Study on Failure of 10 kV Primary Devices and Their Impact on Distribution Network Induced by HEMP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approach to Analyze E1 Impact on Distribution Network
2.1. CDF of Coupled Voltage for Critical Device
2.2. Failure Probability of Critical Device
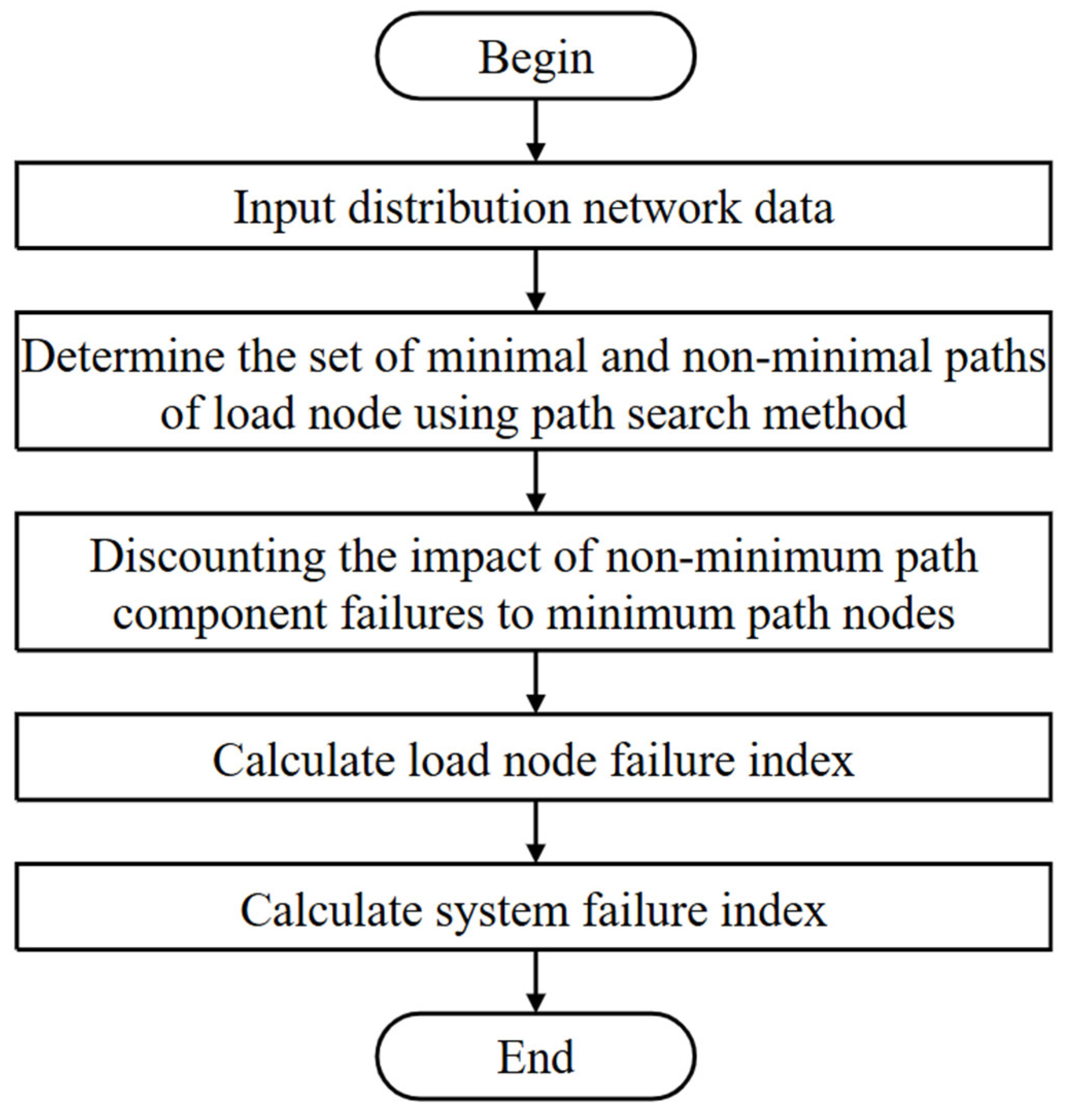
2.3. Method to Analyze E1 Effect on Distribution Network
3. Threshold Voltages of Primary Devices and Parameters of Typical 10 kV Distribution Network
3.1. Failure Threshold of 10 kV-Distribution Primary Device
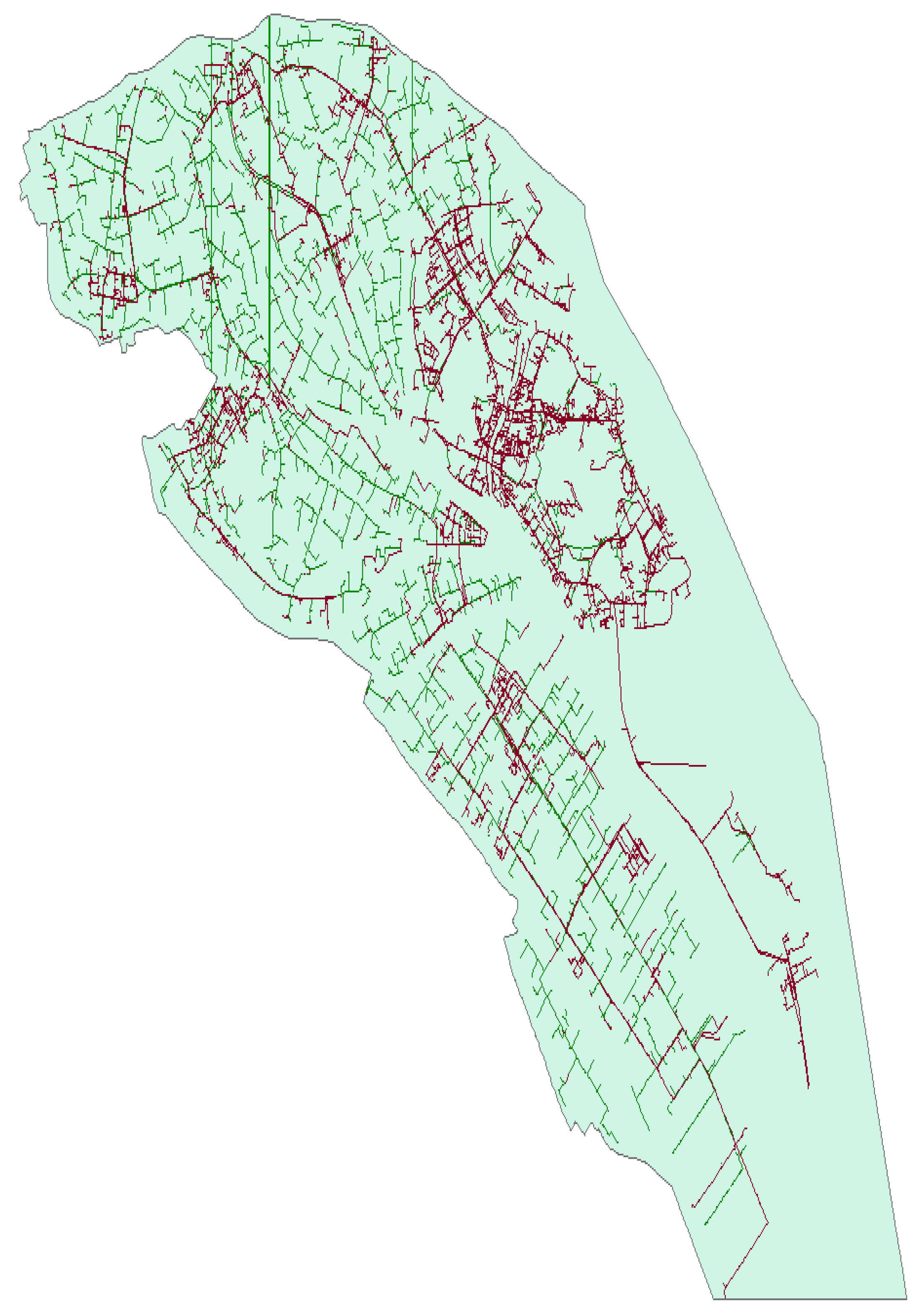
3.2. Configurations and Parameters of Tpical 10 kV Distribution Network
4. Results and Discussion
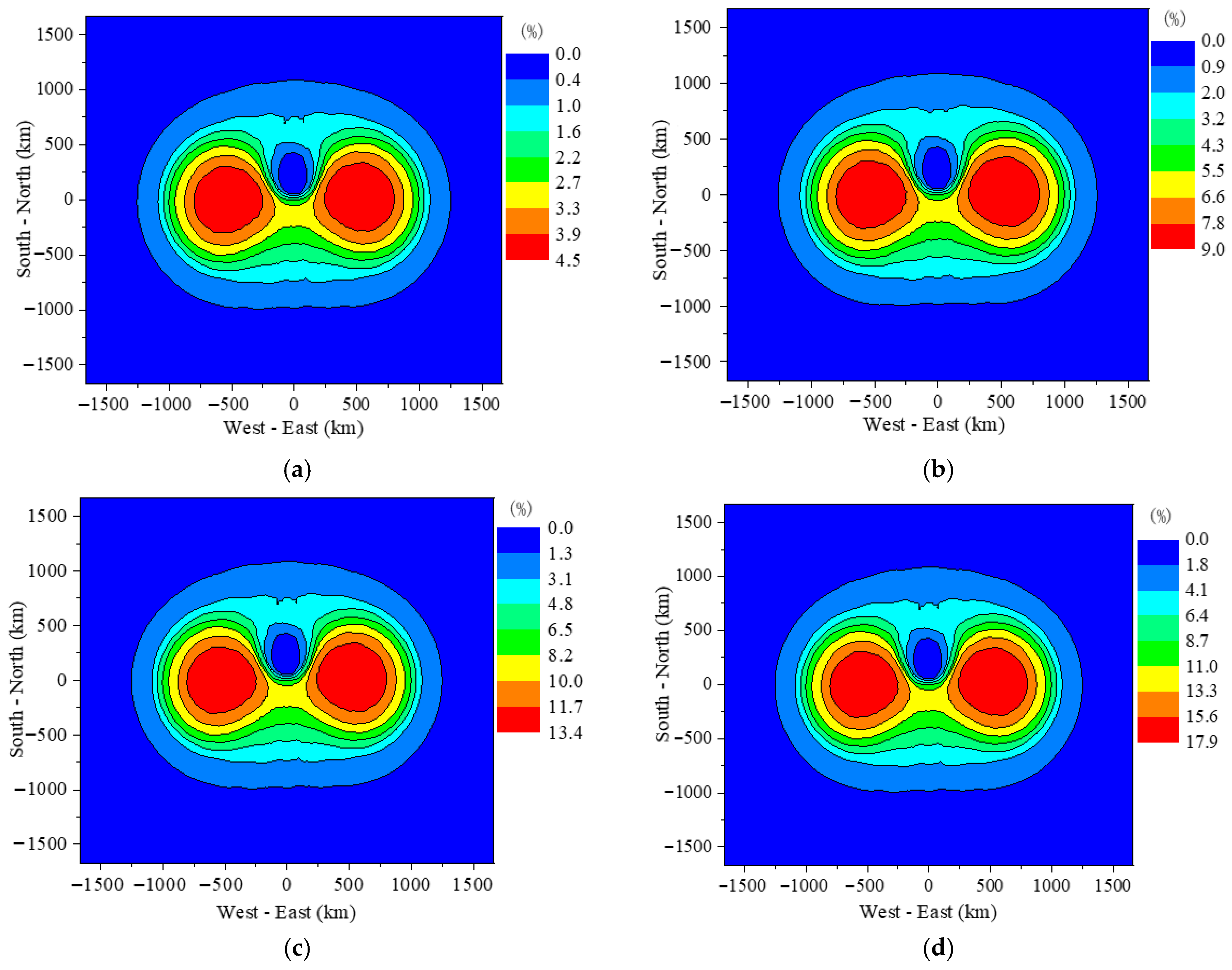
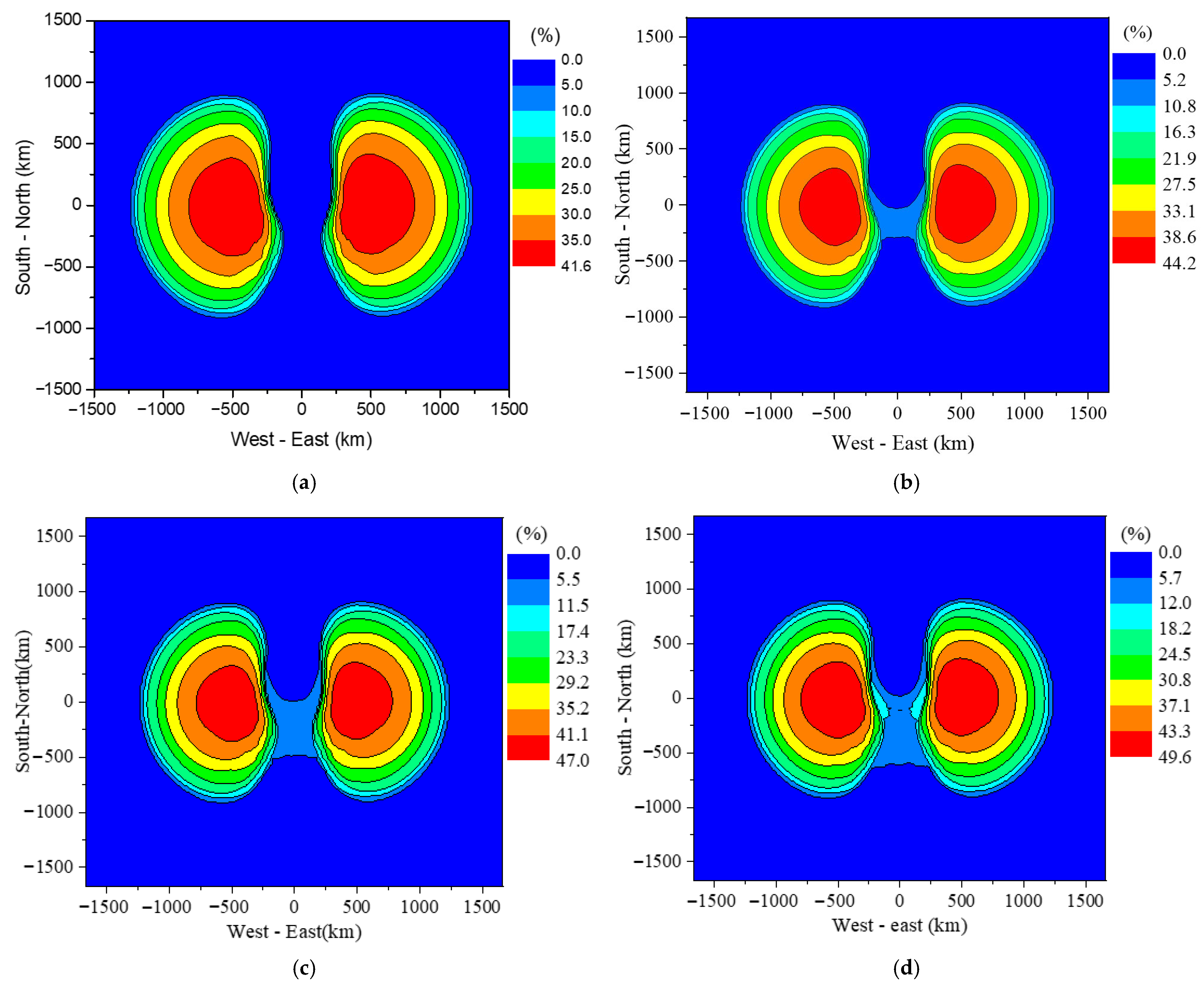
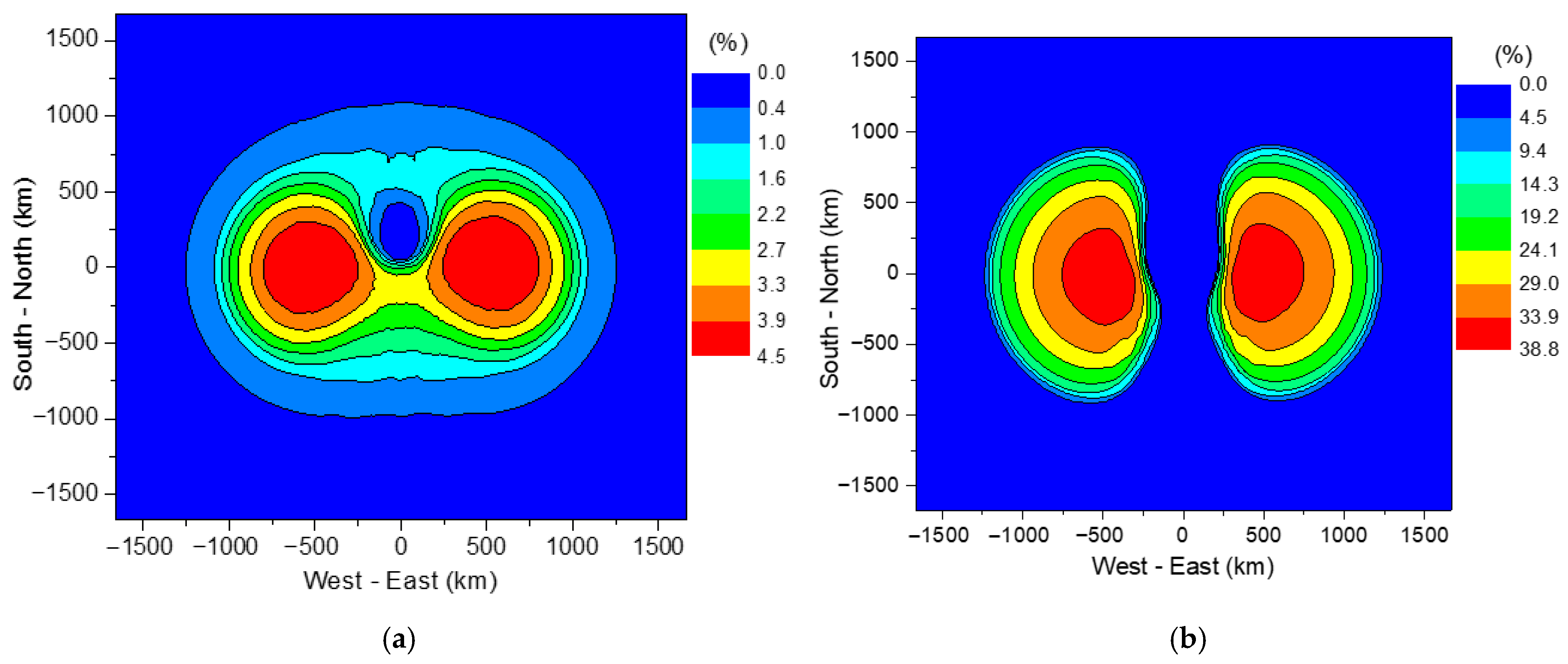
4.1. Spatial Distribution of E1 and Coupled Voltage
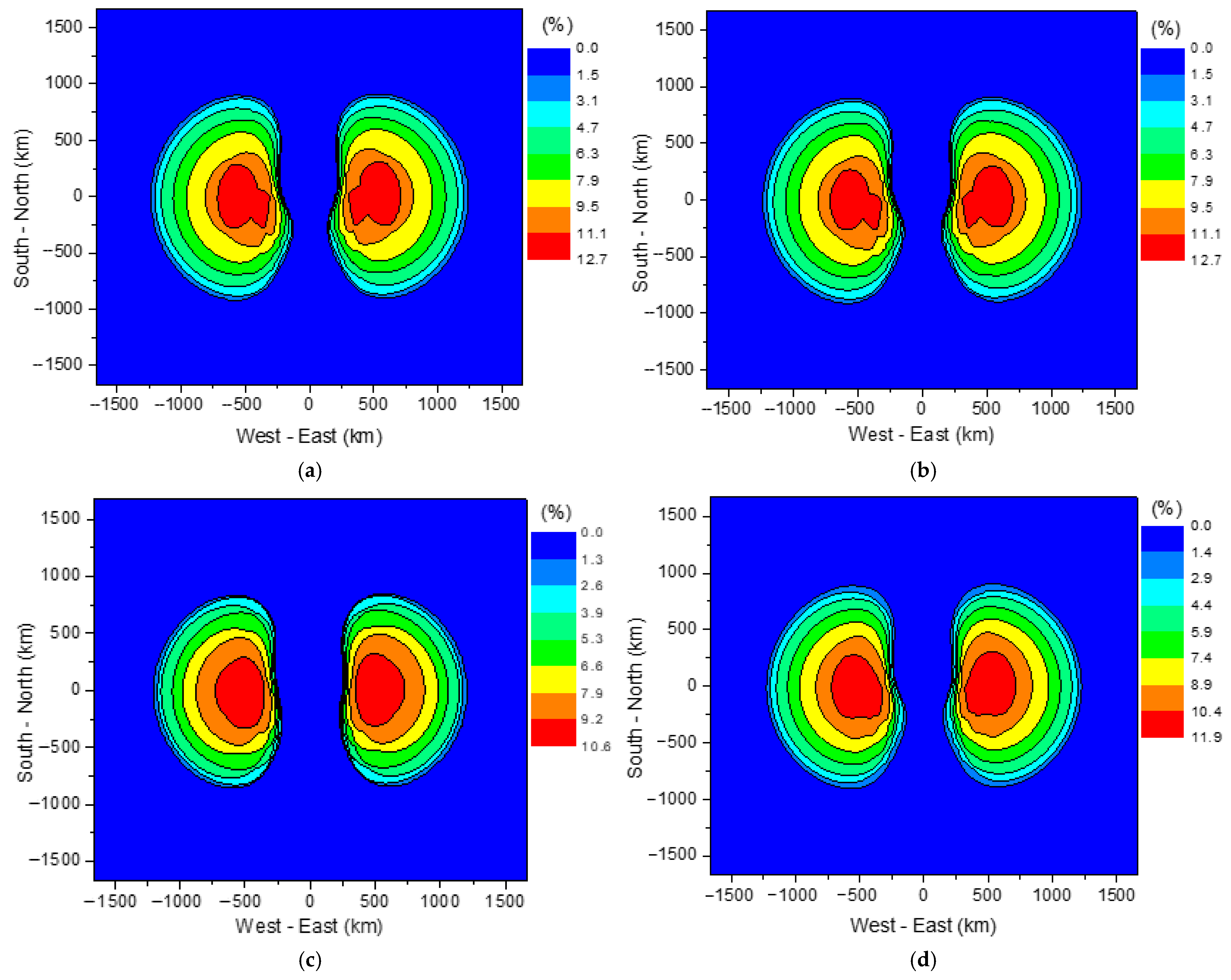
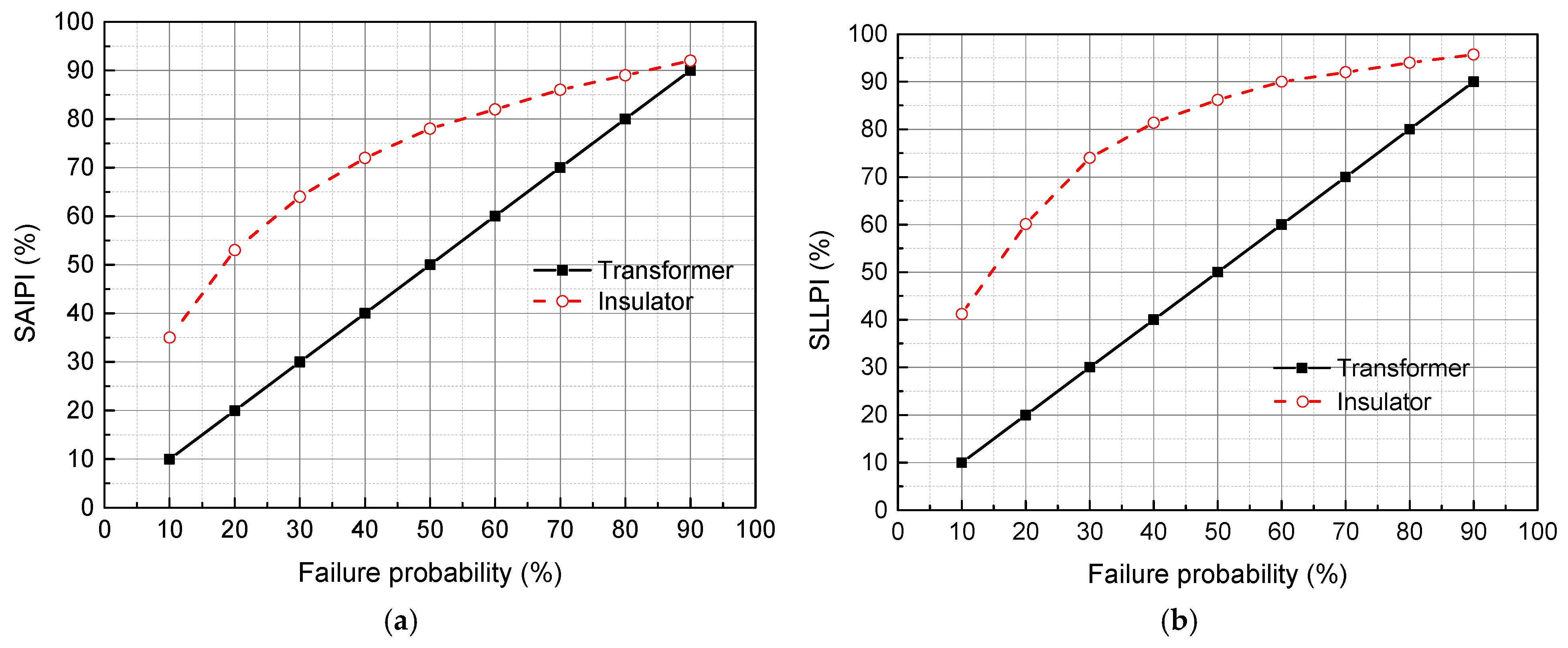
4.2. Failure Pobabilities of 10 kV-Distribution Primary Devices
4.3. Effect on 10 kV Distribution Network
4.4. Sensitivity Analysis of Primary Equipment Failure
5. Conclusions and Suggestion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEC 61000-2-9; IEC Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC-Part 2 Environment-Section 9 Description of HEMP Environment-Radiated Disturbance Basic EMC Publication First Edition. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Niu, S.; Ouyang, X. Numerical simulation of the intermediate-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulse. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2022, 64, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Du, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Qiao, H.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J. Theoretical and experimental study of effective coupling length for transmission lines illuminated by HEMP. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2015, 57, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Yang, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Radiated and conducted research on damage characteristics of digital protective relays in substations under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse environment. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 95, 114710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Weiss, M. An assessment of threats to the American power grid. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2019, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 61000-1-3; Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)—Part 1–3: General—The Effects of High-Altitude EMP (HEMP) on Civil Equipment and Systems. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Savage, E.; Gibert, J.; Radasky, W. The Early-Time (E1) High-Altitude Electromagnetic Pulse (HEMP) and Its Impact on the U.S. Power Grid; Meta-R-320; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.; Lux, A.; Grzybowski, S.; Barnes, P. The effect of steep-front, short-duration impulses on power distribution components. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1990, 5, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, Y.V.; Zdoukhov, L.N.; Shurupov, A.V.; Kozlov, A.V. Research of flashover of power line insulators due to high-voltage pulses with power on and power off. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2013, 55, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, D.-C.; Gou, M.-Y.; Dong, N. 10-kV transmission line experimental platform for HEMP immunity test of electrical equipment in operation. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 36, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thotakura, N.L.; Wu, Y.; Mignardot, D.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, W.; Markel, L.C.; Liao, D.; McConnell, B.W.; Liu, Y. Mignardot Impact analysis of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse coupling effects on power grid protection relays. Electronics 2024, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, H.; Su, Y.; Meng, J. Analysis of immunity of relay protection equipment under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.S.; Gjelde, E.; Graham, W.R.; Hermann, R.G. Report of the Commission to Assess the Threat to the United States from Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) Attack: Critical National Infrastructures; EMP Commission: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- NERC. High-Impact, Low-Frequency Event Risk to the North American Bulk Power System; North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.; Kappenman, J.; Radasky, W. The Late-Time (E3) High-Altitude Electromagnetic Pulse (HEMP) and Its Impact on the U.S. Power Grid; Meta-R-321; Metatech Corporation: Mumbai, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, I. Vulnerability assessment of Korean electric power systems to late-time (E3) high-altitude electromagnetic pulses. Energies 2019, 12, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, V.; Tesche, F.; Liu, T.; Barnes, P. Flashover vulnerability of transmission and distribution lines to high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP). IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1990, 5, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, H. A prediction model based on artificial neural network for E1 HEMP coupling with distribution power lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Qiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, T.; Huang, S. Numerical study of HEMP coupling with overhead lines in large range by using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2025, 72, 3551–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Nie, X.; Wu, W. Quantitative grading of insulation damage to distribution transformers caused by high-altitude electromagnetic pulse based on partial discharge detection. High Volt. 2024, 10, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y. A fast prediction model for HEMP-E1 environment based on artificial neural network. Mod. Appl. Phys. 2025, 16, 011318. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ianoz, M.; Nicoara, B.I.C.; Radasky, W.A. Modeling of an EMP conducted environment. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1996, 38, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Qiao, H.; Wang, J. Empirical formula of effective coupling length for transmission lines illuminated by E1 HEMP. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2016, 58, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, F.M.; Barnes, P.R. A multiconductor model for determining the response of power transmission and distribution lines to a high altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP). IEEE Power Eng. Rev. 1989, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, C.; Wang, X. Reliability analysis of distribution networks. Electr. Power 1997, 30, 10–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bie, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, G.; Hua, B.; Meehan, M.; Wang, X. Reliability evaluation of active distribution systems including microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Nie, X.; Cui, Z.; Mao, C. Transient response and failure mechanism of distribution transformer under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse. Proc. CSEE 2023, 43, 6924–6932. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, L.; Xie, Y. Effect Experiments of 10 kV Distribution Transformer Excited by High-altitude Electromagnetic Pulse. High Volt. Eng. 2023, 49, 3119–3124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Type | Effect Phenomenon | Average Open-Circuit Voltage Threshold (kV) |
|---|---|---|
| dry-type transformers | internal insulating material breakdown | 280 |
| oil-type transformers | internal insulating material breakdown | 216 |
| Type | Effect Phenomenon | Average Voltage Threshold (kV) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 kV porcelain insulators | flashover | 330 1 |
| 10 kV composite insulators | flashover | 334 2 |
| 10 kV glass insulators | flashover | 380 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Qiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Huang, S.; Du, T. Study on Failure of 10 kV Primary Devices and Their Impact on Distribution Network Induced by HEMP. Energies 2025, 18, 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226053
Xie H, Li Y, Zhang D, Li G, Qiao H, Liu Y, Yang C, Huang S, Du T. Study on Failure of 10 kV Primary Devices and Their Impact on Distribution Network Induced by HEMP. Energies. 2025; 18(22):6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226053
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Haiyan, Yong Li, Dingmao Zhang, Gengfeng Li, Hailiang Qiao, Yu Liu, Chao Yang, Shaohua Huang, and Taijiao Du. 2025. "Study on Failure of 10 kV Primary Devices and Their Impact on Distribution Network Induced by HEMP" Energies 18, no. 22: 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226053
APA StyleXie, H., Li, Y., Zhang, D., Li, G., Qiao, H., Liu, Y., Yang, C., Huang, S., & Du, T. (2025). Study on Failure of 10 kV Primary Devices and Their Impact on Distribution Network Induced by HEMP. Energies, 18(22), 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18226053





