Slag Behavior in Gasifiers. Part II: Constitutive Modeling of Slag
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Governing Equations of Motion and Heat Transfer
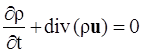
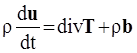
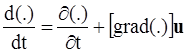 . The balance of moment of momentum reveals that, in the absence of couple stresses, the stress tensor is symmetric.
. The balance of moment of momentum reveals that, in the absence of couple stresses, the stress tensor is symmetric.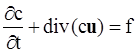
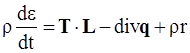
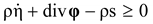
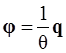 , and
, and 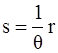 , where θ is the absolute temperature, then Equation (2.5) reduces to the Clausius-Duhem inequality:
, where θ is the absolute temperature, then Equation (2.5) reduces to the Clausius-Duhem inequality:
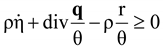
3. The Importance of Slag layer Viscosity in Gasification and Combustion Processes
3.1. Viscosity of Slags
3.2. A Brief Review of Various Viscosity Models
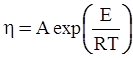
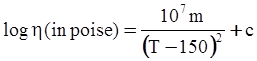
c = 0.0415 SiO2 +0.0192 Al2O3 +0.0276 Equiv Fe2O3 +0.0160 CaO − 3.92
SiO2 + Al2O3 + Equiv Fe2O3 +CaO+ MgO = 100 (wt%)
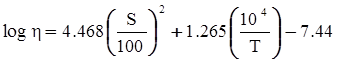
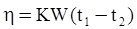
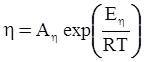
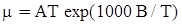
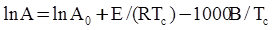
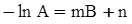
n = 11.57
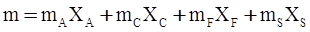
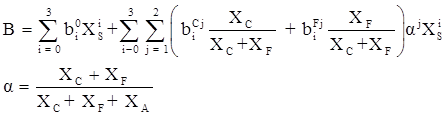
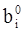 values are parameters for the Al2O3-SiO2 system, while
values are parameters for the Al2O3-SiO2 system, while 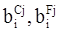 are parameters for CaO-‘FeO’ system, all obtained by optimization.
are parameters for CaO-‘FeO’ system, all obtained by optimization. 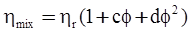
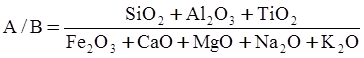
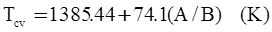
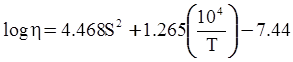
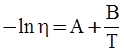
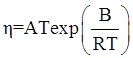
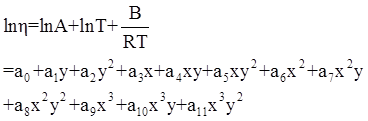
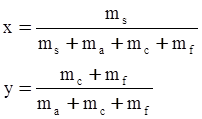
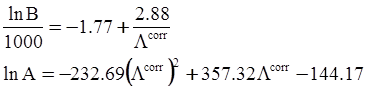
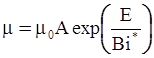
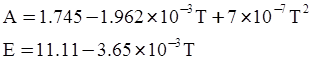

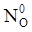 value takes into account the depolymerization and subsequent breakdown of the silicate network structure, and E is the energy needed to break the bond, given by a polynomial function:
value takes into account the depolymerization and subsequent breakdown of the silicate network structure, and E is the energy needed to break the bond, given by a polynomial function:
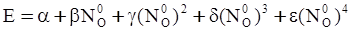
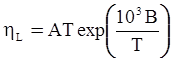
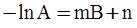
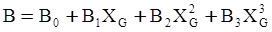
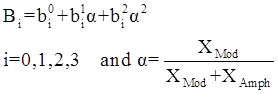
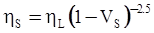
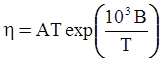
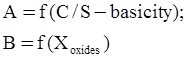
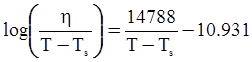
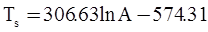
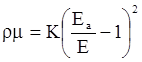
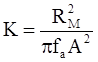
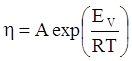
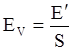
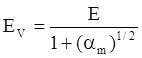
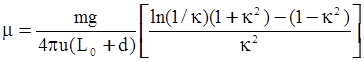
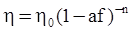
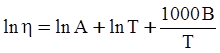
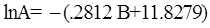
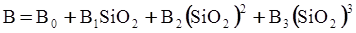
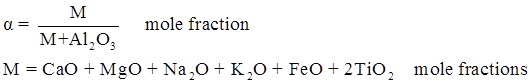
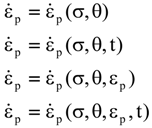
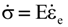
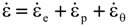
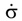 is the stress rate,
is the stress rate, 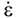 is the total strain rate,
is the total strain rate, 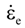 is the elastic strain rate,
is the elastic strain rate, 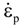 is the inelastic (plastic) strain rate,
is the inelastic (plastic) strain rate, 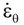 is the thermal strain rate, and θ is the temperature in Kelvin. A significant contribution of this work was the recognition of the difficulty of measuring and the importance that the Young’s modulus E plays in this kind of problem. They used the experimental results of Mizukami et al. [98], where:
is the thermal strain rate, and θ is the temperature in Kelvin. A significant contribution of this work was the recognition of the difficulty of measuring and the importance that the Young’s modulus E plays in this kind of problem. They used the experimental results of Mizukami et al. [98], where:
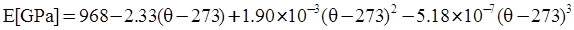
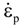 as functions of stress, temperature, carbon content, activation energy, and various adjustable parameters such as temperature dependent stress exponent, etc. (see also Thomas [99,100] for a review of this subject). In the continuous casting of steel, when mold powder is added to the free surface of the liquid steel, it begins to melt and flow. The re-solidified mold powder, also called slag forms a layer adjacent to the walls; there is an increase in its viscosity and it begins to act as a solid-like material [101,102]. Once the slag cools, it creates a glassy layer. Heat conduction across the slag layer plays a major role in the operation; it is a function of the thickness of the slag and depends on the conductivity of the various layers and particles embedded in the slag. In the model that they developed, Meng and Thomas [101] suggested that the viscosity of molten slag depends on the temperature in the following way:
as functions of stress, temperature, carbon content, activation energy, and various adjustable parameters such as temperature dependent stress exponent, etc. (see also Thomas [99,100] for a review of this subject). In the continuous casting of steel, when mold powder is added to the free surface of the liquid steel, it begins to melt and flow. The re-solidified mold powder, also called slag forms a layer adjacent to the walls; there is an increase in its viscosity and it begins to act as a solid-like material [101,102]. Once the slag cools, it creates a glassy layer. Heat conduction across the slag layer plays a major role in the operation; it is a function of the thickness of the slag and depends on the conductivity of the various layers and particles embedded in the slag. In the model that they developed, Meng and Thomas [101] suggested that the viscosity of molten slag depends on the temperature in the following way:
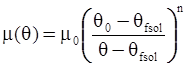
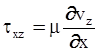
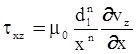
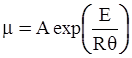
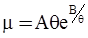
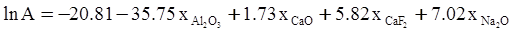
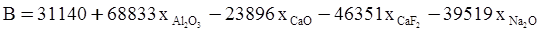
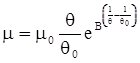
| Viscosity as a function of temperature | See for example Equations (3.1), or (3.2), and others. Generally expressed as an exponential function or some type of power-law [see Equation (3.49)] |
|---|---|
| Viscosity as a function of time | See Equation (3.5) |
| Viscosity as a function of chemical composition | See Equations (3.9)–(3.12) and others. Generally expressed as a polynomial equation |
| Viscosity as a function of concentration | See Equation (3.13), generally expressed as a polynomial [see also Table 2 in Section 4] |
| Viscosity as a function of the shear rate | See Equation (3.50), generally expressed as the power-law type non-Newtonian fluid model |
4. Constitutive Modeling of Slag
4.1. Background
- The ability to shear-thin or shear-thicken
- The ability to creep
- The ability to relax stresses
- The presence of normal stress differences in simple shear flows
- The presence of yield stress
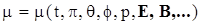
4.2. Yield Stress
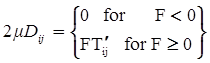
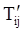 denotes the stress deviator and F, called the yield function, is given by:
denotes the stress deviator and F, called the yield function, is given by:
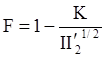
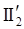 is the second invariant of the stress deviator, and in simple shear flows it is equal to the square of the shearing stress and K is called yield stress (a constant). For one-dimensional flow, these relationships reduce to the ones proposed by Bingham [104]:
is the second invariant of the stress deviator, and in simple shear flows it is equal to the square of the shearing stress and K is called yield stress (a constant). For one-dimensional flow, these relationships reduce to the ones proposed by Bingham [104]:
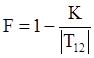
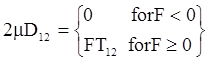
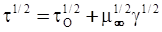
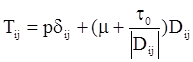
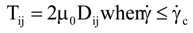
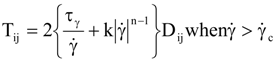
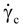 is a critical shear rate. There are obviously other yield criteria which can be used. For example, by including the gradient of the volume fraction as one of the important parameters in proposing a constitutive equation for the stress tensor, a theory could be devised for the flow of granular materials (see Massoudi and Mehrabadi [110]). In this theory a critical yield condition called the Mohr-Coulomb emerges naturally, as does the transition between the frictional flow regimes, characterized by the absence of deformation and the viscous flow regime, characterized by deformation. More work is needed in this area before an appropriate yield-stress can be formulated for slags.
is a critical shear rate. There are obviously other yield criteria which can be used. For example, by including the gradient of the volume fraction as one of the important parameters in proposing a constitutive equation for the stress tensor, a theory could be devised for the flow of granular materials (see Massoudi and Mehrabadi [110]). In this theory a critical yield condition called the Mohr-Coulomb emerges naturally, as does the transition between the frictional flow regimes, characterized by the absence of deformation and the viscous flow regime, characterized by deformation. More work is needed in this area before an appropriate yield-stress can be formulated for slags.4.3. Effects of Concentration, Shear Rate, and Pressure
4.3.1. Concentration Effect
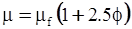
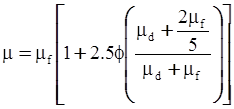
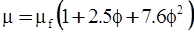
| Mooney (1951) [115] | 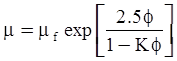 [Equation (4.13)] where K is the crowding factor [Equation (4.13)] where K is the crowding factor |
| Roscoe (1952) [87] | 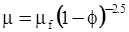 [Equation (4.14)] [Equation (4.14)] |
| Brinkman (1952) [112] | 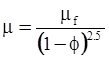 [Equation (4.15)] [Equation (4.15)] |
| Krieger and Dougherty (1959) [113] | 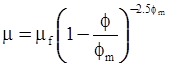 [Equation (4.16)] [Equation (4.16)] |
| Nielsen (1970)[114] | 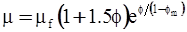 [Equation (4.17)] [Equation (4.17)] |
| Choi et al. (2000) [116], Kwon et al. (1998) [117] | 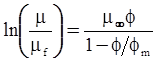 ; non-spherical particles where φm is the maximum packing volume fraction. [Equation (4.18)] ; non-spherical particles where φm is the maximum packing volume fraction. [Equation (4.18)] |
4.3.2. Normal Stress Effects and Shear-Rate Dependent Viscosity
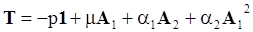
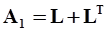
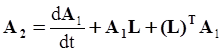
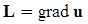
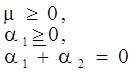
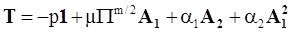
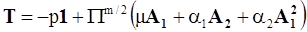
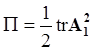
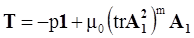
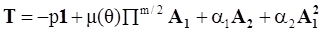
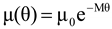
4.3.3. Pressure Effects
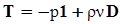
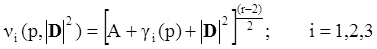
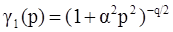
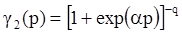
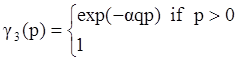
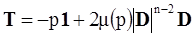
5. Concluding Remarks
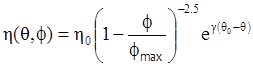
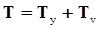
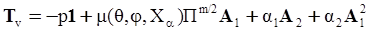
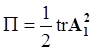 is the second invariant of the symmetric part of the velocity gradient, and m is a material parameter. When m < 0, the fluid is shear-thinning, and if m > 0, the fluid is shear-thickening. This model is a general frame invariant model, suitable for flows of non-linear fluids with the viscosity being a function of temperature, concentration, and shear rate, and the material exhibiting both normal stress differences. Obviously the methodology that we have presented here is not very rigorous. Of course, in the studies reviewed here, the concept of normal stress was not discussed, and it is not known whether some or none of the various kinds of slag would exhibit normal stress effects. The measurement of these material parameters presents new opportunities for the slag community.
is the second invariant of the symmetric part of the velocity gradient, and m is a material parameter. When m < 0, the fluid is shear-thinning, and if m > 0, the fluid is shear-thickening. This model is a general frame invariant model, suitable for flows of non-linear fluids with the viscosity being a function of temperature, concentration, and shear rate, and the material exhibiting both normal stress differences. Obviously the methodology that we have presented here is not very rigorous. Of course, in the studies reviewed here, the concept of normal stress was not discussed, and it is not known whether some or none of the various kinds of slag would exhibit normal stress effects. The measurement of these material parameters presents new opportunities for the slag community.References
- Tonmukayakul, N.; Nguyen, Q.D. A new rheometer for direct measurement of the flow properties of coal ash at high temperatures. Fuel 2002, 81, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.M.; Sarofim, A.F.; Beer, J.M. Fouling of convection heat-exchangers by lignitic coal ash. Energy Fuels 1992, 6, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.E.; Fletcher, C.A.J.; Shin, S.H.; Kwon, S.B. Computational study of fouling deposit due to surface-coated particles in coal-fired power utility boilers. Fuel 2002, 81, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Harb, J.N. Modeling of ash deposition in large-scale combustion facilities burning pulverized coal. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 1997, 23, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, T.A.; Allan, S.E.; McCollor, D.P.; Hurley, J.P.; Srinivasachar, S.; Kang, S.G.; Baker, J.E.; Morgan, M.E.; Johnson, S.A.; Borio, R. Modeling of fouling and slagging in coal-fired utility boilers. Fuel Process. Technol. 1995, 44, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.J.; Yu, G.S.; Guo, Q.H.; Dai, Z.H.; Wang, F.C. Modeling and comparison of different syngas cooling types for entrained-flow gasifier. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbogar, A.; Frandsen, F.J.; Jensen, P.A.; Glarborg, P. Heat transfer in ash deposits: A modelling tool-box. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 371–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jak, E.; Degterov, S.; Zhao, B.; Pelton, A.D.; Hayes, P.C. Coupled experimental and thermodynamic modeling studies for metallurgical smelting and coal combustion slag systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2000, 31, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, C.W.; Pelton, A.D.; Thompson, W.T. Facility for the Analysis of Chemical Thermodynamics (FACT); École Polytechnique de Montréal: Palaiseau, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Breault, R.W. Gasification processes old and new: a basic review of the major technologies. Energies 2010, 3, 216–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergios, G.; Fernandez-Turiel, J.L.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Gimeno, D. Slag and ash chemistry after high-calcium lignite combustion in a pulverized coal-fired power plant. Glob. Nest J. 2007, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Vorres, K.S.; Greenberg, S.; Poeppel, R. Viscosity of synthetic coal ash slags. Acs Symp. Ser. 1986, 301, 156–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lawn, C.J. Principles of Combustion Engineering for Boilers; Academic Press: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Jak, E.; Saulov, D.; Kondratiev, A.; Hayes, P.C. Prediction of phase equilibria and viscosity in complex coal ash slag systems. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 227, 1079. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, G.J.; Bryant, G.W.; Hurst, H.J.; Lucas, J.A.; Wall, T.F. An empirical method for the prediction of coal ash slag viscosity. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W.; Gupta, S.; Saha-Chaudhury, N.; Sahajwalla, V. Wetting and interfacial reaction investigations of coke/slag systems and associated liquid permeability of blast furnaces. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int. 2005, 45, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G.; Samarasekera, I.V.; Brimacombe, J.K. Mathematical-model of the thermal-processing of steel ingots: Part I. Heat-flow model. Metal. Trans. B Process Metall. 1987, 18, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G.; Samarasekera, I.V.; Brimacombe, J.K. Mathematical-model of the thermal-processing of steel ingots: Part II. Stress model. Metal. Trans. B Process Metall. 1987, 18, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Vanka, S.P.; Thomas, B.G. Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in a molten flux layer. Int.J. Heat Fluid Flow 2005, 26, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanova, E.; Avdeev, G.; Karamanov, A. Ceramics from blast furnace slag, kaolin and quartz. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.W.; Cai, L.C.; Wu, Y.G. Freeze-thaw cycle test and damage mechanics models of alkali-activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3144–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachemi, M.; Hossain, K.M.A.; Lambros, V.; Bouzoubaa, N. Development of cost-effective self-consolidating concrete incorporating fly ash, slag cement, or viscosity-modifying admixtures. Aci Mater. J. 2003, 100, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Ekmann, J.M.; Winslow, J.C.; Smouse, S.M.; Ramezan, M. International survey of cofiring coal with biomass and other wastes. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 54, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterly, J.L.; Burnham, M. Overview of biomass and waste fuel resources for power production. Biomass Bioenergy 1996, 10, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V.; Toft, A.J.; Brammer, J.G. A techno-economic comparison of power production by biomass fast pyrolysis with gasification and combustion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 181–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V. Renewable fuels and chemicals by thermal processing of biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 91, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondreal, E.A.; Benson, S.A.; Hurley, J.P.; Mann, M.D.; Pavlish, J.H.; Swanson, M.L.; Zygarlicke, C.J. Review of advances in combustion technology and biomass cofiring. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 71, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open-Cycle Magnetohydrodynamic Electrical Power Generation; Petrick, M.; Ya, S.B. (Eds.) Argonne National Laboratory: Argonne, IL, USA, 1978.
- Pian, C.C.P.; Yoshikawa, K. Development of a high-temperature air-blown gasification system. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 79, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.X.; Horio, M.; Kojima, T. Use of numerical modeling in the design and scale-up of entrained flow coal gasifiers. Fuel 2001, 80, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willimas, A.; Pourkashanian, M.; Jones, J.M. The combustion of coal and some other solid fuels. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2000, 28, 2141–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backreedy, R.I.; Fletcher, L.M.; Jones, J.M.; Ma, L.; Pourkashanian, M.; Williams, A. Co-firing pulverised coal and biomass: a modeling approach. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 2955–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkvall, J.; Du, S.C.; Stolyarova, V.; Seetharaman, S. A model description of the thermochemical properties of multicomponent slags and its application to slag viscosities. Glass Phys. Chem. 2001, 27, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnaro, F.; Salatino, P. Analysis of char-slag interaction and near-wall particle segregation in entrained-flow gasification of coal. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Iman, F.; Lu, P.S.; Sears, R.; Kong, L.B.; Rokanuzzaman, A.S.; McCollor, D.P.; Benson, S.A. A comprehensive slagging and fouling prediction tool for coal-fired boilers and its validation/application. Fuel Process.Technol. 2007, 88, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koric, S.; Thomas, B.G. Thermo-mechanical models of steel solidification based on two elastic visco-plastic constitutive laws. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, L. Constitutive-equations for the rate-dependent deformation of metals at elevated-temperatures. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 1982, 104, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, P.F.; Thomas, B.G.; Azzi, J.A.; Hao, W. Simple constitutive-equations for steel at high-temperature. Metall. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1992, 23, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, H.R.; Gupta, R.P.; Bryant, G.W.; Hart, J.T.; Liu, G.S.; Bailey, C.W.; Wall, T.F.; Miyamae, S.; Makino, K.; Endo, Y. Thermal conductivity of coal ash and slags and models used. Fuel 2000, 79, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoudi, M.; Wang, P. A Brief. Review of Viscosity Models for Slag in Coal Gasification; DOE report 103673; U.S. Department of Energy, National Energy Technology Laboratory: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2012. Available online: http://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1036735/ (accessed on 20 September 2012).
- Slattery, J.C. Advanced Transport. Phenomena; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, I.S. Continuum Mechanics; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, I. On entropy inequality. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1967, 26, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, H. An Introduction to Thermomechanics, 2nd ed.; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell, C.; Noll, W. The Non-Linear Field Theories of Mechanics; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bills, P.M. Viscosities in silicate slag systems. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1963, 201, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.H.; Sohn, I.; Min, D.J. The effect of MgO on the viscosity of the CaO-SiO2-20 wt% Al2O3-MgO slag system. Steel Res. Int. 2010, 81, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jie, C.; Ruan, F.; Chou, K.C. Experimental measurements and modelling of viscosity in CaO-Al2O3-MgO slag system. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K. Rheological properties of high-temperature melts of coal ashes and other silicates. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2001, 27, 237–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Brooker, D.D.; Welch, P.J.; Oh, M.S. Gasification slag rheology and crystallization in titanium-rich, iron-calcium-aluminosilicate glasses. Fuel Process. Technol. 1998, 56, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.X.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Bai, Z.Q.; Guo, Z.X. Effect of lime addition on slag fluidity of coal ash. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2011, 39, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanmore, B.R.; Budd, S. Measuring the viscous flow of molten coal ash. Fuel 1996, 75, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsbacka, L.; Holappa, L.; Iida, T.; Kita, Y.; Toda, Y. Experimental study of viscosities of selected CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 slags and application of the Iida model. Scand. J. Metall. 2003, 32, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Hori, N.; Nakashima, K.; Mori, K. Viscosity of blast furnace type slags. Metall. and Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2003, 34, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.C.; Raj, M.; Lenka, S.N.; Suresh, P.; Balasubramaniam, K. Measurement of viscosity and melting characteristics of mould powder slags by ultrasonics. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Mukai, K.; Sichen, D. Viscosities of slags—an overview. Steel Res. Int. 2005, 76, 267–728. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Theory of the Brownian Movement; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. The Viscosity of a Fluid Containing Small Drops of Another Fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1932, 138, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Transport Properties of Two-Phase Materials with Random Structure. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1974, 6, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Oh, M.S. Slagging of petroleum coke ash using Korean anthracites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducret, A.C.; Chao, M.C.; Steyn, A.J.; Fortune, S.M.; Deng, L.L; Rubin, E.J. Liquidus temperatures and viscosities of FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2-CaO-MgO slags at compositions relevant to nickel matte smelting. Scand. J. Metall. 2002, 31, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, C.P.; Franken, M.; Gould, D.; Mills, K.C. Standard Reference Material (SRM) for High Temperature Viscosity Measurements. In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Molten Slags and Fluxes, Sendai, Japan, 8–11 June 1992; pp. 439–443.
- Sridhar, S. Estimation models for molten slag and alloy viscosities. Jom J. Miner. Metals Mater. Soc. 2002, 54, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.H.; Hurst, H.J. Ash and slag qualities of Australian bituminous coals for use in slagging gasifiers. Fuel 2000, 79, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Tang, L.H.; Zhu, X.D.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.B.; Koyama, S. Flow properties and rheology of slag from coal gasification. Fuel 2010, 89, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, J.D.; Fereday, F. Flow properties of slags formed from ashes of british coals. 1. Viscosity of homogeneous liquid slags in relation to slag composition. J. Inst. Fuel. 1969, 42, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, H.R.; Roberts, A.G.; Wilkins, D.M. Behaviour of mineral matter in slagging gasification processes. J. Inst. Gas Engrs. 1965, 5, 444–469. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Minowa, S. Viscosity measurements of molten slag - properties of slag at elevated temperature .I. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1969, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Urbain, G. Viscosity estimation of slags. Steel Res. 1987, 58, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Weymann, H.D. On hole theory of viscosity, compressibility, and expansivity of liquids. Kolloid-Zeitschrift Zeitschrift Fur Polym. 1962, 181, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboud, P.V.; Larrecq, M. Lubrication and heat transfer in a continuous casting mold. Steelmak. Proc. 1979, 62, 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kondratiev, A.; Jak, E. Predicting coal ash slag flow characteristics (viscosity model for the Al2O3-CaO-'FeO'-SiO2 system). Fuel 2001, 80, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, A.; Jak, E. Review of experimental data and modeling of the viscosities of fully liquid slags in the Al2O3-CaO-'FeO'-SiO2 system. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2001, 32, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowok, J.W. Viscosity and phase-transformation in coal ash slags near and below the temperature of critical viscosity. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowok, J.W. Viscosity and structural state of iron in coal ash slags under gasification conditions. Energy Fuels 1995, 9, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M. Modelling and simulation of time varying slag flow in a Prenflo entrained-flow gasifier. Fuel 1998, 77, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.T.; Cohen, P. The Flow Characteristics of Coal-Ash Slags in the Solidification Range. J. Eng. Power Trans. ASME 1944, 66, 83–97. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.K. A non-Newtonian flow model for coal-ash slag. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1984, 106, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.J.; Novak, F.; Patterson, J.H. Viscosity measurements and empirical predictions for some model gasifier slags. Fuel 1999, 78, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.J.; Patterson, J.H.; Quintanar, A. Viscosity measurements and empirical predictions for some model gasifier slags—II. Fuel 2000, 79, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Sridhar, S. Viscosities of ironmaking and steelmaking slags. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Sakai, H.; Kita, Y.; Shigeno, K. An equation for accurate prediction of the viscosities of blast furnace type slags from chemical composition. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.G.; Hebbar, K. Viscosity of FeO-SiO2 slags. Miner. Metall. Process. 2001, 18, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bockris, J.O.M.; Reddy, A.K.N. Modern Electrochemistry; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, R.G.; Hebbar, K. Prediction of Viscosities of Binary Silicate Melts EPD Congress 91; Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1991; pp. 523–540. [Google Scholar]
- Urbain, G.; Cambier, F.; Deletter, M.; Anseau, M.R. Viscosity of silicate melts. Trans. J. Br. Ceram. Soc. 1981, 80, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe, R. The viscosity of suspensions of rigid spheres. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 3, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Jahanshahi, S. Viscosity of a CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 melt containing spinel particles at 1646 K. Metall. Mater.Trans. B 2000, 31, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudersbach, D.; Drissen, P.M.; Kuhn, M.; Geiseler, J. Viscosity of slags. Steel Res. 2001, 72, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, P.; Reid, W.T. Viscosity of coal ash slags. Trans. ASME 1940, 62, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, S.; Kimura, Y. Viscosity measurement of slag formed in the carbon-bearing iron oxide during the rapid heating. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, M.; Lee, J.; Tanaka, T. A model for estimation of viscosity of molten silicate slag. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, B.J.P.; Browning, G.J.; Gupta, R.P.; Wall, T.F. Measurement of the viscosity of coal-derived slag using thermomechanical analysis. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.H.; Jung, S.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, D.J. Viscosity of highly basic slags. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalicka, Z.; Kawecka-Cebula, E.; Pytel, K. Application of the lida model for estimation of slag viscosity for Al2O3-Cr2O3-CaO-CaF2 systems. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2009, 54, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- van Dyk, J.C.; Benson, S.A.; Laumb, M.L.; Waanders, B. Coal and coal ash characteristics to understand mineral transformations and slag formation. Fuel 2009, 88, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar]
- van Dyk, J.C.; Waanders, F.B.; Benson, S.A.; Laumb, M.L.; Hack, K. Viscosity predictions of the slag composition of gasified coal, utilizing FactSage equilibrium modelling. Fuel 2009, 88, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, H.; Murakami, K.; Miyashita, Y. Mechanical properties of continuously cast steels at high temperatures. Tetsu-to-Hagane (Iron Steel) 1977, 63, 652. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, B.G. Issues in thermal-mechanical modeling of casting processes. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G. Modeling of the continuous casting of steel-past, present, and future. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process Sci. 2002, 33, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.A.; Thomas, B.G. Heat-transfer and solidification model of continuous slab casting: CON1D. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process Sci. 2003, 34, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.A.; Thomas, B.G. Modeling transient slag-layer phenomena in the shell/mold gap in continuous casting of steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process Sci. 2003, 34, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Truesdell, C. Introduction to Rational Elasticity; Noordhoff International Publishing: Leyden, The Netherlands, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, E.C. Fluidity and Plasticity; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1922. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, W. Introduction to Mechanics of Continua; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Casson, N. A Flow Equation for Pigment-Oil Suspensions of the Printing Ink Type. In Rheology of Disperse Systems; Mill, C.C., Ed.; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Oldroyd, J.G. An approach to non-newtonian fluid-mechanics. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1984, 14, 9–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, G.G.; Denn, M.M. Flow of bingham fluids in complex geometries. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1984, 14, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, R.I. Engineering Rheology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Massoudi, M.; Mehrabadi, M.M. A continuum model for granular materials: considering dilatancy and the Mohr-Coulomb criterion. Acta Mech. 2001, 152, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K.; Green, J.T. Determination of bulk stress in a suspension of spherical-particles to order C-2. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 56, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H.C. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. A mechanism for non-newtonian flow in suspensions of rigid spheres. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.E. Generalized equation for elastic moduli of composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 4626–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M. The viscosity of a concentrated suspension of spherical particles. J. Colloid Sci. 1951, 6, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Kwon, T.M.; Jhon, M.S. Effects of shear rate and particle concentration on rheological properties of magnetic particle suspensions. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.M.; Jhon, M.S.; Choi, H.J. Viscosity of magnetic particle suspension. J. Mol. Liq. 1998, 75, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, R.S.; Ericksen, J.L. Stress-deformation relations for isotropic materials. J. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1955, 4, 323–425. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.E.; Fosdick, R.L. Thermodynamics, stability, and boundedness of fluids of complexity-2 and fluids of second grade. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1974, 56, 191–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.S. Nonsteady channel flow of ice as a modified 2nd-order fluid with power-law viscosity. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1992, 119, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoudi, M.; Vaidya, A. On some generalizations of the second grade fluid model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2008, 9, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.B.; Armstrong, R.C.; Hassager, J. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Macosko, C.W. Rheology: Principles, Measurements and Applications; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.; Massoudi, M. Flow of a generalized 2nd-grade fluid between heated plates. Acta Mech. 1993, 99, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeri, A.Z. Fluid Film Lubricatio; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Franta, M.; Malek, J.; Rajagopal, K.R. Oil steady flows of fluids with pressure- and shear-dependent viscosities. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Engi. Sci. 2005, 461, 651–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hron, J.; Malek, J.; Rajagopal, K.R. Simple flows of fluids with pressure-dependent viscosities. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Engi. Sci. 2001, 457, 1603–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.W. The dynamics of lava flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000, 32, 477–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.Y.; Novack, M.; Roffe, G. Rheological and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Flowing Coal-Water Mixtures; General Applied Science Laboratory: Ronkonkoma, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Renner, J.; Evans, B.; Hirth, G. On the theologically critical melt fraction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 181, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, R. Suspensions. In Flow Properties of Disperse Systems; Hermans, J.J., Ed.; North Holland: New York, NY, USA, 1953; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Massoudi, M.; Phuoc, T.X. Flow of a generalized second grade non-Newtonian fluid with variable viscosity. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2004, 16, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; White, L.; Sridhar, S. Modeling inclusion approach to the steel/slag interface. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2008, 495, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.N.; Rozelle, P.L.; Pisupati, S.V.; Sridhar, S. Conditions for entrainment into a FeOx containing slag for a carbon-containing particle in an entrained coal gasifier. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanao, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kawamoto, M.; Takatani, K. Evaluation of Surface Tension of Molten Slag in Multi-Component Systems. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, J.; Sridhar, S.; Bennett, J.; Kwong, K.S.; Moss, T. Interactions of refractory materials with molten gasifier slags. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 4595–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soll-Morris, H.; Sawyer, C.; Zhang, Z.T.; Shannon, G.N.; Nakano, J.; Sridhar, S. The interaction of spherical Al2O3 particles with molten Al2O3-CaO-FeOx-SiO2 slags. Fuel 2009, 88, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Massoudi, M.; Wang, P. Slag Behavior in Gasifiers. Part II: Constitutive Modeling of Slag. Energies 2013, 6, 807-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6020807
Massoudi M, Wang P. Slag Behavior in Gasifiers. Part II: Constitutive Modeling of Slag. Energies. 2013; 6(2):807-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6020807
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassoudi, Mehrdad, and Ping Wang. 2013. "Slag Behavior in Gasifiers. Part II: Constitutive Modeling of Slag" Energies 6, no. 2: 807-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6020807
APA StyleMassoudi, M., & Wang, P. (2013). Slag Behavior in Gasifiers. Part II: Constitutive Modeling of Slag. Energies, 6(2), 807-838. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6020807





