Optimum Design of a Photovoltaic Inverter System Based on Ga, Pso and Gwo Algorithms with a Mppt Sliding Mode Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
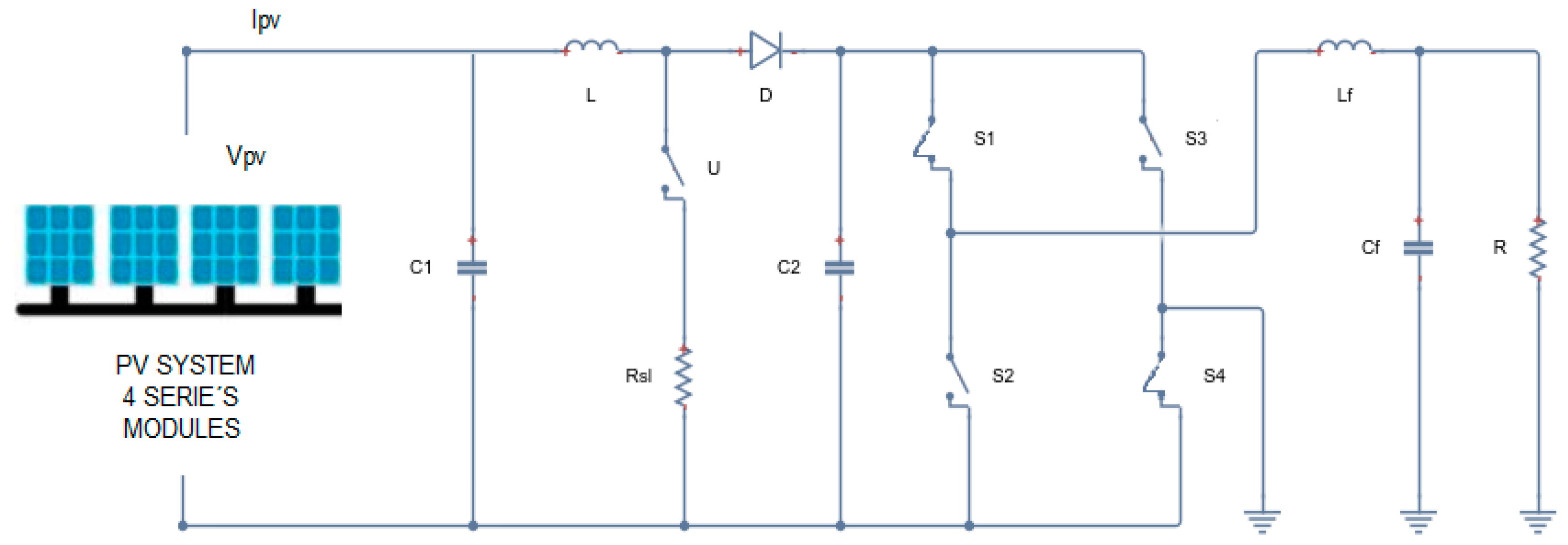
2.1. System Description
2.2. Control Algorithms
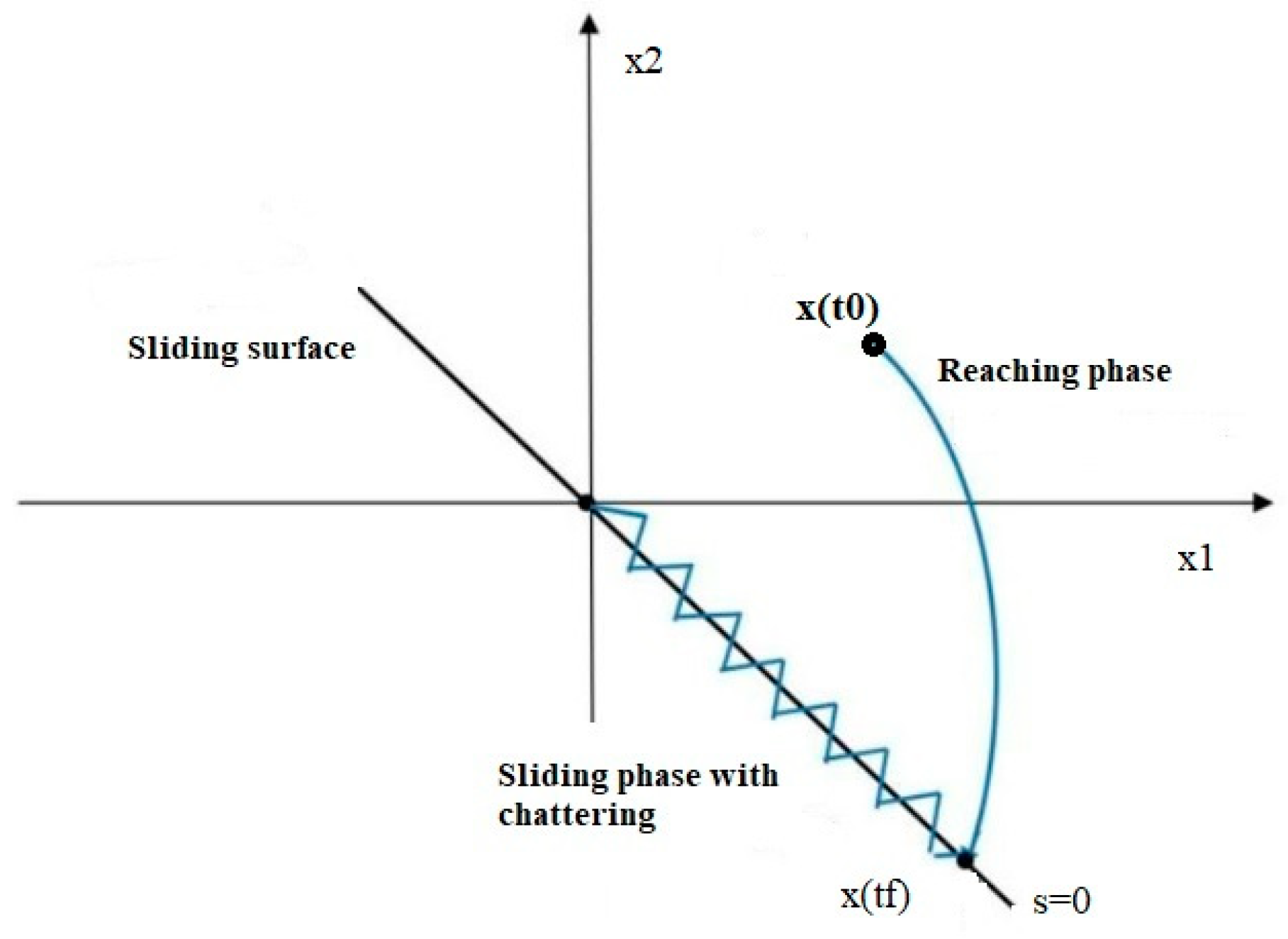
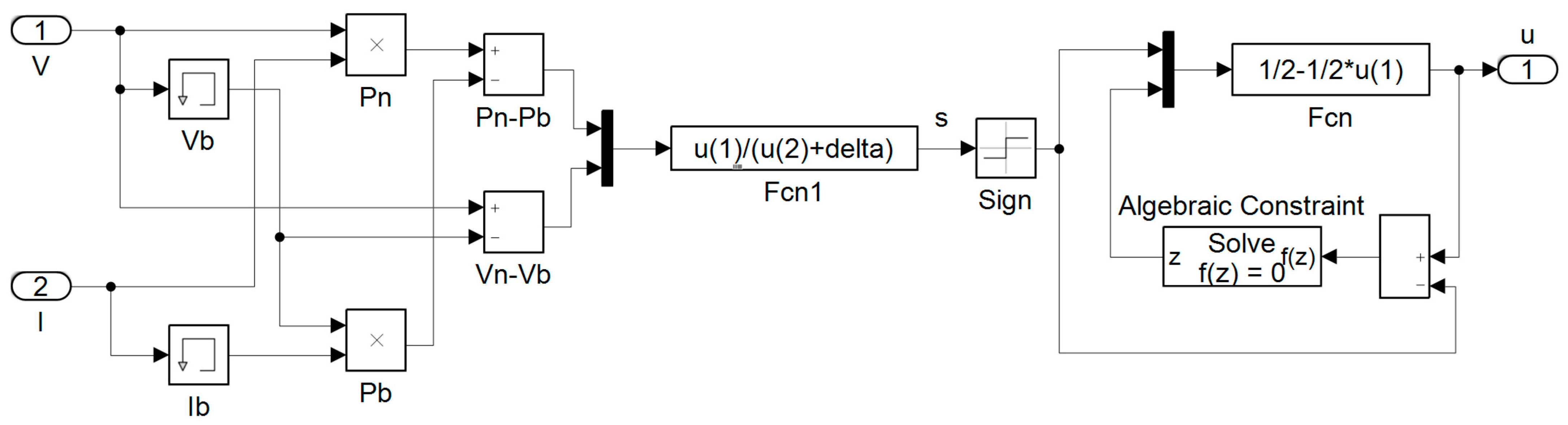
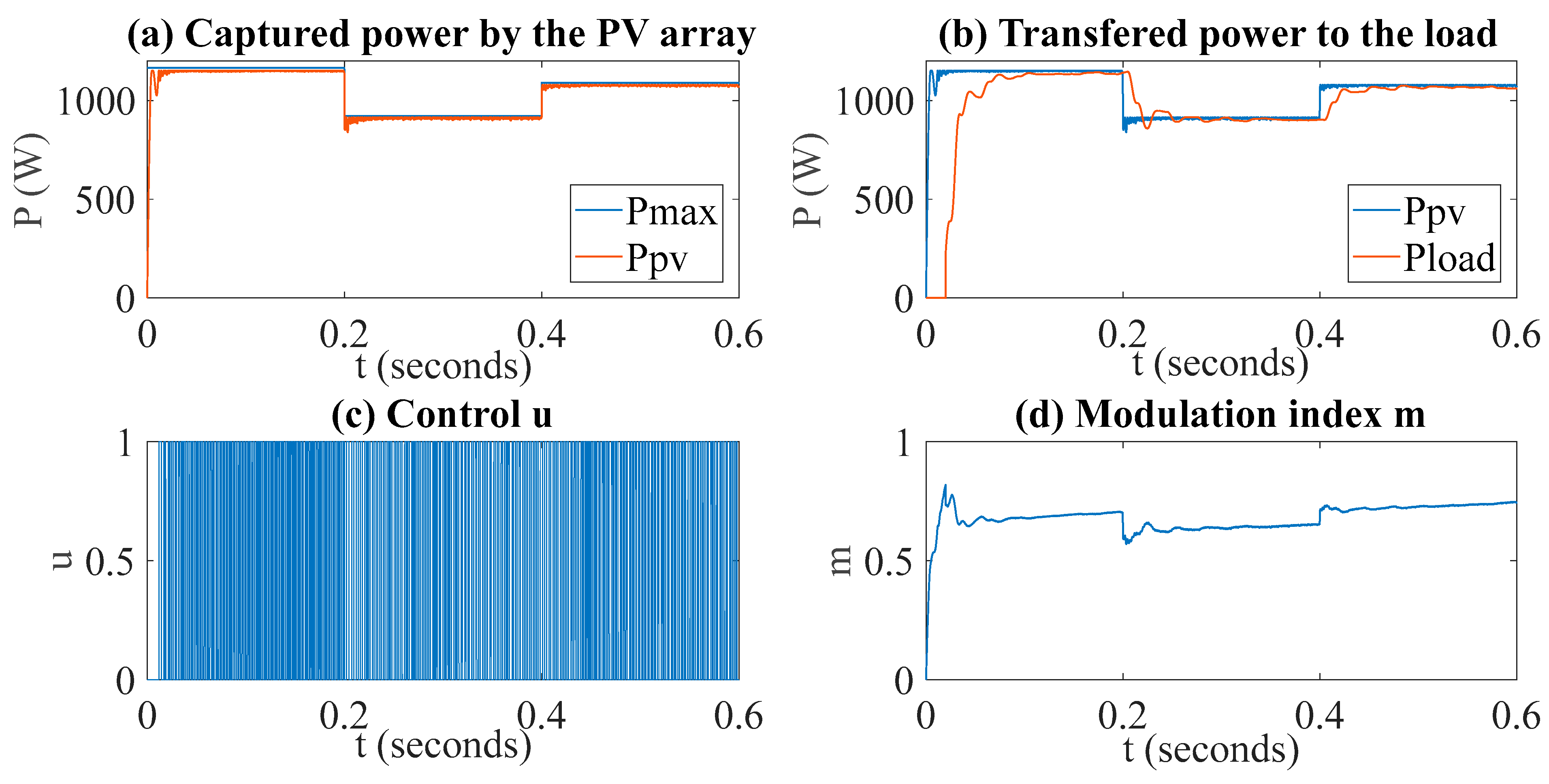
2.2.1. MPPT with SMC
2.2.2. Inverter PI Control
3. Results
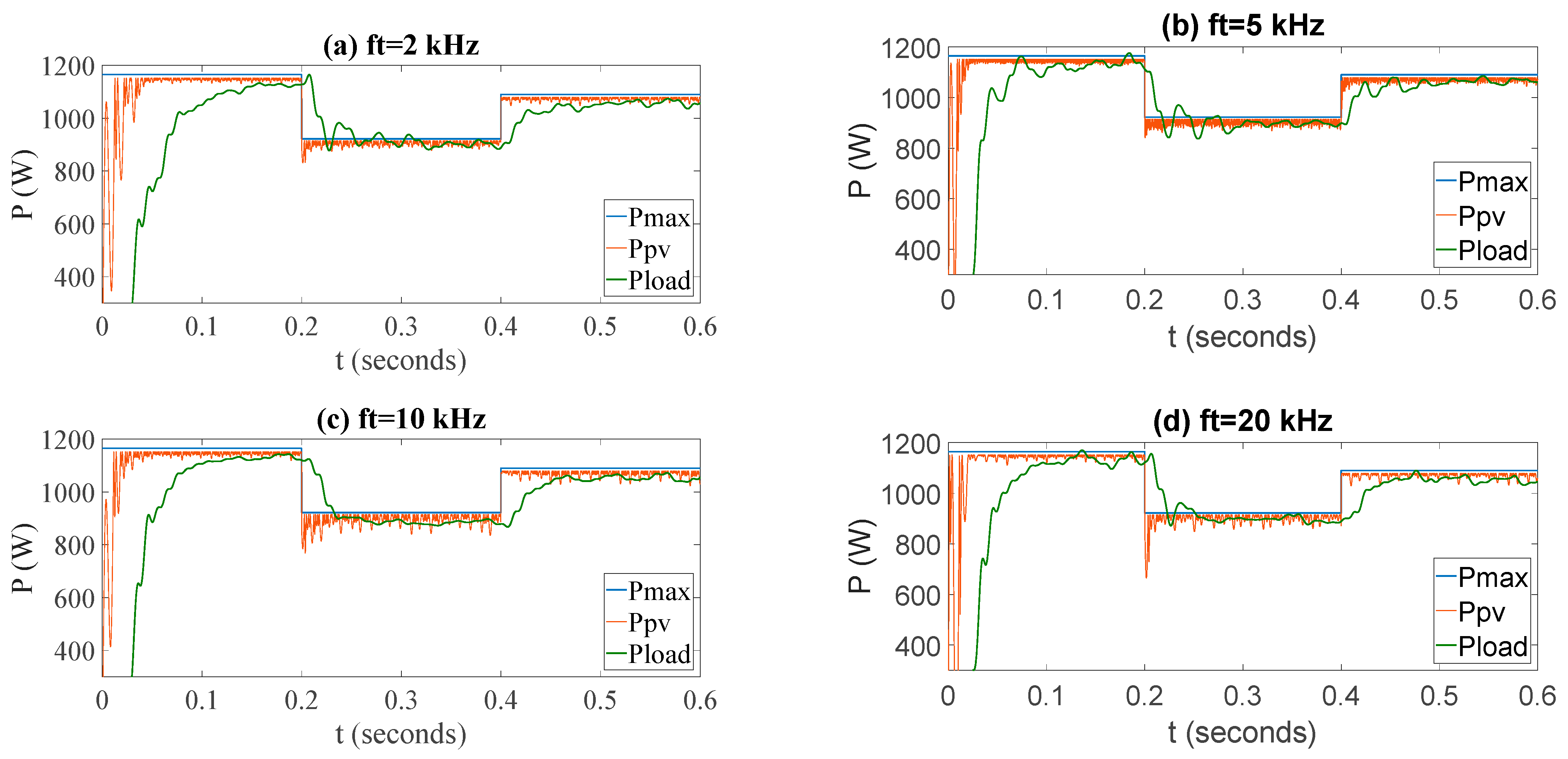
3.1. System Behavior at Different Commutation Frequencies
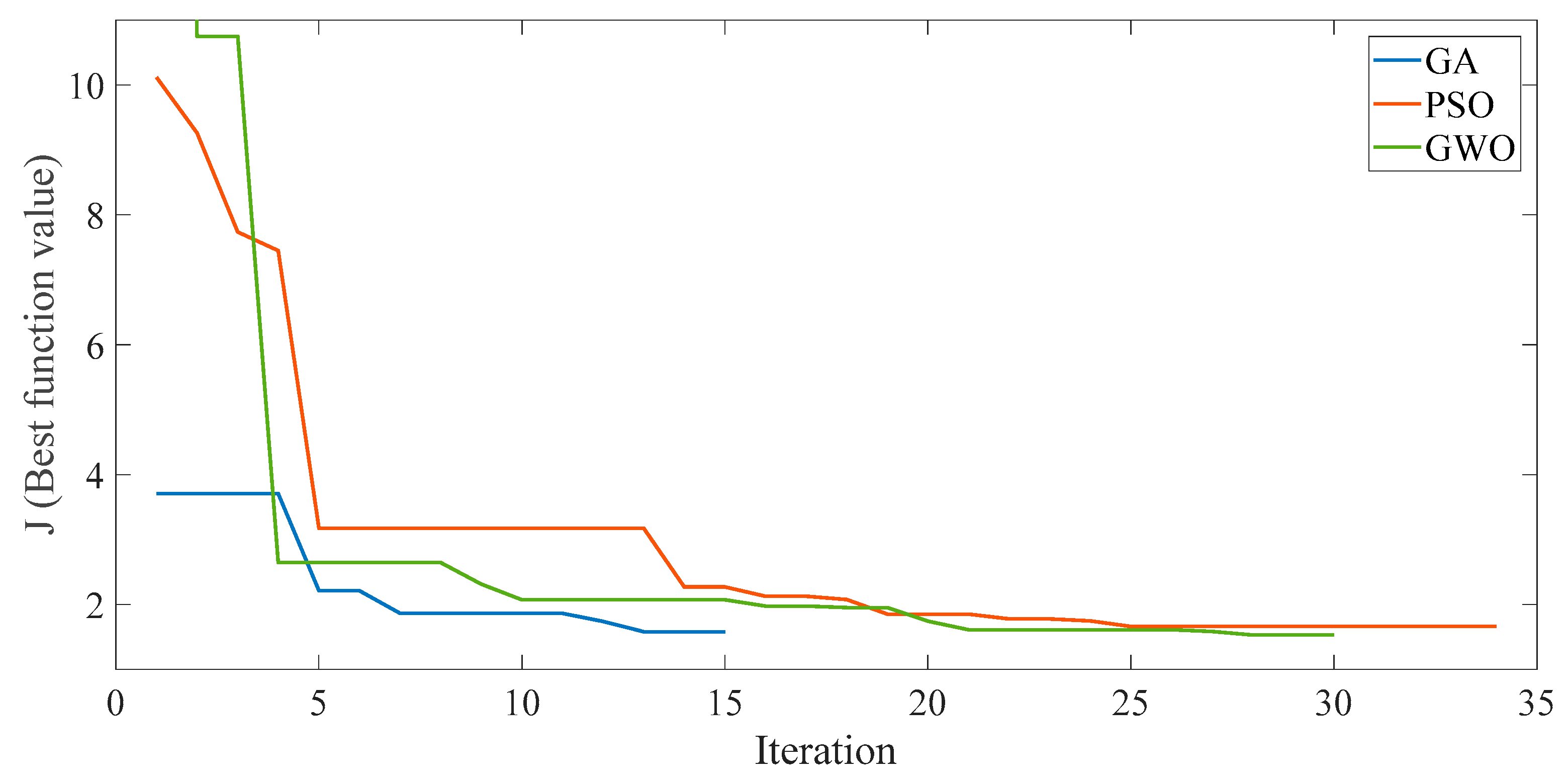
3.2. Comparison with Others Optimization Algorithms
3.2.1. Particle Swarm Optimization
3.2.2. Gray Wolf Optimizer
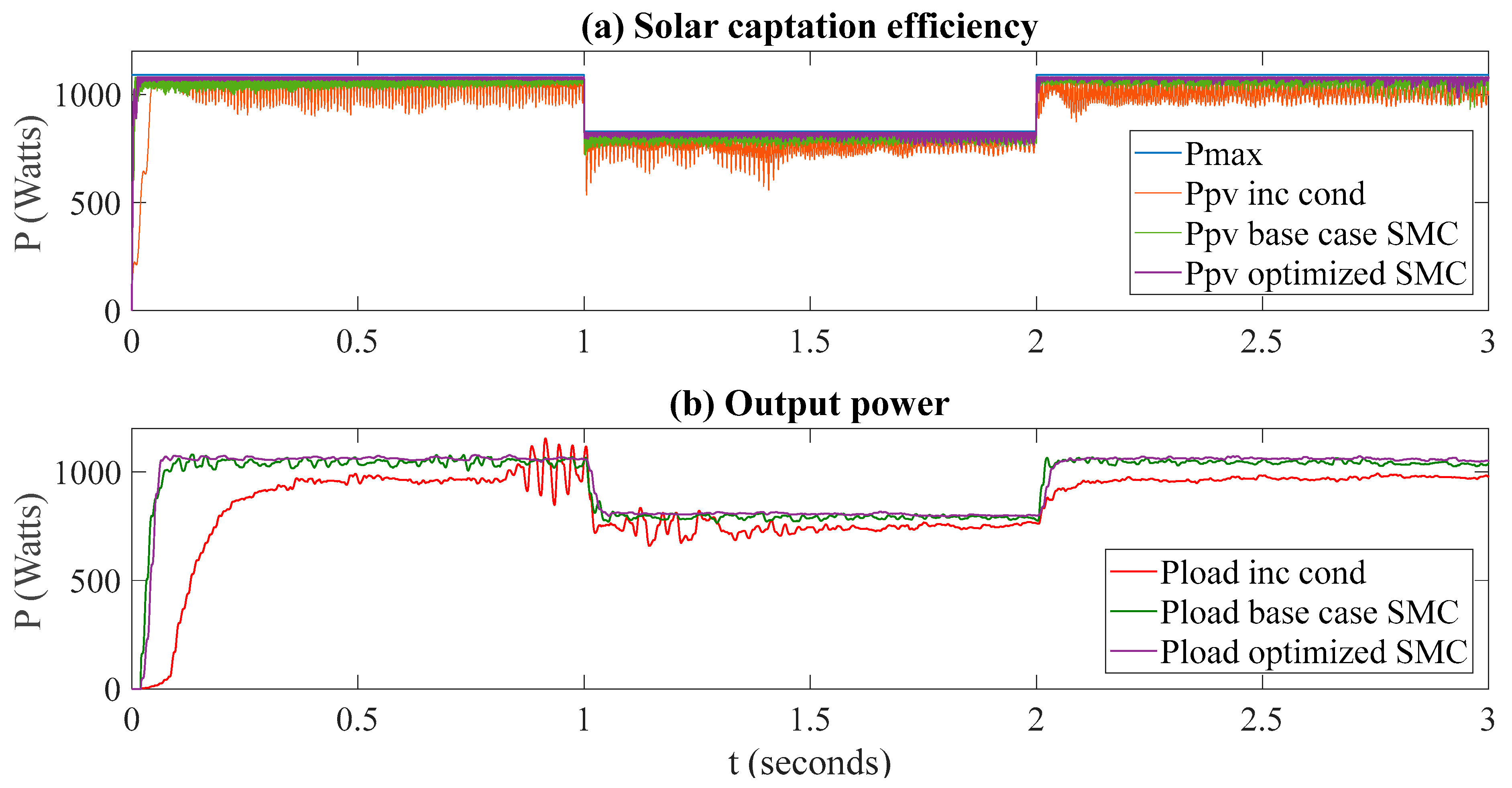
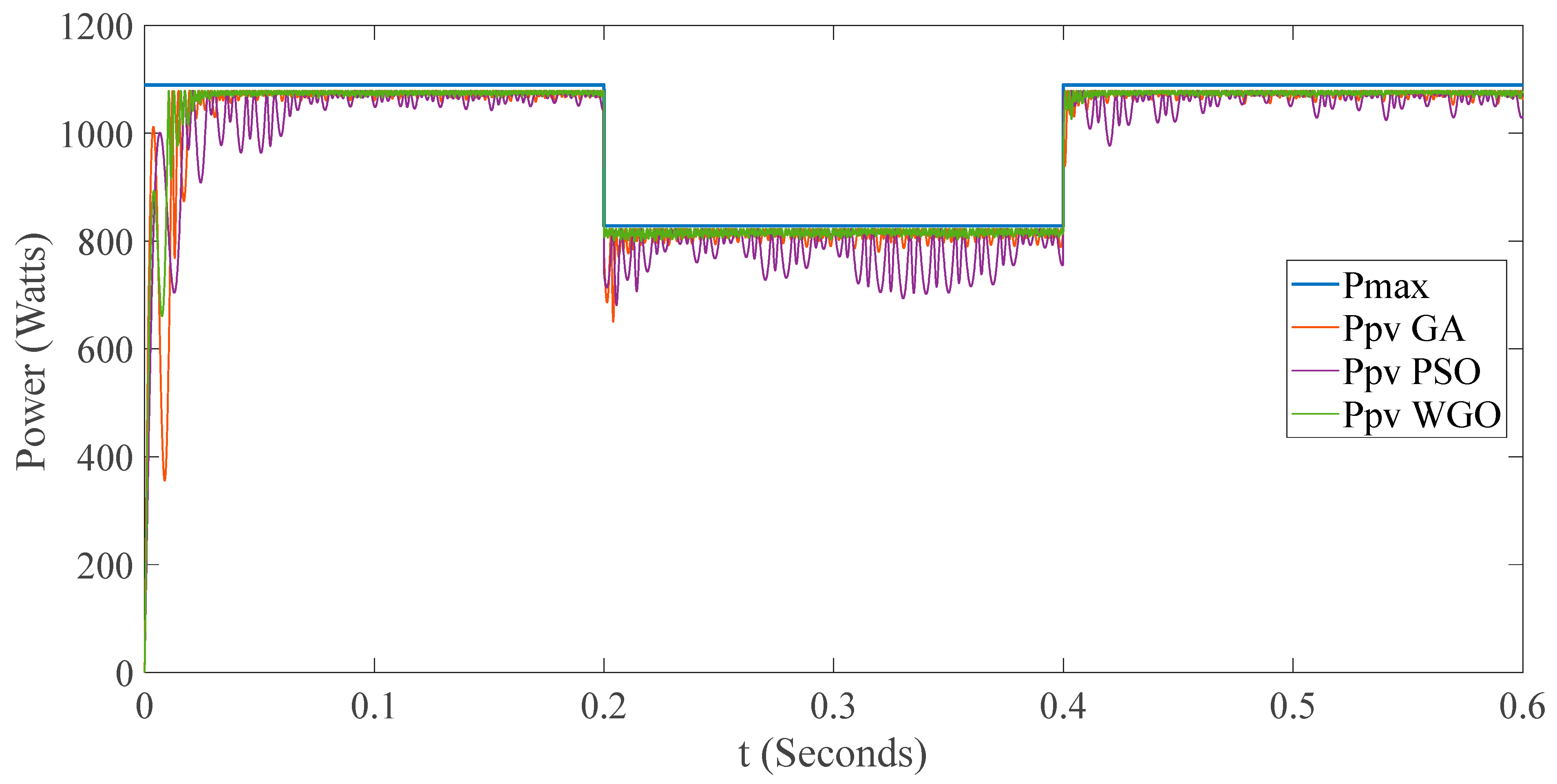
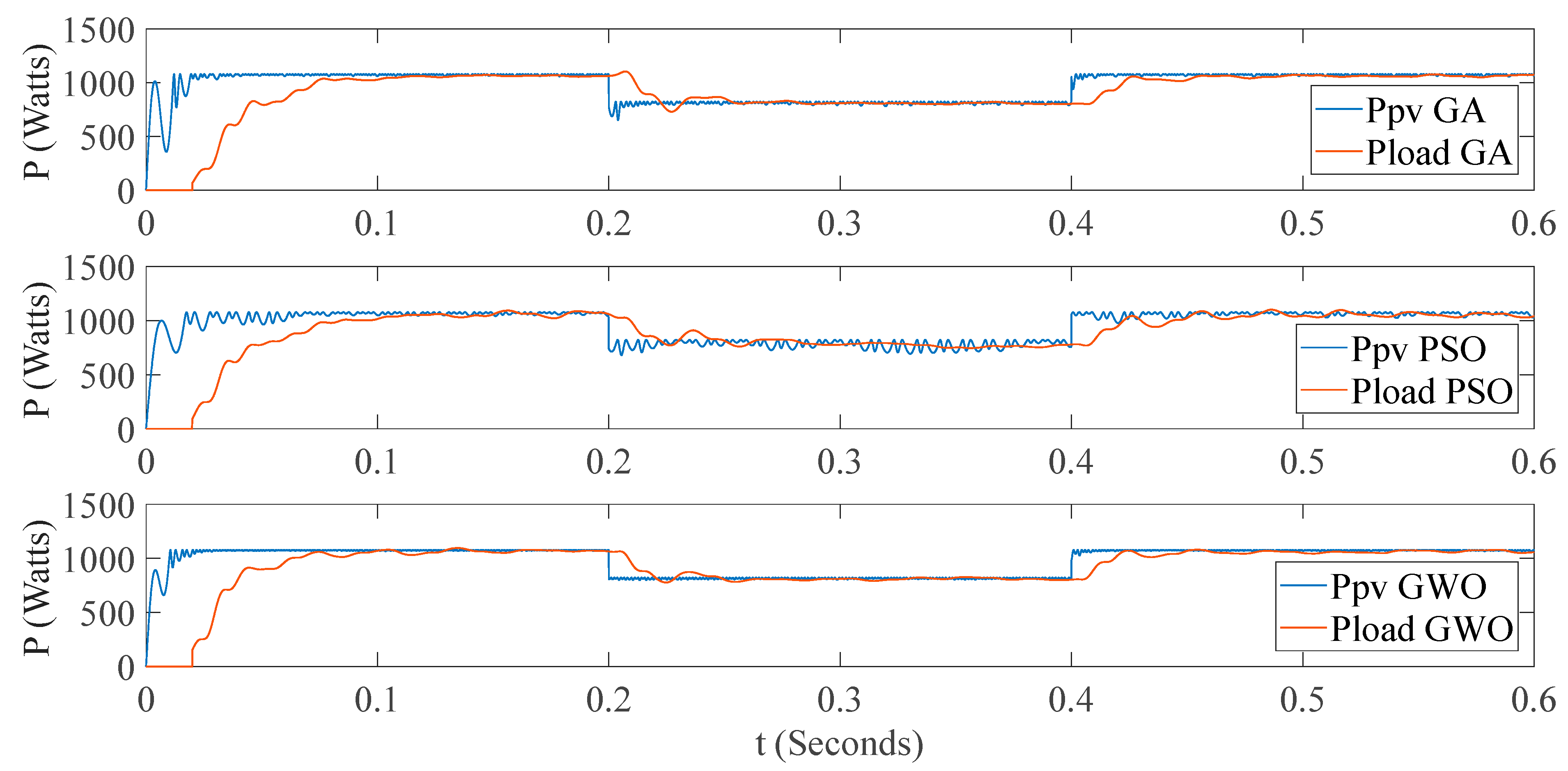
3.3. Results of the GA, PSO and GWO Implementation
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karami-Mollaee, A.; Barambones, O. Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of DC-DC Converter to Extract the Maximum Power of Photovoltaic System Using Dual Sliding Observer. Electronics 2022, 11, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, R.; Mahjoub, S.; Masmoudi, F.; Derbel, N. MPPT Control Strategies for Photovoltaic Applications: Algorithms and Comparative Analysis. In Proceedings of the 16th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices (SSD), Istanbul, Turkey, 21–24 March 2019; pp. 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flota-Bañuelos, M.; Espinosa-Trujillo, M.; Cruz-Chan, J.; Kamal, T. Experimental Study of an Inverter Control for Reactive Power Compensation in a Grid-Connected Solar Photovoltaic System Using Sliding Mode Control. Energies 2023, 16, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Dash, P.K. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control of a grid interactive PV-VSC system with LCL filter. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2016, 6, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Vega, D.; Alazki, H. Robust maximum power point tracking scheme for PV systems based on attractive ellipsoid method. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 25, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fei, J. Adaptive Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Grid-connected Photovoltaic System Using Fuzzy Neural Network Approach. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9476–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, K.; Islam, S.U.; Din, W.U.; Khan, I.; Ishfaq, M.; Busarello, T.D.C.; Ahmad, I.; Kim, H.J. Design of Fuzzy-PI and Fuzzy-Sliding Mode Controllers for Single-Phase Two-Stages. Electronics 2019, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Khan, L.; Ali, N.; Alam, Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Khan, M.A. Soft Computing Technique based Nonlinear Sliding Mode Control for Stand-Alone Photovoltaic System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Smart Technologies (ICETST), Karachi, Pakistan, 26–27 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanaban, S.; Priyadarshi, N.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Azam, F.; Sharma, A.K.; Hossain, E. A novel modified sine-cosine optimized MPPT algorithm for grid integrated PV system under real operating conditions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10467–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Su, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Dan, H.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, B. A Robust Second-Order Sliding Mode Control for Single-Phase Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Voltage Source Inverter. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 53202–53212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Su, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Pou, J.; Yang, Y.; Davari, P. Optimization Design and Control of Single-Stage Single-Phase PV Inverters for MPPT Improvement. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 13000–13016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.-C. High-performance pure sine wave inverter with robust intelligent sliding mode maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic applications. Micromachines 2020, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortajarena, J.A.; Barambones, O.; Alkorta, P.; De Marcos, J. Sliding mode control of grid-tied single-phase inverter in a photovoltaic MPPT application. Sol. Energy 2017, 155, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yu, T.; Shu, H.; Zhu, D.; Sang, Y.; Jiang, L. Passivity-based fractional-order sliding-mode control design and implementation of grid-connected photovoltaic systems. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 043701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Shao, W.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H. Sliding-mode control based on index control law for MPPT in photovoltaic systems. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2018, 2, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, B.; Abdelhak, B.; Noureddine, B.; Thameur, A.; Abdelkader, L.; Layachi, Z. Optimization of the fuzzy MPPT controller by GA for the single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system controlled by sliding mode. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2190, 020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feshara, H.F.; Ibrahim, A.M.; El-Amary, N.H.; Sharaf, S.M. Performance evaluation of variable structure controller based on sliding mode technique for a grid-connected solar network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 84349–84359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikant, U.; Singh, V.; Rani, A. PV fed sliding mode controlled SEPIC converter with single phase inverter. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems ICCES, Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaga, D.; Sankaranarayanan, V. Performance comparison for grid connected photovoltaic system using sliding mode control. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 33, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.B.; Urundady, V. Sliding Mode Controller with Integral Action for DC-Link Voltage Control of Grid-Integrated Domestic Photovoltaic Systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 6583–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.G.; Vilanova, R.; Pelez-Restrepo, J. Perturb Observe based Adaptive Sliding Mode MPPT Control of Solar Photovoltaic System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2020 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe, EEEIC/I and CPS Europe, Madrid, Spain, 9–12 June 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado-Mendoza, A.; Pérez-Cisneros, M.A.; Domínguez-Navarro, J.A.; Osuna-Enciso, V.; Zúñiga-Grajeda, V.; Gurubel-Tun, K.J. Dynamic phasors modeling for a single phase two stage inverter. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Flores, E.; Ortiz, A.; Macias, I.; Molina, A. Experimental Validation of an Enhanced MPPT Algorithm and an Optimal DC–DC Converter Design Powered by Metaheuristic Optimization for PV Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadji, F.; Bouyakoub, I.; Mehedi, F.; Kacemi, W.M.; Reguieg, Z. Optimization of grid power quality using third order sliding mode controller in PV systems with multilevel inverter. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 5177–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, I.; Merzouk, I.; Rezaoui, M.M.; Rezk, H.; Lashab, A. Output current observation and control of grid-connected modular multilevel converter using a simplified super twisting algorithm sliding mode. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupangu, C.; Saha, A.K.; Bansal, R.C.; Justo, J.J. Critical Performance Comparison Between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Incremental Conductance MPPT Algorithms for DC/DC Boost-Converter Applied in PV Systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2022, 50, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltamaly, A.M. A novel musical chairs algorithm applied for MPPT of PV systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltamaly, A.M. A Novel Strategy for Optimal PSO Control Parameters Determination for PV Energy Systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado-Mendoza, A.; Bernal-Agustín, J.L.; Domínguez-Navarro, J.A. Photovoltaic boost converter system with dynamic phasors modelling. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Ang, S.P.; Dani, M.N.; Rahman, M.I.; Petra, R.; Sulthan, S.M. Optimizing Step-Size of Perturb & Observe and Incremental Conductance MPPT Techniques Using PSO for Grid-Tied PV System. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 13079–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
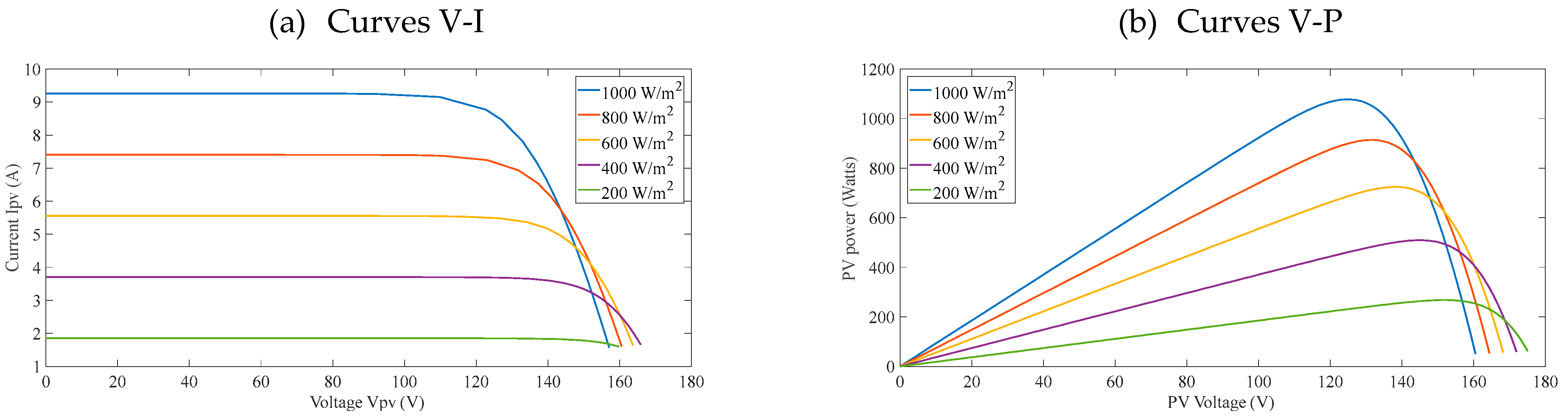

| Author | THD | Tracking Error | Convergence Speed | Efficiency | Robustness | DC Bus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | x | x | ||||
| [6] | x | |||||
| [13] | x | x | x | |||
| [14] | x | x | ||||
| [15] | x | |||||
| [7] | x | x | x | x | x | |
| [9] | ||||||
| [2] | x | x | ||||
| [16] | x | x | ||||
| [17] | x | x | ||||
| [10] | x | x | x | x | ||
| [8] | x | x | x | x | x | |
| [18] | x | x | x | |||
| [19] | x | x | ||||
| [20] | x | x | x | |||
| [21] | x | x | ||||
| [11] | x | x | x | x | x | |
| [12] | x | x | ||||
| [5] | x | x | x | x | ||
| [22] | x | x | x | x | x | |
| [23] | x | x | x | x | x | |
| [1] | x | x | ||||
| [24] | x | x | x | x | ||
| [25] | x | x | x | x |
| Parameter | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incremental Conductance | Base Case | 2 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | |
| (µF) | 2000 | 250 | 235 | 150 | 240 | 110 |
| (µF) | 2000 | 250 | 669 | 539 | 526 | 551 |
| (µF) | 250 | 250 | 602 | 238 | 452 | 374 |
| (mH) | 10 | 10 | 24 | 19 | 20 | 35 |
| (mH) | 25 | 15 | 39 | 34 | 46 | 47 |
| (µS) | 50 | 50 | 56 | 61 | 55 | 89 |
| Kp | 0.000014 | 0.00014 | 8.4656 × 10−4 | 4.1857 × 10−4 | 4.7661 × 10−4 | 0.0014 |
| Ki | 0.0447 | 0.00847 | 0.0256 | 0.0211 | 0.0360 | 0.0447 |
| 0.002 | ||||||
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ppv | 320 W | Npp | 1 |
| Isc | 9.26 A | Rsl | 0.5 Ω |
| Vocm | 45.3 V | R | 10 Ω |
| Nps | 4 |
| Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 kHz | 5 kHz | 10 kHz | 20 kHz | |
| 32.5780 | 30.9658 | 37.1880 | 35.7368 | |
| 105.5042 | 76.9908 | 94.5706 | 87.3150 | |
| 0.0226 | 0.0278 | 0.0233 | 0.0297 | |
| 0.0198 | 0.0216 | 0.0182 | 0.0217 | |
| J | 1.5332 | 1.4289 | 1.4942 | 2.0137 |
| Global efficiency (%) | 89.08 | 91.36 | 89.71 | 90.70 |
| Index | Incremental Conductance | Non-Optimized SMC | Optimized SMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 72.2026 | 30.4095 | 18.4982 | |
| 98.4475 | 34.3239 | 29.9648 | |
| 0.0410 | 0.0360 | 0.0307 | |
| 0.0313 | 0.0292 | 0.0259 | |
| J | 9.1166 | 1.0991 | 0.4409 |
| Global efficiency (%) | 84.42 | 94.47 | 95.80 |
| Variable | GA | PSO | GWO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best objective function value | 1.57887 | 1.6620 | 1.529 |
| Execution time (s) | 7897 | 185.1613 | 4640.9 |
| Number of iterations/generations | 14 | 32 | 30 |
| The number of function evaluations | 1201 | 740 | |
| 198 | 344 | 232 | |
| 27 | 44 | 24 | |
| 561 | 617 | 400 | |
| 43 | 42 | 50 | |
| 475 | 417 | 180 | |
| 60 | 125 | 41 | |
| 0.00058 | 0.0006684 | 0.0004326 | |
| 0.0270 | 0.02613 | 0.02473 |
| GA | PSO | GWO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3549 | 3974 | 2181 | |
| 17.15 | 27.07 | 13.18 |
| GA | PSO | GWO | |
|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | |||
| 28.6291 | 45.2218 | 21.99 | |
| 91.2996 | 99.6000 | 78.5964 | |
| 0.0253 | 0.0329 | 0.0284 | |
| 0.0214 | 0.0255 | 0.0227 | |
| J | 1.57887 | 1.6620 | 1.529 |
| Global efficiency (%) | 90.0176 | 88.6323 | 91.3961 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coronado-Mendoza, A.; Camas-Náfate, M.; Artal-Sevil, J.S.; Domínguez-Navarro, J.A. Optimum Design of a Photovoltaic Inverter System Based on Ga, Pso and Gwo Algorithms with a Mppt Sliding Mode Control. Energies 2025, 18, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081911
Coronado-Mendoza A, Camas-Náfate M, Artal-Sevil JS, Domínguez-Navarro JA. Optimum Design of a Photovoltaic Inverter System Based on Ga, Pso and Gwo Algorithms with a Mppt Sliding Mode Control. Energies. 2025; 18(8):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081911
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoronado-Mendoza, Alberto, Mónica Camas-Náfate, Jesús Sergio Artal-Sevil, and José Antonio Domínguez-Navarro. 2025. "Optimum Design of a Photovoltaic Inverter System Based on Ga, Pso and Gwo Algorithms with a Mppt Sliding Mode Control" Energies 18, no. 8: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081911
APA StyleCoronado-Mendoza, A., Camas-Náfate, M., Artal-Sevil, J. S., & Domínguez-Navarro, J. A. (2025). Optimum Design of a Photovoltaic Inverter System Based on Ga, Pso and Gwo Algorithms with a Mppt Sliding Mode Control. Energies, 18(8), 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081911






