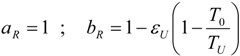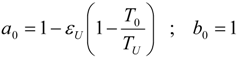Energy and Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Combined Heat and Power Systems. Comparison of Various Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
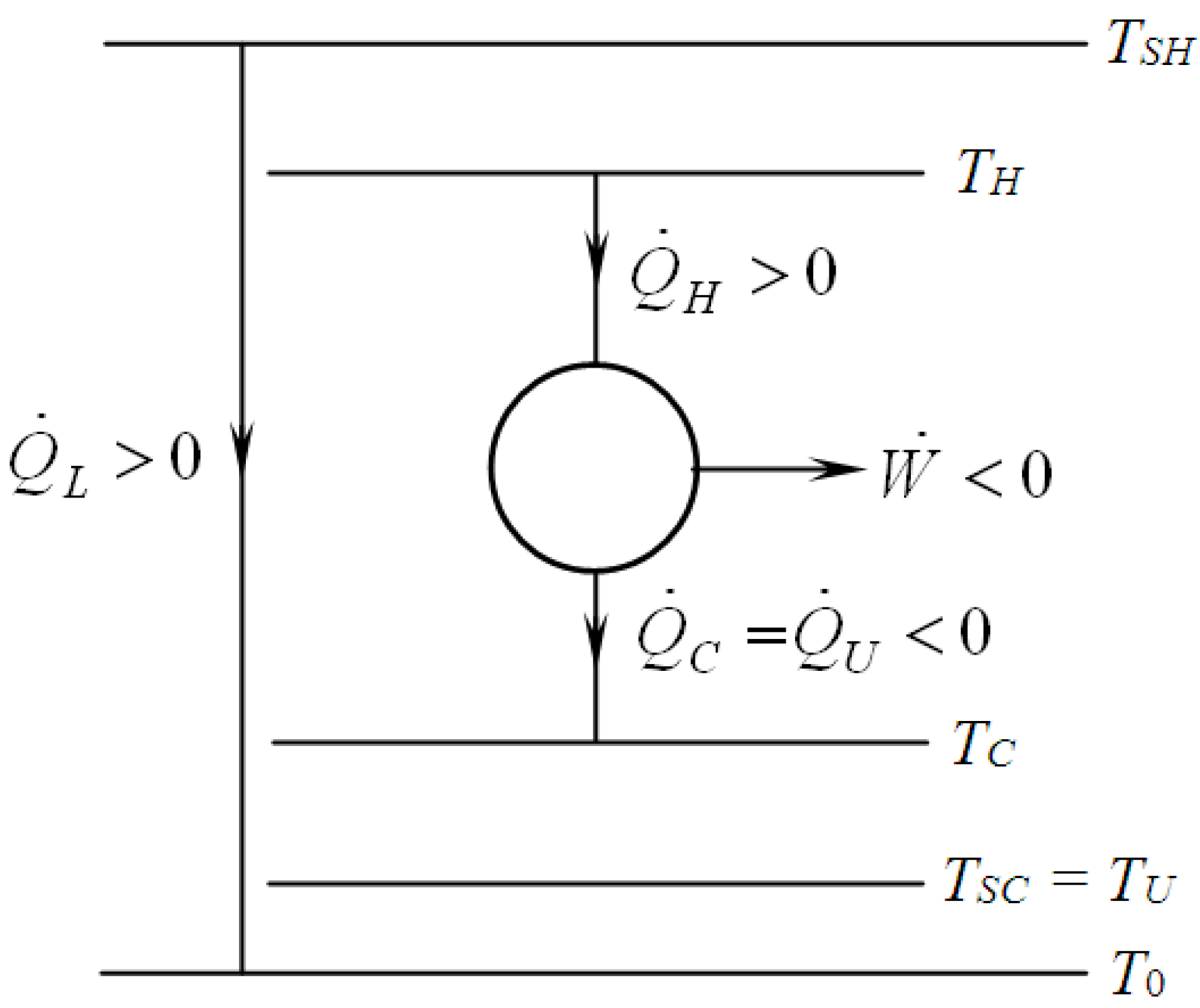
2. Modelling of Various CHP Systems
3. Criteria and Optimizations
3.1. First Law Efficiency Criterion, ηICHP
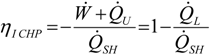
3.2. Exergetic Criterion
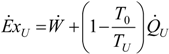
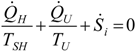
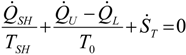
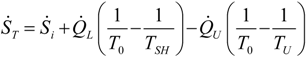
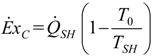
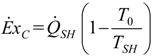 . The same methodology will be applied to ICE hereafter.
. The same methodology will be applied to ICE hereafter.3.3. General Optimization Procedure
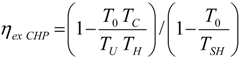
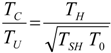
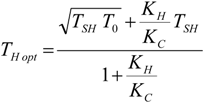
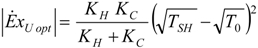
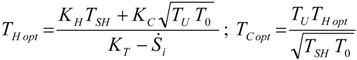
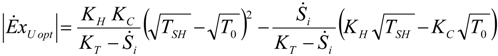
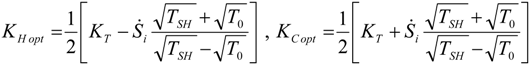
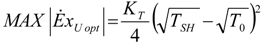
4. Optimization with Constraints
4.1. Carnot CHP System with R Imposed
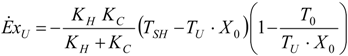
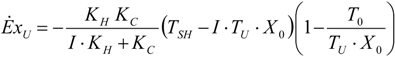
4.2. Carnot CHP System with Imposed
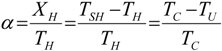
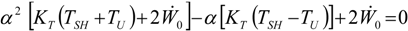
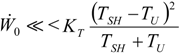 , an interesting limit appears:
, an interesting limit appears:
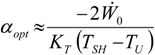
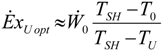
4.3. Useful Heat Transfer Rate Imposed
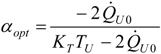
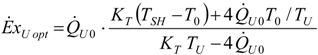
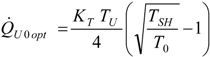
4.4. Heat Transfer Rate at the Source Imposed
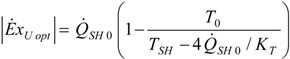
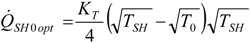
4.5. Partial Conclusion
5. Discussion—Comparisons
5.1. Thermodynamic Optimization of Carnot CHP Systems
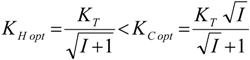
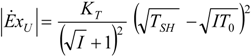
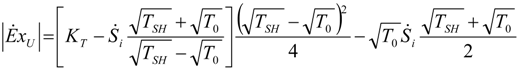
| optimum | TH opt | TC opt | ||
| Added constraint | ||||
| without | 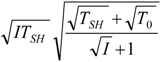 | 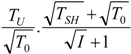 |  | |
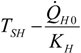 | 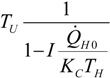 | 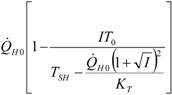 | ||
| R = R0 | 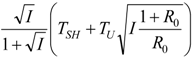 | 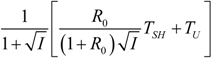 | 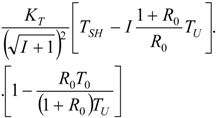 | |
| * | 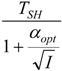 | 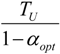 |  | |
| * | 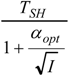 | 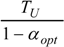 | 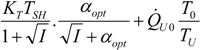 | |
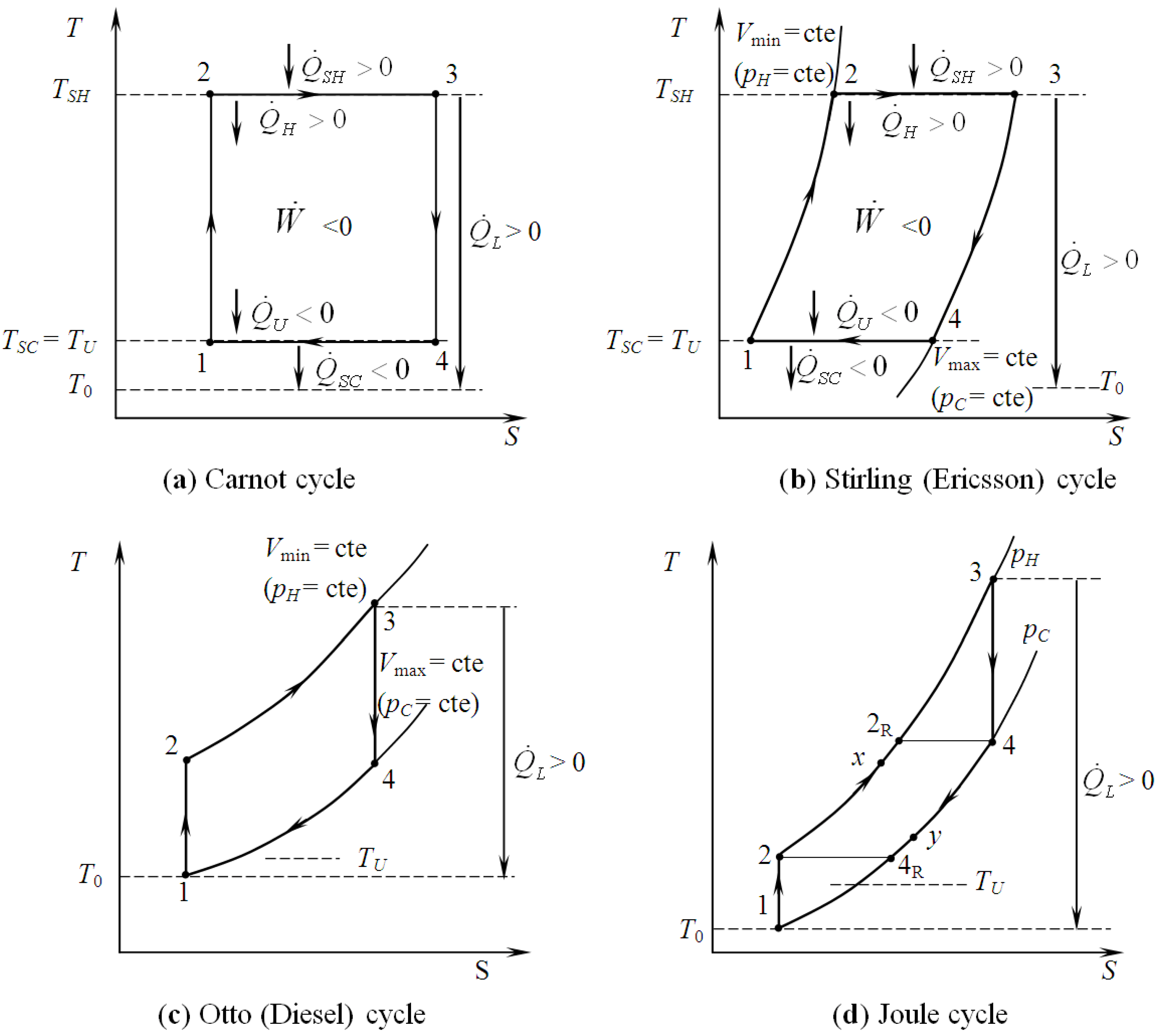
5.2. Optimization of Other CHP Configurations
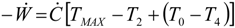
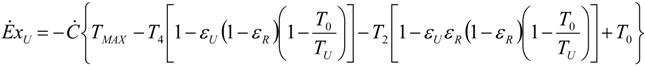
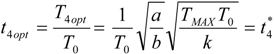
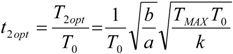
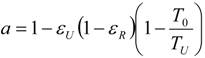
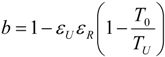
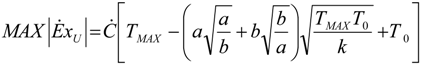
- perfect heat recuperation given by εR = 1. It involves:
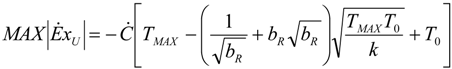
- perfect useful heat HEX provided by εU = 1. It involves:
- perfect heat exchangers: εR = 1 and εU = 1. It involves:
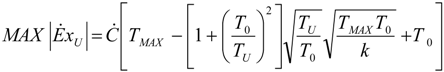
- no heat recuperation: εR = 0. For this case:
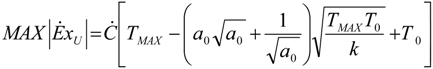
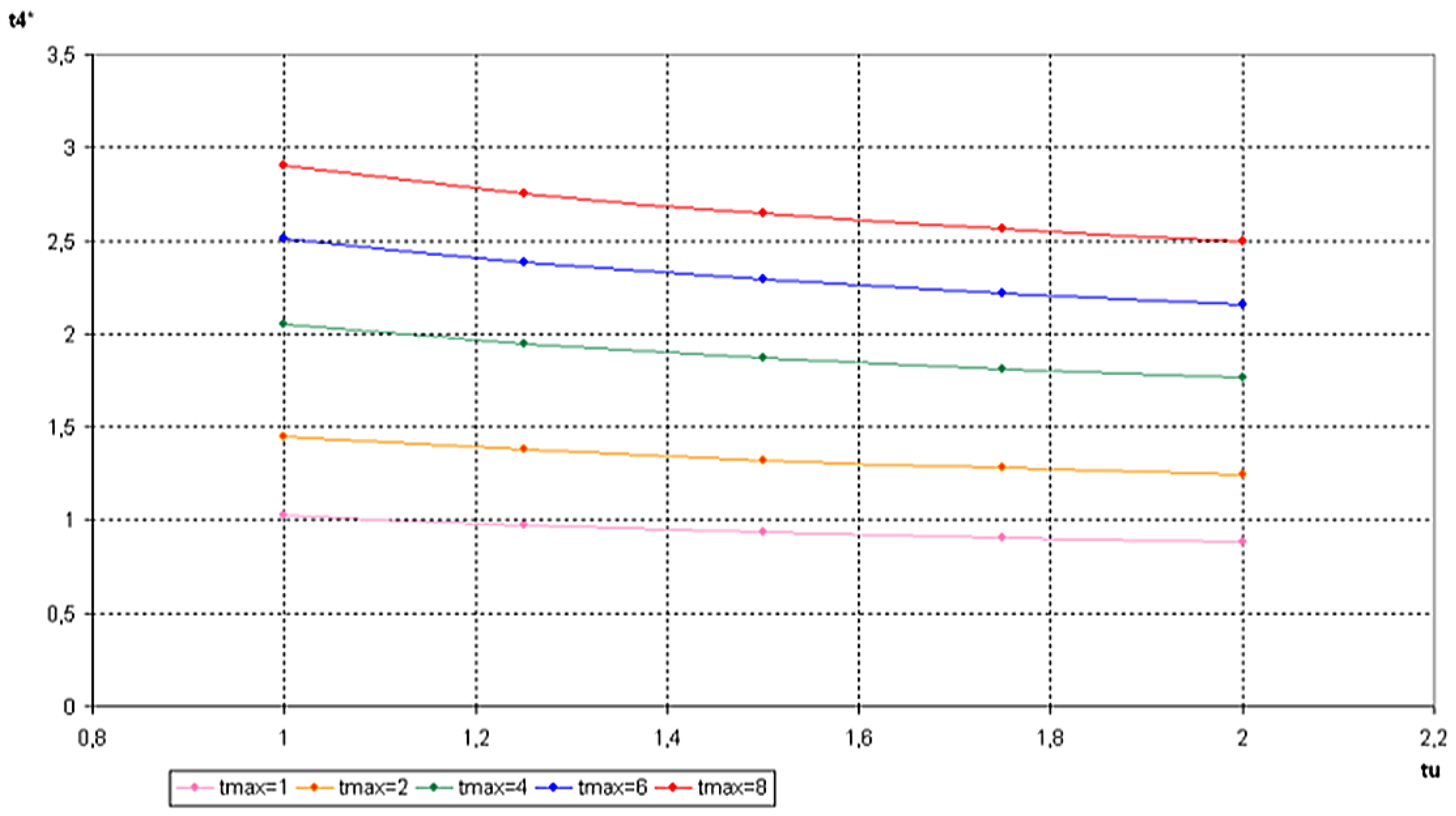
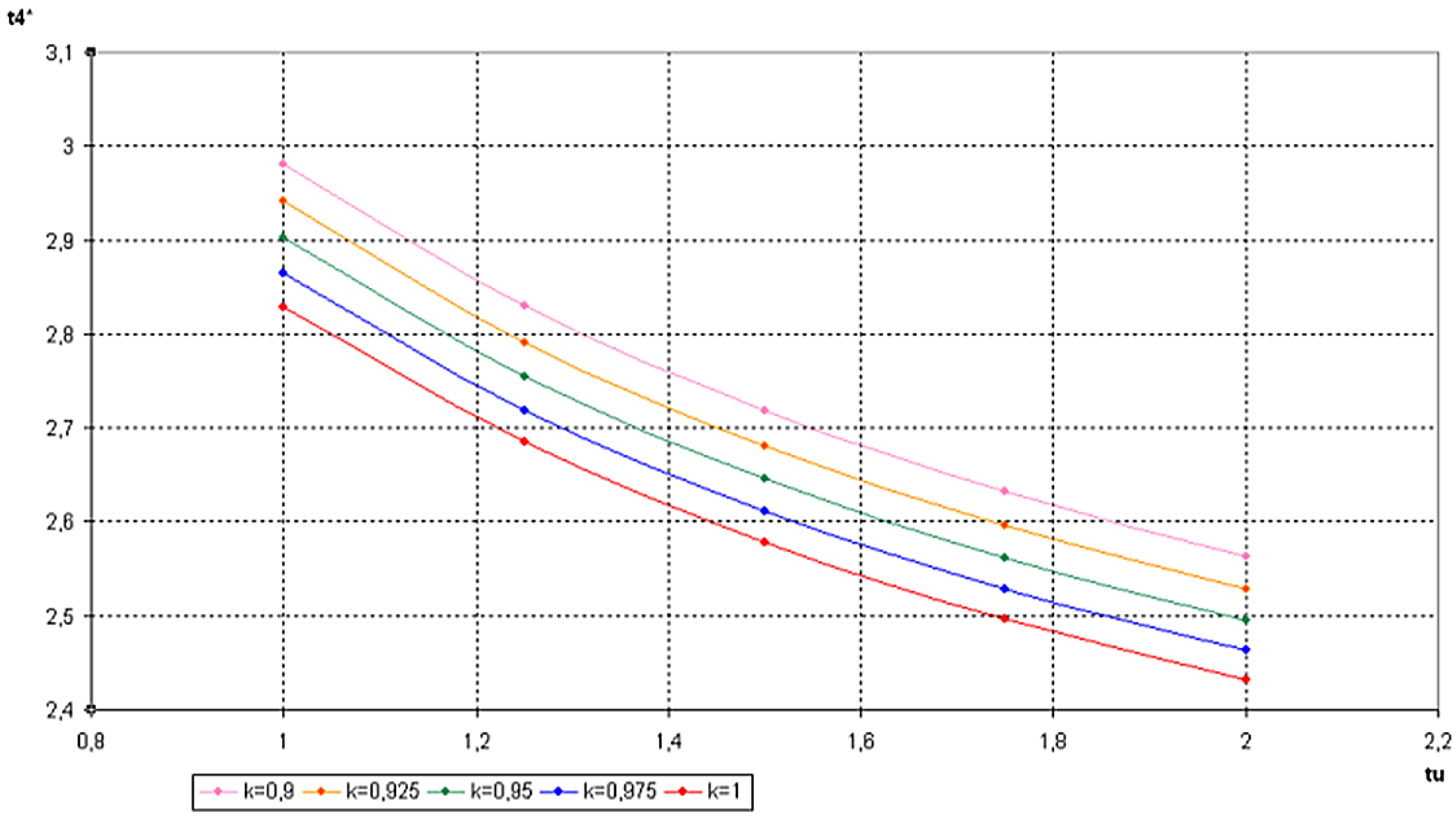
6. Conclusions
- -
- ECE, External Combustion Engine;
- -
- ICE, Internal Combustion Engine;
Nomenclature
heat capacity rate [W K−1]; | |
| cp | mass specific heat at constant pressure [W kg−1 K−1]; |
exergy rate [W]; | |
mass flow rate of the
working gas in the cycle [kg s−1]; | |
| I | irreversibility ratio; |
| K | heat transfer conductance [W K−1]; |
| NTU | number of heat transfer units; |
heat transfer rate
[W]; | |
| R | ratio of useful heat transfer rate to useful power; |
entropy rate [W K−1]; | |
| T | temperature [K]; |
| t | no dimensional temperature; |
| X | temperature difference [K]; |
mechanical power [W]; |
Greek symbols
heat exchanger
effectiveness; | |
efficiency; | |
intermediate variable; |
Subscripts and superscripts
| C | related to the working fluid, at the sink; |
| c | consumed or Carnot; |
| CHP | combined heat and power system; |
| ECE | external combustion engine; |
| ex | exergetic; |
| GT | gas turbine; |
| H | related to the working fluid, at the source; |
| i | internal; |
| ICE | internal combustion engine; |
| L | loss; |
| PV/T | photovoltaic/thermal system; |
| R | recuperator; |
| SH | source; |
| SC | sink; |
| T | total; |
| U | useful; |
| I | related to first law; |
| 0 | ambient or imposed value; |
| * | optimal |
Appendix
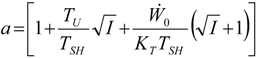
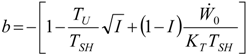
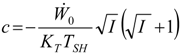
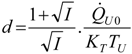
References
- Wakui, T.; Yokoyama, R. Optimal sizing of residential gas engine cogeneration system for power interchange operation from energy-saving viewpoint. Energy 2011, 36, 3816–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, M. Combined Electricity and Heat Production Systems with PEMFC or SOFC Fuel Cells and External Vapor Reforming. Ph.D. Thesis, Nancy University, Nancy, France, September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Milia, D.; Sciubba, E. Exergy-based lumped simulation of complex systems: An interactive analysis tool. Energy 2006, 31, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descieux, D. Modelling and Exergetic Comparison of Cogeneration Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Nancy University, Nancy, France, November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pehnt, M. Environmental impacts of distributed energy systems—The case of micro cogeneration. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusoglu, A.; Kanoglu, M. First and second law analysis of diesel engine powered cogeneration systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Dai, Y.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, R.Z. Energy and exergy analyses on a novel hybrid solar heating, cooling and power generation system for remote areas. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusoglu, A.; Kanoglu, M. Exergoeconomic analysis and optimization of combined heat and power production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussant, C.D.; Fung, A.S.; Ugursal, V.I.; Taherian, H. Residential application of internal combustion engine based cogeneration in cold climate—Canada. Energy Build. 2009, 41, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, J.; Dincer, I. Comparative exergy analyses of gasoline and hydrogen fuelled ICEs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 5124–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, R.S.; Dincer, I. Energy and exergy analyses of a combined molten carbonate fuel cell—Gas turbine system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8927–8935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, E.; Kılkış, B.; Eralp, C. Exergy based performance analysis of high efficiency poly-generation systems for sustainable building applications. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doluweera, G.H.; Jordaan, S.M.; Moore, M.C.; Keith, D.W.; Bergerson, J.A. Evaluating the role of cogeneration for carbon management in Alberta. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7963–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, L.; Bidini, G.; Gallorini, F.; Ottaviano, A. An energetic–Exergetic comparison between PEMFC and SOFC-based micro-CHP systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Liu, K.; Chow, T.T.; Pei, G.; He, H. Thermal Analysis of PV/T Evaporator of A Solar Assisted Heat Pump. Int. J. Energy Res. 2007, 31, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilak Raj, N.; Iniyan, S.; Goic, R. A review of renewable energy based cogeneration technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Othman, M.Y.; Ruslan, M.H.; Mat, S.; Sopian, K. Recent advances in flat plate photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) solar collectors. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Carlsen, H.; Biedermann, F. State of the Art and Future Developments Regarding Small Scale Biomass CHP Systems with a Special Focus on ORC and Stirling Engine Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Nordic Bioenergy Conference, Jyväskylä, Finland, 2–5 September 2003.
- Uddin, S.N.; Barreto, L. Biomass-fired cogeneration systems with CO2 capture and storage. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Brandon, N. A new analytical approach to evaluate and optimize the performance of an irreversible solid oxide fuel cell-gas turbine hybrid system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15304–15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillecard, C.; Hubert, C.E.; Contreau, R.; Mazzenga, A.; Stabat, P.; Adnot, J. Small scale impact of gas technologies on electric load management—μCHP & hybrid heat pump. Energy 2011, 36, 2912–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R. Combined heat and power considered as a virtual steam cycle heat pump. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 5528–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.F. Weighting Methodologies in Multicriteria Evaluations of CHP Systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 33, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.J.; Yang, W.M.; Wong, T.Z.; Ho, C.A. Integrating renewable energy technologies to support building trigeneration—A multi-criteria analysis. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Maya, C.; Uche-Marcuello, J.; Martínez-Gracia, A.; Bayod-Rújula, A.A. Design optimization of a polygeneration plant fuelled by natural gas and renewable energy sources. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, C. Les techniques de cogénération. In Techniques de l’Ingénieur, Traité de Génie Energétique; Editions TI: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Feidt, M. L’Integration des Systèmes Energétiques. In Energétique; Dunod: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 889–909. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A. Recent Advances in Finite Time Thermodynamics; Wu, C., Chen, L., Chen, J., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Feidt, M. Optimal Thermodynamics—New Upper Bounds. Entropy 2009, 11, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidt, M.; Lang, S. Conception optimale de systèmes combinés à génération de puissance, chaleur et froid. Entropie 2002, 242, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chambadal, P. Les Centrales Nucléaires; Armand Colin: Paris, France, 1957; pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, I.I. The Efficiency of Atomic Power Stations. J. Nucl. Energy 1958, 7, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Feidt, M.; Costea, M.; Petre, C.; Petrescu, S. Optimization of Direct Carnot Cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samba, A. Microcogeneration: Thermodynamic Optimization and Adaptability to Different Fuels. M.Sc. Thesis, Ecole des Mines, Nancy, France, February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Feidt, M.; Costea, M.; Postelnicu, V. Comparison between the Brayton Cycle with Imposed Thermal Input and Maximal Temperature Constraint. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. 2006, 61, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, M.; Feidt, M.; Alexandru, G.; Descieux, D. Optimization of Gas Turbine Cogeneration System for Various Heat Exchanger Configurations. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. 2012, 67, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirca-Dragomirescu, G.; Costea, M.; Feidt, M.; McGovern, J.; Dobrovicescu, A.; Tutica, D.; Kheiri, A. Modelling and Optimization of Heat Exchangers within Gas Turbine Systems. In Proceedings of Engineering Systems Design and Analysis Conference (ESDA 2012), Nantes, France, 2–4 July 2012.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Feidt, M.; Costea, M. Energy and Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Combined Heat and Power Systems. Comparison of Various Systems. Energies 2012, 5, 3701-3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5093701
Feidt M, Costea M. Energy and Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Combined Heat and Power Systems. Comparison of Various Systems. Energies. 2012; 5(9):3701-3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5093701
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeidt, Michel, and Monica Costea. 2012. "Energy and Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Combined Heat and Power Systems. Comparison of Various Systems" Energies 5, no. 9: 3701-3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5093701
APA StyleFeidt, M., & Costea, M. (2012). Energy and Exergy Analysis and Optimization of Combined Heat and Power Systems. Comparison of Various Systems. Energies, 5(9), 3701-3722. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5093701