Magnetron Sputtering as a Fabrication Method for a Biodegradable Fe32Mn Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Microstructure
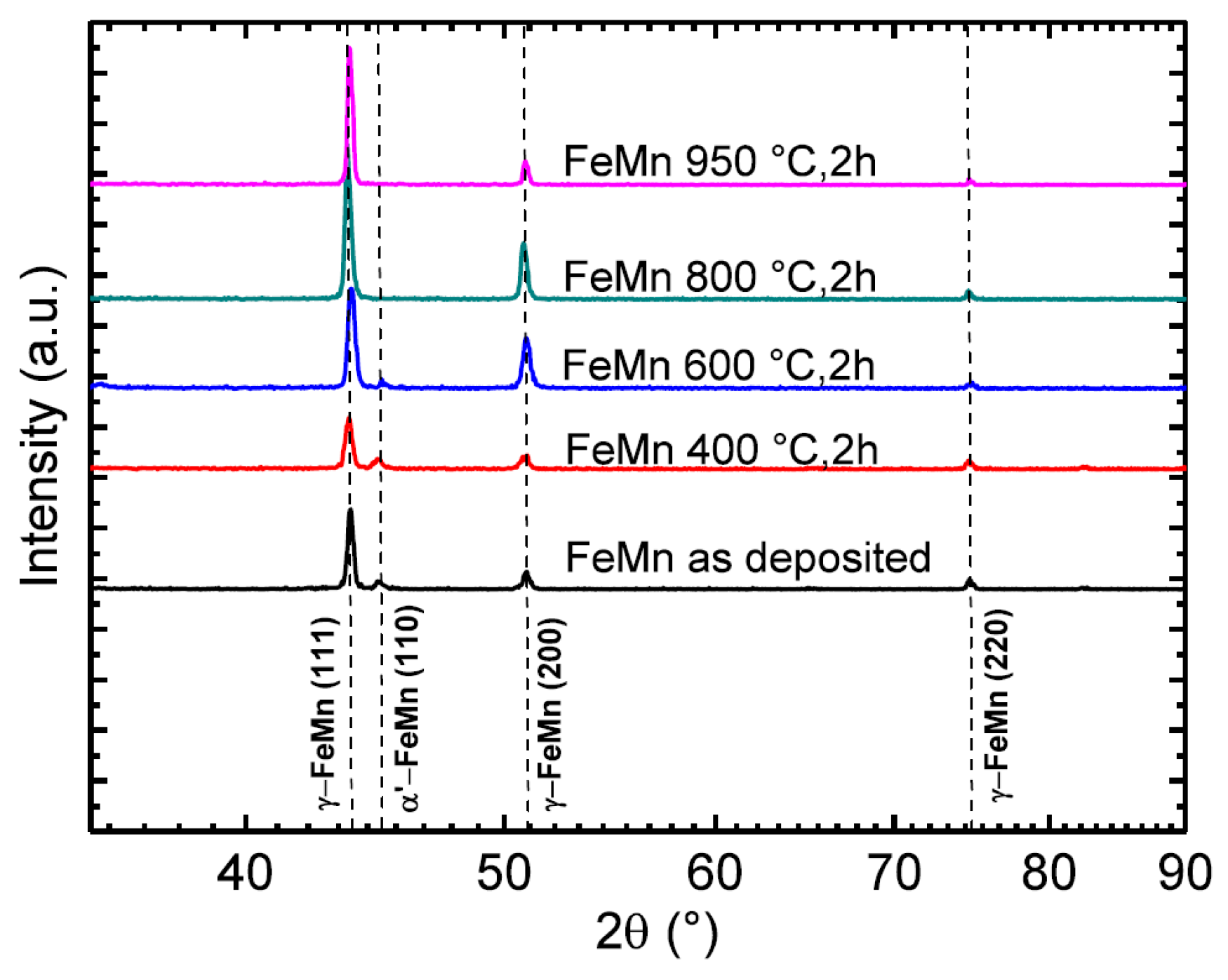
2.2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
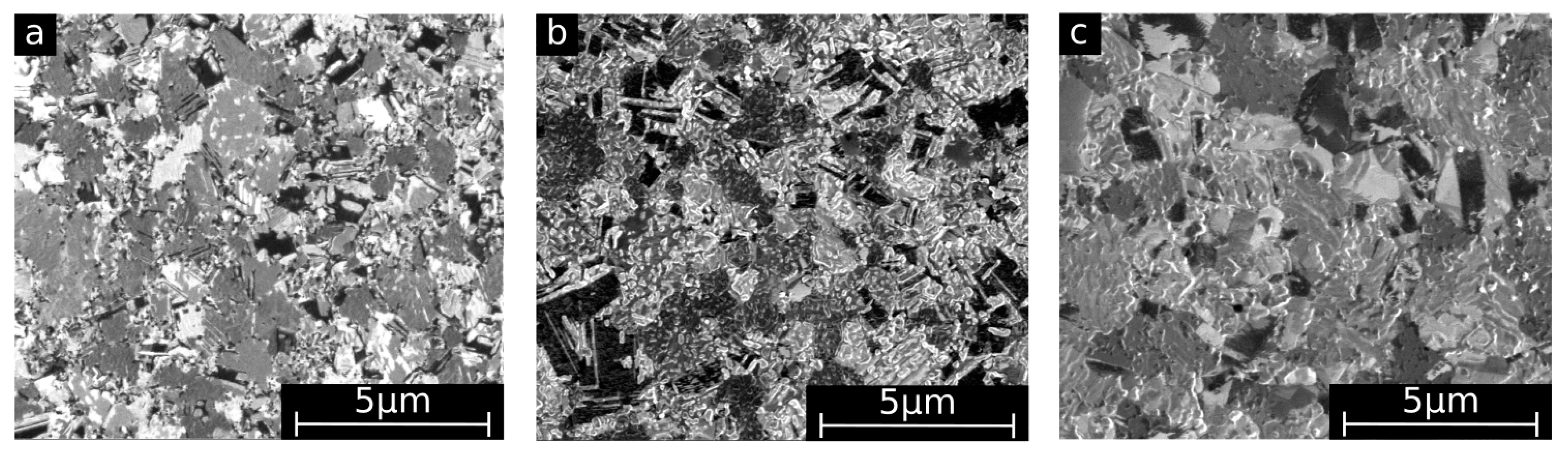
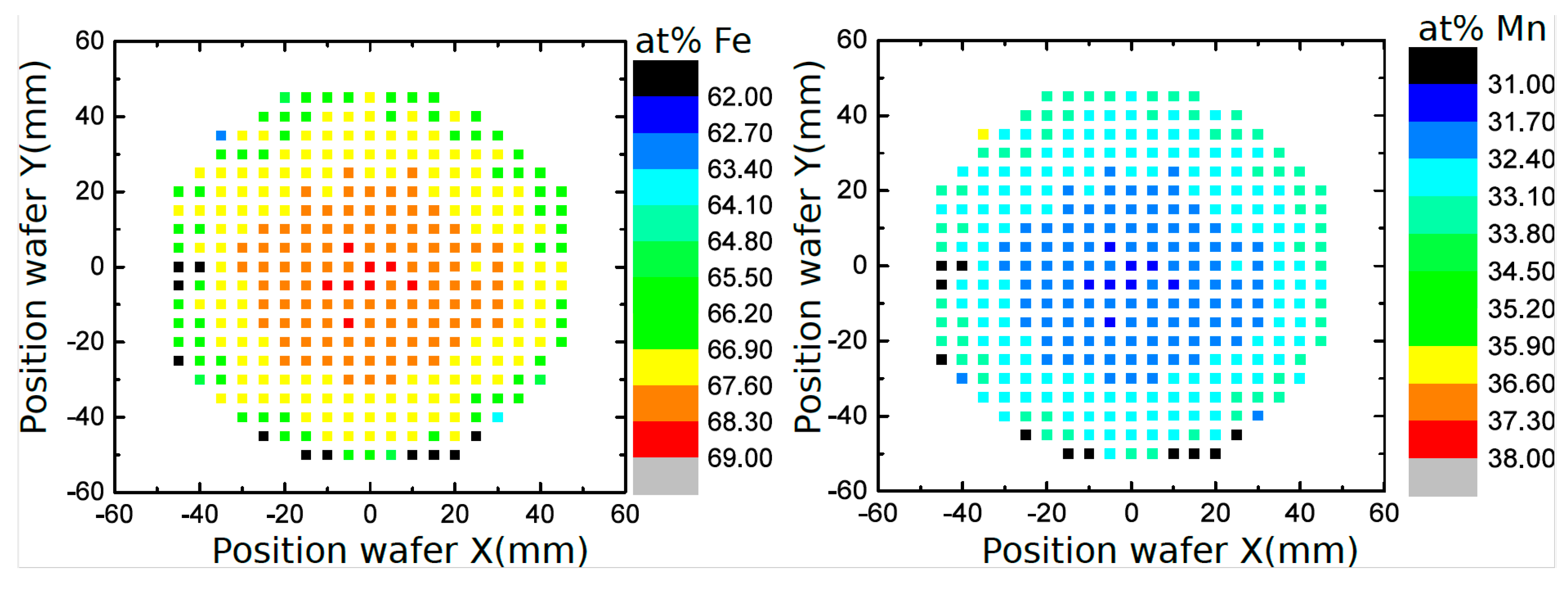
2.2.2. Electron Microscopy (SEM/EDX)
2.3. Corrosion
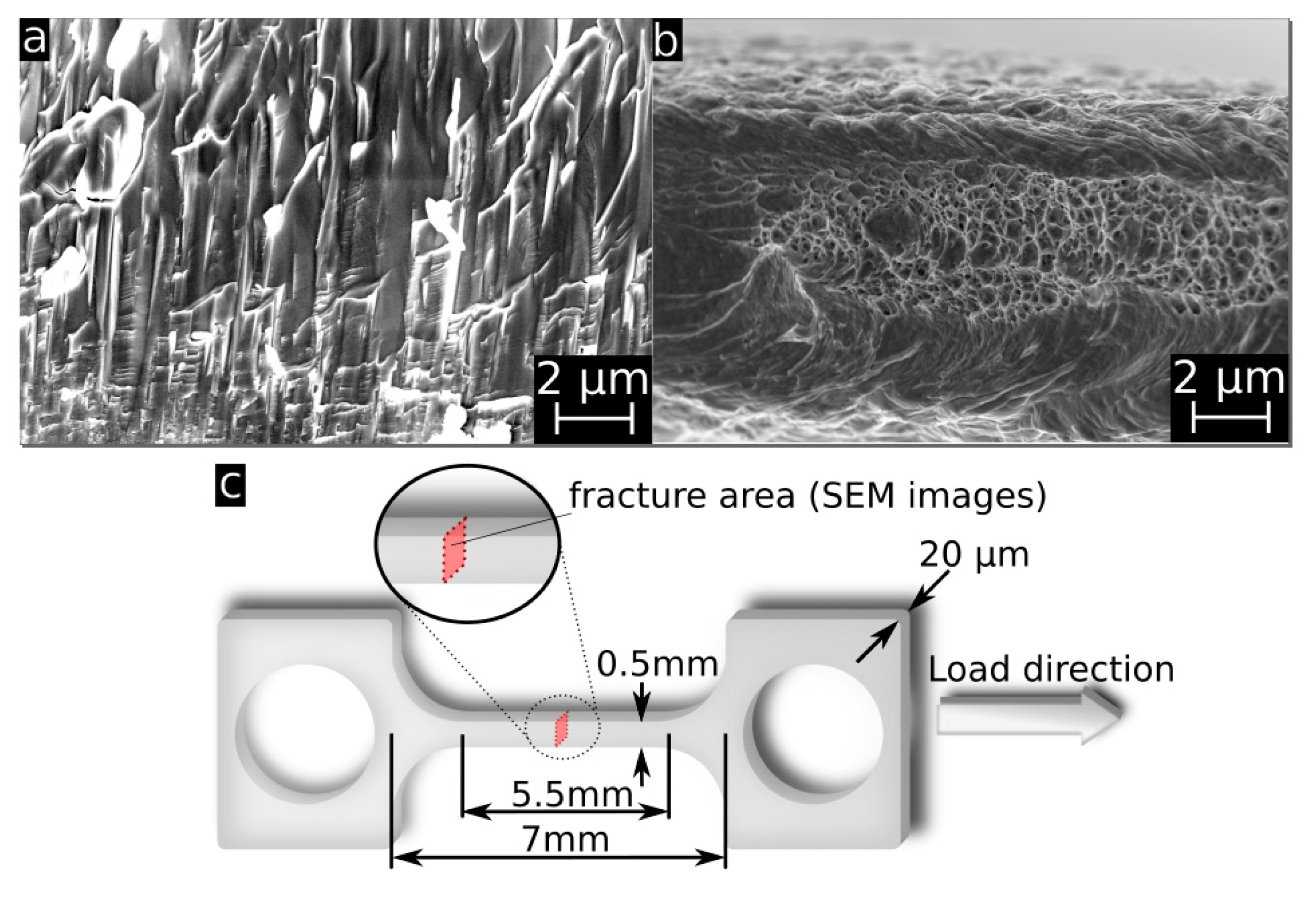
2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Magnetic Properties
3. Results
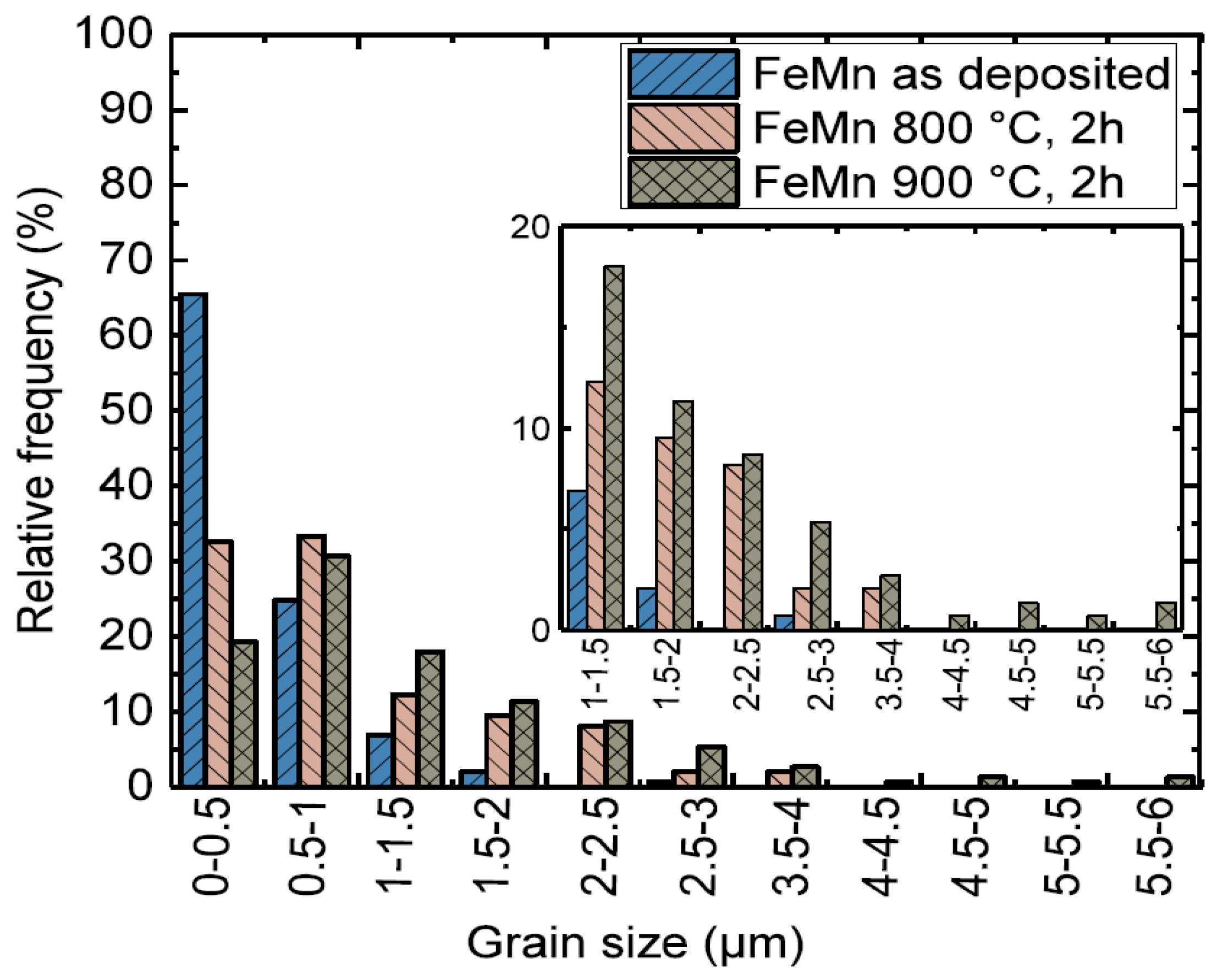
3.1. Microstructure
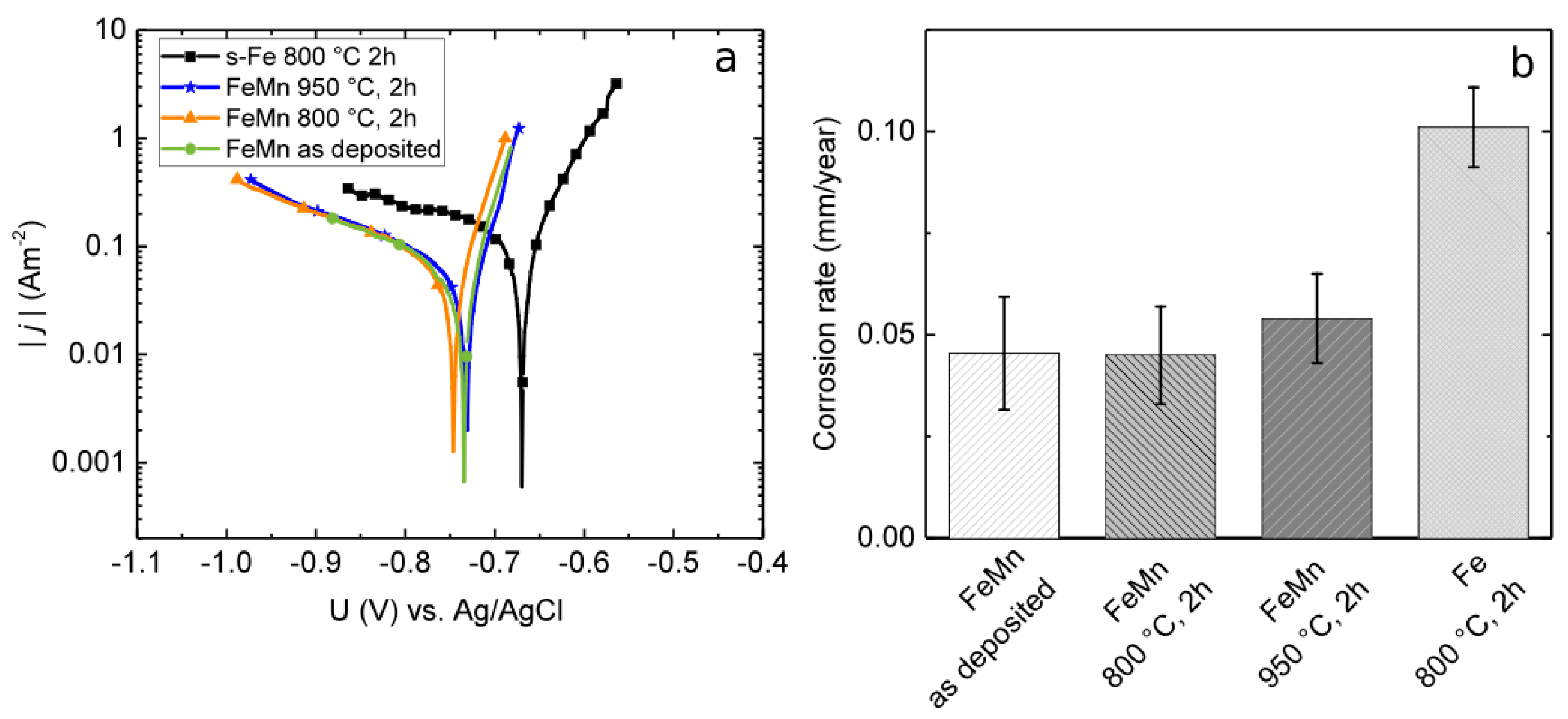
3.2. Corrosion
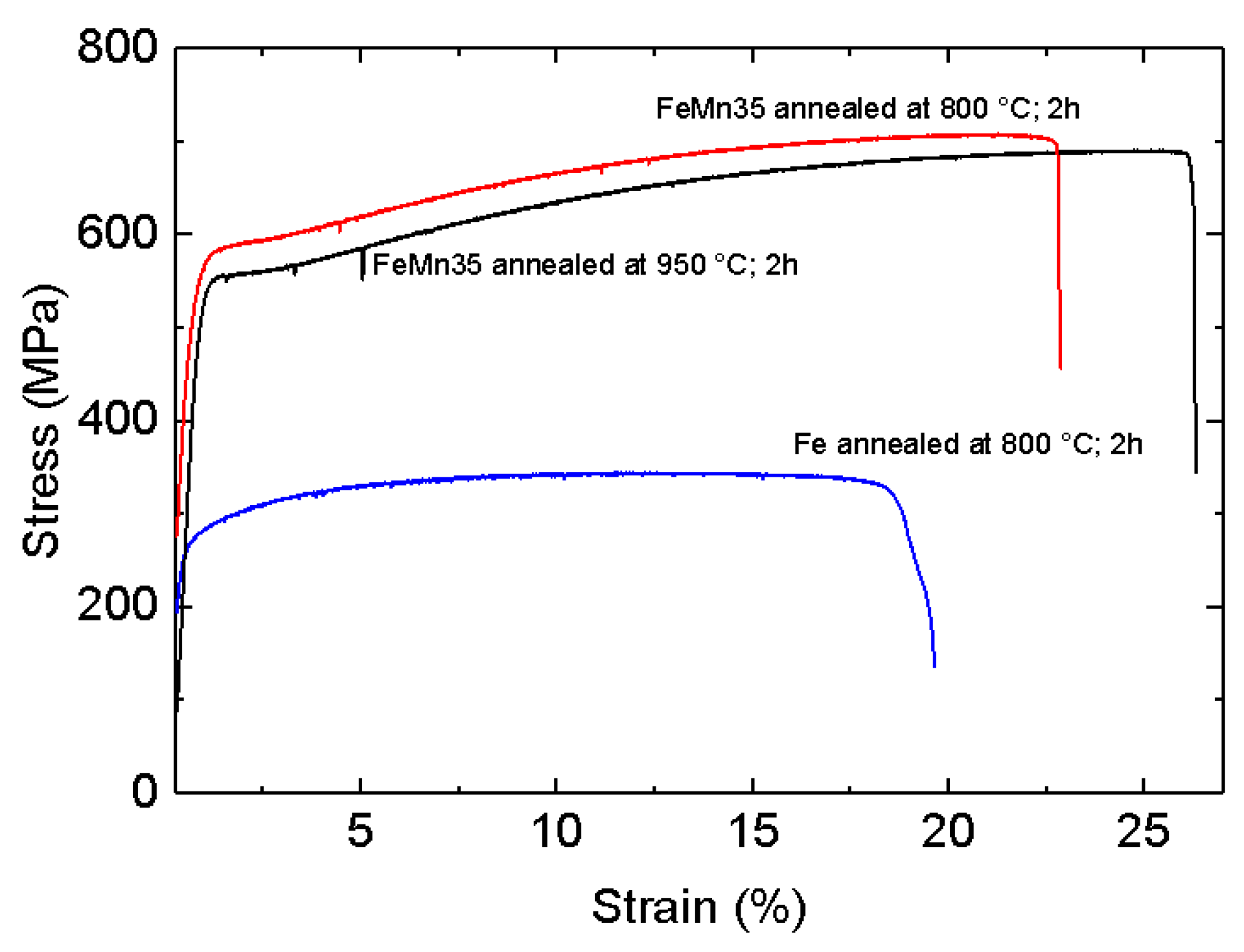
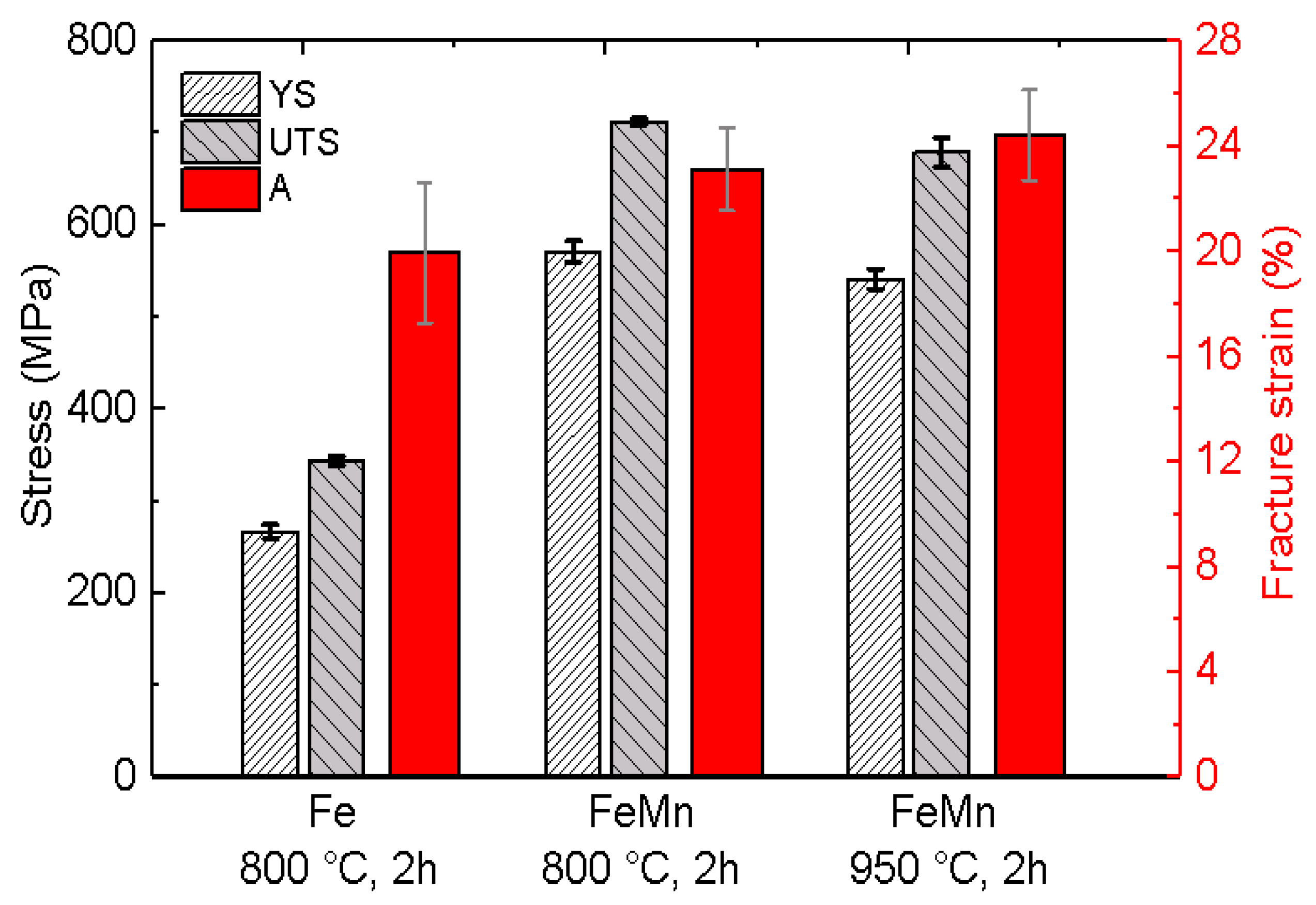
3.3. Mechanical Properties
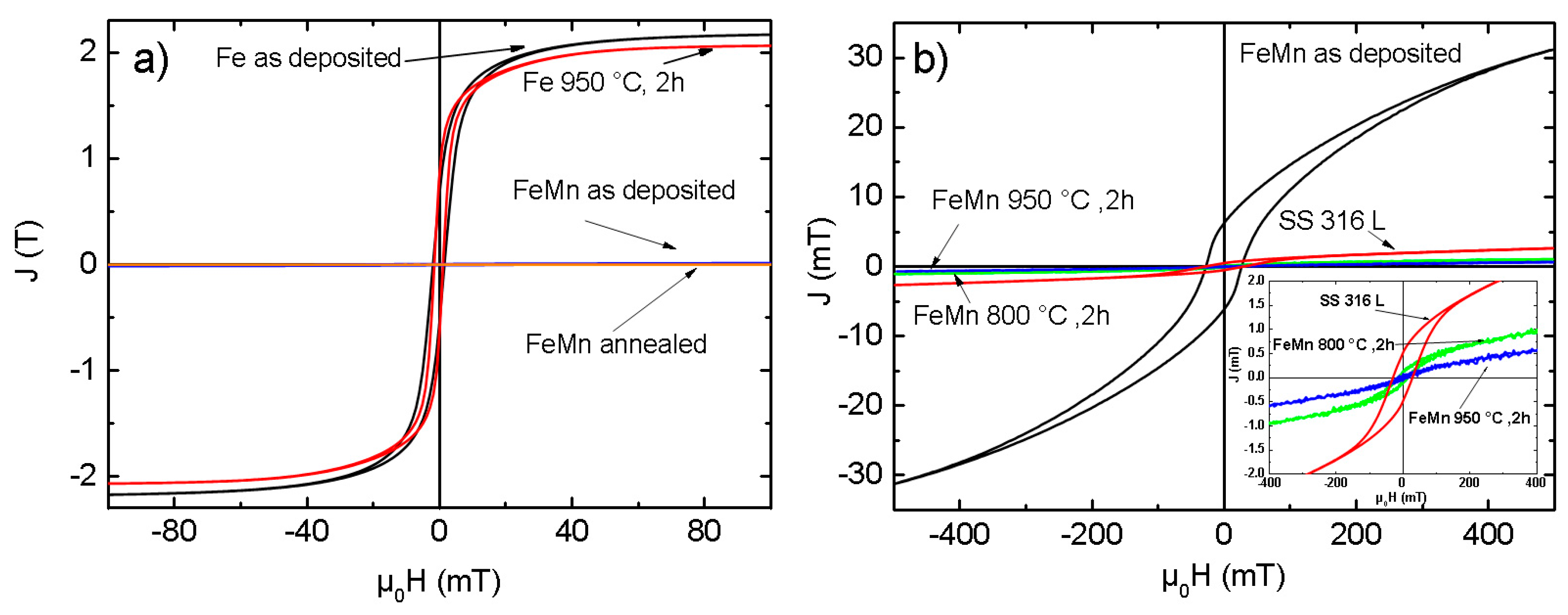
3.4. Magnetic Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermawan, H. Biodegradable Metals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Peuster, M.; Wohlsein, P.; Brügmann, M.; Ehlerding, M.; Seidler, K.; Fink, C.; Brauer, H.; Fischer, A.; Hausdorf, G. A novel approach to temporary stenting: Degradable cardiovascular stents produced from corrodible metal-results 6–18 months afterimplantation into New Zealand white rabbits. Heart 2001, 86, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, P.K.; Drelich, J.; Goldman, J. Zinc exhibits ideal physiological corrosion behavior for bioabsorbable stents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peuster, M.; Hesse, C.; Schloo, T.; Fink, C.; Beerbaum, P.; von Schnakenburg, C. Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4955–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, J.F. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med. Phys. 1996, 23, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravej, M.; Prima, F.; Fiset, M.; Mantovani, D. Electroformed iron as new biomaterial for degradable stents: Development process and structure properties relationship. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravej, M.; Purnama, A.; Fiset, M.; Couet, J.; Mantovani, D. Electroformed pure iron as a new biomaterial for degradable stents: In vitro degradation and preliminary cell viability studies. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgeleit, T.; Quandt, E.; Zamponi, C. Magnetron Sputtering a New Fabrication Method of Iron Based Biodegradable Implant Materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 294686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayi, C.S.; Tolouei, R.; Paternoster, C.; Turgeon, S.; Okorie, B.A.; Obikwelu, D.O.; Cassar, G.; Buhagiar, J.; Mantovani, D. Influence of cross-rolling on the micro-texture and biodegradation of pure iron as biodegradable material for medical implants. Acta Biomater. 2015, 17, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obayi, C.S.; Tolouei, R.; Mostavan, A.; Paternoster, C.; Turgeon, S.; Okorie, B.A.; Obikwelu, D.O.; Mantovani, D. Effect of grain sizes on mechanical properties and biodegradation behavior of pure iron for cardiovascular stent application. Biomatter 2016, 6, e959874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.X.; Nie, F.L.; Zhang, J.X.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.F.; Hu, C.; Yang, G. Corrosion and ion release behavior of ultra-fine grained bulk pure copper fabricated by ECAP in Hanks solution as potential biomaterial for contraception. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wei, S.C.; Hu, C.; Yang, G. In vitro corrosion, cytotoxicity and hemocompatibility of bulk nanocrystalline pure iron. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 65015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, F.L.; Zheng, Y.F. Surface chemistry of bulk nanocrystalline pure iron and electrochemistry study in gas-flow physiological saline. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moszner, F.; Sologubenko, A.S.; Schinhammer, M.; Lerchbacher, C.; Hänzi, A.C.; Leitner, H.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. Precipitation hardening of biodegradable Fe–Mn–Pd alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinhammer, M.; Steiger, P.; Moszner, F.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Degradation performance of biodegradable Fe-Mn-C(-Pd) alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinhammer, M.; Pecnik, C.M.; Rechberger, F.; Hänzi, A.C.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Recrystallization behavior, microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of biodegradable Fe–Mn–C(–Pd) TWIP alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2746–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.F. In vitro degradation and biocompatibility of Fe-Pd and FE-Pt composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 35, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamponi, C.; Schürmann, U.; Jurgeleit, T.; Kienle, L.; Quandt, E. Microstructures of magnetron sputtered Fe Au thin films. IJMR 2015, 106, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Cheng, J.; Bian, D.; Zheng, Y. Fe-Au and Fe-Ag composites as candidates for biodegradable stent materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgeleit, T.; Quandt, E.; Zamponi, C. Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Degradation of Sputtered Biodegradable Fe-Au Foils. Materials 2016, 9, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, T.; Zheng, Y.F. Relatively uniform and accelerated degradation of pure iron coated with micro-patterned Au disc arrays. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 48, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, T.; Zheng, Y.F. Microstructure, mechanical property, biodegradation behavior, and biocompatibility of biodegradable Fe-Fe2O3 composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.F. In vitro study on newly designed biodegradable Fe-X composites (X = W, CNT) prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101B, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.F. Effects of alloying elements (Mn, Co, Al, W, Sn, B, C and S) on biodegradability and in vitro biocompatibility of pure iron. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermawan, H.; Alamdari, H.; Mantovani, D.; Dubé, D. Iron-manganese. Powder Met. 2013, 51, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, D.-T.; Wells, D.; Hong, D.; Lee, B.; Kuhn, H.; Kumta, P.N. Novel processing of iron-manganese alloy-based biomaterials by inkjet 3-D printing. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8593–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufenbach, J.; Wendrock, H.; Kochta, F.; Kühn, U.; Gebert, A. Novel biodegradable Fe-Mn-C-S alloy with superior mechanical and corrosion properties. Mater. Lett. 2017, 186, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Purnama, A.; Dube, D.; Couet, J.; Mantovani, D. Fe-Mn alloys for metallic biodegradable stents: Degradation and cell viability studies. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermawan, H.; Mantovani, D. Process of prototyping coronary stents from biodegradable Fe-Mn alloys. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8585–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.H.; Rong, Y.; Chen, S.; Hsu, T.Y. Deformation Behavior of FeMnSi-Based Shape-Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2002, 394–395, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Dubé, D.; Mantovani, D. Degradable metallic biomaterials: Design and development of Fe-Mn alloys for stents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, N.B.; Mostavan, A.; Hamzah, E.; Mantovani, D.; Hermawan, H. Degradation behavior of biodegradable Fe35Mn alloy stents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojtěch, D.; Kubásek, J.; Čapek, J. Comparative mechanical and corrosion studies on magnesium, zinc and iron alloys as biodegradable metals. Mater. Tehnol. 2015, 49, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, J.; Kubasek, J.; Vojtech, D.; Jablonska, E.; Lipov, J.; Ruml, T. Microstructural, mechanical, corrosion and cytotoxicity characterization of the hot forged FeMn30 (wt. %) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinhammer, M.; Hanzi, A.C.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Design strategy for biodegradable Fe-based alloys for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drynda, A.; Hassel, T.; Bach, F.W.; Peuster, M. In vitro and in vivo corrosion properties of new iron-manganese alloys designed for cardiovascular applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, P. Degradable porous Fe-35 wt. %Mn produced via powder sintering from NH4HCO3 porogen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 163, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, Y.; Ishikawa, Y. Antiferromagnetism of γ Iron Manganes Alloys. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 30, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Jun, J.-H.; Choi, C.-S. Damping Capacity in Fe-Mn Binary Alloys. ISIJ Int. 1997, 37, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, C.; Rumpf, H.; Schmutz, C.; Quandt, E. Structuring of sputtered superelastic NiTi thin films by photolithography and etching. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481–482, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.L.; Zamponi, C.; Quandt, E. Fabrication of TiNi thin film stents. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miranda, R.L.; Zamponi, C.; Quandt, E. Micropatterned Freestanding Superelastic TiNi Films. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekmeyer, G.; Schüßler, A.; de Miranda, R.L.; Quandt, E. Comparison of the Fatigue Performance of Commercially Produced Nitinol Samples versus Sputter-Deposited Nitinol. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, K.; Zamponi, C.; Piorra, A.; Quandt, E. Comparison of the corrosion behaviour of bulk and thin film magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3973–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, K.; Zamponi, C.; Hort, N.; Kainer, K.U.; Quandt, E. Polycrystalline and amorphous MgZnCa thin films. Corros. Sci. 2012, 63, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, K.; Shi, Z.; Zamponi, C.; Cao, F.; Quandt, E.; Atrens, A. Corrosion performance and mechanical properties of sputter-deposited MgY and MgGd alloys. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, D.; Zamponi, C.; de Miranda, R.L.; Quandt, E. Micropatterned freestanding magnetron sputtered Mg-alloy scaffolds. BioNanoMaterials 2015, 16, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics-crc, 90th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuo, E.; Yasuhisa, N.; Masashi, I. Lattice Dynamics and Invar Properties in f.c.c. FeMn Alloy. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 50, 469–475. [Google Scholar]
- Kushibiki, J.; Takanaga, I.; Nishiyama, S. Accurate measurements of the acoustical physical constants of synthetic/spl alpha/-quartz for SAW devices. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2002, 49, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahn, R.W.; Haasen, P. (Eds.) Physical Metallurgy, 4th ed.; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing Materials. Annual Book of ASTM Standards: Metal Test Methods and Analytical Procedures; Metals—Mechanical Testing; Elevated and Low-Temperature Tests; Metallography. Section 3. Volume 03.01; American Society for Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, M.; Geary, A.L. Electrochemical polarization I. A theoretical analysis of the shape of polarization curves. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A. Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, 2nd ed.; Pearson-Prentice Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.; Leng, Y. Biocompatibility of pure iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009, 29, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzou, E.; Paternoster, C.; Tolouei, R.; Chevallier, P.; Biffi, C.A.; Tuissi, A.; Mantovani, D. CO2-rich atmosphere strongly affects the degradation of Fe-21Mn-1C for biodegradable metallic implants. Mater. Lett. 2016, 181, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyama, K.; Ohshima, N.; Nakamura, Y. Magnetic Properties of Metastable [alpha]-Mn-Type Mn1 yFey Alloys Produced by Vapor Quenching. Phys. Status Solidi A 1986, 98, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. The microstructure of sputter-deposited coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1986, 4, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. High Rate Thick Film Growth. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1977, 7, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Goldbeck, O.K. IRON—Binary Phase Diagrams, 1st ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bunshah, R.F. 3.1 mechanical properties of PVD films. Vacuum 1977, 27, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.D.; Reisner, G.; Werner, E.; Tanaka, K.; Cailletaud, G.; Antretter, T. A new view on transformation induced plasticity (TRIP). Int. J. Plast. 2000, 16, 723–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grässel, O.; Krüger, L.; Frommeyer, G.; Meyer, L. High strength Fe–Mn–(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP steels development—Properties—Application. Int. J. Plast. 2000, 16, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, R.W. Performance and Characterization of TWIP Steels for Automotive Applications. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2013, 2, 20130009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.O. The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J. XVI. The ductile fracture of polycrystalline α-iron. Philos. Mag. 1956, 1, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Ruan, L. In vitro investigation of Fe30Mn6Si shape memory alloy as potential biodegradable metallic material. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Dube, D.; Mantovani, D. Developments in metallic biodegradable stents. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzou, E.; Paternoster, C.; Tolouei, R.; Purnama, A.; Chevallier, P.; Dube, D.; Prima, F.; Mantovani, D. In vitro degradation behavior of Fe-20 Mn-1.2C alloy in three different pseudo-physiological solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 61, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinhammer, M.; Gerber, I.; Hanzi, A.C.; Uggowitzer, P.J. On the cytocompatibility of biodegradable Fe-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, M.; Walker, E.; Stanciu, L. Magnesium, Iron and Zinc Alloys, the Trifecta of Bioresorbable Orthopaedic and Vascular Implantation—A Review. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2015, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
| Sample | (nm) | dmax (nm) | dmin (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeMn as-deposited | 451 | 2517 | 30 |
| FeMn 800 °C, 2 h | 965 | 3193 | 68 |
| FeMn 950 °C, 2 h | 1305 | 5078 | 143 |
| Sample | JS (T) | JR (T) | µ0HC (mT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe as-deposited | 2.146 | 0.823 | 1.584 |
| Fe 950 °C, 2 h | 2.032 | 0.715 | 1.147 |
| FeMn as-deposited | 0.031 | 6.21 × 10−3 | 26.576 |
| FeMn 800 °C, 2 h | 1.09 × 10−3 | 0.13 × 10−3 | 14.752 |
| FeMn 950 °C, 2 h | 0.64 × 10−3 | 0.04 × 10−3 | 8.586 |
| SS 316L | 2.65 × 10−3 | 0.51 × 10−3 | 30.212 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurgeleit, T.; Quandt, E.; Zamponi, C. Magnetron Sputtering as a Fabrication Method for a Biodegradable Fe32Mn Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101196
Jurgeleit T, Quandt E, Zamponi C. Magnetron Sputtering as a Fabrication Method for a Biodegradable Fe32Mn Alloy. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101196
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurgeleit, Till, Eckhard Quandt, and Christiane Zamponi. 2017. "Magnetron Sputtering as a Fabrication Method for a Biodegradable Fe32Mn Alloy" Materials 10, no. 10: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101196
APA StyleJurgeleit, T., Quandt, E., & Zamponi, C. (2017). Magnetron Sputtering as a Fabrication Method for a Biodegradable Fe32Mn Alloy. Materials, 10(10), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101196





