Significance of a Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment on LDPE Biodegradation with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
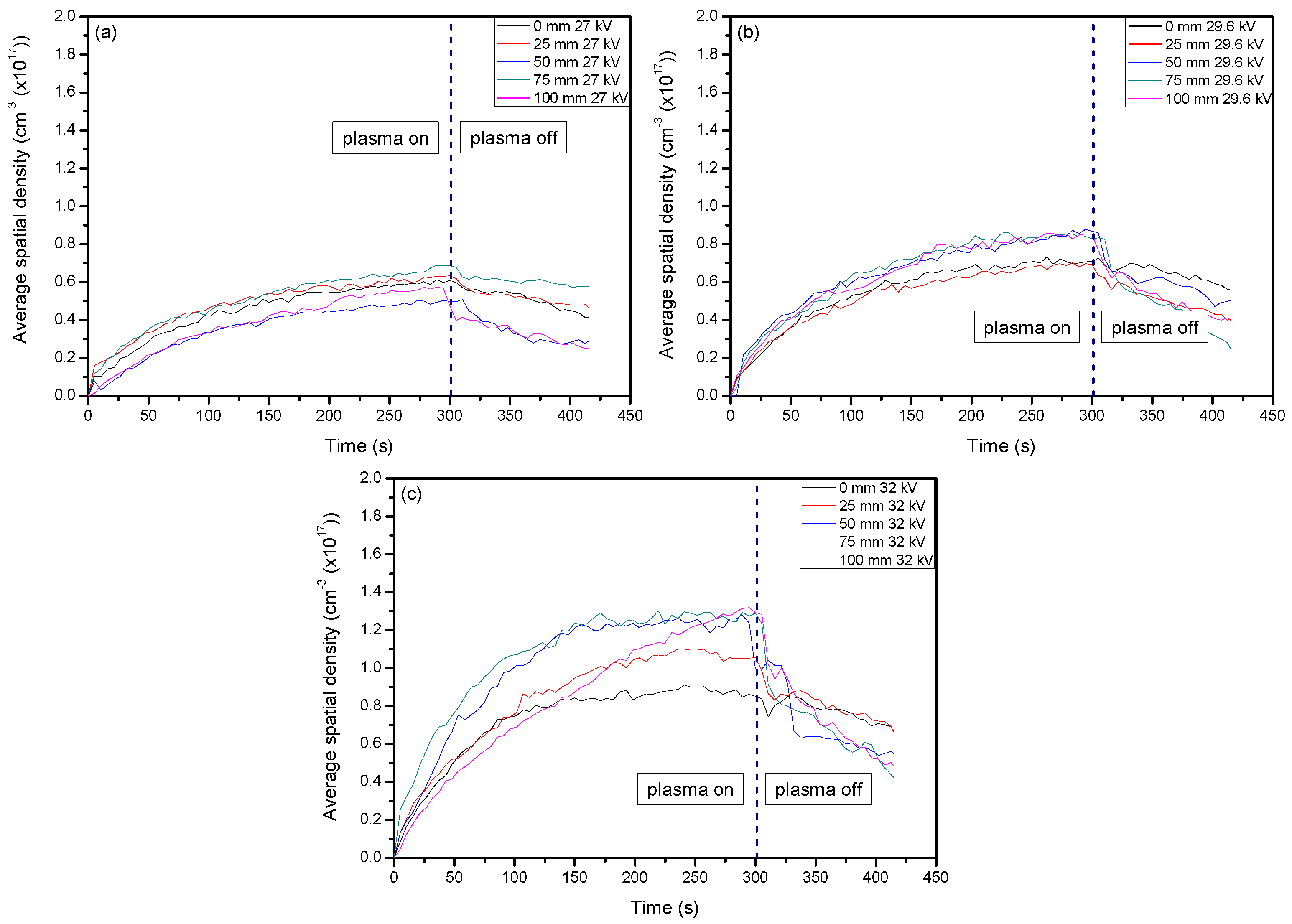
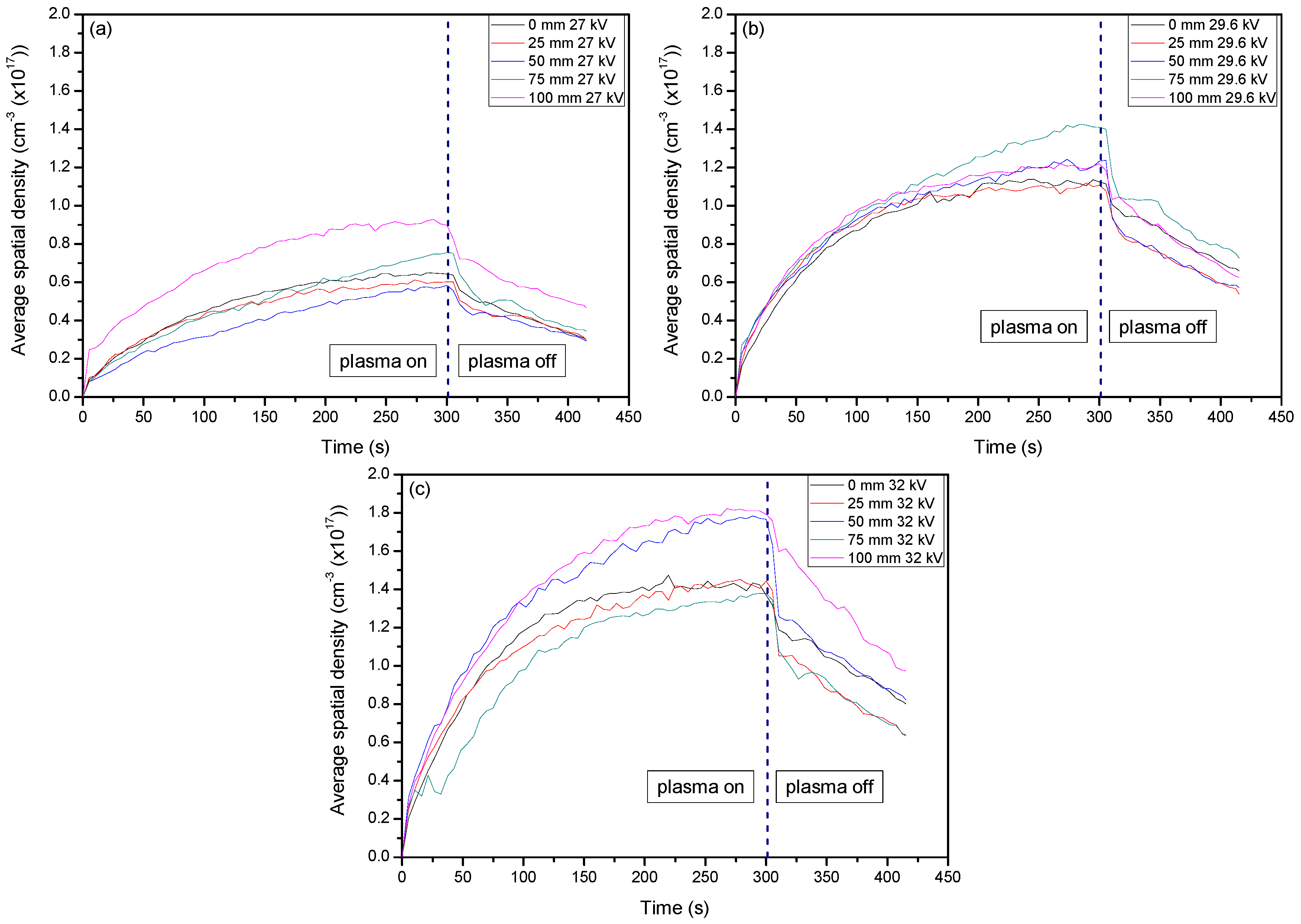
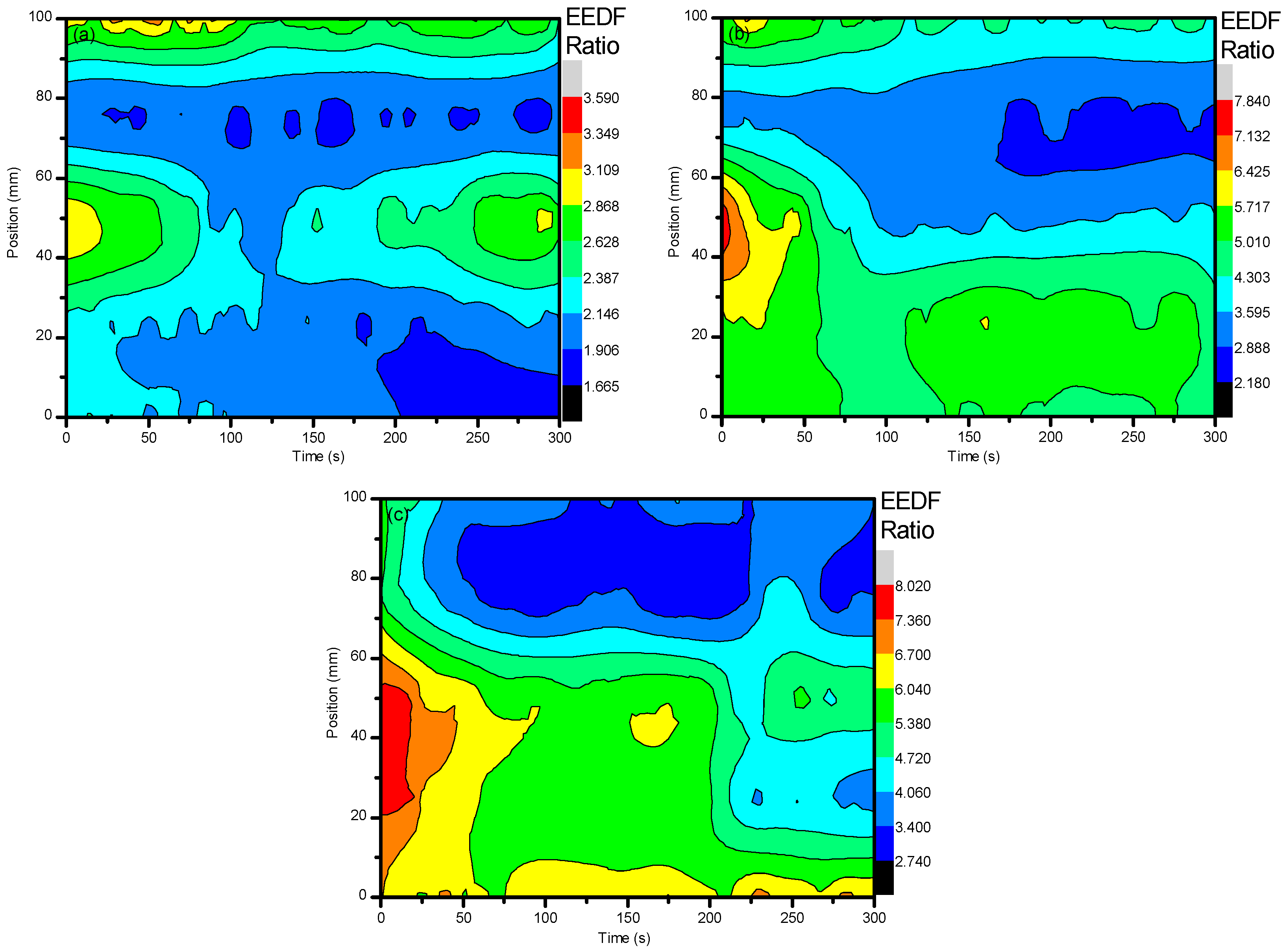
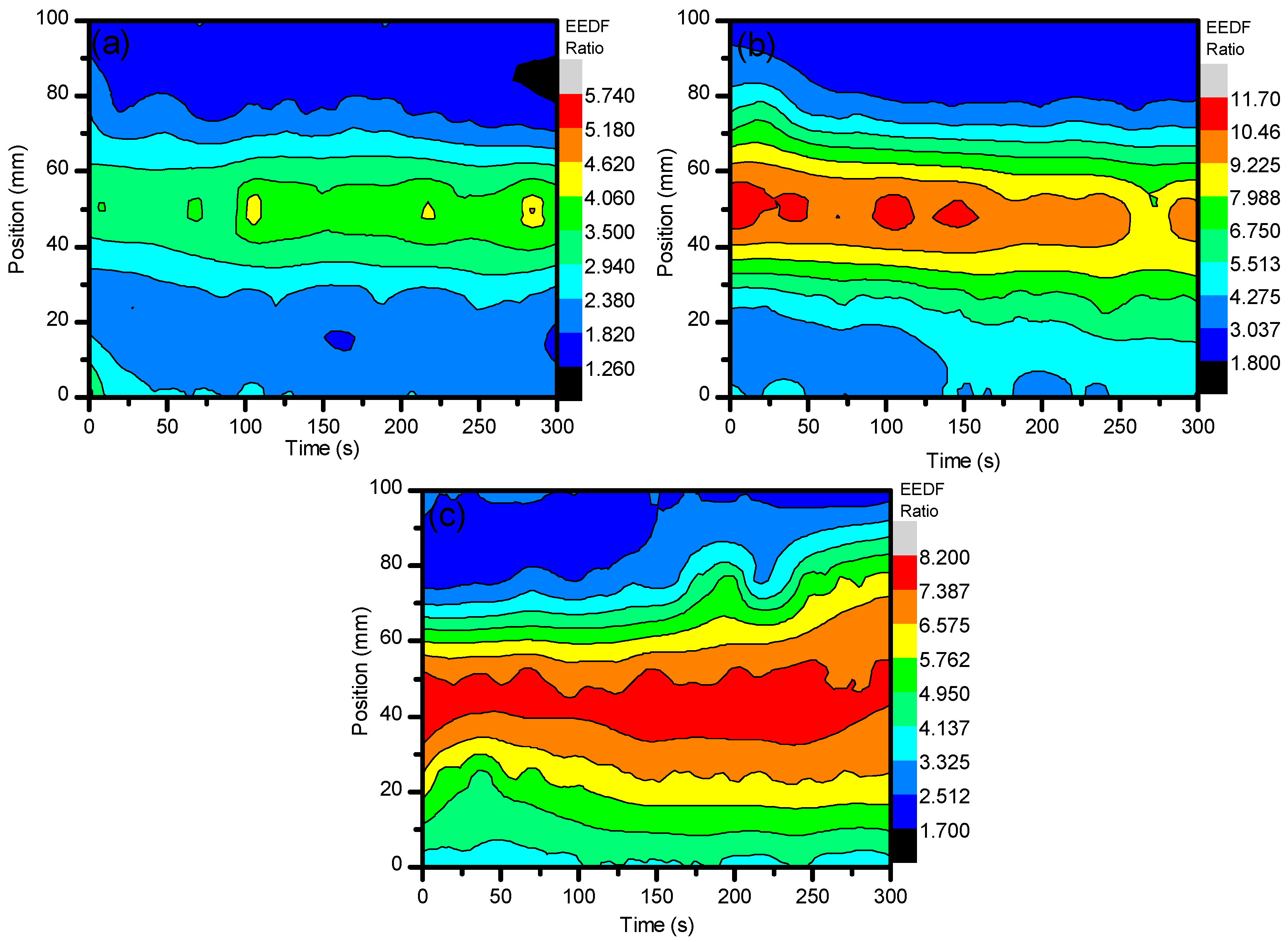
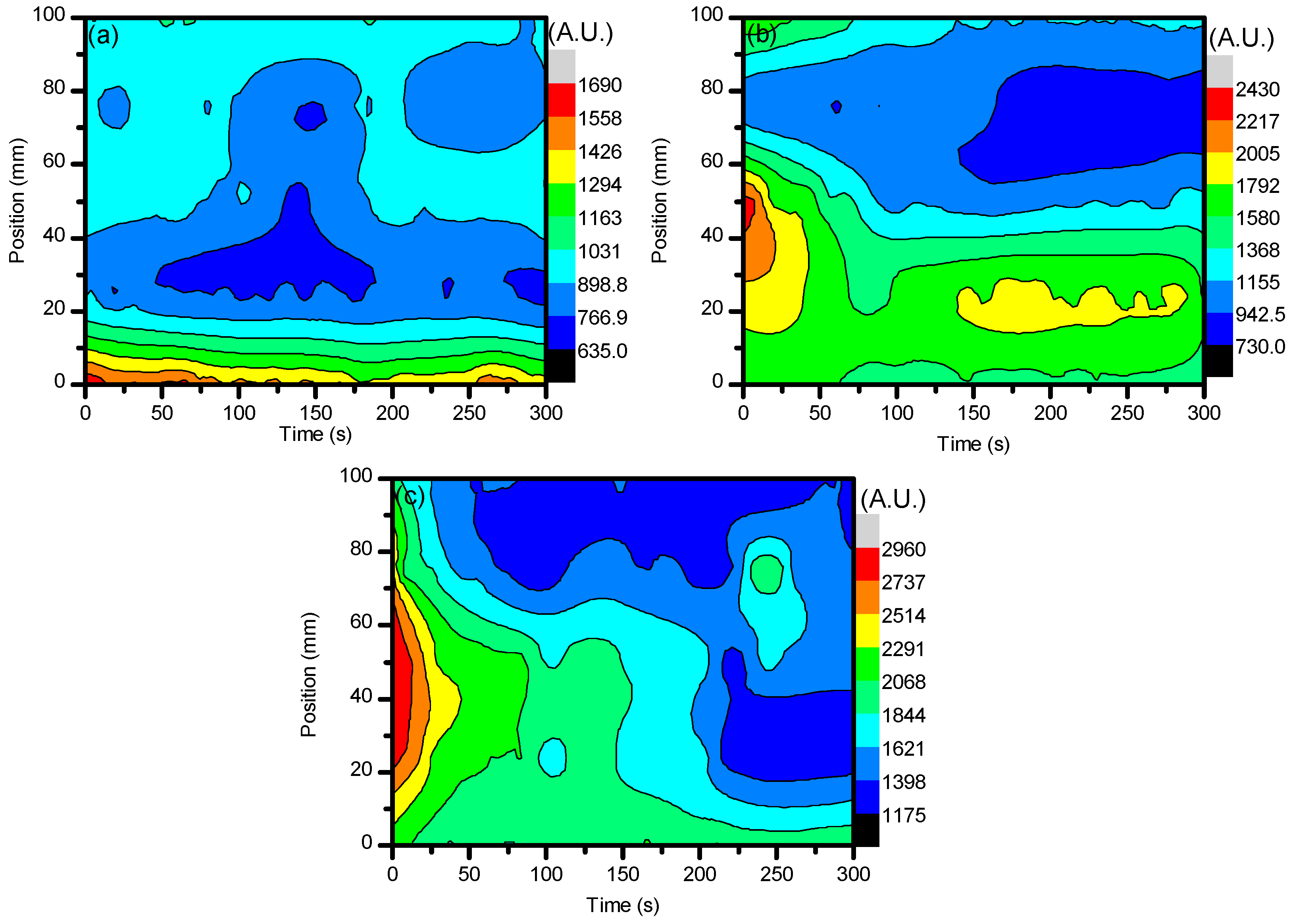
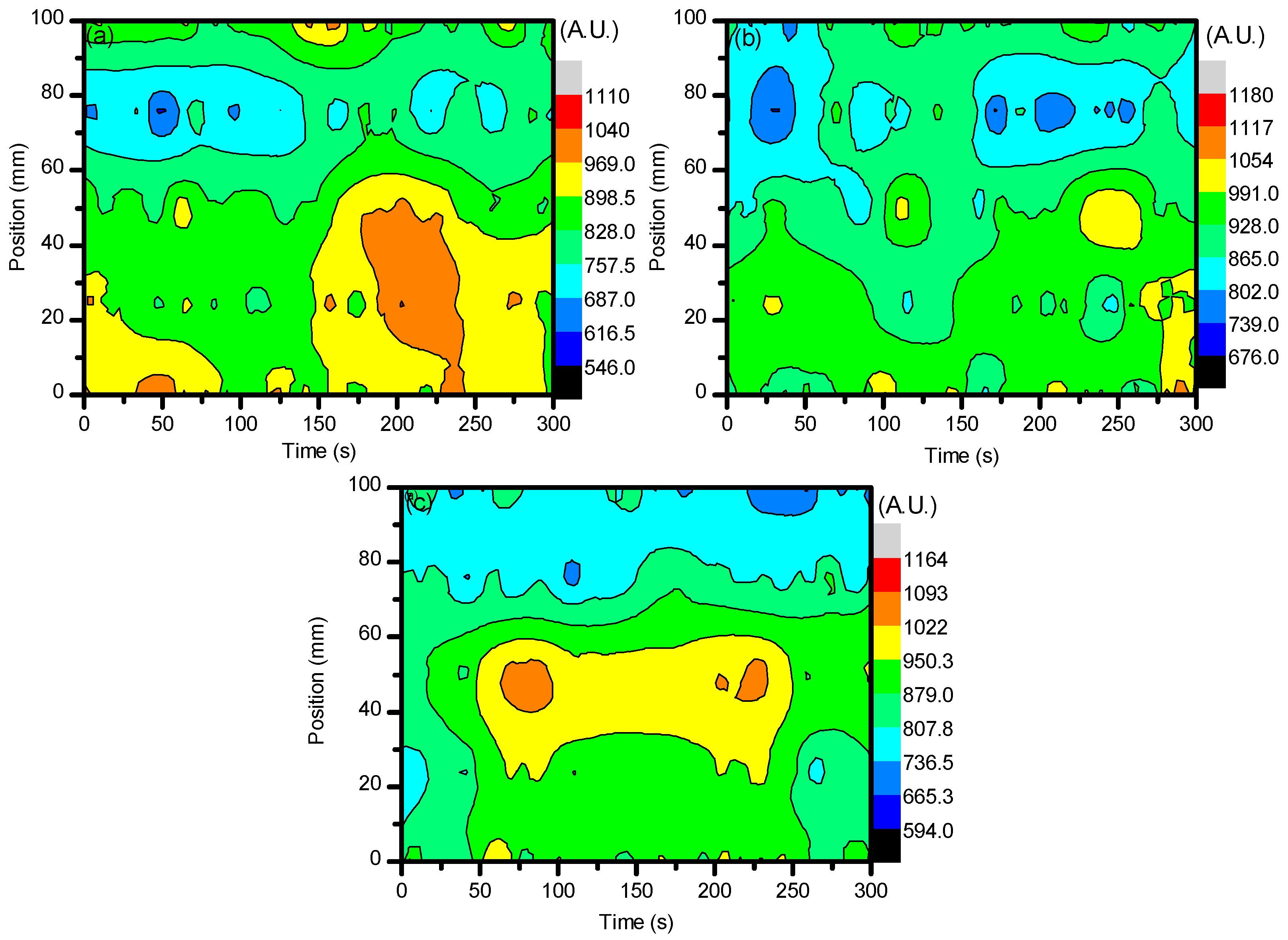
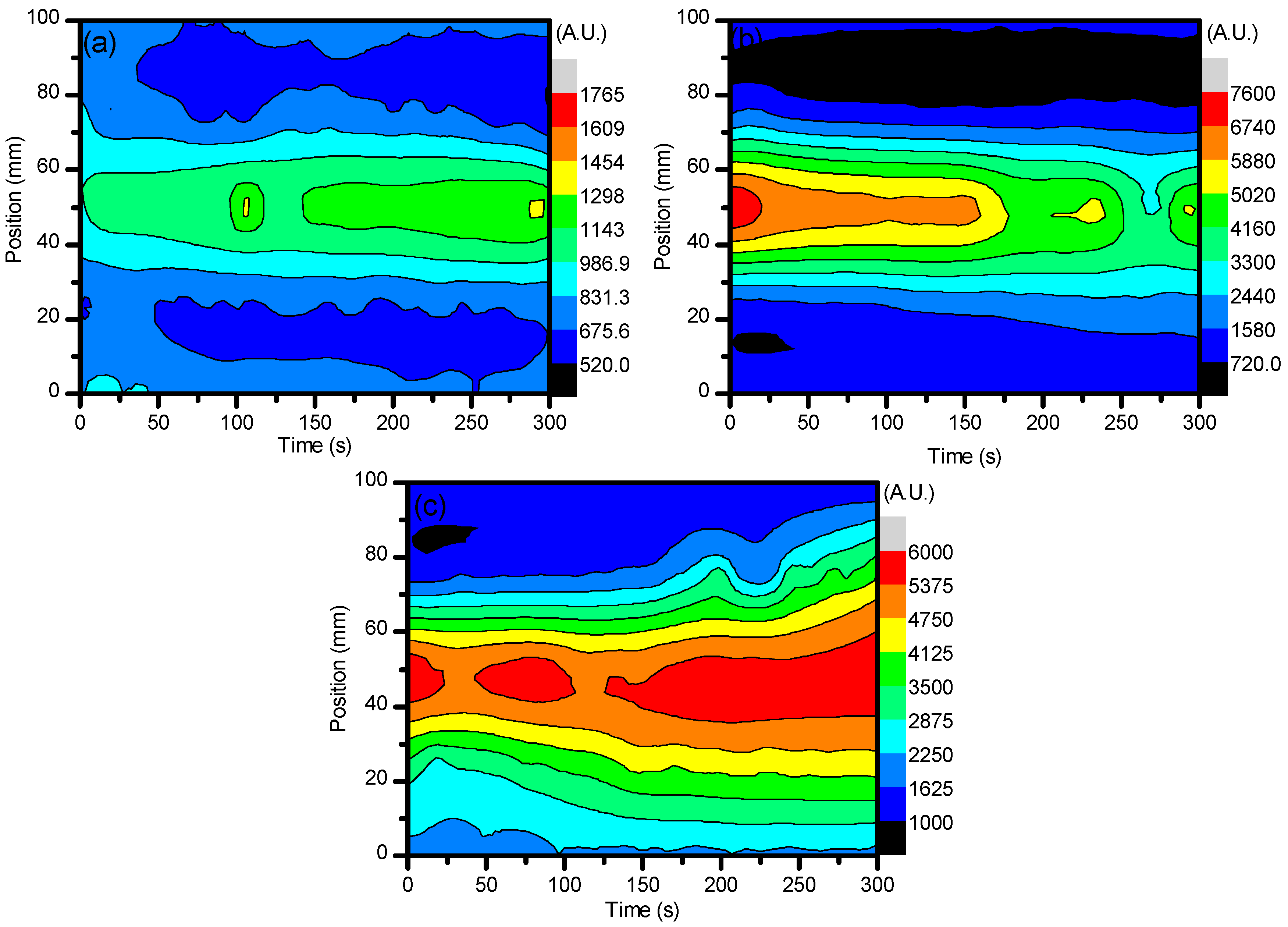
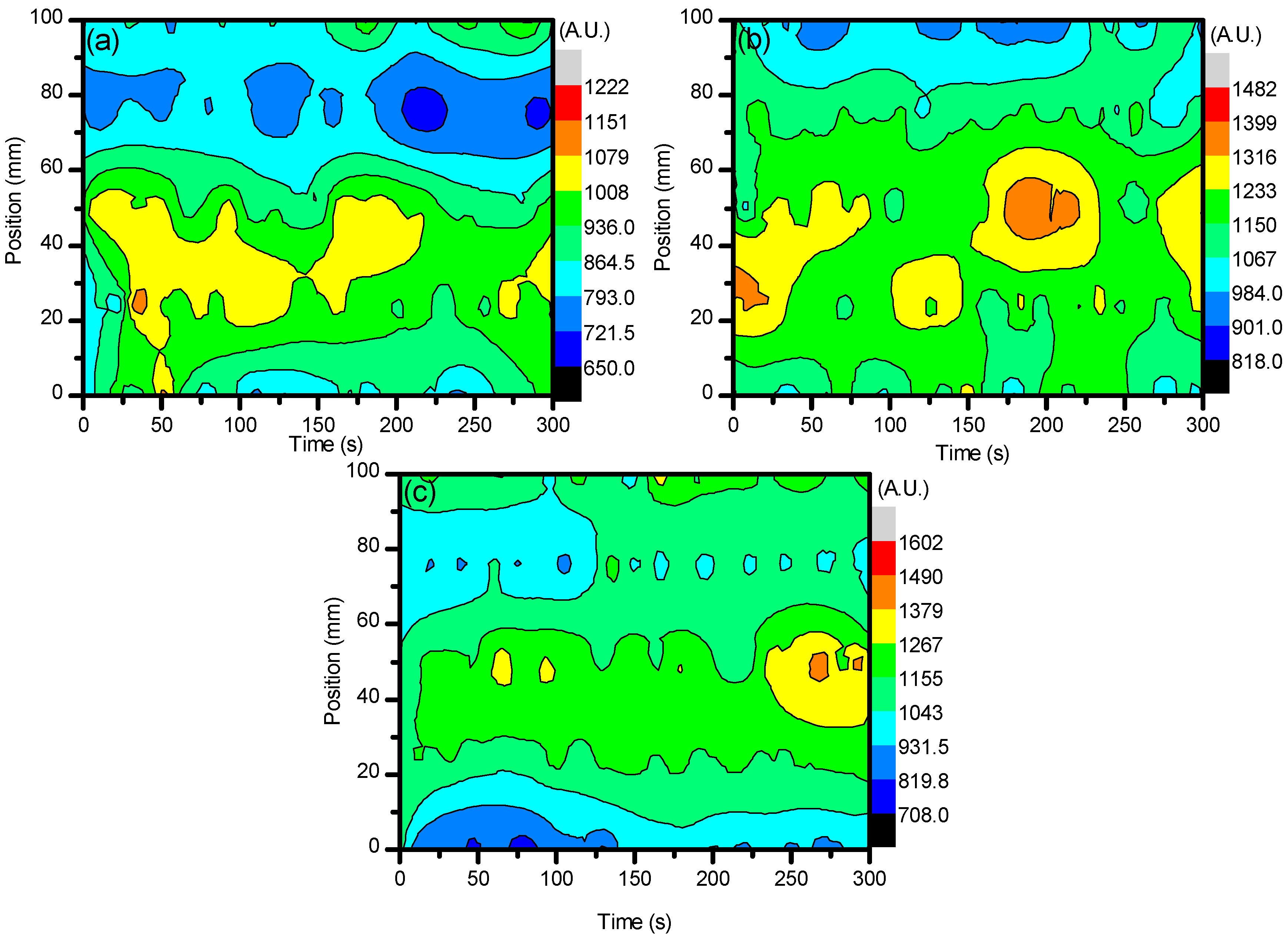
2. Results and Discussion
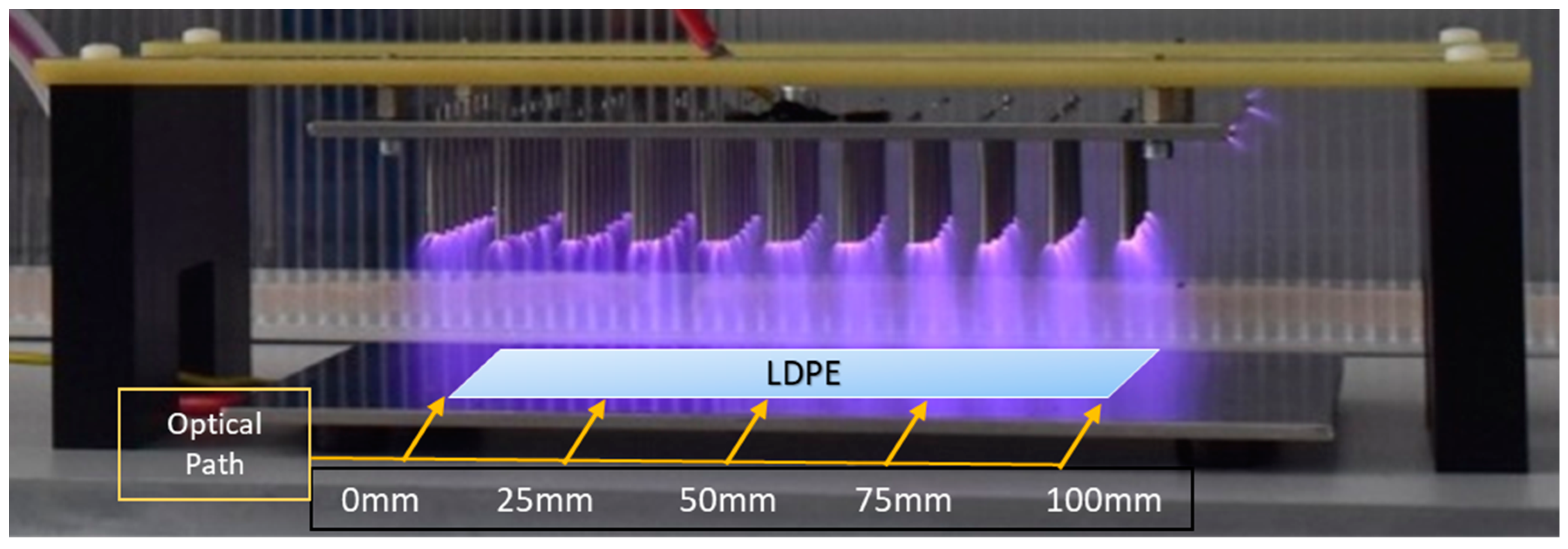
2.1. Optical Diagnostics
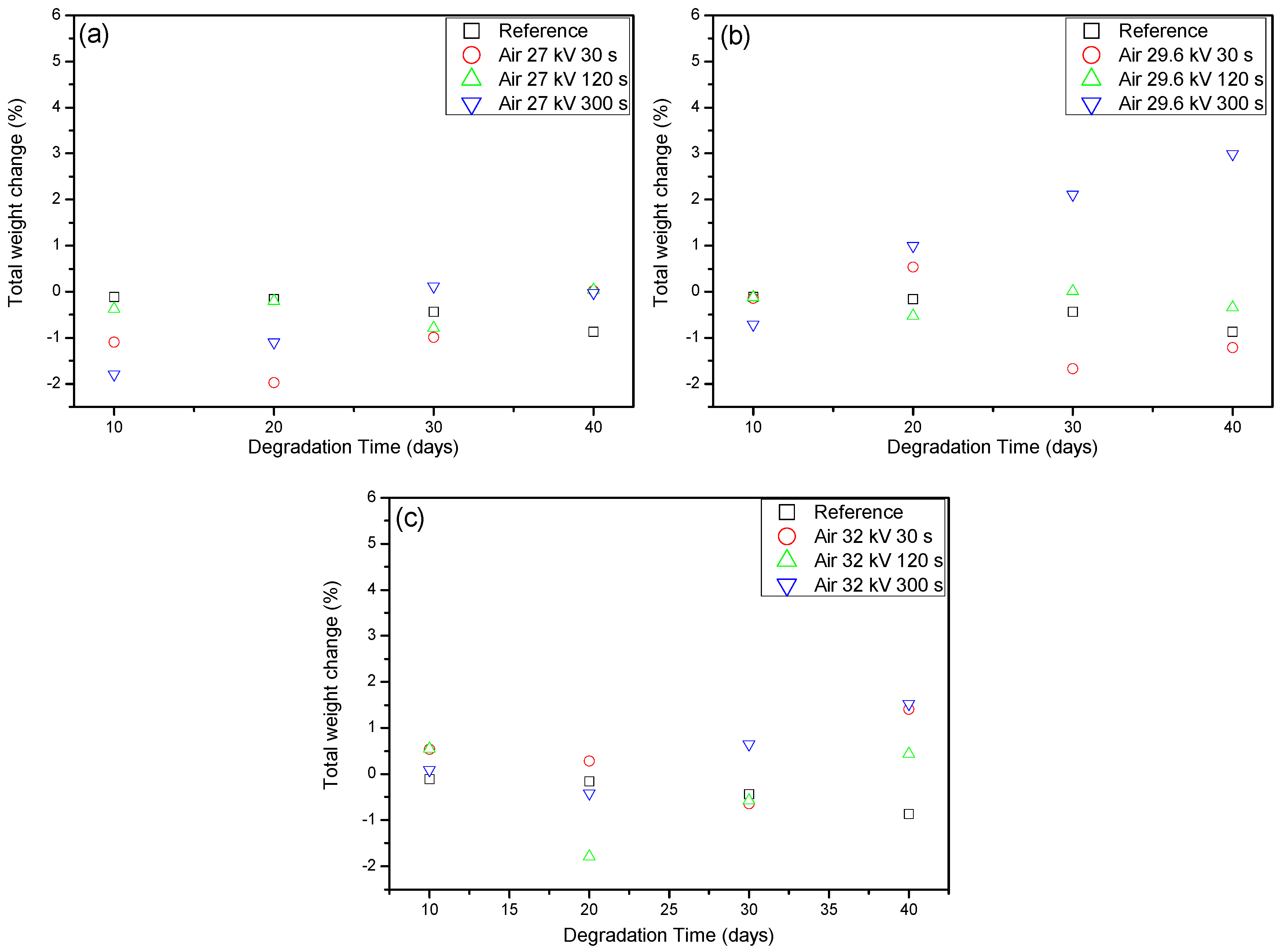
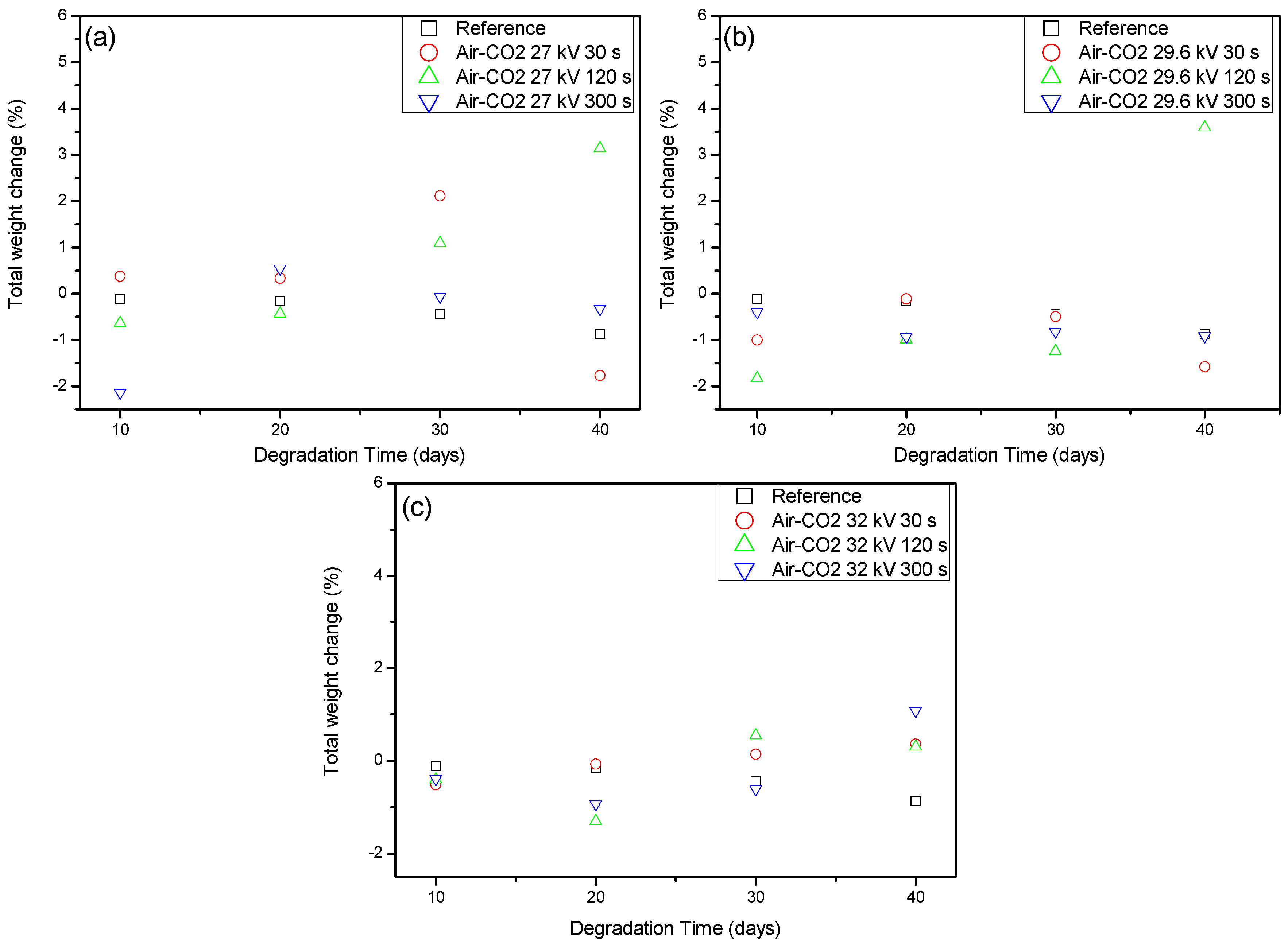
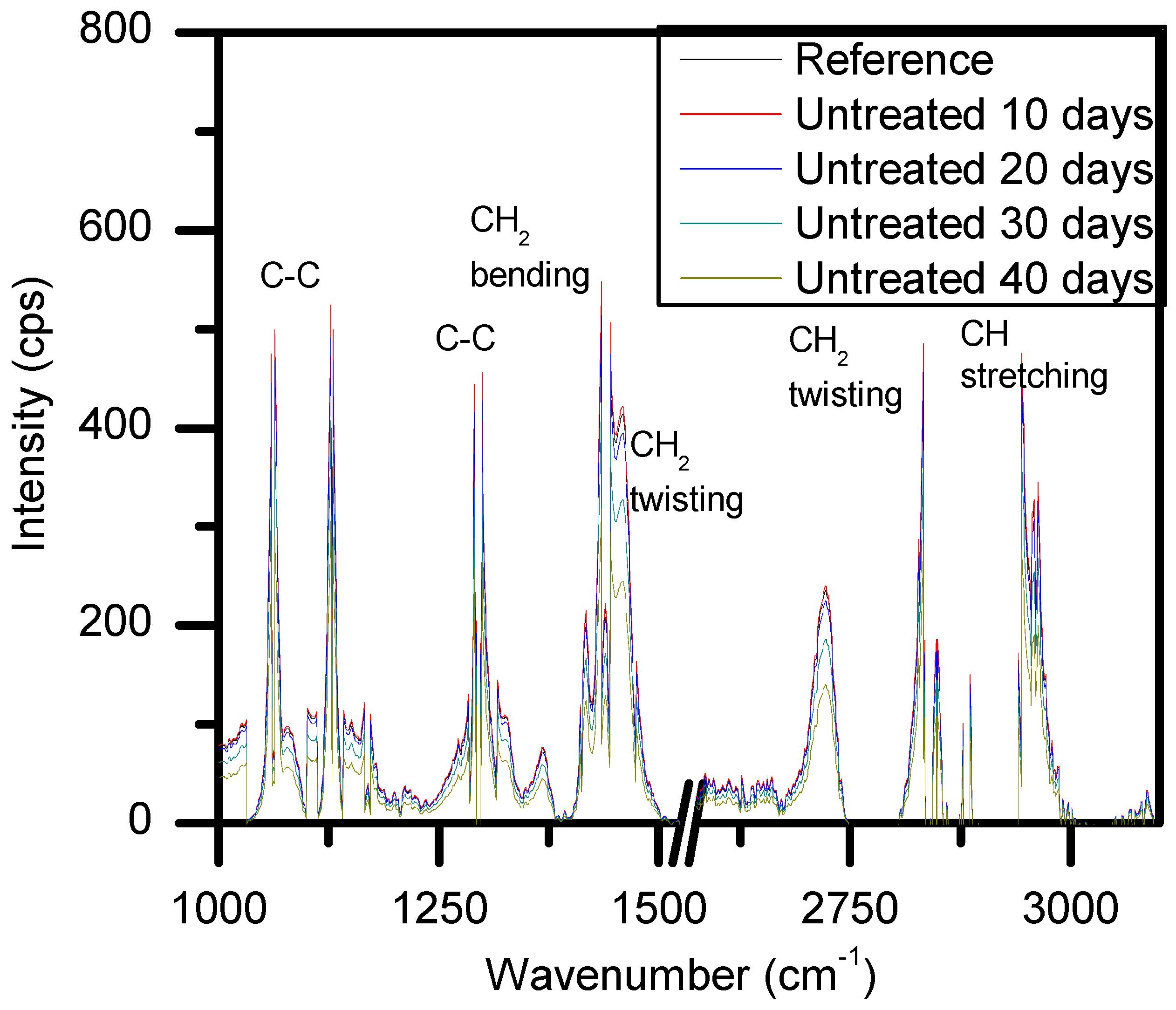
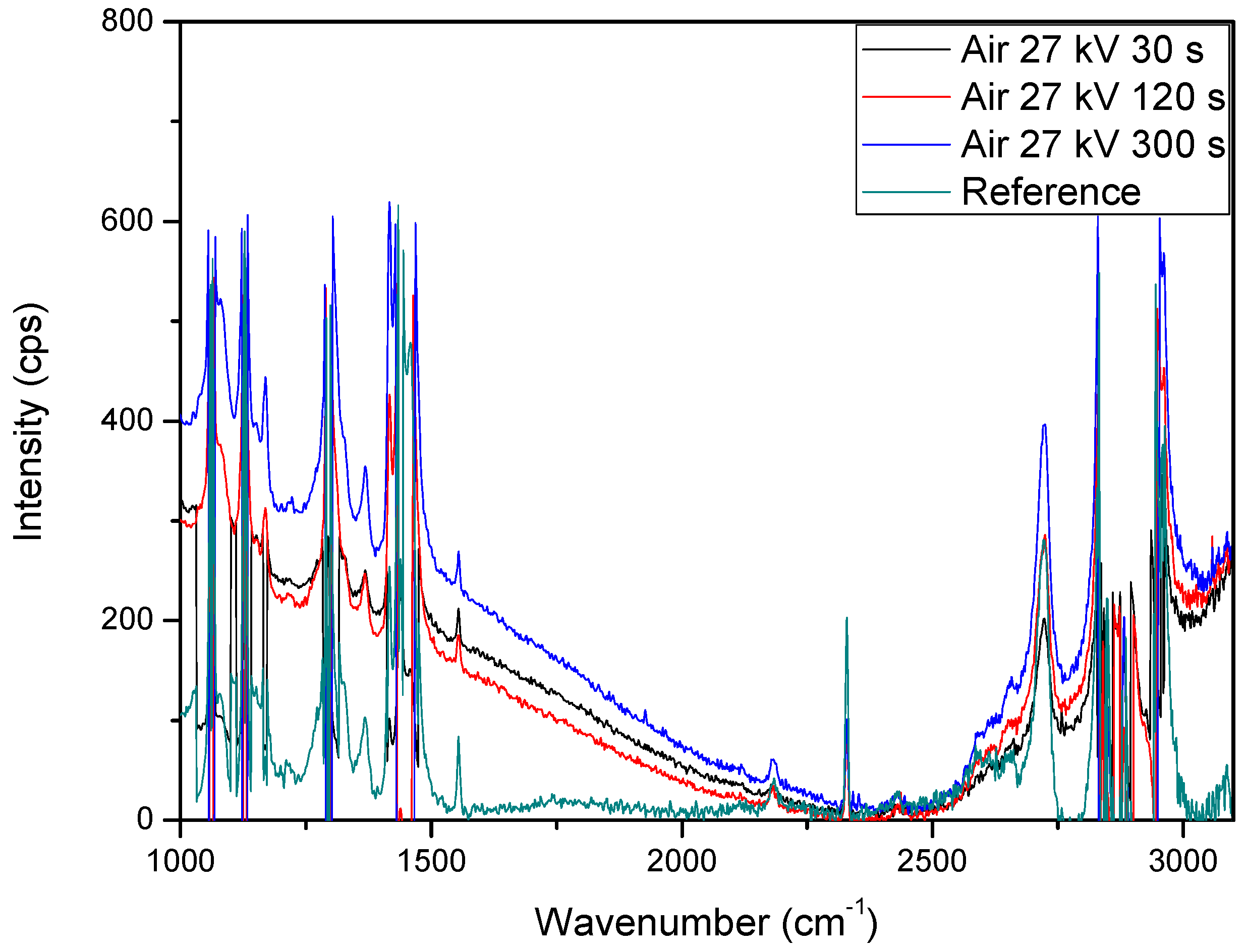
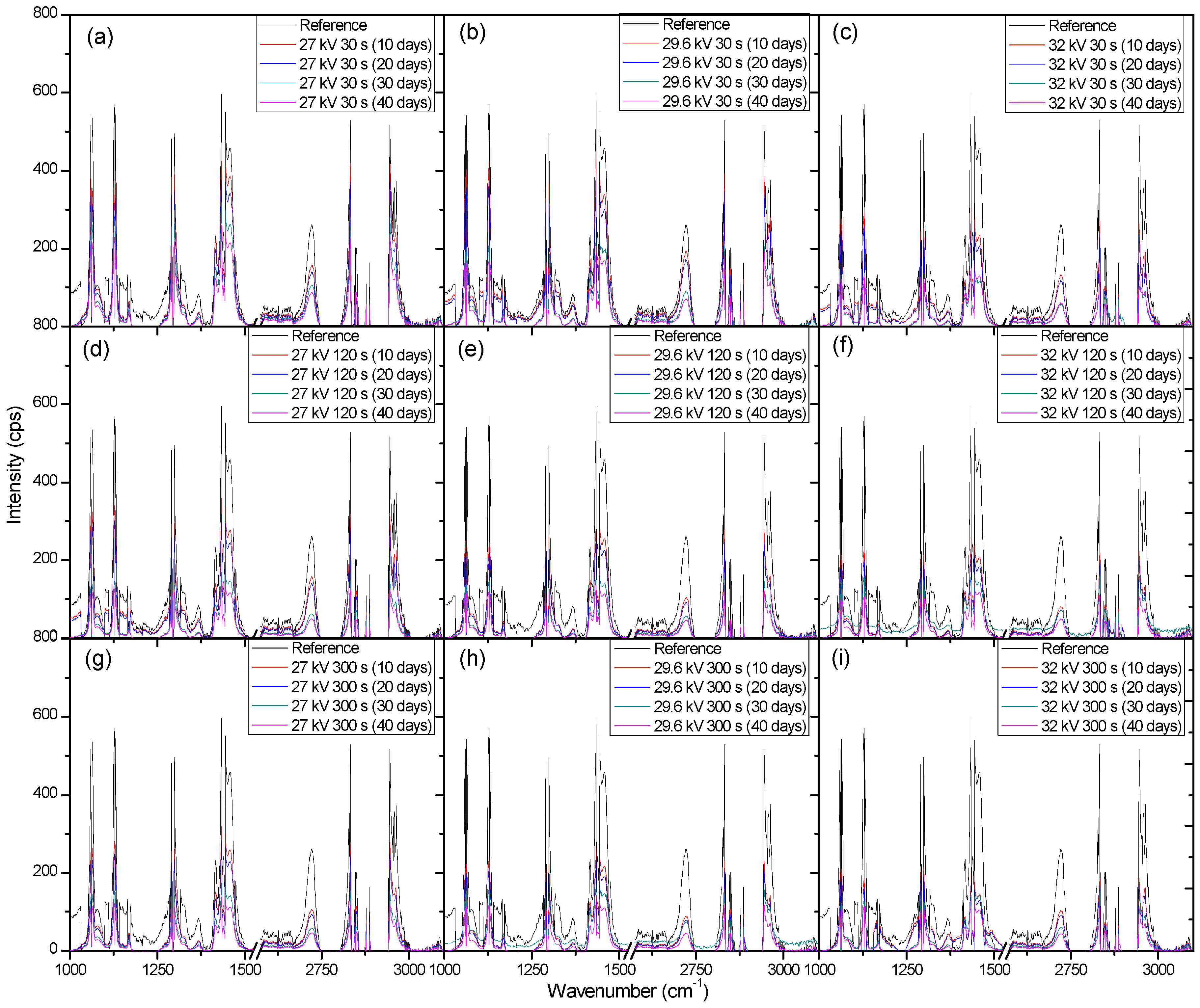
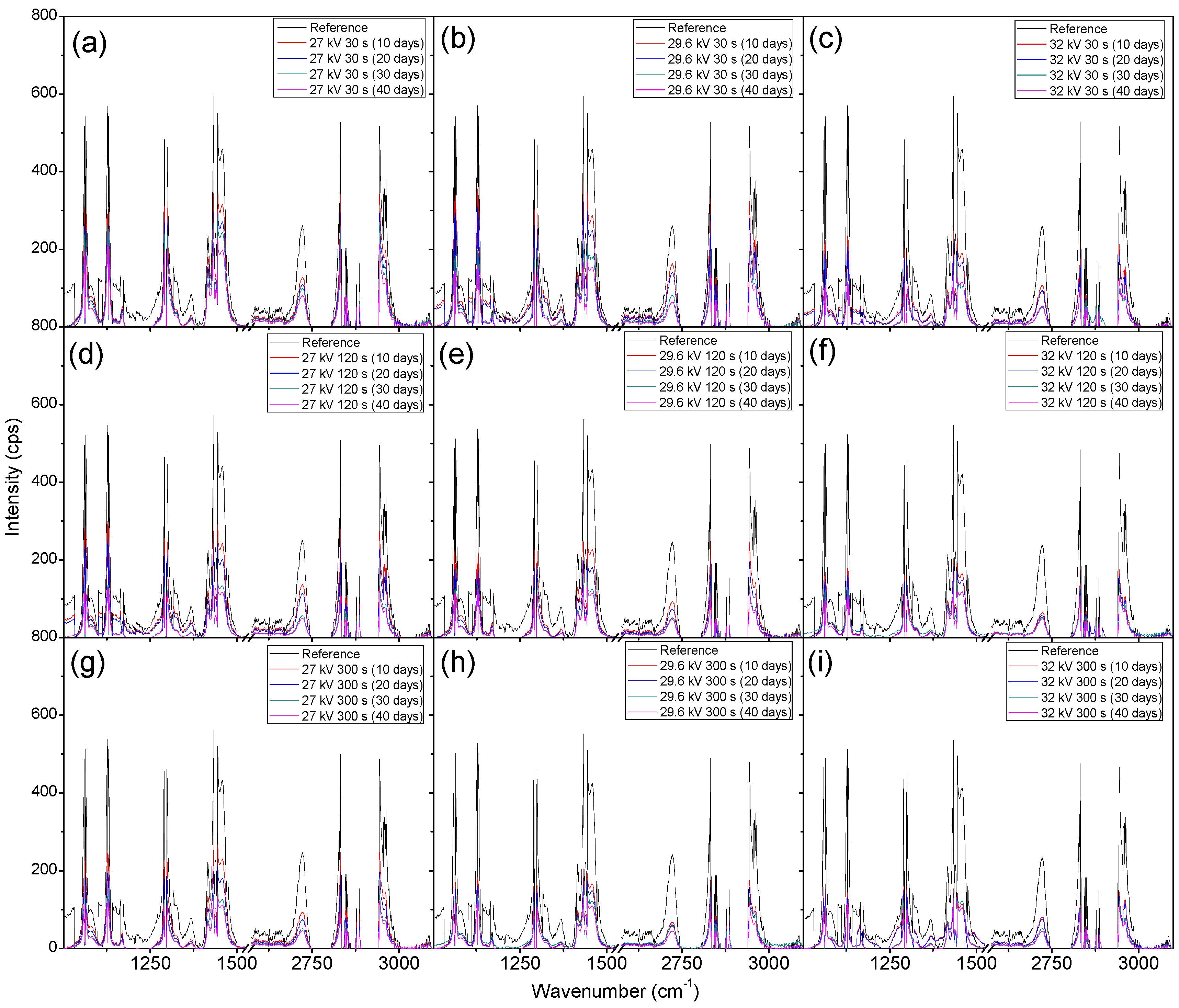
2.2. Weight Loss and Raman Spectroscopy
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment
3.2. LDPE Sterilization and Bacterial Broth
3.3. Optical Emission and Absorption
3.4. Raman Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and Societal Benefits of Plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, E.J.; Halden, R.U. Plastics and Environmental Health: The Road Ahead. Rev. Environ. Health 2013, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.A. Microbial, Weather, and Chemical Resistance of Polymeric Materials. In Selection of Polymeric Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is Rapidly Accumulating Plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic Debris in Seafood: Plastic Debris and Fibers from Textiles in Fish and Bivalves Sold for Human Consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haward, M. Plastic Pollution of the World’s Seas and Oceans as a Contemporary Challenge in Ocean Governance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rillig, M.C. Microplastic in Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Soil? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6453–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, N.; Kono, Y.; Oya, M.; Sakai, W.; Nagata, M. Recent Development of Biodegradable Network Polyesters Obtained from Renewable Natural Resources. Clean Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, S. Durability of Starch Based Biodegradable Plastics Reinforced with Manila Hemp Fibres. Materials 2011, 4, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological Degradation of Plastics: A Comprehensive Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodros, E.; Pillin, I.; Montrelay, N.; Baley, C. Could Biopolymers Reinforced by Randomly Scattered Flax Fiber be Used in Structural Applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Balestri, E.; Mallegni, N.; Stefanelli, E.; Rossi, A.; Lardicci, C.; Lazzeri, A. Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments. Materials 2018, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, A.; Pourbabaee, A.A.; Alikhani, H.A.; Shabani, F.; Esmaeili, E. Biodegradation of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) by Mixed Culture of Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus and Aspergillus niger in Soil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo-Flórez, J.M.; Bassi, A.; Thompson, M.R. Microbial Degradation and Deterioration of Polyethylene—A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 88, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciari, I.; Quatrini, P.; Zirletta, G.; Mincione, E.; Vinciguerra, V.; Lupattelli, P.; Giovannozzi Sermanni, G. Isotactic Polypropylene Biodegradation by a Microbial Community: Physicochemical Characterization of Metabolites Produced. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3695–3700. [Google Scholar]
- Fatimah, A. Biodegradation of Synthetic and Natural Plastic by Microorganisms. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, I.C.; Memetea, L.; Cole, W.J. A Study of the Products of PVC Thermal Degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 49, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P.; Ugwu, C.U.; Aiba, S. Biodegradability of Plastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3722–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers as Orthopedic Devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappitelli, F.; Sorlini, C. Microorganisms Attack Synthetic Polymers in Items Representing Our Cultural Heritage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, N.; Yau, J.Y.; Loushine, R.J.; Armstrong, S.R.; Weller, R.N.; King, N.M.; Pashley, D.H.; Tay, F.R. Susceptibility of a Polycaprolactone-Based Root Canal-Filling Material to Degradation. III. Turbidimetric Evaluation of Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, A. New Perspectives in Plastic Biodegradation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, M.; Girdhar, A.; Tiwari, A.; Nayarisseri, A. Implications of a Novel Pseudomonas Species on Low Density Polyethylene Biodegradation: An in vitro to in silico Approach. SpringerPlus 2014, 1, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Na, J. Study on Preparation Process and Properties of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 312, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A Bacterium that Degrades and Assimilates Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmet, T.; Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Leys, C.; Schacht, E.; Dubruel, P. Nonthermal Plasma Technology as a Versatile Strategy for Polymeric Biomaterials Surface Modification: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2009, 9, 2351–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerapandian, S.; Leys, C.; De Geyter, N.; Morent, R. Abatement of VOCs Using Packed Bed Non-Thermal Plasma Reactors: A Review. Catalysts 2017, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.S.; Li, H.Q.; He, J.C.; Ye, Q.H.; Huang, Q.R.; Luo, Y.W. Removal of dimethyl sulfide by the combination of non-thermal plasma and biological process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobslaw, D.; Schulz, A.; Helbich, S.; Dobslaw, C.; Engesser, K.-H. VOC Removal and Odor Abatement by a Low-Cost Plasma Enhanced Biotrickling Filter Process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 5501–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Li, J.; Liao, D.; Tu, X.; Xu, M.; Sun, G. Performance of a Combined System of Biotrickling Filter and Photocatalytic Reactor in Treating Waste Gases from a Paint Manufacturing Plant. Environ. Technol. 2015, 2, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runye, Z.; Christian, K.; Zhuowei, C.; Lichao, L.; Jianming, Y.; Jianmeng, C. Styrene Removal in a Biotrickling Filter and a Combined UV–Biotrickling Filter: Steady- and Transient-State Performance and Microbial Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xi, J.-Y.; Hu, H.-Y.; Yao, Y. Advantages of Combined UV Photodegradation and Biofiltration Processes to Treat Gaseous Chlorobenzene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribedi, P.; Sil, A.K. Low-density Polyethylene Degradation by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertsson, A.C. The Shape of the Biodegradation Curve for Low and High Density Polyethylene in Prolonged Series of Experiments. Eur. Polym. J. 1980, 16, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scally, L.; Lalor, J.; Gulan, M.; Cullen, P.J.; Milosavljević, V. Spectroscopic Study of Excited Molecular Nitrogen Generation Due to Interactions of Metastable Noble Gas Atoms. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, e1800018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, V.; Cullen, P.J. Spectroscopic Investigation of a Dielectric Barrier Discharge in Modified Atmosphere Packaging. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 80, 20801–20816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scally, L.; Lalor, J.; Cullen, P.J.; Milosavljević, V. Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Nonequilibrium Plasma Discharge on Polymer Surface Metrology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2017, 35, 03E105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, B.M.; Champakalakshmi, R.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Lim, C.S.; Sakharkar, K.R. Biodegradation of Low Density Polythene (LDPE) by Pseudomonas Species. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajendiran, A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Abraham, J. Microbial Degradation of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) by Aspergillus Clavatus Strain JASKI from Landfill Soil. Biotech 2016, 6, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Milosavljević, V.; Donegan, M.; Cullen, P.; Dowling, D. Diagnostics of an O2-He RF Atmospheric Plasma Discharge by Spectral Emission. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 83, 014501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Polymer | Uses | Structure | Contribution to Plastic Pollution % | Means of Degradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low/no biodegradability | ||||
| PET | Clothing fibers, food and liquid containers, engineering resins. | [C10H9O4]n | 12.8 | UV exposure, thermal oxidation, Ideonella sakaiensis. |
| LDPE | Lab equipment, plastic bags, food packaging. | [C2H4]n | 23.9 | UV exposure, oxidising solvents, Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus, Pseudomonas, and Aspergillus niger |
| HDPE | Plastic bottles, food containers, corrosion protectors, 3-D printing filament. | [C2H4]n | 17.6 | UV exposure, oxidative solvents, hydrolysis. |
| PP | Dielectric sheets, medical implantations, piping systems, hinges. | [C3H6]n | 24.3 | UV exposure, microbial communities mixed with starch. |
| PVC | Electrical cables, flooring, window insulation. | [C2H3Cl]n | 2.9 | UV exposure, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Lentinus tigrinus, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus sydowi |
| Biodegradable | ||||
| PLA | Medical implants, packaging material, injection molding. | [C3H4O2]n | Amycolatopsis and Saccharotrix. | |
| PGA | Medical suture, food packaging, tissue engineering. | [C2H2O2]n | Hydrolysis. | |
| PVA | Wood glue, nonwoven binder, primer, adhesive. | [C4H6O2]n | Filamentous fungi, bacterial, fungal species, algae. | |
| PCL | Tissue repair scaffold, targeted drug delivery, dentistry, herbicide containers. | [C6H10O2]n | Penicillium and Aspergillus. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scally, L.; Gulan, M.; Weigang, L.; Cullen, P.J.; Milosavljevic, V. Significance of a Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment on LDPE Biodegradation with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Materials 2018, 11, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101925
Scally L, Gulan M, Weigang L, Cullen PJ, Milosavljevic V. Significance of a Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment on LDPE Biodegradation with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Materials. 2018; 11(10):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101925
Chicago/Turabian StyleScally, Laurence, Miroslav Gulan, Lars Weigang, Patrick J. Cullen, and Vladimir Milosavljevic. 2018. "Significance of a Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment on LDPE Biodegradation with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa" Materials 11, no. 10: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101925




