Creep Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Subjected to Elevated Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Plan
2.1. Experimental Conditions
2.2. Materials
2.3. Specimen Preparation
2.4. Experimental Method
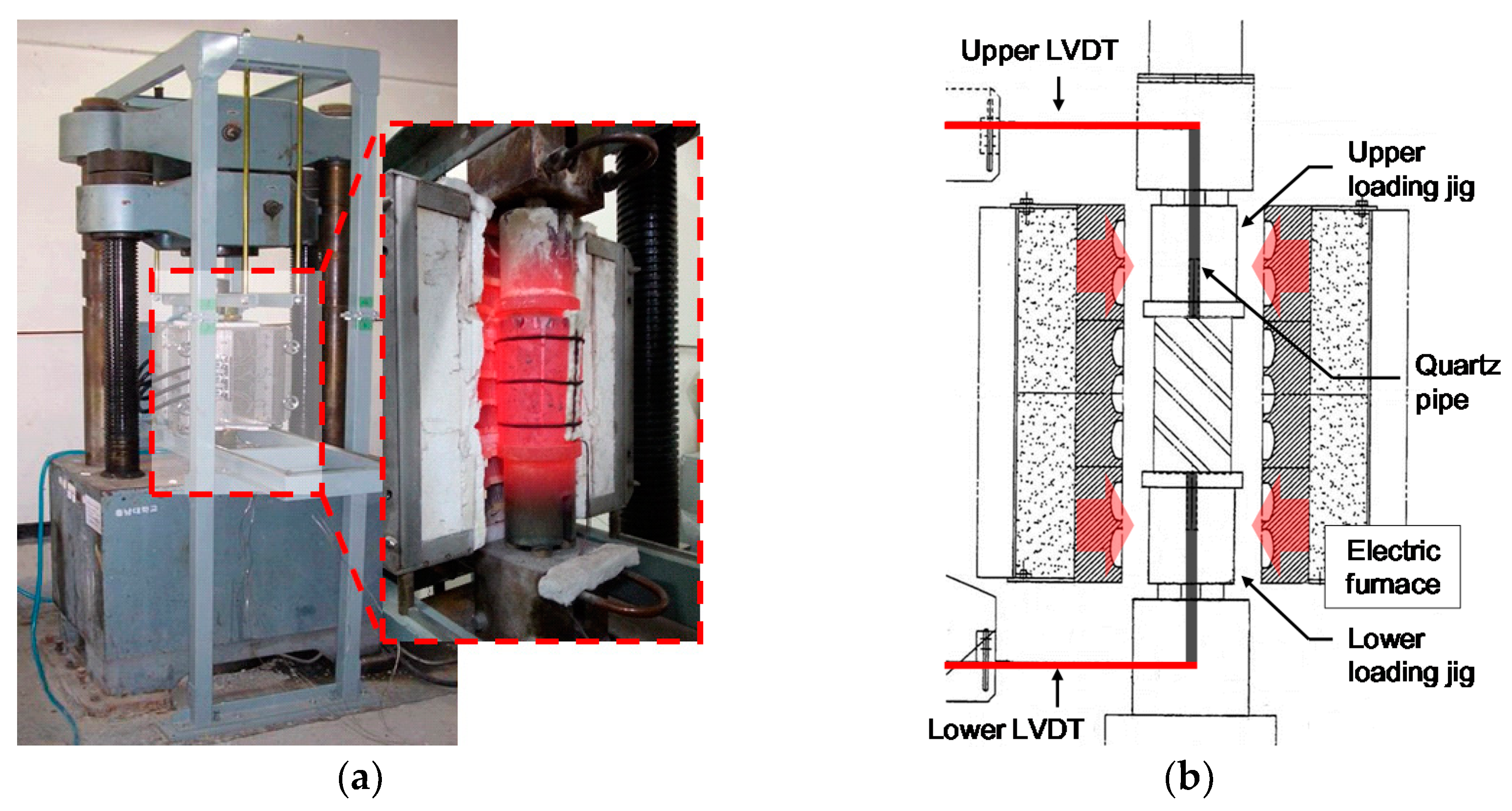
2.4.1. Heating Apparatus and Method
2.4.2. Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus Measuring Method
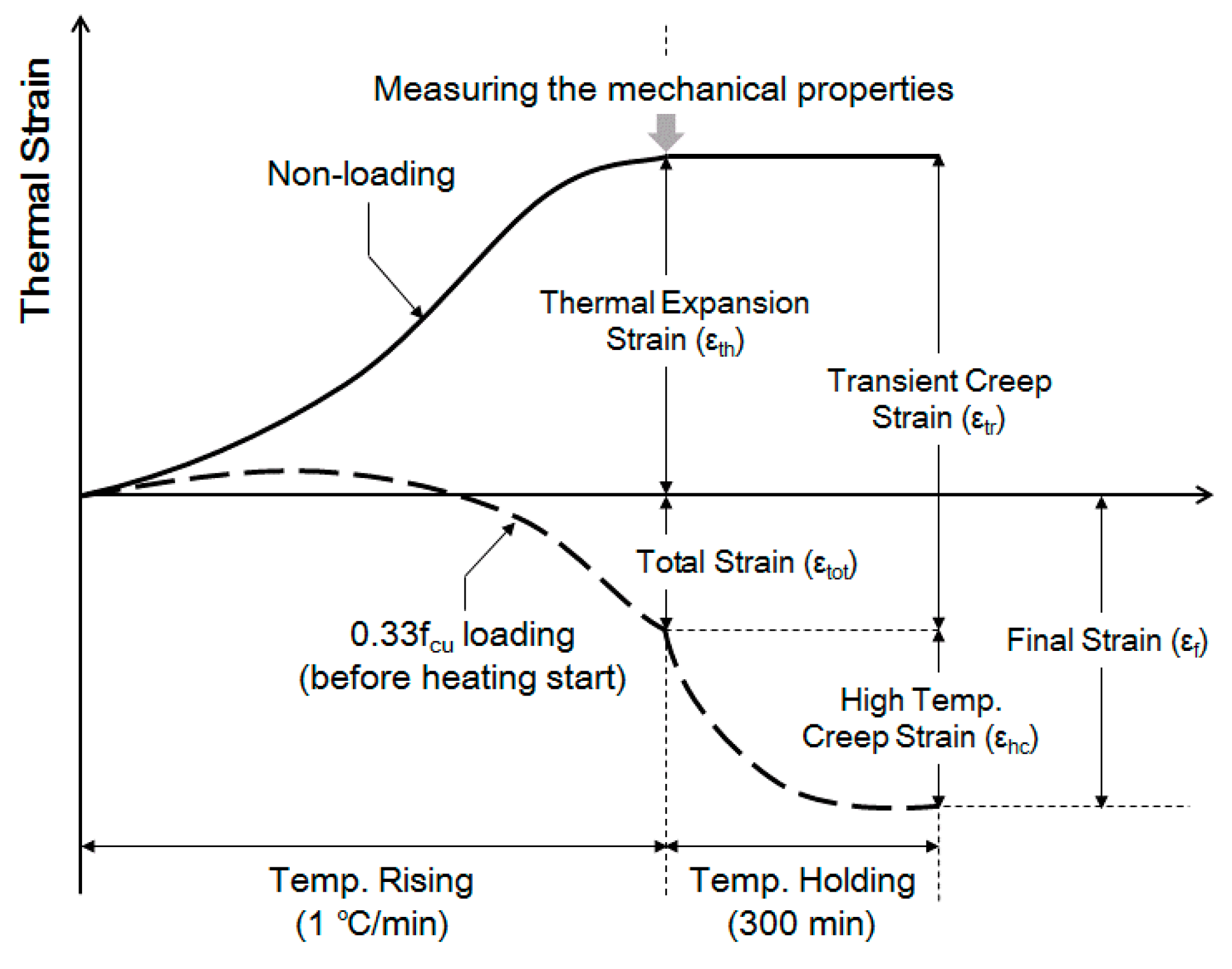
2.4.3. Strain Measuring Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stress–Strain Relation of HSC at Elevated Temperature
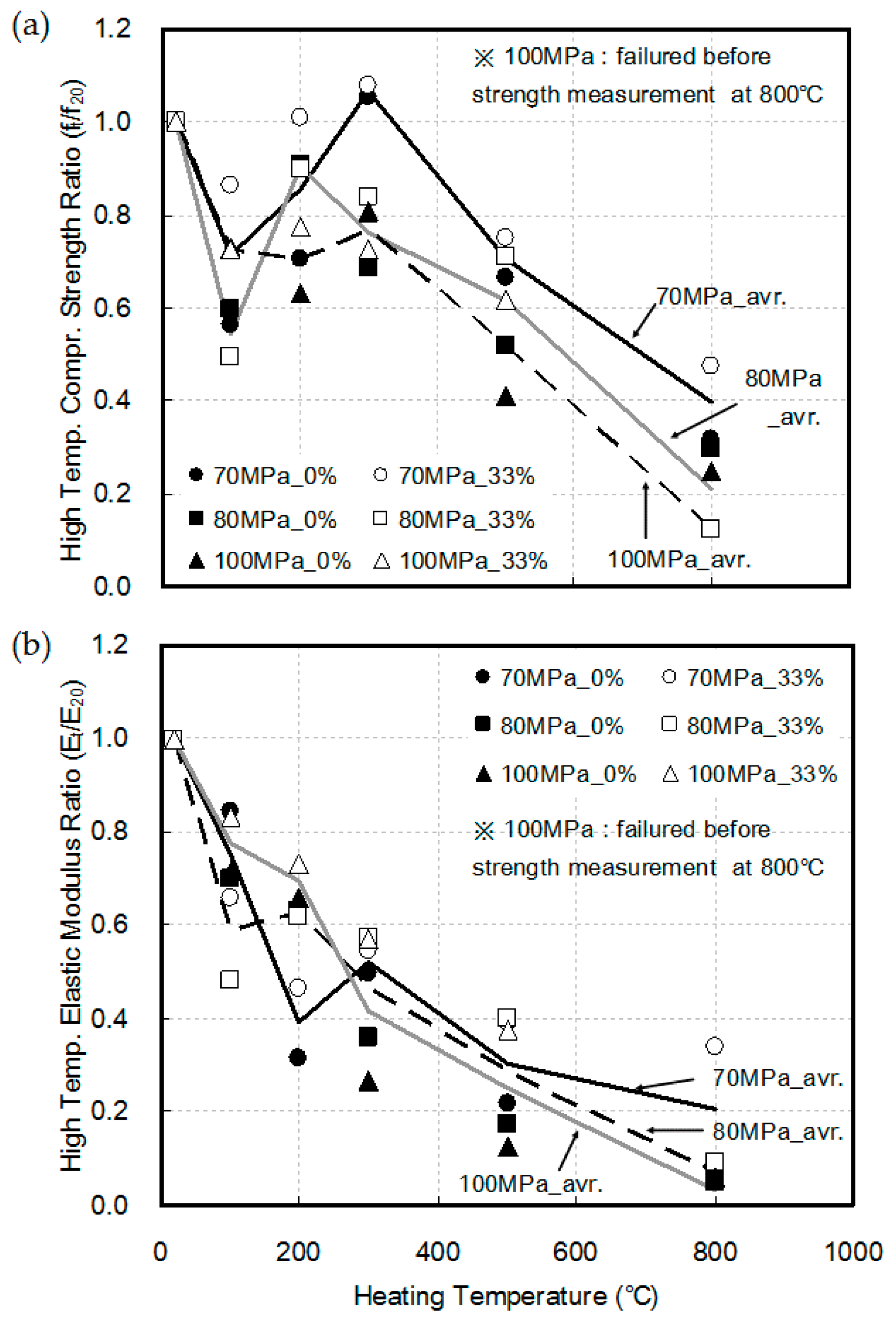
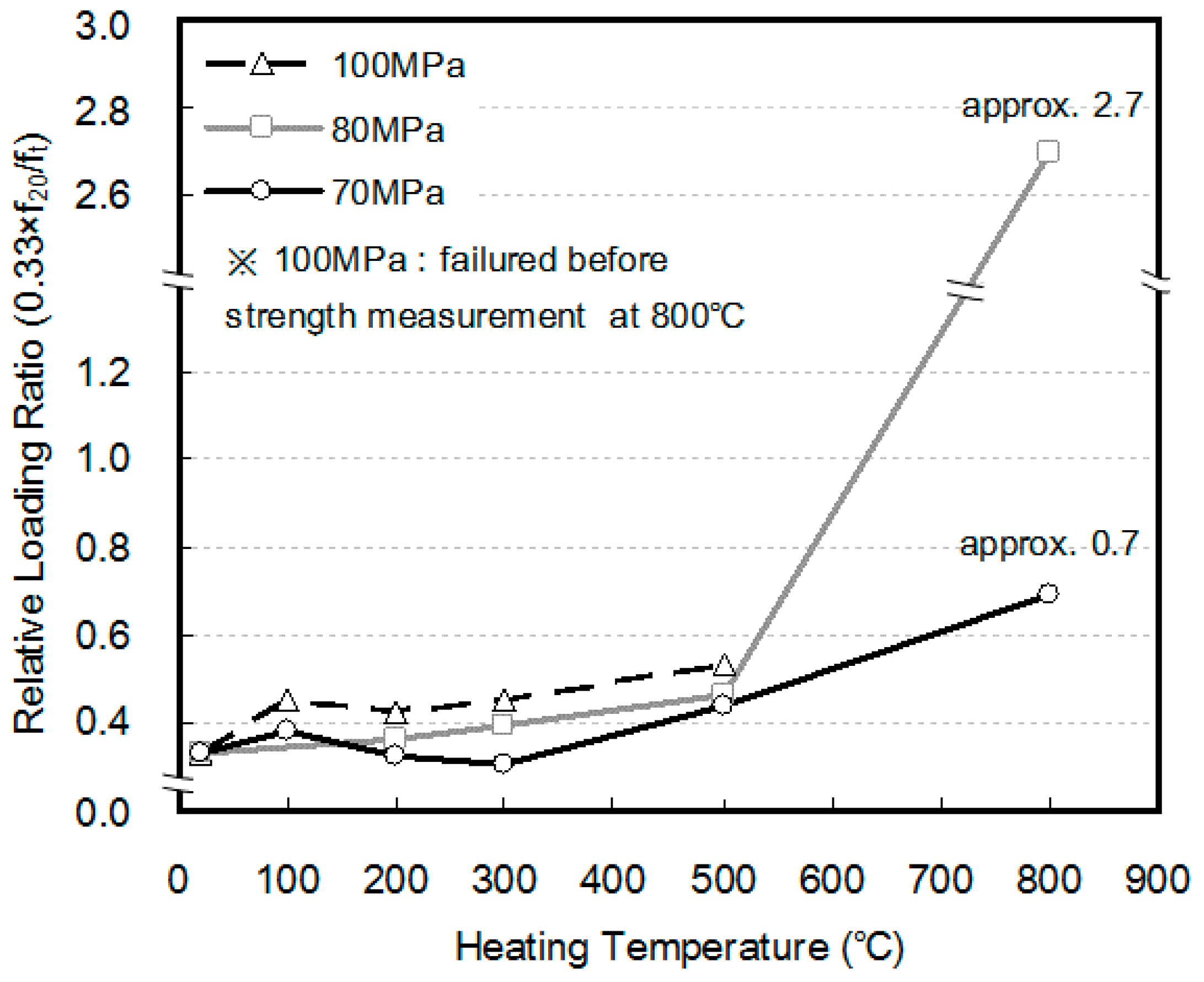
3.2. Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus
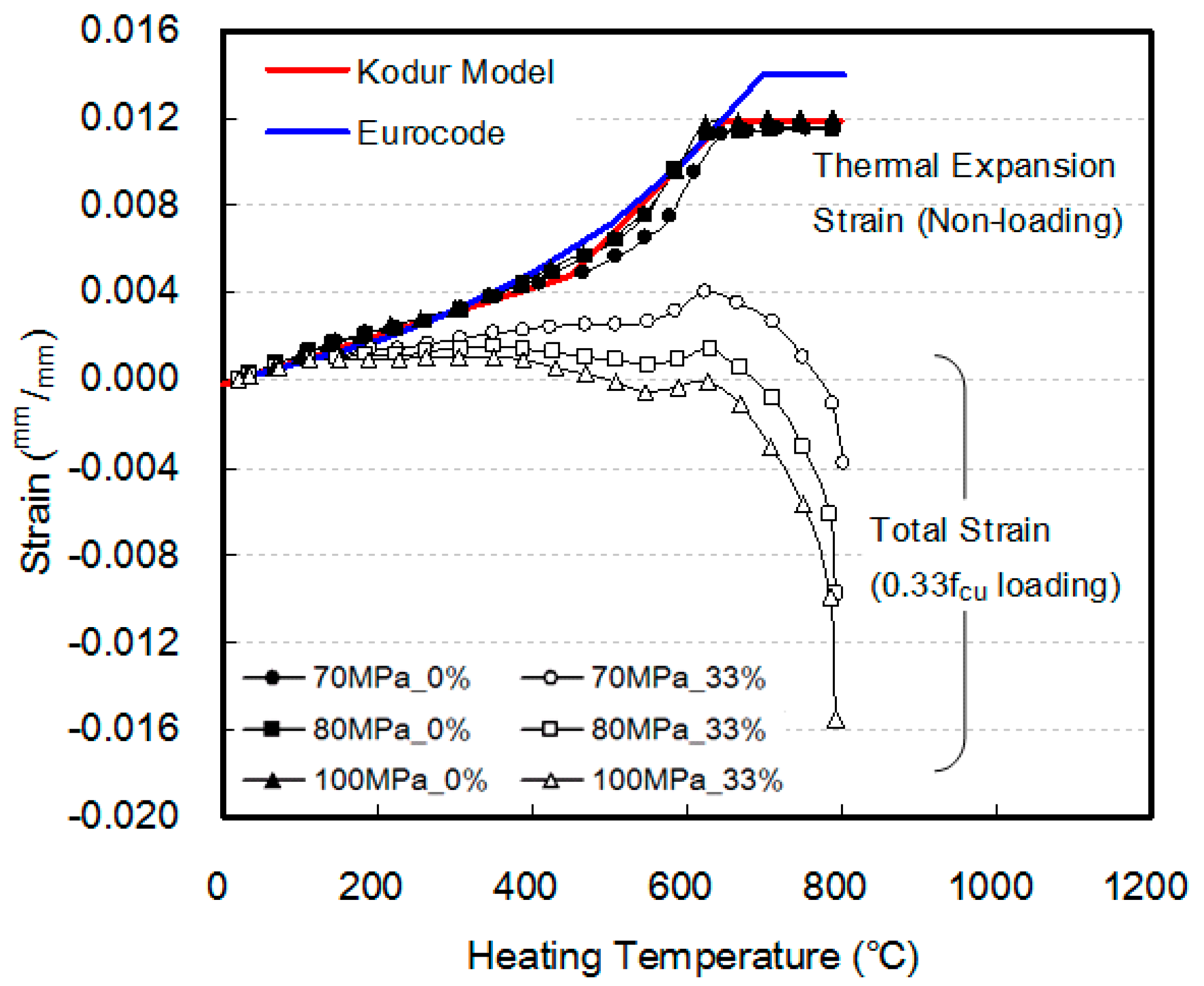
3.3. Thermal Expansion and Total Strain
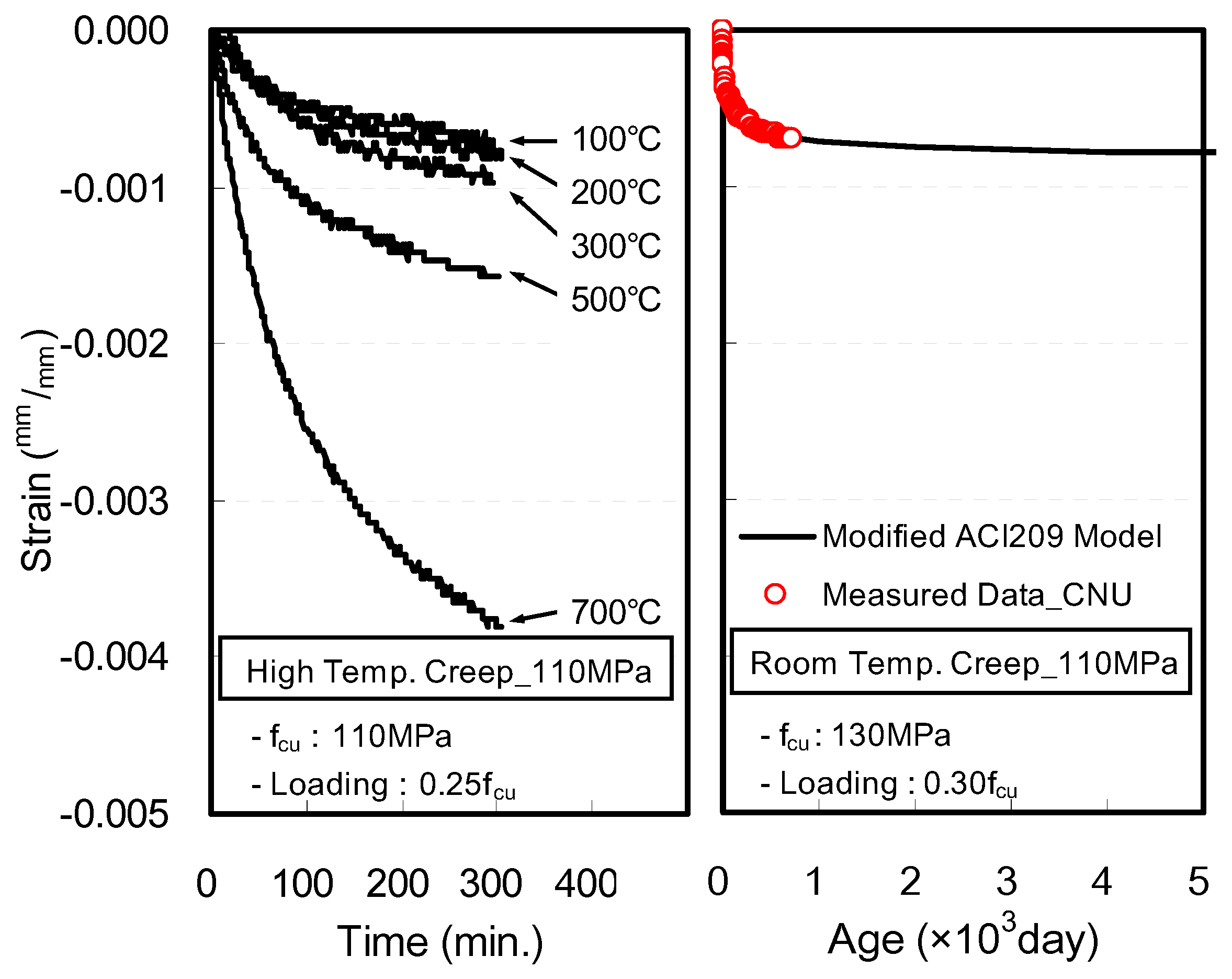
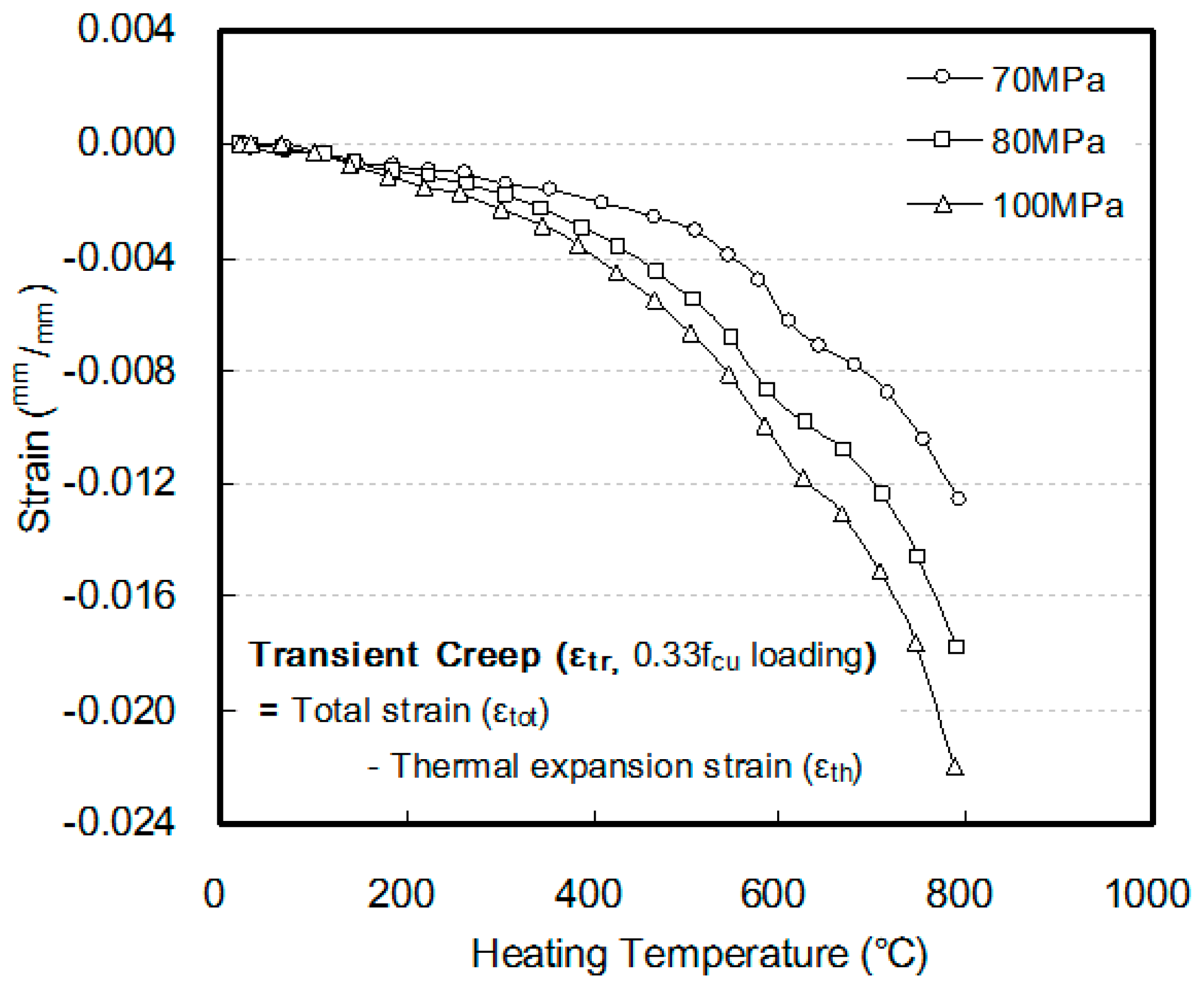
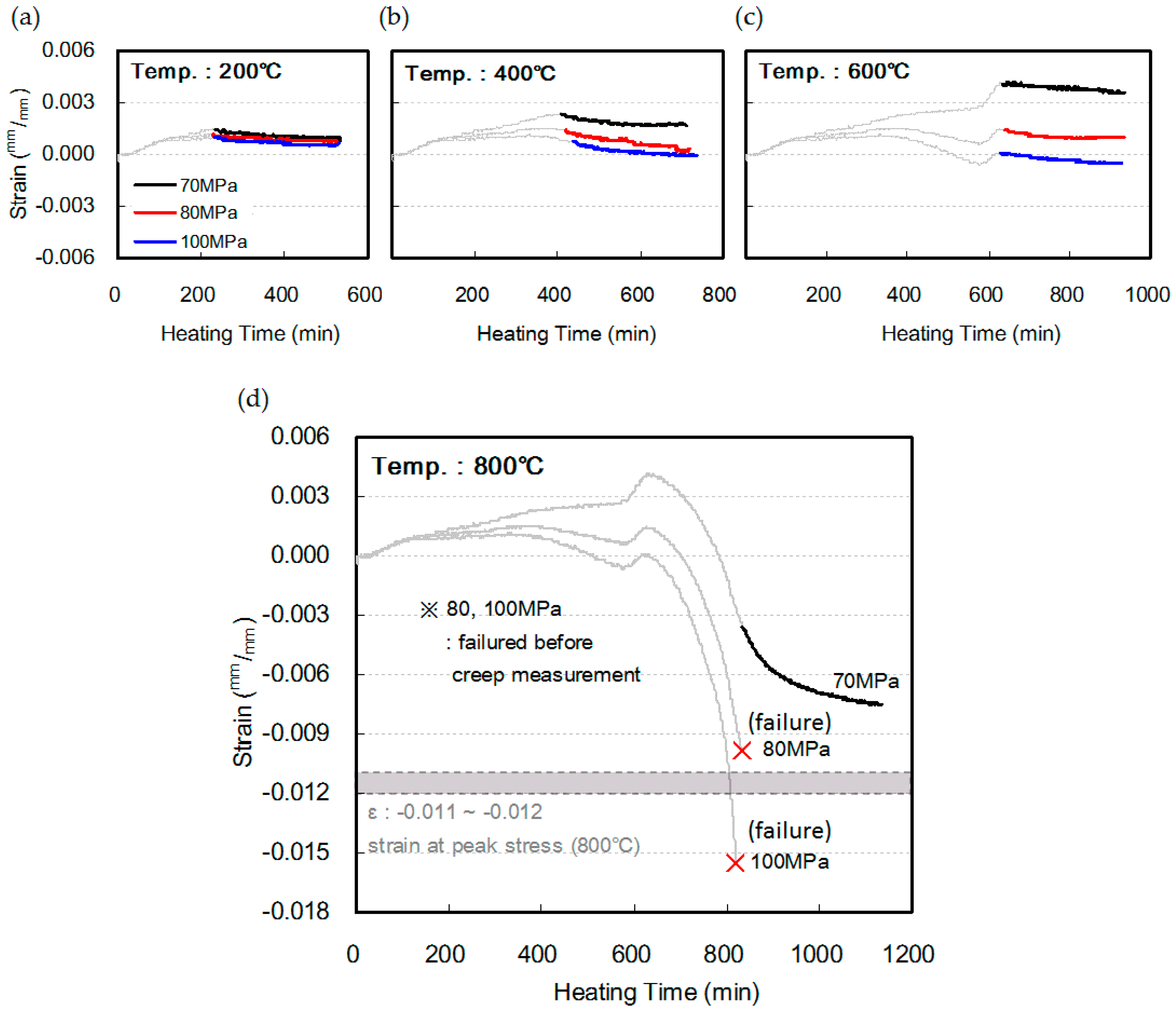
3.4. High Temperature Creep and Final Strain
4. Conclusions
- In this study, transient creep, which is generated upon heating an HSC specimen loaded with a predetermined amount of load (0.33fcu), and creep at elevated temperatures, which is generated upon maintaining a certain level of temperature for a certain amount of time, were measured in order to understand the strain behavior that occurs in HSC at loaded and heated conditions.
- Within the scope of this study, the amount of creep of HSC at elevated temperatures showed similar results at respective heating temperature levels, regardless of the compressive strength. However, when the point at which creep occurs at elevated temperatures after the occurrence of transient creep was considered, a larger shrinkage strain was observed as the compressive strength of concrete increased.
- At a heating temperature of 800 °C, the 80 and 100 MPa specimens reached failure when their final strains were similar to or slightly higher than the strain at the maximum load during the measurement of compressive strength at 800 °C. Therefore, it was found that as the compressive strength of concrete increases, an even larger shrinkage strain occurs owing to heating and loading, which in turn can lead to creep failure during heating.
- In order to guarantee the strain stability of a structure made of HSC during and after a fire, the destruct limit state, thermal expansion in all heating segments, total strain, transient creep, and creep of concrete at elevated temperature should be considered.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, T.-G.; Kim, G.-Y. An experimental study on the residual mechanical properties of fiber reinforced concrete with high temperature and load. Mater. Struct. 2012, 46, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Falkner, H. On residual strength of high-performance concrete with and without polypropylene fibres at elevated temperatures. Fire Saf. J. 2006, 41, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ye, G.; De Schutter, G.; Yuan, Y.; Taerwe, L. On the mechanism of polypropylene fibres in preventing fire spalling in self-compacting and high-performance cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.-F.; Yang, W.-W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Bian, S.-H.; Zhao, L.-H. Explosive spalling and residual mechanical properties of fiber-toughened high-performance concrete subjected to high temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalifa, P.; Chéné, G.; Gallé, C. High-temperature behaviour of hpc with polypropylene fibres: From spalling to microstructure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, N.; Pliya, P.; Beaucour, A.L.; Simon, A.; Noumowé, A. Influence of steel and/or polypropylene fibres on the behaviour of concrete at high temperature: Spalling, transfer and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, W.; Kodur, V. Thermal and mechanical properties of fiber reinforced high performance self-consolidating concrete at elevated temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivenko, P.V.; Guzii, S.G.; Bodnarova, L.; Valek, J.; Hela, R.; Zach, J. Effect of thickness of the intumescent alkali aluminosilicate coating on temperature distribution in reinforced concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.J.; Lim, Y.M.; Won, J.P.; Park, H.G. Fire resistant behavior of newly developed bottom-ash-based cementitious coating applied concrete tunnel lining under rabt fire loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Kim, G.; Choe, G.C.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T. Effect of coarse aggregate type and loading level on the high temperature properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wong, Y.L.; Poon, C.S.; Anson, M. Impact of high temperature on PFA concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzer, N.; Aköz, F.; Öztürk, L.D. Compressive strength–color change relation in mortars at high temperature. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.H.; Lam, L. Compressive behavior of fiber reinforced high-performance concrete subjected to elevated temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.K.R.; Sultan, M.A. Effect of temperature on thermal properties of high-strength concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, O.; Abdullah, M.; Hussin, K.; Ismail, K.; Binhussain, M. Mechanical and microstructural evaluations of lightweight aggregate geopolymer concrete before and after exposed to elevated temperatures. Materials 2013, 6, 4450–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, M.J.; Lavallée, Y.; Laumann, A.; Hess, K.U.; Meredith, P.G.; Dingwell, D.B.; Huismann, S.; Weise, F. The influence of thermal-stressing (up to 1000 °C) on the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of siliceous-aggregate, high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Cao, W.; Bian, J.; Zhang, J. The fire resistance performance of recycled aggregate concrete columns with different concrete compressive strengths. Materials 2014, 7, 7843–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, G.Y.; Gucunski, N.; Choe, G.C.; Yoon, M.H. Thermal strain behavior and strength degradation of ultra-high-strength-concrete. Mater. Struct. 2015, 49, 3411–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Han, D.; Han, M.-C.; Han, C.-G.; Son, H.-J. Combining polypropylene and nylon fibers to optimize fiber addition for spalling protection of high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Testing of Concrete—Part 3: Making and Curing Test Specimens; ISO 1920-3; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, T.-G. Mechanical properties of high-strength concrete subjected to high temperature by stressed test. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, s128–s133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing Materials. Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens; ASTM C39; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing Materials. Standard Test Method for Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in Compression; ASTM C469/C469M-14; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- RILEM TC 129-MHT. Test methods for mechanical properties of concrete at high temperatures Part 8 Steady-state creep and creep recovery for service and accident conditions. Mater. Struct. 2000, 33, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Arioz, O. Effects of elevated temperatures on properties of concrete. Fire Saf. J. 2007, 42, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Recycled concrete made with different natural coarse aggregates exposed to high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standards Institution. Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures. General Rules. Structural Fire Design; BS EN 1992-1-2; BSI: London, UK, 2005.
- Sadaoui, A.; Khennane, A. Effect of transient creep on the behaviour of reinforced concrete columns in fire. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niry Razafinjato, R.; Beaucour, A.-L.; Hebert, R.L.; Ledesert, B.; Bodet, R.; Noumowe, A. High temperature behaviour of a wide petrographic range of siliceous and calcareous aggregates for concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, A.; Manita, P.; Sideris, K.K. Influence of elevated temperatures on the mechanical properties of blended cement concretes prepared with limestone and siliceous aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderberg, Y.; Thelandersson, S. Stress and Deformation Characteristics of Concrete at High Temperatures. 2. Experimental Investigation and Material Behaviour Model; (Bulletin of Division of Structural Mechanics and Concrete Construction, Bulletin 54; Volume Bulletin 54); Lund Institute of Technology: Lund, Sweden, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-Y.; Purkiss, J. Stress–strain constitutive equations of concrete material at elevated temperatures. Fire Saf. J. 2005, 40, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


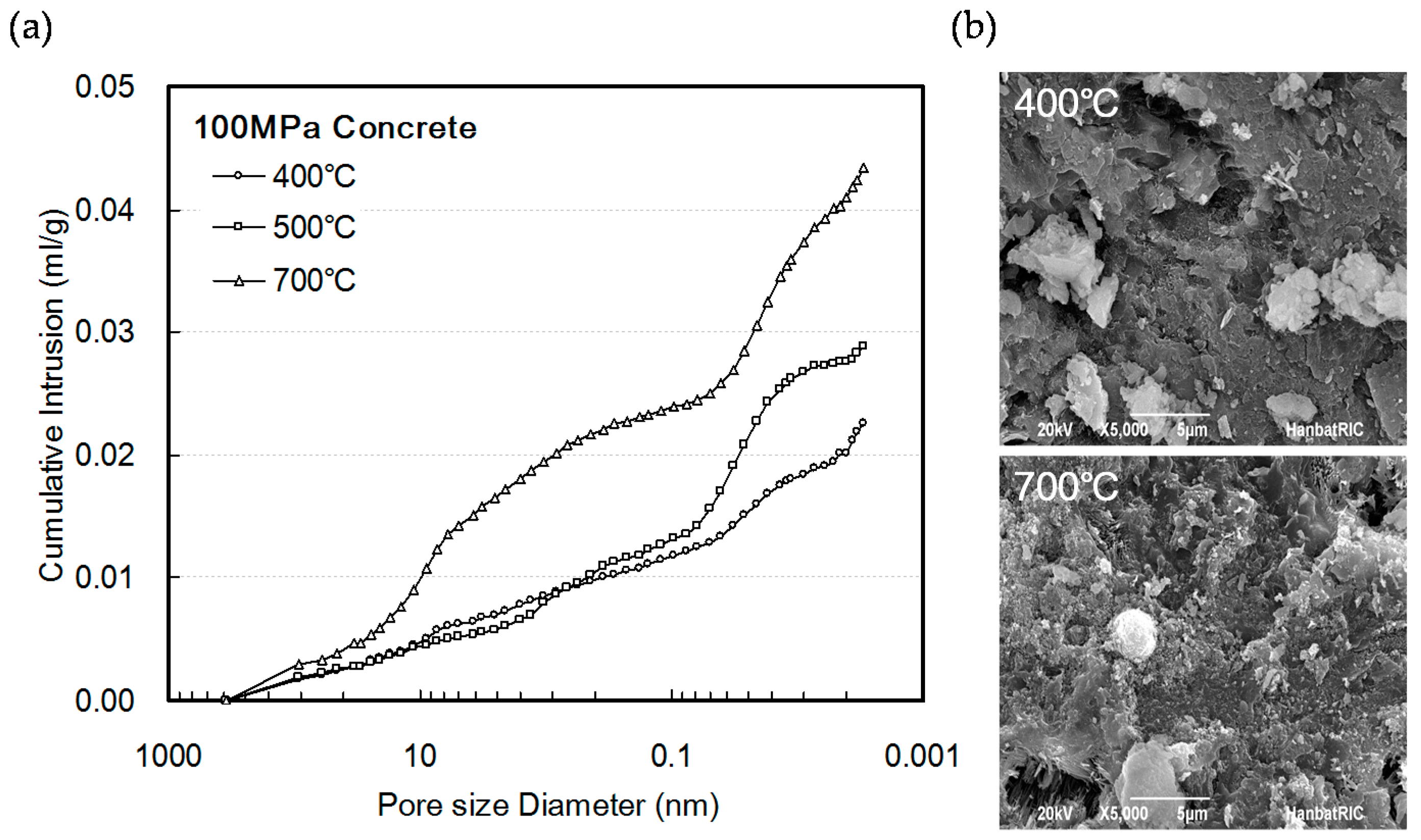

| ID (fck 1) | Fiber Mixing Ratio (vol.%) | Pre-Loading Level (×fcu) | Target Temp. (°C) 2 | Heating VeloCity (°C/min) | Properties Evaluated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 MPa | 0.045 | 0.00 0.33 | 20, 100, 200, 300, 500, 800 | 1 |
|
| 80 MPa | 0.073 | ||||
| 100 MPa | 0.091 |
| ID (fck) | W–B 1 (%) | Slump-Flow (mm) | Air (%) | S/a 2 (%) | Unit Weight (kg/m3) 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | C | GGBS | FA | S | G | Fiber | SP | |||||
| 70 MPa | 30 | 650 ± 50 | 2 ± 1 | 49 | 164 | 380 | 136 | 27 | 810 | 860 | 0.6 | 3.9 |
| 80 MPa | 26 | 47 | 163 | 392 | 180 | 50 | 743 | 854 | 0.8 | 4.5 | ||
| 100 MPa | 23 | 46 | 399 | 210 | 91 | 718 | 859 | 1.0 | 8.4 | |||
| Materials | Physical Properties |
|---|---|
| Cement | Ordinary Portland Cement Density: 3.15 g/cm3, Specific surface area: 3630 cm2/g |
| Fine aggregate | Washed sand Density: 2.60 g/cm3, Water absorption ratio: 1.03% |
| Coarse aggregate | Crushed granite Max size: 20 mm, Density: 2.62 g/cm3, Water absorption ratio: 0.97% |
| Fly ash | Density: 2.20 g/cm3, Specific surface area: 4600 cm2/g |
| Ground granulated blast furnace slag | Density: 2.90 g/cm3, Specific surface area: 4530 cm2/g |
| Nylon fiber | Density: 1.10 g/cm3, Length: 13 mm, Melting point: 225 °C |
| Admixture | Polycarboxylic water reducing agent |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, M.; Kim, G.; Kim, Y.; Lee, T.; Choe, G.; Hwang, E.; Nam, J. Creep Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Subjected to Elevated Temperatures. Materials 2017, 10, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070781
Yoon M, Kim G, Kim Y, Lee T, Choe G, Hwang E, Nam J. Creep Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Subjected to Elevated Temperatures. Materials. 2017; 10(7):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070781
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Minho, Gyuyong Kim, Youngsun Kim, Taegyu Lee, Gyeongcheol Choe, Euichul Hwang, and Jeongsoo Nam. 2017. "Creep Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Subjected to Elevated Temperatures" Materials 10, no. 7: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070781
APA StyleYoon, M., Kim, G., Kim, Y., Lee, T., Choe, G., Hwang, E., & Nam, J. (2017). Creep Behavior of High-Strength Concrete Subjected to Elevated Temperatures. Materials, 10(7), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070781






