Laser Indirect Shock Welding of Fine Wire to Metal Sheet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
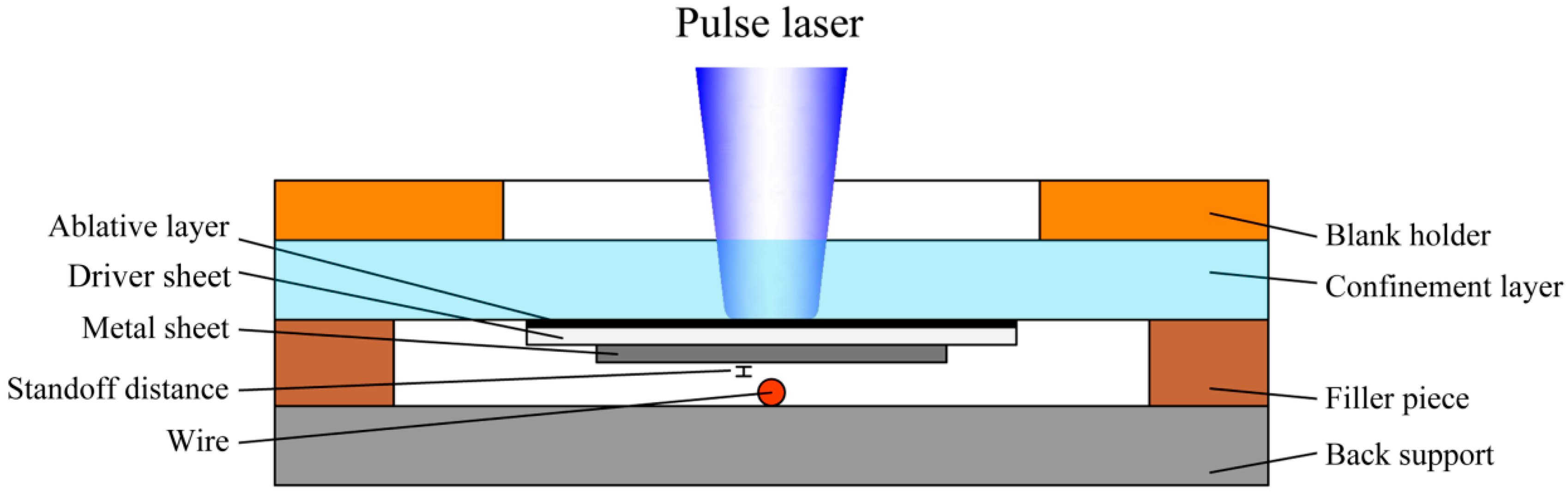
2. Mechanism of Laser Indirect Shock Welding
3. Experimental Preparation and Equipment
3.1. Experimental Preparation
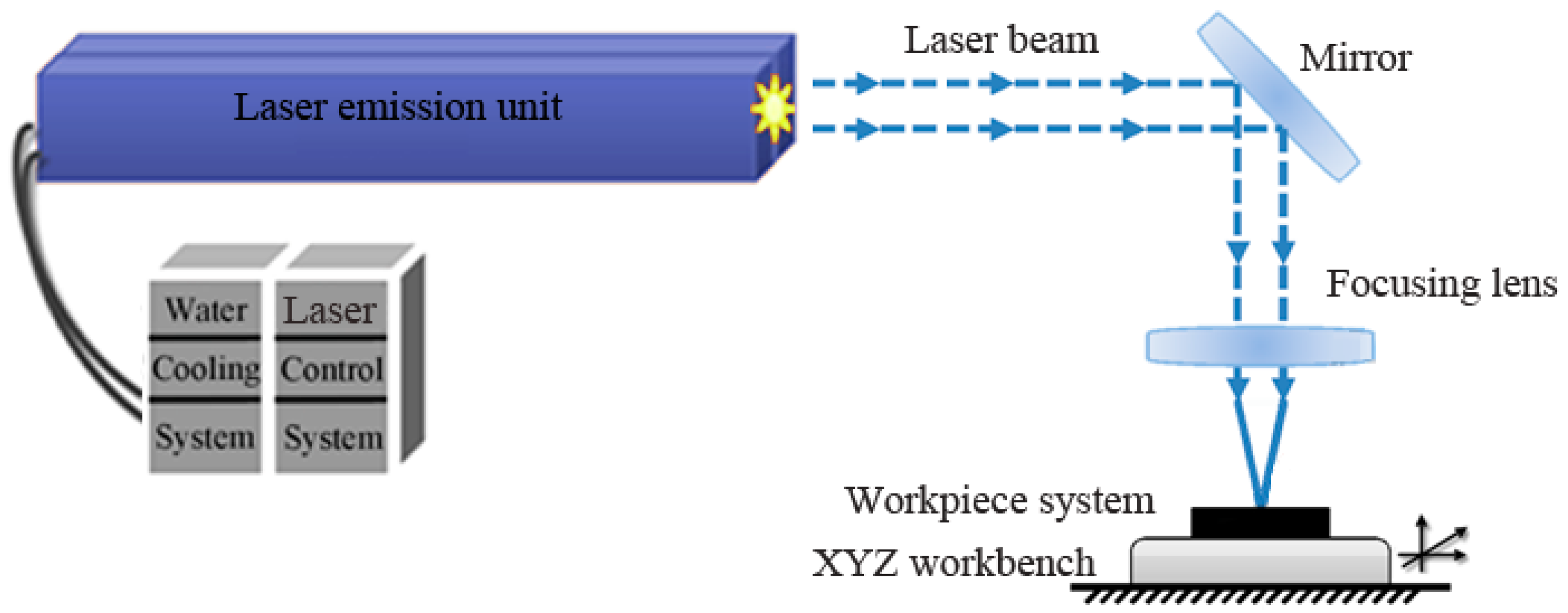
3.2. Experimental Equipment
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
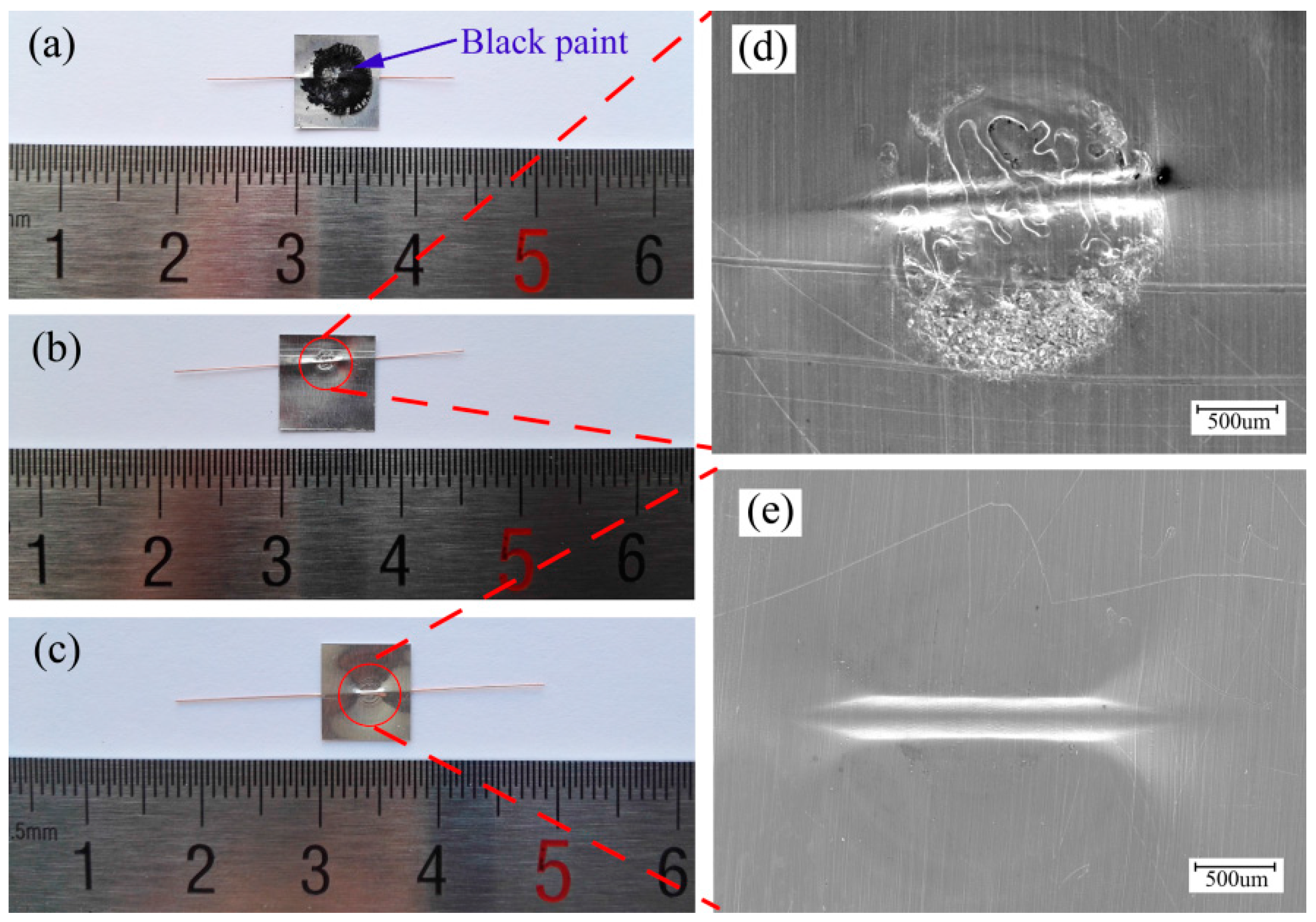
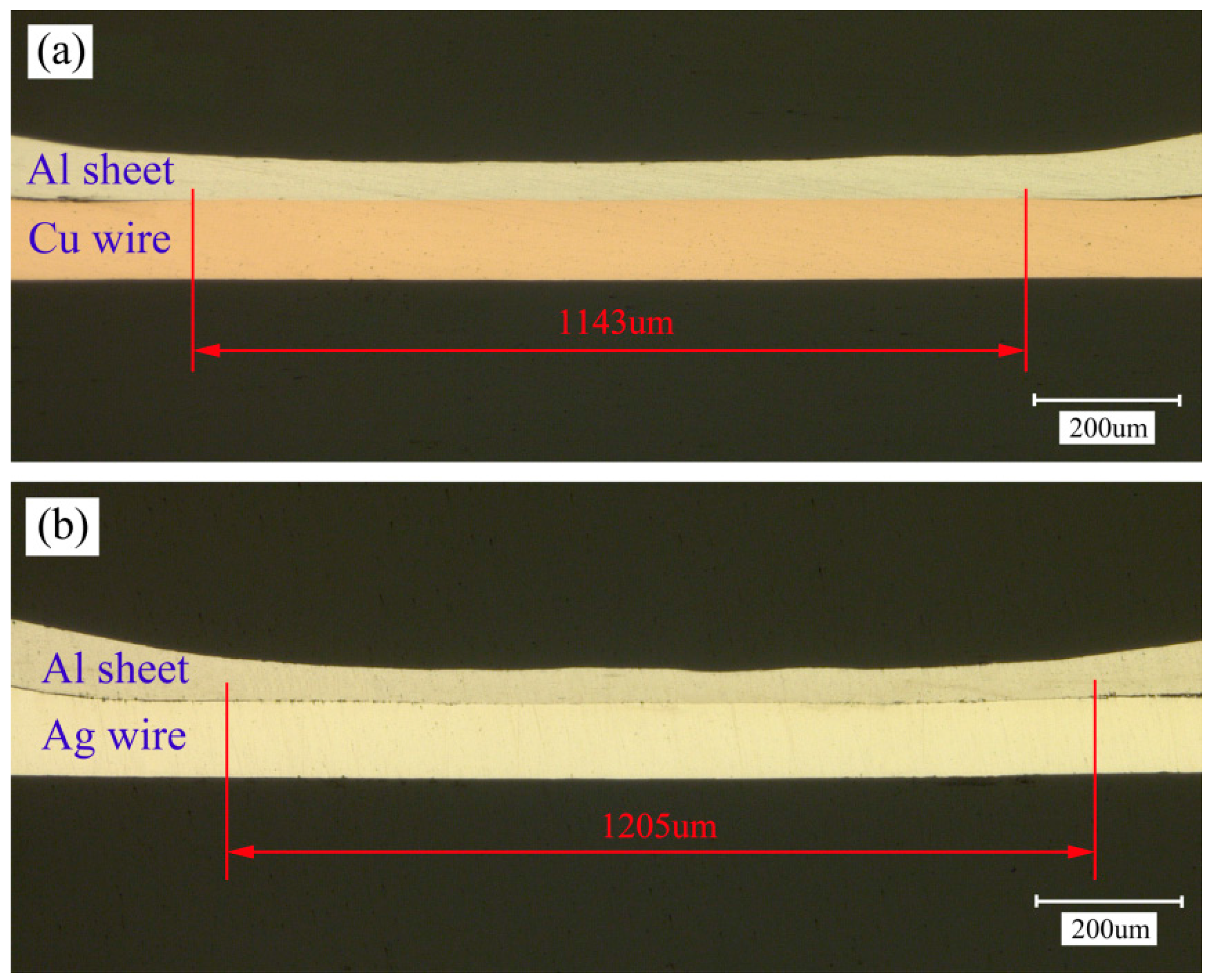
4.1. Morphology of Welding Examples
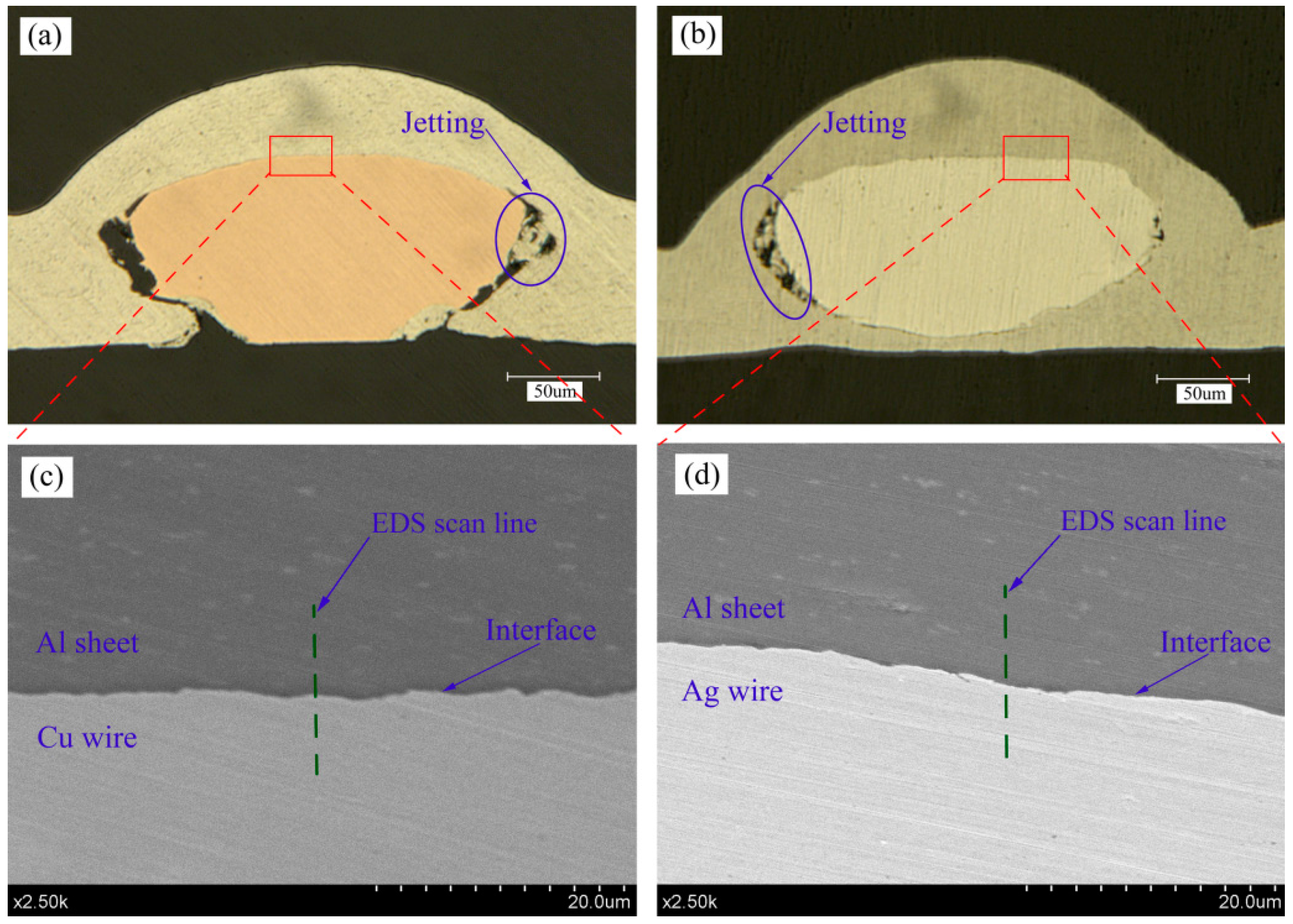
4.2. Welding Interface
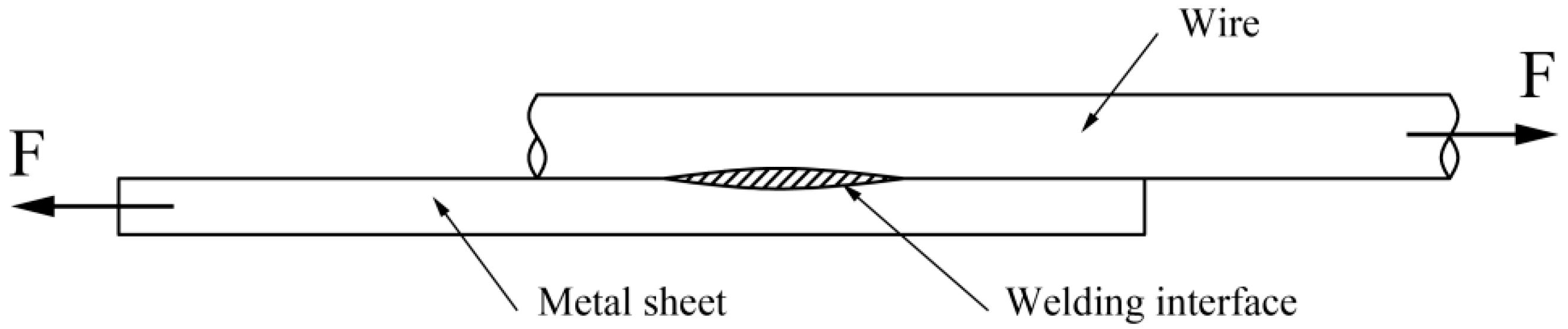
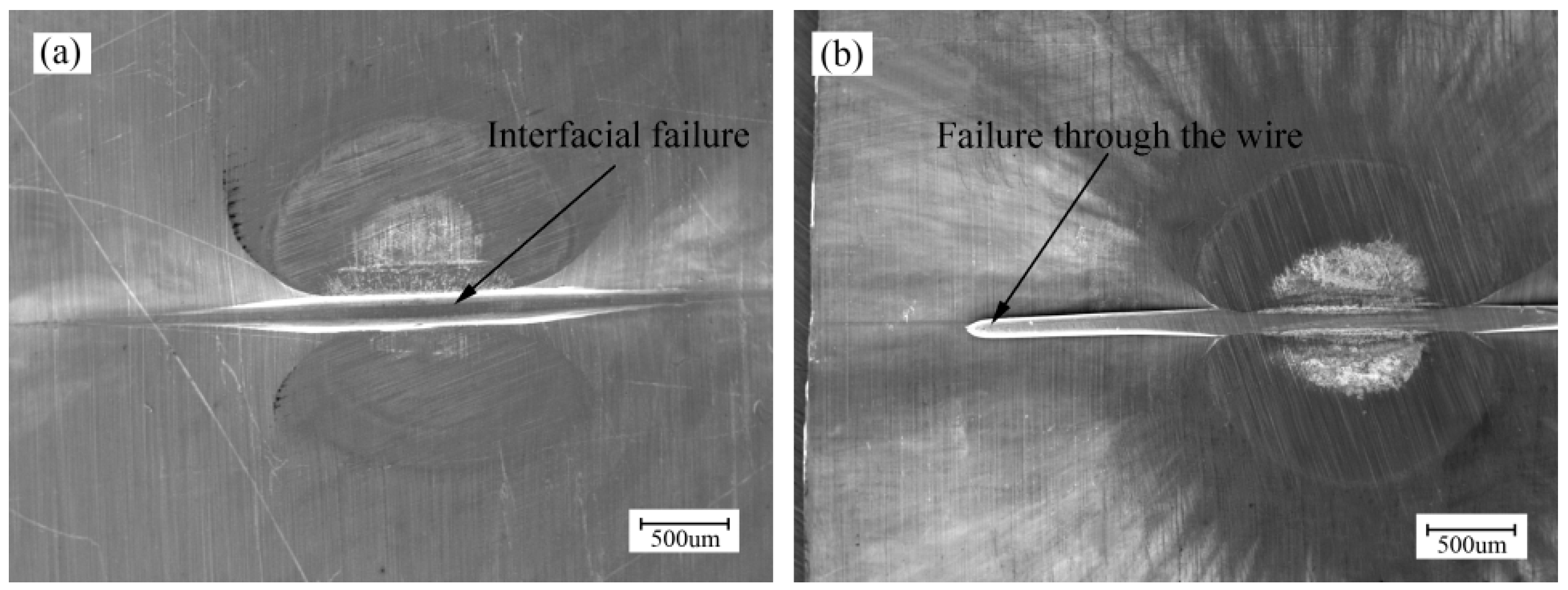
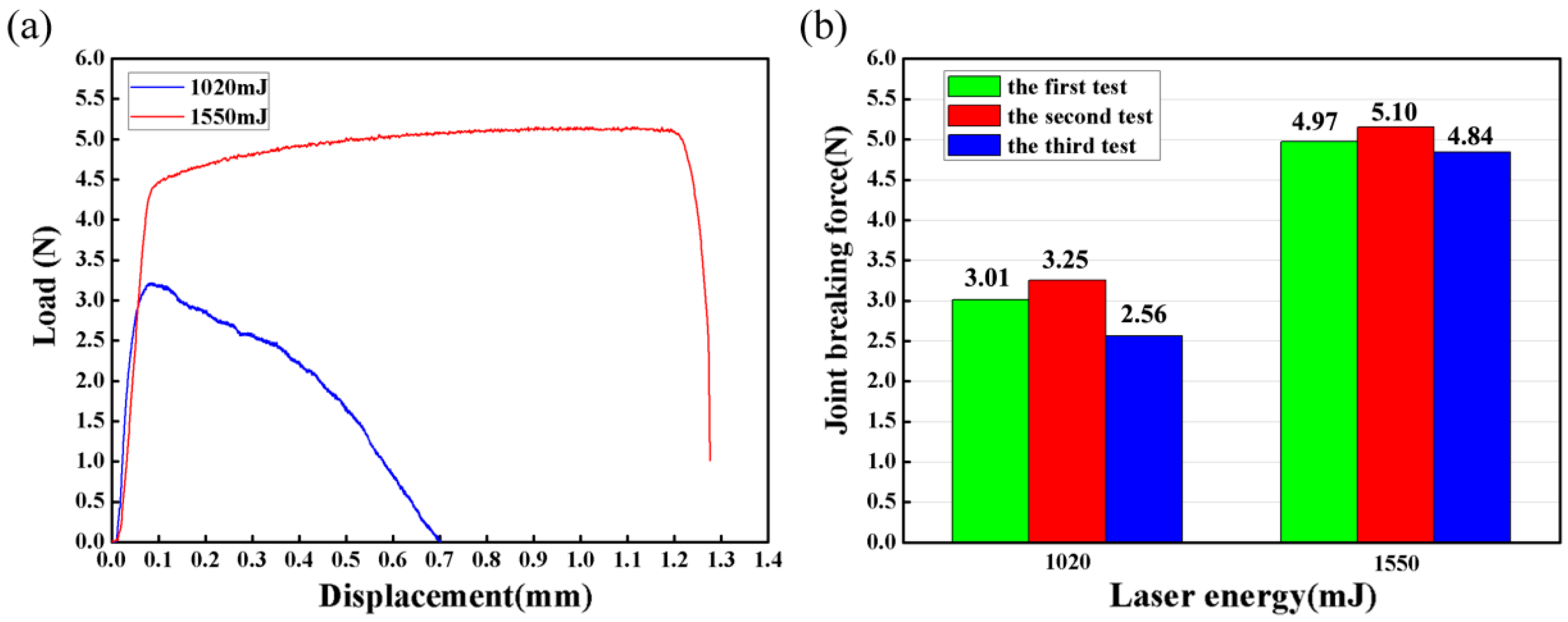
4.3. Tensile Shear Test
4.4. Microhardness Variation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cu wire and Ag wire were successfully welded to Al sheets by LISW. High surface quality was obtained with the use of driver sheet in comparison to focusing the laser beam directly on Al sheet.
- (2)
- With the increase of laser pulse energy, the bonding area of sheet/wire increased. The bottom of the Ag wire can also be welded to the Al sheet due to the good plasticity of the Ag wire. Jetting was observed and was essential for the shock welding between wire and metal sheet. The welding interfaces are nearly flat and the waves are small. According to the EDS analysis, the intermetallic phases are absent and a short element diffusion layer emerges at the sheet/wire welding interface.
- (3)
- There were two failure modes in the tensile shear tests. Samples welded by 1020 mJ failed through the interface and samples welded by 1550 mJ failed through the wire. According to the load-displacement curves, failure through the wire indicates adequately stronger bonds than failure through the interface.
- (4)
- As the distance to the welding interface decreases, the microhardness increases gradually. The microhardness measured near the interface was obviously increased owing to the heavy plastic deformation, cold quenching, and microstructure evolution. In addition, the sudden shock of the laser can also contribute to the increase of microhardness on the surface of Al sheet.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friis, K.S.; Khan, M.I. Resistance microwelding of 316L stainless steel wire to block. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Joint formation mechanism and strength in resistance microwelding of 316L stainless steel to Pt wire. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 5756–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, B.; Guo, Z. Mechanism of resistance microwelding of insulated copper wire to phosphor bronze sheet. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.A.; Uhm, C.; Kwon, T.J. Reliability study of low cost alternative Ag bonding wire with various bond pad materials. In Proceedings of the 11th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, Singapore, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, W. Laser micro-welding of Cu-Al dissimilar metals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, A.S.; Black, T.J.; Crossland, B. The mechanics of wave formation in explosive welding. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. A 1967, 296, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, A. Principles and Practices of Explosive Metalworking; Industrial Newspapers Ltd.: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, T.A.; Elmer, J.W. Development of an explosive welding process for producing high-strength welds between niobium and 6061-T651 aluminum. Weld. J. 2006, 85, 252. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Artzy, A.; Stern, A. Interface phenomena in aluminium-magnesium magnetic pulse welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2008, 13, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Babu, S.S. Application of high velocity impact welding at varied different length scales. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülenç, B.; Kaya, Y. Production of wire reinforced composite materials through explosive welding. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, J. Experimental and numerical study on the ballistic resistance of steel-fibre reinforced two-layer explosively welded plates. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Babu, S.; Daehn, G.S. Impact welding in a variety of geometric configurations. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on High Speed Forming, Columbus, OH, USA, 9–10 March 2010; pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daehn, G.S.; Lippold, J.C. Low Temperature Spot Impact Welding Driven without Contact. U.S. Patent PCT/US09/36299, 11 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Vivek, A. Laser impact welding application in joining aluminum to titanium. J. Laser Appl. 2016, 28, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, C. Laser shock welding of aluminum/aluminum and aluminum/copper plates. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y. An experimental and numerical study of laser impact spot welding. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, S. Investigation on a novel laser impact spot welding. Metals 2016, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, W. An experimental study determines the electrical contact resistance in resistance welding. Weld. J. 2005, 84, 73s–76s. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, A.A.A.; Al-Hassani, S.T.S. Numerical and experimental studies of the mechanism of the wavy interface formations in explosive/impact welding. J. Mech. Phys. Solid 2005, 53, 2501–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Y. Numerical study of the mechanism of explosive/impact welding using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapanathan, T.; Raoelison, R.N. Depiction of interfacial characteristic changes during impact welding using computational methods: Comparison between Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian and Eulerian simulations. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignon, F.; Benson, D. Explosive welding of aluminum to aluminum: Analysis, computations and experiments. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2004, 30, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Experimental and numerical investigation of laser shock synchronous welding and forming of Copper/Aluminum. Opt. Laser Eng. 2016, 86, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti/Al explosive cladding. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgutlu, A.; Okuyucu, H. Investigation of effect of the stand-off distance on interface characteristics of explosively welded copper and stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kumai, S. Interfacial microstructure and strength of steel/aluminum alloy lap joint fabricated by magnetic pressure seam welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 471, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Al | Mn | Si | Cu | Mg | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.2 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.4 |
| Cu | Bi | Sb | As | Fe | Pb | S | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.9 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| Ag | Cu | Bi | Fe | Pb | Sb | Pd | Se | Te |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.99 | 0.003 | 0.0008 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Material combinations | Al sheet/Cu wire, Al sheet/Ag wire |
| Sheet size (mm) | 8 × 8 × 0.1 |
| Diameter of wire (mm) | 0.15 |
| Standoff distance (mm) | 0.2 |
| Diameter of laser spot (mm) | 1.5 |
| Laser pulse energy (mJ) | 1020, 1200, 1380, 1550 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Pulse energy | 80–1800 mJ |
| Pulse Width | 8 ns |
| Wave Length | 1064 nm |
| Exit spot diameter | 9 mm |
| Energy Stability | <±1% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Luo, Y.; Liu, H. Laser Indirect Shock Welding of Fine Wire to Metal Sheet. Materials 2017, 10, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091070
Wang X, Huang T, Luo Y, Liu H. Laser Indirect Shock Welding of Fine Wire to Metal Sheet. Materials. 2017; 10(9):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091070
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Tao Huang, Yapeng Luo, and Huixia Liu. 2017. "Laser Indirect Shock Welding of Fine Wire to Metal Sheet" Materials 10, no. 9: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091070
APA StyleWang, X., Huang, T., Luo, Y., & Liu, H. (2017). Laser Indirect Shock Welding of Fine Wire to Metal Sheet. Materials, 10(9), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091070






