The Application of Functionalized Pillared Porous Phosphate Heterostructures for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Φx-PPH Adsorbent Materials
2.2. Adsorption Experiments AB113 in Solution Data Analysis
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
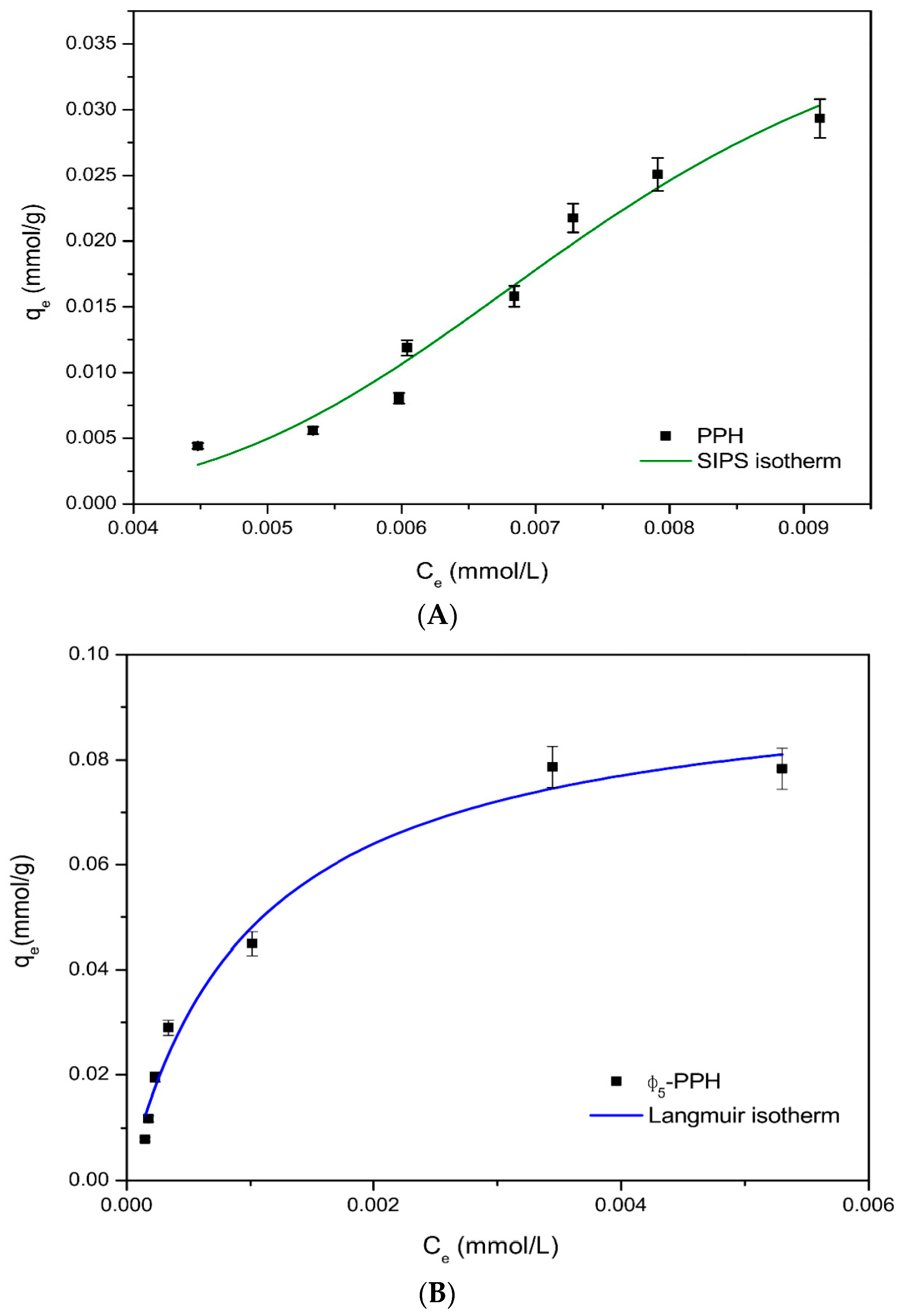
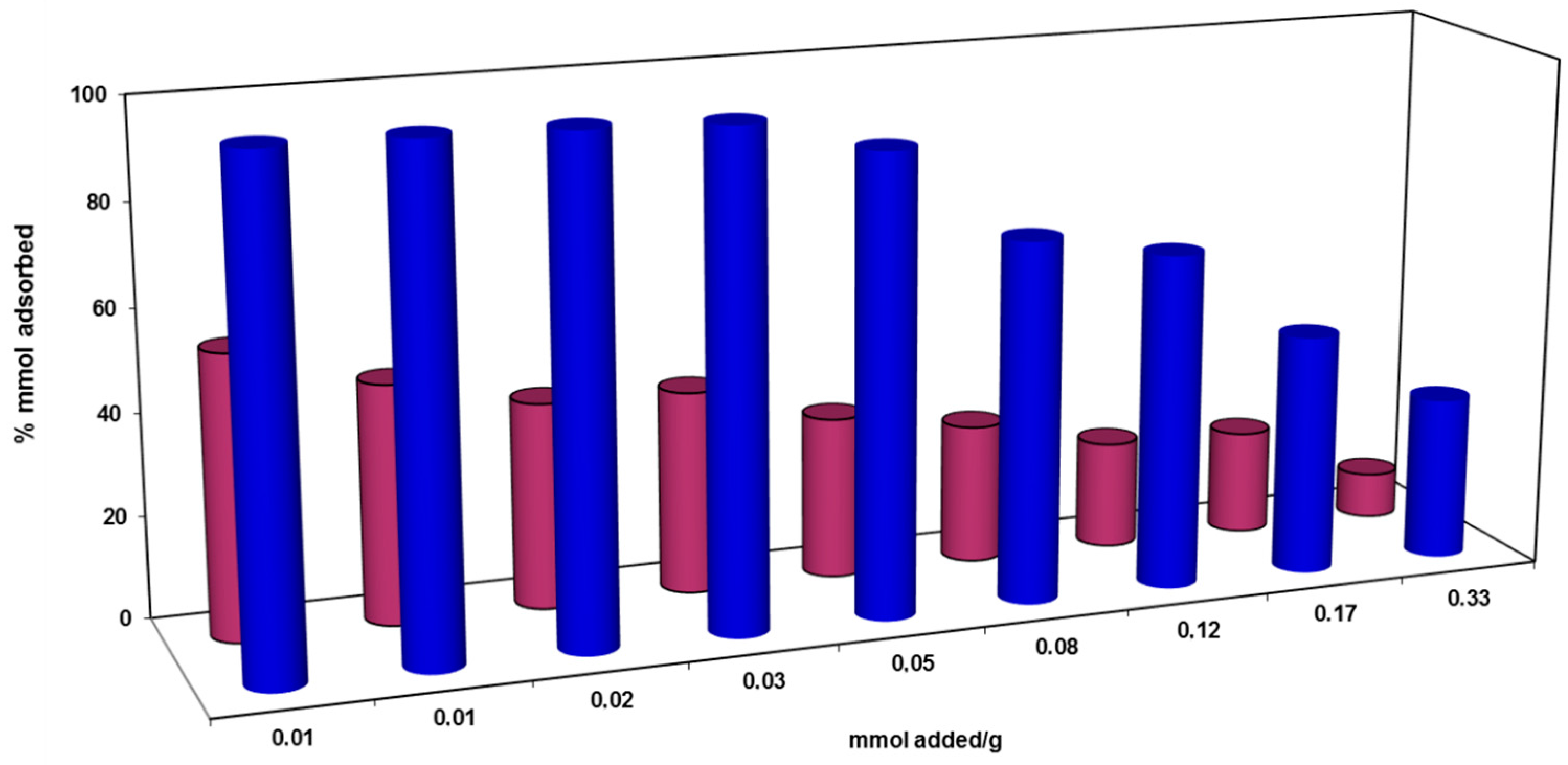
3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
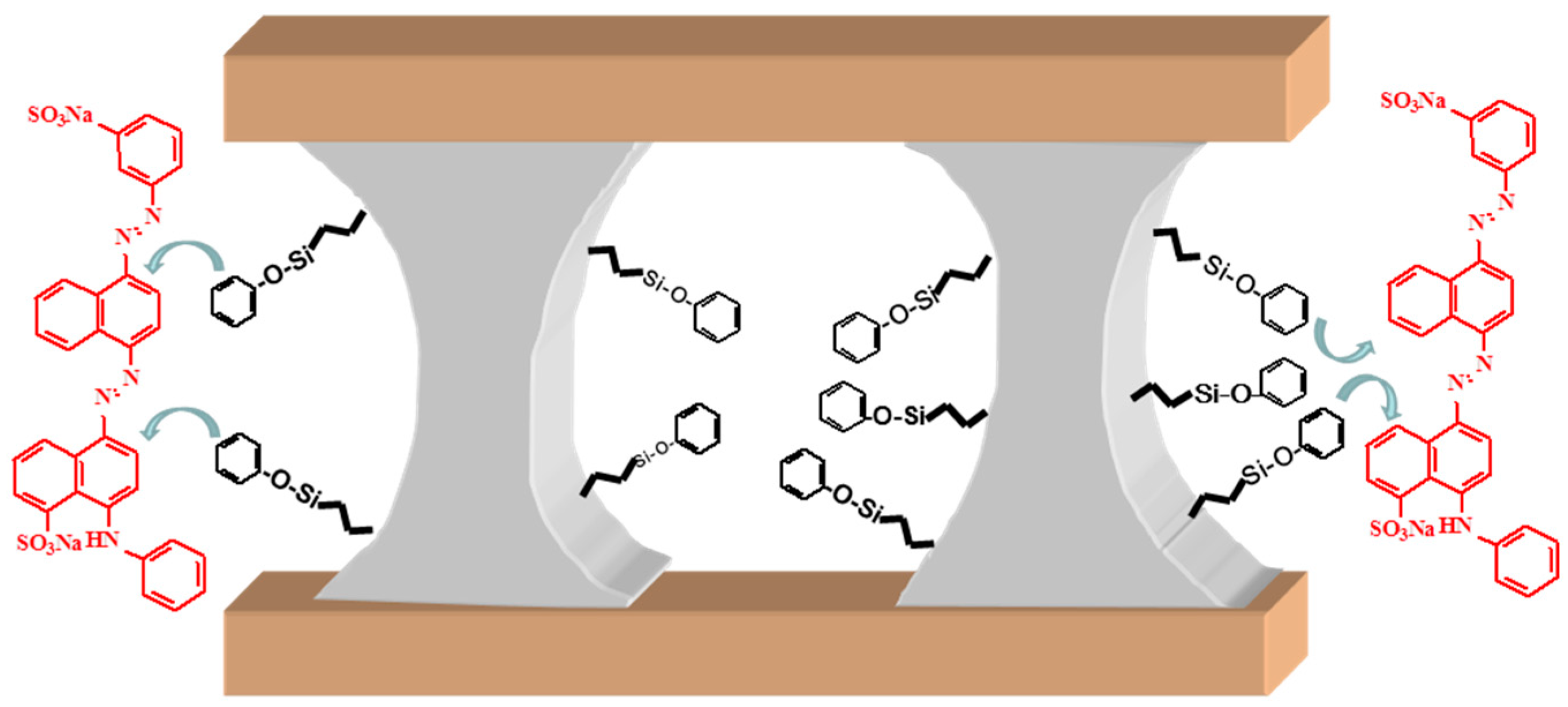
3.3. Application in Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lichtfouse, E.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Robert, D. Environmental Chemistry. Green Chemistry and Pollutants in Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, K. (Ed.) Industrial Dyes. Chemistry, Properties, Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Feng, C.; Tang, H. Removal of direct dyes by coagulation: The performance of preformed polymeric aluminum species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinsafi, A.; Khemis, M.; Pons, M.N.; Leclerc, J.P.; Yaacoubi, A.; Benhammou, A.; Nejmeddine, A. Electro-coagulation of reactive textile dyes and textile wastewater. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2005, 44, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, P.; Martínez, F.; Jiménez, C.; Lobato, J.; Rodrígo, M.A. Coagulation and electrocoagulation of wastes polluted with dyes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6418–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonoozi, M.H.; Moghaddam, M.R.; Arami, M. Coagulation/flocculation of dye-containing solutions using polyaluminium chloride and alum. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, S.S.; Moghaddam, M.R.A.; Arami, M. Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: Optimization through response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, G.; Schwarz, S.; Mende, M.; Jaeger, W. Dye flocculation using polyampholytes and polyelectrolyte-surfactant nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemlikchi, W.; Sharrock, P.; Mecherri, M.O.; Fiallo, M.; Nzihou, A. Reaction of calcium phosphate with textile dyes for purification of wastewaters. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raïs, Z.; El Hassani, L.; Maghnouje, J.; Hadji, M.; Ibnelkhayat, R.; Nejjar, R.; Kherbeche, A.; Chaqroune, A. Dyes’ removal from textile wastewater by phosphogypsum using coagulation and precipitation method. Phys. Chem. News 2002, 7, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.S.; Algarra, M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Péres, J.A. Catalytic Activity of Porous Phosphate Heterostructures-Fe towards Reactive Black 5 Degradation. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 658231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Tavares, P.B.; Péres, J.A.; Farias, J.L.; Rocha, M.; Pereira, C.; Freire, C. Photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Black 5 with TiO2-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senan, R.C.; Shaffiqu, T.S.; Roy, J.J.; Abaham, T.E. Aerobic Degradation of a Mixture of Azo Dyes in a Packed Bed Reactor Having Bacteria-Coated Laterite Pebbles. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De los Cobos-Vasconcelos, D.; Ruiz-Ordaz, N.; Galíndez-Mayer, J.; Galíndez-Mayer, H.; Juàrez-Ramírez, C.; Aarón, L.M. Aerobic biodegradation of a mixture of sulfonated azo dyes by a bacterial consortium immobilized in a two-stage sparged packed-bed biofilm reactor. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.; López, A.; Esteves, S.; Hawkes, F.R.; Hawkes, D.L.; Wilcox, S. Azo-dye degradation in an anaerobic-aerobic treatment system operating on simulated textile effluent. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.D.; Dave, S.R.; Rao, M.S. Enzymatic degradation of textile dye Reactive Orange 13 by newly isolated bacterial strain Alcaligenes faecalis PMS-1. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 69, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffiqu, T.S.; Roy, J.J.; Nair, R.A.; Abraham, T.E. Degradation of textile dyes mediated by plant peroxidases. Appl. Biocem. Biotechnol. 2002, 102–103, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I. Reactive dye removal in dye/salt mixtures by nanofiltration membranes containing vinylsulphone dyes: Effects of feed concentration and cross flow velocity. Desalinisation 2002, 143, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul’neva, T.Y.; Titoruk, G.N.; Kucheruk, D.D.; Goncharuk, V.V. Purification of wastewaters of direct dyes by ultra-and nanofiltration ceramic membranes. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2013, 35, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomesa, A.C.; Gonçalves, I.C.; de Pinho, M.N. The role of adsorption on nanofiltration of azo dyes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 255, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, N.; Yilmaz, L.; Yetis, U. Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for reuse of indigo dye rinsing waters. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körbahti, B.K.; Artut, K.; Geçgel, C.; Özer, A. Electrochemical decolorization of textile dyes and removal of metal ions from textile dye and metal ion binary mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Oatley, D.L.; Williams, P.M.; Wright, C.J. Characterisation and application of a novel positively charged nanofiltration membrane for the treatment of textile industry wastewaters. Water Res. 2012, 46, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramowleeswaran, M.; Palanivelu, K. Treatability studies on textile effluent for total dissolved solids reduction using electrodialysis. Desalination 2006, 201, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delval, F.; Crini, G.; Morin, N.; Vebrel, J.; Bertini, S.; Torri, G. The sorption of several types of dye on crosslinked polysaccharides derivatives. Dyes Pigm. 2002, 53, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.X.; Li, Y.P.; Xie, M.; Xin, H.Z. Sorption of an anionic dye by uncalcined and calcined layered double hydroxides: A case study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 120, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mon, J.; Flury, M.; Harsh, J.B. Sorption of four triarylmethane dyes in a sandy soil determined by batch and column experiments. Geoderma 2006, 133, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M. Removal of C.I. Basic Blue 3 dye by sorption onto cation exchange resin, functionalized and non-functionalized polymeric sorbents from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Široký, J.; Blackburn, R.S.; Bechtold, T.; Taylor, J.; White, P. Alkali treatment of cellulose II fibres and effect on dye sorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Brame, J.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Nanotechnology for a safe and sustainable water supply: Enabling integrated water treatment and reuse. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rubio-Alonso, M.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; Rodriguez-Castellón, E.; Jiménez-López, A. Synthesis and characterisation of acid mesoporous phosphate heterostructure (PPH) materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rubio-Alonso, M.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; Castellón, E.R.; Jiménez-López, A. Synthesis and characterization of mixed silica/zirconia and silica/titania porous phospate heterostructures (PPH). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Algarra, M.; Castellón, E.R.; Jiménez-López, A.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Hybrid porous phosphate heterostructures as adsorbents of Hg(II) and Ni(II) from industrial sewage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603. [Google Scholar]
- Lowell, S. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Springer: Berlin, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Tost, R.; Oliveira, M.L.; Eliche-Quesada, D.L.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Jiménez-López, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Evaluation of Cu-PPHs as active catalysts for the SCR process to control NOx emissions from heavy duty diesel vehicles. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliche-Quesada, D.; Macias-Ortiz, M.I.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Jiménez-López, A. Catalysts based on Ru/mesoporous phosphate heterostructures (PPH) for hydrotreating of aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Catal. A 2006, 255, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, M.D.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Concepción, P.; Jiménez-López, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; López Nieto, J.M. Selective oxidation of H2S to sulfur over vanadia supported on mesoporous zirconium phosphate heterostructure. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 92, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.; Heller, W. On Adsorption in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Biggs, M.J.; Skinner, W.; Bandosz, T.J. Effect of visible light and electrode wetting on the capacitive performance of S- and N-doped nanoporous carbons: Importance of surface chemistry. Carbon 2014, 78, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, B.; Rastogi, A.; Agarwal, S.; Nayak, A. A comparative investigation on adsorption performances of mesoporous activated carbon prepared from waste rubber tire and activated carbon for a hazardous azo dye—Acid Blue 113. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirzad-Siboni, M.; Jafari, S.J.; Giahi, O.; Kim, I.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, J.K. Removal of acid blue 113 and reactive black 5 dye from aqueous solutions by activated red mud. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, C.; Seaton, N.A. Modeling of Organically Functionalized Mesoporous Silicas for the Design of Adsorbents. Adsorption 2005, 11, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Sha, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, B.; Deng, C. Preparation of phenyl group-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for fast extraction and analysis of acetaldehyde in mainstream cigarette smoke by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 115, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, N.; Al-Mawla, M.; Moubarak, E.; Al-Ghoul, M.; El-Rassy, H. Surface-functionalized silica aerogels and alcogels for methylene blue adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraji, M.; Khaje, N. Phenyl-functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of chlorobenzenes, and their determination by GC-electron capture detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
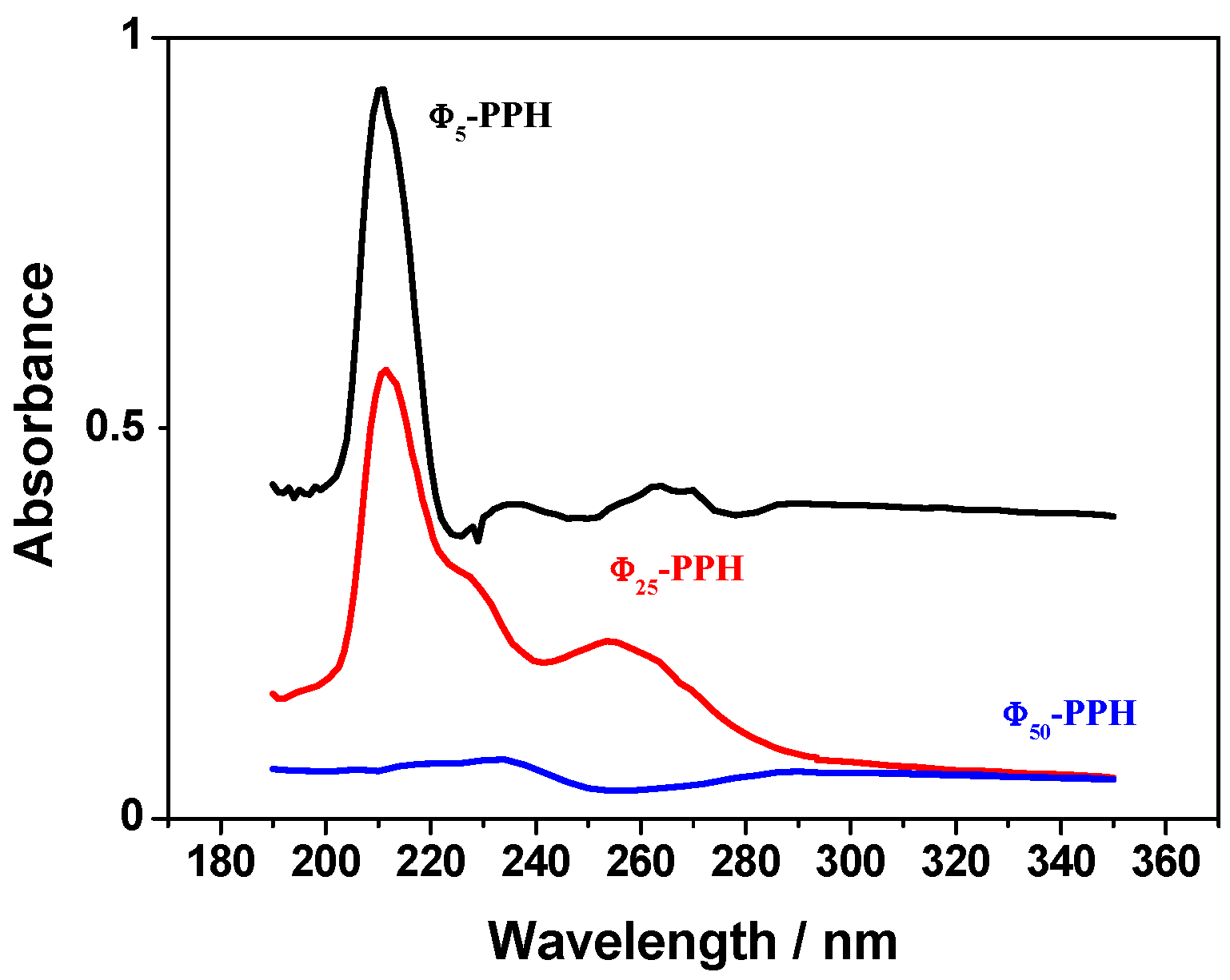
 ) and compared with raw PPH (
) and compared with raw PPH (  ).
).
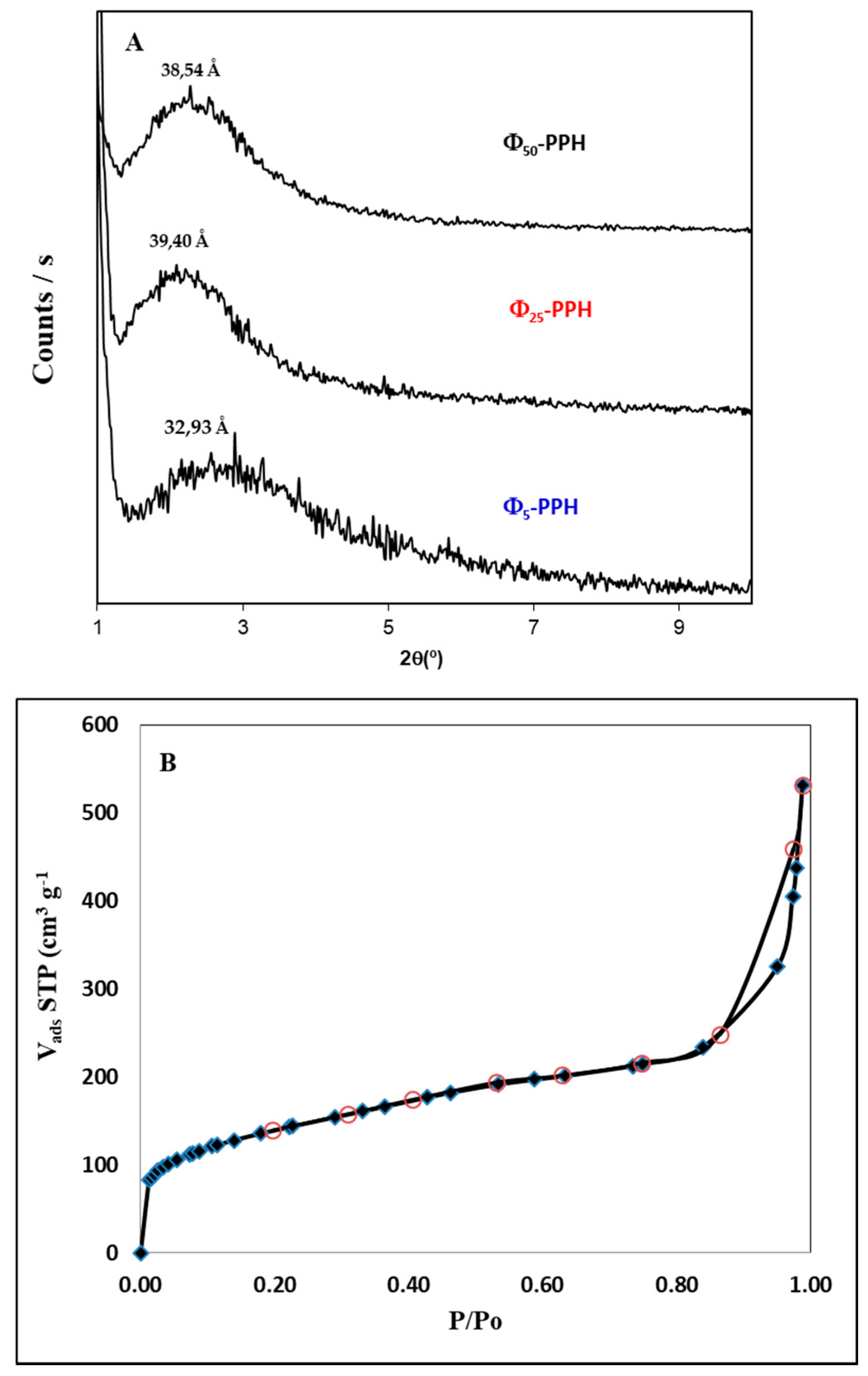
 ) and compared with raw PPH (
) and compared with raw PPH (  ).
).
| Material | %C | %N | %C * | %N * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ5-PPH | 9.04 | 0.147 | 19.53 | 1.30 |
| Φ25-PPH | 3.81 | 0.217 | 18.91 | 1.27 |
| Φ50-PPH | 2.62 | 0.222 | 18.53 | 1.28 |
| Material | mmol Φ/g | mmol P/g | Φ/P (Exp) | Φ/P (Exp) | SBET (m2/g) | Vp (cm3/g) | CBET | Sac (m2/g) * | ΣVp (cm3/g) ● | Dp (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ5 −PPH | 0.047 | 1.73 | 0.027 | 0.6 | 498 | 0.516 | 133 | 482 | 0.472 | 39.13 |
| Φ25– PPH | 0.042 | 1.86 | 0.023 | 0.12 | 545 | 0.596 | 123 | 540 | 0.565 | 41.87 |
| Φ50– PPH | 0.003 | 1.78 | 0.002 | 0.06 | 571 | 0.657 | 133 | 546 | 0.609 | 44.59 |
| Sample | C | N | O | Si | P | Zr | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ5-PPH | 24.50 | 0.50 | 50.07 | 19.55 | 3.52 | 1.86 | - |
| Φ5-PPH + AB113 | 29.56 | 0.94 | 46.00 | 18.42 | 2.19 | 1.69 | 0.36 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Algarra, M.; Guimarães, V.; Bobos, I.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. The Application of Functionalized Pillared Porous Phosphate Heterostructures for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Wastewater. Materials 2017, 10, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101111
Jiménez-Jiménez J, Algarra M, Guimarães V, Bobos I, Rodríguez-Castellón E. The Application of Functionalized Pillared Porous Phosphate Heterostructures for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Wastewater. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101111
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Jiménez, José, Manuel Algarra, Vanessa Guimarães, Iuliu Bobos, and Enrique Rodríguez-Castellón. 2017. "The Application of Functionalized Pillared Porous Phosphate Heterostructures for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Wastewater" Materials 10, no. 10: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101111
APA StyleJiménez-Jiménez, J., Algarra, M., Guimarães, V., Bobos, I., & Rodríguez-Castellón, E. (2017). The Application of Functionalized Pillared Porous Phosphate Heterostructures for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Wastewater. Materials, 10(10), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101111








