Laboratory-Scale Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction Numerical Simulation Under Phase Transition Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Analysis
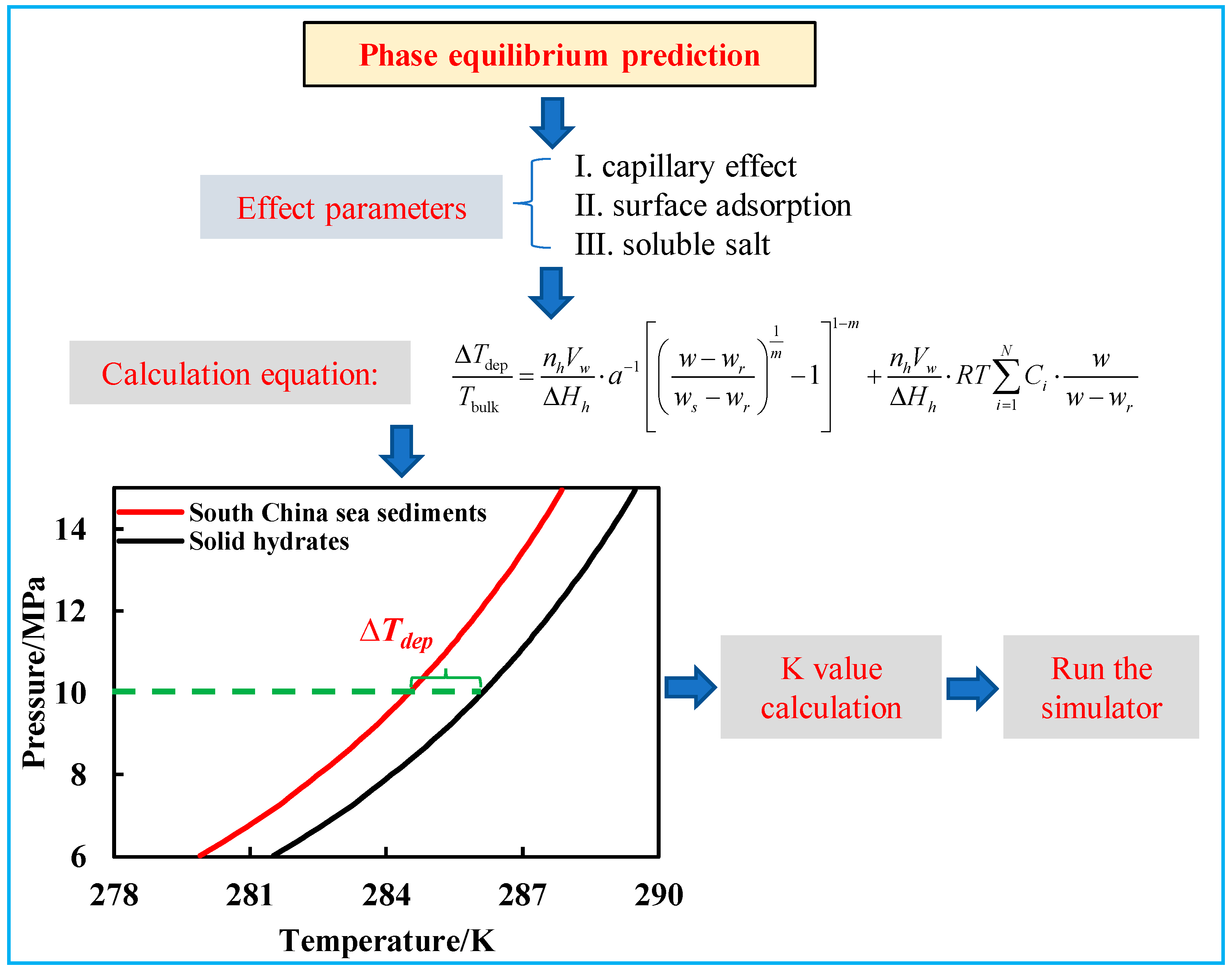
2.1. Phase Transition Model
2.2. Mathematical Model Development
2.2.1. Kinetic Model for Natural Gas Hydrate Formation
2.2.2. The Law of Conservation of Mass Equation
2.2.3. Conservation of Energy Equation
2.2.4. The Relationship Between Porosity and Permeability
2.2.5. Relative Permeability Model
2.2.6. Equation of State
2.3. Numerical Model Description
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gas Production Dynamics of Different Sediments with a Fixed Water Content of 0.3 and Salinity of 1.5%
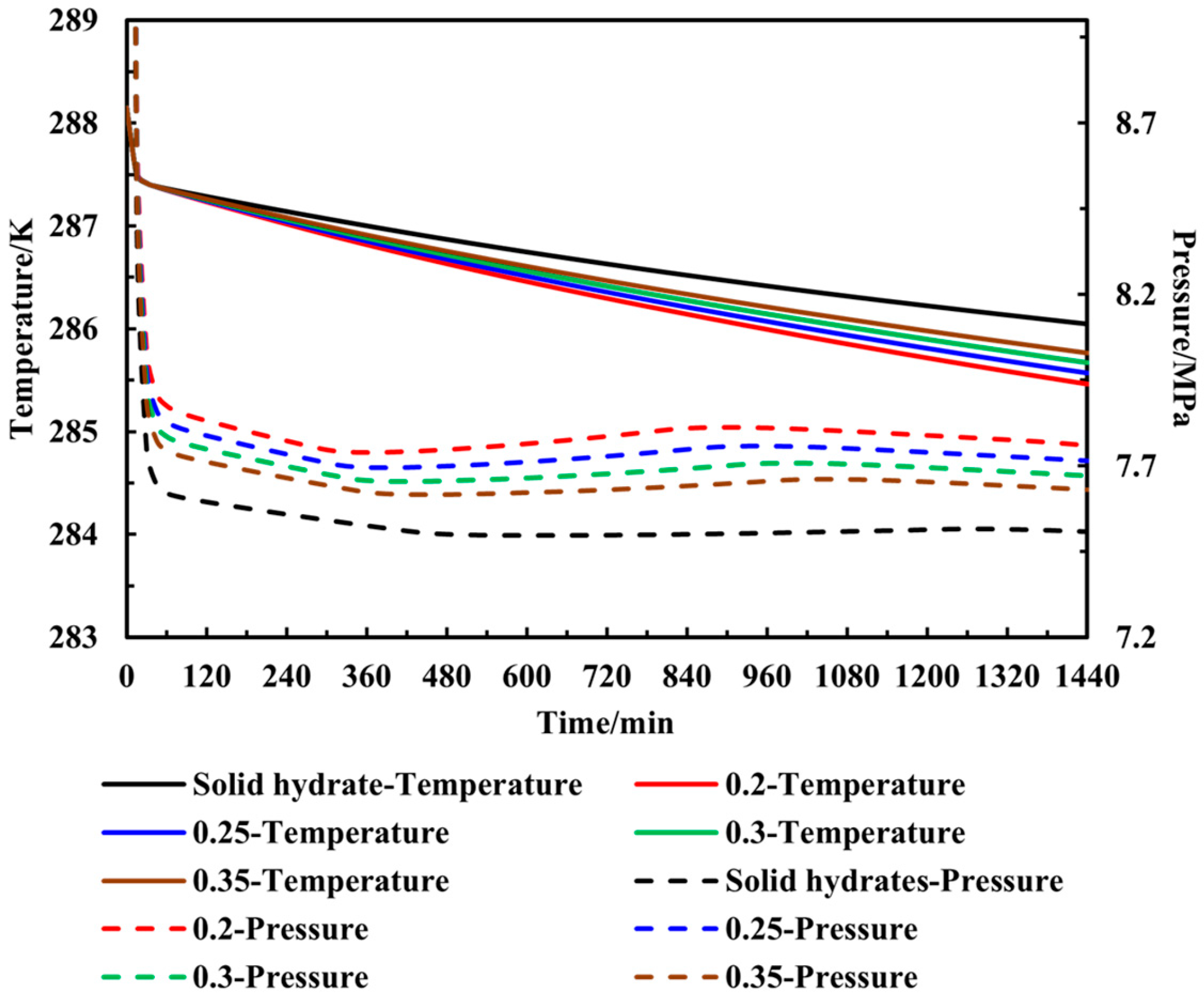
3.2. Gas Production Dynamics of Sediments with Fixed Salinity of 1.5% Under Different Water Contents
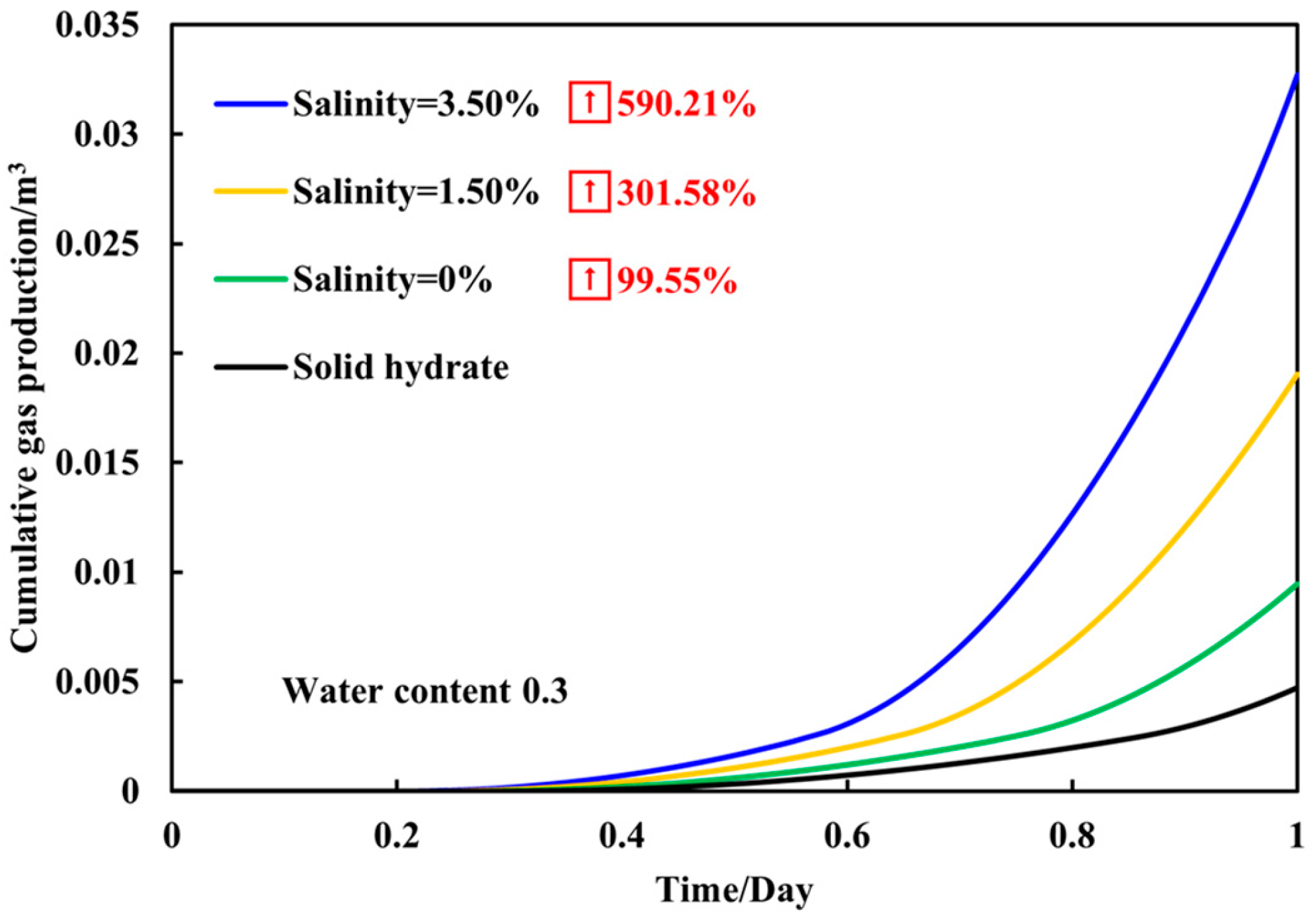
3.3. Gas Production Dynamics of Sediments with a Fixed Water Content of 0.3 Under Different Salinities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Hydrate concentration. | |
| Hydrate decomposition rate constant. | |
| Specific surface area of hydrate per unit volume. | |
| Equilibrium pressure. | |
| Gas phase pressure. | |
| Frequency factor of hydrate decomposition reaction. | |
| Activation energy. | |
| The equilibrium value of hydrates at a certain pressure and temperature. | |
| Gas constant. | |
| The specific surface area of hydrate particles. | |
| Concentration of hydrate. | |
| Rate constant of hydrate formation. | |
| Surface area per unit volume of hydrate. | |
| Balance pressure. | |
| Vapor pressure. | |
| The frequency factor of hydrate formation reaction. | |
| Flow rate. | |
| Mass change caused by hydrate decomposition or formation. | |
| S | Phase saturation, with subscripts g, w, and h representing methane, water, and hydrate, respectively. |
| Intrinsic porosity. | |
| Gas production rate of the well. | |
| Water production rate of the well. | |
| Density. | |
| Phase saturation. | |
| The enthalpy of each phase, where the subscripts s, h, g, and w represent the rock skeleton, hydrate, gas, and water. | |
| The heat required for the decomposition or formation of hydrates. | |
| Thermal conductivity. | |
| Effective permeability at porosity φ. | |
| The effective permeability at porosity . | |
| Experience parameter (generally ranges from 1 to 10). | |
| Bound water saturation. | |
| Bound gas saturation. | |
| Power-law coefficient. | |
| An empirical parameter. | |
| Initial capillary pressure. | |
| Van Genuchten index. | |
| K | Equilibrium value of the reaction, controlling the activation of hydrate formation and decomposition reactions; when K > 1, hydrates decompose, and when K < 1, hydrates form. |
| Fitting parameters. |
References
- Tang, X.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Guo, Y.L.; Liang, F.C.; Wang, C. Development Status of Combustible Ice Mining and Test Production Technologies. Nat. Gas Oil 2020, 38, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Wang, J.L. On the China’s successful gas production test from marine gas hydrate reservoirs. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Li, Z.D.; Zhao, J.B. New progress in the study of natural gas hydrate in Shenhu area. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2021, 35, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Zhou, S.W.; Zhao, J.F.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J. Research Status and Prospects of Natural Gas Hydrate Exploitation Technology. Chin. Acad. Eng. 2022, 24, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Cao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. The Crack Propagation Behaviour of CO2 Fracturing Fluid in Unconventional Low Permeability Reservoirs: Factor Analysis and Mechanism Revelation. Processes 2025, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y. Wellhead Stability during Development Process of Hydrate Reservoir in the Northern South China Sea: Evolution and Mechanism. Processes 2024, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wang, H.; Shen, R.R.; Yin, X.H. Development of Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction and Utilization Technology—A New Direction for Deep-Sea Oil and Gas Exploration. China Resour. Compr. Util. 2023, 41, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Sun, W. Numerical simulation of natural gas hydrate production enhancement measures in Shenhu area of South China Sea. In Abstracts of the 12th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics; Intelligent Oil and Gas Field Research Institute, School of Petroleum Engineering, China University of Petroleum (East China): Qingdao, China, 2022; 1p. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.W.; Lu, C.; Wang, P.K.; Liang, Q.Y. Hydrate phase transition and seepage mechanism during natural gas hydrate production tests in the South China Sea:A review and prospect. Geol. China 2022, 49, 749–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Sun, Z.T. Current status and future trends of exploration and pilot production of gas hydrate in the world. Mar. Geol. Front. 2018, 34, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Qin, X.W.; Sun, Y.H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Lu, C.; Qu, Y.Z.; Lu, J.H.; et al. Research Progress on Natural Gas Hydrate Drilling &Production in the South China Sea. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.B.; Liang, J.Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Li, T.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. Numerical simulation of gas hydrate migration-accumulation system and trial mining optimization of orebodies in the Shenhu area. Geol. Bull. China 2021, 40, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Lu, X.B.; Li, P. A comprehensive review in natural gas hydrate recovery methods. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 49, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Qiu, Z.C.; Yi, R.; Zhou, X. Current status and considerations of natural gas hydrate exploration and development technology. Committee of China Petroleum Society, Sichuan Petroleum Society, Zhejiang Petroleum Society. In Proceedings of the 2017 National Natural Gas Academic Annual Conference, Hangzhou, China, 19–20 October 2017; China Petroleum Exploration and Development Research Institute: Beijing, China, 2017; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.D.; Sun, Y.M.; Chen, W.C.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Analyses of gas production methods and offshore production tests of natural gas hydrates. J. Eng. Geol. 2019, 27, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F. Numerical Simulation Study on Efficient Exploitation Schemes of Shenhu Hydrate Reservoir in South China Sea. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.X.; Li, Q.P.; Zhou, S.W. Research and development strategy of natural gas hydrate development. Int. Pet. Econ. 2022, 30, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southeast Sea. Several thoughts on NGH’s exploitation. Int. Pet. Econ. 2017, 25, 19–25. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Z.; Zhao, K.B.; Sun, C.Q.; Sun, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Xuan, L. Current Research in Natural Gas Hydrate Production. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2008, 27, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.L. Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation of Gas Production from Natural Gas Hydrate. Master Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.K.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, S.D.; Wang, L.; Duan, R.; Fu, Y. Research progresses on the influencing factors of natural gas hydrates phase transition process in porous media. J. Eng. Geol. 2021, 29, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.F. Molecular Dynamies Study on the Microscopic Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrate Phase Transformation. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Study on Pore Permeation Characteristics of Gas Hydrate Reservoir in Shenhu Sea, South China Sea. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X. Study on Phase Transition Micro-characteristic and Gas Replacement Mechanism of Natural Gas Hydrate. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.M. Study of the Effects of Microscopic Phase Transition of Hydrate on Gas-Water Transport in Porous Media. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Yi, W.Q.; Chen, L.; Gui, B.; Hao, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, R. Super-resolution CT image recognition of micro-occurrence characteristics of natural gas hydrates from Shenhu area in northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2024, 44, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B. Modeling the Dissociation of Methane Hydrate by Depressurization in Different Scale Cores. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L. Numerical Study on the Optimization Producing Scheme of Hydrate Reservoirs in Shenhu Area. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Dongying, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, J.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Cen, X.; Chen, X. Research Progress of Numerical Simulation Technology of Natural Gas Hydrates Production. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 11891–11899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W. Numerical Simulation Study on Horizontal Well Depressurization Production of Natural Gas Hydrate. Master’s Thesis, Qilu University of Technology (QLU), Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gu, J.T.; Xu, H.P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y. Analysis and numerical simulation of factors affecting natural gas hydrate phase equilibrium. Pet. Eng. Constr. 2021, 47, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Lei, X.H.; Xu, H.; Xiang, H. A review on researches on factors affecting gas hydrate phase equilibrium. Nat. Gas Chem. Ind. 2012, 37, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Song, H.B.; Yan, W. The change of external conditions effects on the phase equilibrium curve of gas hydrate and the thickness of hydrate stability zone. Prog. Geophys. 2005, 20, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, T.; Sun, X.F.; Qu, J.; Yao, D. Study on influence factors and rules of gas hydrate phase equilibrium based on multiflash software. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2020, 47, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Experimental and modeling investigations of hydrate phase equilibria in natural clayey-silty sediments. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, H.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Li, S.; Wu, D. Enhanced gas production efficiency of class 1, 2, 3 hydrate reservoirs using hydraulic fracturing technique. Energy 2023, 263, 126003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Temperature T/K | Pressure P/MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Hydrate | Montmorillonite | South China Sea Sediments | Kaolinite | Silt | |
| 281.514 | 279.114 | 279.896 | 280.628 | 280.823 | 6.031 |
| 282.093 | 279.693 | 280.475 | 281.207 | 281.402 | 6.413 |
| 282.693 | 280.293 | 281.075 | 281.807 | 282.002 | 6.842 |
| 283.293 | 280.893 | 281.675 | 282.407 | 282.602 | 7.288 |
| 283.764 | 281.364 | 282.146 | 282.878 | 283.073 | 7.701 |
| 284.321 | 281.921 | 282.703 | 283.435 | 283.630 | 8.178 |
| 284.857 | 282.457 | 283.239 | 283.971 | 284.166 | 8.671 |
| 285.286 | 282.886 | 283.668 | 284.400 | 284.595 | 9.101 |
| 285.779 | 283.379 | 284.161 | 284.893 | 285.088 | 9.626 |
| 286.164 | 283.764 | 284.546 | 285.278 | 285.473 | 10.05 |
| 286.443 | 284.043 | 284.825 | 285.557 | 285.752 | 10.38 |
| 286.721 | 284.321 | 285.103 | 285.835 | 286.030 | 10.72 |
| 286.979 | 284.579 | 285.361 | 286.093 | 286.288 | 11.05 |
| 287.236 | 284.836 | 285.618 | 286.350 | 286.545 | 11.40 |
| 287.493 | 285.093 | 285.875 | 286.607 | 286.802 | 11.74 |
| 287.814 | 285.414 | 286.196 | 286.928 | 287.123 | 12.21 |
| 288.114 | 285.714 | 286.496 | 287.228 | 287.423 | 12.66 |
| 288.521 | 286.121 | 286.903 | 287.635 | 287.830 | 13.28 |
| 288.843 | 286.443 | 287.225 | 287.957 | 288.152 | 13.80 |
| 289.164 | 286.764 | 287.54 | 288.278 | 288.473 | 14.34 |
| Temperature T/K | Pressure P/MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Water | Water Content = 0.2 | Water Content = 0.25 | Water Content = 0.3 | Water Content = 0.35 | |
| 281.514 | 278.875 | 279.4147 | 279.896 | 280.322 | 6.031 |
| 282.093 | 279.454 | 279.9937 | 280.475 | 280.901 | 6.413 |
| 282.693 | 280.054 | 280.5937 | 281.075 | 281.501 | 6.842 |
| 283.293 | 280.654 | 281.1937 | 281.675 | 282.101 | 7.288 |
| 283.764 | 281.125 | 281.6647 | 282.146 | 282.572 | 7.701 |
| 284.321 | 281.682 | 282.2217 | 282.703 | 283.129 | 8.178 |
| 284.857 | 282.218 | 282.7577 | 283.239 | 283.665 | 8.671 |
| 285.286 | 282.647 | 283.1867 | 283.668 | 284.094 | 9.101 |
| 285.779 | 283.140 | 283.6797 | 284.161 | 284.587 | 9.626 |
| 286.164 | 283.525 | 284.0647 | 284.546 | 284.972 | 10.05 |
| 286.443 | 283.804 | 284.3437 | 284.825 | 285.251 | 10.38 |
| 286.721 | 284.082 | 284.6217 | 285.103 | 285.529 | 10.72 |
| 286.979 | 284.340 | 284.8797 | 285.361 | 285.787 | 11.057 |
| 287.236 | 284.597 | 285.1367 | 285.618 | 286.044 | 11.407 |
| 287.493 | 284.854 | 285.3937 | 285.875 | 286.301 | 11.741 |
| 287.814 | 285.175 | 285.7147 | 286.196 | 286.622 | 12.218 |
| 288.114 | 285.475 | 286.0147 | 286.496 | 286.922 | 12.66 |
| 288.521 | 285.882 | 286.4217 | 286.903 | 287.329 | 13.284 |
| 288.843 | 286.204 | 286.7437 | 287.225 | 287.651 | 13.809 |
| 289.164 | 286.525 | 287.064 | 287.546 | 287.972 | 14.34 |
| Temperature T/K | Pressure P/MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water | Salinity = 0% | Salinity = 1.5% | Salinity = 3.5% | |
| 281.514 | 280.833 | 279.89 | 278.932 | 6.031 |
| 282.093 | 281.412 | 280.47 | 279.511 | 6.413 |
| 282.693 | 282.012 | 281.075 | 280.111 | 6.842 |
| 283.293 | 282.612 | 281.675 | 280.711 | 7.288 |
| 283.764 | 283.0831 | 282.146 | 281.182 | 7.701 |
| 284.321 | 283.640 | 282.703 | 281.739 | 8.178 |
| 284.857 | 284.176 | 283.239 | 282.275 | 8.671 |
| 285.286 | 284.605 | 283.668 | 282.704 | 9.101 |
| 285.779 | 285.098 | 284.161 | 283.197 | 9.626 |
| 286.164 | 285.483 | 284.546 | 283.582 | 10.05 |
| 286.443 | 285.762 | 284.825 | 283.861 | 10.38 |
| 286.721 | 286.040 | 285.103 | 284.139 | 10.72 |
| 286.979 | 286.298 | 285.361 | 284.397 | 11.05 |
| 287.236 | 286.555 | 285.618 | 284.654 | 11.40 |
| 287.493 | 286.812 | 285.875 | 284.911 | 11.74 |
| 287.814 | 287.133 | 286.196 | 285.232 | 12.21 |
| 288.114 | 287.433 | 286.496 | 285.532 | 12.66 |
| 288.521 | 287.840 | 286.903 | 285.939 | 13.28 |
| 288.843 | 288.162 | 287.225 | 286.261 | 13.80 |
| 289.164 | 288.483 | 287.546 | 286.582 | 14.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Q.; Pang, W.; Chen, M.; Pang, S. Laboratory-Scale Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction Numerical Simulation Under Phase Transition Effect. Energies 2025, 18, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18030755
Fu Q, Pang W, Chen M, Pang S. Laboratory-Scale Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction Numerical Simulation Under Phase Transition Effect. Energies. 2025; 18(3):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18030755
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Qiang, Weixin Pang, Mingqiang Chen, and Sheng Pang. 2025. "Laboratory-Scale Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction Numerical Simulation Under Phase Transition Effect" Energies 18, no. 3: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18030755
APA StyleFu, Q., Pang, W., Chen, M., & Pang, S. (2025). Laboratory-Scale Natural Gas Hydrate Extraction Numerical Simulation Under Phase Transition Effect. Energies, 18(3), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18030755





