Comparative Experimental Analysis of Wet-State Thermal Performance in Pipe Mineral Wool Insulation with Different Hydrophobic Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Thermal Conductivity of Mineral Wool in Moist Conditions
1.2. Thermal Conductivity of Mineral Wool Pipe Insulations
1.3. Effects of the Quality Mineral Wool on the Insulation Thermal Performance
2. Material Selection and Characterization
3. Thermal Conductivity Measurements
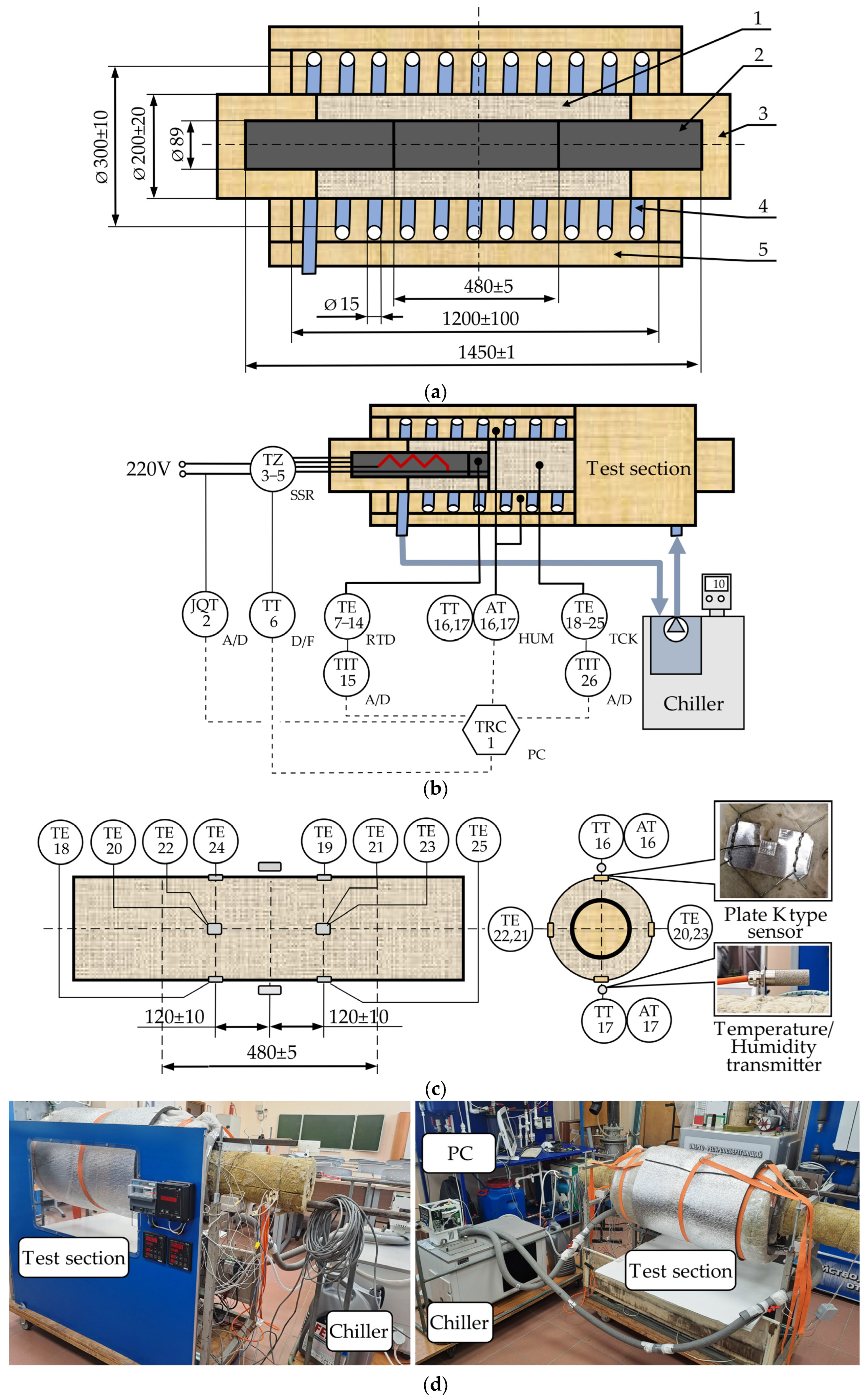
3.1. Experimental Setup
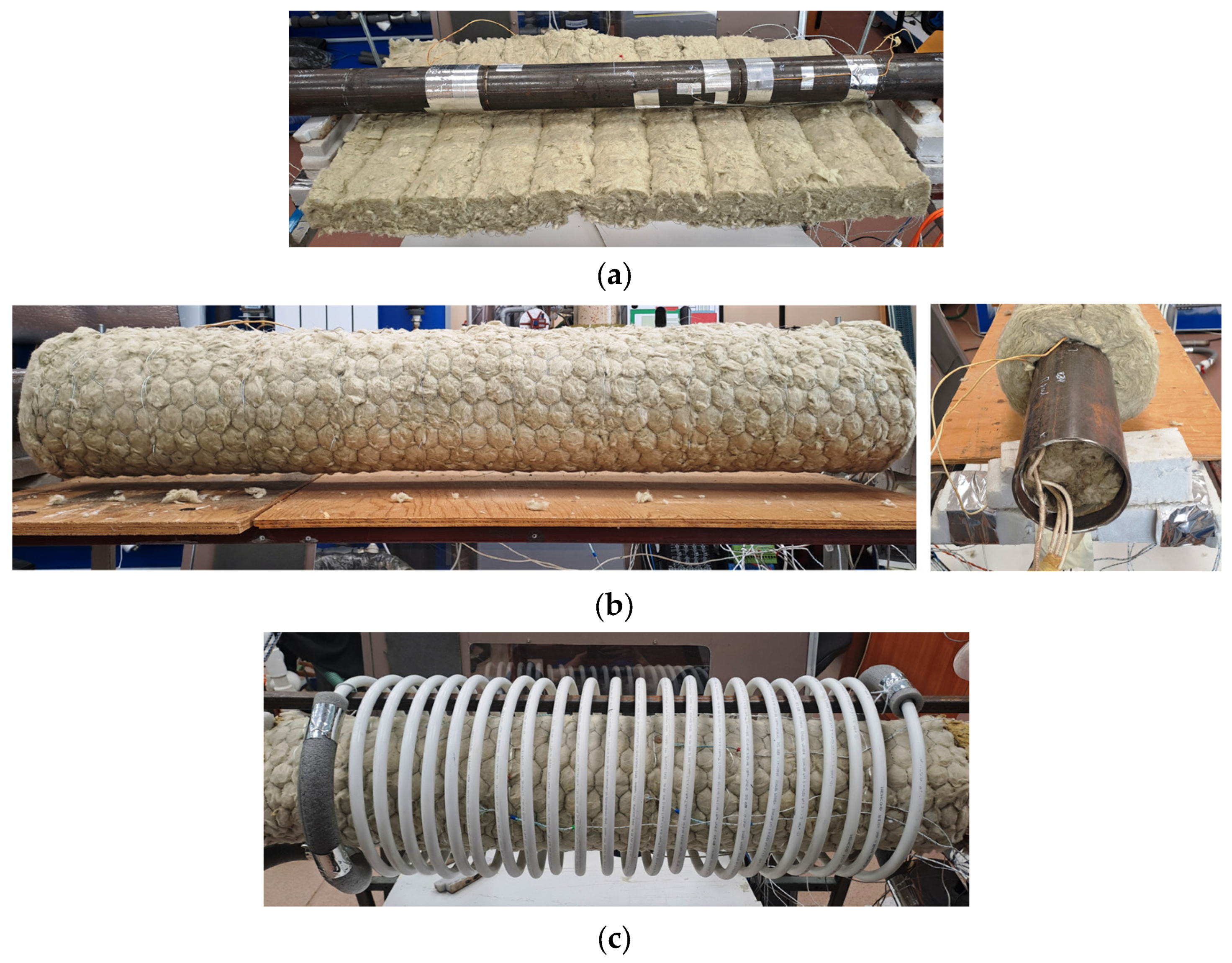
3.2. Sample and Test Rig Preparation
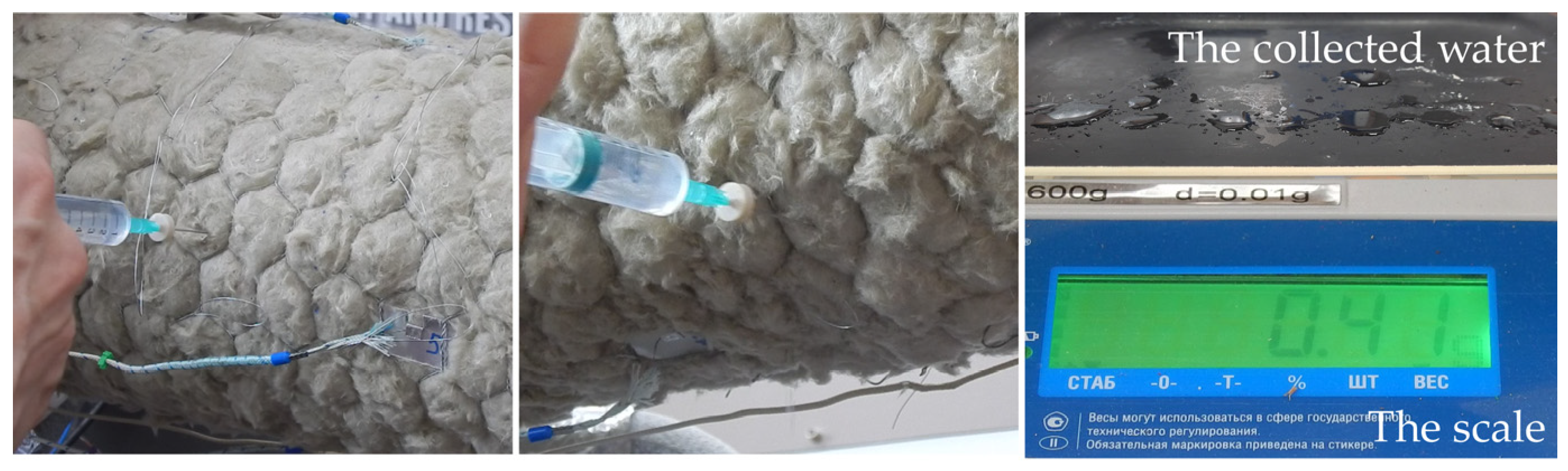
3.3. Moisture Ingress Protocol
3.4. Measurement Procedure
3.5. Uncertainty Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
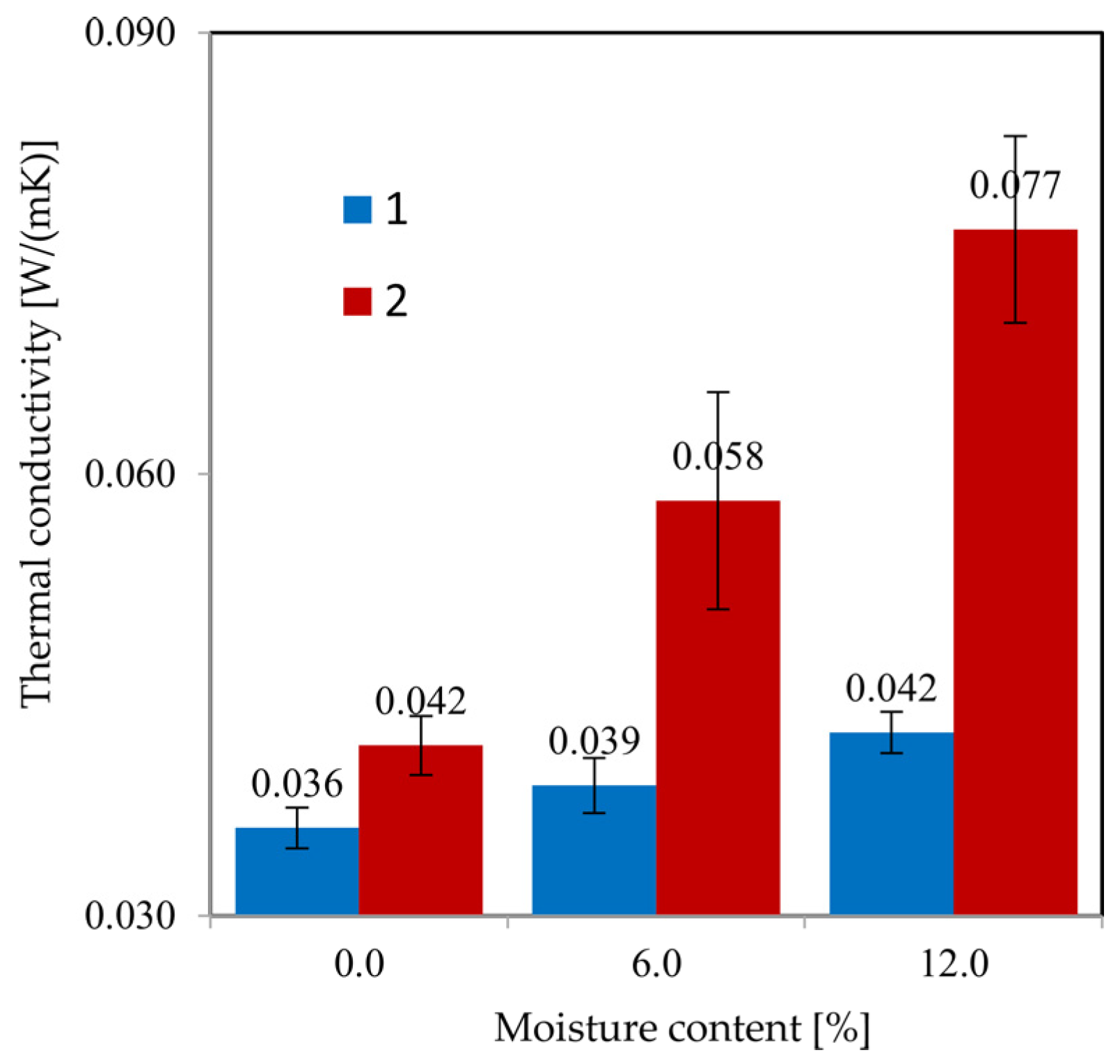
4.1. Results of Material Selection
4.2. The Aim and Constraints of the Thermal Conductivity Measurement
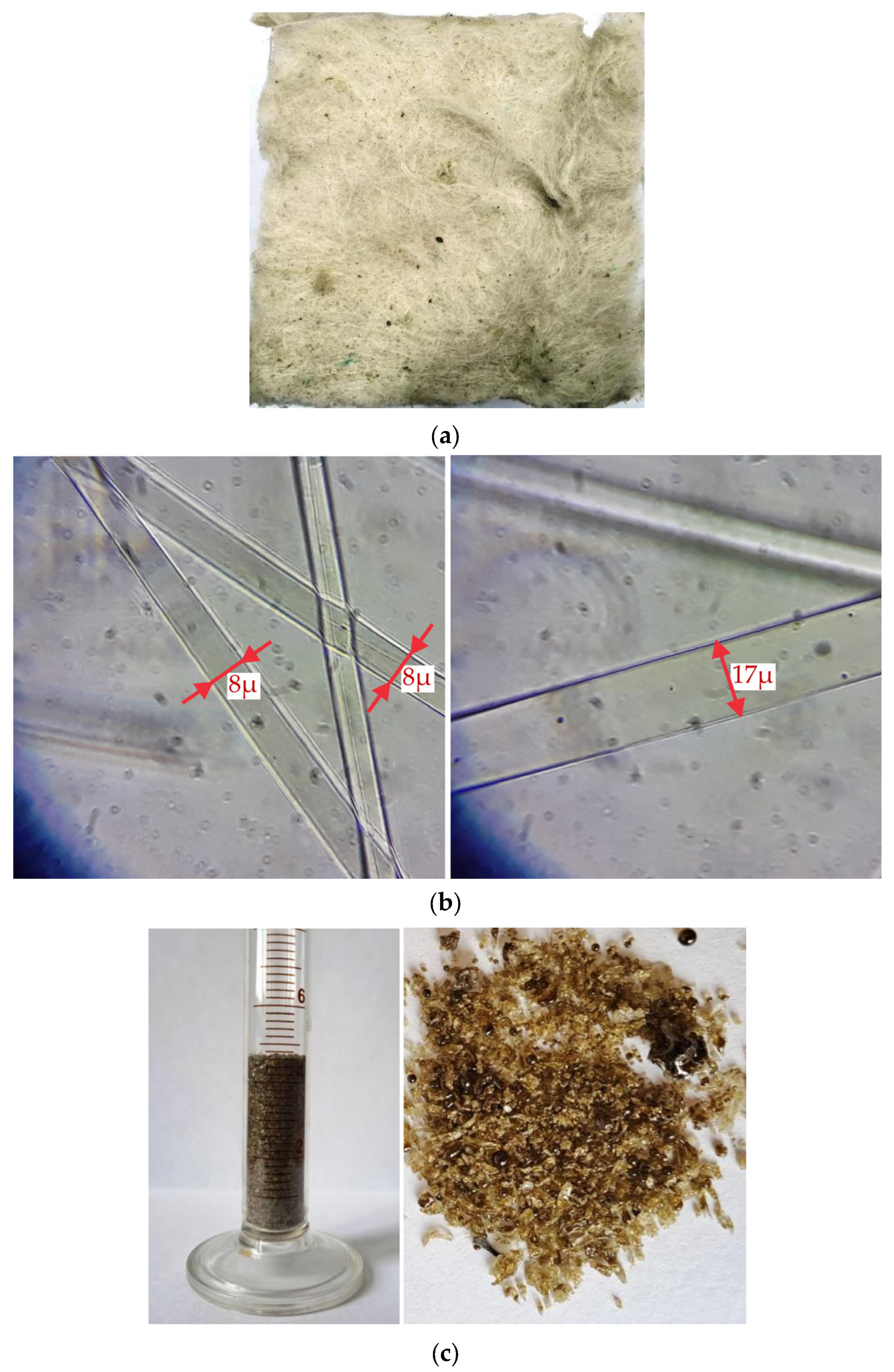
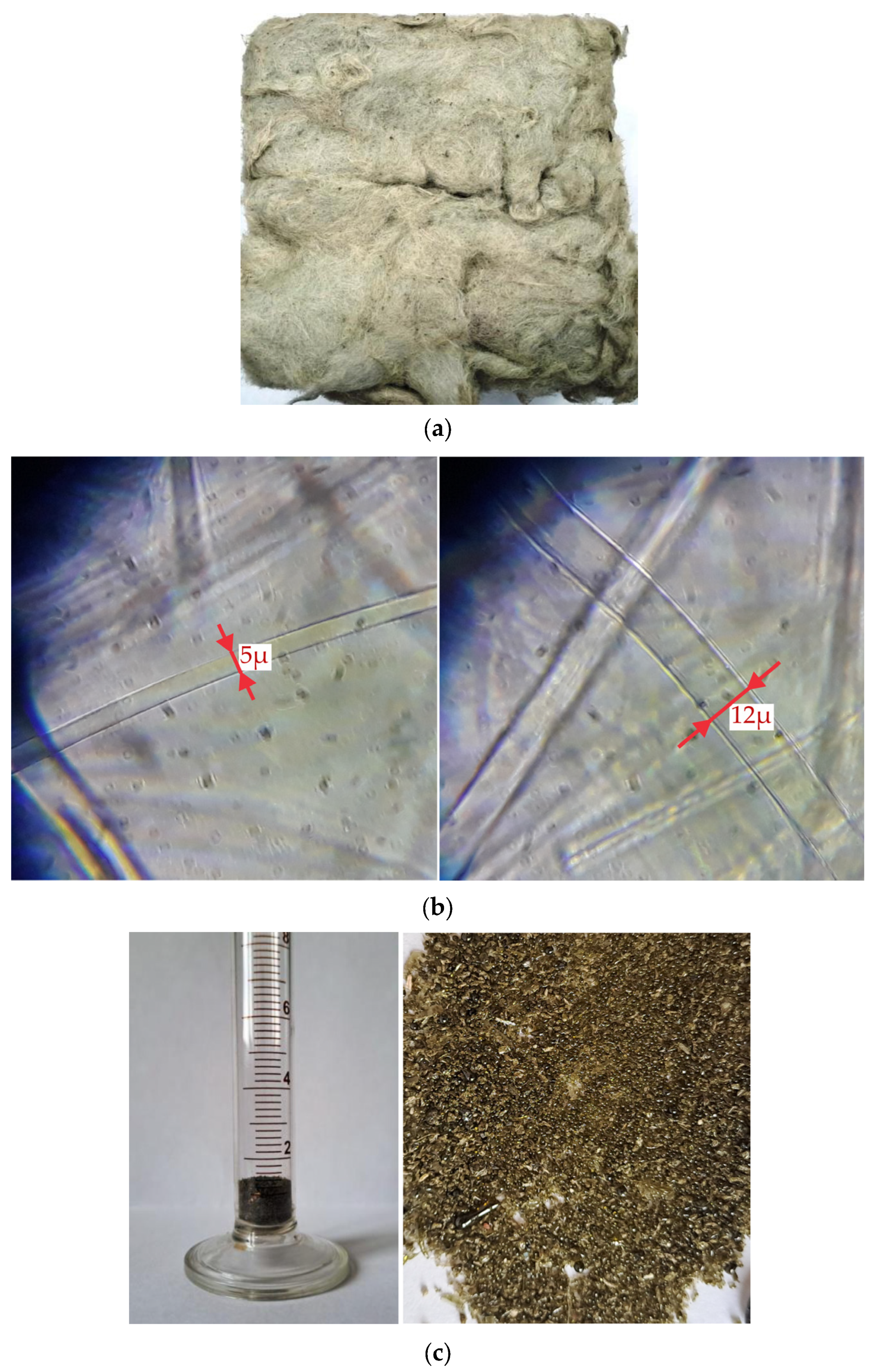
4.3. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Samples
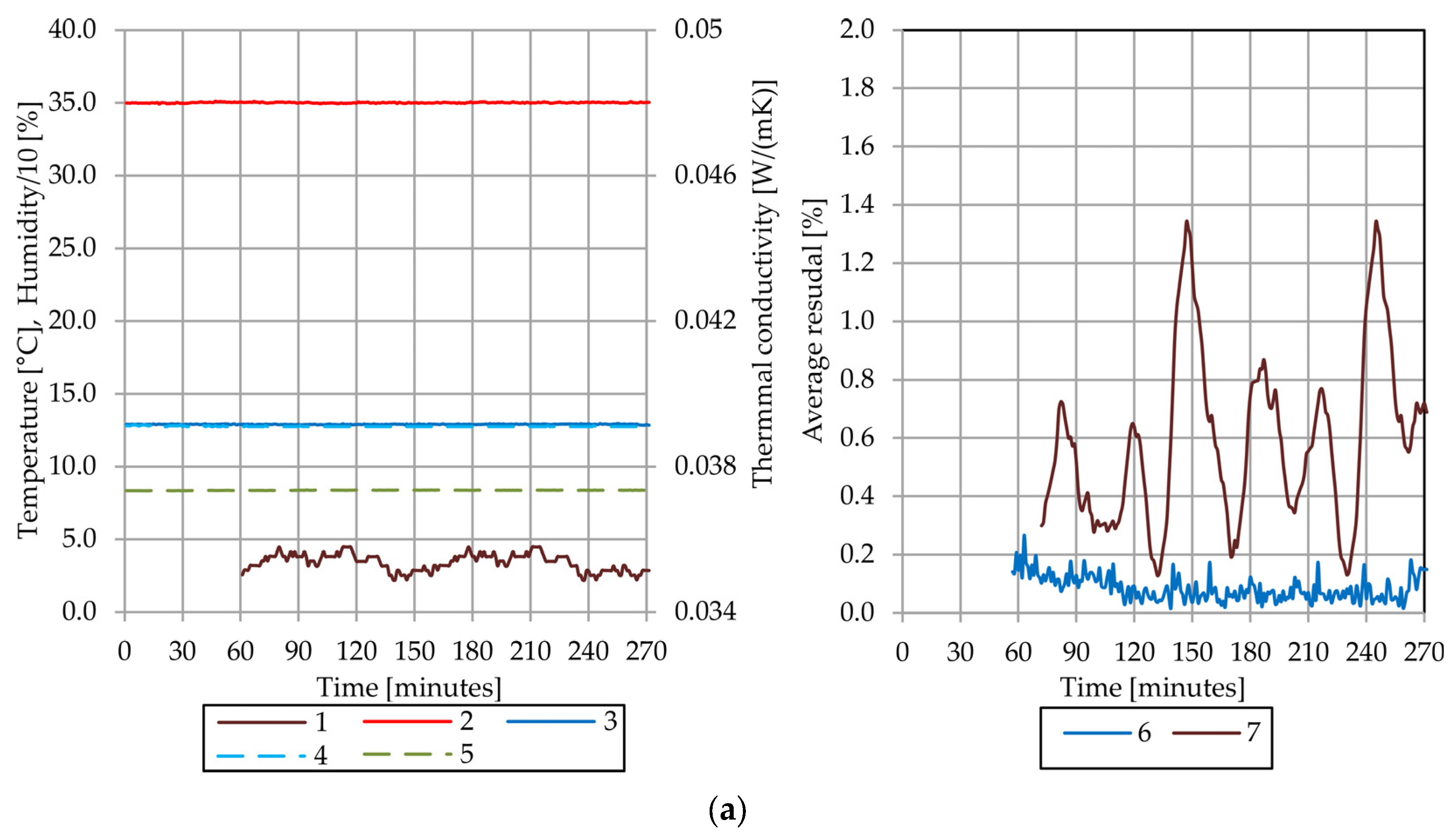
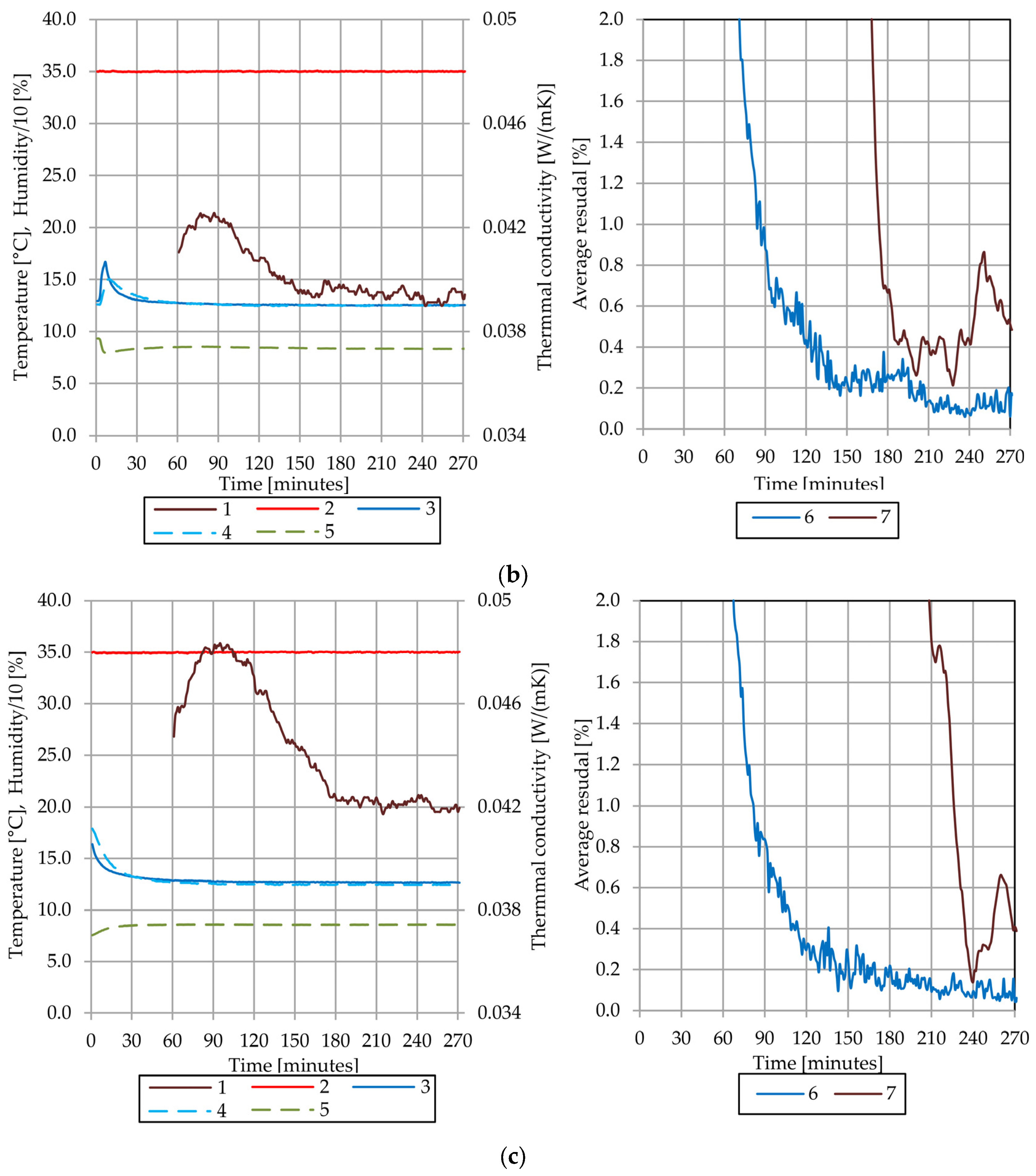
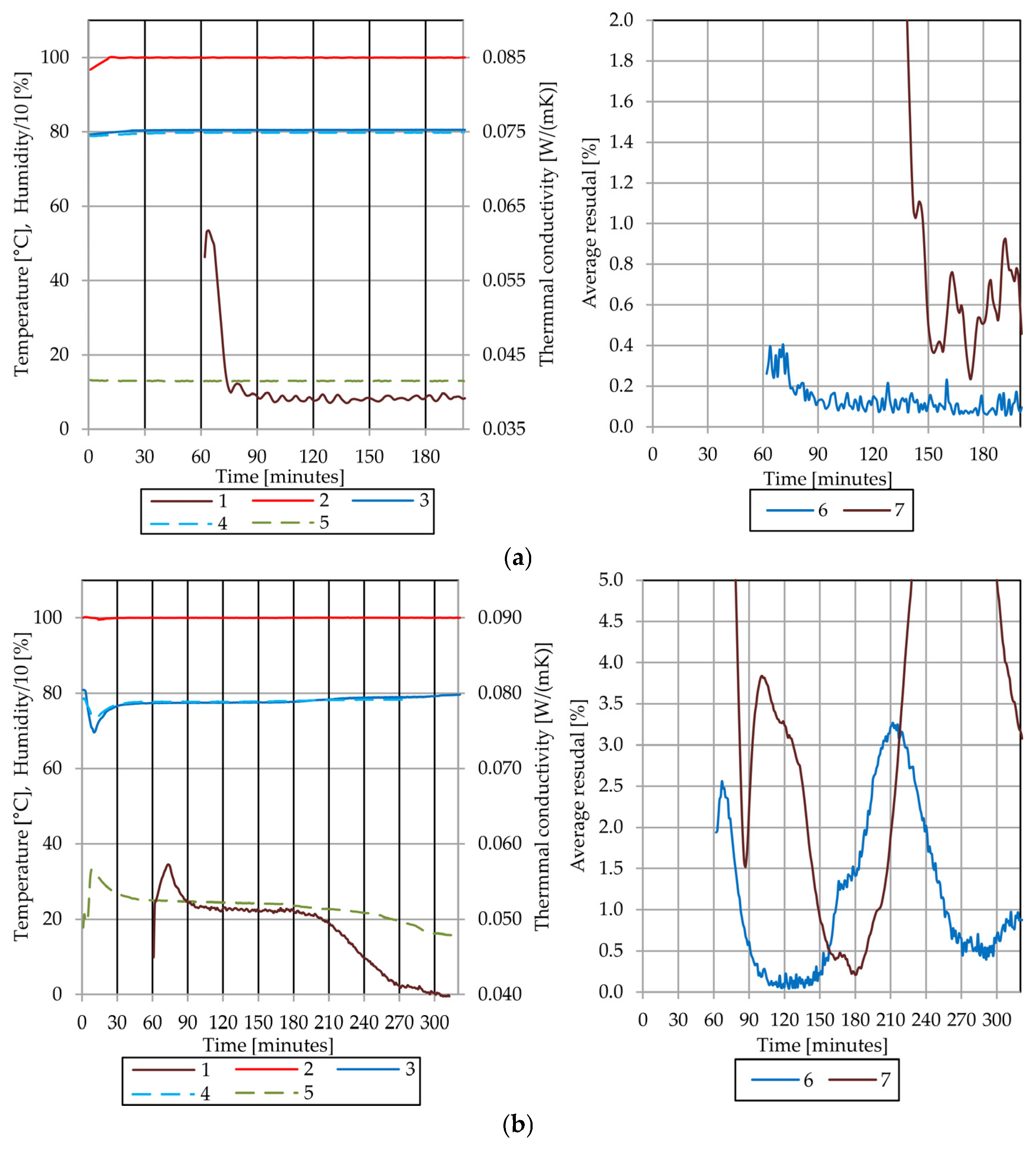
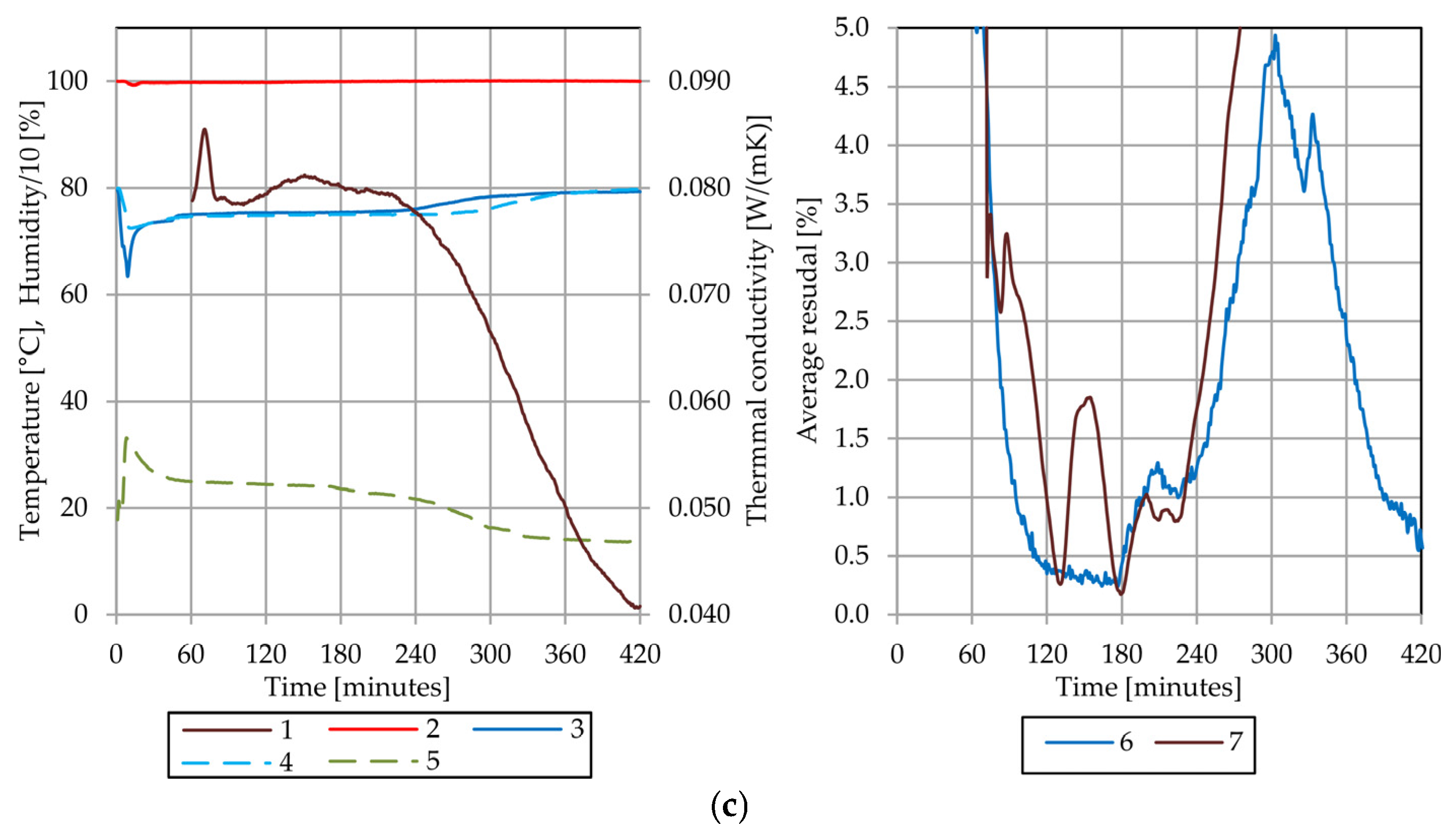
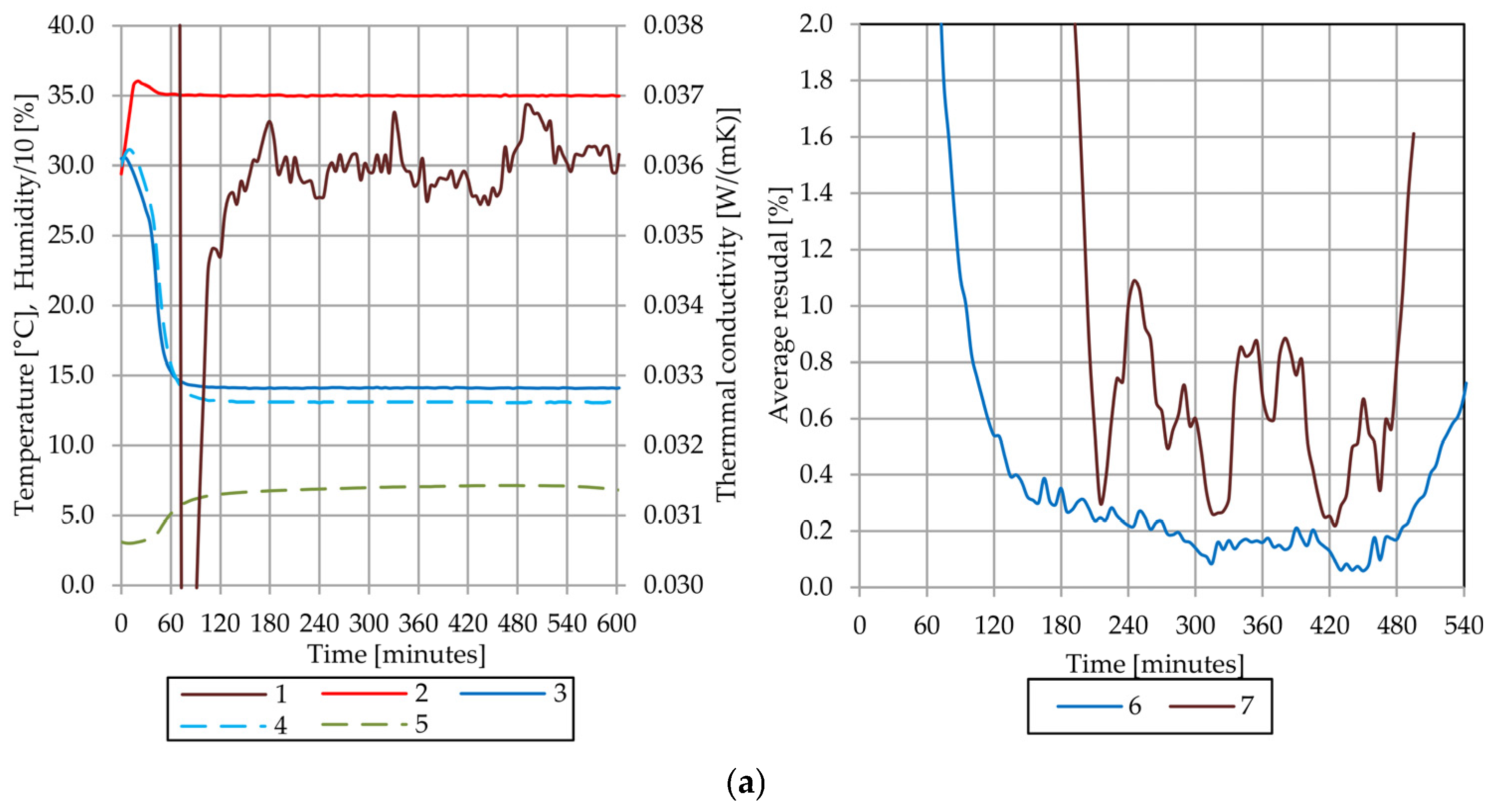
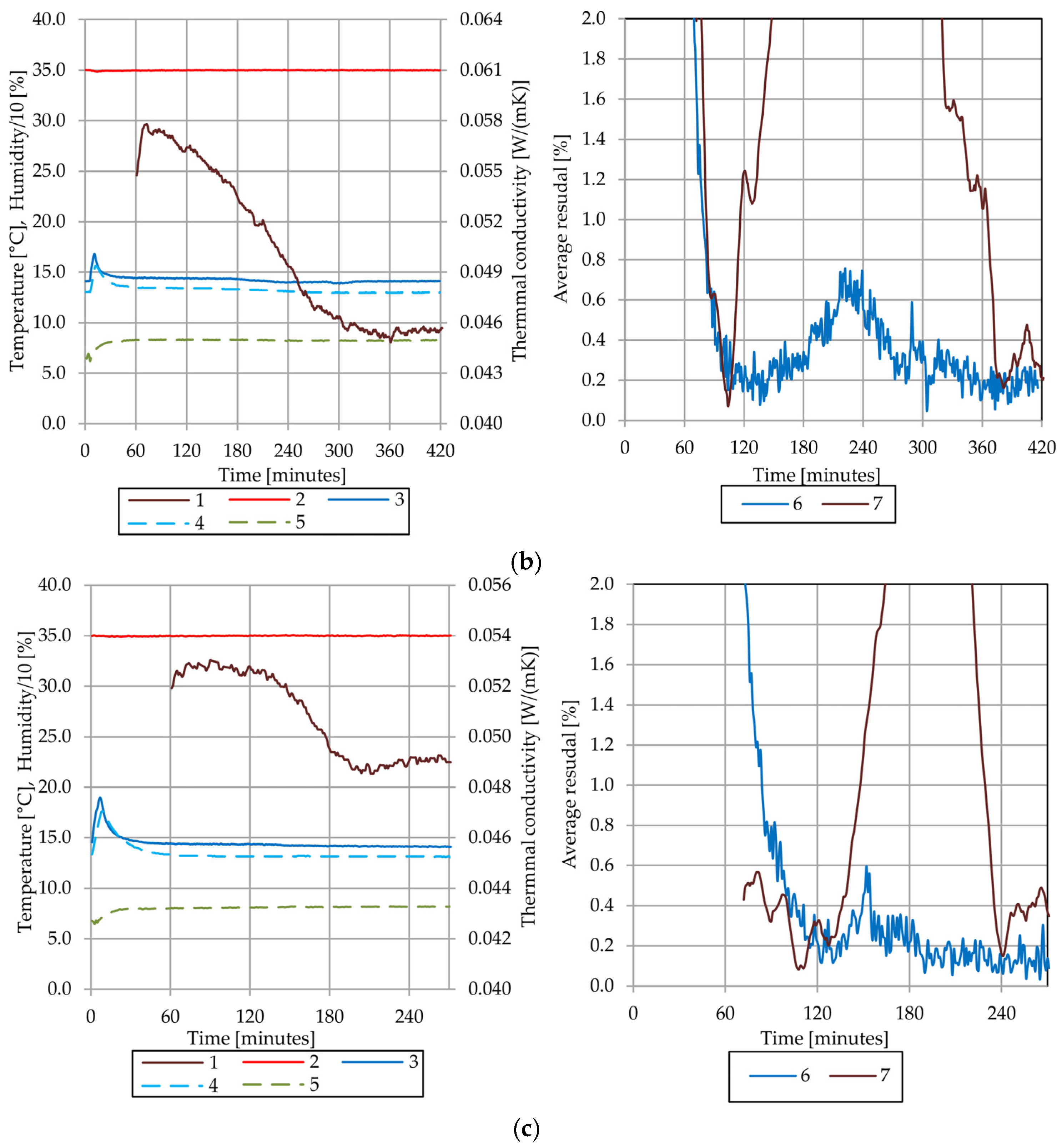
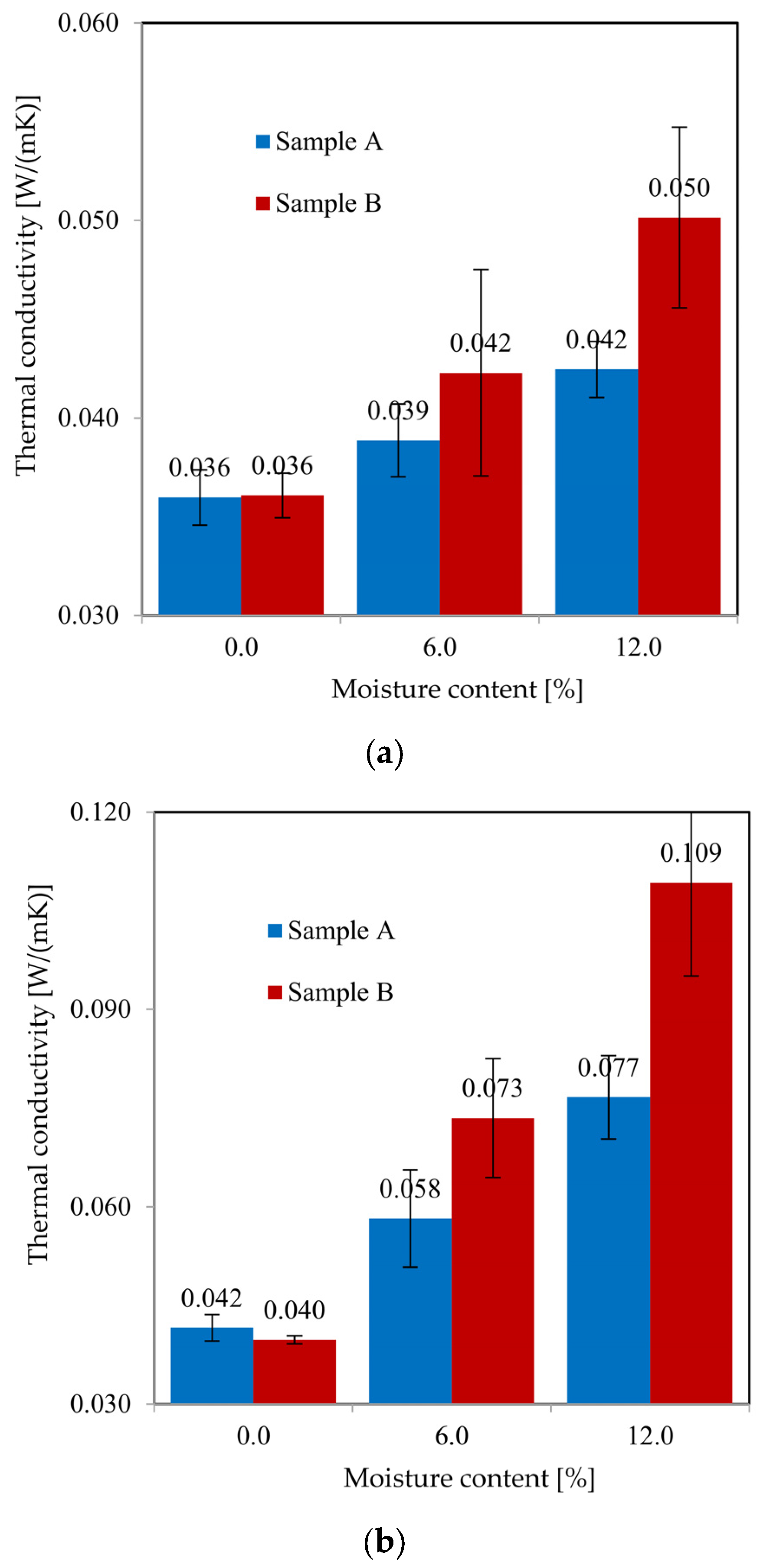
4.4. Results of the Thermal Conductivity Test of the Sample A
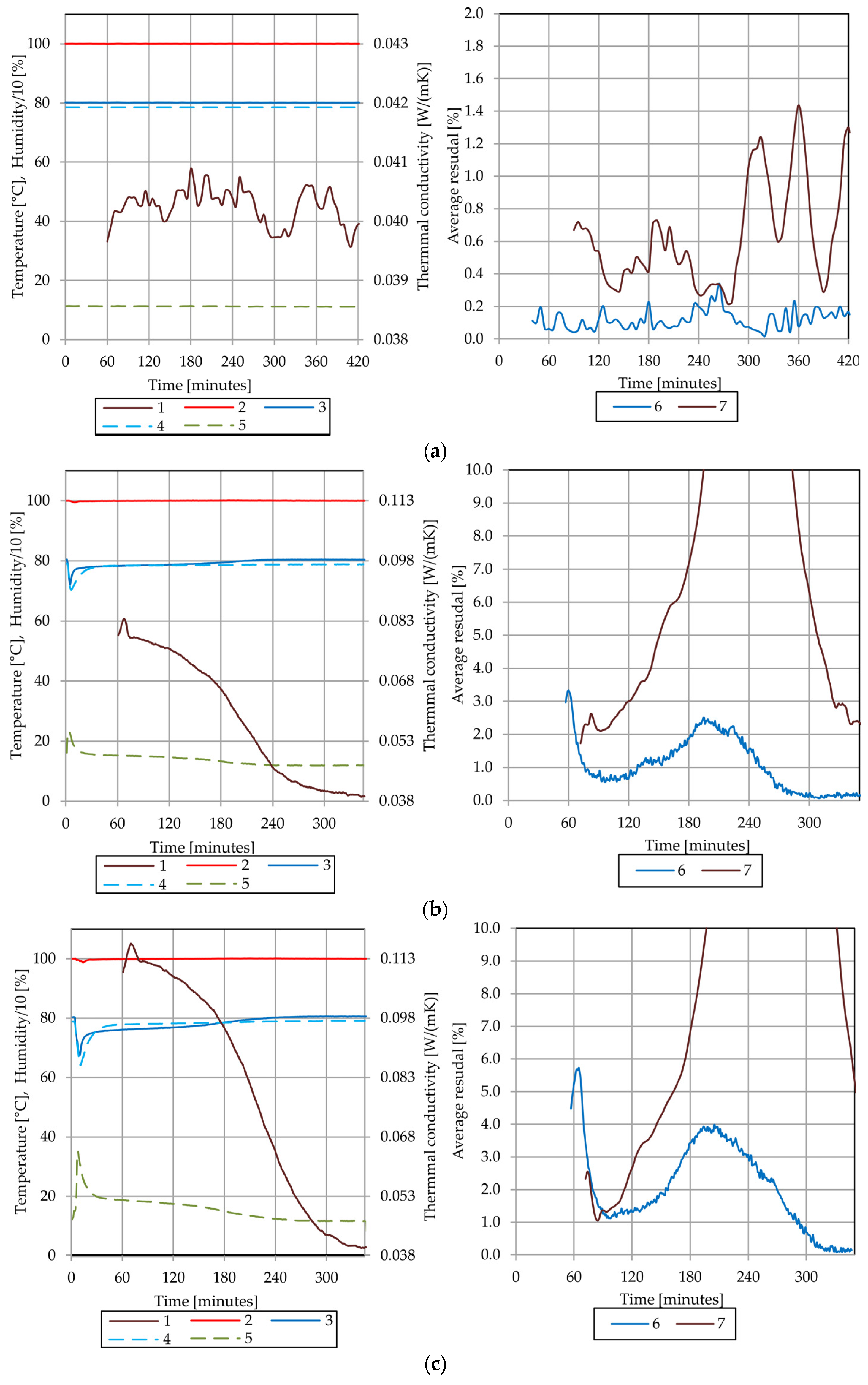
4.5. Results of the Thermal Conductivity Test of the Sample B
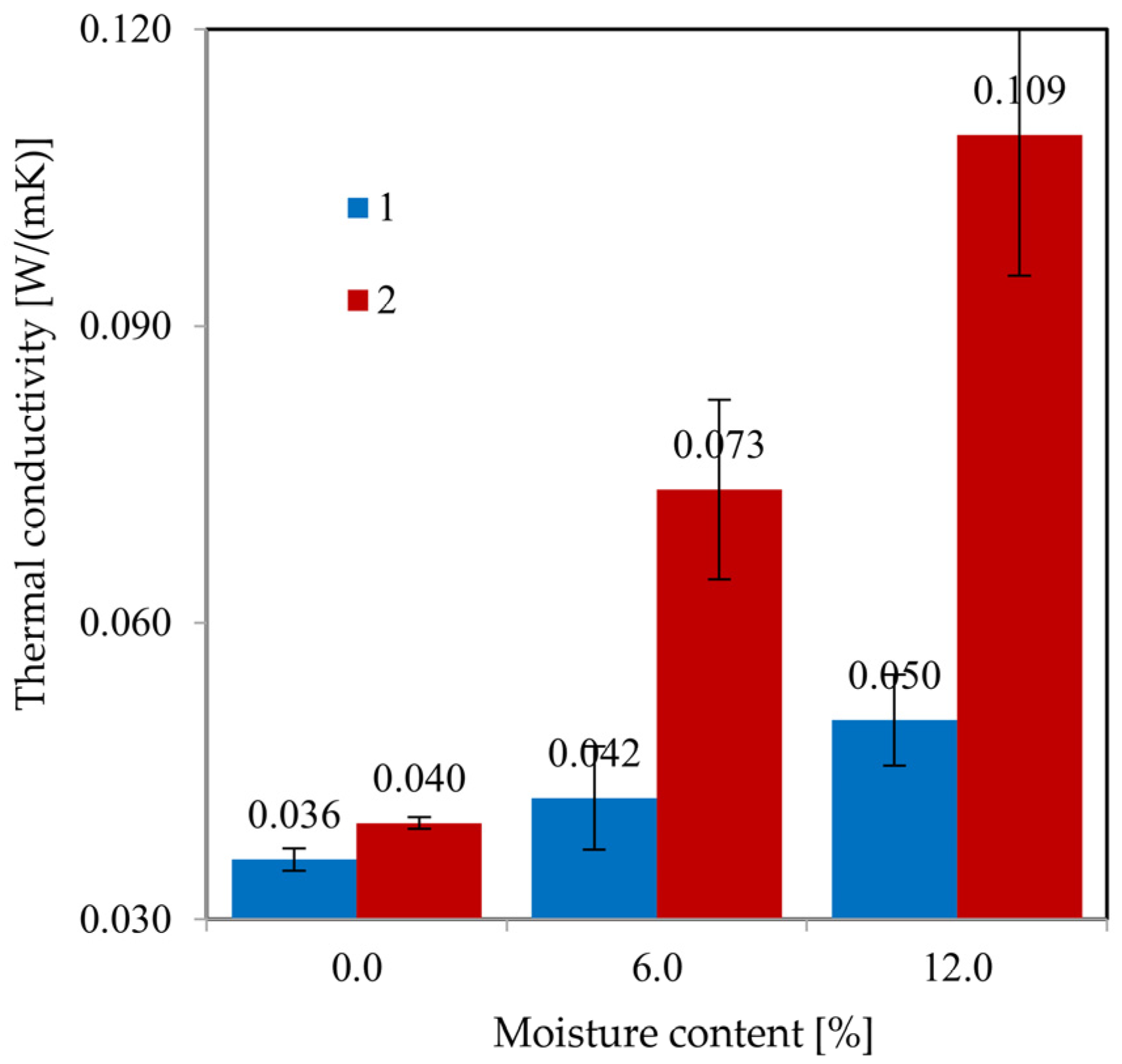
4.6. Comparative Analysis of Sample A and Sample B
4.7. Discussion of Observed Phenomena
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nomenclature | |
| CF | compaction factor |
| D | diameter, m |
| E | electric energy, J |
| L | length, m |
| m | mass, kg |
| N | number |
| Q | electric power, W |
| t | temperature, °C |
| T | time period, s |
| w | moisture content, % |
| Greek symbols | |
| Δ | uncertainty |
| λ | effective thermal conductivity, W∙m−1∙K−1 |
| σ | standard deviation |
| τ | current time, s |
| Subscripts | |
| i | index |
| l | measuring intervals along the length |
| s | sensor |
| time | time intervals |
| 1,2,3 | injected water, drainage water, a work zone of the sample |
| Supersubscripts | |
| avg | average value |
| in, out | a inner wall, a outer wall |
References
- Abdou, A.; Budaiwi, I. The variation of thermal conductivity of fibrous insulation materials under different levels of moisture content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, L.D.H.; Pásztory, Z. An overview of factors influencing thermal conductivity of building insulation materials. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antepara, Í. Moisture dependent thermal properties of hydrophilic mineral wool: Application of the effective media theory. Mater. Sci. 2015, 21, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusyachkin, A.; Sabitov, L.; Khakimova, A.; Hayrullin, A. Effects of moisture content on thermal conductivity of thermal insulation materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 570, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrullin, A.; Haibullina, A.; Gusyachkin, A. Thermal Conductivity of Insulation Material: Effect of Moisture Content and Wet-Drying Cycle. Mater. Sci. Forum 2023, 1085, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, M.; Černý, R. Effect of moisture content on heat and moisture transport and storage properties of thermal insulation materials. Energy Build. 2012, 53, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiřičková, M.; Pavlík, Z.; Fiala, L.; Černý, R. Thermal Conductivity of Mineral Wool Materials Partially Saturated by Water. Int. J. Thermophys. 2006, 27, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanos, A.; Hadiarakou, S.; Papadopoulos, A. The impact of temperature and moisture on the thermal performance of stone wool. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, F.; Müller-Steinhagen, H. Temperature and Moisture Dependence of the Thermal Conductivity of Insulation Materials; NATO Advanced Study Institute on Thermal Energy Storage for Sustainable Energy Consumption (TESSEC): Izmir, Turkey, 2005; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Cai, S.; Cremaschi, L. Thermal performance and moisture accumulation of fibrous mechanical pipe insulation systems operating at below-ambient temperature in wet conditions with moisture ingress. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 2015, 21, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehendner, H. Thermal Conductivity of Thermal Insulation Materials on Pipes. J. Therm. Insul. 1983, 7, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Cremaschi, L.; Ghajar, A.J. Pipe Insulation Thermal Conductivity Under Dry and Wet Condensing Conditions with Moisture Ingress: A Critical Review, HVAC&R Research. 2014. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10789669.2014.882678 (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Hayrullin, A.; Haibullina, A.; Sinyavin, A. Insulation thermal conductivity heating networks during transportation thermal energy under dry and moisturizing condition: A comparative study of the guarded hot plate and guarded hot pipe method. Transp. Res. Procedia 2022, 63, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrullin, A.; Habibullina, I.; Haibullina, A.; Ilyin, V. Experimental study pipe insulation heat losses with moisture ingress. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 979, 012125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Kaviany, M.; Williams, J.; Addison-Smith, T. Heat, mass and momentum transport in wet mineral-wool insulation: Experiment and simulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 228, 125644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovic, H.; Damaceno, D.S.; Meyer, O.H.H.; Ervik, Å. Water transport and corrosion under insulation: Experimental investigations of drying in mineral wool. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamian, Y.; Serate, D.; Yuen, S.; Guo, H.; Mehta, N.; Soni, N.; Bohra, S.; Mcdonald, A. A Case Study of External Cracking in Steam Piping under Mineral Wool Insulation. In Proceedings of the CONFERENCE 2025, Nashville, TN, USA, 6–10 April 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Simon, T.K.; Nemes, R. Effect of built-in mineral wool insulations durability on its thermal and mechanical performance. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, M.; Soltan, A.; Schlüter, S.; Hamzawy, E.; Farrag, A.; El-Kammar, A.; Yahya, A.; Pollmann, H. Optimization of microstructure of basalt-based fibers intended for improved thermal and acoustic insulations. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanič, A.; Kravanja, G.; Kidess, W.; Rudolf, R.; Lubej, S. The Influences of Moisture on the Mechanical, Morphological and Thermogravimetric Properties of Mineral Wool Made from Basalt Glass Fibers. Materials 2020, 13, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiński, P. Moisture Transport in Loose Fibrous Insulations under Steady-State Boundary Conditions. Materials 2023, 16, 7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Y. Pore structure characterization and effective thermal conductivity modeling of fibrous building thermal insulation materials based on X-ray tomography. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 154, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishulkin, S.Y.; Starinskiy, I.V.; Tran, P.L.; Shaidorov, A.A. Influence of incineration ash and slag waste impurities on thermal conductivity of mineral basalt wool. ESSUTM Bull. 2024, 3, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiřičková, M.; Černý, R. Effect of hydrophilic admixtures on moisture and heat transport and storage parameters of mineral wool. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.-K.; Lee, J.; Chung, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J. A Study on Insulation Characteristics of Glass Wool and Mineral Wool Coated with a Polysiloxane Agent. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 3938965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, J.; Pavlíková, M.; Žumár, J.; Pavlík, Z.; Černý, R. Moisture Transport Properties of Hydrophilic Mineral Wool. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 982, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 17177-94; Thermal Insulating Materials and Products for Construction. Test Methods. МНТКС: Khabarovsk, Russia, 1996. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/901710454 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- GOST 32025-2012; Thermal Insulation Products for Building Applications. Determination of Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties of Thermal Insulation for Circular Pipes (EN ISO 8497:1996). МНТКС: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2013. Available online: https://www.neostrom.ru/gosts/32025-2012.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Porzuczek, J. Comparative Study on Selected Insulating Materials for Industrial Piping. Materials 2024, 17, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrullin, A.; Sinyavin, A.; Haibullina, A.; Ilyin, V. Experimental investigation of the heat transport and pressure drop in open-cell polyurethane foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 217, 124709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakos, J.T. Uncertainty Analysis of Thermocouple Measurements Used in Normal and Abnormal Thermal Environment Experiments at Sandia’s Radiant Heat Facility and Lurance Canyon Burn Site. Sandia National Laboratories. 2004. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/71304534.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2025).

| Property | Sample A | Sample B |
|---|---|---|
| Density, kg∙m−3 | 89 ± 6 | 79 ± 5 |
| Nominal thickness, mm | 80 ± 5 | 60 ± 4 |
| Average fibers’ diameter, μm | 9 ± 5 | 7 ± 4 |
| Max fiber diameter, μm | 34 | 21 |
| Min fiber diameter, μm | 1 | 2 |
| Shots percentage, % | 22.0 ± 2.4 | 6.7 ± 1.1 |
| Water absorption, % | 944 ± 53 | 211 ± 31 |
| Property | Sample A | Sample B |
|---|---|---|
| Mean out diameter (Dout), mm | 208 ± 6 | 185 ± 2 |
| Mean thickness, mm | 60 ± 3 | 48 ± 1 |
| Compaction factor | 1.34 ± 0.10 | 1.25 ± 0.09 |
| Actual density, kg∙m−3 | 102 ± 7 | 95 ± 7 |
| Coefficient of variance of thicknesses’ distribution, % | 5.1 | 4.6 |
| The average drainage water percentage, % | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
| Actual average values of moisture content (w), % | 5.9 ± 0.2 11.8 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.3 11.6 ± 0.5 |
| Sample | Average Temperature | Slope | Intercept | Determination Coefficient R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 20 | 0.0005 | 0.0359 | 0.996 |
| A | 85 | 0.0029 | 0.0413 | 0.991 |
| B | 20 | 0.0058 | 0.0394 | 0.9997 |
| B | 85 | 0.0012 | 0.0358 | 0.9954 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sinyavin, A.; Hayrullin, A.; Khusnutdinova, M.; Dyachuk, J.; Haibullina, A.; Ilyin, V.; Bronskaya, V.; Bashkirov, D. Comparative Experimental Analysis of Wet-State Thermal Performance in Pipe Mineral Wool Insulation with Different Hydrophobic Treatments. Energies 2025, 18, 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226074
Sinyavin A, Hayrullin A, Khusnutdinova M, Dyachuk J, Haibullina A, Ilyin V, Bronskaya V, Bashkirov D. Comparative Experimental Analysis of Wet-State Thermal Performance in Pipe Mineral Wool Insulation with Different Hydrophobic Treatments. Energies. 2025; 18(22):6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226074
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinyavin, Alex, Aidar Hayrullin, Margarita Khusnutdinova, Julia Dyachuk, Aigul Haibullina, Vladimir Ilyin, Veronika Bronskaya, and Dmitry Bashkirov. 2025. "Comparative Experimental Analysis of Wet-State Thermal Performance in Pipe Mineral Wool Insulation with Different Hydrophobic Treatments" Energies 18, no. 22: 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226074
APA StyleSinyavin, A., Hayrullin, A., Khusnutdinova, M., Dyachuk, J., Haibullina, A., Ilyin, V., Bronskaya, V., & Bashkirov, D. (2025). Comparative Experimental Analysis of Wet-State Thermal Performance in Pipe Mineral Wool Insulation with Different Hydrophobic Treatments. Energies, 18(22), 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226074





