Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
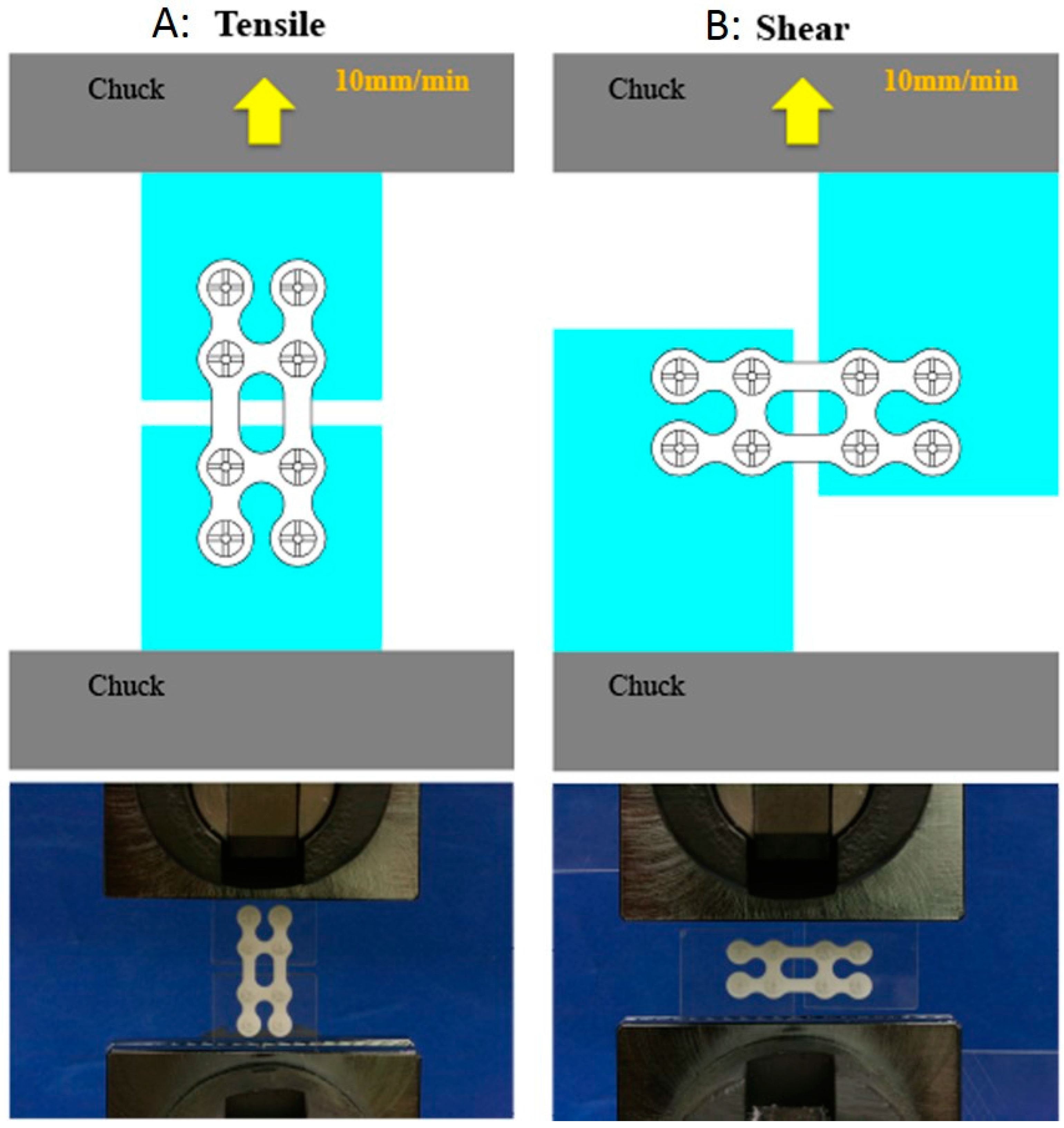
2.2. Tensile and Shear Strength Evaluation
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
- a single u-HA/PLLA straight plate, fixing the plate on each side with two screws (total four screws)
- double u-HA/PLLA straight plate, fixing the plate on each side with two screws (total eight screws)
- one u-HA/PLLA ladder plate, fixing the plate on each side with two screws (total eight screws)
2.2.2. Strength Tests
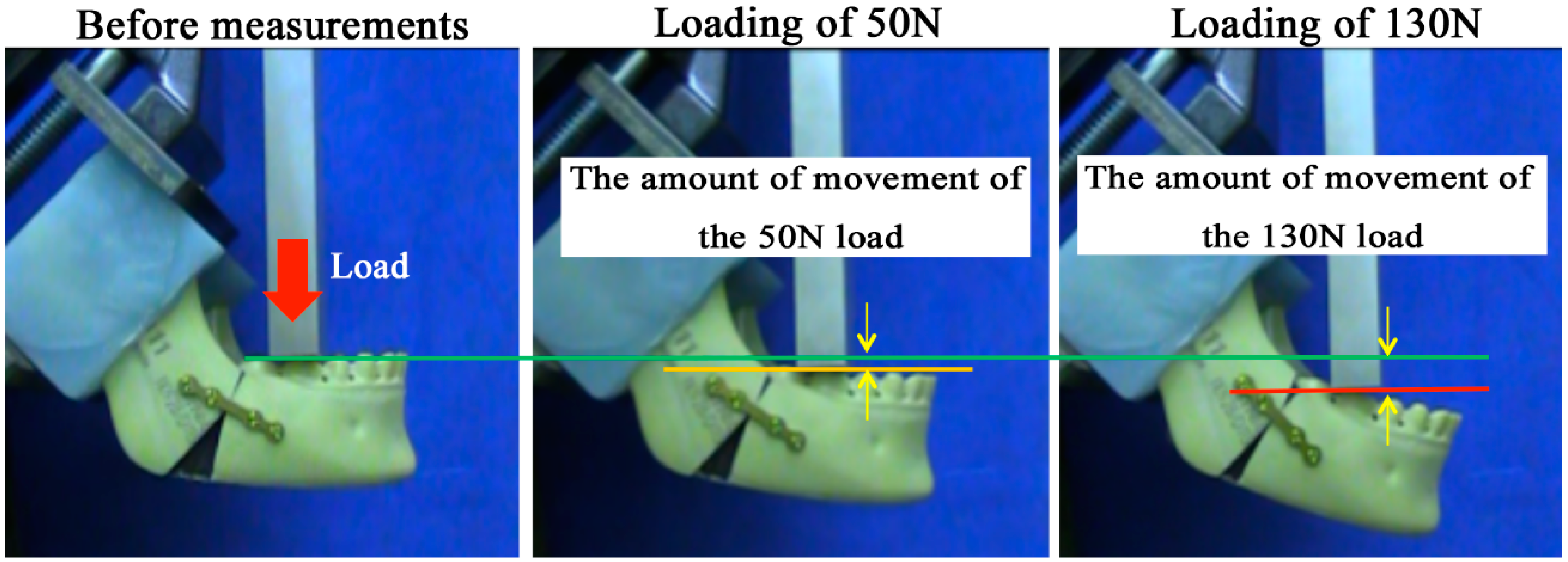
2.3. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
- (a)
- a single conventional titanium straight plate (Synthes (Oberdorf, Switzerland) Compact Lock 2.0: 1.5 mm) with four screws (2.0 mm diameter × 6 mm long monocortical screws) was installed in each bone segment
- (b)
- a single u-HA/PLLA straight plate (OSTEOTRANS MX®; thickness: 1.4 mm) with four screws (2.0 mm diameter × 6 mm long monocortical screws) was installed in each bone segment
- (c)
- double u-HA/PLLA straight plates (OSTEOTRANS MX®; thickness: 1.4 mm), each with four screws (2.0 mm diameter × 6 mm long monocortical screws), were installed in each bone segment
- (d)
- one u-HA/PLLA ladder plate (OSTEOTRANS MX®; thickness: 1.4 mm) with eight screws (2.0 mm diameter × 6 mm long monocortical screws) was installed in each bone segment.
2.3.2. Loading Test
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tensile and Shear Strength Evaluation
3.1.1. Tensile Strength
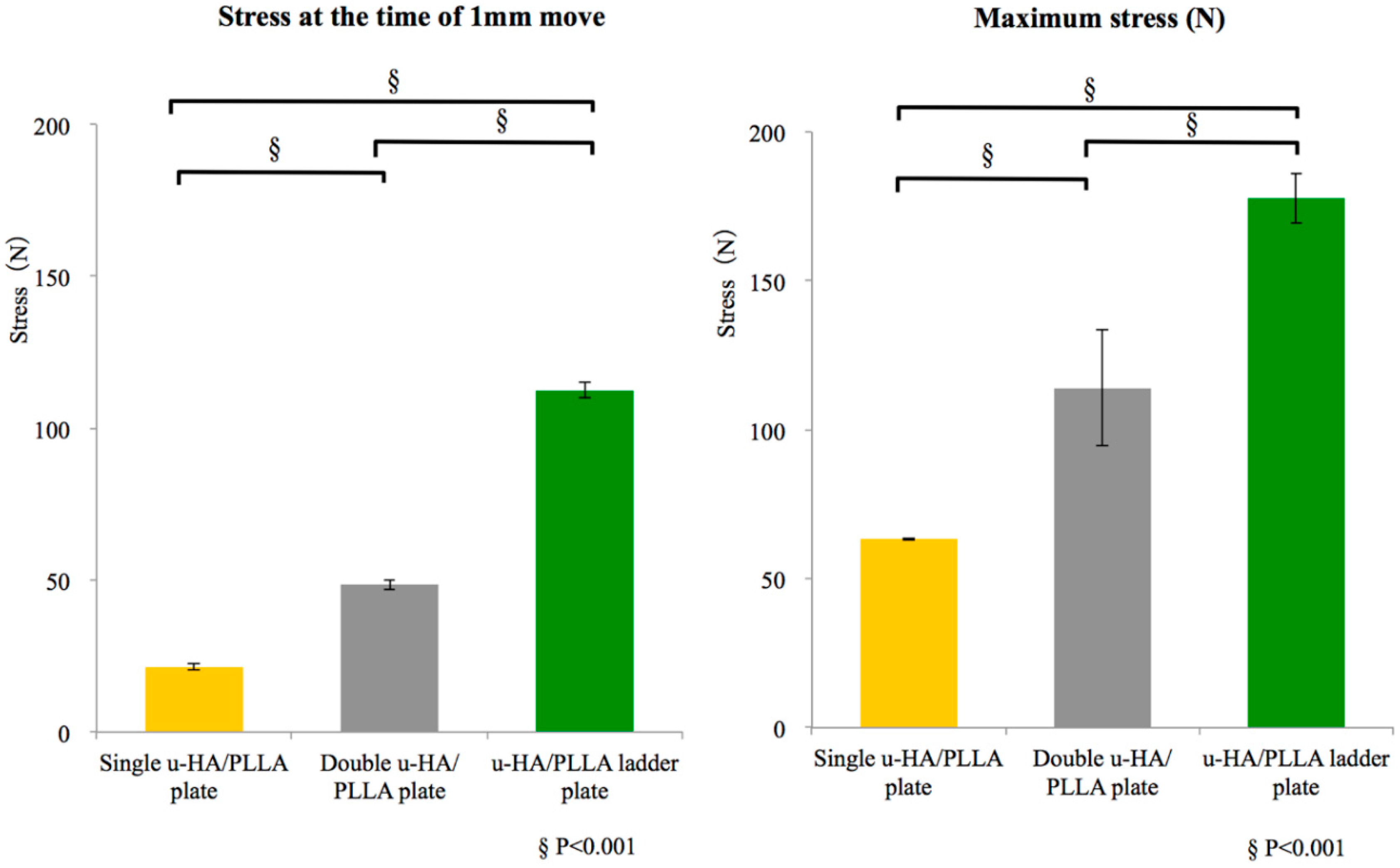
3.1.2. Shear Strength
3.2. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| u-HA | unsintered hydroxyapatite; |
| PLLA | poly-l-lactide-acid; |
| SSRO | sagittal split ramus osteotomy |
References
- Buijs, G.J.; van Bakelen, N.B.; Jansma, J.; de Visscher, J.G.A.M.; Hoppenreijs, T.J.M.; Bergsma, J.E.; Stegenga, B.; Bos, R.R.M. A randomized clinical trial of biodegradable and titanium fixation systems in maxillofacial surgery. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bakelen, N.B.; Buijs, G.J.; Jansma, J.; de Visscher, J.G.A.M.; Hoppenreijs, T.J.M.; Bergsma, J.E.; Stegenga, B.; Bos, R.R.M. Decision-making considerations in application of biodegradable fixation systems in maxillofacial surgery—A retrospective cohort study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkmen, E.; Simşek, B.; Yücel, E.; Kurt, A. Three-dimensional finite element analysis used to compare methods of fixation after sagittal split ramus osteotomy: Setback surgery-posterior loading. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 43, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Moraissi, E.A.; Ellis, E. Biodegradable and Titanium Osteosynthesis Provide Similar Stability for Orthognathic Surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikinami, Y.; Matsusue, Y.; Nakamura, T. The complete process of bioresorption and bone replacement using devices made of forged composites of raw hydroxyapatite particles/poly l-lactide (F-u-HA/PLLA). Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5542–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Kawai, H.; Shibata, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Nagatsuka, H.; Furuki, Y. Long-Term Bioresorption of Bone Fixation Devices Made from Composites of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite Particles and Poly-l-Lactide. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2015, 24, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oe, M. Comparison of Mechanical Stiffness of Titanium and Biodegradable Osteofixation Systems. J. Jpn. Soc. Plastic Reconstr Surg. 2013, 33, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Nakakuki, K.; Kurohara, K.; Arikawa, K.; Harada, K. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactic Acid Plate in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy. Jpn. J. Jaw Deform. 2014, 24, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ohkura, K.; Enomoto, S. Measure of bite force and occlusal contact area before and after bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy of the mandible using a new pressure-sensitive device: A preliminary report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 58, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiely, K.D.; Wendfeldt, K.S.; Johnson, B.E.; Haskell, B.S.; Edwards, R.C. One-year postoperative stability of LeFort I osteotomies with biodegradable fixation: A retrospective analysis of skeletal relapse. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2006, 130, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turvey, T.A.; Bell, R.B.; Tejera, T.J.; Proffit, W.R. The use of self-reinforced biodegradable bone plates and screws in orthognathic surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turvey, T.A.; Bell, R.B.; Phillips, C.; Proffit, W.R. Self-Reinforced Biodegradable Screw Fixation Compared With Titanium Screw Fixation in Mandibular Advancement. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-G.; Baik, S.-M.; Kim, B.-O.; Kim, H.-K.; Moon, S.-Y.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yun, P.-Y.; Son, J.-S. Comparative study between resorbable and nonresorbable plates in orthognathic surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Mizuashi, K.; Shigematsu, M.; Goto, M. Masticatory function and neurosensory disturbance after mandibular correction by bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy: A comparison between miniplate and bicortical screw rigid internal fixation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Katase, N.; Shibata, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Furuki, Y. Clinical Evaluation of an Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/Poly-L-Lactide Osteoconductive Composite Device for the Internal Fixation of Maxillofacial Fractures. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, T.; Tatsumi, H.; Karino, M.; Yoshino, A.; Koike, T.; Ide, T.; Sekine, J. Applicability of an Unsintered Hydroxyapatite Particles/Poly-L-Lactide Composite Sheet with Tack Fixation for Orbital Fracture Reconstruction. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2016, 25, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Hotaka, K.; Akane, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Sukegawa-Takahashi, Y.; Sakaida, K.; Nagatsuka, H.; Furuki, Y. Surgical Treatment and Dental Implant Rehabilitation after the Resection of an Osseous Dysplasia. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2016, 25, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusue, Y.; Yamamuro, T.; Yoshii, S.; Oka, M.; Ikada, Y.; Hyon, S.; Shikinami, Y. Biodegradable screw fixation of rabbit tibia proximal osteotomies. J. Appl. Biomater. 1991, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsusue, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Iida, H.; Shimizu, K. A long-term clinical study on drawn poly-L-lactide implants in orthopaedic surgery. J. Long. Term. Eff. Med. Implants 1997, 7, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergsma, J.E.; de Bruijn, W.C.; Rozema, F.R.; Bos, R.R.; Boering, G. Late degradation tissue response to poly(L-lactide) bone plates and screws. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landes, C.A.; Ballon, A.; Tran, A.; Ghanaati, S.; Sader, R. Segmental stability in orthognathic surgery: Hydroxyapatite/Poly-l-lactide osteoconductive composite versus titanium miniplate osteosyntheses. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikinami, Y.; Hata, K.; Okuno, M. Ultra-high-strength resorbable implants made from bioactive ceramic particles/polylactide composites. Bioceramics 1996, 9, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Van Sickels, J.E.; Peterson, G.P.; Holms, S.; Haug, R.H. An in vitro comparison of an adjustable bone fixation system. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Pang, K.-M.; Kim, H.-E.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, J.-H. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 402.e1–402.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharanon, W. Comparison between the rigidity of bicortical screws and a miniplate for fixation of a mandibular setback after a simulated bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1998, 56, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, B.; Alkan, A.; Arici, S.; Erdem, E. In vitro comparison of biomechanical characteristics of sagittal split osteotomy fixation techniques. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, L.B.; Sant’ Ana, E.; Manzato, A.J.; Guerra, F.L.B.; Arnett, G.W. Biomechanical in vitro evaluation of three stable internal fixation techniques used in sagittal osteotomy of the mandibular ramus: A study in sheep mandibles. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredbenner, T.L.; Haug, R.H. Substitutes for human cadaveric bone in maxillofacial rigid fixation research. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 90, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, I.; Arıcı, S.; Bereket, C.; Tek, M. In vitro biomechanical evaluation of modified plating techniques for bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy in mandibular advancement. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Junior, P.D.; Magro-Filho, O.; Shastri, K.A.; Papageorge, M.B. In vitro biomechanical evaluation of the use of conventional and locking miniplate/screw systems for sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, K.; Hashiba, Y.; Marukawa, K.; Alam, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamamoto, E. Skeletal stability after mandibular setback surgery: Bicortical fixation using a 2.0-mm locking plate system versus monocortical fixation using a nonlocking plate system. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkmen, E.; Simşek, B.; Yücel, E.; Kurt, A. Comparison of different fixation methods following sagittal split ramus osteotomies using three-dimensional finite elements analysis. Part 1: Advancement surgery-posterior loading. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 34, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tams, J.; Otten, B.; van Loon, J.P.; Bos, R.R. A computer study of fracture mobility and strain on biodegradable plates used for fixation of mandibular fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymach, Z.; Nei, H.; Kawamura, H.; Bell, W. Biomechanical evaluation of a T-shaped miniplate fixation of a modified sagittal split ramus osteotomy with buccal step, a new technique for mandibular orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 111, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

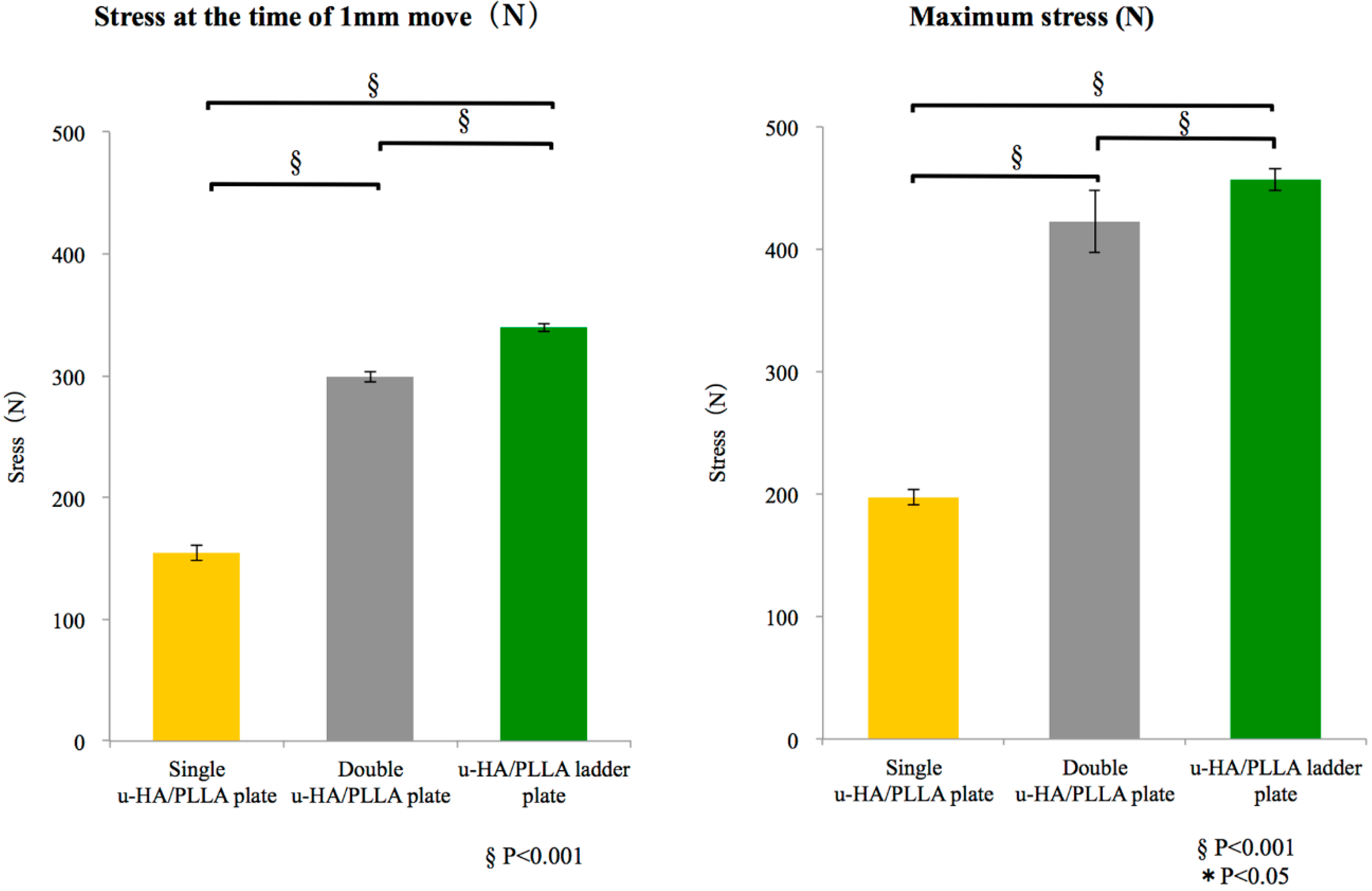
| Tensile Strength Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress at the Time of 1 mm Move (N) | |||
| Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA Plate | Double u-HA/PLLA Plate | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 152.3 | 300.4 | 335.5 |
| #2 | 161.5 | 302.8 | 342.2 |
| #3 | 149.9 | 294.5 | 341.4 |
| Ave. | 154.6 | 299.2 | 339.7 |
| S.D. | 6.1 | 4.3 | 3.7 |
| Maximum Stress (N) | |||
| Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA Plate | Double u-HA/PLLA Plate | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 198.3 | 394.7 | 459.1 |
| #2 | 190.8 | 443.7 | 446.4 |
| #3 | 202.6 | 428.5 | 464.4 |
| Ave. | 197.2 | 422.3 | 456.6 |
| S.D. | 6.0 | 25.1 | 9.3 |
| Shear Strength Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress at the Time of 1 mm Move (N) | |||
| Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA Plate | Double u-HA/PLLA Plate | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 22.4 | 46.9 | 110.2 |
| #2 | 20.6 | 50.1 | 115.1 |
| #3 | 21.1 | 48.6 | 111.8 |
| Ave. | 21.4 | 48.5 | 112.4 |
| S.D. | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.5 |
| Maximum Stress (N) | |||
| Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA Plate | Double u-HA/PLLA Plate | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 63.8 | 126.8 | 187.2 |
| #2 | 63.3 | 123.3 | 174.7 |
| #3 | 63.0 | 91.5 | 171.3 |
| Ave. | 63.4 | 113.9 | 177.7 |
| S.D. | 0.4 | 19.4 | 8.4 |
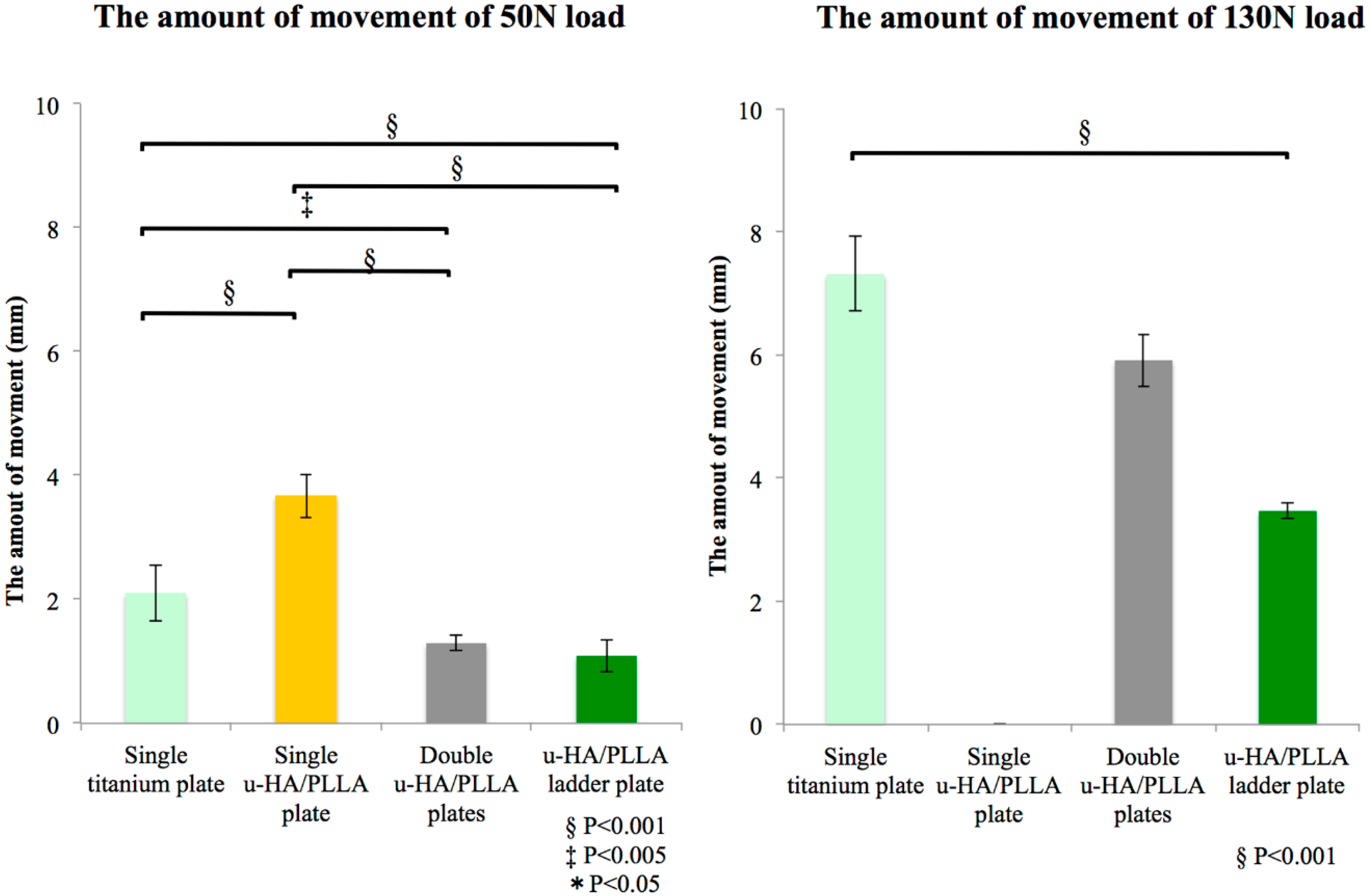
| The Amount of Movement of 50N Load (mm) | ||||
| Plate | Single Titanium Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA Plate | Double u-HA/PLLA Plates | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 2.58 | 4.02 | 1.34 | 0.80 |
| #2 | 2.05 | 3.64 | 1.16 | 1.32 |
| #3 | 1.68 | 3.33 | 1.38 | 1.14 |
| Ave. | 2.10 | 3.66 | 1.29 | 1.09 |
| S.D. | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.26 |
| The Amount of Movement of 130N Load (mm) | ||||
| Plate | Single Titanium Plate | Single u-HA/PLLA | Double u-HA/PLLA | u-HA/PLLA Ladder Plate |
| #1 | 7.39 | - | - | 3.33 |
| #2 | 6.67 | - | 6.21 | 3.57 |
| #3 | 7.87 | - | 5.61 | 3.49 |
| Ave. | 7.31 | - | - | 3.46 |
| S.D. | 0.60 | - | - | 0.12 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukegawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Manabe, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Sukegawa-Takahashi, Y.; Masui, M.; Furuki, Y. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy. Materials 2017, 10, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070764
Sukegawa S, Kanno T, Manabe Y, Matsumoto K, Sukegawa-Takahashi Y, Masui M, Furuki Y. Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy. Materials. 2017; 10(7):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070764
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukegawa, Shintaro, Takahiro Kanno, Yoshiki Manabe, Kenichi Matsumoto, Yuka Sukegawa-Takahashi, Masanori Masui, and Yoshihiko Furuki. 2017. "Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy" Materials 10, no. 7: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070764
APA StyleSukegawa, S., Kanno, T., Manabe, Y., Matsumoto, K., Sukegawa-Takahashi, Y., Masui, M., & Furuki, Y. (2017). Biomechanical Loading Evaluation of Unsintered Hydroxyapatite/poly-l-lactide Plate System in Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy. Materials, 10(7), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070764






