Dual-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Wind-Integrated Microgrids Based on Carbon Emission Flow
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Carbon Emission Flow Theory Research
2.1. Basic Concepts of Carbon Emission Flow in Power Systems
2.2. Carbon Flow Density and Its Relationship with Power Flow
2.3. Node Carbon Potential
3. Generator Carbon Emission Calculation Model
4. Problem Formulation
4.1. Optimization Model
4.1.1. Objective Function
4.1.2. Detailed Cost Component Modeling
4.1.3. Carbon Emission Cost Model
4.1.4. Demand Response Cost Model
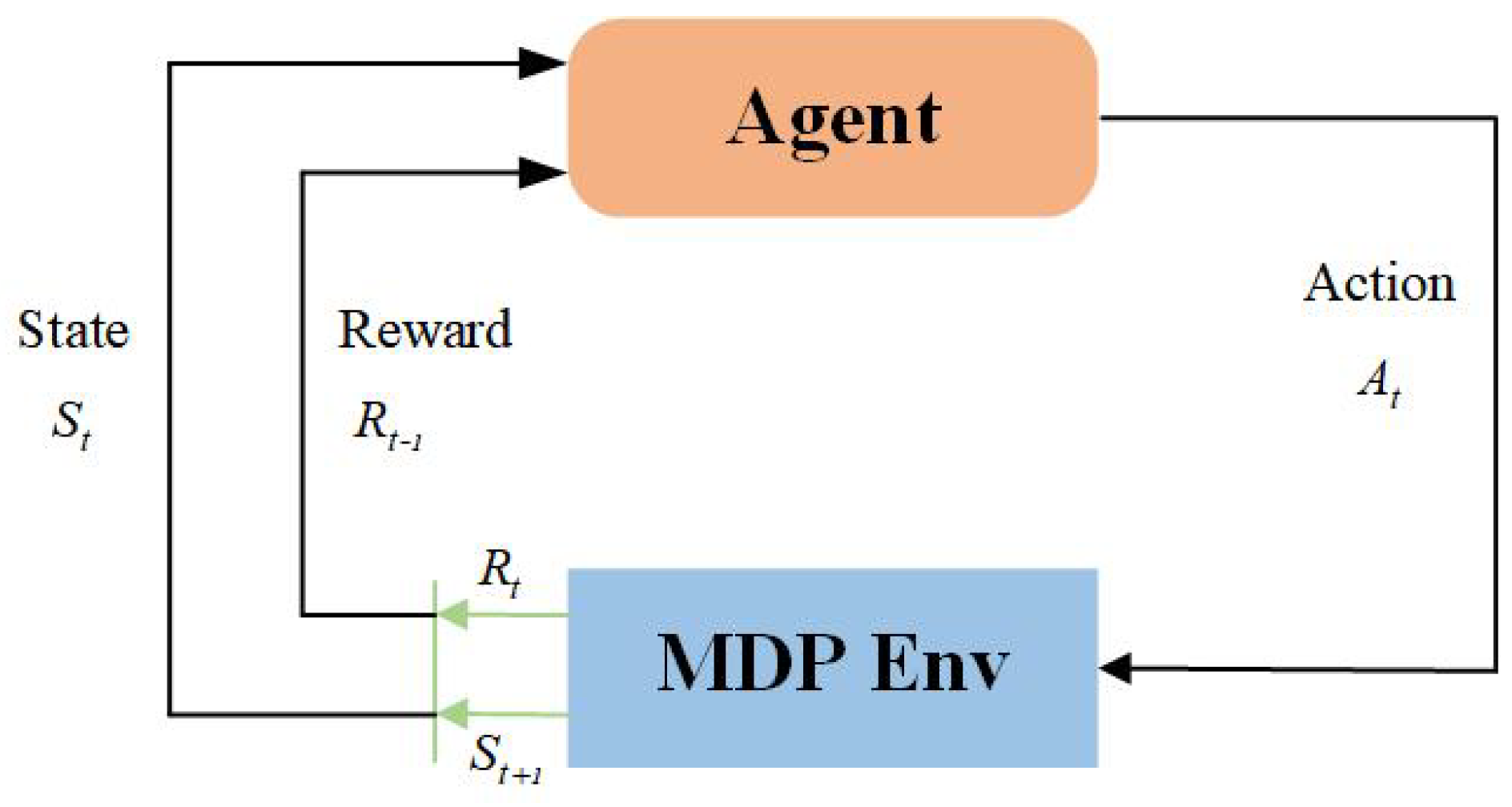
4.2. Markov Decision Process Modeling
4.2.1. State Space Definition
4.2.2. Action Space Design
4.2.3. Reward Function Design
4.3. System Operational Constraints
4.3.1. Power Balance Constraint
4.3.2. Generator Operational Constraints
4.3.3. Demand Response Constraints
4.3.4. Network Security Constraints
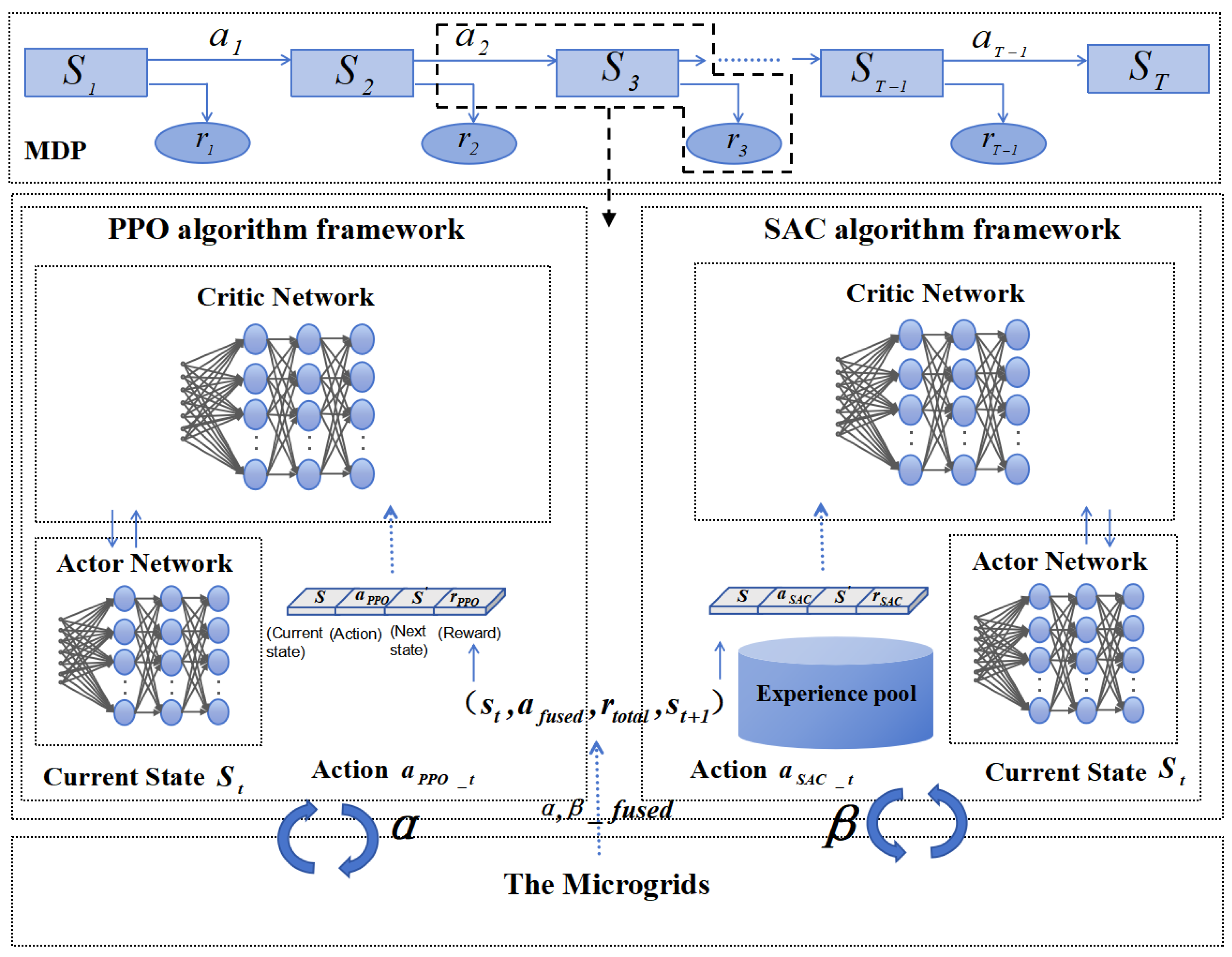
5. Solving Low-Carbon Dispatch Model Based on Dual-Agent
5.1. PPO for Economic Dispatch
5.2. SAC for Low-Carbon Dispatch
5.3. Dual-Agent Coordination and Action Fusion Strategy
6. Simulation Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). World Energy Transitions Outlook 2024: 1.5 °C Pathway; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2024; Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications (accessed on 10 December 2025).
- Arévalo, P.; Ochoa-Correa, D.; Villa-Ávila, E. Optimizing Microgrid Operation: Integration of Emerging Technologies and Artificial Intelligence for Energy Efficiency. Electronics 2024, 13, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhu, R.; Kong, D.; Guo, H. Considering the tiered low-carbon optimal dispatching of multi-integrated energy microgrid with P2G-CCS. Energies 2024, 17, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, C.; Mo, C. Low-carbon economic dispatch strategy for integrated power system based on the substitution effect of carbon tax and carbon trading. Energy 2024, 294, 130960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Ding, Y.; He, J.; Han, J. The carbon reduction effects of stepped carbon emissions trading and hybrid renewable energy systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 2184–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Han, H. Low-carbon dispatch of multi-regional integrated energy systems considering integrated demand side response. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1361306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi Tabar, V.; Abbasi, V. Energy management in microgrid with considering high penetration of renewable resources and surplus power generation problem. Energy 2019, 189, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Cui, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xiao, W. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Microgrid Energy Transmission Dispatching. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Shi, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, X.; Tang, Z.; Jia, H.; Geng, H. Multi-objective interval optimization dispatch of microgrid via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, T.M.; Lawrence, N.P.; Lu, L.; Yang, Z.; Gopaluni, R.B. Automated deep reinforcement learning for real-time scheduling strategy of multi-energy system integrated with post-carbon and direct-air carbon capture systems. Appl. Energy 2023, 333, 120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, P.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Yun, J.; Zhang, C. A control strategy based on deep reinforcement learning under the combined wind-solar storage system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 6547–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Wang, Y.; Dang, Z.; Xiang, T.; Gan, Z.; Yang, T. Low-carbon dispatch method for active distribution network based on carbon emission flow theory. Energies 2024, 17, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hu, W.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Deep reinforcement learning based approach for optimal power flow of distribution networks embedded with renewable energy and storage devices. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Nakanishi, Y. Low-carbon economic dispatch considering integrated demand response and multistep carbon trading for multi-energy microgrid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; He, X.T.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J. Low-carbon optimal learning scheduling of the power system based on carbon capture system and carbon emission flow theory. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 218, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, W.; Xie, J.; Xie, D.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Yang, C. Low-Carbon Dispatch Method Considering Node Carbon Emission Controlling Based on Carbon Emission Flow Theory. Energies 2025, 18, 5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.Y. Real-time emission and cost estimation based on unit-level dynamic carbon emission factor. Energy Convers. Econ. 2023, 4, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Mao, Z.Z. Microgrid economic dispatch using information-enhanced deep reinforcement learning with consideration of control periods. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 239, 111244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, C.L.P.; Wang, X. Proximal policy optimization with policy feedback. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 52, 4600–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, W. Soft Actor-Critic-based grid dispatching with distributed training. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Mobile Internet, Cloud Computing and Information Security (MICCIS), Nanjing, China, 24–26 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; Zhang, R.F.; Jiang, T.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; Cui, H.; Li, X. Optimal dispatch strategy for integrated energy systems with CCHP and wind power. Appl. Energy 2017, 192, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Lever, G.; Heess, N.; Degris, T.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 387–395. [Google Scholar]
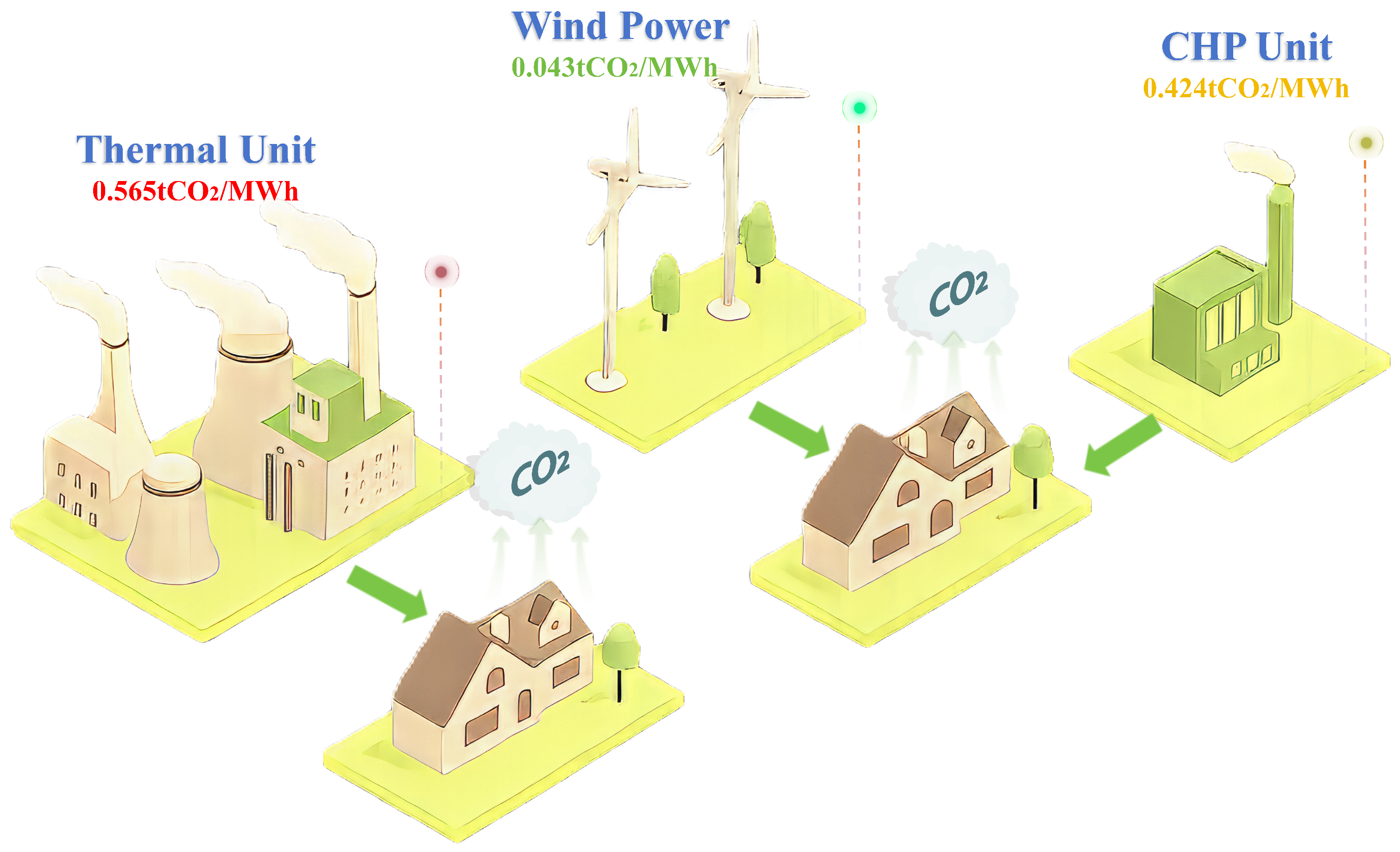
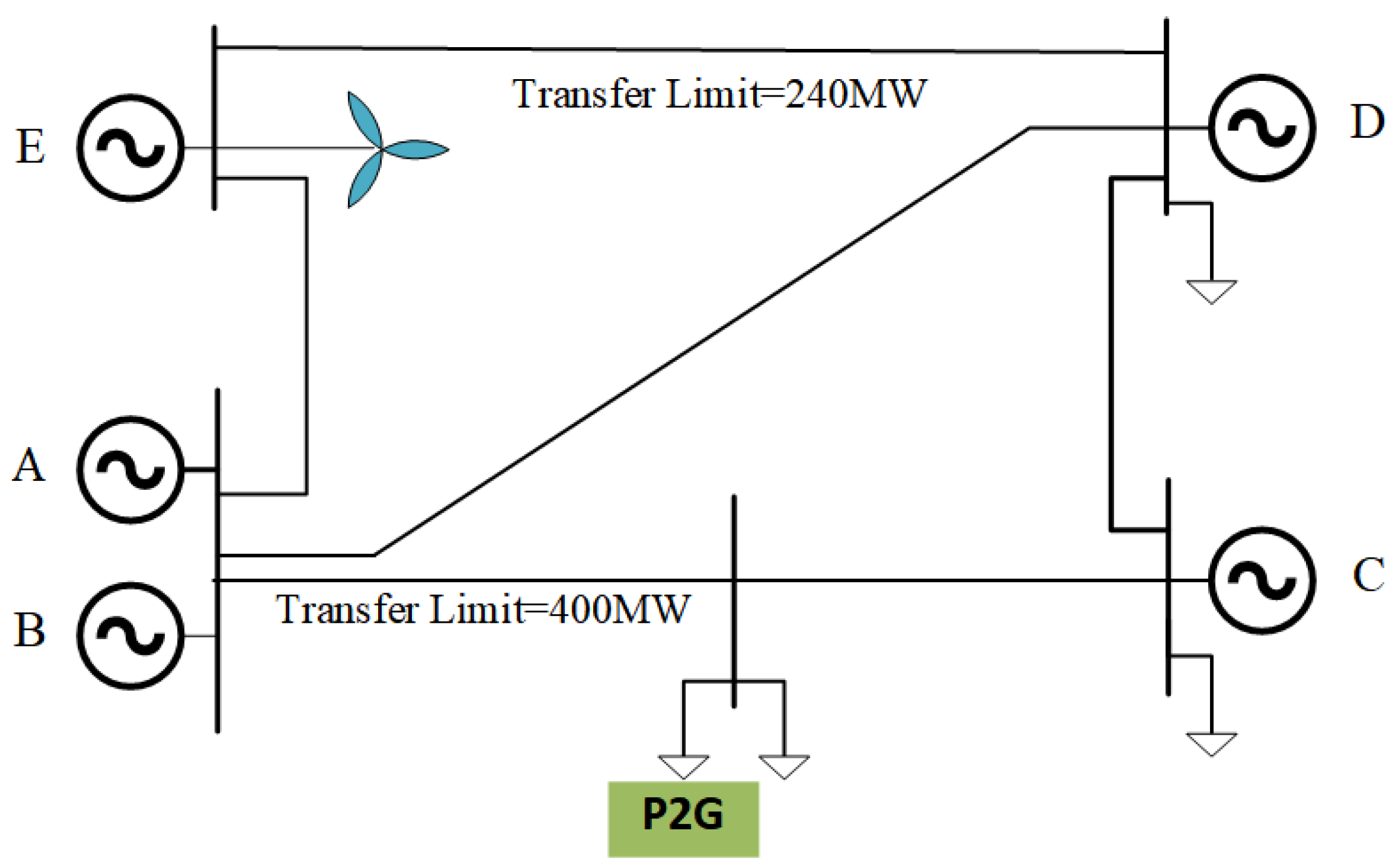
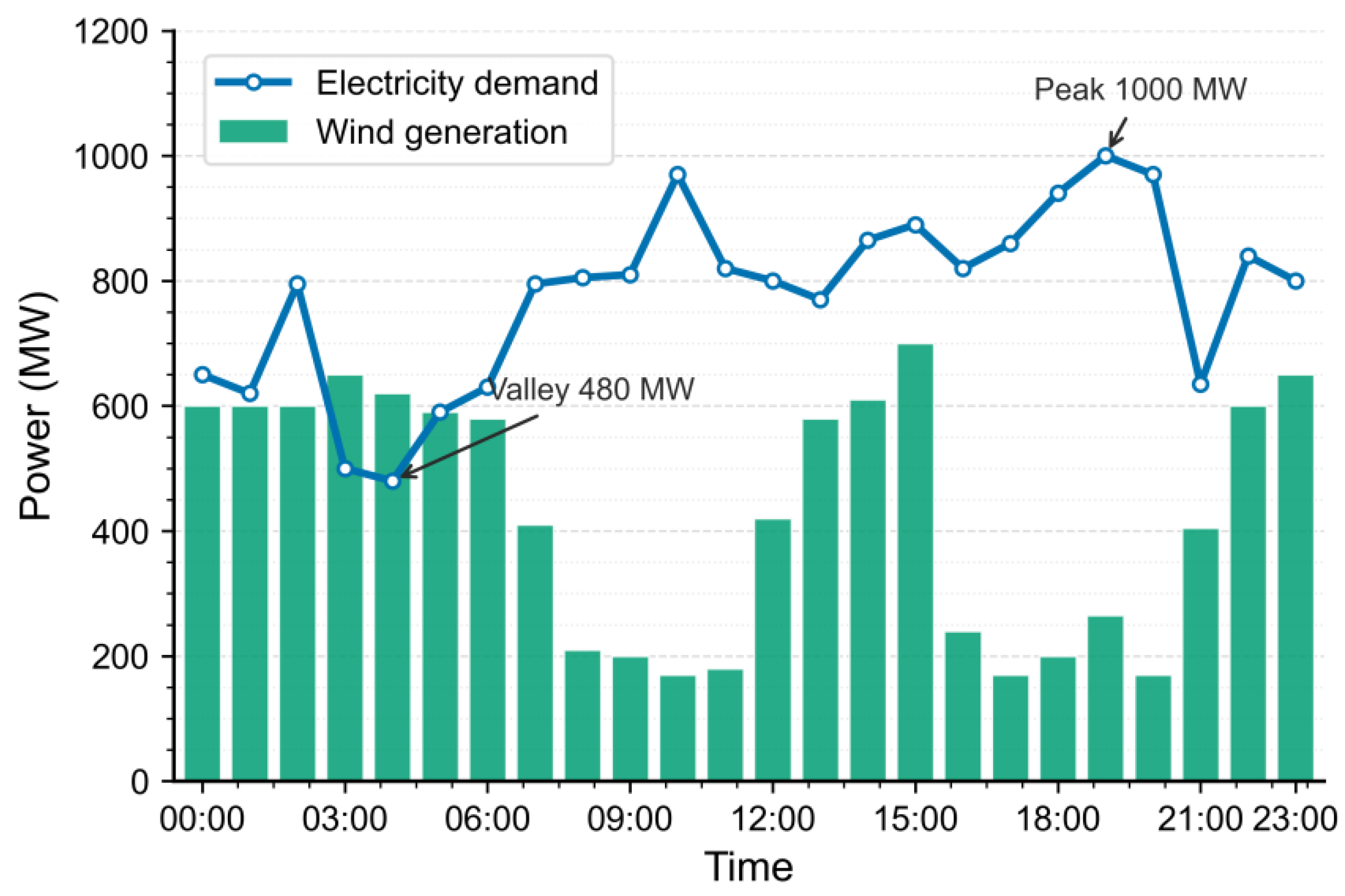
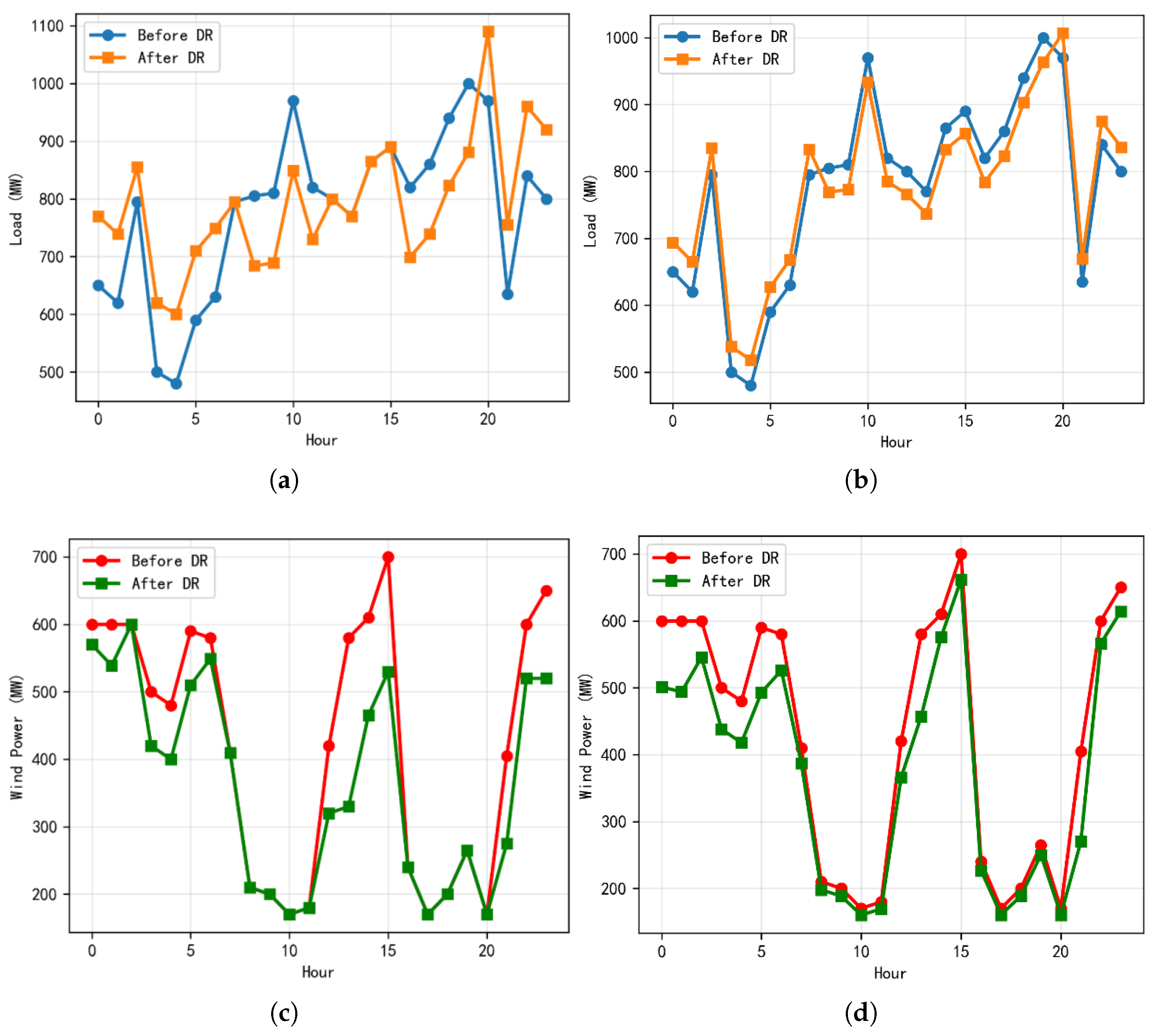
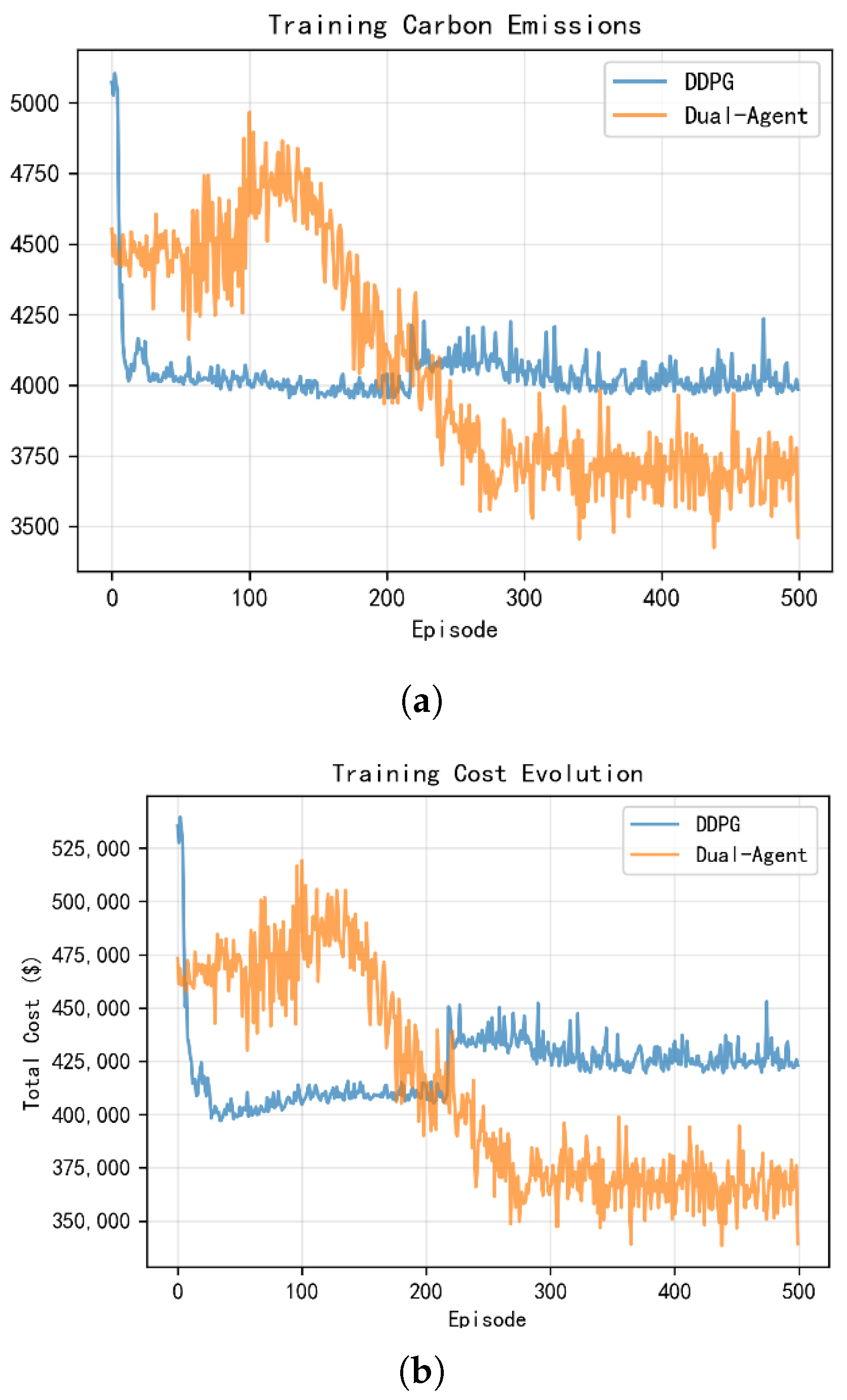
| Bus | Unit Type | Max Output (MW) | Bid Price ($/MWh) | Carbon Emission Factor (t/MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Thermal Unit | 110 | 14 | 0.565 |
| B | Thermal Unit | 100 | 15 | 0.565 |
| C | CHP Unit | 520 | 30 | 0.424 |
| D | CHP Unit | 200 | 35 | 0.424 |
| E | Wind Power | 700 | 10 | 0.043 |
| Parameter | DDPG | Dual-Agent (PPO + SAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Replay Buffer Capacity | 50,000 | 50,000 |
| Discount Factor | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Batch Size | 64 | PPO: 64/SAC: 256 |
| Training Episodes | 1000 | 1000 |
| Soft Update Factor | 0.0001 | 0.005 |
| Actor Learning Rate | 0.0002 | PPO: 0.0002/SAC: 0.0002 |
| Critic Learning Rate | 0.0002 | PPO: 0.0002/SAC: 0.0002 |
| Metric | DDPG (Baseline) | Dual-Agent (PPO + SAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost ($) | 422,867 | 351,894 |
| Carbon (t) | 3978.0 | 3526.9 |
| Curtailment (MWh) | 1657.0 | 1403.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Qiu, W.; Ruan, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Z. Dual-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Wind-Integrated Microgrids Based on Carbon Emission Flow. Energies 2026, 19, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19020551
Qiu W, Ruan H, Yu X, Li Y, Liu Y, He Z. Dual-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Wind-Integrated Microgrids Based on Carbon Emission Flow. Energies. 2026; 19(2):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19020551
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Wenjun, Hebin Ruan, Xiaoxiao Yu, Yuhang Li, Yicheng Liu, and Zhiyi He. 2026. "Dual-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Wind-Integrated Microgrids Based on Carbon Emission Flow" Energies 19, no. 2: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19020551
APA StyleQiu, W., Ruan, H., Yu, X., Li, Y., Liu, Y., & He, Z. (2026). Dual-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Wind-Integrated Microgrids Based on Carbon Emission Flow. Energies, 19(2), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19020551





