Numerical Analysis of Factors Affecting NOx Emissions in Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Hydrogen Combustion Background
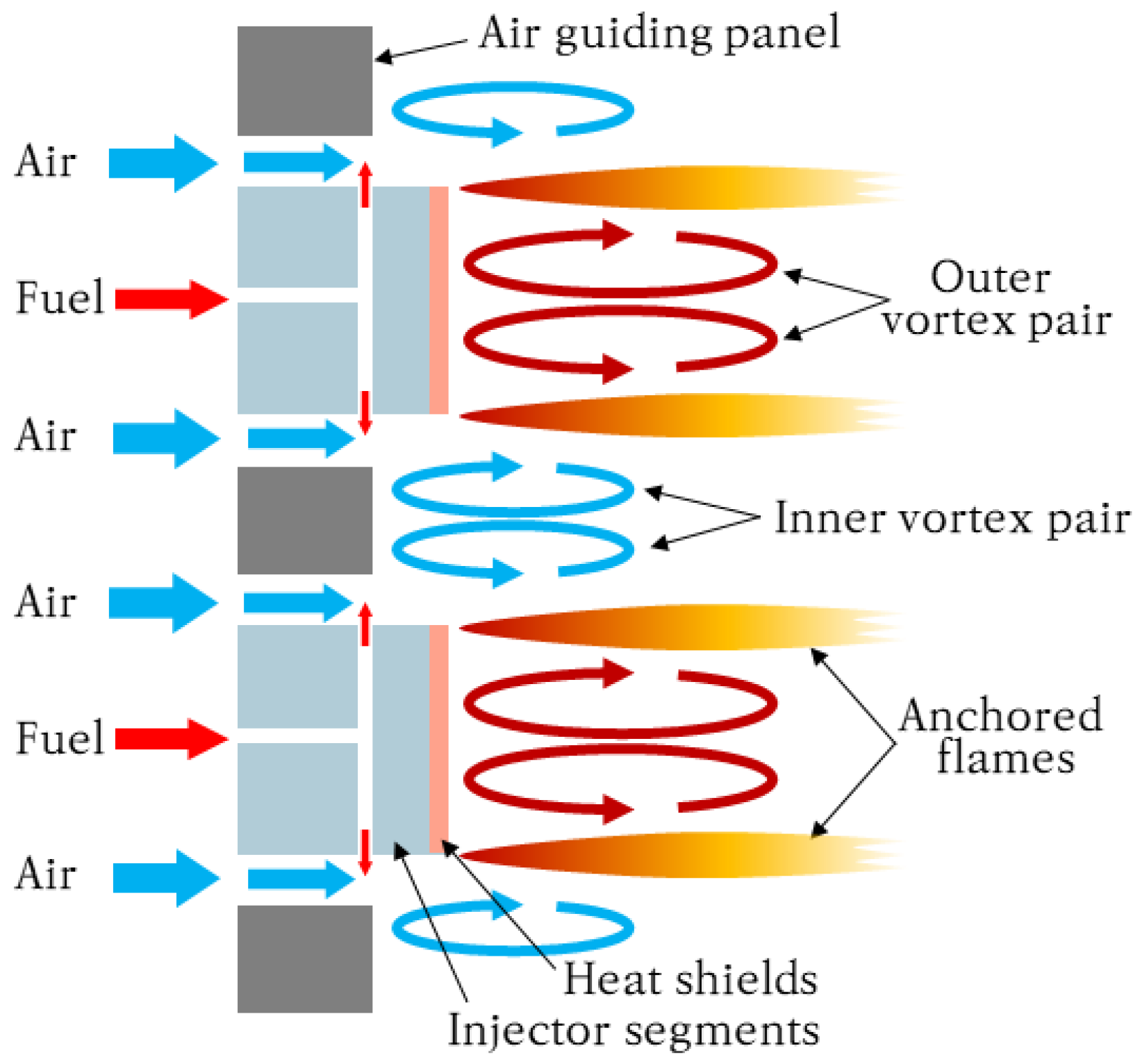
2.2. Principles of Micromix Combustion
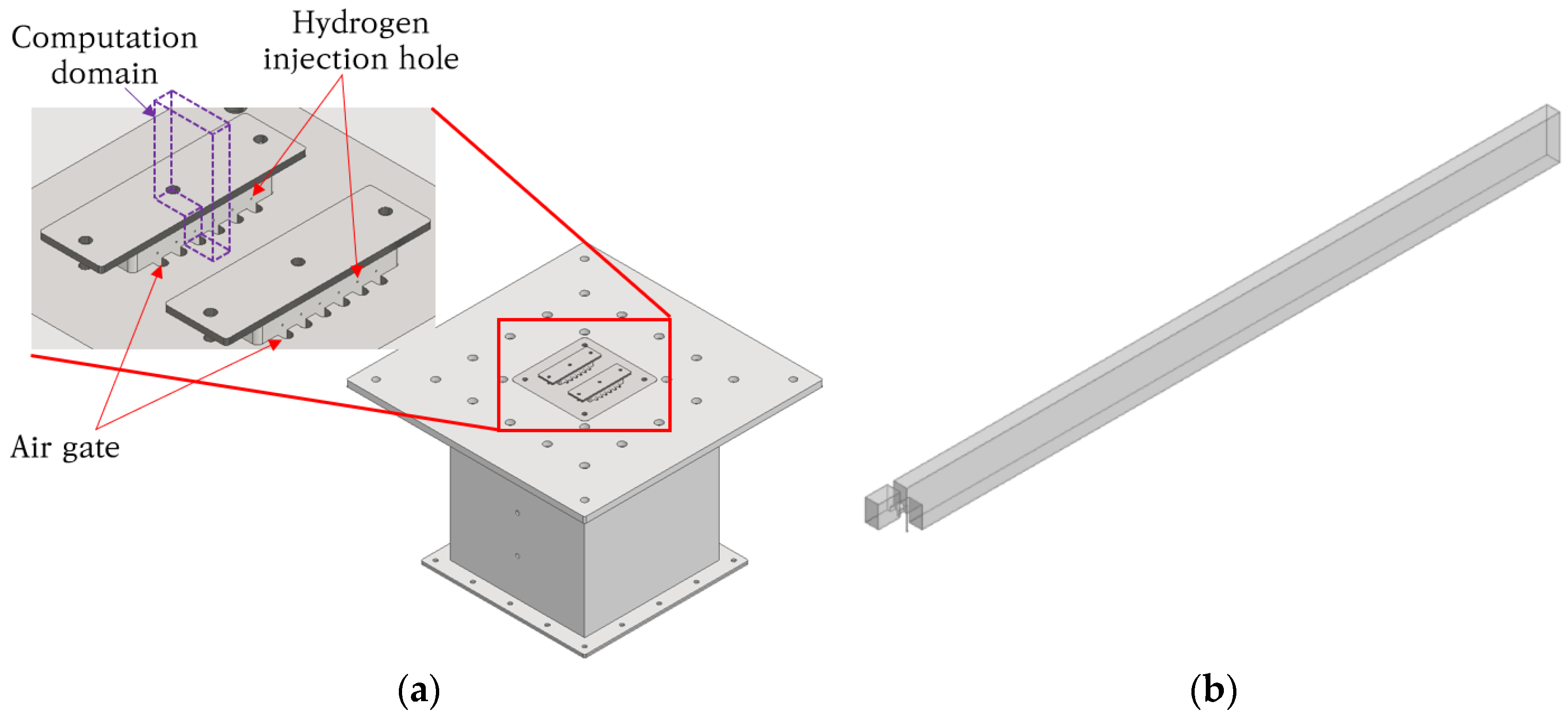
2.3. Micromix Combustor Geometry
2.4. Governing Equations and Numerical Model
2.5. Boundary Conditions and Operating Ranges for Numerical Analysis
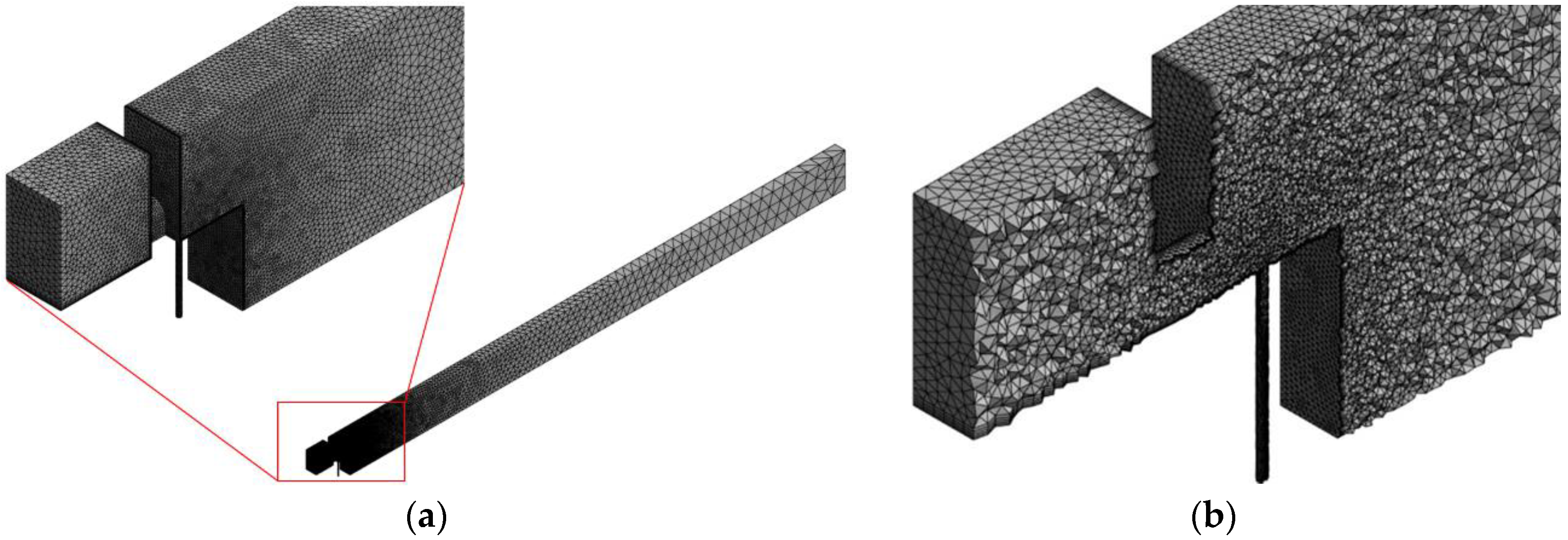
2.6. Mesh Generation Setup
3. Results and Discussion
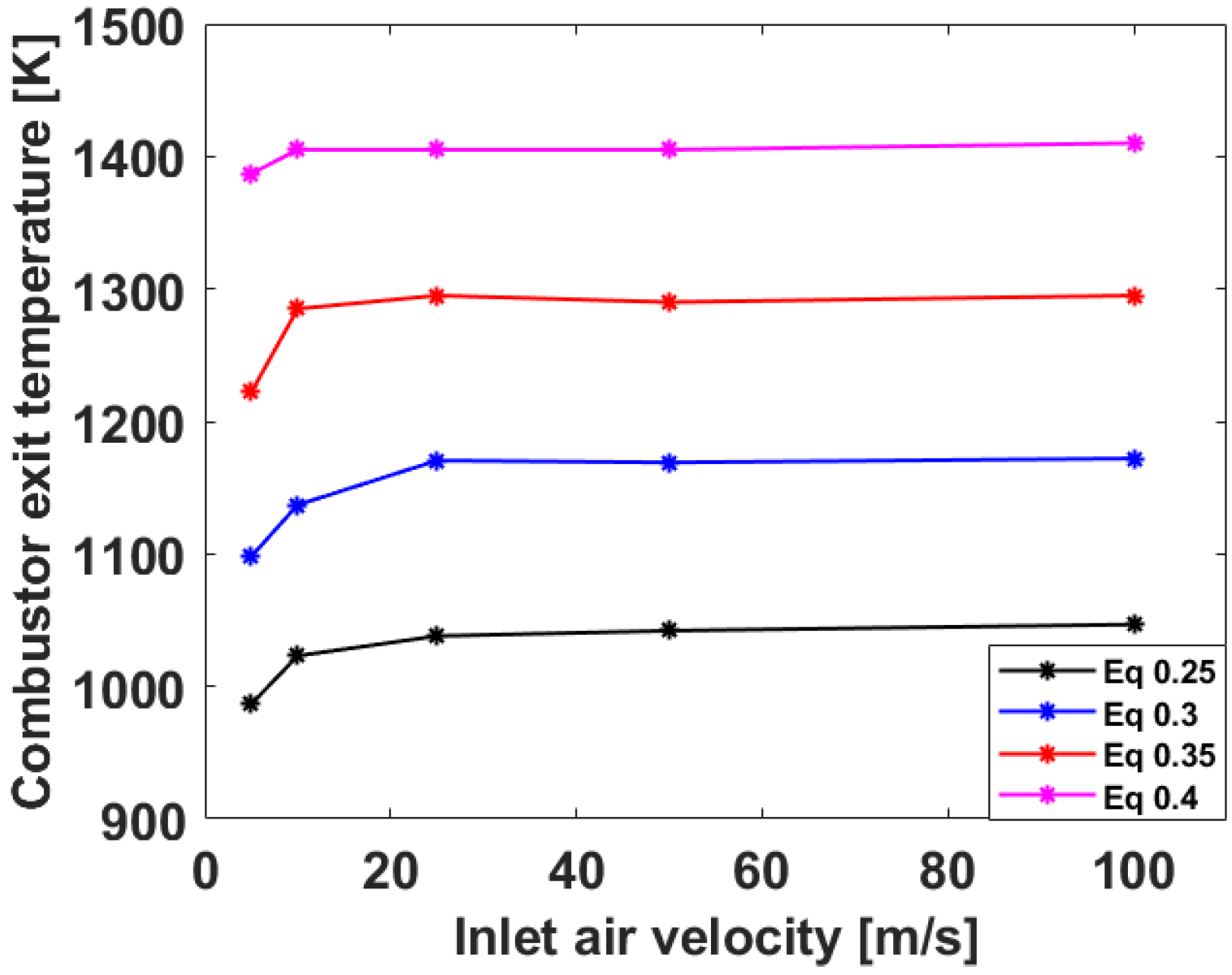
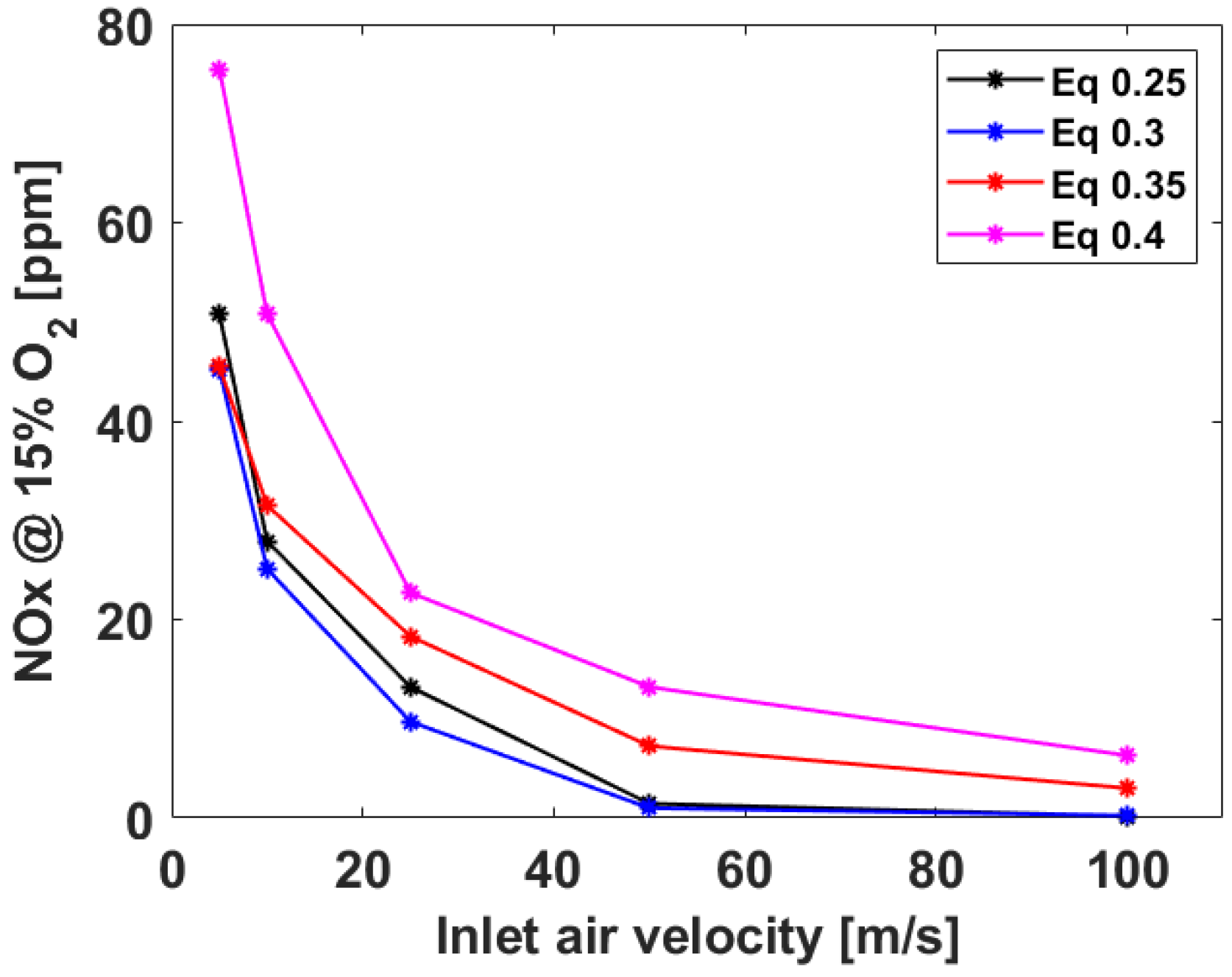
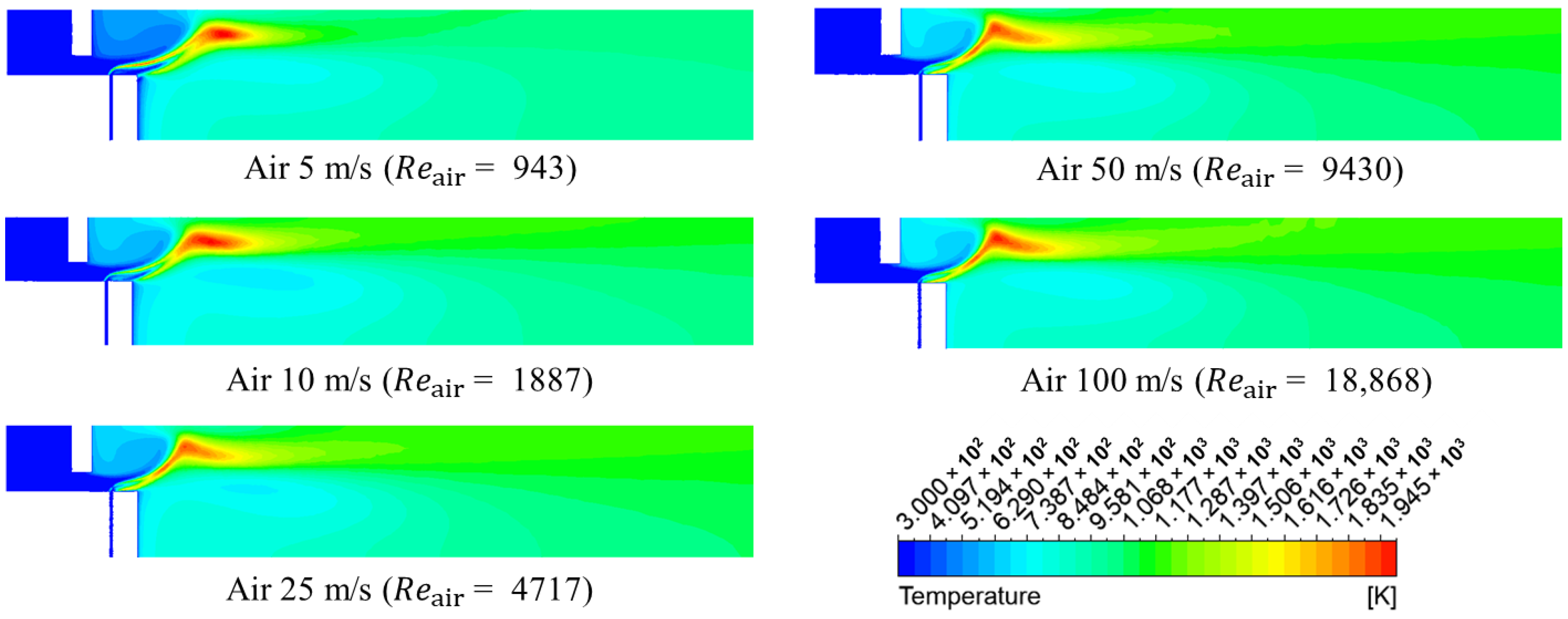
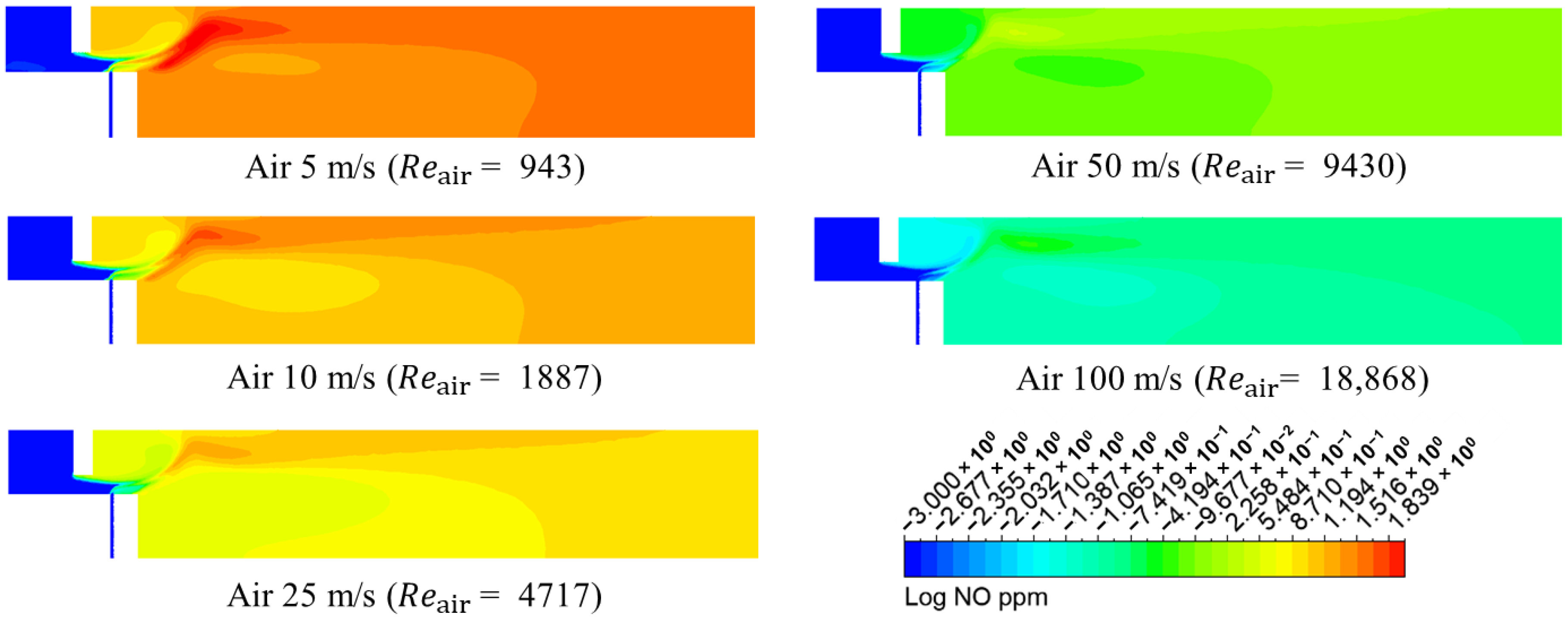
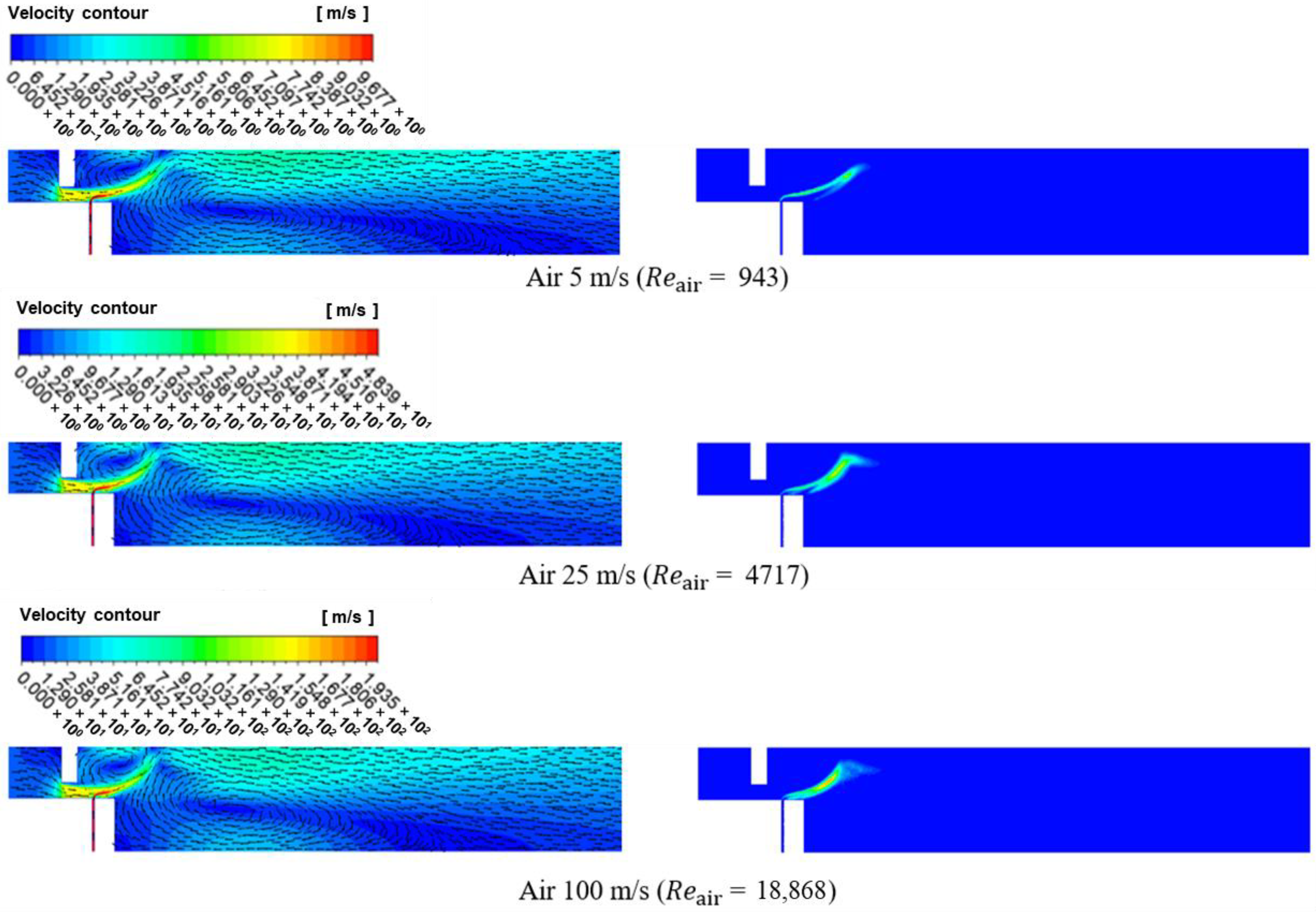
3.1. Numerical Analysis Results According to Air Flow Rate Changes
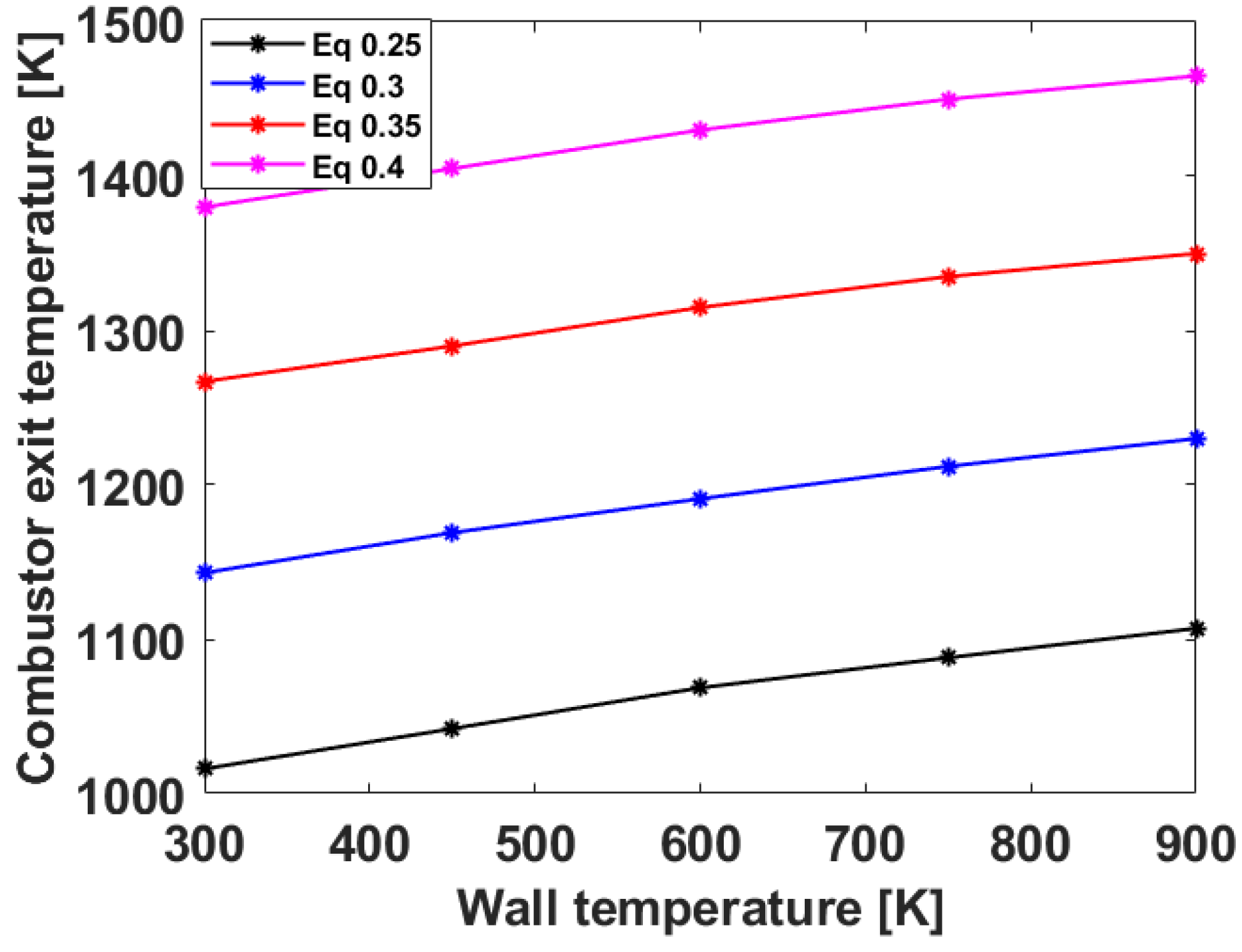
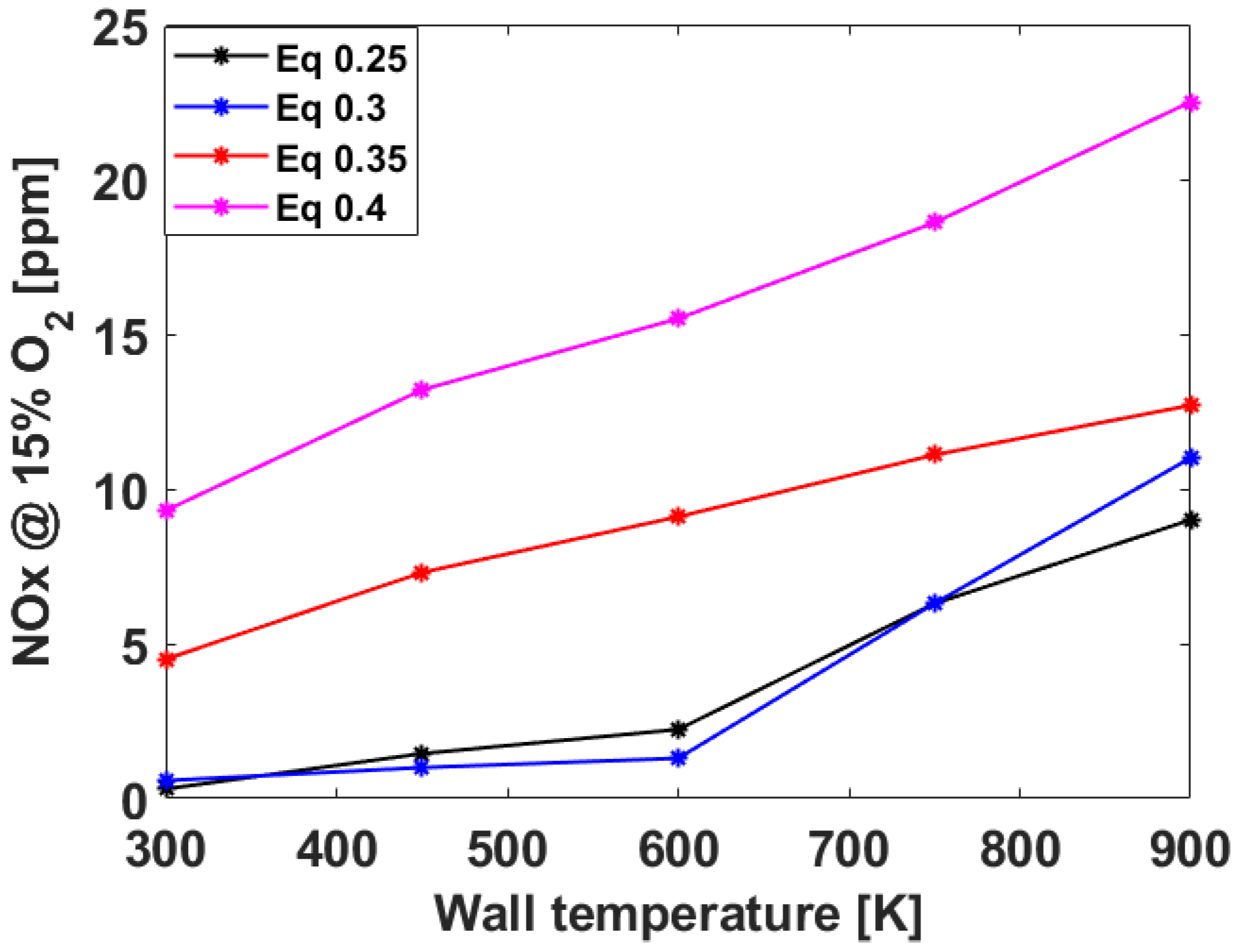
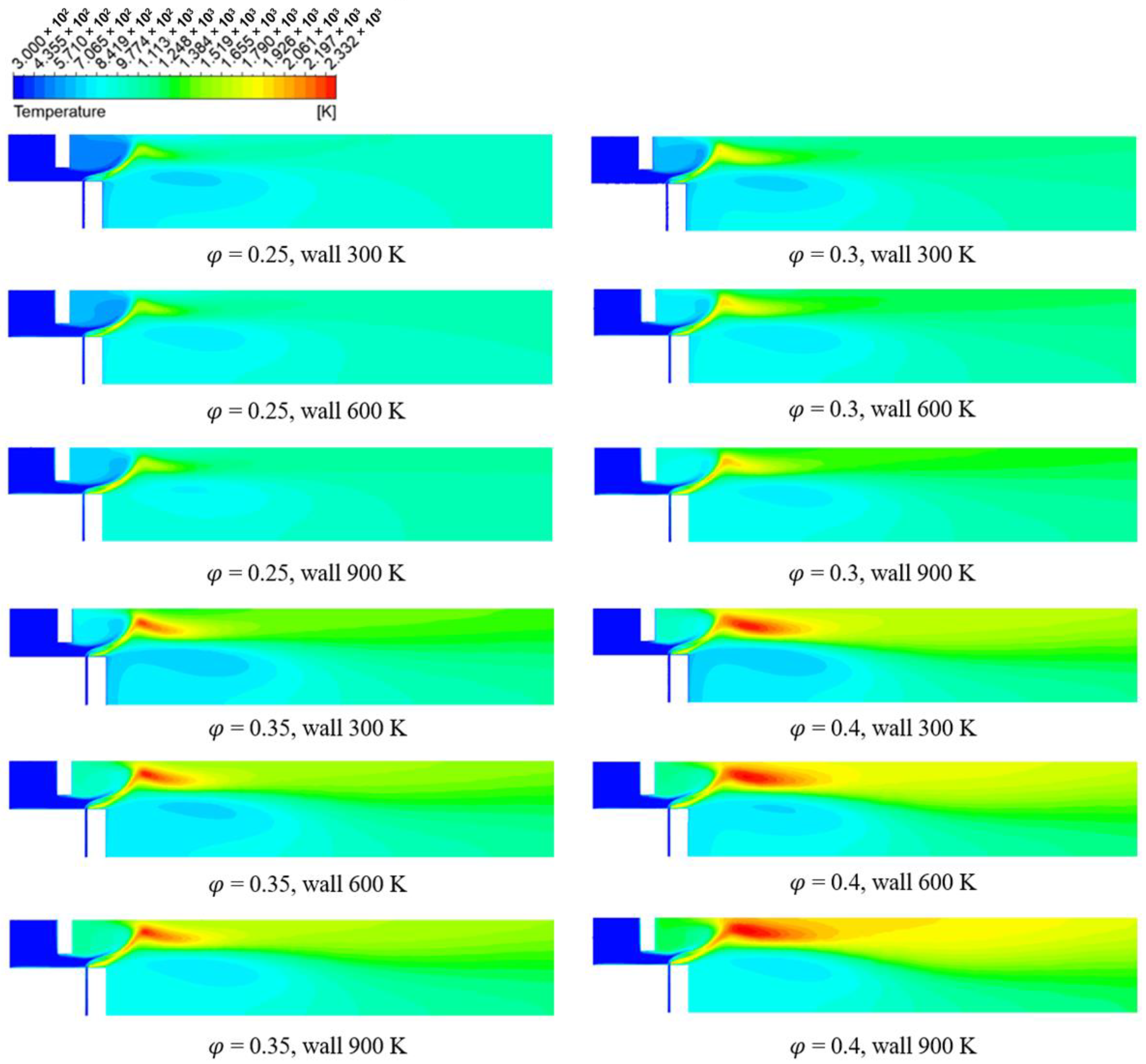
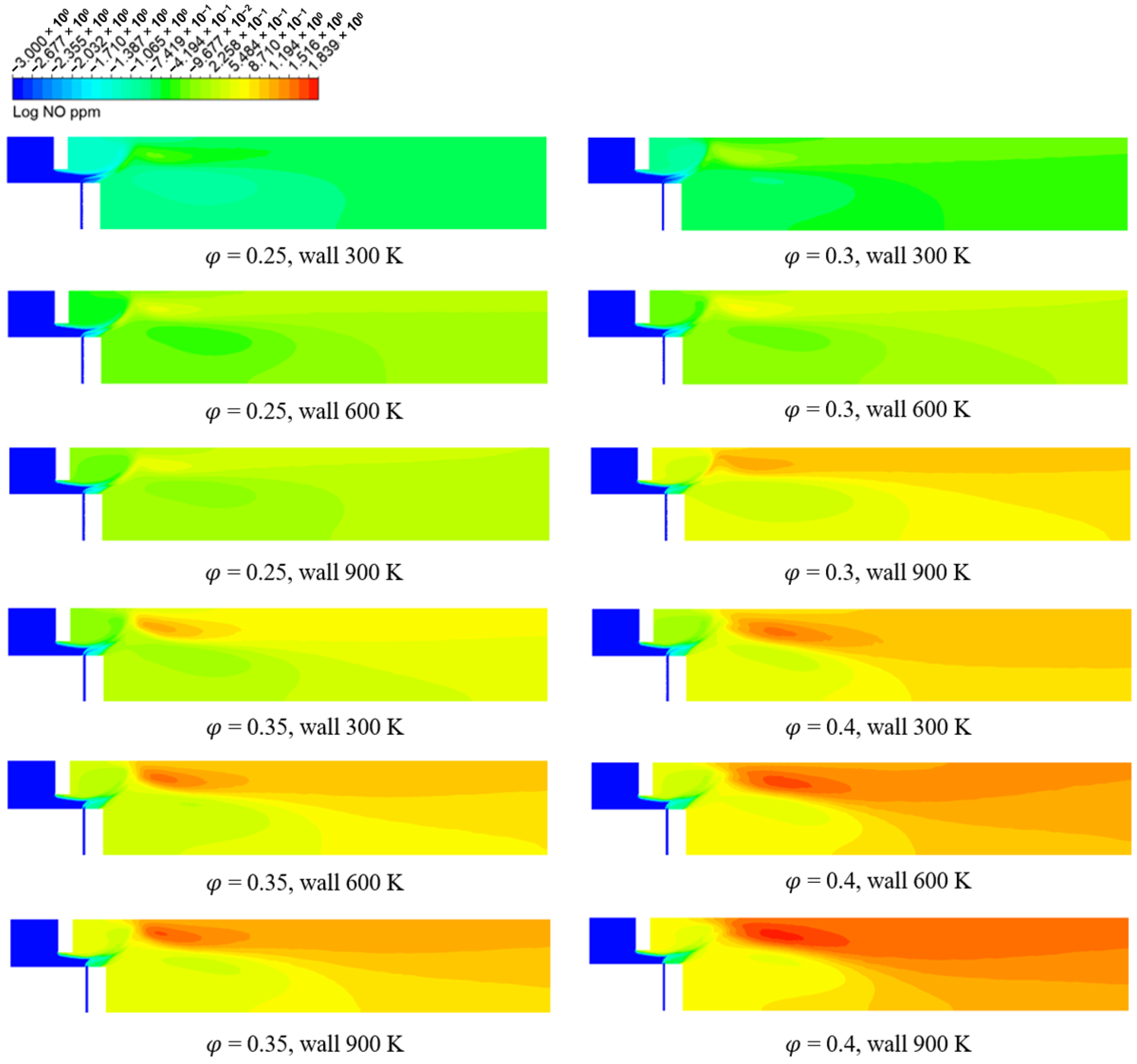
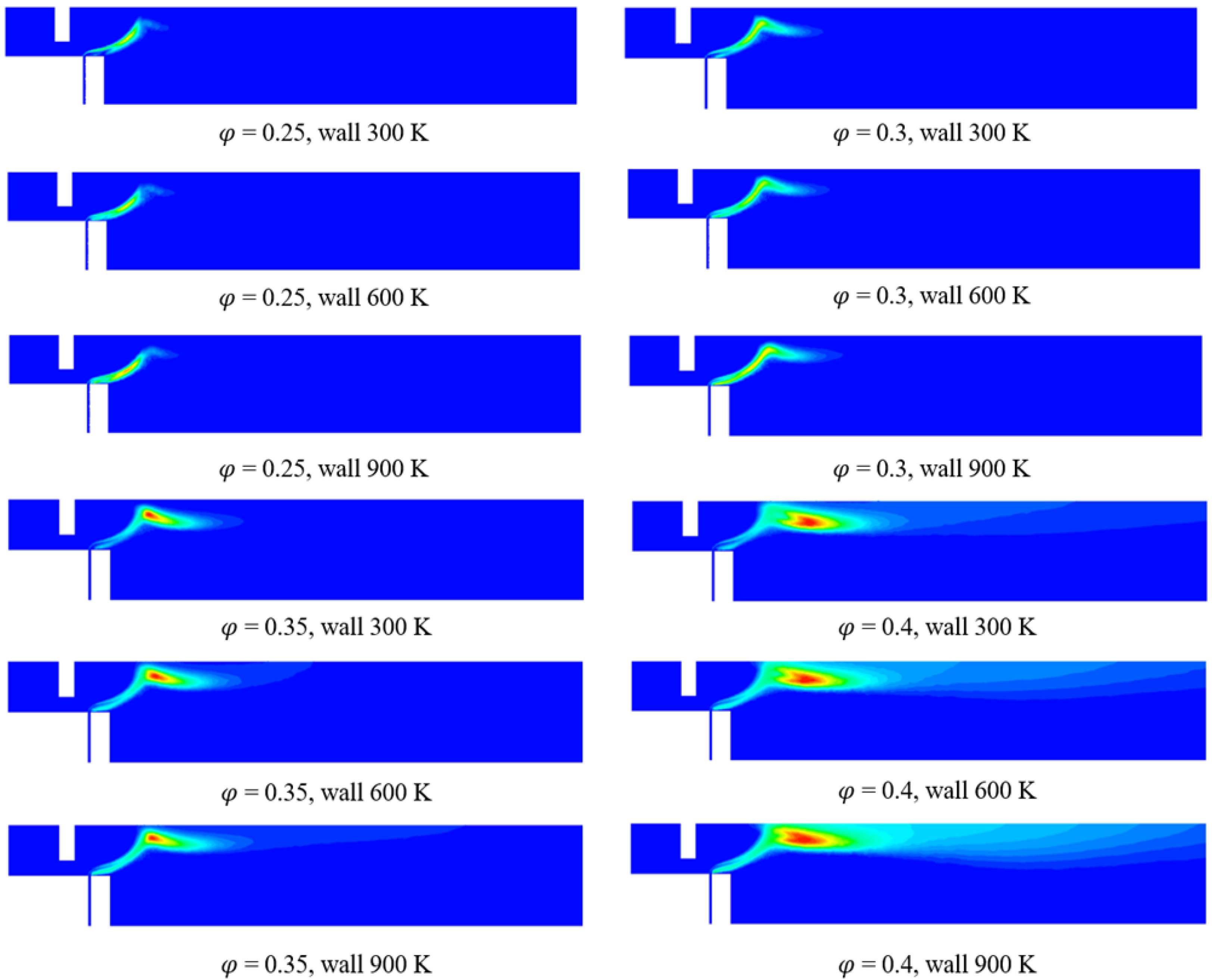
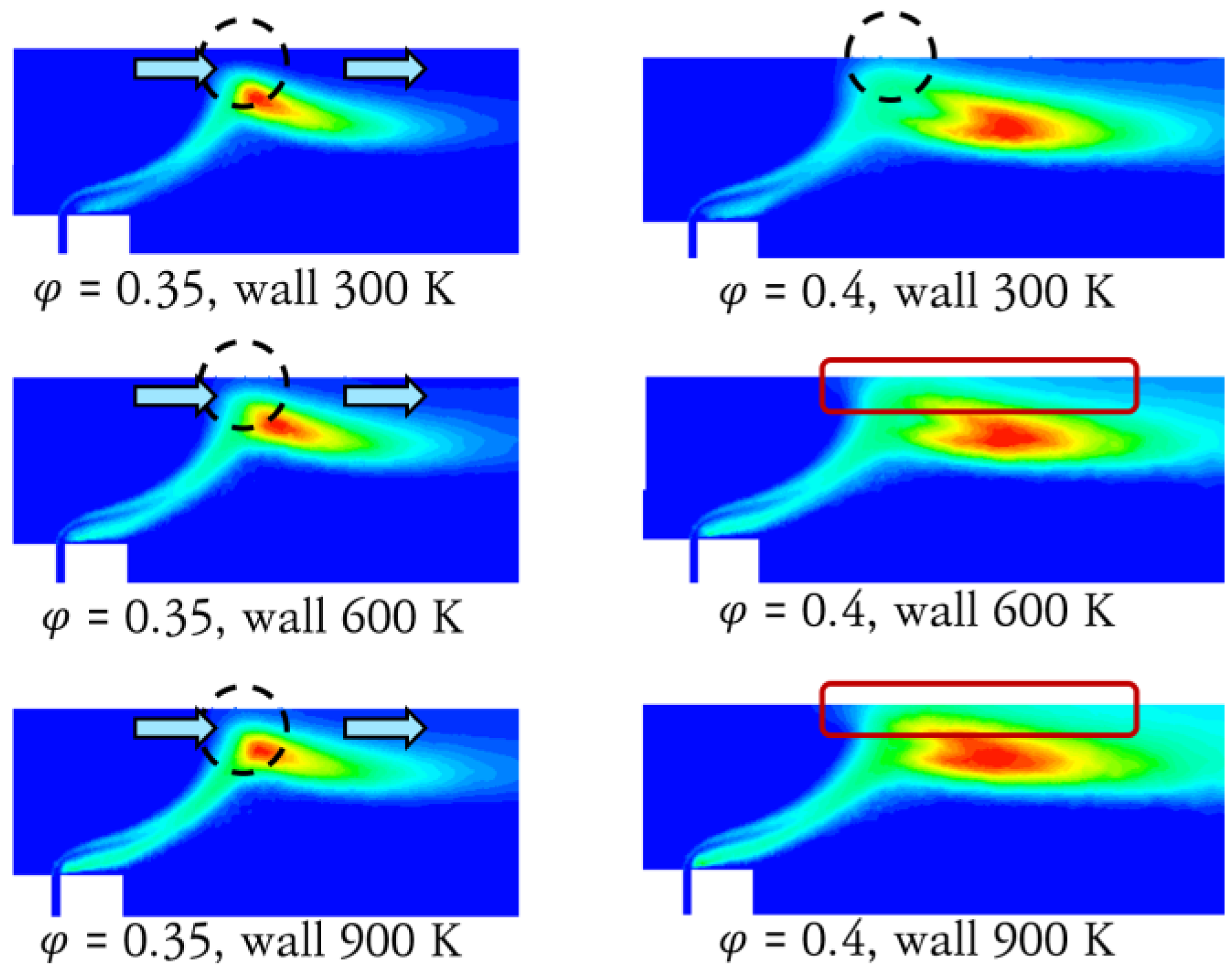
3.2. Numerical Analysis Results According to Equivalence Ratio and Surface Temperature Change of Combustor Parts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Lee, T. A Case Study on the Use of Low-Carbon Energy for Korean Energy Policy; Korea Energy Economics Institute Regular Research Report: Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 2021; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ock, S.; Kim, M.; Park, S. Development of a 30 kW Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustor for Research. J. Aerosp. Syst. Eng. 2023, 17, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fumey, B.; Buetler, T.; Vogt, U.F. Ultra-Low NOx Emissions from Catalytic Hydrogen Combustion. Appl. Energy 2018, 213, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Agarwal, P.; Carbonara, F.; Abbott, D.; Gauthier, P.; Sethi, B. Numerical Investigation into the Impact of Injector Geometrical Design Parameters on Hydrogen Micromix Combustion Characteristics. In Volume 3: Ceramics; Coal, Biomass, Hydrogen, and Alternative Fuels, Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2020: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Virtual, Online, 21 September 2020; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: London, UK, 2020; p. V003T03A015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. Review on the Development Trend of Hydrogen Gas Turbine Combustion Technology. JKSC 2019, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Choi, C.; Jeong, H.; Jo, S.; Cho, E.-S. Study on Combustion Characteristics of Multi-tube H2 Nozzles. JKSC 2023, 28, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Park, H.; Kim, S. Hydrogen Combustion Gas Turbine of Hanwha Aerospace; Korean Society for Fluid Machinery: Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, 2021; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D. Hydrogen Turbine Combustion Technology. J. KSME 2022, 62, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, G.; Suttrop, F. Engine Control and Low- NOx Combustion for Hydrogen Fuelled Aircraft Gas Turbines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj Ayed, A.; Kusterer, K.; Funke, H.H.-W.; Keinz, J.; Striegan, C.; Bohn, D. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Dry-Low-NOx Hydrogen Micromix Combustion Chamber of an Industrial Gas Turbine. Propuls. Power Res. 2015, 4, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj Ayed, A.; Kusterer, K.; Funke, H.H.-W.; Keinz, J.; Bohn, D. CFD Based Exploration of the Dry-Low-NOx Hydrogen Micromix Combustion Technology at Increased Energy Densities. Propuls. Power Res. 2017, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj Ayed, A. Numerical Characterization and Development of the Dry Low NOx High Hydrogen Content Fuel Micromix Combustion for Gas Turbine Applications. Ph.D. Dissertation, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Funke, H.H.-W.; Beckmann, N.; Abanteriba, S. An Overview on Dry Low NOx Micromix Combustor Development for Hydrogen-Rich Gas Turbine Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 6978–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouloudis, A.; Sun, X.; Corsar, M.R.; Booden, S.J.; Singh, G.; Abbott, D.; Nalianda, D.; Sethi, B. On the Development of an Experimental Rig for Hydrogen Micromix Combustion Testing. In Proceedings of the 10th European Combustion Meeting, Naples, Italy, 14–15 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Ruiz, G.; Alava, I.; Blanco, J.M. Study on the Feasibility of the Micromix Combustion Principle in Low NO H2 Burners for Domestic and Industrial Boilers: A Numerical Approach. Energy 2021, 236, 121456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zuo, W.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, G.; E, J. Numerical Investigations on the Performance of a Hydrogen-Fueled Micro Planar Combustor with V-Shaped Baffle for Thermophotovoltaic Applications. Energy 2025, 326, 136270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, D.G.; Steele, R.C.; Marinov, N.M.; Malte, P.C. The Importance of the Nitrous Oxide Pathway to NOx in Lean-Premixed Combustion. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1995, 117, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.H.; Ballal, D.R. Gas Turbine Combustion: Alternative Fuels and Emissions, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4200-8604-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tamang, S.; Park, H. A Numerical Investigation on Temperature Uniformity Factor and Thermal NOx Concentration in 1.15MW Hydrogen Combustor. J. Comput. Fluids Eng. 2023, 28, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G. Gri-Mech.—An Optimized Detailed Chemical Reaction Mechanism for Methane Combustion. 1999. Available online: http://www.me.berkeley.edu/gri_mech (accessed on 18 November 2025).
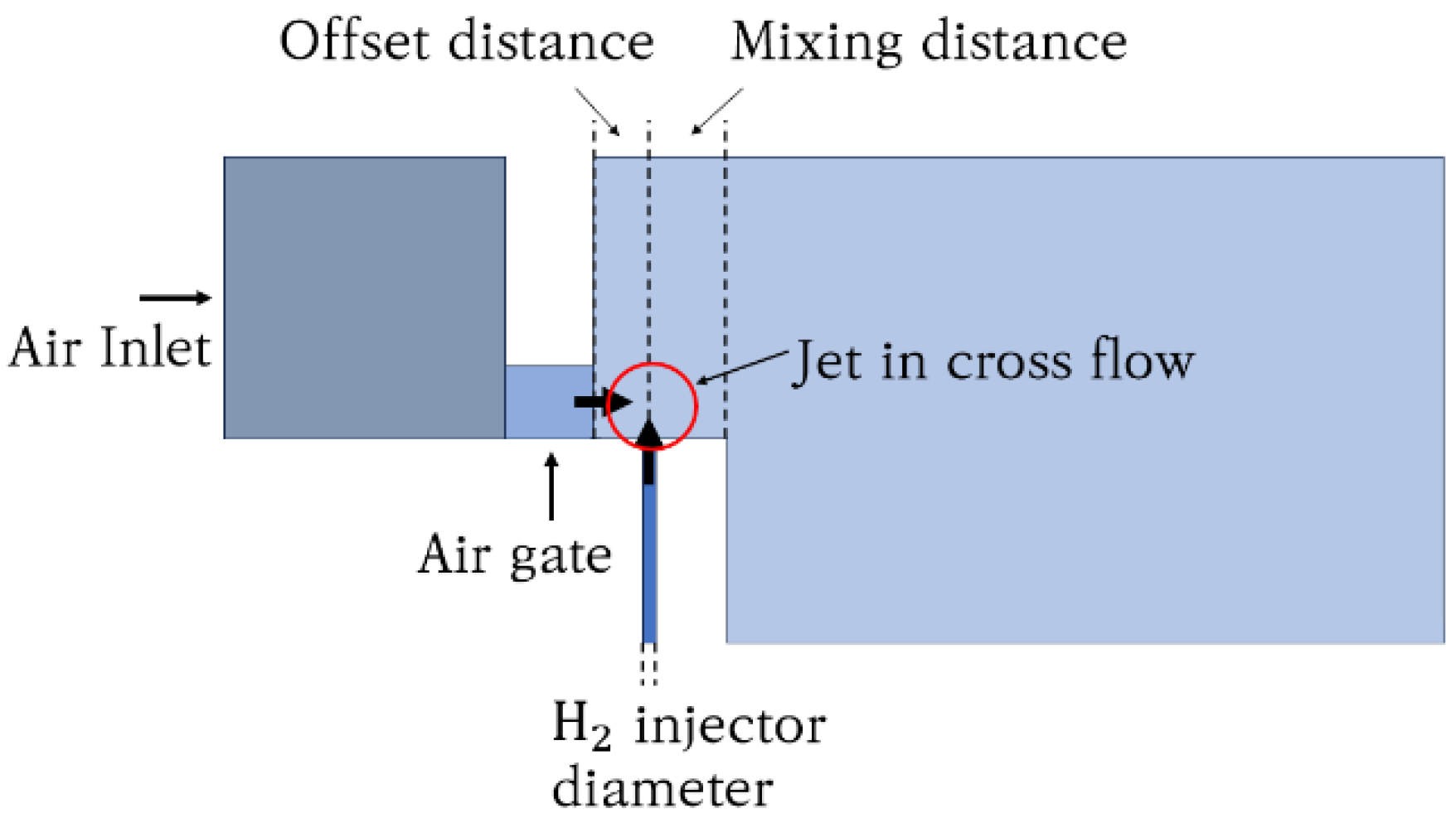
| Geometrical Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Offset distance | 3 mm |
| Mixing distance | 4 mm |
| Air gate aspect ratio | 1 |
| H2 injection hole diameter | 0.5 mm |
| Air gate area | 8.034 mm2 |
| Boundary Conditions | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| 300 K | |
| 101.325 kPa | |
| 300 K | |
| 101.325 kPa | |
| 5–100 m/s | |
| 0.0471–0.942 g/s | |
| 943–18,868 | |
| 0.000343–0.011 g/s | |
| 1.247–2.444 | |
| 0.25–0.4 | |
| 300–900 K |
(kg/s) | (kg/s) | (kg/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 0.25 | = 0.3 | = 0.35 | = 0.4 | |||
| 5 | 943 | 6.80 × 10−5 | 4.95 × 10−7 | 5.94 × 10−7 | 6.93 × 10−7 | 7.92 × 10−7 |
| 10 | 1886 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 9.89 × 10−7 | 1.19 × 10−6 | 1.39 × 10−6 | 1.58 × 10−6 |
| 25 | 4717 | 3.40 × 10−4 | 2.47 × 10−6 | 2.97 × 10−6 | 3.46 × 10−6 | 3.96 × 10−6 |
| 50 | 9434 | 6.80 × 10−4 | 4.95 × 10−6 | 5.94 × 10−6 | 6.93 × 10−6 | 7.92 × 10−6 |
| 100 | 18,868 | 1.36 × 10−3 | 9.90 × 10−6 | 1.19 × 10−5 | 1.39 × 10−5 | 1.58 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Ock, S.; Park, S. Numerical Analysis of Factors Affecting NOx Emissions in Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustors. Energies 2025, 18, 6168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236168
Kim M, Ock S, Park S. Numerical Analysis of Factors Affecting NOx Emissions in Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustors. Energies. 2025; 18(23):6168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236168
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minsu, Seojun Ock, and Suhyeon Park. 2025. "Numerical Analysis of Factors Affecting NOx Emissions in Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustors" Energies 18, no. 23: 6168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236168
APA StyleKim, M., Ock, S., & Park, S. (2025). Numerical Analysis of Factors Affecting NOx Emissions in Hydrogen-Fueled Micromix Combustors. Energies, 18(23), 6168. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236168







