Influence of Porous Spherical-Shaped Hydroxyapatite on Mechanical Strength and Bioactive Function of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment I: The Effects of Varying the Conditions Used to Combine the Additives with GIC
2.1.1. Preparation of Specimens
2.1.2. Morphological and Strength Analyses of Additives
2.1.3. Compressive Strength Test
2.1.4. Fluoride Ion Release Test
2.2. Experiment II: The Effects of HAp on the Mechanical Strength and Various Ion Release Properties of AIC
2.2.1. Preparation of Specimens
2.2.2. Morphological and Strength Analyses of the Additive
2.2.3. Compressive Strength Test
2.2.4. Fluoride Ion Release and Multi-Element Release Tests
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment I: The Effects of Varying the Conditions Used to Combine Additives with the GIC
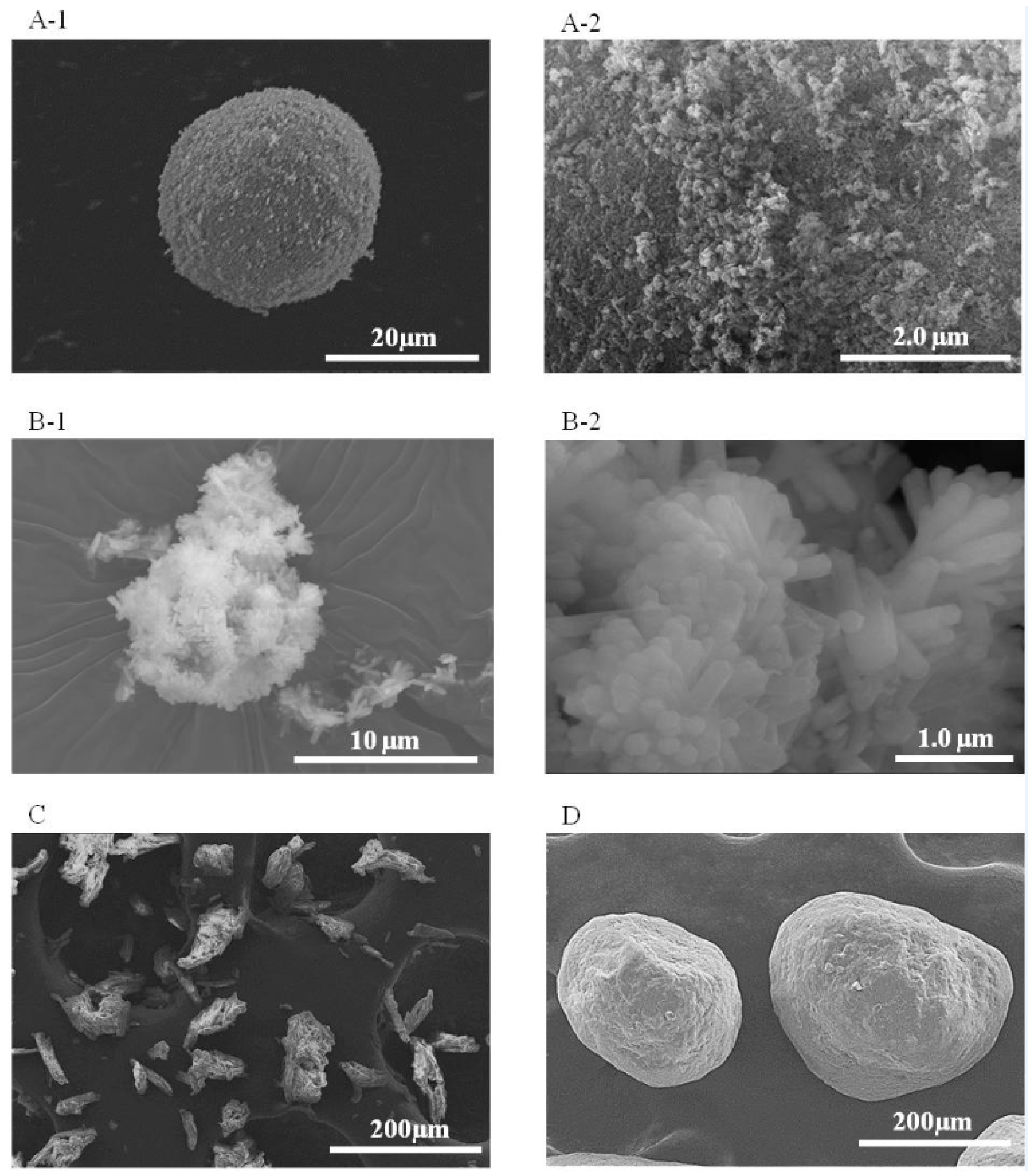
3.1.1. Morphological Characteristics of Additives
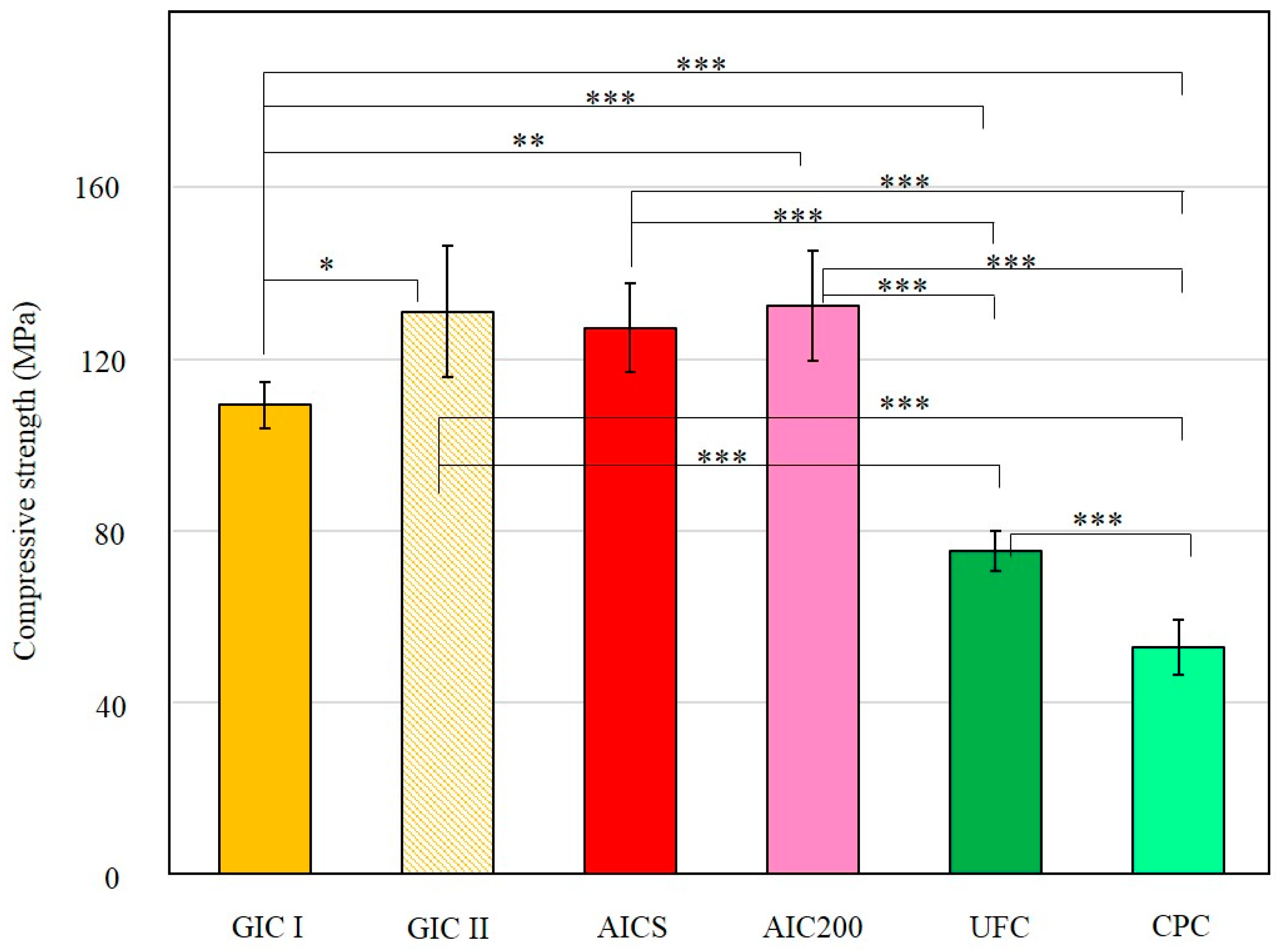
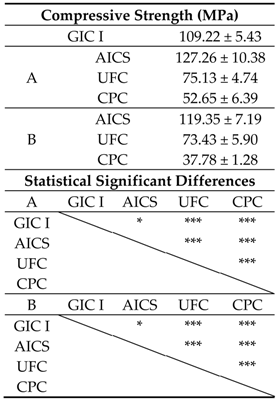
3.1.2. Compressive Strengths of Specimens
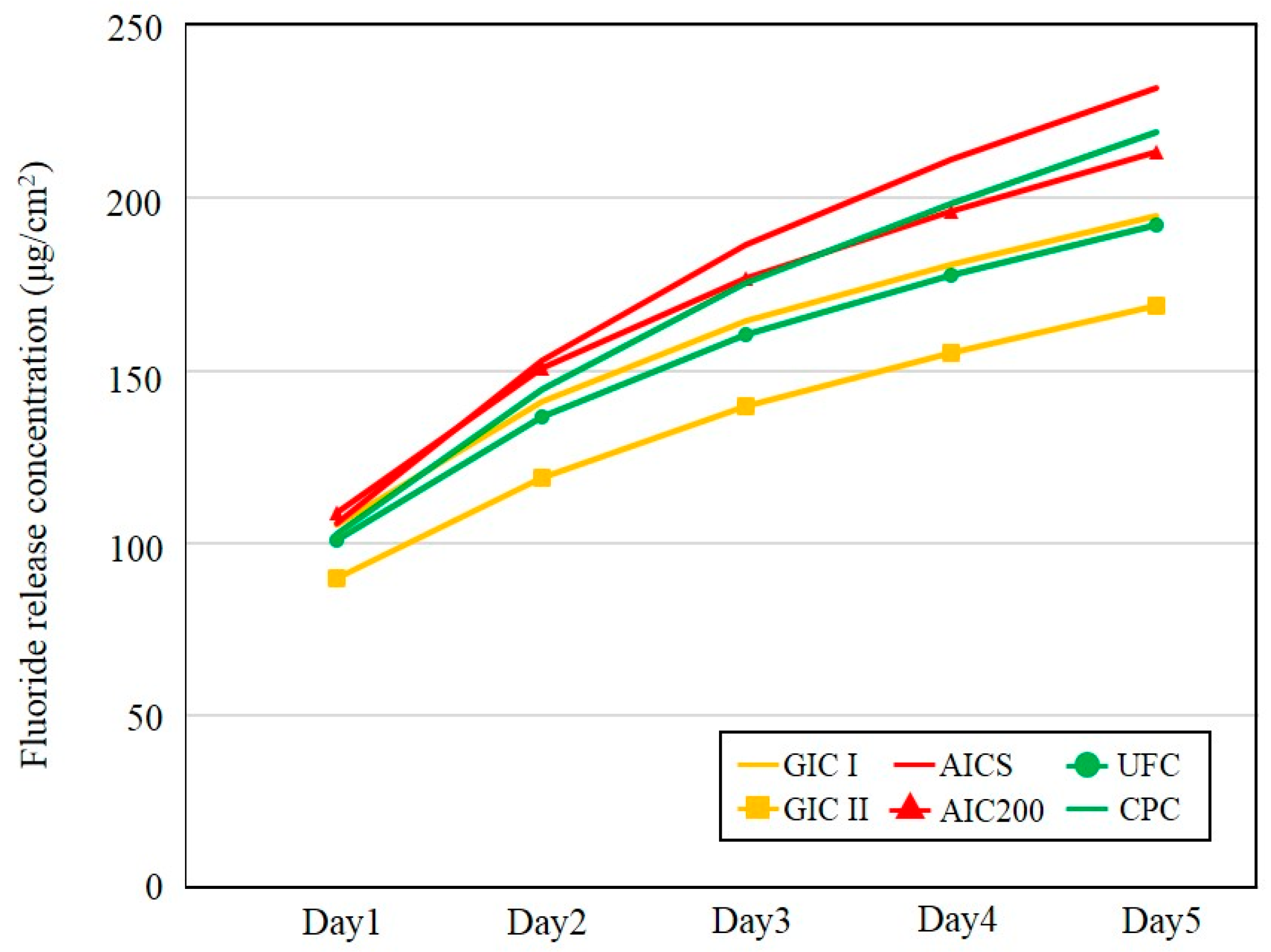
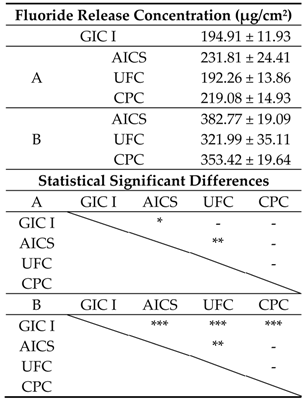
3.1.3. Fluoride Ion Release Properties
3.2. Experiment II
3.2.1. Morphological Characteristics of the Additives
3.2.2. Compressive Strengths of Specimens
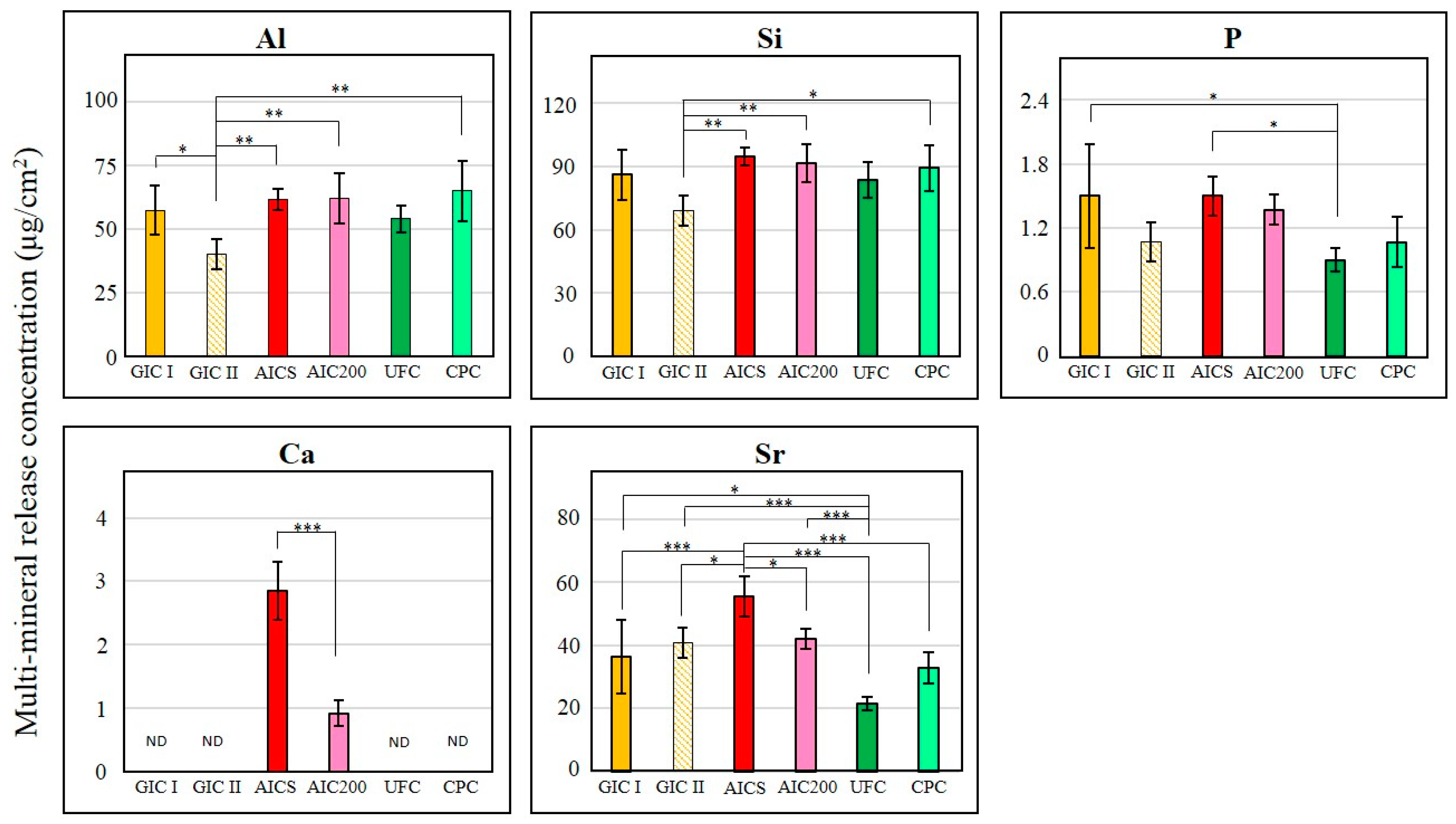
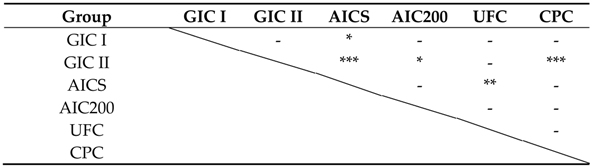
3.2.3. Fluoride Ion and Multi-Mineral Release Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail, A.I.; Sohn, W.; Tellez, M.; Amaya, A.; Sen, A.; Hasson, H.; Pitts, N.B. The international caries detection and assessment system (ICDAS): An integrated system for measuring dental caries. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2007, 35, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, N.B.; Ekstrand, K.R. International caries detection and assessment system (ICDAS) and its international caries classification and management system (ICCMS)—Methods for staging of the caries process and enabling dentists to manage caries. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2013, 41, e41–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahovuo-Saloranta, A.; Forss, H.; Walsh, T.; Hiiri, A.; Nordblad, A.; Mäkelä, M.; Worthington, H.V. Sealants for preventing dental decay in the permanent teeth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 28, CD001830. [Google Scholar]
- Francci, C.; Deaton, T.G.; Arnold, R.R.; Swift, E.J., Jr.; Perdigão, J.; Bawden, J.W. Fluoride release from restorative materials and its effects on dentin demineralization. J. Dent. Res. 1999, 78, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korwar, A.; Sharma, S.; Logani, A.; Shah, N. Pulp response to high fluoride releasing glass ionomer, silver diamine fluoride, and calcium hydroxide used for indirect pulp treatment: An in vivo comparative study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2015, 6, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Six, N.; Lasfargues, J.J.; Goldberg, M. In vivo study of the pulp reaction to Fuji IX, a glass ionomer cement. J. Dent. 2000, 28, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Costa, C.A.; Hebling, J.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Hanks, C.T. In vitro cytotoxicity of five glass-ionomer cements. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.K.; Tay, F.R.; Ngo, H.C.; Smales, R.J.; Pashley, D.H. Bonding of contemporary glass ionomer cements to dentin. Dent. Mater. 2001, 17, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Inoue, S.; Sano, H.; Suzuki, K.; Shintani, H.; Van Meerbeek, B. Bonding efficacy of polyalkenoic acids to hydroxyapatite, enamel and dentin. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Nakayama, Y.; Snauwaert, J.; Hellemans, L.; Lambrechts, P.; Vanherle, G.; Wakasa, K. Evidence of chemical bonding at biomaterial-hard tissue interfaces. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagetti, M.G.; Carta, G.; Cocco, F.; Sale, S.; Congiu, G.; Mura, A.; Strohmenger, L.; Lingström, P.; Campus, G. Italian Experimental Group on Oral Health. Effect of fluoridated sealants on adjacent tooth surfaces: A 30-mo randomized clinical trial. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 59S–65S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionysopoulos, P.; Kotsanos, N.; Koliniotou-Koubia, E.; Papagodiannis, Y. Secondary caries formation in vitro around fluoride-releasing restorations. Oper. Dent. 1994, 19, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frencken, J.E. The ART approach using glass-ionomers in relation to global oral health care. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smales, R.J.; Gao, W. In vitro caries inhibition at the enamel margins of glass ionomer restoratives developed for the ART approach. J. Dent. 2000, 28, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Brantley, W.A.; Culbertson, B.M.; Wang, G. Mechanical properties and microstructures of glass-ionomer cements. Dent. Mater. 2000, 16, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarczyk, A.; Ottl, P.; Lauer, H.C. Laboratory strength of glass ionomer and zinc phosphate cements. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 10, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yli-Urpo, H.; Lassila, L.V.; Närhi, T.; Vallittu, P.K. Compressive strength and surface characterization of glass ionomer cements modified by particles of bioactive glass. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yli-Urpo, H.; Vallittu, P.K.; Närhi, T.O.; Forsback, A.P.; Väkiparta, M. Release of silica, calcium, phosphorus, and fluoride from glass ionomer cement containing bioactive glass. J. Biomater. Appl. 2004, 19, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Du, X.; Huang, C.; Fu, D.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial and physical properties of EGCG-containing glass ionomer cements. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.E.; Arita, K.; Nishino, M. Toughness, bonding and fluoride-release properties of hydroxyapatite-added glass ionomer cement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3787–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Shinonaga, Y.; Harada, K.; Abe, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Sugiyama, S. Hydroxyapatite particle characteristics influence the enhancement of the mechanical and chemical properties of conventional restorative glass ionomer cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, K.; Lucas, M.E.; Nishino, M. The effect of adding hydroxyapatite on the flexural strength of glass ionomer cement. Dent. Mater. J. 2003, 22, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Shinonaga, Y.; Abe, Y.; Kawai, S.; Arita, K. Porous hydroxyapatite can improve strength and bioactive functions of glass ionomer cement. Nano Biomed. 2014, 6, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shinonaga, Y.; Arita, K.; Nishimura, T.; Chiu, S.Y.; Chiu, H.H.; Abe, Y.; Sonomoto, M.; Harada, K.; Nagaoka, N. Effects of porous-hydroxyapatite incorporated into glass-ionomer sealants. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, A.; Buchalla, W.; Attin, T. Review on fluoride-releasing restorative materials—Fluoride release and uptake characteristics, antibacterial activity and influence on caries formation. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Sudo, A.; Komlev, V.S.; Barinov, S.M.; Uchida, A. High release of antibiotic from a novel hydroxyapatite with biomodel pore size distribution. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 70, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, C.L.; Mjӧr, I.A. Advances in Glass-Ionomer Cements; Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc.: DuPage, IL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.M.; Santos, P.H.N.; Souza, L.B.; Dumont, V.C.; Soares, J.A.; Santos, M.H. Effects of cellulose fibers on the physical and chemical properties of glass ionomer dental restorative materials. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.M.; Carvalho, V.X.; Dumont, V.C.; Santos, M.H.; Carvalho, A.M.M.L. Addition of mechanically processed cellulosic fibers to ionomer cement: Mechanical properties. Braz. Oral Res. 2015, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, M.G.; Chersoni, S.; Acquaviva, G.L.; Piana, G.; Prati, C.; Mongiorgi, R. Fluoride release and absorption at different PH from glass-ionomer cements. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.D.; Yang, L.; Wan, W.; Rizkalla, A.S. Fluoride release from dental cements and composites: A mechanistic study. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, M.; Takahashi, H.; Iwasaki, N.; Wada, T.; Uo, M. Effect of immersion time of restorative glass ionomer cements and immersion duration in calcium chloride solution on surface hardness. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, e377–e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D.; Kent, B.E.; Clinton, D.; Miller, R.P. The formation and microstructure of dental silicate cements. J. Mater. Sci. 1972, 7, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletsi-Kounari, H.; Mamai-Homata, E.; Diamanti, I. An in vitro study of the effect of aluminum and the combined effect of strontium, aluminum, and fluoride elements on early enamel carious lesions. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennou, H.E.; Lebugle, A.A.; Grégoire, G.L. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the dentin-glass ionomer cement interface. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Powders | Liquid | Powder/Liquid (g/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuji III (g) | Additives (g) | Total (g) | Proportion of Additives (wt %) | Fuji III (g) | |||
| [Volume(cm3)] | [Volume(cm3)] | [Volume(cm3)] | [Volume %] | ||||
| GIC I | 1.0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.83 | 1.2 | |
| [0.357] | [0.357] | ||||||
| A | AICS | 1.0 | 0.24 HApS | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| [66.9] | |||||||
| UFC | 1.0 | 0.24 UF-711 | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 | |
| [75.3] | |||||||
| CPC | 1.0 | 0.24 CP-203 | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 | |
| [43.5] | |||||||
| B | AICS | 0.76 | 0.24 HApS | 1 | 24 | 0.83 | 1.2 |
| [0.72] | [71.4] | ||||||
| UFC | 0.76 | 0.16 UF-711 | 0.92 | 17.4 | 0.83 | 1.1 | |
| [0.72] | [71.4] | ||||||
| CPC | 0.76 | 0.63 CP-203 | 1.39 | 45.3 | 0.83 | 1.67 | |
| [0.72] | [71.4] | ||||||
| Group | Powders | Liquid | Powder/Liquid (g/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuji III (g) | Additives (g) | Total (g) | Proportion of Additives (wt %) | Fuji III (g) | ||
| GIC I | 1.0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.83 | 1.2 |
| GIC II | 1.24 | 0 | 1.24 | 0 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| AICS | 1.0 | 0.24 HApS | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| AIC200 | 1.0 | 0.24 HAp200 | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| UFC | 1.0 | 0.24 UF-711 | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| CPC | 1.0 | 0.24 CP-203 | 1.24 | 19.4 | 0.83 | 1.49 |
| Specimen | Micro-Compressive Strength (MPa) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|
| HApS | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 42.14 ± 0.08 |
| HAp200 | 1.54 ± 0.23 [21] | 6.52 ± 0.08 [21] |
| UF-711 | - | 1.08 ± 0.02 |
| CP-203 | 23.49 ± 5.66 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, S.-Y.; Shinonaga, Y.; Abe, Y.; Harada, K.; Arita, K. Influence of Porous Spherical-Shaped Hydroxyapatite on Mechanical Strength and Bioactive Function of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement. Materials 2017, 10, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010027
Chiu S-Y, Shinonaga Y, Abe Y, Harada K, Arita K. Influence of Porous Spherical-Shaped Hydroxyapatite on Mechanical Strength and Bioactive Function of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement. Materials. 2017; 10(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Szu-Yu, Yukari Shinonaga, Yoko Abe, Kyoko Harada, and Kenji Arita. 2017. "Influence of Porous Spherical-Shaped Hydroxyapatite on Mechanical Strength and Bioactive Function of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement" Materials 10, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010027
APA StyleChiu, S.-Y., Shinonaga, Y., Abe, Y., Harada, K., & Arita, K. (2017). Influence of Porous Spherical-Shaped Hydroxyapatite on Mechanical Strength and Bioactive Function of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement. Materials, 10(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10010027





