Constitutive Equation and Hot Compression Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Al–7.5Zn–1.5Mg–0.2Cu–0.2Zr Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
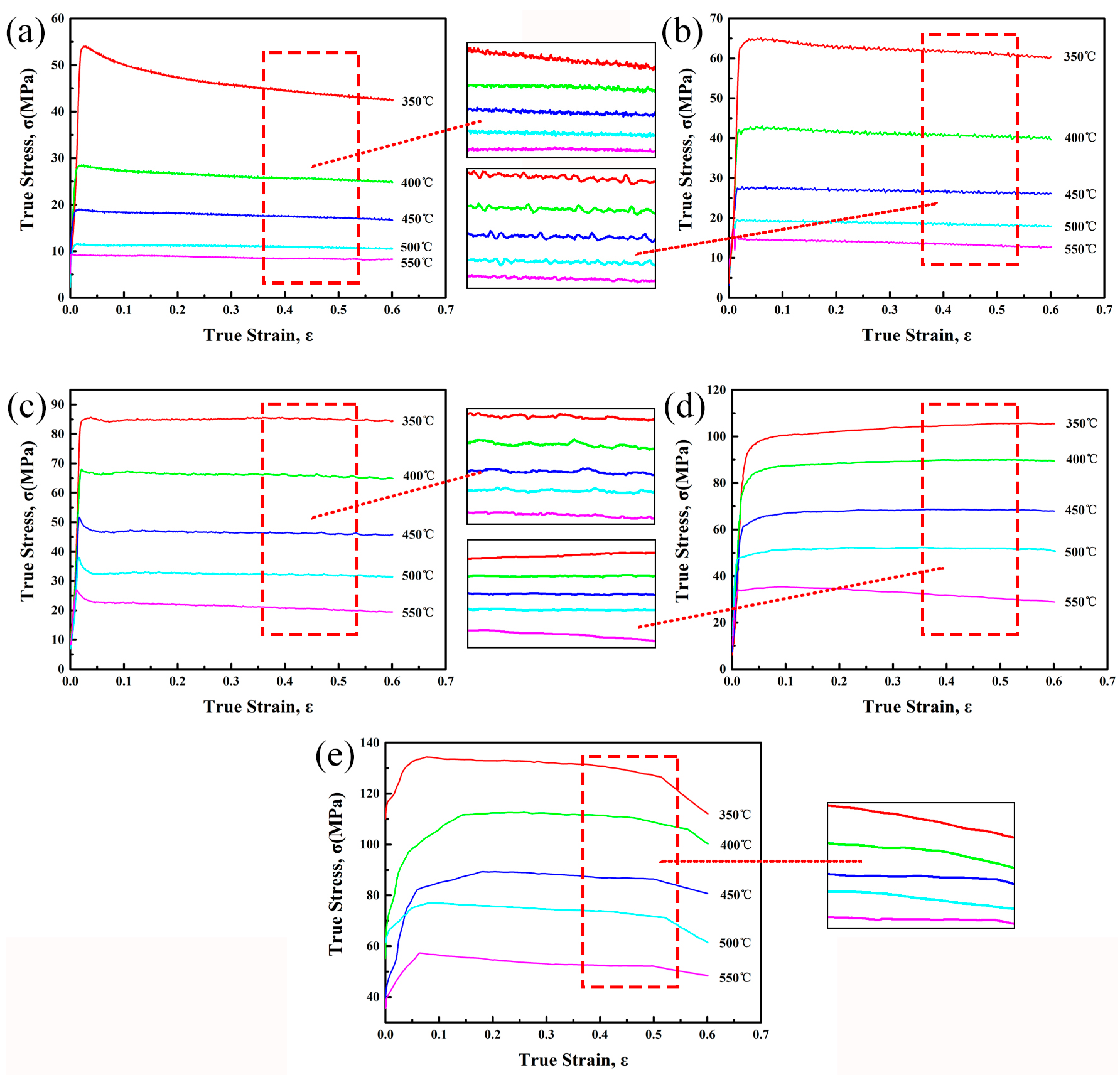
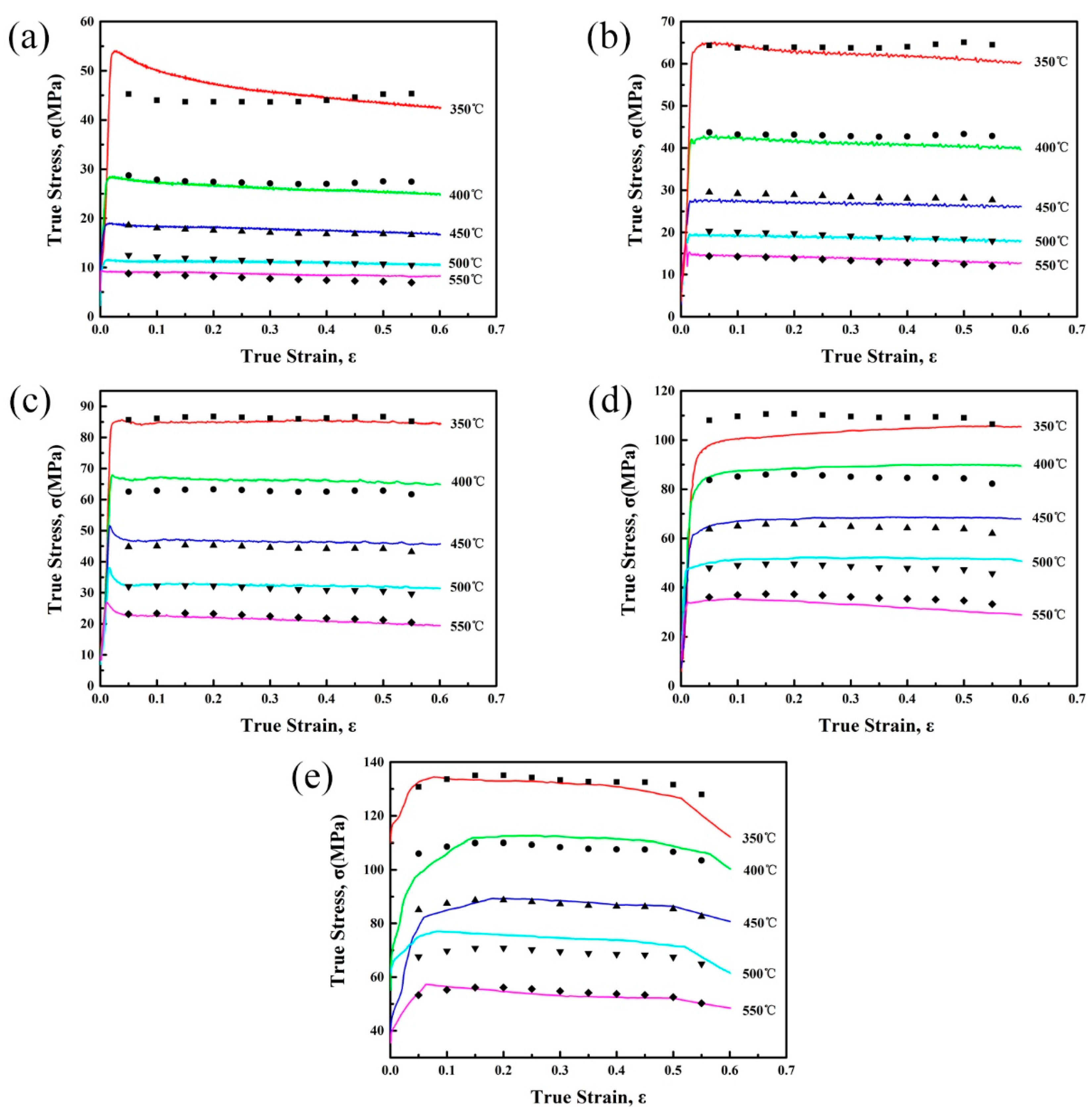
2.1. True Stress-Strain Curves
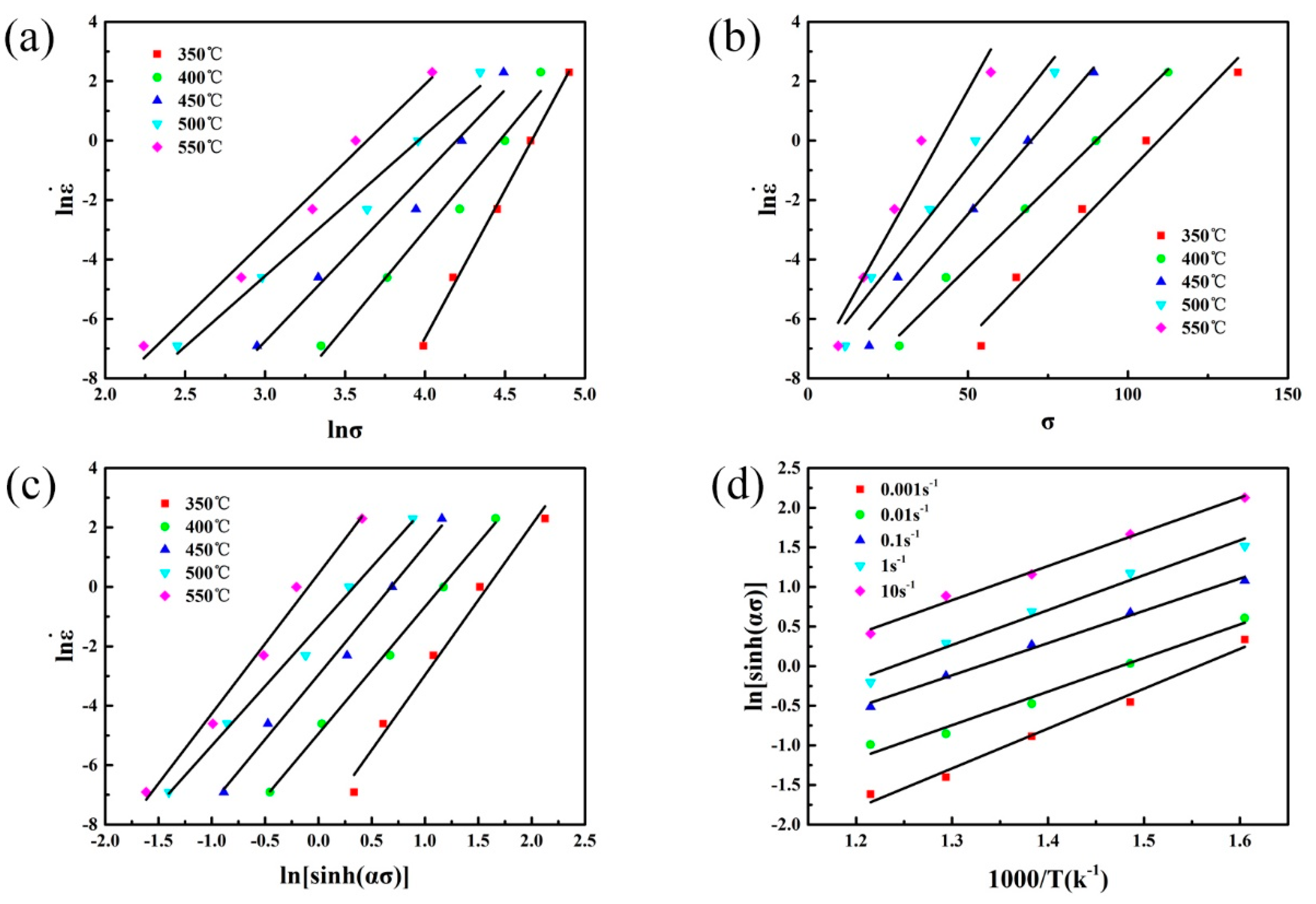
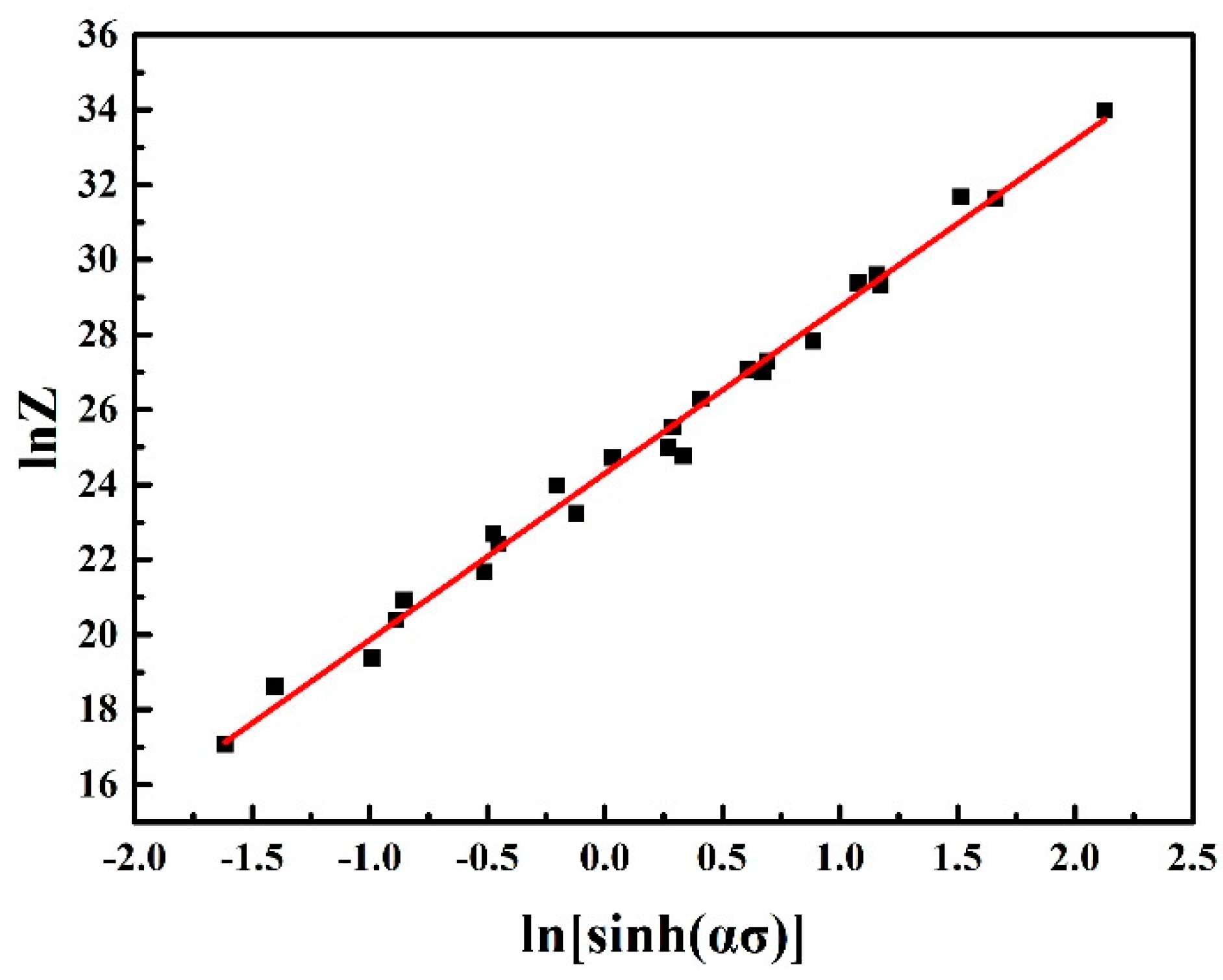
2.2. Constitutive Equation
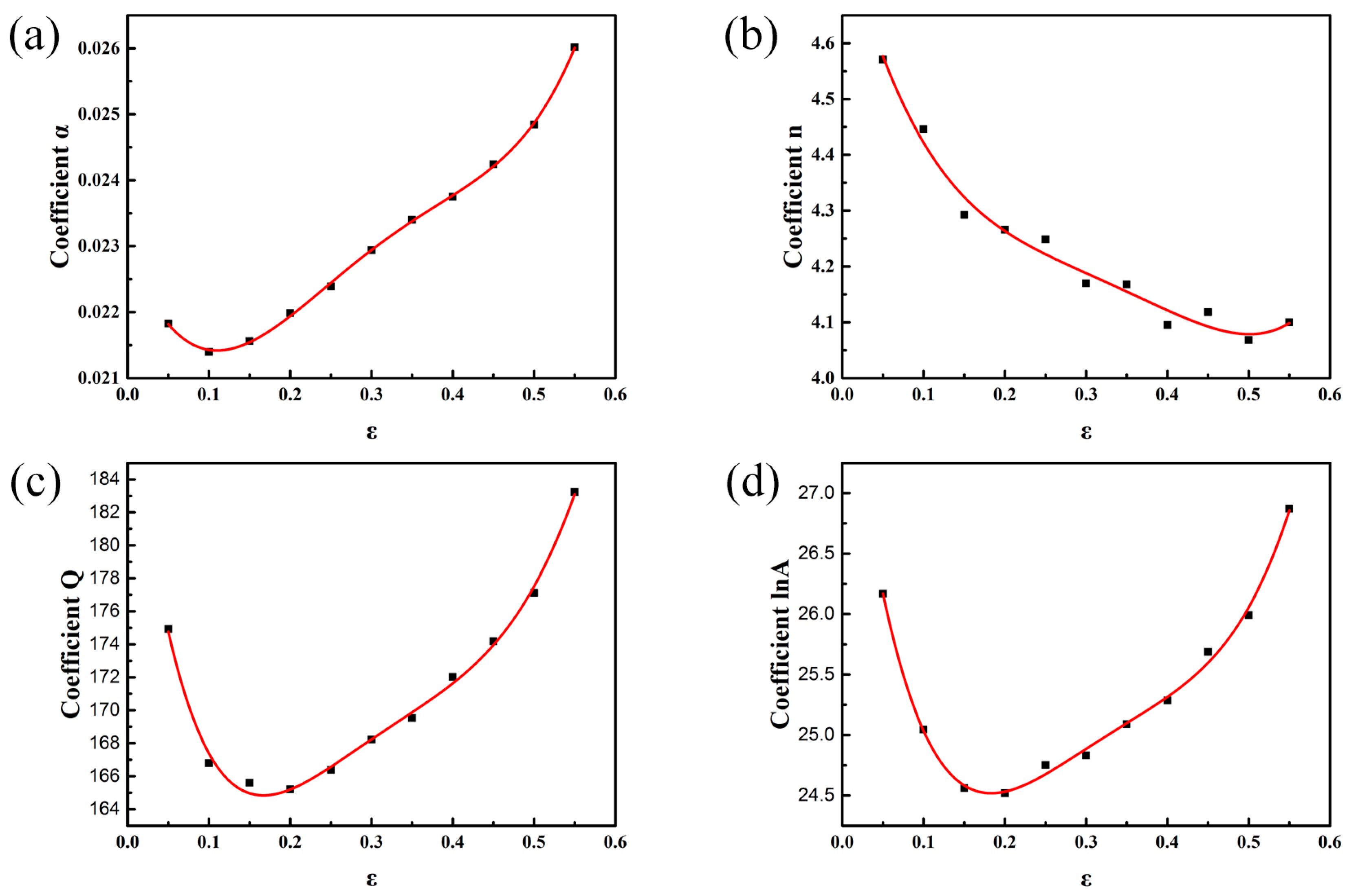
2.3. Compensation of Strain
2.4. Verification of Constitutive Equation
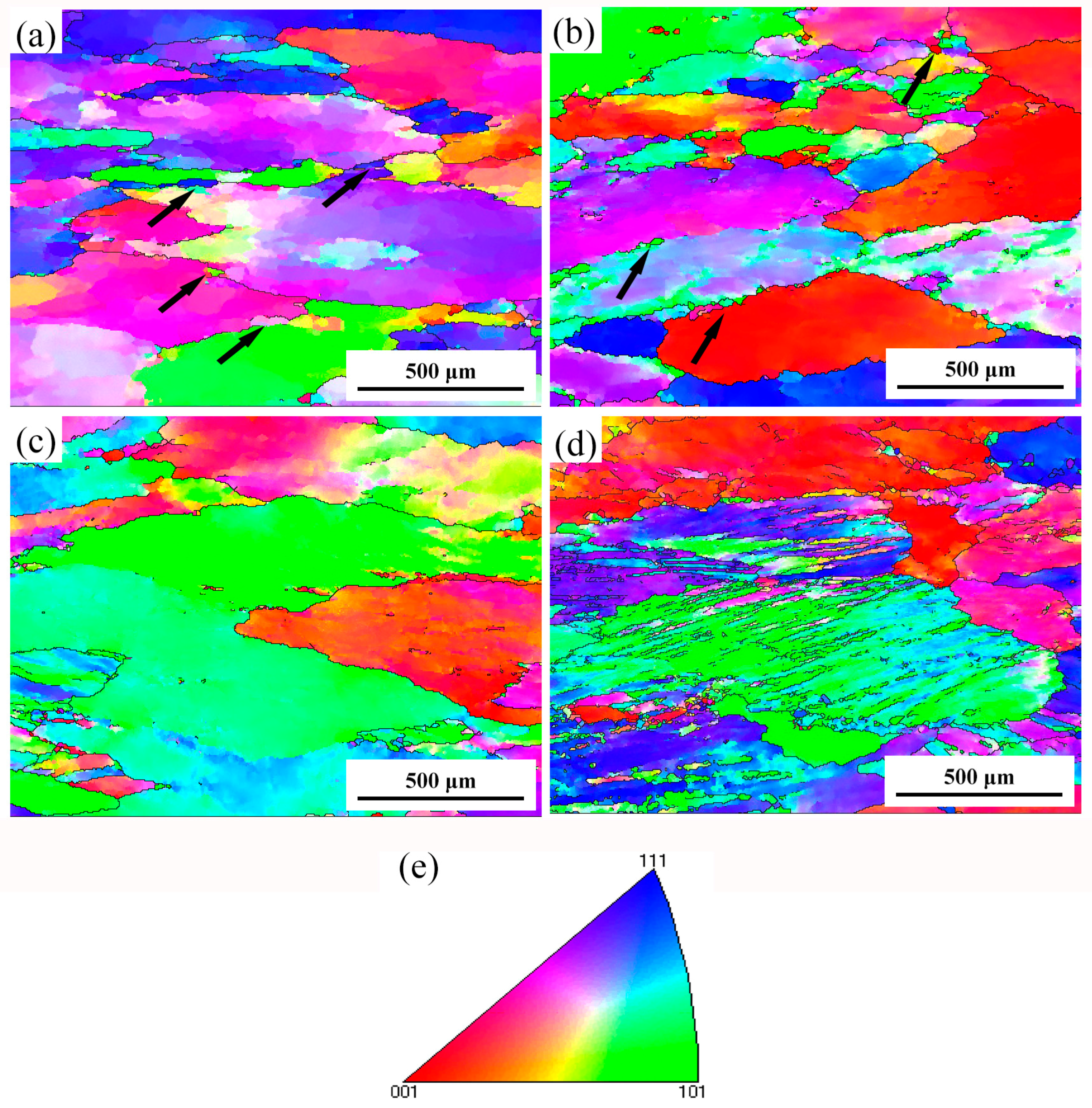
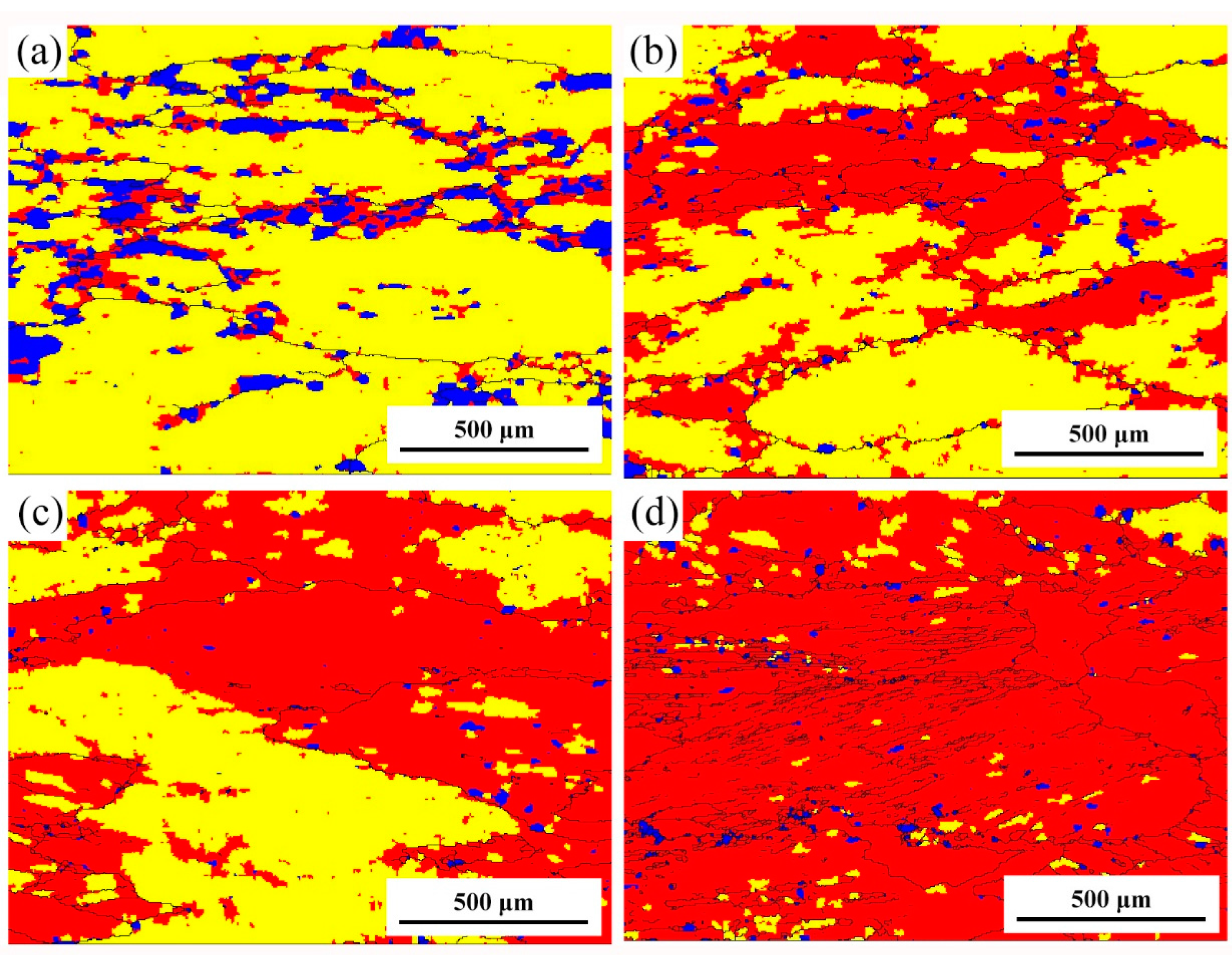
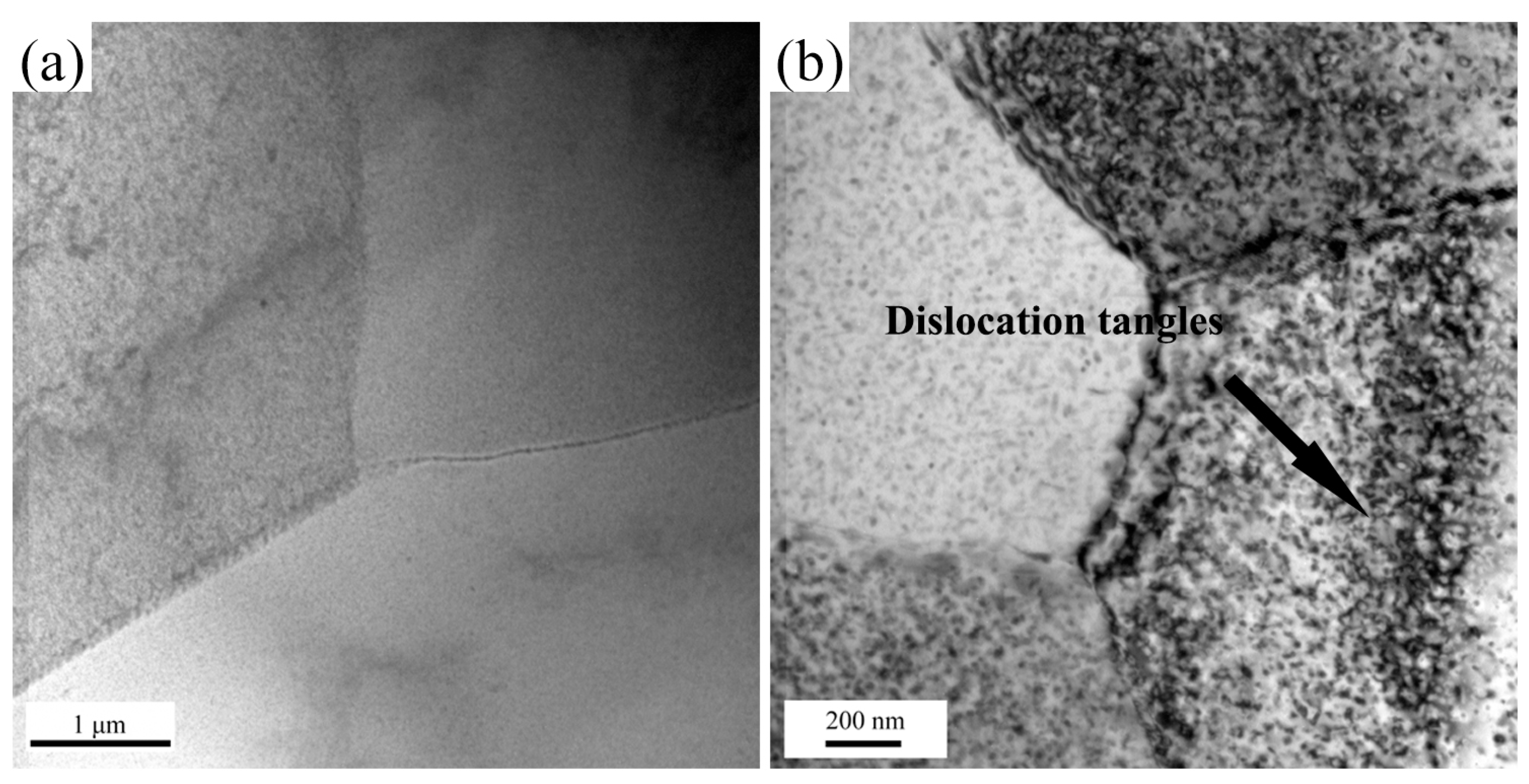
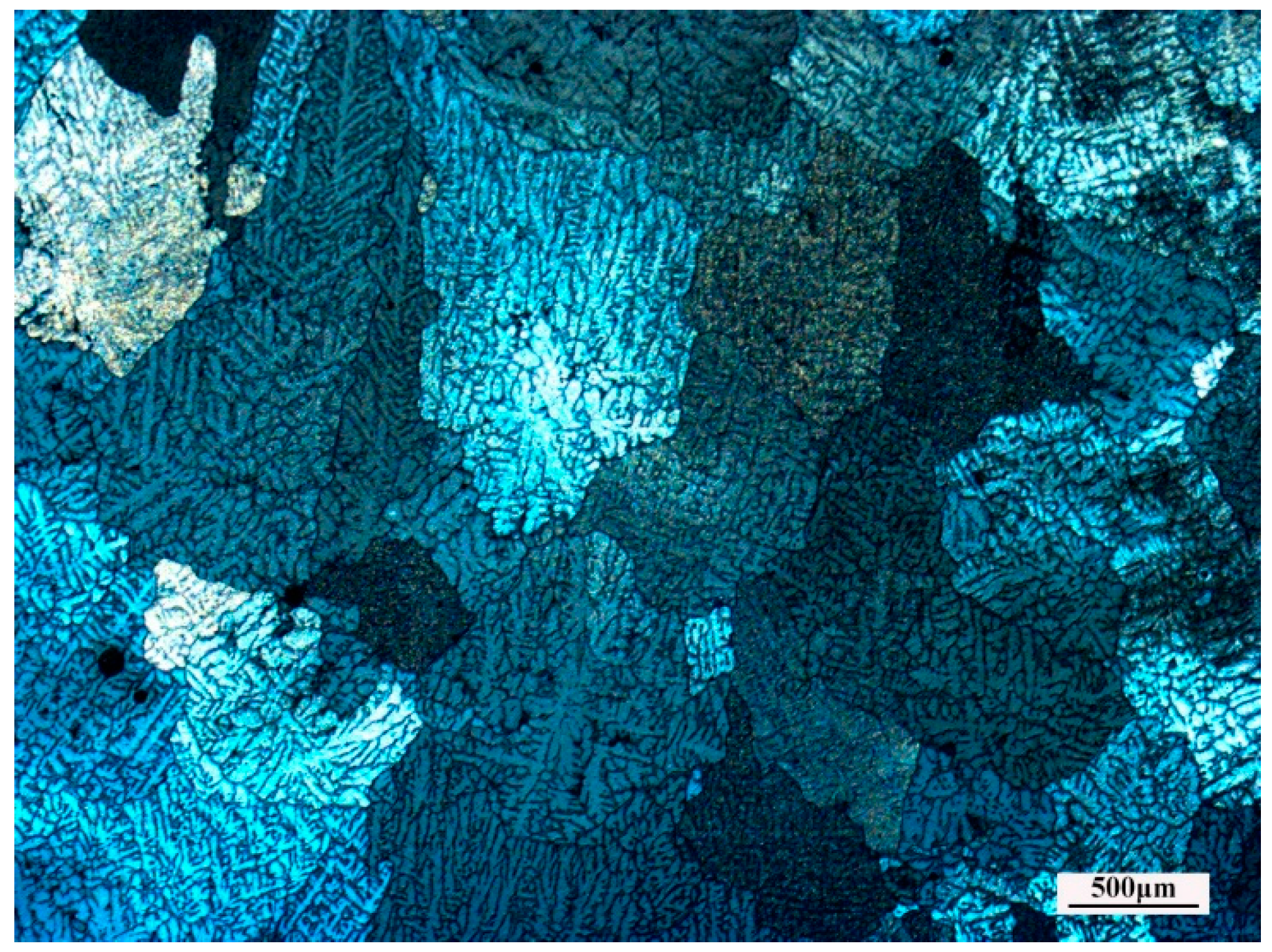
2.5. Microstructure Evolution
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The flow stress of the studied alloy increases with a decreasing deformation temperature or an increasing strain rate. Serrate true stress-strain curves are obtained at low strain rates (≤0.1 s−1) conditions, owing to the occurrence of DRX.
- (2)
- The deformation activation energy Q is 164.075 kJ·mol−1. Two constitutive equations without and with strain compensation are established. The constitutive equation with strain compensation can predict the flow stress more accurately with the R and AARE values of 0.9953 and 4.90%, respectively.
- (2)
- Obvious shear bands exit in the specimens deformed at high Z conditions, while specimens deformed at low Z conditions exhibit a more homogeneous microstructure. The main softening mechanism of the studied alloy is DRV accompanied with DRX, particularly at low Z deformation conditions.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinz, A.; Haszler, A.; Keidel, C.; Moldenhauer, S.; Benedictus, R.; Miller, W.S. Recent development in aluminum alloys for aerospace application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 280, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, C.Q.; Wang, R.C.; Wang, X.F.; Li, T.T. Recent development and prospects for giant plane aluminum alloys. Chin. J. Nonferrous Metals 2010, 20, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.C.; Starke, E.A., Jr. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5775–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, X.M. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1733–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Martin, D.; Hodgson, P. Physically-based constitutive modelling of hot deformation behavior in a LDX 2101 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, K.; Peng, G.; Chen, X.; Ceng, Q. Effect of heat treatment on hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of 7085 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 537, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, J. Hot deformation behavior of 2026 aluminum alloy during compression at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, G.Q.; Guan, Y.J.; Gao, A.J.; Sun, W.C. Constitutive equation and processing maps of an Al–Mg–Si aluminum alloy: Determination and application in simulating extrusion process of complex profiles. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, S.D.; Deng, Y.L. Constitutive equation and hot deformation behavior of homogenized Al–7.68Zn–2.12Mg–1.98Cu–0.12Zr alloy during compression at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 608, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, J.L.; Shen, J.; Yan, X.D.; Chen, J. Flow behavior and processing maps of 2099 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 613, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.F.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, J.; Wei, L.L.; Zhong, M.C.; Liu, X.T. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of as-homogenized Al–6Mg–0.4Mn–0.25Sc–0.1Zr alloy during compression at elevated temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 644, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R. The flow behavior modeling of cast A356 aluminum alloy at elevated temperatures considering the effect of strain. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 535, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, G.Q.; Yu, J.Q.; Zhang, W.D. Constitutive analysis of homogenized 7005 aluminum alloy at evaluated temperature for extrusion process. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, H.R.R.; Parsa, M.H.; Bisadi, H. Constitutive equations for elevated temperature flow behavior of commercial purity aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Xia, Y.C.; Chen, X.M.; Chen, M.S. Constitutive descriptions for hot compressed 2124-T851 aluminum alloy over a wide range of temperature and strain rate. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 50, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, M.R.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Widener, C.A.; Changizian, P. The Strain-Compensated Constitutive Equation for High Temperature Flow Behavior of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perfor. 2014, 23, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, M.R.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Roostaei, A.A.; Abolhasani, A. Constitutive base analysis of a 7075 aluminum alloy during hot compression testing. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4955–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, M.Q.; Ma, D.W. The flow behavior and constitutive equations in isothermal compression of 7050 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 542, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yin, Z.M.; Huang, J.W. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of homogenized 7050 aluminum alloy during compression at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.P.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, W.X.; Chen, J.H. Hot deformation behavior of 7150 aluminum alloy during compression at elevated temperature. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Li, L.T.; Fu, Y.X.; Jiang, Y.Q. Hot compressive deformation behavior of 7075 Al alloy under elevated temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, M.Q.; Ma, D.W. The deformation behavior and processing maps in the isothermal compression of 7A09 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, D.; Mandal, S.; Bhaduri, A.K. Constitutive analysis to predict high-temperature flow stress in modified 9Cr–1Mo (P91) steel. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Guo, C.; Guo, X.Y. Constitutive modeling of hot deformation behavior of H62 brass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6510–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Rakesh, V.; Sivaprasad, P.V.; Venugopal, S.; Kasiviswanathan, K.V. Constitutive equations to predict high temperature flow stress in a Ti-modified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 500, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, F.G.; Liu, T.Y.; Chen, B.; He, M. Constitutive equations for elevated temperature flow stress of Ti–6Al–4V alloy considering the effect of strain. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdet, S.; Montheillet, F. A model of continuous dynamic recrystallization. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2685–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Khalesian, A.R. Artificial neural network modeling to predict the hot deformation behavior of an A356 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Cizek, P.; Beladi, H. A novel high-strain-rate ferrite dynamic softening mechanism facilitated by the interphase in the austenite/ferrite microstructure. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| α | n | Q | lnA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0.02298 | C0 | 4.81256 | D0 | 190.25642 | E0 | 28.35338 |
| B1 | −0.03302 | C1 | −5.71977 | D1 | −417.04791 | E1 | −57.06825 |
| B2 | 0.21595 | C2 | 21.87165 | D2 | 2439.5926 | E2 | 299.59736 |
| B3 | −0.43515 | C3 | −39.33363 | D3 | −6262.72669 | E3 | −669.06005 |
| B4 | 0.22117 | C4 | 19.28741 | D4 | 7391.72494 | E4 | 627.70979 |
| B5 | 0.15942 | C5 | 11.82051 | D5 | −2984.10256 | E5 | −136.35385 |
| Zn | Mg | Cu | Zr | Fe | Si | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.65 | 1.57 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.03 | Balance |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, W. Constitutive Equation and Hot Compression Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Al–7.5Zn–1.5Mg–0.2Cu–0.2Zr Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101193
He J, Zhang D, Zhang W, Qiu C, Zhang W. Constitutive Equation and Hot Compression Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Al–7.5Zn–1.5Mg–0.2Cu–0.2Zr Alloy. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101193
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jianliang, Datong Zhang, Weiweng Zhang, Cheng Qiu, and Wen Zhang. 2017. "Constitutive Equation and Hot Compression Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Al–7.5Zn–1.5Mg–0.2Cu–0.2Zr Alloy" Materials 10, no. 10: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101193
APA StyleHe, J., Zhang, D., Zhang, W., Qiu, C., & Zhang, W. (2017). Constitutive Equation and Hot Compression Deformation Behavior of Homogenized Al–7.5Zn–1.5Mg–0.2Cu–0.2Zr Alloy. Materials, 10(10), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101193




