Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ultrahigh Permeability Sample
2.2. Measurement Method
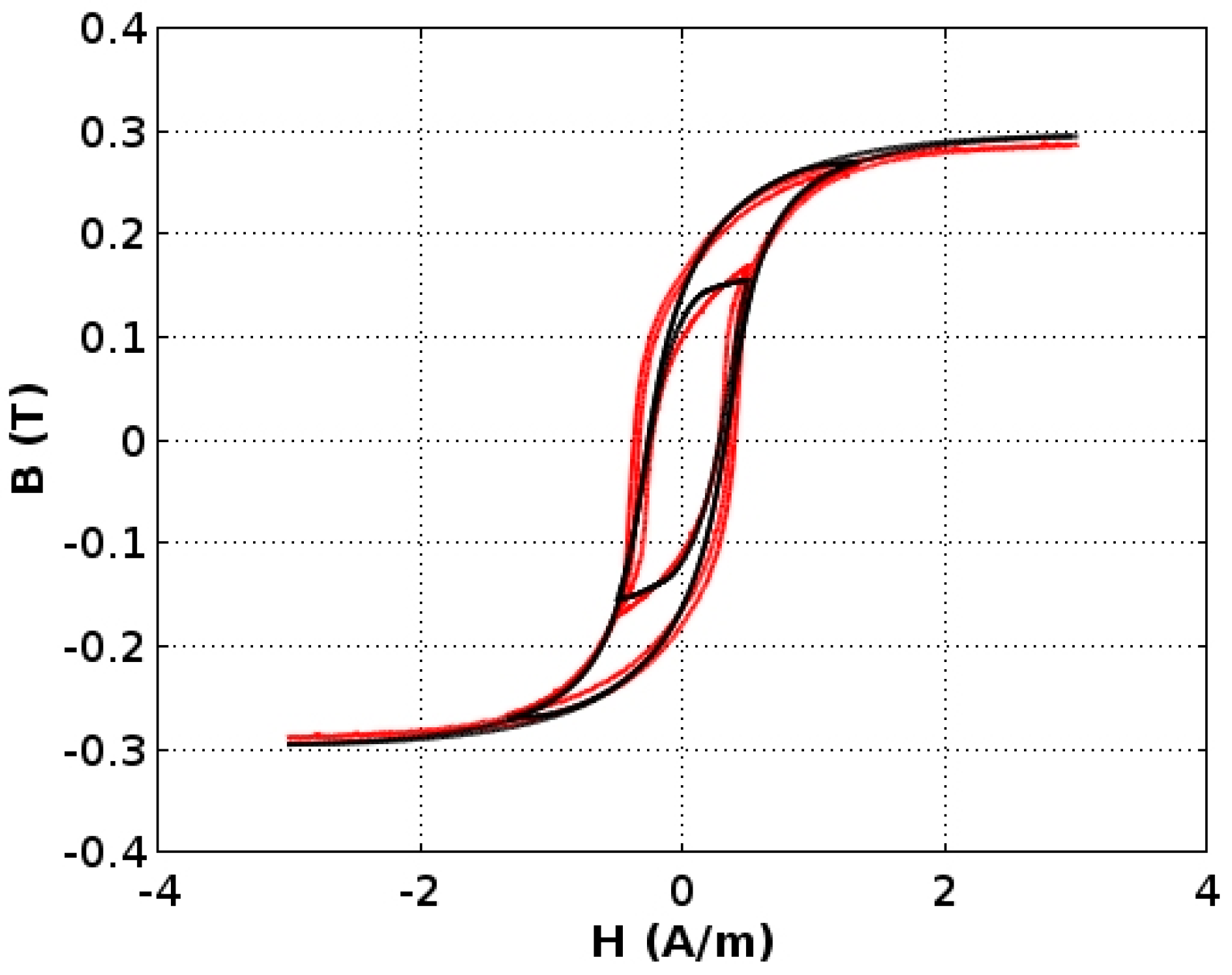
3. Results
3.1. Jiles-Atherton Hysteresis Model and Its Modifications
3.2. Modeling Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ripka, P. Review of fluxgate sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1992, 33, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primdahl, F. The fluxgate magnetometer. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1979, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, A.; Belyayev, S.; Ivchenko, N.; Olsson, G.; Edberg, T.; Marusenkov, A. Miniaturized digital fluxgate magnetometer for small spacecraft applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 015202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small Explorer for Advanced Missions. Available online: http://www.isr.lviv.ua/SEAM.htm (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- Marusenkov, A. Possibilities of further improvement of 1s fluxgate variometers. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2017, 6, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, B.; Baglio, S.; La Malfa, S.; Bulsara, A.R. Adaptive Modeling of Hysteretic Magnetometers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C.; Atherton, D.L. Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1986, 61, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackiewicz, D.; Szewczyk, R.; Salach, J. Mathematical and computer modelling of the influence of stress on magnetic characteristics of the steels. Theor. Appl. Inform. 2013, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, N.C.; Caltun, O.F. Jiles-Atherton magnetic hysteresis parameters identification. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 120, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirka, S.E.; Moroz, Y.I.; Harrison, R.G.; Chwastek, K. On physical aspects of the Jiles-Atherton hysteresis models. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 043916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nosenko, V.K.; Maslov, V.V.; Kirilchuk, V.V.; Kochkubey, A.P. Some industrial applications of amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, R.; Kimura, S.; Watanabe, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Makino, A.; Koyama, K. Magnetic field effects on crystallization of iron-based amorphous alloys. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfus, Y.; Yeshurun, Y.; Felner, I.; Wolny, J. Crystallization kinetics in amorphous ferromagnets effect of temperature and magnetic field. Philos. Mag. B 1987, 56, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Qi, M. Crystallization behavior of Fe78Si13B9 metallic glass under high magnetic field. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2008, 15, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoirard, S. High steady magnetic field processing of functional magnetic materials. JOM 2013, 65, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milyutin, V.A.; Gervaseva, I.V.; Beaugnon, E.; Gaviko, V.S.; Volkova, E.G. The process of crystallization from amorphous state in ribbons of Fe–Si–B–based alloys under the effect of a high DC magnetic field. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2017, 118, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charubin, T.; Nowak, P.T.; Nowicki, M.; Szewczyk, R.; Urbański, M. Automatic measurement station for ferrite materials testing. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2018, 133, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Jiles, D.C.; Roderik, J. A model of anisotropic anhysteretic magnetization. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 32, 4234–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, B.; Baglio, S.; La Malfa, S.; Bulsara, A.R. SPICE simulation of coupled core fluxgate magnetometers. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, B.; Baglio, S.; Bulsara, B.; La Malfa, S. RTD Fluxgate behavioral model for circuit simulation. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskill, S.G.; Weisshaar, A. Compact equivalent circuit modeling of microfluxgate devices with thin-film magnetic cores. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, R. Validation of the anhysteretic magnetization model for soft magnetic materials with perpendicular anisotropy. Materials 2014, 7, 5109–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Szewczyk, R. Modified description of magnetic hysteresis in Jiles-Atherton model. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2018, 743, 648–654. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman, R.; Krisnaprasad, P.S. Qualitative analyse of a bulk ferromagnetic hysteresis model. In Proceedings of the 37th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Tampa, FL, USA, 18 December 1998; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 2443–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, R. Computational problems connected with Jiles-Atherton model of magnetic hysteresis. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2014, 267, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Biedrzycki, R.; Jackiewicz, D.; Szewczyk, R. Reliability and efficiency of differential evolution based method of determination of Jiles-Atherton model parameters for X30Cr13 corrosion resisting martensitic steel. J. Autom. Mob. Robot. Intell. Syst. 2014, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, R. Two step, differential evolution-based identification of parameters of Jiles-Atherton model of magnetic hysteresis loops. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2018, 743, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Digital Magnetometer for Microsatellites LEMI-020. Available online: http://www.isr.lviv.ua/lemi020.htm (accessed on 6 October 2018).


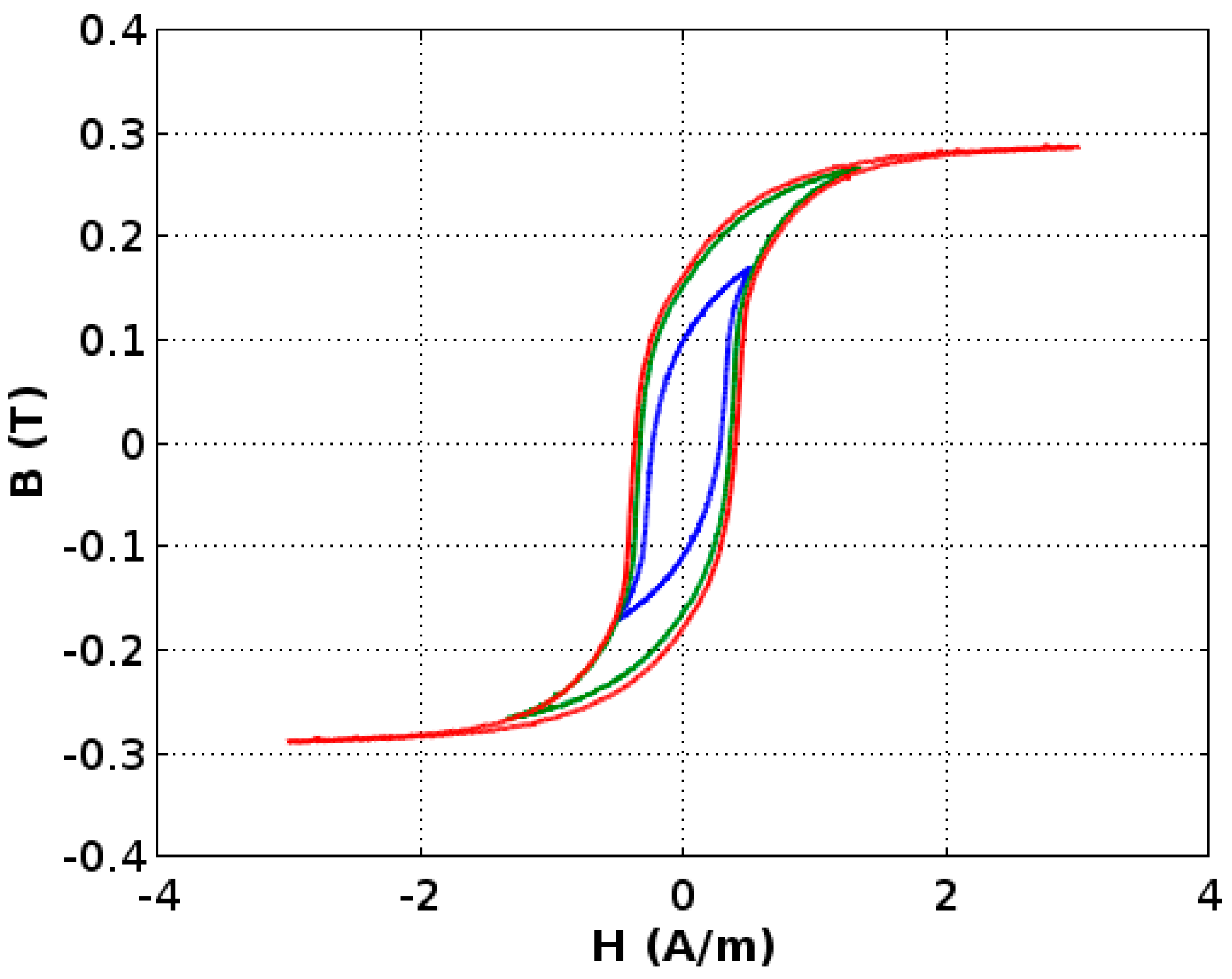

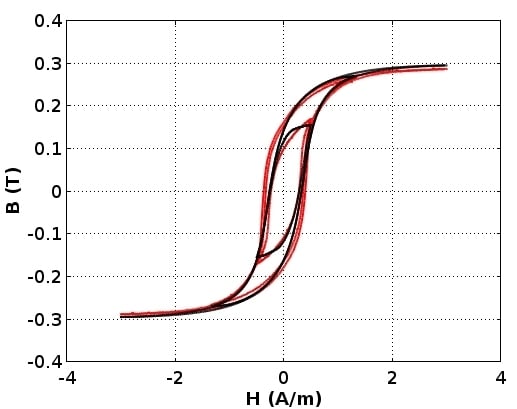
| Parameter | Unit | Jiles-Atherton | Venkataraman et al. | Cheng et al. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ms | A/m | 219,600 | 216,600 | 237,200 |
| a | A/m | 0.269 | 0.268 | 1.669 |
| α | - | 2.824 × 10−8 | 1.151 × 10−8 | 6.268 × 10−6 |
| Kan | J/m3 | 2.383 | 32.08 | 1230 |
| ψ | rad | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| k | A/m | 0.318 | 0.322 | 0.263 |
| c | - | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.459 |
| R2 | - | 0.984 | 0.984 | 0.992 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowicki, M.; Szewczyk, R.; Charubin, T.; Marusenkov, A.; Nosenko, A.; Kyrylchuk, V. Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112079
Nowicki M, Szewczyk R, Charubin T, Marusenkov A, Nosenko A, Kyrylchuk V. Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112079
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowicki, Michał, Roman Szewczyk, Tomasz Charubin, Andriy Marusenkov, Anton Nosenko, and Vasyl Kyrylchuk. 2018. "Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications" Materials 11, no. 11: 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112079
APA StyleNowicki, M., Szewczyk, R., Charubin, T., Marusenkov, A., Nosenko, A., & Kyrylchuk, V. (2018). Modeling the Hysteresis Loop of Ultra-High Permeability Amorphous Alloy for Space Applications. Materials, 11(11), 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112079