Impacts of Modification of Alloying Method on Inclusion Evolution in RH Refining of Silicon Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Oxide Inclusions in RH Refining
3.2. Quality and Cost Analysis of the Pre-Alloying Innovation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
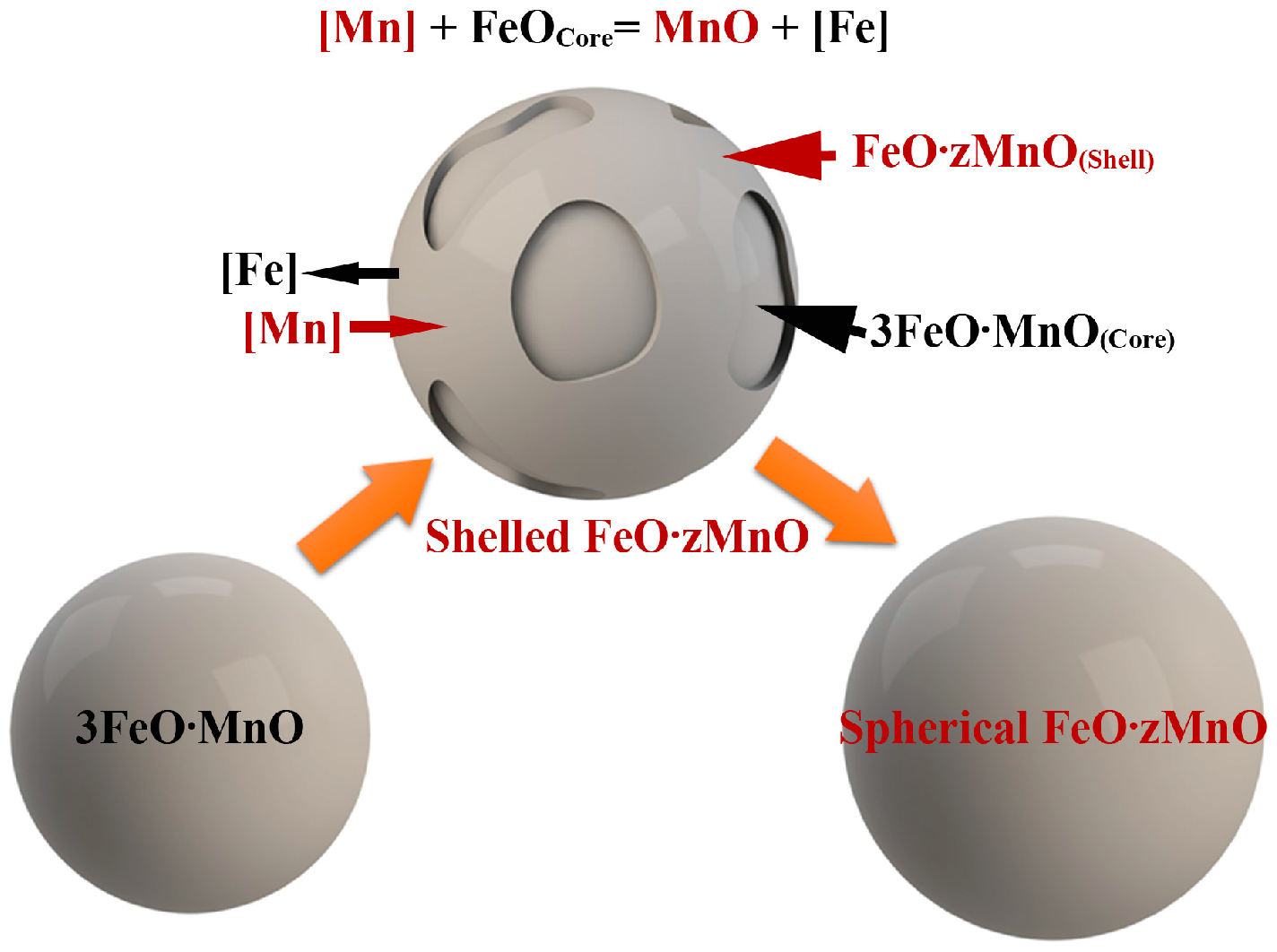
- MnO-FeO inclusions formed as a by-product of pre-alloying. The evolution of the oxide is as follows: spherical Fe-rich 3FeO·MnO becomes shelled Fe-rich, low-melting point 3FeO·MnO in the core and Mn-rich, high-melting point FeO·zMnO on the surface of the shell. Some of shelled inclusions become spherical Mn-rich FeO·zMnO. These inclusions are eliminated at the beginning of the degassing stage.
- (2)
- Inclusion evolution in pre-alloying RH refining is different from that in conventional RH refining, but the ingots produced by pre-alloying are of a quality that meets or exceeds industry-wide specifications with respect to quality, carbon content, and inclusion size.
- (3)
- When pre-alloying is used, the amount of high-cost, low-carbon FeMn alloy required during the deoxidization/alloying stage is reduced by 20%, thus reducing the overall cost of the process by 3%.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Y.F.; Ye, F.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Effect of annealing temperature on magnetic properties of cold rolled high silicon steel thin sheet. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 491, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, J.P.; Descotes, V.; Jardy, A. Numerical modeling of inclusion behavior in liquid metal processing. JOM 2013, 65, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Todoroki, H. Control of MgO·Al2O3 spinel inclusions in stainless steels. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuhiro, S.; Mizukami, Y. Reaction mechanism between alumina graphite immersion nozzle and low carbon steel. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.Q.; Lei, H.; He, J.C. Effect of traveling magnetic field on flow, mixing, decarburization and inclusion removal during RH refining process. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Pires, J.C.; Cheung, N.; Garcia, A. Influence of refining time on nonmetallic inclusions in a low-carbon, silicon-killed steel. Mater. Charact. 2003, 51, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ende, M.A.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, M.K.; Choi, J.; Jung, I.H. A kinetic model for the Ruhrstahl Heraeus (RH) degassing process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.I.; Liu, C.J.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, M.F. Effect of deoxidation process on distribution characteristics of inclusions in silicon steel slabs. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2015, 22, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, S.; Louhenkilpi, S.; Holappa, L. Optimization of intensified silicon deoxidation. Steel Res. Int. 2013, 84, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Choi, J.; Sridhar, S. The morphology and chemistry evolution of inclusions in Fe-Si-Al-O melts. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2011, 42, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, N.; Ishido, K.; Mori, K.; Kawai, Y. Rate of reduction of MnO in slag by liquid iron containing carbon. Tetsu-to-Hagané 1984, 70, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suito, H.; Inoue, R. Assessment of maganese distribution in hot metal and steel. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hils, G.; Newirkowez, A.; Kroker, M.; Grethe, U.; Jürgensen, R.S.; Kroos, J.; Spitzer, K.H. Conventional and tailored Mn-bearing alloying agents for the production of high manganese steels. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Rhee, C.H.; Min, D.J. Thermodynamic properties of manganese oxide in BOF slags. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Eriksson, G.; Pelton, A.D. Critical evaluation and optimization of the thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams of the CaO-FeO, CaO-MgO, CaO-MnO, FeO-MgO, FeO-MnO, and MgO-MnO systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ende, M.A.; Guo, M.; Proost, J.; Blanpain, B.; Wollants, P. Formation and morphology of Al2O3 inclusions at the onset of liquid Fe deoxidation by Al addition. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Taniguchi, S.; Cai, K. Fluid flow and inclusion removal in continuous casting tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2000, 31, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, H.; Karasev, A.; Jönsson, P.G. A comparison of a two-dimensional and a three-dimensional method for inclusion determinations in tool steel. Steel Res. Int. 2010, 81, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, R.; Blanpain, B.; Wollants, P. Crystal growth in liquid steel during secondary metallurgy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, N. Production of ultra-low carbon steel by combined process of bottom-blown converter and RH degasser. Kawasaki Steel Tech. Rep. 1983, 8, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, R. Low-carbon steels manufactured by circulating flow vacuum degassing process. JOM 1966, 18, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.D.; Lee, B.W.; Pak, J.J. Manganese loss during the oxygen refining of high-carbon ferromanganese melts. Met. Mater. Int. 1999, 5, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Metal. Available online: http://www.asianmetal.com/FerromanganesePrice/Ferromanganese.html. (accessed on 25 August 2017).
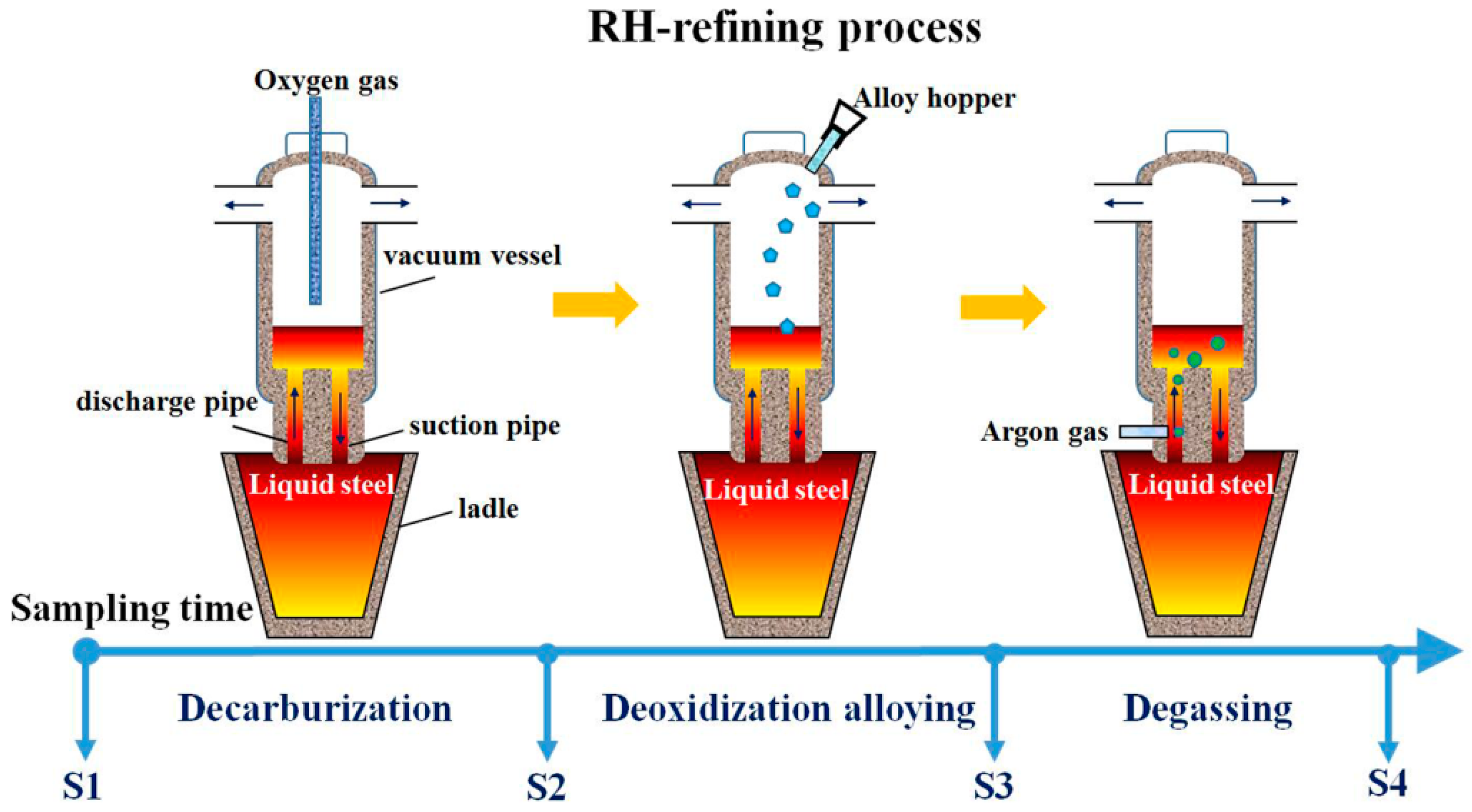
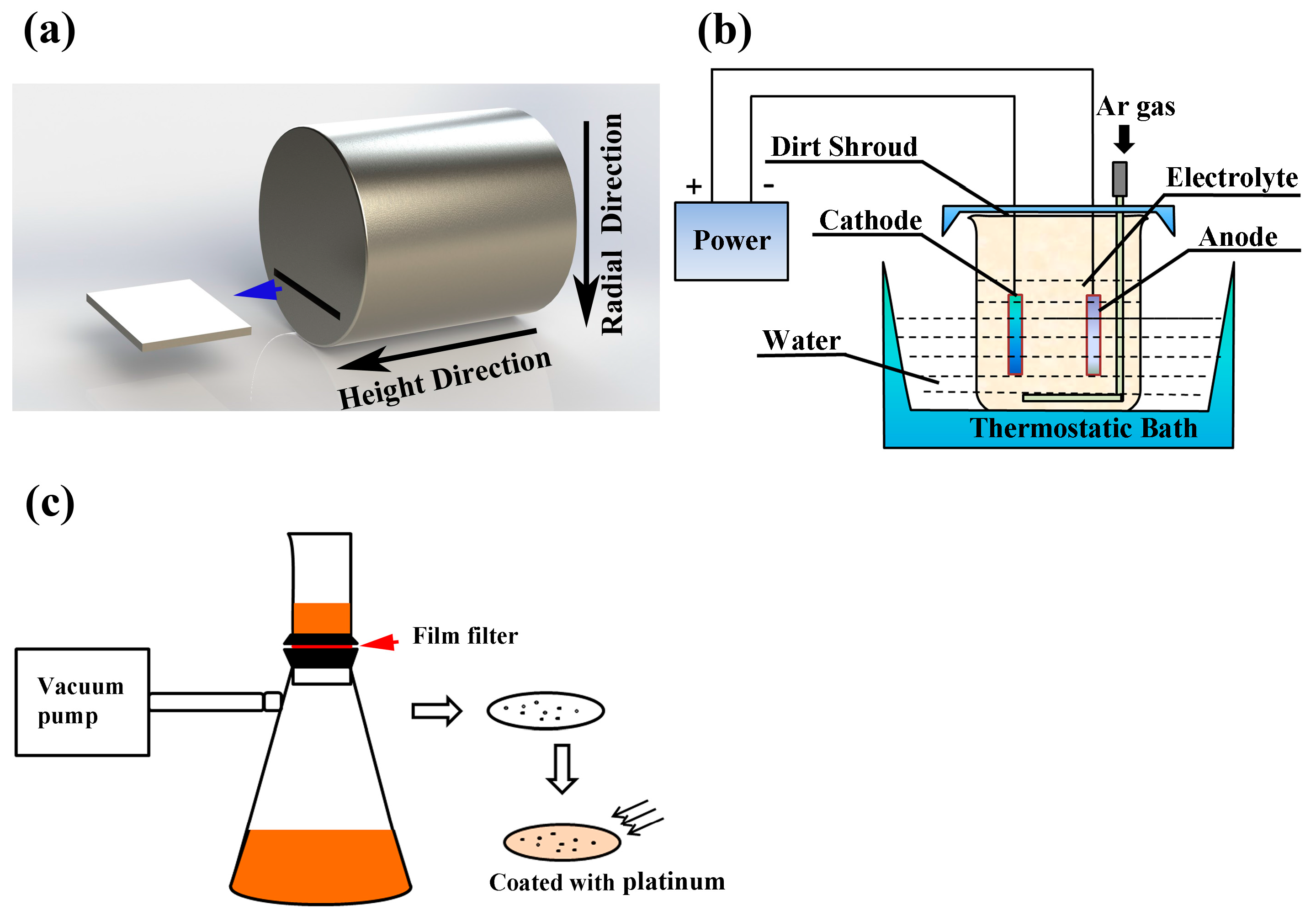
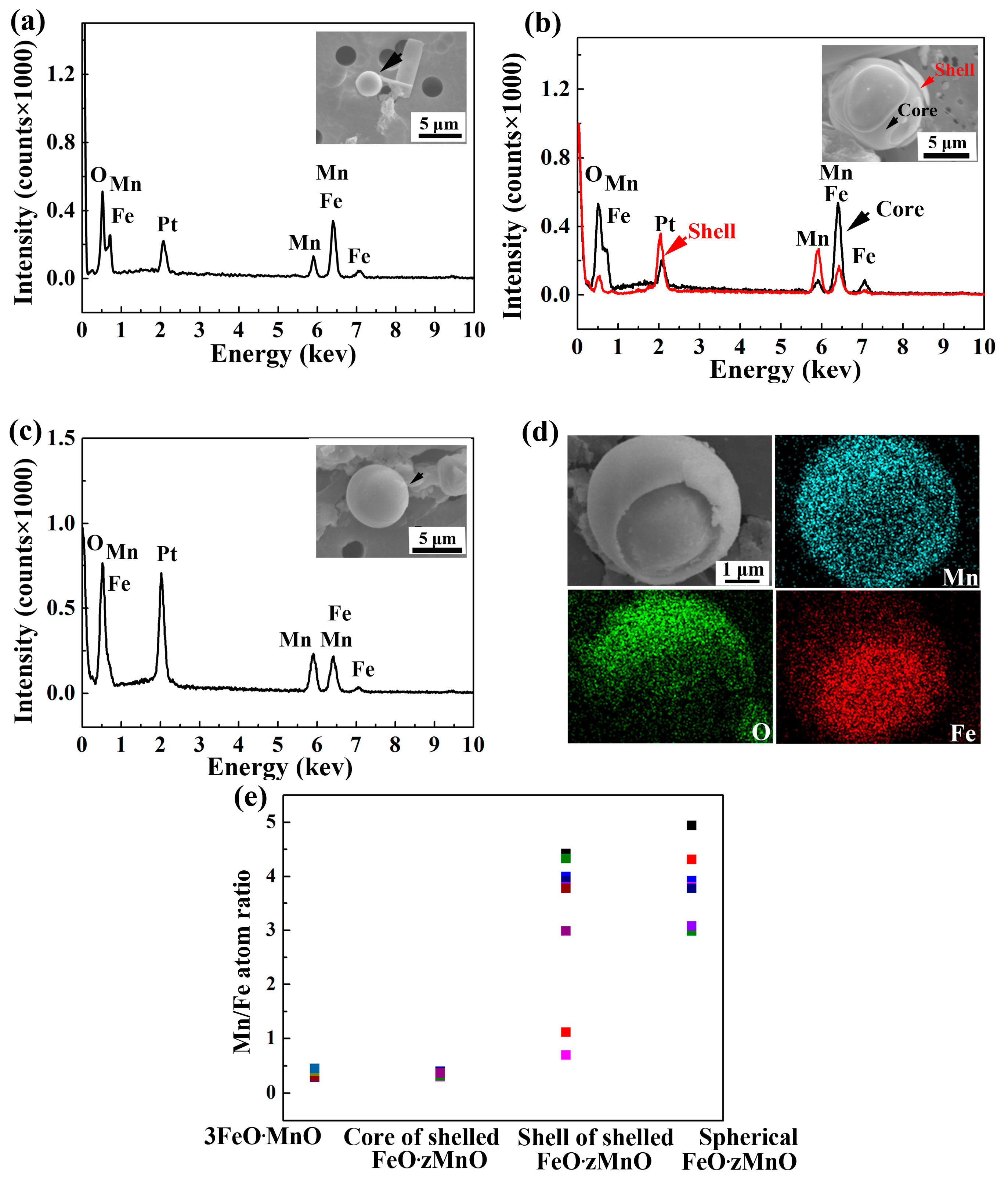
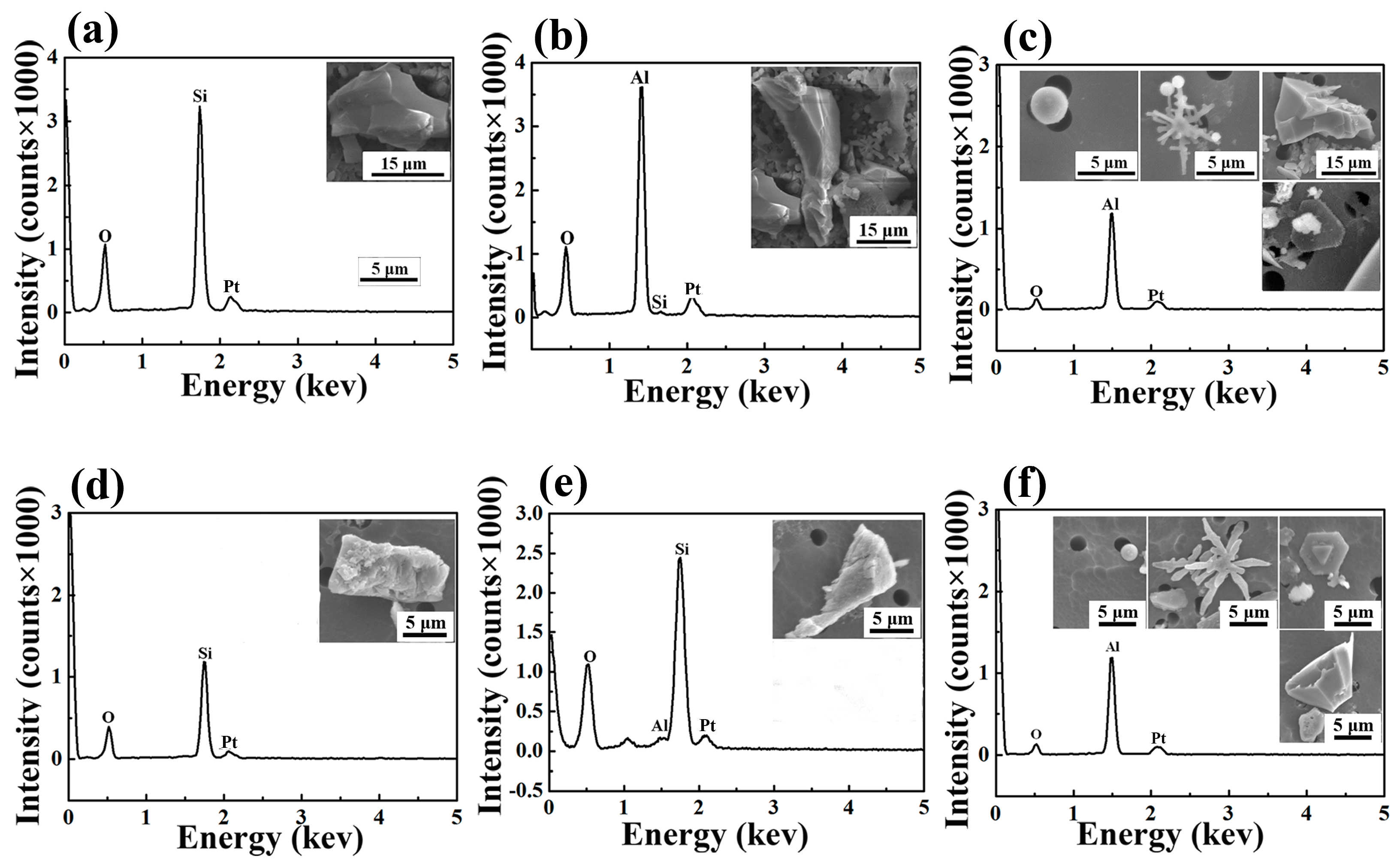
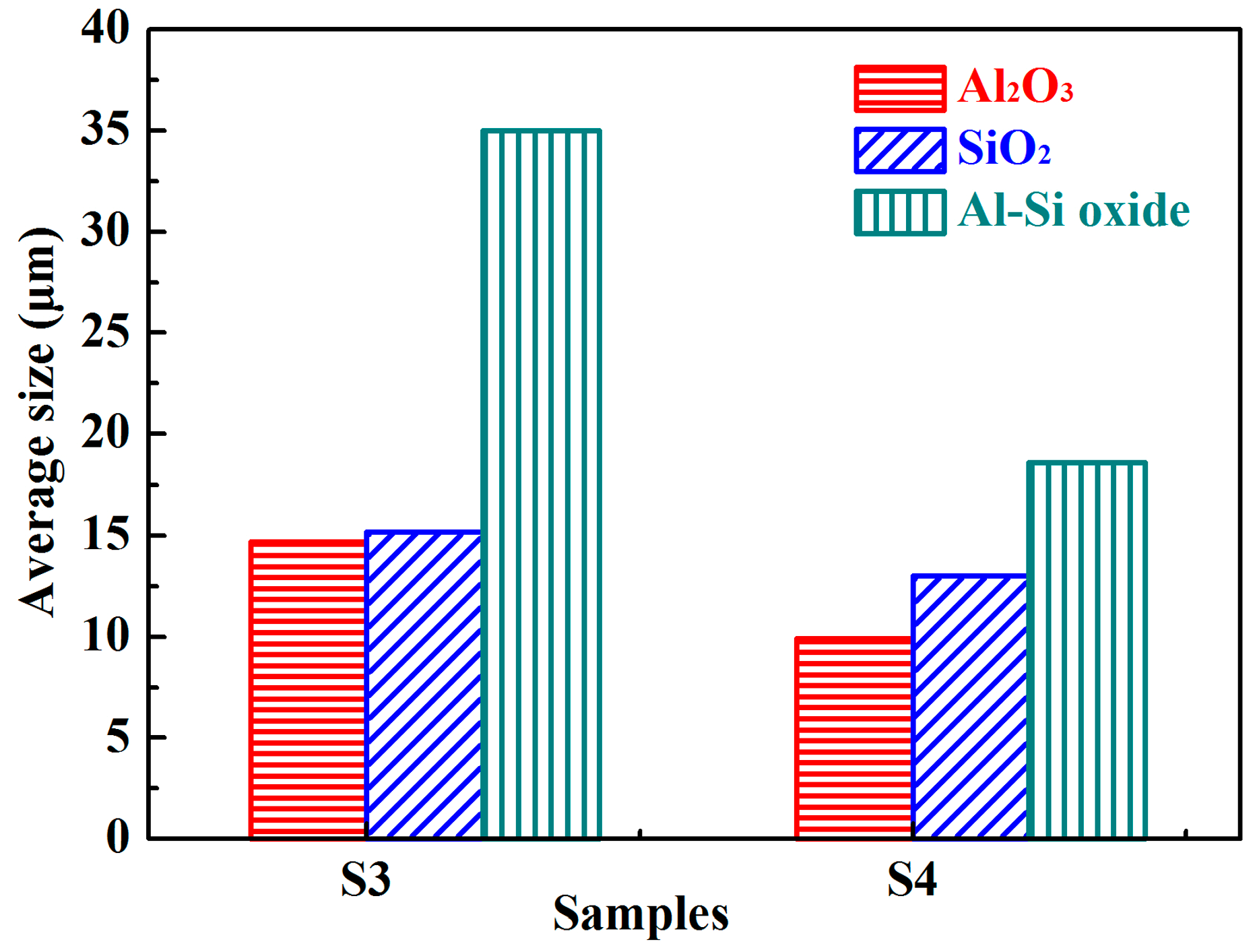
| Process | Point | C | Si | Mn | Als |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-alloying process | S1 | 4.4 × 10−2 | 2.1 × 10−3 | 6.1 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−3 |
| S2 | 1.0 × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 4.9 × 10−2 | 1.9 × 10−3 | |
| S3 | 5.0 × 10−3 | 2.6 × 10−1 | 3.0 × 10−1 | 3.3 × 10−1 | |
| S4 | 1.0 × 10−3 | 2.6 × 10−1 | 3.6 × 10−1 | 2.8 × 10−1 | |
| Conventional alloying process | End of RH | <5.0 × 10−3 | 2.5 × 10−1 | 3.5 × 10−1 | 2.8 × 10−1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; You, J.; Han, K.; Zhai, Q. Impacts of Modification of Alloying Method on Inclusion Evolution in RH Refining of Silicon Steel. Materials 2017, 10, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101206
Li F, Li H, Zheng S, You J, Han K, Zhai Q. Impacts of Modification of Alloying Method on Inclusion Evolution in RH Refining of Silicon Steel. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101206
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fangjie, Huigai Li, Shaobo Zheng, Jinglin You, Ke Han, and Qijie Zhai. 2017. "Impacts of Modification of Alloying Method on Inclusion Evolution in RH Refining of Silicon Steel" Materials 10, no. 10: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101206
APA StyleLi, F., Li, H., Zheng, S., You, J., Han, K., & Zhai, Q. (2017). Impacts of Modification of Alloying Method on Inclusion Evolution in RH Refining of Silicon Steel. Materials, 10(10), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101206







