Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
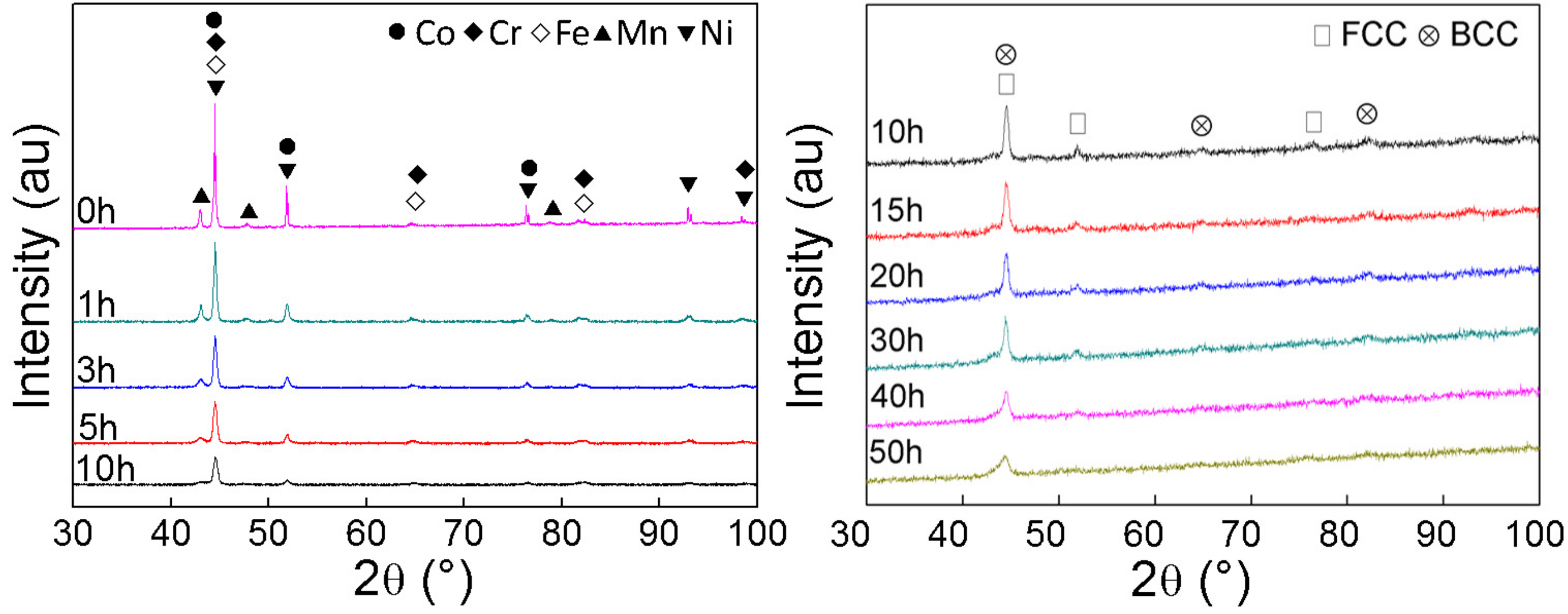
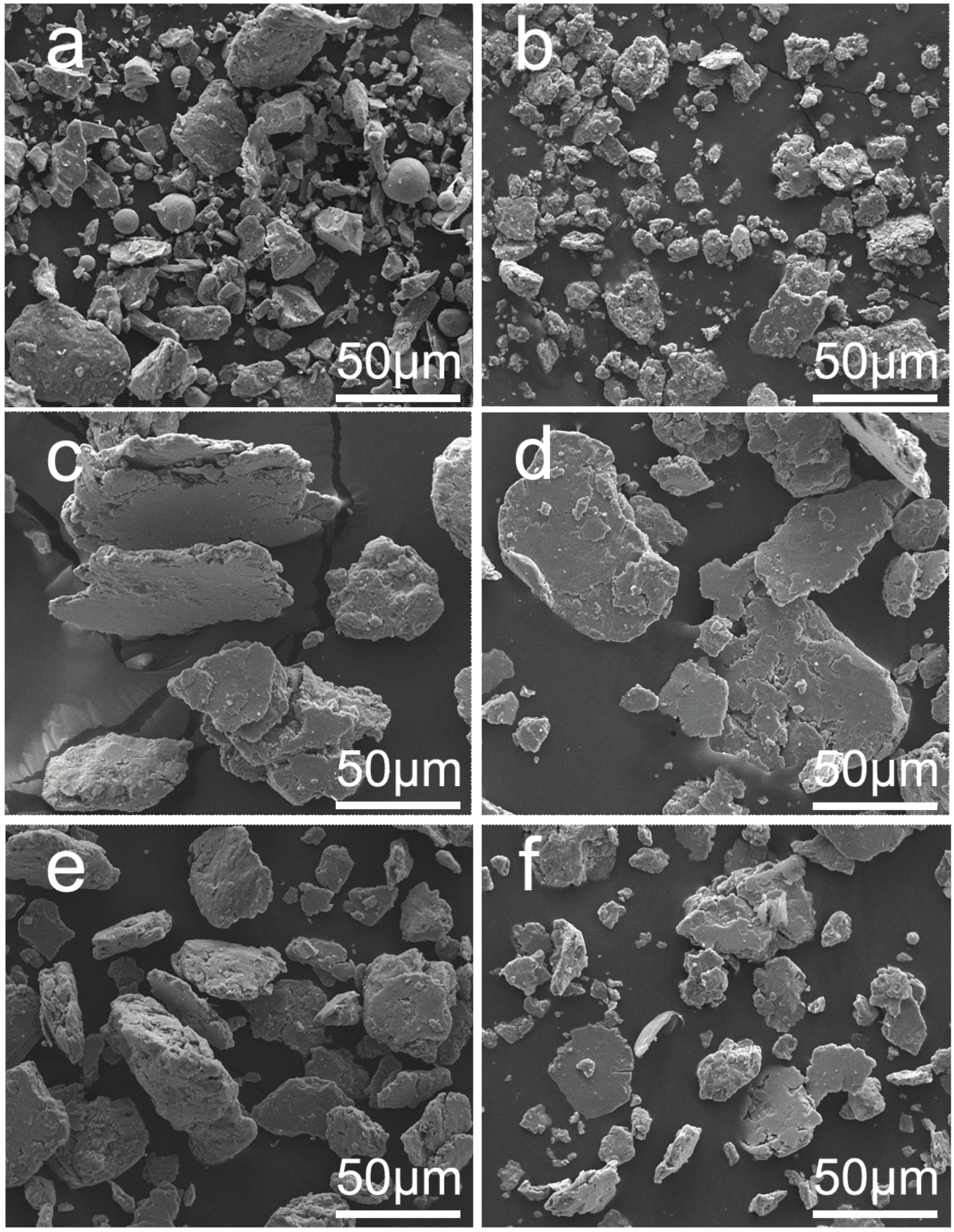
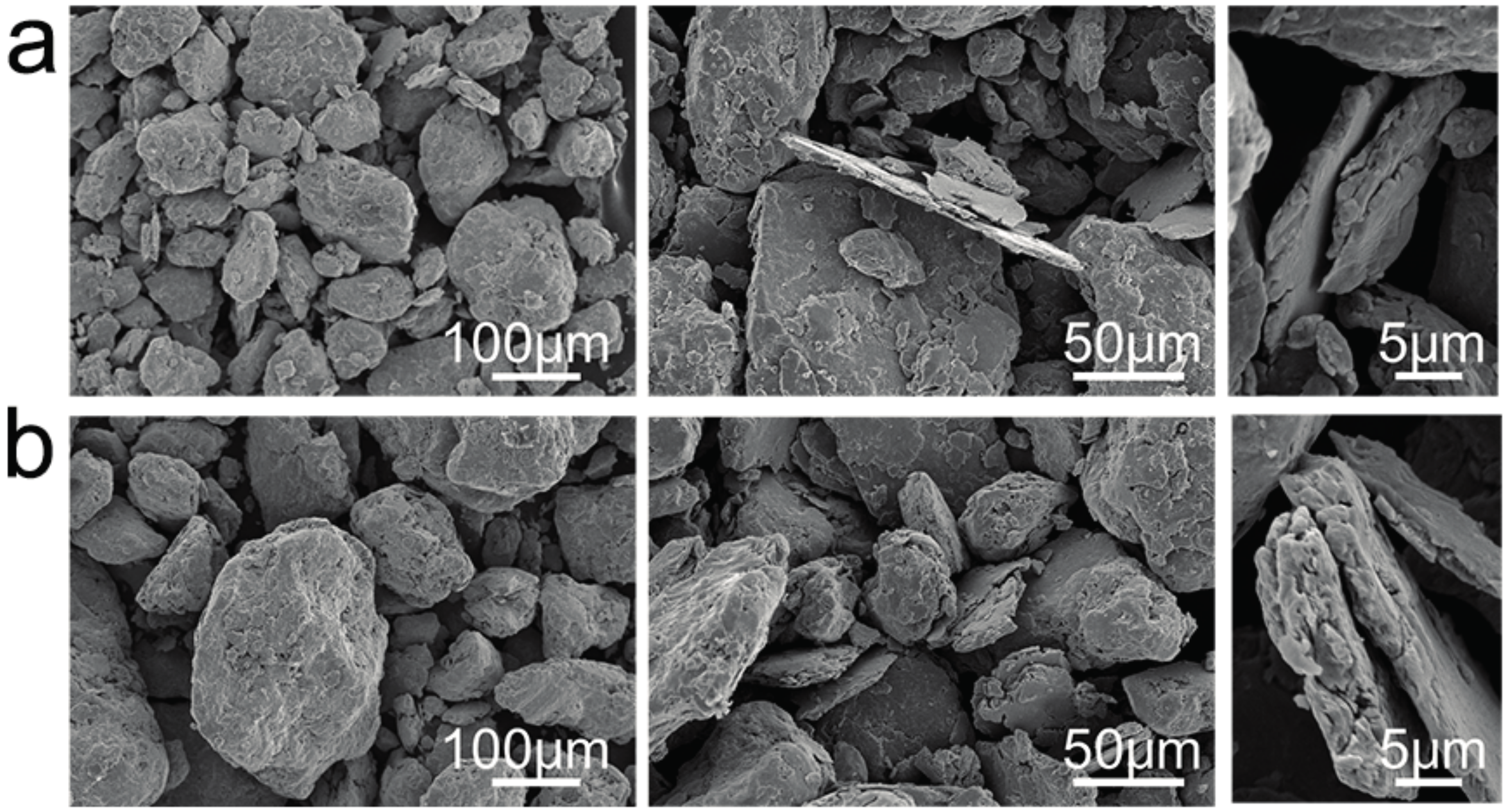
3.1. Phase Evolution and Microstructure during MA
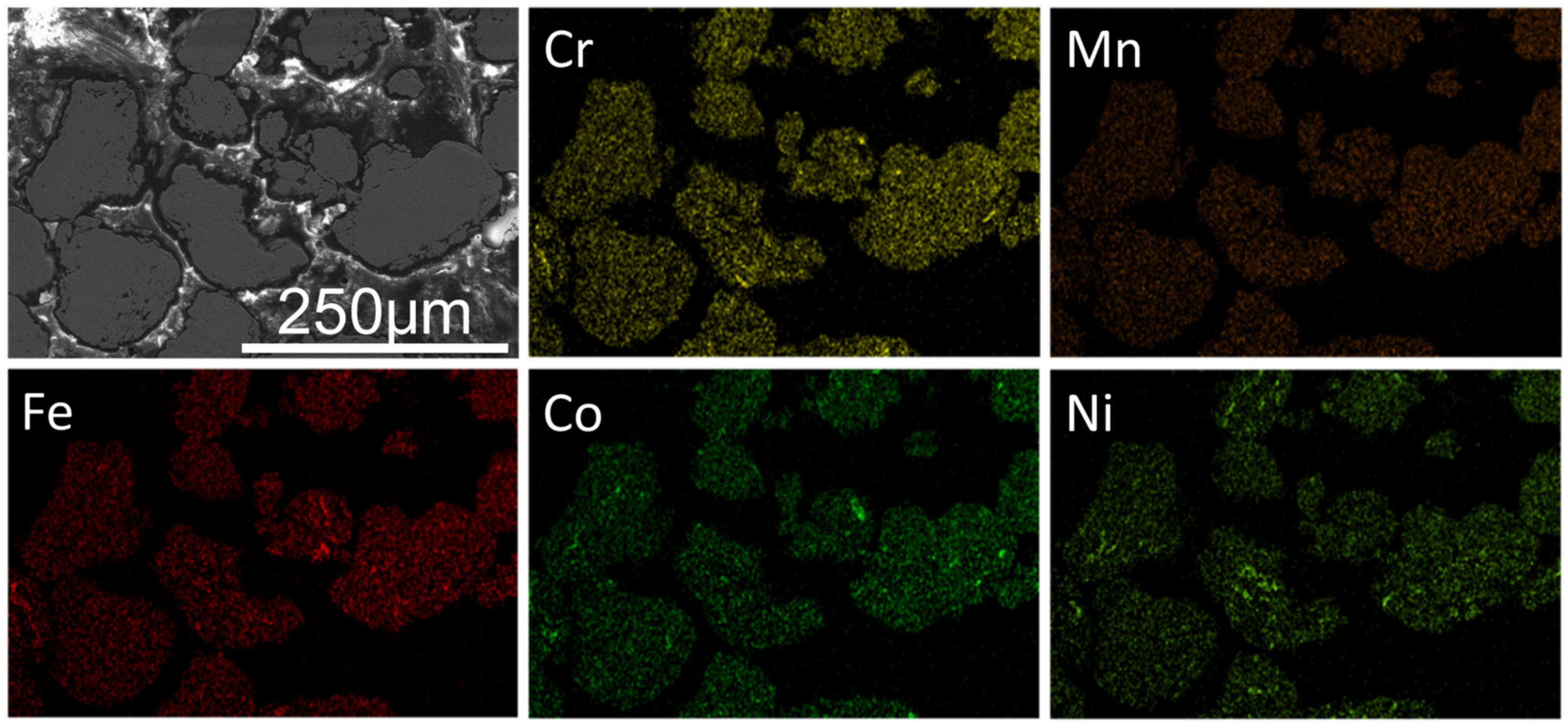
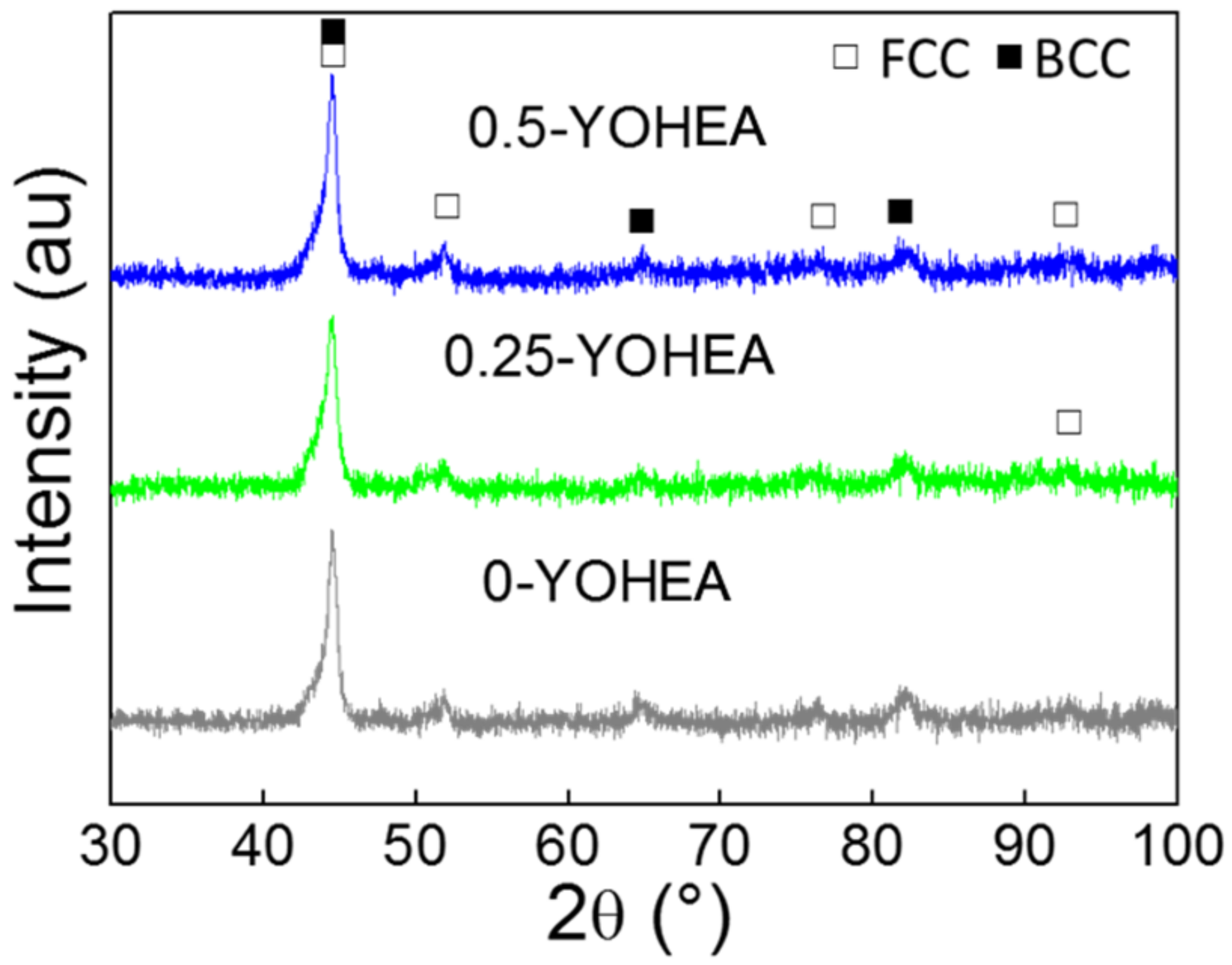
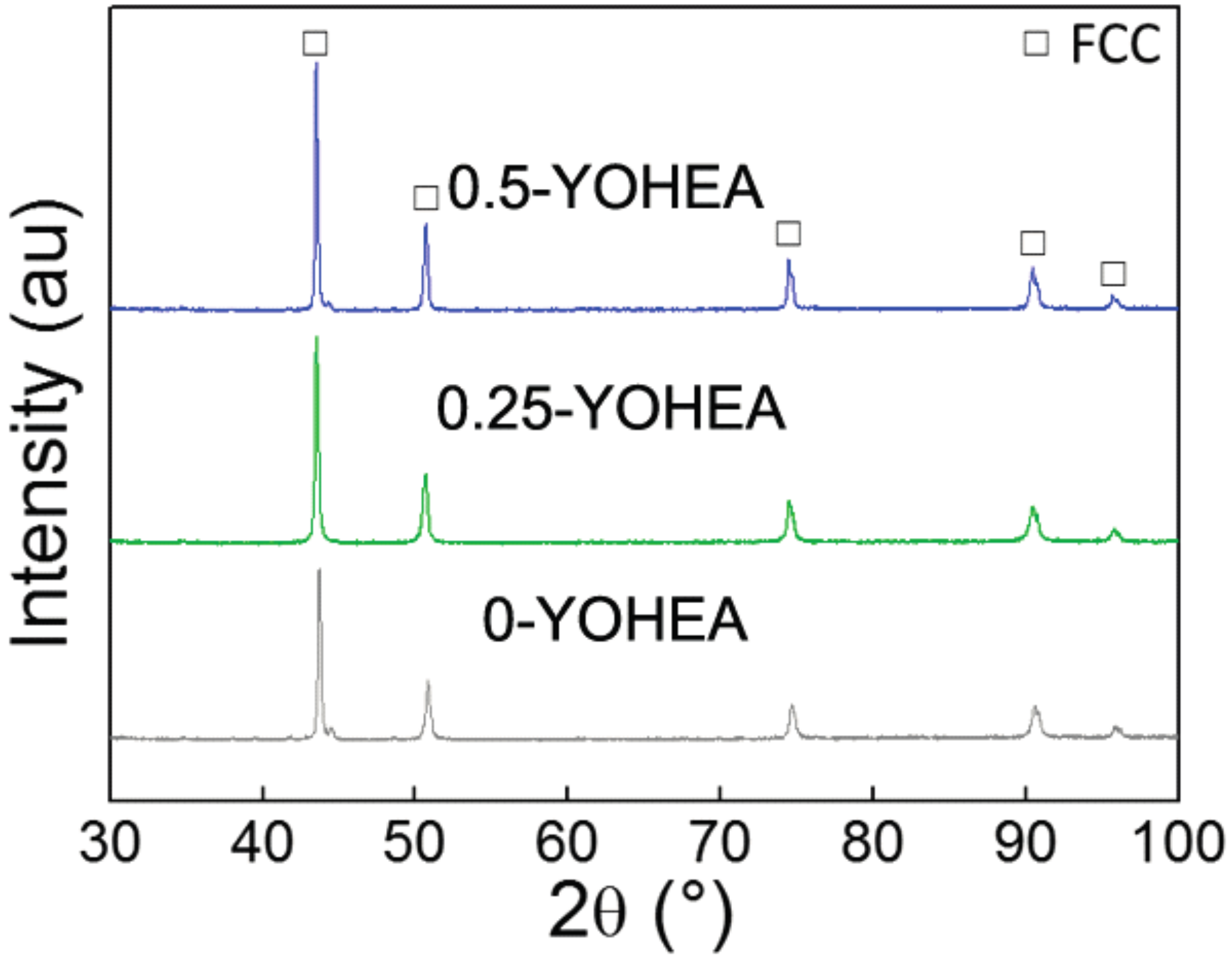
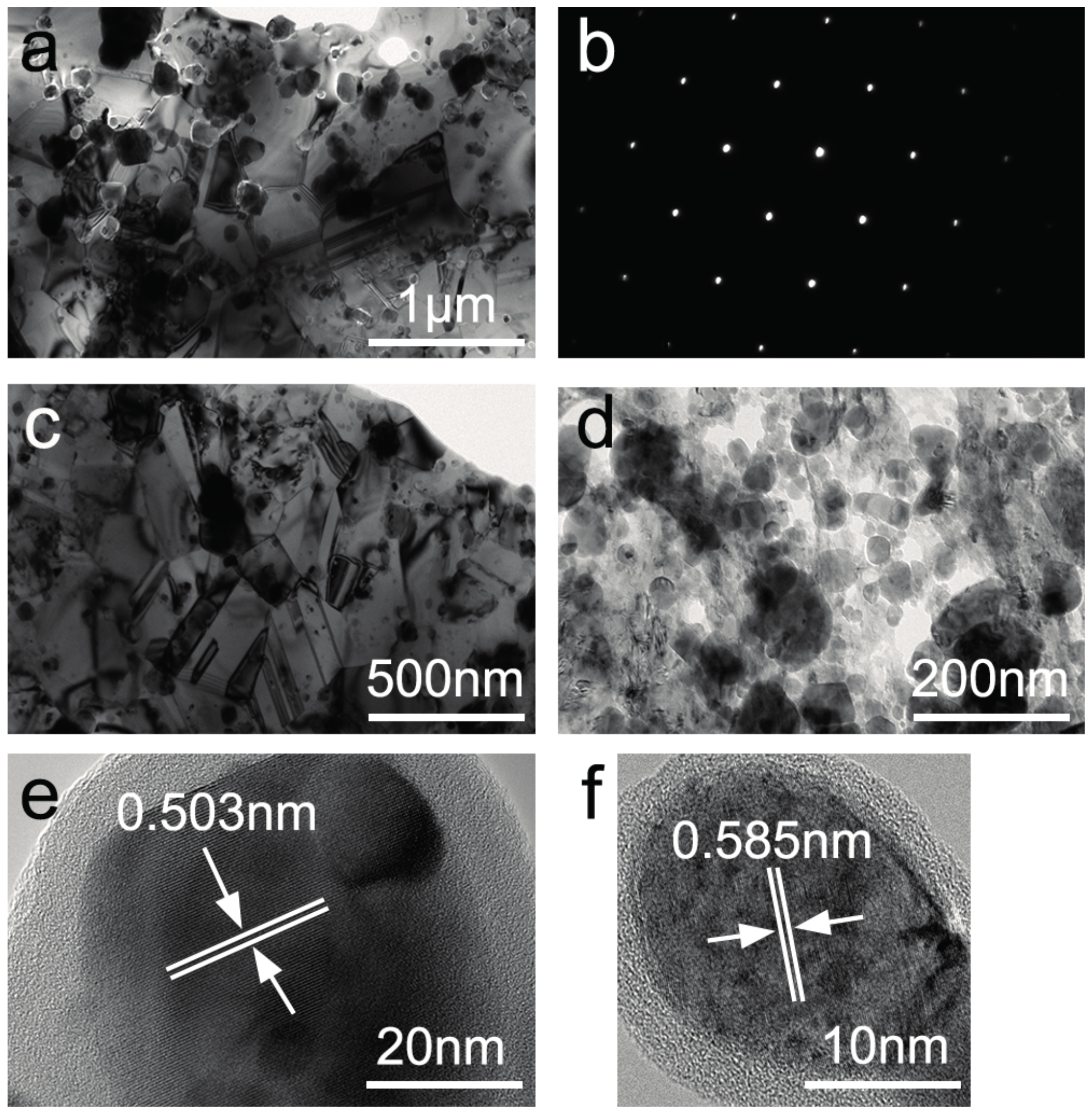
3.2. Phase Evolution and Microstructure after SPS
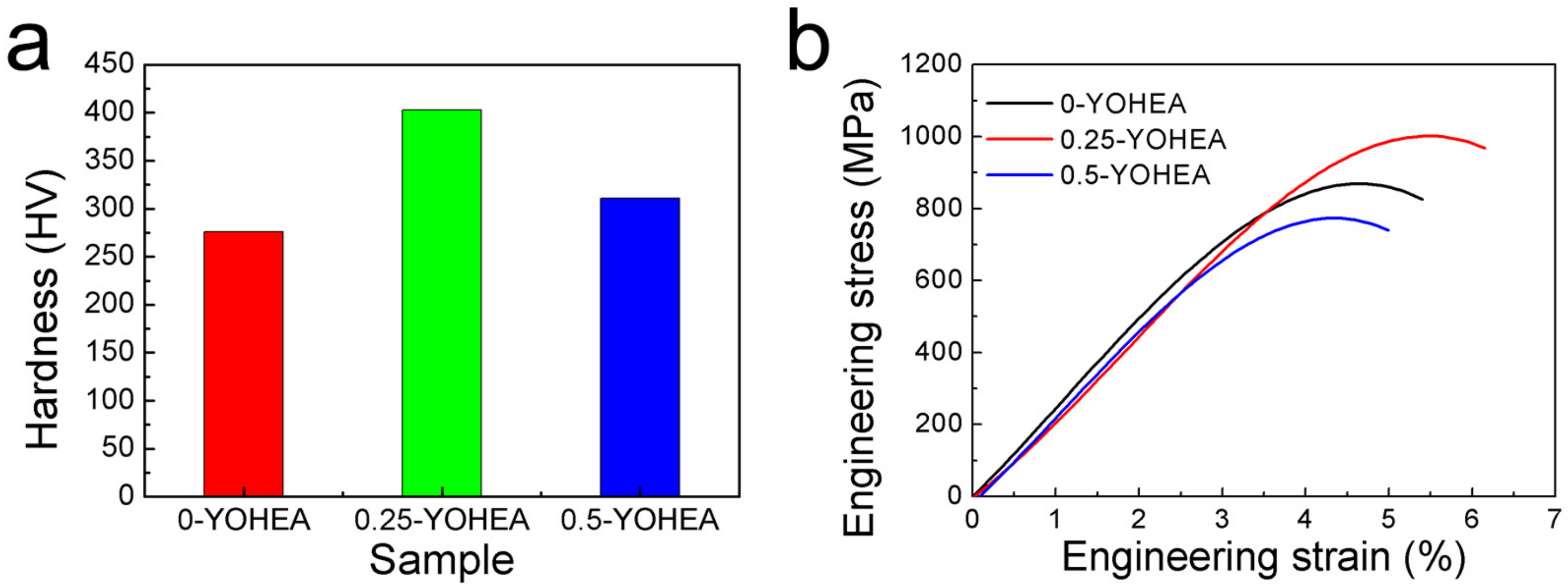
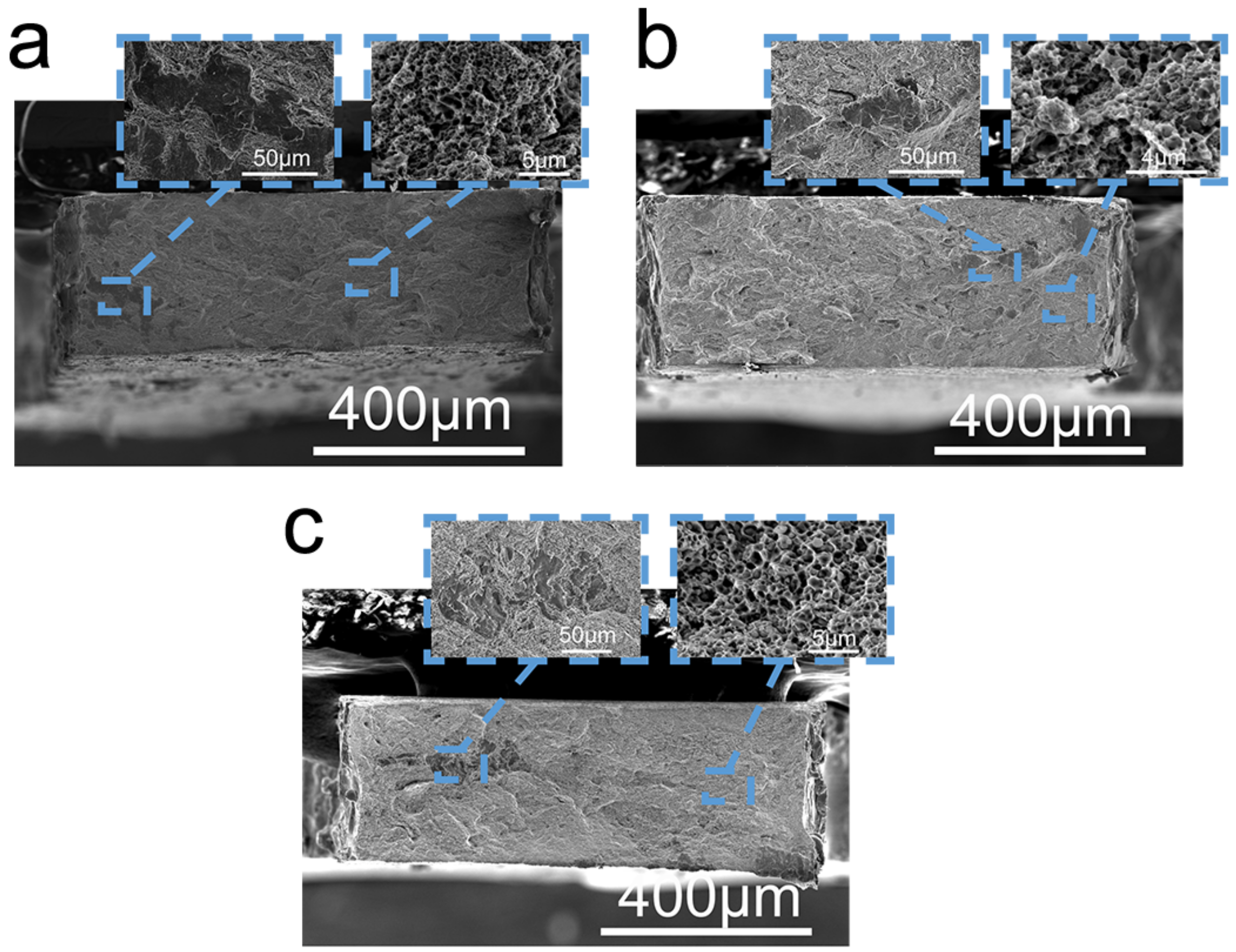
3.3. Mechanical Properties
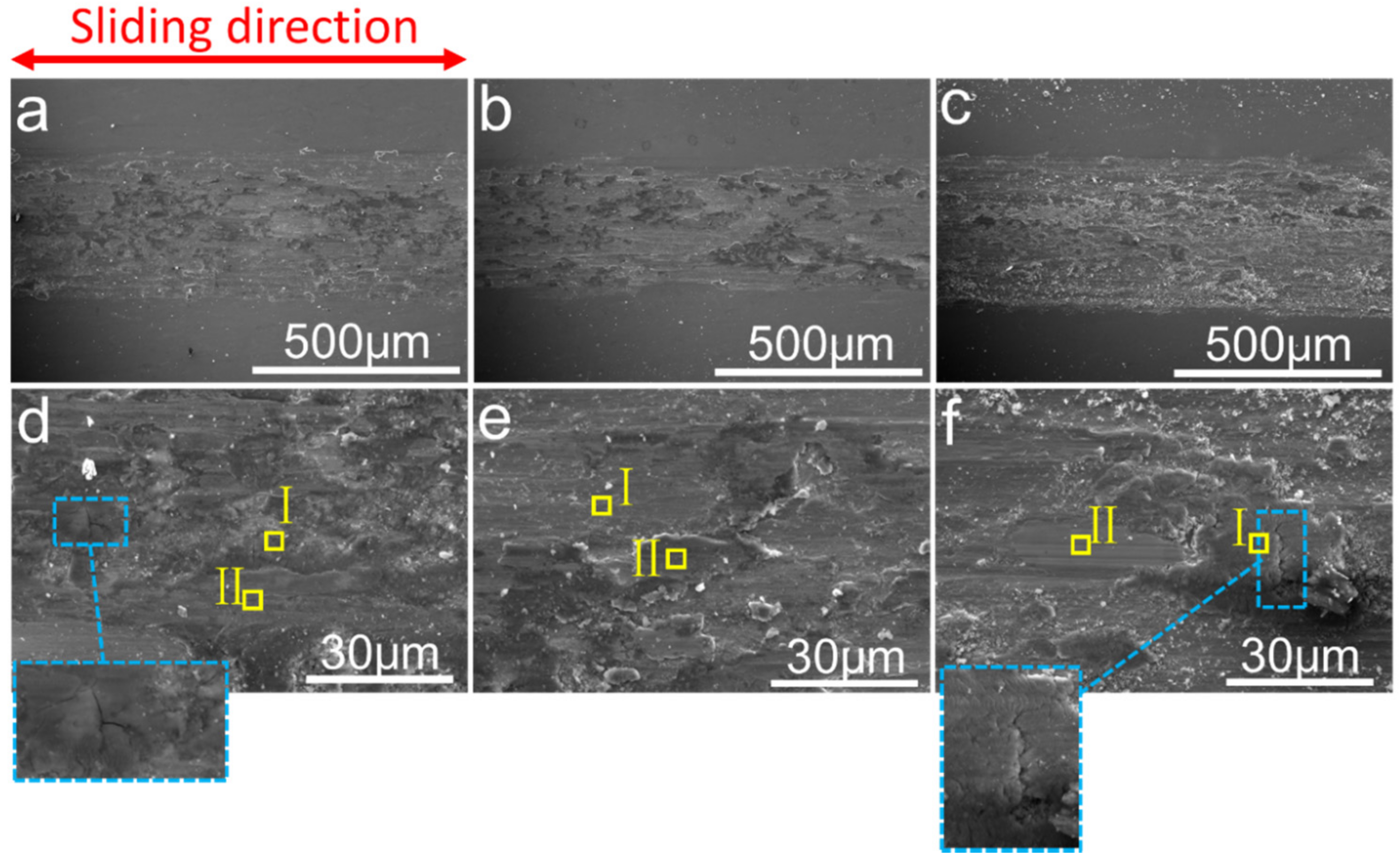
3.4. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
- A new ODS-CrMnFeCoNi HEA matrix composite was successfully prepared from elemental powders by using MA and SPS. The as-milled HEA powders exhibited FCC phase and BCC phase. After sintering, the composite material consists of a single FCC structure and Y2O3 nanoparticles in homogeneous dispersion state.
- With increasing content of Y2O3, only 0.25 wt % Y2O3 nanoparticles can improve the strength to 1000 MPa, which was 15.2% higher than the CrMnFeCoNi matrix. Additionally, the strain also increased from 5.4% to 6.1%. This is mainly because of the grain boundary strengthening effect, orowan looping, and load transfer effect. However, with 0.5 wt % Y2O3 nanoparticles, both the strength and strain were decreased, and this may contributed to some complicated reasons.
- The addition of Y2O3 nanoparticles increased the hardness of alloy, from 246 HV to 403 HV and 311 HV, respectively. The increase in hardness due to the fine grain strengthening effect, while the decrease in hardness may be caused by the inverse Hall-Petch effect.
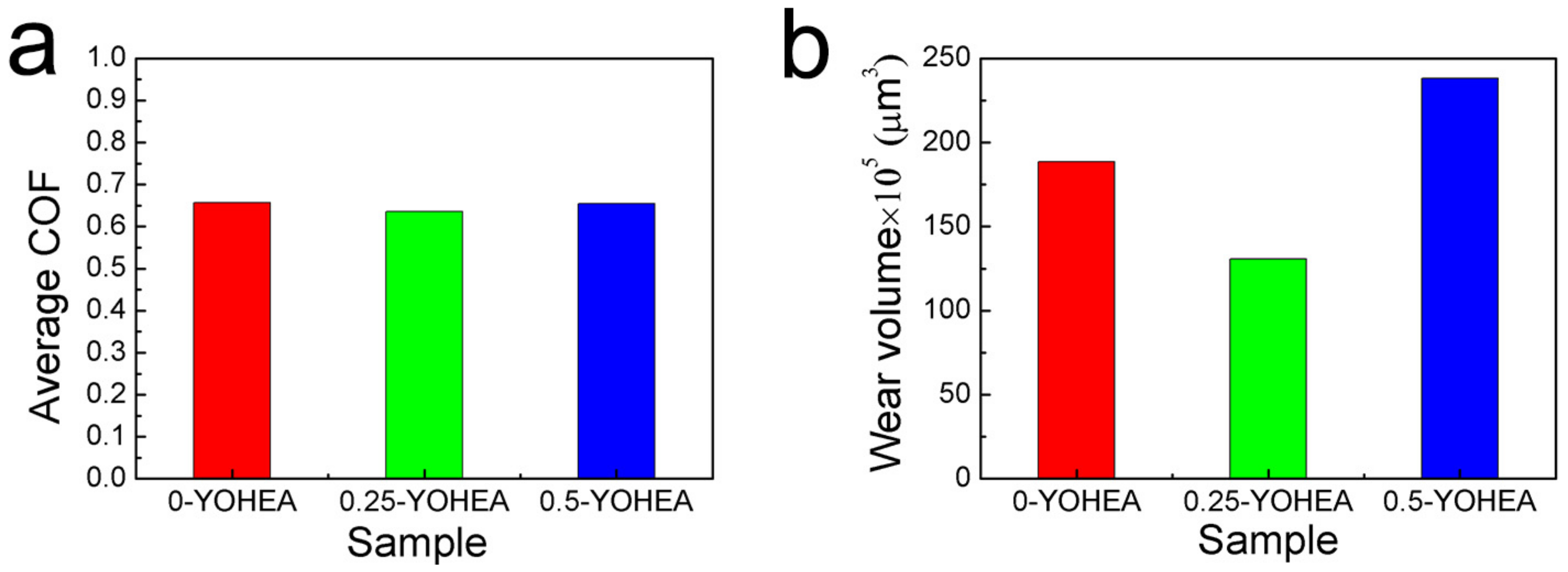
- All of the composites exhibited a similar COF, which showed the excellent friction-reducing abilities, meanwhile the addition of 0.25 wt % Y2O3 nanoparticles showed the best anti-wear abilities.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lui, H.-W.; Cai, M.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure, hardness, resistivity and thermal stability of sputtered oxide films of AlCoCrCu0.5NiFe high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 473, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł.; Czerwinski, F.; Jochym, P.T.; Litynska-Dobrzynska, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the novel Hf25Sc25Ti25Zr25 equiatomic alloy with hexagonal solid solutions. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.; Wang, T.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.; Jie, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Dang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T. Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 656, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł.; Morgiel, J.; Świątek, Z.; Czerwiński, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the new Nb25Sc25Ti25Zr25 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jie, J.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Ruan, H.; et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Moon, J.; Ji, J.M.; Yim, D.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.S. Trade-off between tensile property and formability by partial recrystallization of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of superfine-grained high entropy alloy by spark plasma sintering gas atomized powder. Intermetallics 2016, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.-H.; Kato, H.; Jang, M.J.; Moon, J.; Kim, E.B.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, H.S. Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys produced by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł.; Kalita, D.; Tarasek, A.; Bobrowski, P.; Czerwinski, F. Effect of SiC nano-particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of the CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 708, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Han, J.; Su, B.; Li, P.; Meng, J. Microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological performance of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy matrix self-lubricating composite. Acta Mater. 2017, 114, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Hu, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-A.; Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K. Competition between elements during mechanical alloying in an octonary multi-principal-element alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 481, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.B.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, W.M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, Q.J. Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy solid solution synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 485, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Chen, W.; Fu, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of twinned Al0.5CrFeNiCo0.3C0.2 high entropy alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Arzt, E. Temperature rise during mechanical alloying. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1992, 27, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.D.; Yurchenko, N.Y.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. Effect of carbon content and annealing on structure and hardness of the CoCrFeNiMn based high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 687, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Gavendova, P.; Sheikh, S.; Guo, S.; Dlouhy, I. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 174, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shi, Y.N.; Sauvage, X.; Sha, G.; Lu, K. Grain boundary stability governs hardening and softening in extremely fine nanograined metals. Science 2017, 6331, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, M.A.; Mishra, A.; Benson, D.J. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 427–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detor, J.A.; Schuh, C.A. Tailoring and patterning the grain size of nanocrystalline alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 155, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Metal matrix composites reinforced by nano-particles—A review. Metals 2014, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.; Xiong, D.S.; Li, J.; Dai, J. Elevated temperature tribological behavior of Ni based composites containing nano-silver and hBN. Wear 2010, 269, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Lu, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, G. Microstructure and tribological properties of Fe–Cr matrix self-lubricating composites against Si3N4 at high temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 611, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Han, J.; Wu, G. High-temperature wear behavior of self-lubricating Co matrix alloys prepared by P/M. Wear 2016, 347–346, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, Y.; Hu, L.; Xue, Q. Fabrication of a nanocrystalline Ni-Co/CoO functionally graded layer with excellent electrochemical corrosion and tribological performance. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4614–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Tang, B.; Qiao, J. Dry sliding tribological properties of a dendrite-reinforced Zr-based bulk metallic glass matrix composite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Milling Time (h) | CS (nm) | LS (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30.35414 | 0.145 |
| 3 | 23.81794 | 0.178 |
| 5 | 21.61512 | 0.205 |
| 10 | 17.23008 | 0.245 |
| 15 | 14.33161 | 0.307 |
| 20 | 12.83324 | 0.386 |
| 30 | 11.14773 | 0.468 |
| 40 | 10.17895 | 0.575 |
| 50 | 7.972322 | 0.843 |
| Sample | TS (MPa) | Strain (%) | Microhardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-YOHEA | 868 | 5.4 | 276 |
| 0.25-YOHEA | 1000 | 6.1 | 403 |
| 0.5-YOHEA | 773 | 4.9 | 311 |
| Sample | Place of Analysis | Element (at %) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | O | Y | C | ||
| 0-YOHEA | I | 7.59 | 7.37 | 14.98 | 7.27 | 7.13 | 55.66 | - | - |
| II | 15.61 | 15.18 | 15.17 | 14.3 | 13.6 | 8.97 | - | 17.17 | |
| 0.25-YOHEA | I | 8.45 | 8.32 | 15.62 | 7.7 | 7.43 | 52.1 | 0.16 | - |
| II | 14.33 | 15.1 | 16.86 | 12.34 | 14.52 | 6.41 | 0.1 | 20.06 | |
| 0.5-YOHEA | I | 9.56 | 9.64 | 13.13 | 9.35 | 8.9 | 35.1 | 0.04 | 14 |
| II | 19.06 | 18.63 | 21.05 | 17.92 | 17.72 | 4.74 | 0.43 | - | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Yin, H.; Xu, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Materials 2017, 10, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111312
Liu X, Yin H, Xu Y. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Materials. 2017; 10(11):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111312
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinyu, Hangboce Yin, and Yi Xu. 2017. "Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys" Materials 10, no. 11: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111312
APA StyleLiu, X., Yin, H., & Xu, Y. (2017). Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Materials, 10(11), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111312




