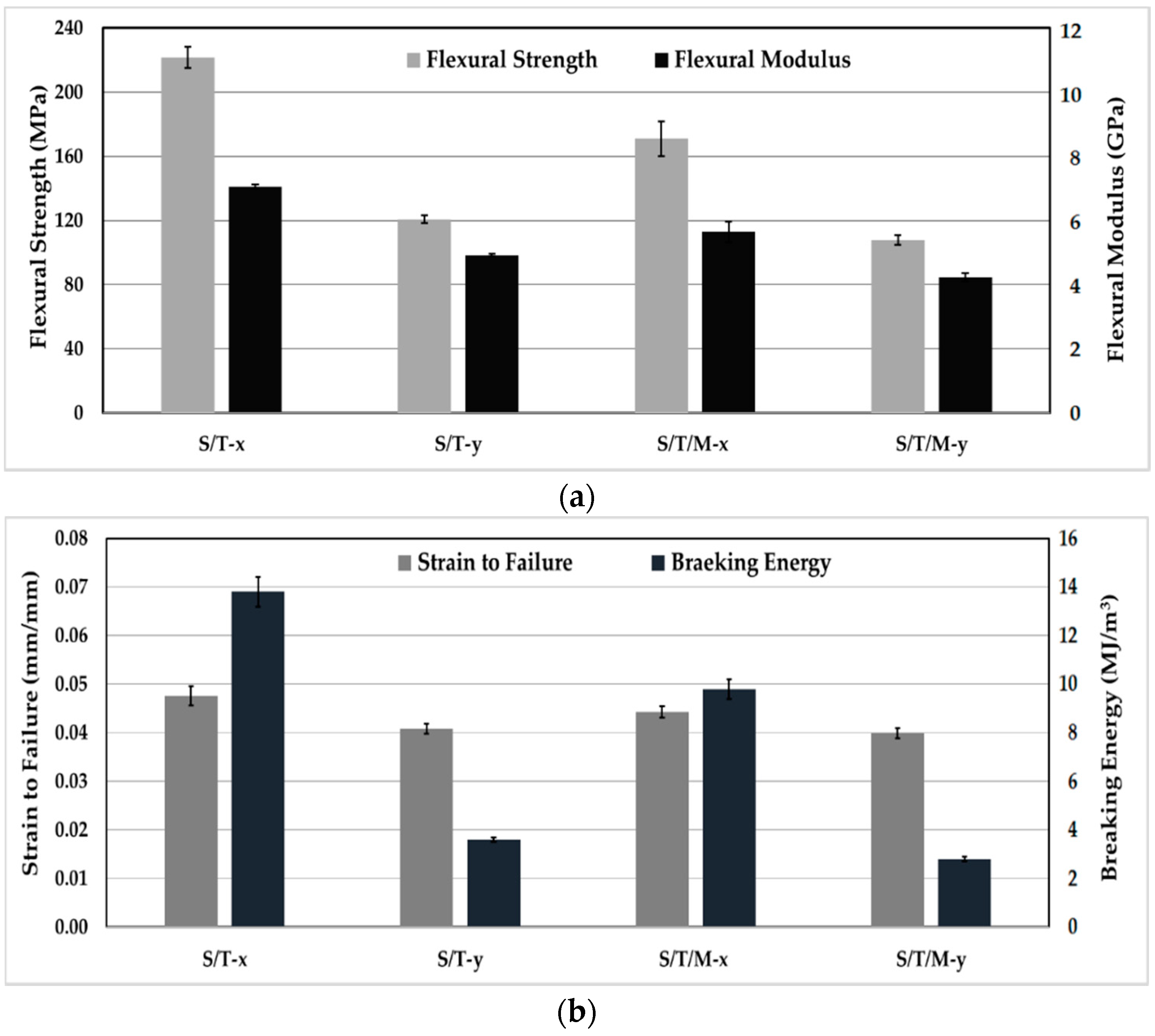
3.5. Fabric Anisotropy Effects on Mechanical Properties of Silk/Epoxy Laminates
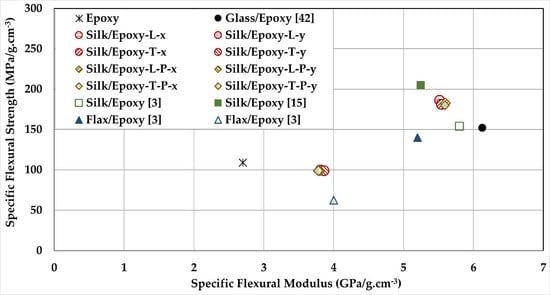
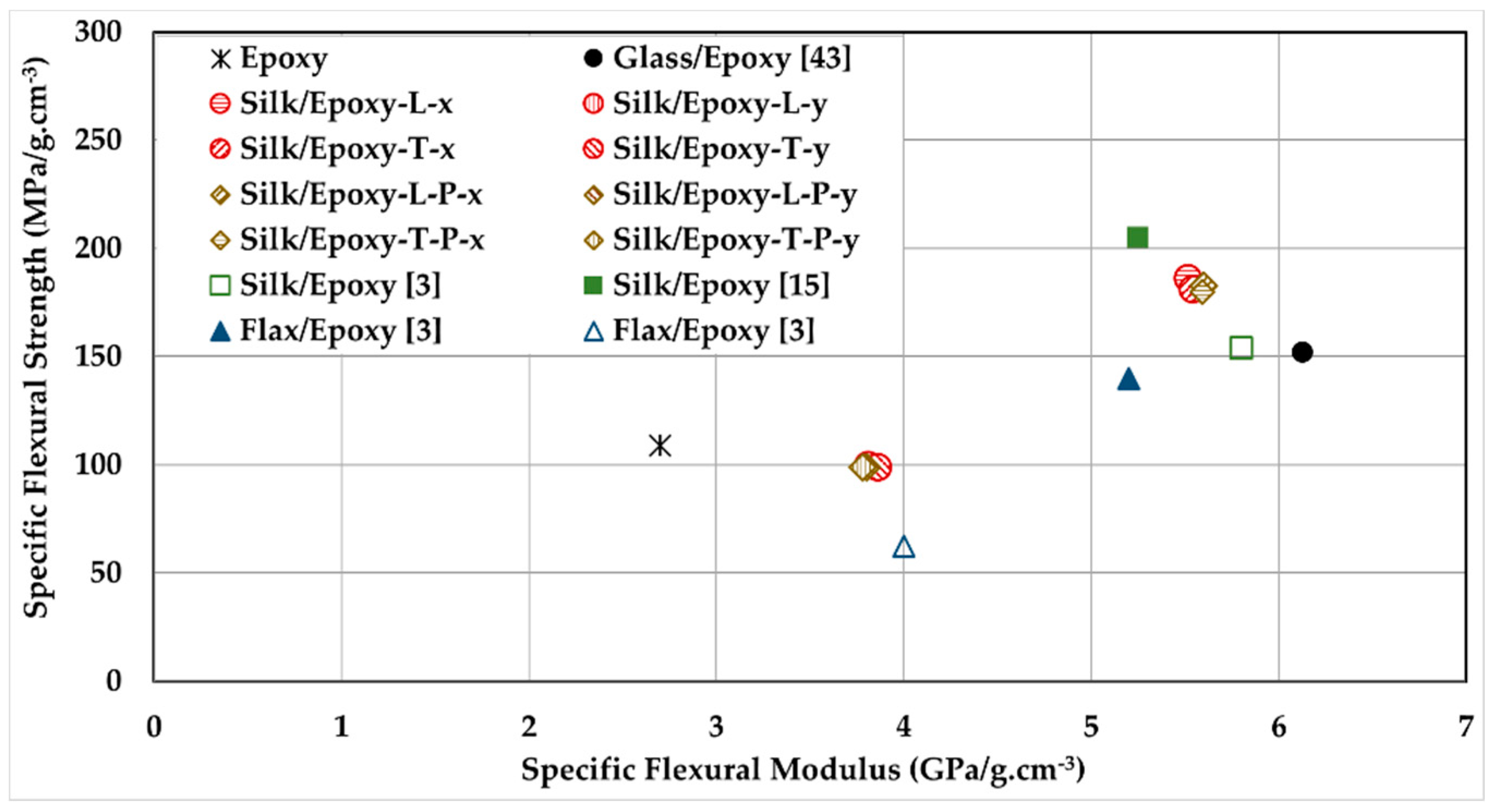
3.6. Silk/Epoxy Laminate Performance Compared to Neat Epoxy and Glass/Epoxy Laminates
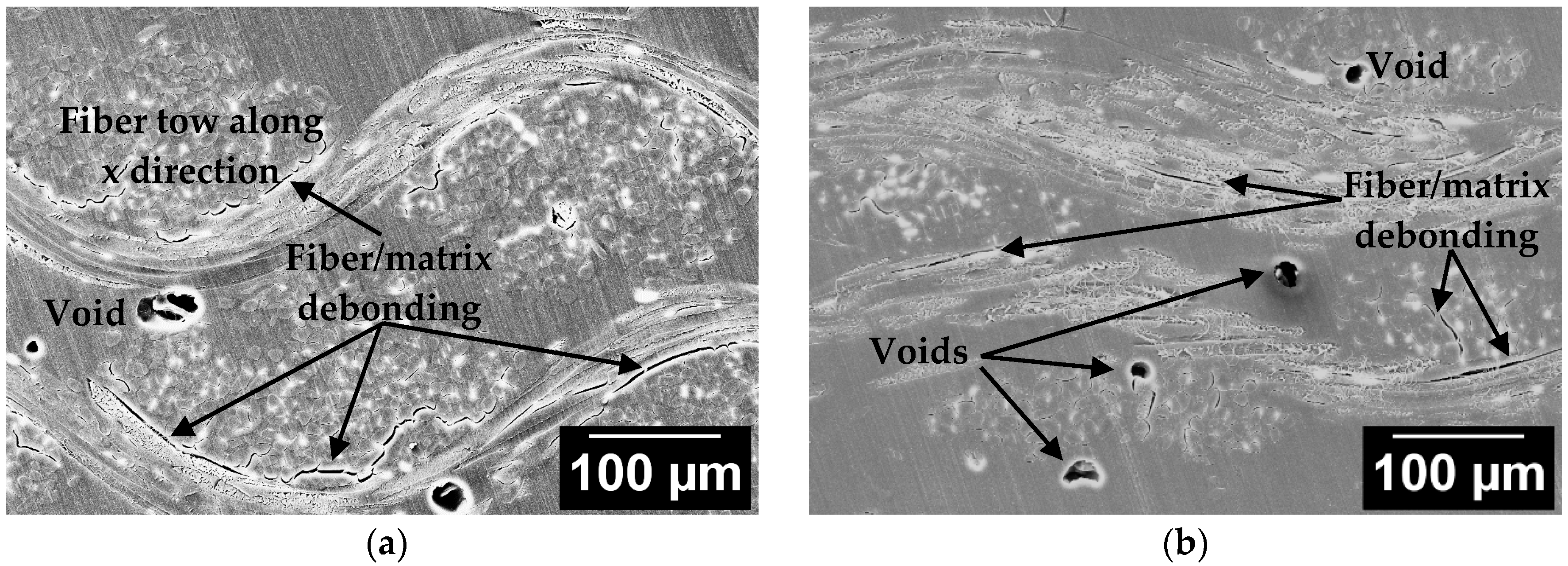
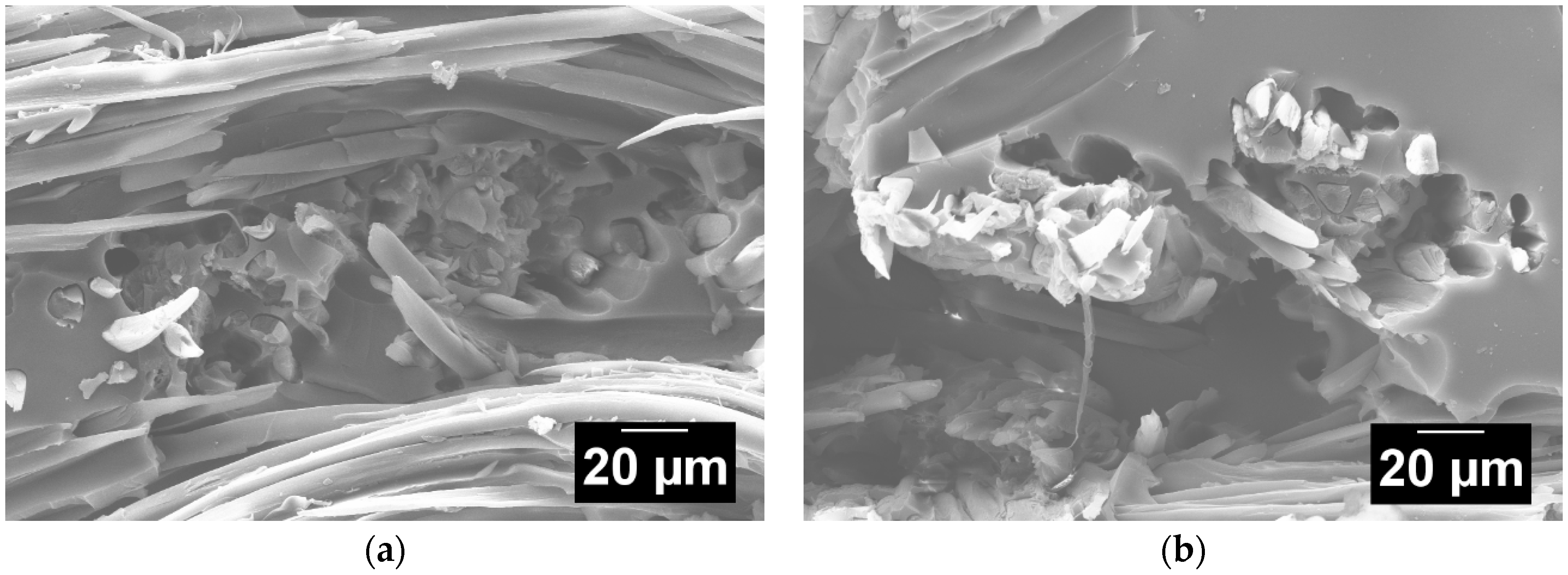
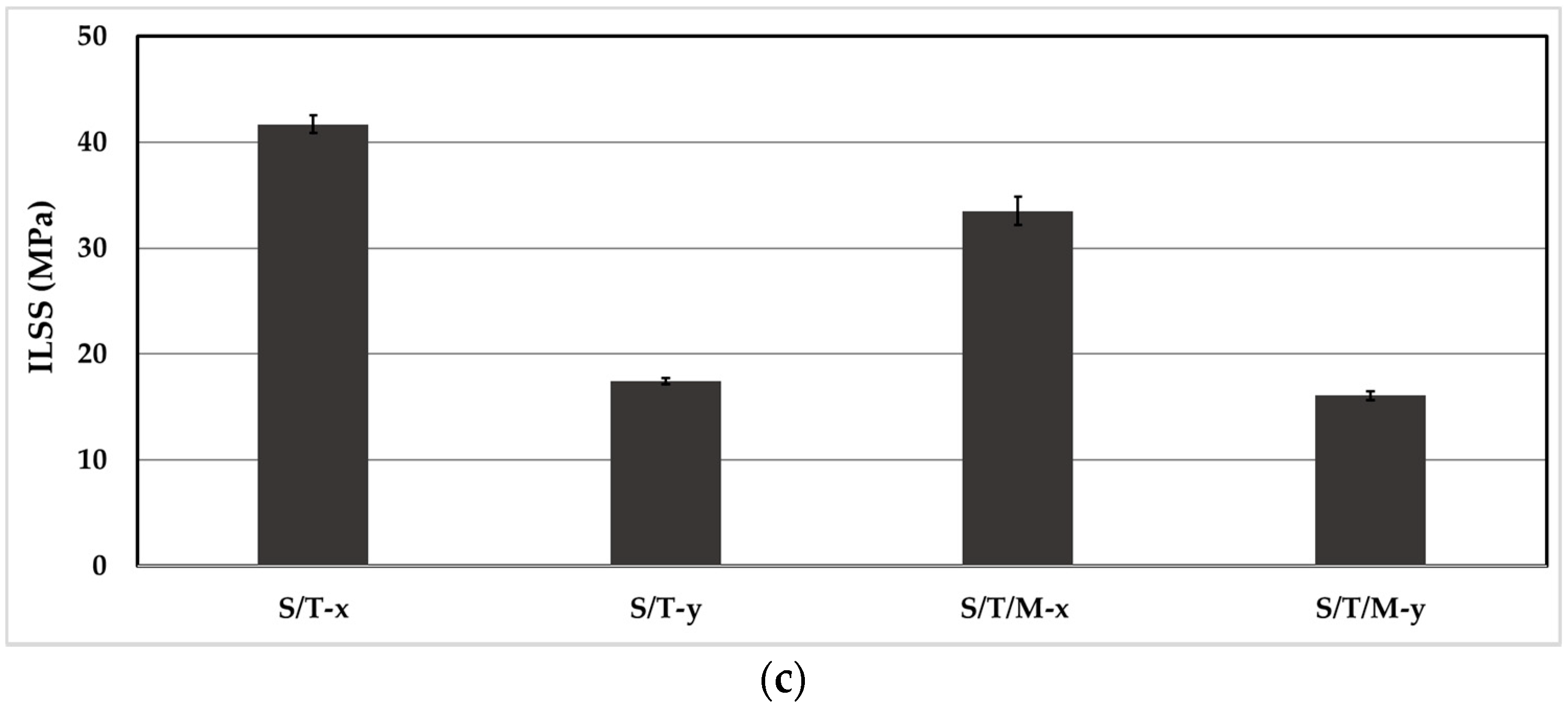
3.7. Silk/Epoxy Interface
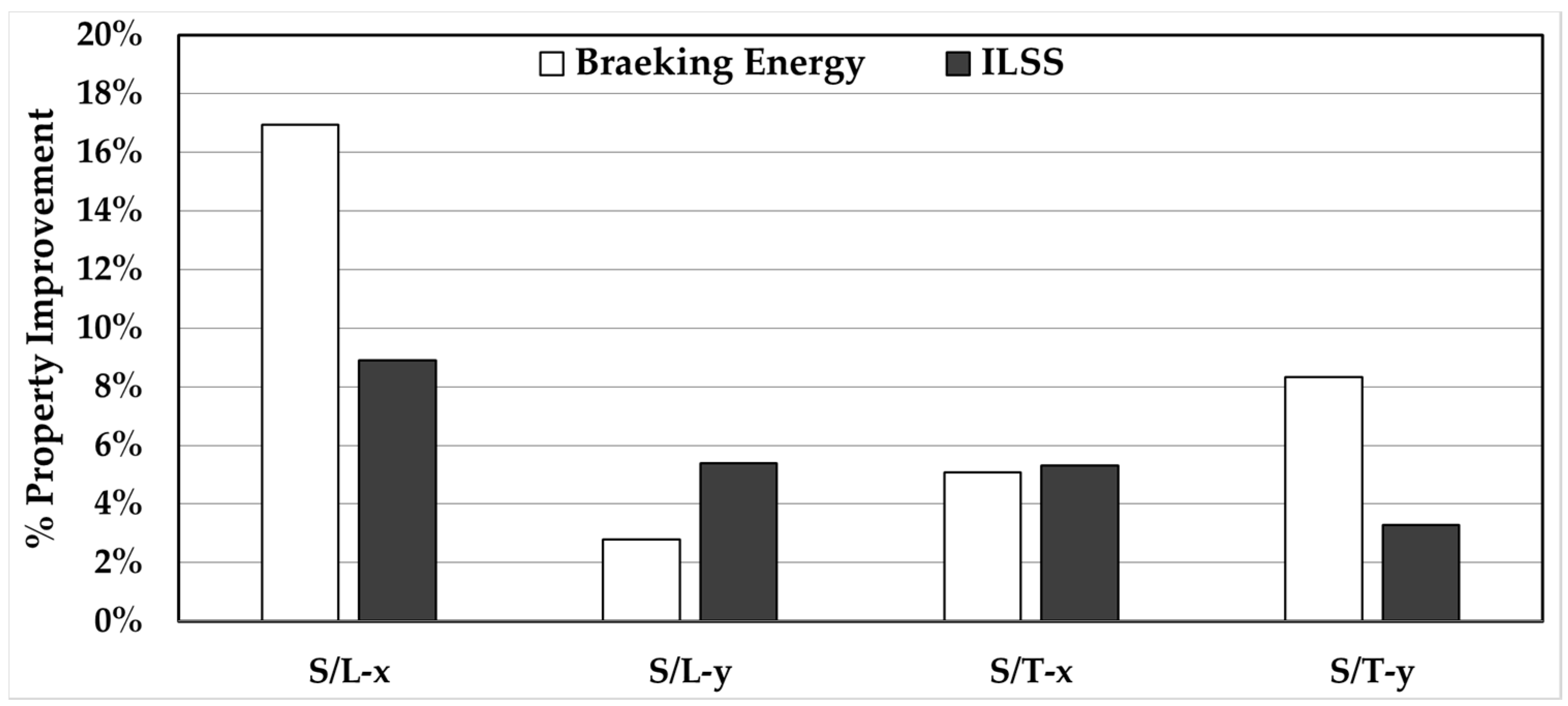
3.8. Effect of Post-Fill External Pressure on Silk/Epoxy Performance
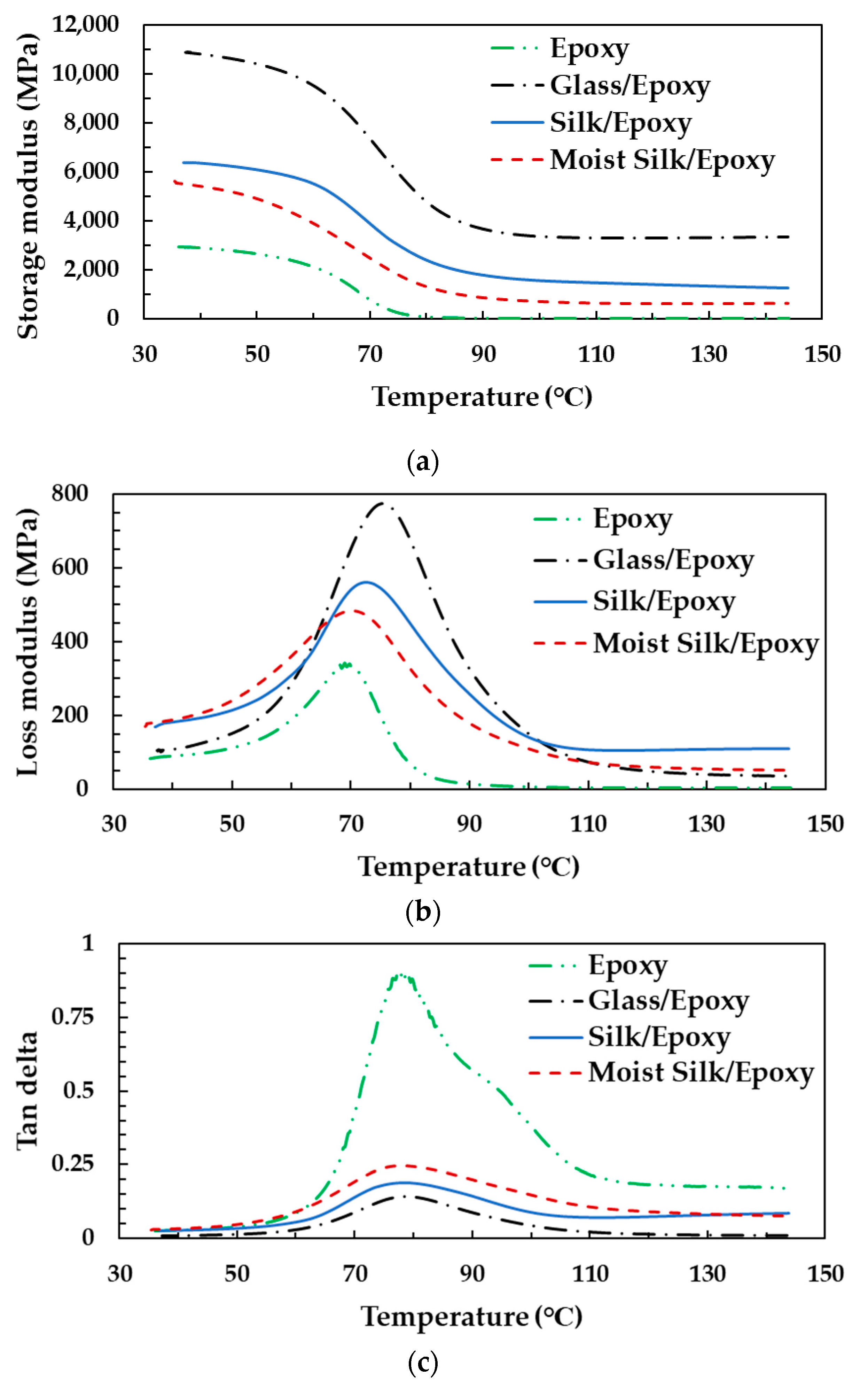
3.9. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Silk/Epoxy
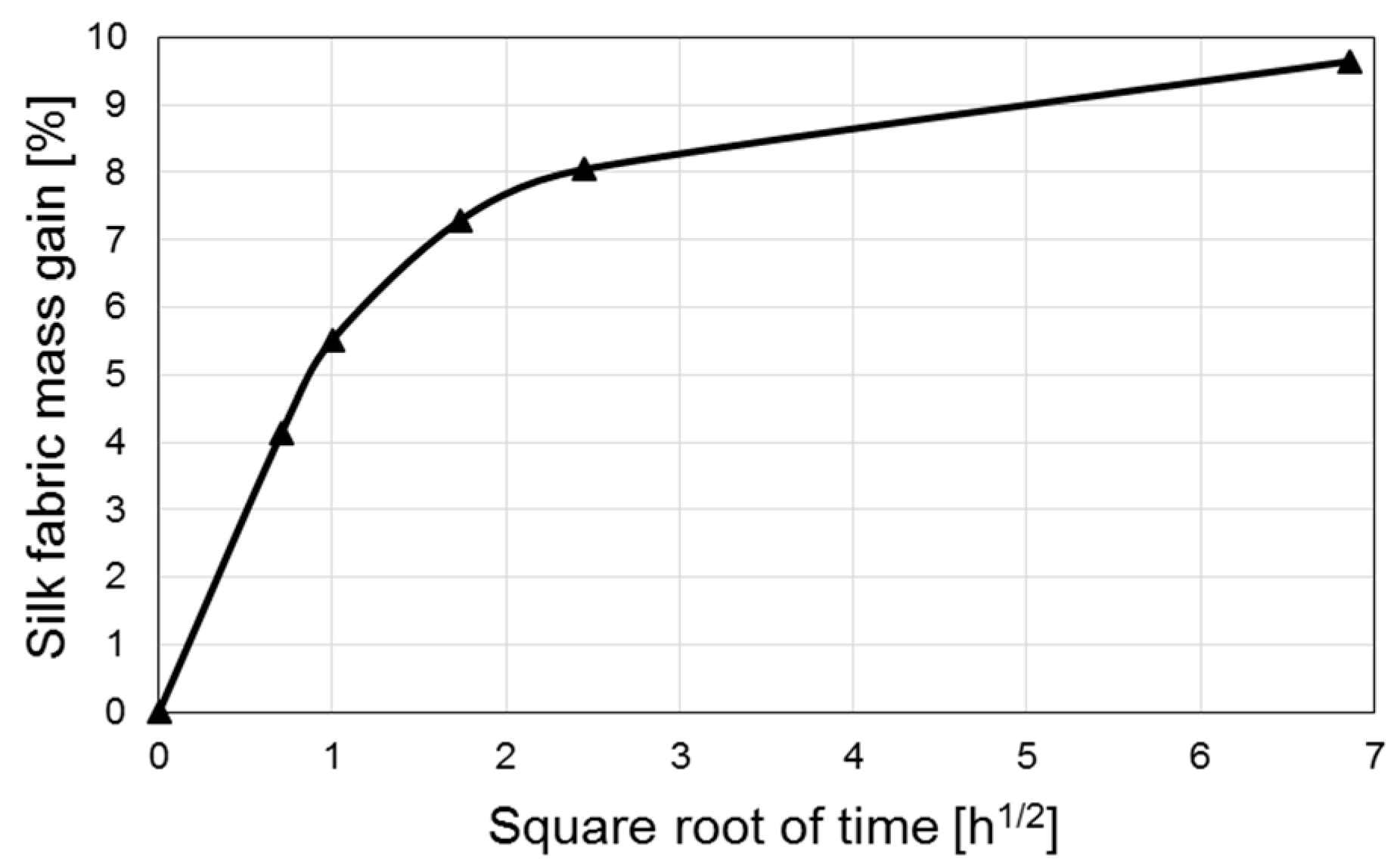
3.10. Silk Moisture Effects on Silk/Epoxy Laminate Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Process-induced defects in resin transfer molded composites. In Comprehensive Composite Materials II, Vol. 2; Beaumont, P.W.R., Zweben, C.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C.; Grady, B.P. Polymer composites. In Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing; Lee, S., Ed.; Decker Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 2313–2322. ISBN 978-0-8247-5563-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, D.U.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Can silk become an effective reinforcing fibre? A property comparison with flax and glass reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 101, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Aruan Efendy, M.G.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Wang, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ho, C.; Lau, K.; Leng, J.; Hui, D. Critical factors on manufacturing processes of natural fibre composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 3549–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.M.; Reddy, Y.V.M.; Reddy, B.C.M. Mechanical properties of burmese silk orchid fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 3116–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.U. Natural fibre composites: Comprehensive Ashby-type materials selection charts. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataollahi, S.; Taher, S.T.; Eshkoor, R.A.; Ariffin, A.K.; Azhari, C.H. Energy absorption and failure response of silk/epoxy composite square tubes: Experimental. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ude, A.U.; Ariffin, A.K.; Azhari, C.H. Impact damage characteristics in reinforced woven natural silk/epoxy composite face-sheet and sandwich foam, coremat and honeycomb materials. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 58, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.U.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Opportunities for silk textiles in reinforced biocomposites: Studying through-thickness compaction behavior. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Paridah, M.T.; Hassan, A. Recent advances in epoxy resin, natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites and their applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, Y.; Gnesa, E.; Jeffery, F.; Tang, S.; Craig Vierra, C. Spider Silk Composites and Applications. In Metal, Ceramic and Polymeric Composites for Various Uses; Cuppoletti, J., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 303–324. ISBN 978-953-307-353-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, J.G.; Scheibel, T.R. Composite materials based on silk proteins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.F.P.; Silva, M.M.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Bombyx mori Silk Fibers: An Outstanding Family of Materials. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 1171–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ritchie, R.O.; Gu, Y.; Wu, S.J.; Guan, J. High volume-fraction silk fabric reinforcements can improve the key mechanical properties of epoxy resin composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Dong, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Suzuki, E.; Furukawa, T.; Takai, Y.; Hamada, H. Flexural and hydrothermal aging behavior of silk fabric/glass mat reinforced hybrid composites. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.P.; Ramakrishna, H.V.; Rai, S.K.; Rajulu, A.V. Tensile, flexural, and chemical resistance properties of waste silk fabric-reinforced epoxy laminates. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2005, 24, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, S.R.; Rai, S.K. Performance analysis of waste silk fabric-reinforced vinyl ester resin laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 2475–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, L.; Huang, H.; Zou, F.; Zhao, H. Fabrication and properties of poly (butylene succinate) biocomposites reinforced by waste silkworm silk fabric. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 95, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Hoagland, D.A.; Farris, R.J. Effect of moisture absorption on the thermal properties of Bombyx mori silk fibroin films. J. Appl. Poly. Sci. 1997, 63, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.L.; Goh, K.L. Consequences of ultra-violet irradiation on the mechanical properties of spider silk. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.; Lau, K.; Wang, H.; Bhattacharyya, D. Characteristics of a silk fiber reinforced biodegradable plastic. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, S.; Nagaraja, G.K.; Naik, J.; Bhajanthri, R.F. Development and characterization study of silk fiber reinforced poly (vinyl alcohol) composites. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2017, 21, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kwon, O.H.; Park, W.H.; Cho, D. Thermal, mechanical, impact, and water absorption properties of novel silk fibroin fiber reinforced poly (butylene succinate) biocomposites. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubhra, Q.T.H.; Alam, A.K.M.M.; Khan, M.A.; Saha, M.; Saha, D.; Khan, J.A.; Quaiyyum, M.A. The preparation and characterization of silk/gelatin biocomposites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshkovr, S.A.; Eshkoor, R.A.; Taher, S.T.; Ariffin, A.K.; Azhari, C.H. Crashworthiness characteristics investigation of silk/epoxy composite square tubes. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, S.; Guan, J.; Shao, Z.; Ritchie, R.O. Enhancing the mechanical toughness of epoxy-resin composites using natural silk reinforcements. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darshan, S.M.; Suresha, B.; Divya, G.S. Waste Silk Fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites: A Review. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2016, 1, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.P.; Rai, S.K. Impact, compression, density, void content, and weight reduction studies on waste silk fabric/epoxy composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2005, 24, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.P.; Rai, S.K. Mechanical performance of biofiber/glass-reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. J. Ind. Text. 2006, 35, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, R.; Azhari, C.H. Effect of silane concentrations on mode I interlaminar fracture of woven silk/epoxy composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 150, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.; Tan, W. Natural silkworm-epoxy resin composite for high performance application. In Metal, Ceramic and Polymeric Composites for Various Uses; Cuppoletti, J., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 325–340. ISBN 978-953-307-353-8. [Google Scholar]
- Izaki, T.; Nakatani, H.; Nam, T.H.; Song, D.Y.; Yoshii, K.; Ogihara, S. Evaluation of mechanical properties of silk fiber reinforced biodegradable plastic composites (part 1, effect of fiber surface treatment on mechanical properties of unidirectional composites). Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. A 2011, 77, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, H.J.; Hamidi, Y.K.; Aktas, L.; Altan, M.C. Performance of glass woven fabric composites with admicellar-coated thin elastomeric interphase. Compos. Interfaces 2017, 24, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, H.J.; Olivero, K.A.; Hamidi, Y.; O’Rear, E.A.; Altan, M.C. Elastomeric sizing for glass fibers and their role in fiber wetting and adhesion in resin transfer molded composites. Compos. Interfaces 2002, 9, 477–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Gonzalez, A.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Olayo, R.; Herrera-Franco, P.J. Effect of fiber surface treatment on the fiber–matrix bond strength of natural fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 1999, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Reihmane, S.; Gassan, J. The effect of alkaline treatment on mechanical properties of kenaf fibers and their epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.P.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Shankar, S.; Rajasekar, R.; Rajini, N. Characterization of natural fiber surfaces and natural fiber composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Yalcinkaya, M.A.; Guloglu, G.E.; Pishvar, M.; Amirkhosravi, M.; Altan, M.C. Manufacturing Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference of the Polymer Processing Society, Taipei, Taiwan, 21–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Process induced defects in liquid molding processes of composites. Int. Polym. Proc. 2017, 32, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, M.A.; Sozer, E.M.; Altan, M.C. Fabrication of high quality composite laminates by pressurized and heated-VARTM. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 102, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhosravi, M.; Pishvar, M.; Altan, M.C. Void Reduction in VARTM Composites by Compaction of Dry Fiber Preforms with Stationary and Moving Magnets. J. Compos. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Dharmavaram, S.; Aktas, L.; Altan, M.C. Effect of fiber content on void morphology in resin transfer molded composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2009, 131, 021014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, Y.K.; Aktas, L.; Altan, M.C. Effect of packing on void morphology in resin transfer molded composites. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloglu, G.E.; Hamidi, Y.K.; Altan, M.C. Fast recovery of non-Fickian moisture absorption parameters for polymers and polymer composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 57, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Designation | Reinforcement Type | Impregnation Direction | Fabric Condition | External Pressure (kPa) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | None | None | None | 0 | 2.76 ± 0.07 |
| G [43] | Glass Mat | Random | Dry | 0 | 1.45 ± 0.02 |
| S/L | Silk Woven | Longitudinal | Dry | 0 | 2.39 ± 0.01 |
| S/T | Silk Woven | Transverse | Dry | 0 | 2.43 ± 0.01 |
| S/L/P | Silk Woven | Longitudinal | Dry | 300 | 2.22 ± 0.01 |
| S/T/P | Silk Woven | Transverse | Dry | 300 | 2.18 ± 0.01 |
| S/T/M | Silk Woven | Transverse | Moist | 0 | 2.51 ± 0.01 |
| Designation | Density (g/cm3) | Fiber Content (%) | Void Content (%) | Average Fill Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 1.140 ± 0.001 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| G | 1.730 ± 0.010 | 45.7 ± 0.1 | 1.86 ± 0.72 | 3 min |
| S/L | 1.227 ± 0.003 | 42.8 ± 0.1 | 0.66 ± 0.21 | 68 min |
| S/T | 1.223 ± 0.001 | 43.5 ± 0.1 | 1.12 ± 0.06 | 20 min |
| S/L/P | 1.237 ± 0.002 | 46.8 ± 0.2 | 0.53 ± 0.17 | 68 min |
| S/T/P | 1.233 ± 0.002 | 48.4 ± 0.1 | 1.24 ± 0.17 | 20 min |
| S/T/M | 1.226 ± 0.002 | 45.7 ± 0.4 | 1.30 ± 0.12 | 32 min |
| Designation | Tg by Storage Modulus (°C) | Tg by Loss Modulus (°C) | Tg by tanδ (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | 59.9 | 69.6 | 78.4 |
| G | 59.9 | 75.2 | 78.2 |
| S/T | 60.9 | 74.0 | 79.5 |
| S/T/M | 57.4 | 71.9 | 79.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamidi, Y.K.; Yalcinkaya, M.A.; Guloglu, G.E.; Pishvar, M.; Amirkhosravi, M.; Altan, M.C. Silk as a Natural Reinforcement: Processing and Properties of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates. Materials 2018, 11, 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112135
Hamidi YK, Yalcinkaya MA, Guloglu GE, Pishvar M, Amirkhosravi M, Altan MC. Silk as a Natural Reinforcement: Processing and Properties of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112135
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamidi, Youssef K., M. Akif Yalcinkaya, Gorkem E. Guloglu, Maya Pishvar, Mehrad Amirkhosravi, and M. Cengiz Altan. 2018. "Silk as a Natural Reinforcement: Processing and Properties of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates" Materials 11, no. 11: 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112135
APA StyleHamidi, Y. K., Yalcinkaya, M. A., Guloglu, G. E., Pishvar, M., Amirkhosravi, M., & Altan, M. C. (2018). Silk as a Natural Reinforcement: Processing and Properties of Silk/Epoxy Composite Laminates. Materials, 11(11), 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112135