Effect of Surface Treatment on Flexural and Tribological Properties of Poly(p-phenylene Benzobisoxazole)/Polyimide Composites under Normal and Elevated Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. PBO Fiber Modification
2.3. Preparation Procedure
2.4. Testing Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT-IR and XPS Analysis of the PBO Fiber Surfaces
- Due to the large effective nuclear charge, the La atom has great chemical activity, and is apt to combine with the oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl groups. The La ions undergo coordination chemical reactions with the oxygen-containing active groups on the surface of the PBO fiber during RES surface treatment. Since the coordination number of La is large and variable, the coordination chemical bonding with the organic reactive functional groups (such as amino groups and carboxyl) in the RES can be continued, and the chemical activity of the PBO surface is enhanced by a method similar to chemical grafting.
- The coupling agent has a bifunctional group in its chemical structure, and its molecular structure can be represented by the general formula RSiX3, where X is a hydroxyl group produced by the hydrolysis of the coupling agent. The hydroxyl group can undergo a dehydration–condensation reaction with the hydroxyl group or carboxyl group on the surface of the PBO fiber. Therefore, more hydroxyl groups are introduced to the surface by coupling agent treatment.
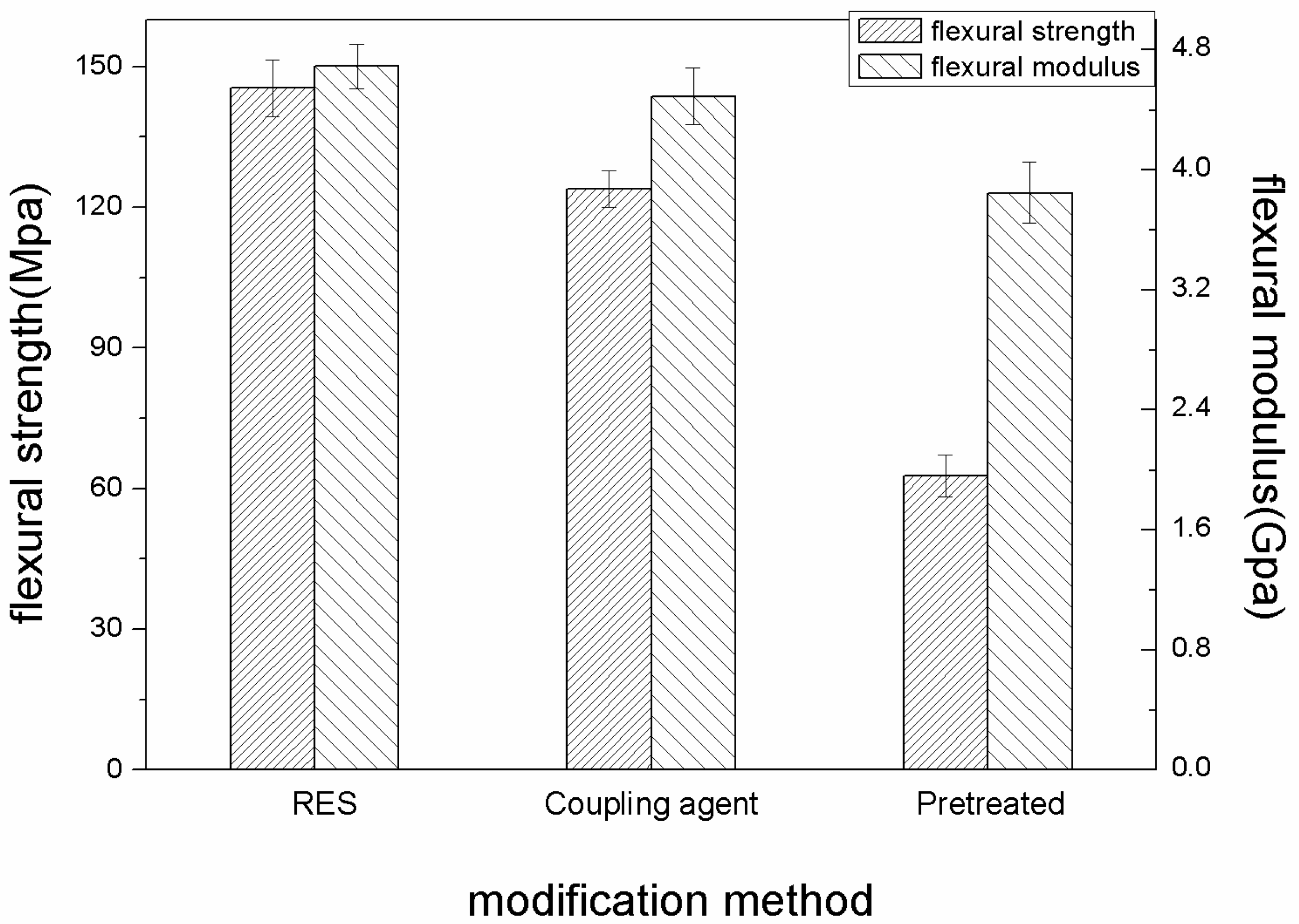
3.2. Flexural Properties
3.3. Tensile Properties
3.4. Friction and Wear Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, R.J.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Riekel, C.; Young, R.J. Crystal lattice deformation in single poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fibres. Polymer 2004, 45, 7693–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Flambard, X. Heat resistance and flammability of high performance fibres: A review. Fire Mater. 2002, 26, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Jenkins, S.E.; Min, B.G.; Polk, M.B.; Kumar, S. Rigid-rod polymers: Synthesis, processing, simulation, structure, and properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.B.; Hong, D.W.; Zhang, L.J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.Y. Surface modification of PBO fibers by direct fluorination and corresponding chemical reaction mechanism. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.X.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, X.F.; Meng, Q.J.; Zheng, Y.S. An excellent ablative composite based on PBO reinforced EPDM. Polym. Bull. 2010, 64, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Flambard, X.; Poutch, F. Study of the thermal degradation of high performance fibres—Application to polybenzazole and p-aramid fibres. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 74, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hokudoh, T.; Yabuki, K. Heat resistance properties of poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole) fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Flambard, X.; Revel, B. Characterisation of poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fibres by solid state NMR. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.P.; Xiao, J.Y.; Zeng, J.C.; Xing, S.L.; Yin, C.P.; Jia, A.Q. Effects of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fiber reinforced phenolic resin composite materials. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, M.; Nishino, T.; Nakamae, K. Temperature dependence of the stress transfer for thermal resistance polymer composites by X-ray diffraction. Compos. Interfaces 2002, 9, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombres, L.; Iorfida, A.; Mazzuca, S.; Verre, S. Bond analysis of thermally conditioned FRCM-masonry joints. Measurement 2018, 125, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Chen, J.F.; D’Anna, J.; La Mendola, L.; Minafò, G. FRCM systems for strengthening masonry structures. In Proceedings of the 8th Biennial Conference on Advanced Composites in Construction, Sheffield, UK, 5 September 2017; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, M.A.; Geever, L.M.; Killion, J.A.; Lyons, J.G.; Higginbotham, C.L. Mechanical and biodegradation performance of short natural fibre polyhydroxybutyrate composites. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.; Mouret, N.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Influence of the degree of retting of flax fibers on the tensile properties of single fibers and short fiber/polypropylene composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Vu, C.M.; Choi, H.J. Improvement of the mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of glass fiber/epoxy composites using polystyrene electrospun nanofibres. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 5089–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.G.; Yang, K.X.; Lei, Q.; Shi, H.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.Y. High residual mechanical properties at elevated temperatures of carbon fiber/acetylene-functional benzoxazine composite. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-M.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, S.-R. Improvement of interfacial adhesion and nondestructive damage evaluation for plasma-treated PBO and Kevlar fibers/epoxy composites using micromechanical techniques and surface wettability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo-Martínez, K.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Montes-Morán, M.A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Effect of oxygen plasma treatment of PPTA and PBO fibers on the interfacial properties of single fiber/epoxy composites studied by Raman spectroscopy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, D.; Jin, J.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Jiang, J. Improvement of surface wettability and interfacial adhesion ability of poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) (PBO) fiber by incorporation of 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (DHTA). Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Hu, X. The effect of addition of SiO2 on the mechanical properties of PBO-fiber-filled HDPE composites. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2015, 51, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z. Enzymatic surface modification of PBO fibres. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4800–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Surface analysis of γ-ray irradiation modified PBO fiber. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 92, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, C.; Bahadur, S. The role of filler deformability, filler–polymer bonding, and counterface material on the tribological behavior of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS). Wear 2001, 251, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, E.; Wang, X. Synthesis and characterization of PBO and determination of the residual phosphorus. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 23, 104–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Z.; Cheng, X.H. Influence of rare-earth-functionalized carbon nanotubes on thermal and mechanical properties of polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposites. J. Reinforced Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.W.; Bai, T.; Dang, J.; Feng, J.J.; Zhang, Q.Y. Surface functionalization of HMPBO fibers with MSA/KH550/GlycidylEthyl POSS and improved interfacial adhesion. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.X.; Feng, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Hu, S.H. Improvement of interfacial adhesion between PBO fibers and cyanate ester matrix. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
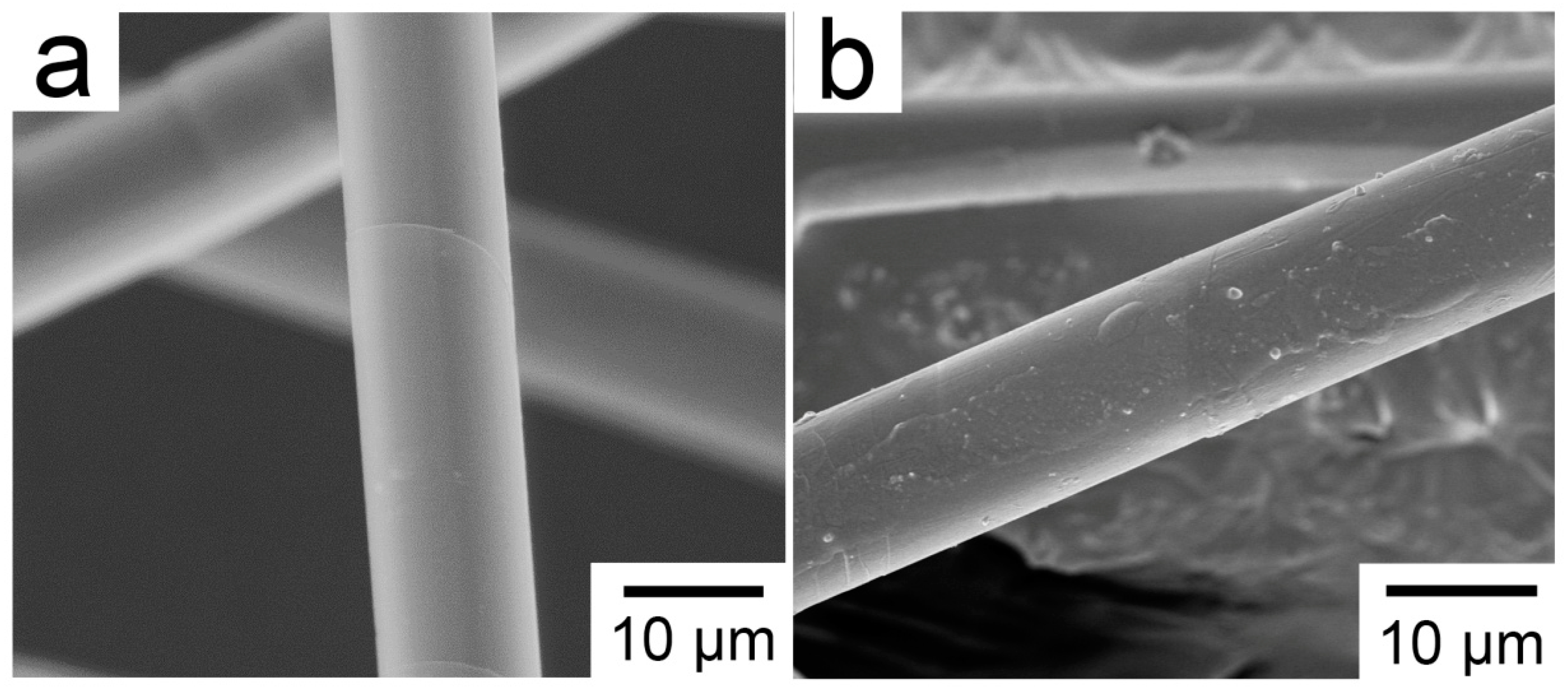













| Surface Treatment | Relative Percentage of Functional Groups Component (%) | Abbe Criterion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–C | C–O | C=N | O=C–O | ||
| pretreated | 58.61 | 21.11 | 17.27 | 3.01 | 0.09 |
| coupling agent | 57.51 | 30.66 | 11.83 | - | 0.38 |
| RES | 42.23 | 27.18 | 15.17 | 15.42 | 0.16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. Effect of Surface Treatment on Flexural and Tribological Properties of Poly(p-phenylene Benzobisoxazole)/Polyimide Composites under Normal and Elevated Temperature. Materials 2018, 11, 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112131
Yu L, He R, Zhang Y, Gao J. Effect of Surface Treatment on Flexural and Tribological Properties of Poly(p-phenylene Benzobisoxazole)/Polyimide Composites under Normal and Elevated Temperature. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112131
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Liang, Ren He, Yuanjie Zhang, and Jicheng Gao. 2018. "Effect of Surface Treatment on Flexural and Tribological Properties of Poly(p-phenylene Benzobisoxazole)/Polyimide Composites under Normal and Elevated Temperature" Materials 11, no. 11: 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112131
APA StyleYu, L., He, R., Zhang, Y., & Gao, J. (2018). Effect of Surface Treatment on Flexural and Tribological Properties of Poly(p-phenylene Benzobisoxazole)/Polyimide Composites under Normal and Elevated Temperature. Materials, 11(11), 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112131




