Influence of Polymer-Clay Interfacial Interactions on the Ignition Time of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
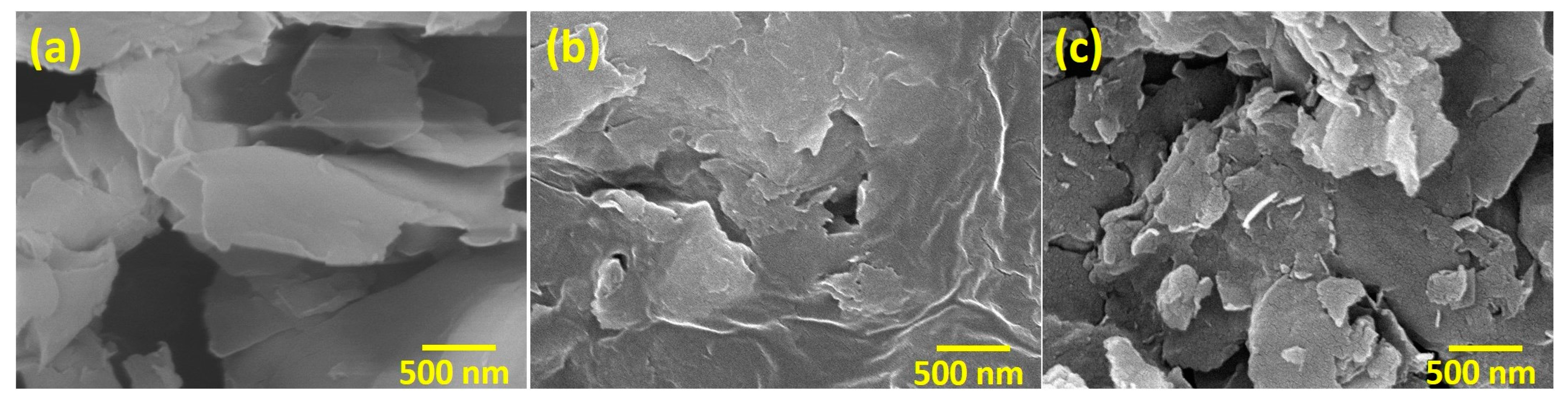
2.1. Analysis of Clay Coatings
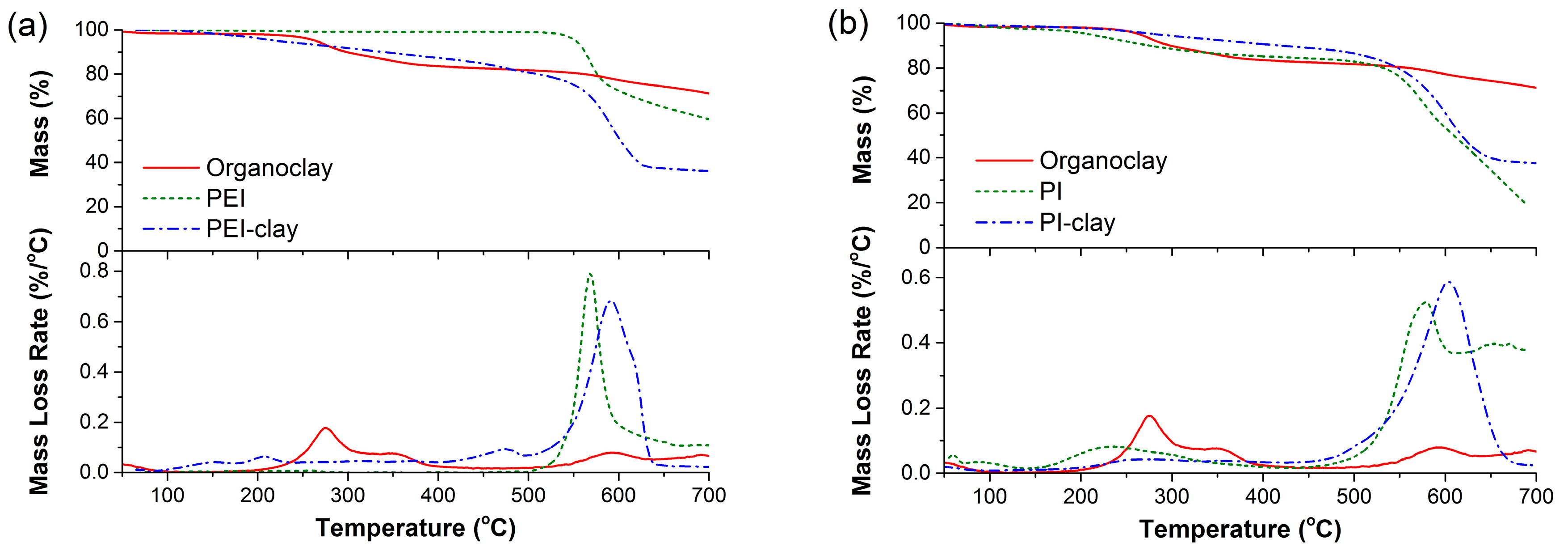
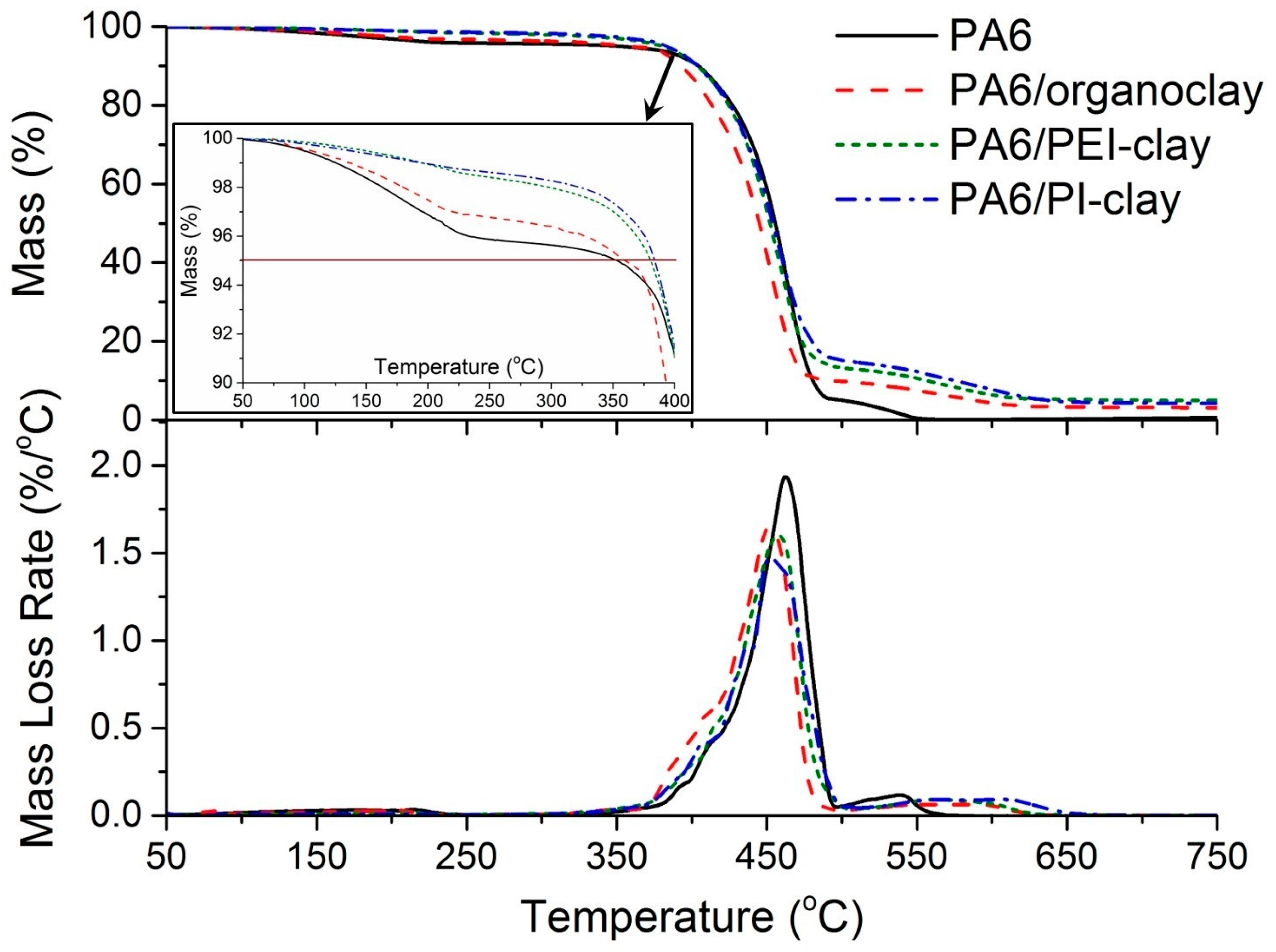
2.2. Thermal Decomposition Behavior of Coated Clays and Their PA6 Nanocomposites
2.3. Combustion Response of PA6 with Coated Clays
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
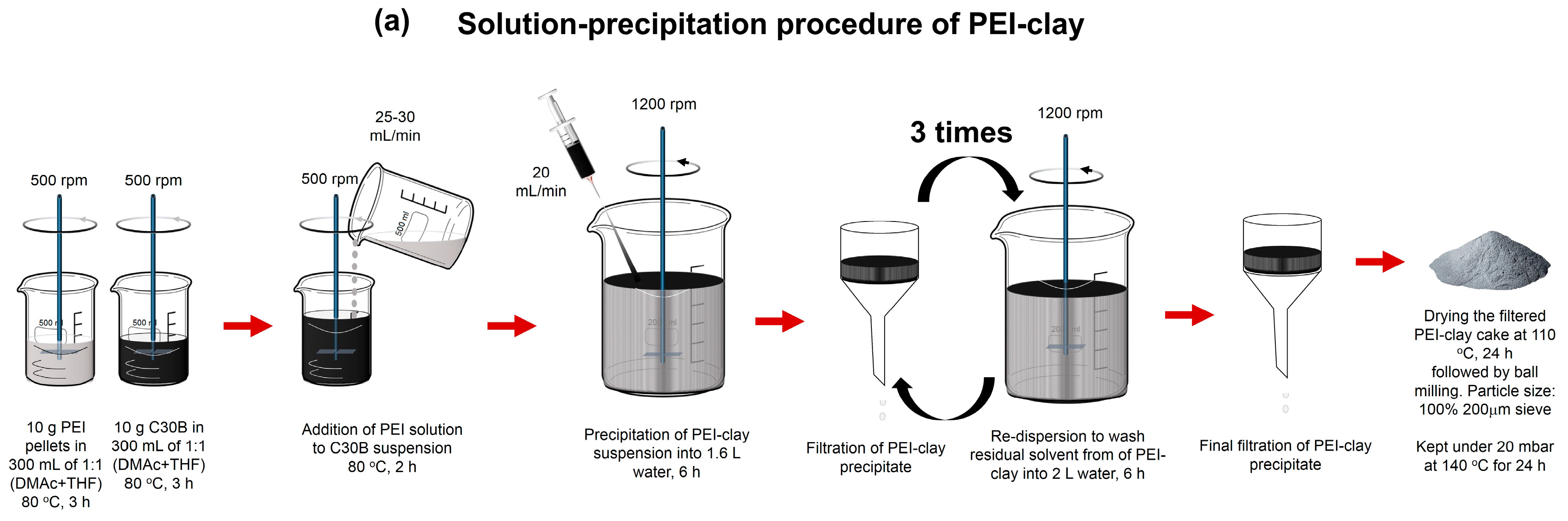
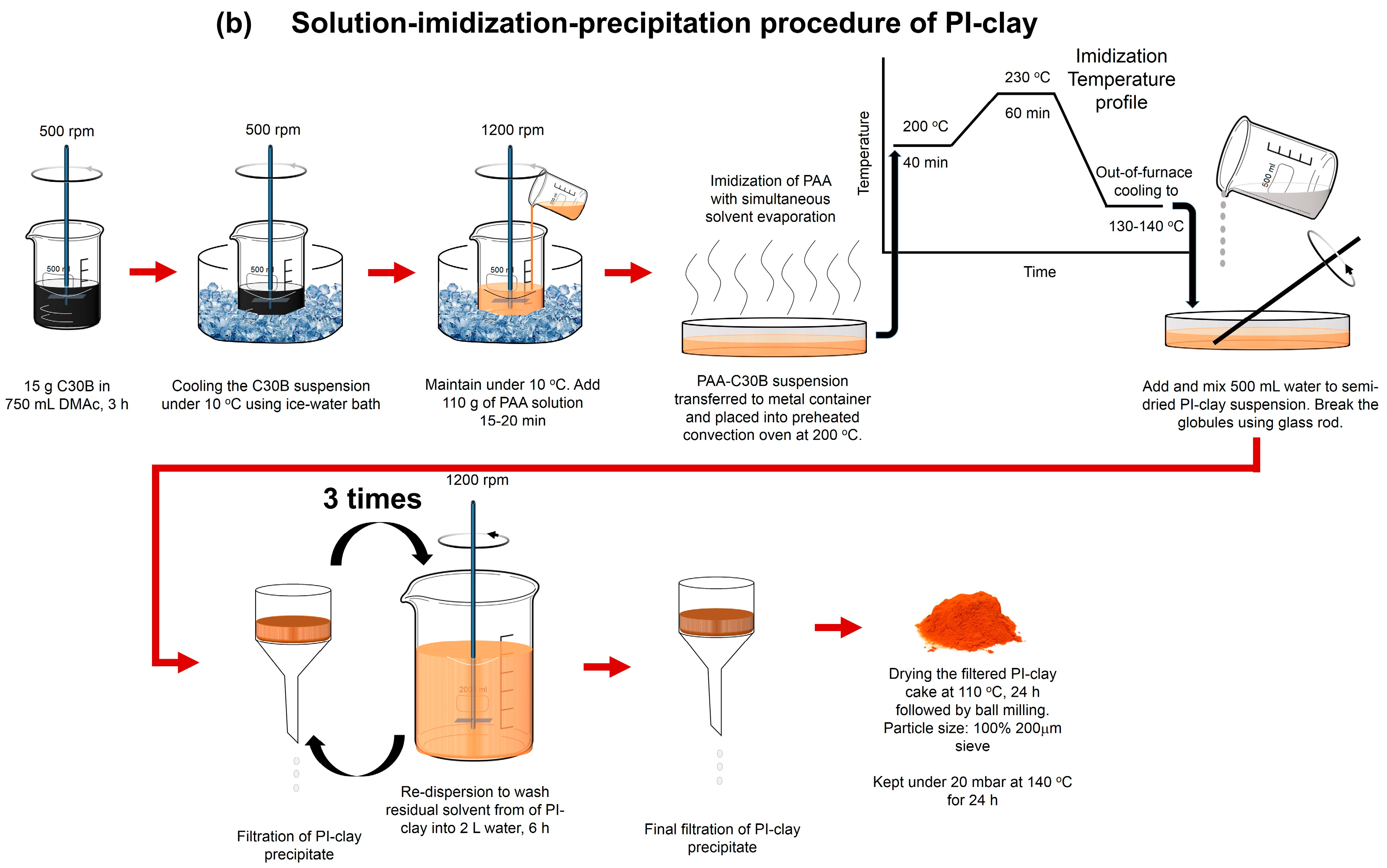
3.2. Synthesis of Coated Clays: PEI-Clay and PI-Clay
3.3. Extrusion Parameters
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Thermo-Oxidation and Combustion Tests
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiliaris, P.; Papaspyrides, C.D. Polymer/layered silicate (clay) nanocomposites: An overview of flame retardancy. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 902–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Cai, G.-P.; Mai, Y.-W. Recent developments in the fire retardancy of polymeric materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1357–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Start, P.; Mauritz, K.A.; Wilkie, C.A. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of poly(methyl methacrylate)-clay nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 77, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.M.; Wan, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Yin, J. PVC/Montmorillonite nanocomposites based on a thermally stable, rigid-rod aromatic amine modifier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.; Boyd, D. Clay: Types, Properties and Uses; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nawani, P.; Gelfer, M.Y.; Hsiao, B.S.; Frenkel, A.; Gilman, J.W.; Khalid, S. Surface Modification of Nanoclays by Catalytically Active Transition Metal Ions. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9808–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zope, I.S.; Dasari, A.; Camino, G. Elucidating the catalytic effect of metal ions in montmorillonite on thermal degradation of organic modifier. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 157, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Bhat, Y.S.; Nagendrappa, G.; Jai Prakash, B.S. Brønsted and Lewis acidity of modified montmorillonite clay catalysts determined by FT-IR spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2009, 141, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Nagendrappa, G.; Jai Prakash, B.S. Surface acidity study of Mn+-montmorillonite clay catalysts by FT-IR spectroscopy: Correlation with esterification activity. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, C.; Moronta, A. Characterization and Catalytic Activity of Aluminum- and Aluminum/Tetra-methylammonium-exchanged Bentonites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zope, I.S.; Dasari, A.; Guan, F.-L.; Yu, Z.-Z. Influence of metal ions on thermo-oxidative stability and combustion response of polyamide 6/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2016, 92, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Chen, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, H.; Ding, Y. Synthesis of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes by Catalytic Combustion of Polypropylene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, W. Catalyzing Carbonization of Polypropylene Itself by Supported Nickel Catalyst during Combustion of Polypropylene/Clay Nanocomposite for Improving Fire Retardancy. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2799–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Regulating Effect of Exfoliated Clay on Intumescent Char Structure and Flame Retardancy of Polypropylene Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5892–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, S.; Russo, P.; Acierno, D.; Rabe, S.; Schartel, B. The synergistic effect of organically modified sepiolite in intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 76, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Bjurhager, I.; Malho, J.-M.; Pere, J.; Ruokolainen, J.; Berglund, L.A.; Ikkala, O. Large-Area, Lightweight and Thick Biomimetic Composites with Superior Material Properties via Fast, Economic, and Green Pathways. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2742–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Qiu, J.; Yang, C.; Sakai, E. Preparation and application of conducting polymer/Ag/clay composite nanoparticles formed by in-situ UV-induced dispersion polymerization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiko, D.J. Process for the preparation of organoclays. U.S. Patent 6,521,678, 18 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tyan, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-C.; Wei, K.-H. Enhancement of imidization of poly(amic acid) through forming poly(amic acid)/organoclay nanocomposites. Polymer 1999, 40, 4877–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Yang, R. Flame-Retardant Polyimide Cross-Linked with Polyhedral Oligomeric Octa(amino-phenyl)silsesquioxane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Vázquez-Torres, H.; Garfias-Mesías, L.F.; Paul, D.R. Thermal degradation of commercially available organoclays studied by TGA–FTIR. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 457, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zammarano, M.; Gilman, J.W.; Davis, R.D.; Kashiwagi, T. Effect of montmorillonite dispersion on flammability properties of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 3092–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyn, F.; Bourbigot, S.; Jama, C.; Bellayer, S. Fire retardancy of polymer clay nanocomposites: Is there an influence of the nanomorphology? Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Tang, T. Mechanism on flame retardancy of polystyrene/clay composites- The effect of surfactants and aggregate state of organoclay. Polymer 2009, 50, 5794–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.B.; Gilman, J.W.; Jackson, C.L. Characterization of the Dispersion of Clay in a Polyetherimide Nanocomposite. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Absorption Range (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| Organoclay | 3650 | Al–Al–OH in MMT, stretch |
| Organoclay | 3250–3500 | –OH in MMT, stretch |
| Organoclay | 2950–2830 | –CH3, –CH2– aliphatic carbon, stretch |
| PI, PEI | 1800 | Imide I C=O, anti-sym. stretch |
| PI, PEI | 1740–1720 | Imide II C=O, sym. stretch |
| PI, PEI | 1610–1600 | C=C in aromatic, stretch |
| PI, PEI | 1500–1490 | aromatic ring stretch |
| PI, PEI | 1390–1380 | Imide III C–N, stretch |
| PEI | 1250 | Tertiary C aliphatic |
| PI, PEI | 1230–1210 | C–O–C aromatic ether |
| Organoclay | 1150–1050 | Si–O–Si in MMT, stretch |
| PI, PEI | ~730 | Imide IV C–N ring deformation |
| Specimen | T5% (°C) | T50% (°C) | TP (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 | 353 | 455 | 462 |
| PA6/organoclay | 360 | 445 | 451 |
| PA6/PEI-clay | 380 | 452 | 458 |
| PA6/PI-clay | 384 | 454 | 453 |
| Specimen | TTI (s) | pHRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | Char (%) | TSP at Ignition (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 | 140 | 840 | 97 | 0 | 0.58 |
| PA6/organoclay | 81 | 338 | 142 | 13.1 | 0.70 |
| PA6/PEI-clay | 133 | 554 | 122 | 7.6 | 0.13 |
| PA6/PI-clay | 139 | 396 | 128 | 9.4 | 0.47 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zope, I.S.; Dasari, A.; Yu, Z.-Z. Influence of Polymer-Clay Interfacial Interactions on the Ignition Time of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. Materials 2017, 10, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080935
Zope IS, Dasari A, Yu Z-Z. Influence of Polymer-Clay Interfacial Interactions on the Ignition Time of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. Materials. 2017; 10(8):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080935
Chicago/Turabian StyleZope, Indraneel S., Aravind Dasari, and Zhong-Zhen Yu. 2017. "Influence of Polymer-Clay Interfacial Interactions on the Ignition Time of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites" Materials 10, no. 8: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080935
APA StyleZope, I. S., Dasari, A., & Yu, Z.-Z. (2017). Influence of Polymer-Clay Interfacial Interactions on the Ignition Time of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. Materials, 10(8), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080935






