Application of Side-Stream Bio-Electrochemical Module to Quickly Reactivate Process Performances in Deteriorated Bench-Scale Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Configuration of Reactors and Equipment
2.2. Inoculum and Substrate
2.3. Sequencing Batch Reactor Operation
2.4. Analysis Methods
2.5. Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
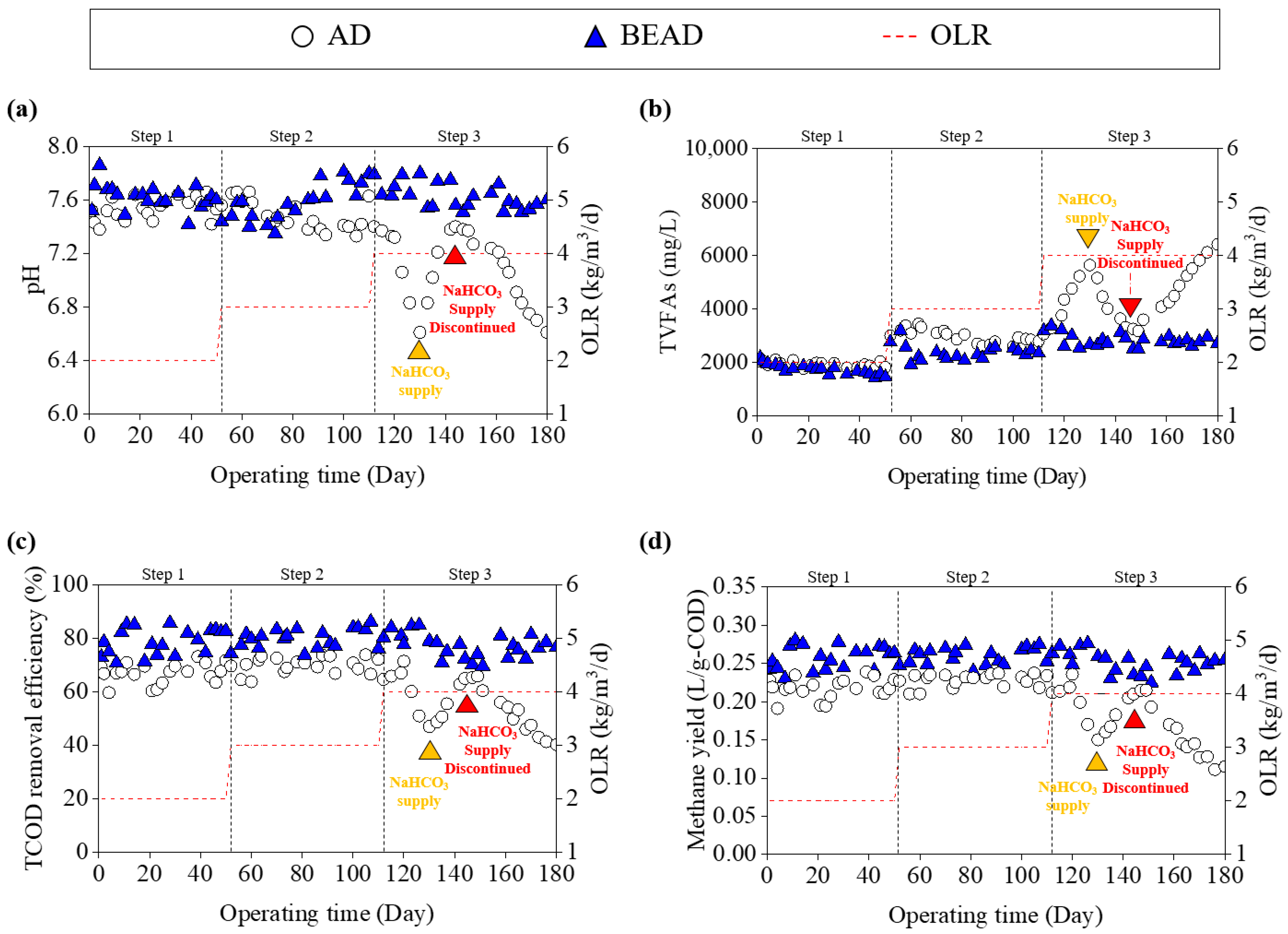
3.1. Performance Comparison Between AD and BEAD Under Moderate OLRs
3.2. Evaluation of AD Performance Recovery via a Side-Stream Module
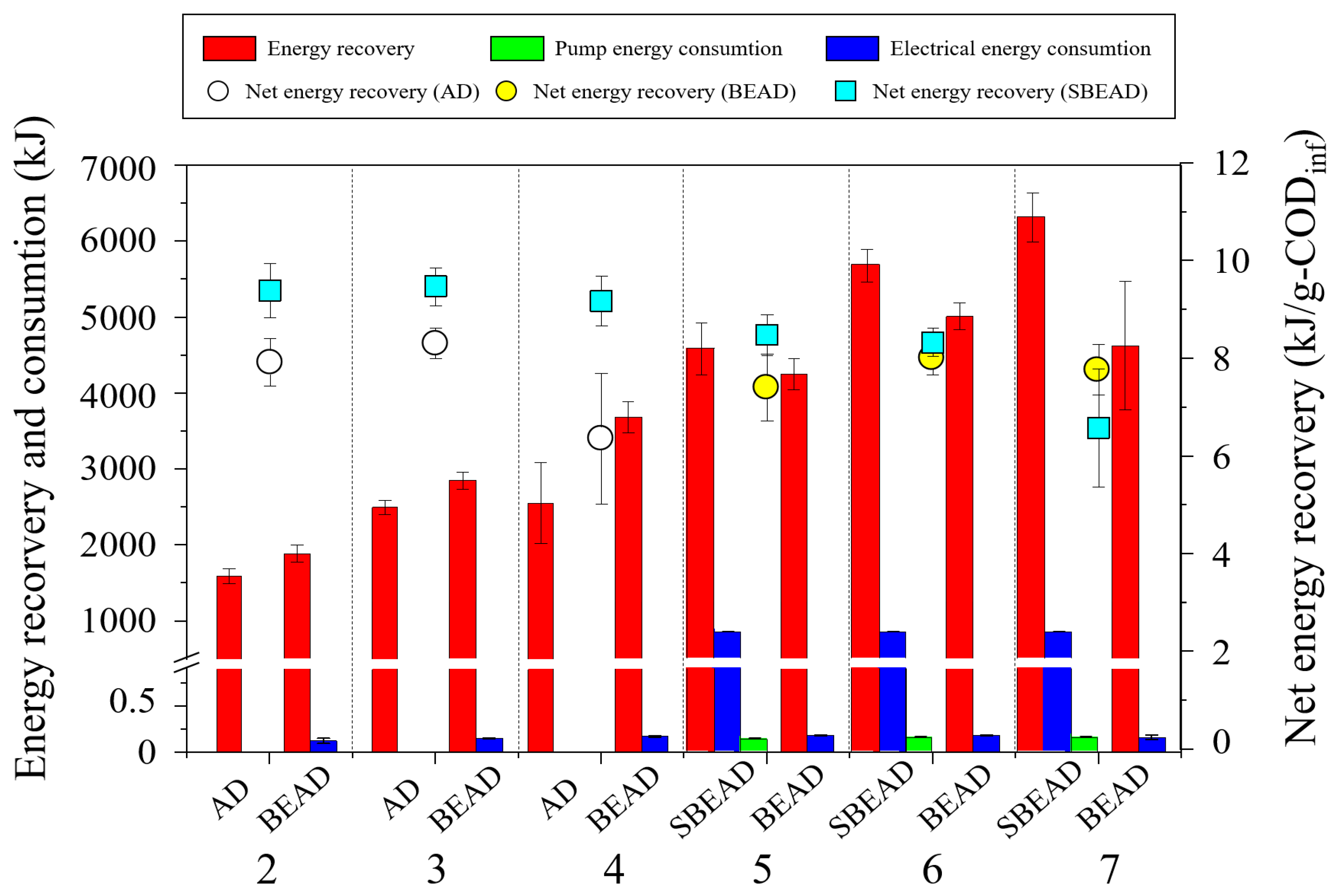
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Performance, Energy Efficiency, and Economic Feasibility Among Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Styles, D.; Yesufu, J.; Bowman, M.; Prysor Williams, A.; Duffy, C.; Luyckx, K. Climate mitigation efficacy of anaerobic digestion in a decarbonising economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, P.M.; D’Silva, T.C.; Adlak, K.; Kumar, S.; Chandra, R.; Vijay, V.K. Anaerobic digestion as a sustainable technology for efficiently utilizing biomass in the context of carbon neutrality and circular economy. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, E.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Guo, J.; Dong, R. Potential biomethane production from crop residues in China: Contributions to carbon neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 111360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Pan, S.; Wang, S. Low-carbon emitting university campus achieved via anaerobic digestion of canteen food wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.R.; Leong, H.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Anjum, H.; Chang, C.-K.; Show, P.L. Effects of anaerobic digestion of food waste on biogas production and environmental impacts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawer, M.U.B.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ali, I.; Arshad, M.; Juchelková, D.; Anjum, M.W.; Naqvi, M. Anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge for biogas & biohydrogen production: State-of-the-art trends and prospects. Fuel 2022, 329, 125416. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Qiao, W.; Westerholm, M.; Huang, G.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Dong, R. Microbiological and technological insights on anaerobic digestion of animal manure: A review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, L.S.R. World Risk Poll 2024 Report: A World of Waste—Risks and Opportunities in Household Waste Management; Lloyd’s Register Foundation: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Programme, U.N.E. Food Waste Index Report 2024: Tracking Progress to Halve Global Food Waste; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, C. Microbial community acclimation during anaerobic digestion of high-oil food waste. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Kulupa, T.; Kubiak, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Pilarski, K.; Niewiadomska, A. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste—A Short Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, F. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and excess sludge by humus composites: Characteristics and microbial community structure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.N.I.; Wahid, Z.A. Achievements and perspectives of anaerobic co-digestion: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisowmeya, G.; Chakravarthy, M.; Devi, G.N. Critical considerations in two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Heo, T.-Y.; Kwon, H.-J.; Shi, W.-Q.; Jun, H.-B. Effects of voltage supply on the methane production rates and pathways in an anaerobic digestion reactor using different electron donors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9459–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabib, A.; Abdallah, M.; Shanableh, A.; Sartaj, M. Effect of substrates and voltages on the performance of bio-electrochemical anaerobic digestion. Renew. Energy 2022, 198, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Chen, R. The separate and synergistic role of biochar and electric field to facilitate mesophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste slurry. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 61, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Workie, E.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Bioelectrochemical enhancement of methanogenic metabolism in anaerobic digestion of food waste under salt stress conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13526–13535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, W.; Pu, R.; Bao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Ding, C.; Bai, X. Alternating current-driven bioelectrochemical regulation prevents acidogenic accumulation in carbohydrate-rich anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 517, 164459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.-K.; Yu, H.-C.; Kim, K.-T.; Ahn, Y.; Feng, Q.; Song, Y.-C. Continuous augmentation of anaerobic digestion with electroactive microorganisms: Performance and stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hua, J.; Cheng, J.; Yue, L.; Zhou, J. Microbial electrochemistry enhanced electron transfer in lactic acid anaerobic digestion for methane production. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 358, 131983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madondo, N.I.; Kweinor Tetteh, E.; Rathilal, S.; Bakare, B.F. Effect of an Electromagnetic Field on Anaerobic Digestion: Comparing an Electromagnetic System (ES), a Microbial Electrolysis System (MEC), and a Control with No External Force. Molecules 2022, 27, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Wang, W.Q.; Chen, C.; Xie, P.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.T.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, A.J.; Lee, D.J.; et al. Bioelectrochemical system for the enhancement of methane production by anaerobic digestion of alkaline pretreated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 123000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Pilot-Scale Case Performance of Bioelectrochemical Systems. Microb. Electrochem. Technol. Fundam. Appl. 2023, 2, 555–582. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zou, X.; Chang, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, M.-H.; Zhang, T.C.; Xi, J.; Chen, C. A feasibility investigation of a pilot-scale bioelectrochemical coupled anaerobic digestion system with centric electrode module for real membrane manufacturing wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 368, 128371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Fessler, M.; Jin, B.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y. Insights into the impact of polyethylene microplastics on methane recovery from wastewater via bioelectrochemical anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Kwon, H.-J.; Sposob, M.; Jun, H.-B. Effect of a side-stream voltage supplied by sludge recirculation to an anaerobic digestion reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-G.; Lee, B.; Kwon, H.-J.; Park, H.-R.; Jun, H.-B. Effects of a novel auxiliary bio-electrochemical reactor on methane production from highly concentrated food waste in an anaerobic digestion reactor. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, D.; Dang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Ji, J.; Lv, T.; Bian, R.; Xiao, Z.; Yan, L.; Holmes, D.E. Enhancing biomethanogenic treatment of fresh incineration leachate using single chambered microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 231, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.-T.; Chen, K.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Xu, X.-J.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D.-F.; Ren, N.-Q.; Lee, D.-J.; Chen, C. The underlying mechanism of enhanced methane production using microbial electrolysis cell assisted anaerobic digestion (MEC-AD) of proteins. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurus, K.; Kremmeter, N.; Ahmed, S.; Kazda, M. High-resolution monitoring of VFA dynamics reveals process failure and exponential decrease of biogas production. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 10653–10663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.; Patil, S.M.; Saha, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Ha, G.-S.; Govindwar, S.P.; Lee, S.S.; Chang, S.W.; Chung, W.J.; Jeon, B.-H. Rapid recovery of methane yield in organic overloaded-failed anaerobic digesters through bioaugmentation with acclimatized microbial consortium. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C. Strategies for stable anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Song, Y.-C.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, D.-H. Influence of the temperature and hydraulic retention time in bioelectrochemical anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-S.; Kondaveeti, S.; Min, B. Bioelectrochemical methane (CH4) production in anaerobic digestion at different supplemental voltages. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Reddy, C.N.; Min, B. In situ integration of microbial electrochemical systems into anaerobic digestion to improve methane fermentation at different substrate concentrations. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.; Min, B. Enhanced methane fermentation of municipal sewage sludge by microbial electrochemical systems integrated with anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 30357–30366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Nie, H.; Jiang, H.; Qian, M.; Zhou, H. Influence of organic loading rate on the performance of a two-phase pressurized biofilm (TPPB) system treating food waste. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Rene, E.R.; Dupont, C.; Wongrod, S.; Van Hullebusch, E.D. Anaerobic digestion of fruit waste mixed with sewage sludge digestate biochar: Influence on biomethane production. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Zi, H. Influence of Organic Loading Rate on Methane Production from Brewery Wastewater in Bioelectrochemical Anaerobic Digestion. Fermentation 2023, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, K.-Y.; Logan, B.E. Impact of surface area and current generation of microbial electrolysis cell electrodes inserted into anaerobic digesters. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Jiang, D.; Lee, B.; Jun, H.-B. Towards the practical application of bioelectrochemical anaerobic digestion (BEAD): Insights into electrode materials, reactor configurations, and process designs. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Lee, B.; Shi, P.; Kim, Y.; Jun, H.-B. Effects of electrode distance and mixing velocity on current density and methane production in an anaerobic digester equipped with a microbial methanogenesis cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27732–27740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Inoculum | Food waste |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.5 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.2 |
| Alkalinity (g/L as CaCO3) | 1.0 ± 0.2 | - |
| TCOD (g/L) | 20.1 ± 2.8 | 124.8 ± 17.9 |
| SCOD (g/L) | 10.7 ± 0.1 | 84.0 ± 9.0 |
| TS (%) | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 11.1 ± 1.0 |
| VS (%) | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 8.6 ± 3.4 |
| Parameters | AD | SBEAD | BEAD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working volume (L) | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Supplied voltage (V) | - | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| Recirculation rate (L/d) | - | 300 | - | |
| OLR (kg/m3/d) | Step 1 | 2.0 | - | 2.0 |
| Step 2 | 3.0 | - | 3.0 | |
| Step 3 | 4.0 | - | 4.0 | |
| Step 4 | - | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| Step 5 | - | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| Step 6 | - | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| Operation period (d) | Step 1 | 0–50 | - | 0–50 |
| Step 2 | 51–110 | - | 51–110 | |
| Step 3 | 111–180 | - | 111–180 | |
| Step 4 | - | 181–240 | 181–240 | |
| Step 5 | - | 241–280 | 241–280 | |
| Step 6 | - | 281–320 | 281–312 | |
| Structure | Component | Material | Unit Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tank and side-stream structure Tank | Tank | Carbon steel | USD 625.16/m3 |
| Side-stream structure | Carbon steel | ||
| Electrode system | Electrode | Carbon cloth | USD 27.19/m2 * |
| Pump and piping system | Pump | - | USD 520.97/unit |
| Pipeline | Polyvinyl Chloride | USD 1.79/m |
| Parameters | AD | BEAD | SBEAD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum stable OLR (kg-COD/m3/d) | 3.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | |
| pH behavior | pH declined sharply at step 3 | pH maintained within neutral range until step 5 | pH remained stable after successful recovery | |
| VFAs response | Rapid accumulation above 6000 mg/L under overload | 4500 mg/L during stable operation, but sharp rise at step 6 | Maintained below inhibitory level even at step 6 | |
| COD removal Efficiency (%) * | 68.6 ± 3.6 | 75.1 ± 5.8 | 77.3 ± 4.8 | |
| Methane yield (L/g-COD) * | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | |
| CoV (%) ** | - | 4.2 | 10.4 | |
| Net energy recovery (kJ/g-CODinf) | Step 1 | 7.94 | 9.41 | - |
| Step 2 | 8.33 | 9.49 | - | |
| Step 3 | 6.33 | 9.20 | - | |
| Step 4 | - | 8.50 | 7.43 | |
| Step 5 | - | 8.35 | 8.03 | |
| Step 6 | - | 6.60 | 7.79 | |
| Category | Component | Quantity /Dimensional Parameters | Total Cost (USD) ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| AD | Tank | 33,333 m3 * | 20,838,667 |
| Total cost | 20,838,667 | ||
| BEAD | Tank | 16,667 m3 * | 10,419,333 |
| Electrode | 120,000 m2 | 3,274,800 | |
| Total cost | 13,694,133 | ||
| SBEAD | Tank | 13,228 m3 * | 8,269,312 |
| Side-stream structure | 1143 m3 | 714,469 | |
| Electrode | 120,000 m2 | 3,274,800 | |
| Pump | 1 unit | 521 | |
| Pipeline | 15 m | 27 | |
| Total cost | 12,259,129 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Jo, S.; Park, J.; Jun, H. Application of Side-Stream Bio-Electrochemical Module to Quickly Reactivate Process Performances in Deteriorated Bench-Scale Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energies 2026, 19, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010160
Yang H, Jo S, Park J, Jun H. Application of Side-Stream Bio-Electrochemical Module to Quickly Reactivate Process Performances in Deteriorated Bench-Scale Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energies. 2026; 19(1):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010160
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hyeonmyeong, Sangyeol Jo, Jungyu Park, and Hangbae Jun. 2026. "Application of Side-Stream Bio-Electrochemical Module to Quickly Reactivate Process Performances in Deteriorated Bench-Scale Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste" Energies 19, no. 1: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010160
APA StyleYang, H., Jo, S., Park, J., & Jun, H. (2026). Application of Side-Stream Bio-Electrochemical Module to Quickly Reactivate Process Performances in Deteriorated Bench-Scale Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energies, 19(1), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/en19010160








