Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Tung Seed Shells and In Situ Characterization by Using TG–FTIR Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
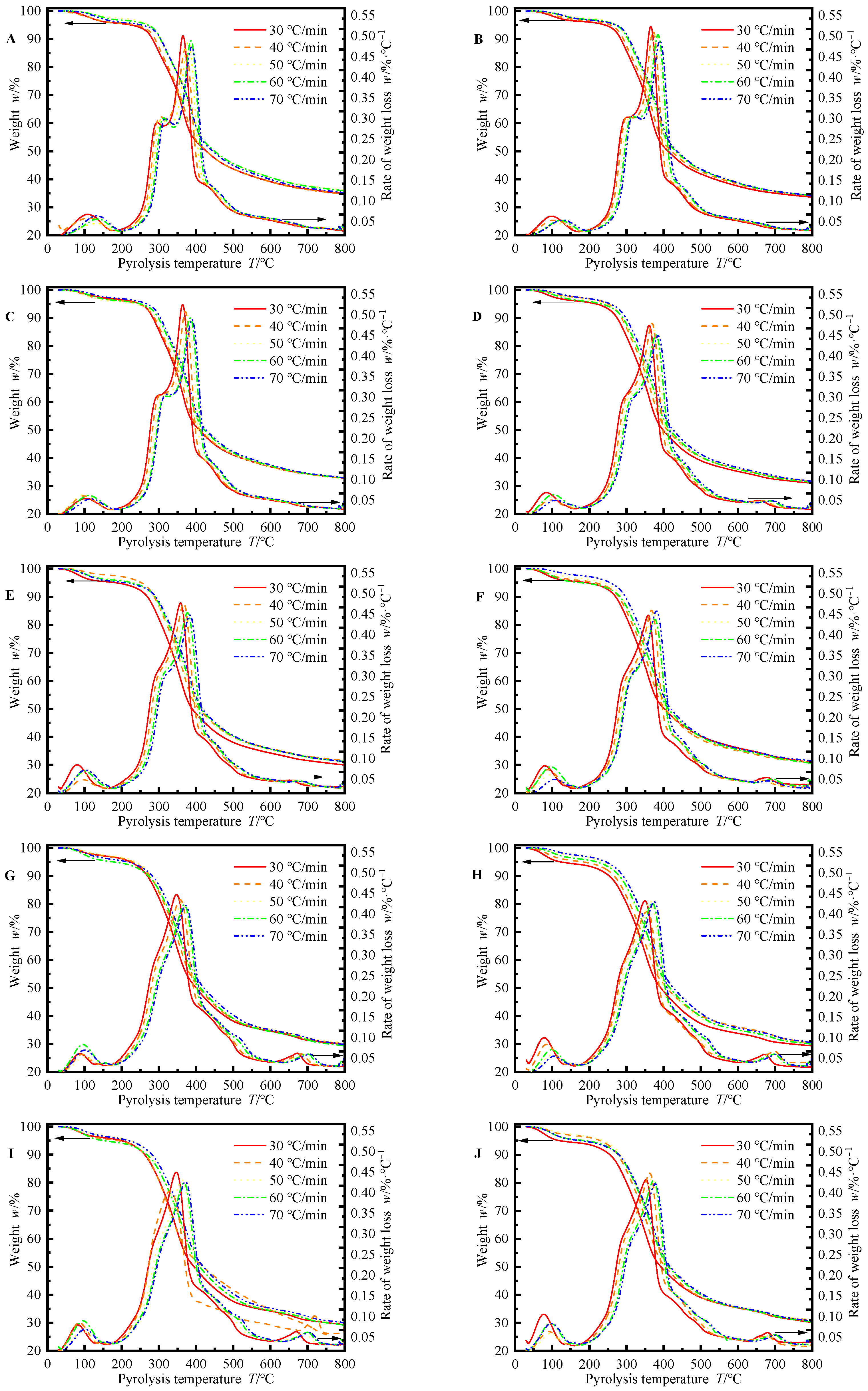
3.1. Thermal Mass Loss and Mass Loss Rate of Tung Seed Shells with Different Particle Sizes
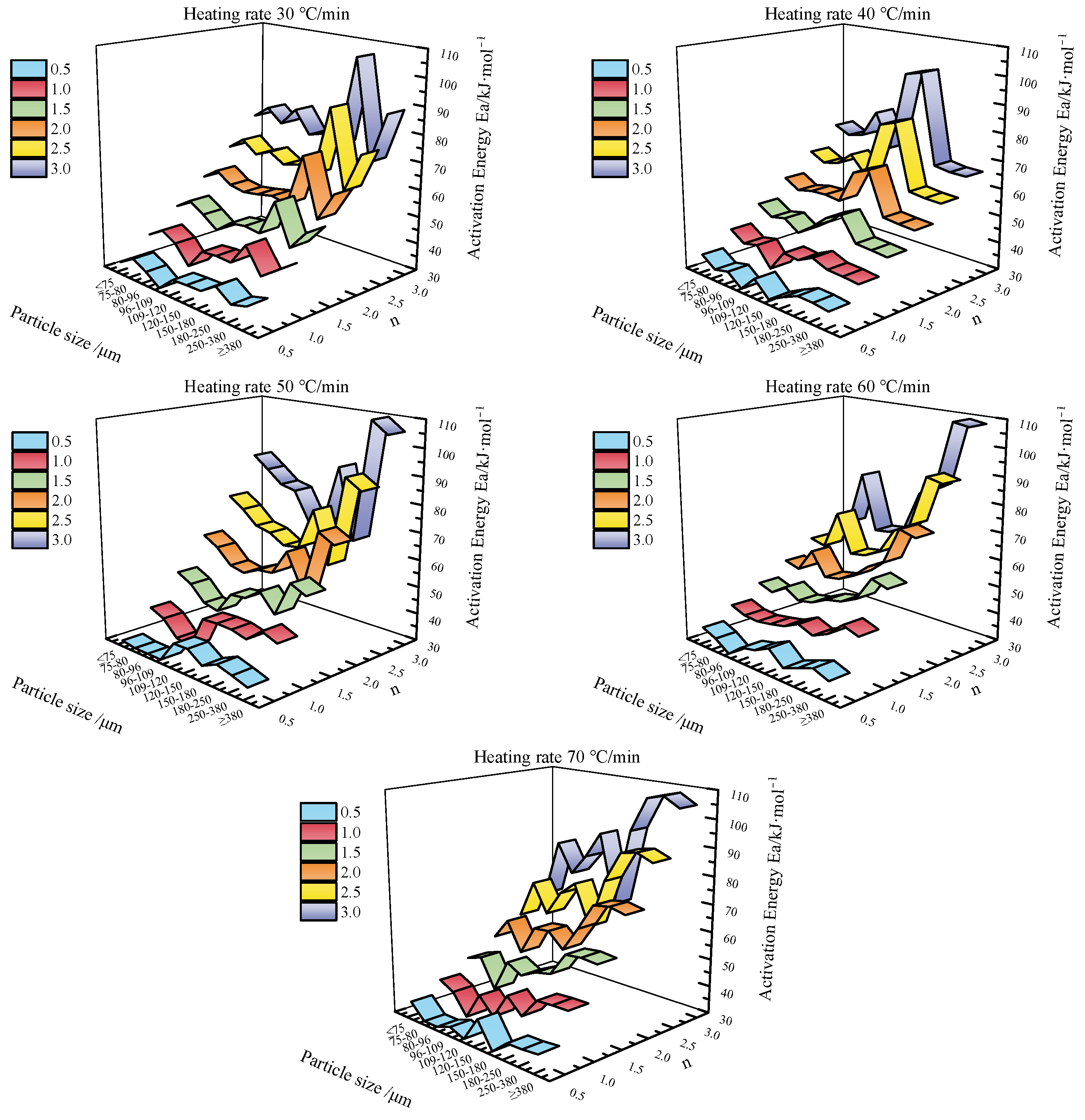
3.2. Calculated Results of the Coats–Redfern Pyrolysis Kinetic Model Parameters
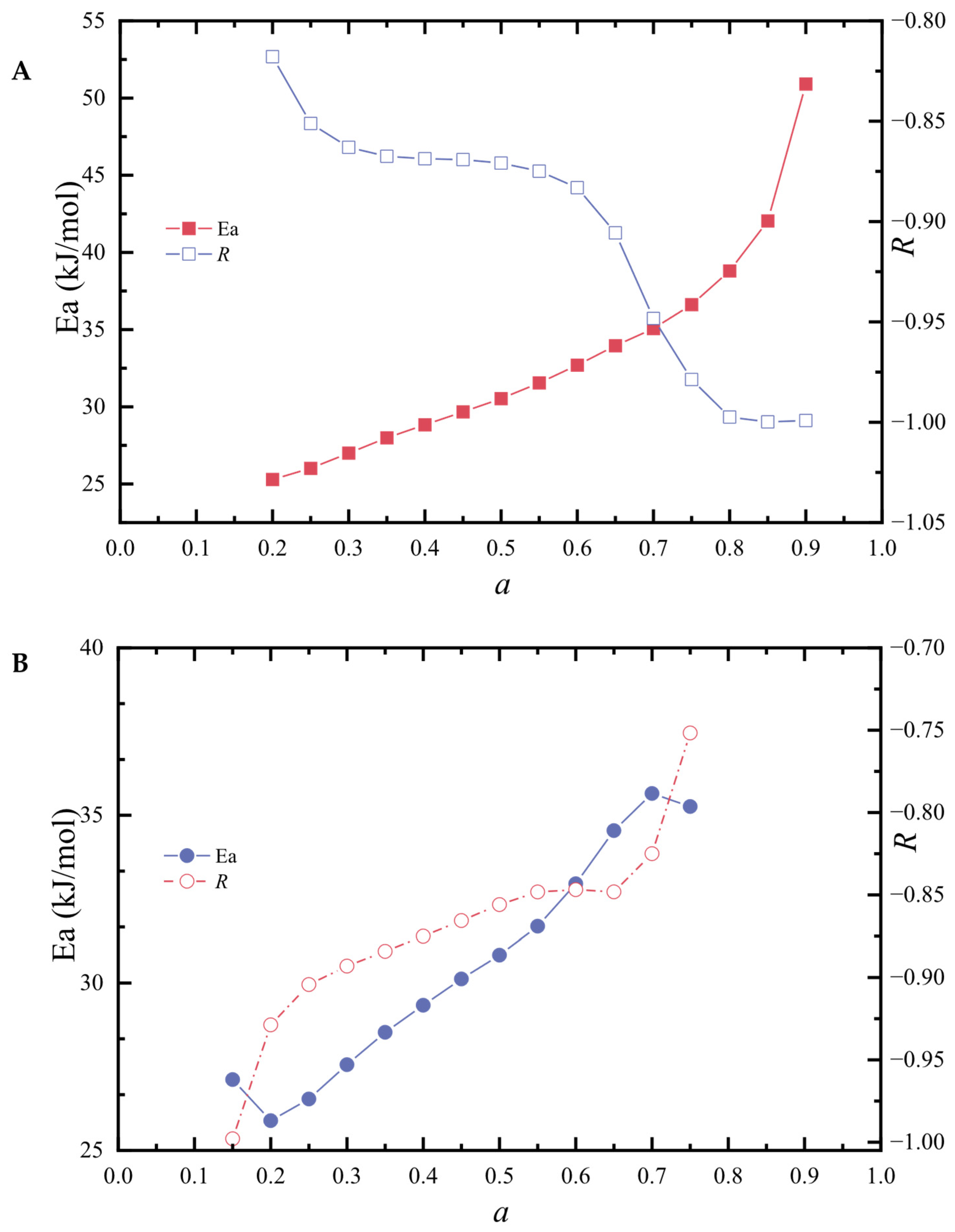
3.3. Calculation of Parameter of Pyrolysis Kinetic Models by the Doyle Method
3.4. Calculation of Parameters of Pyrolysis Kinetic Models by the Kissinger Method
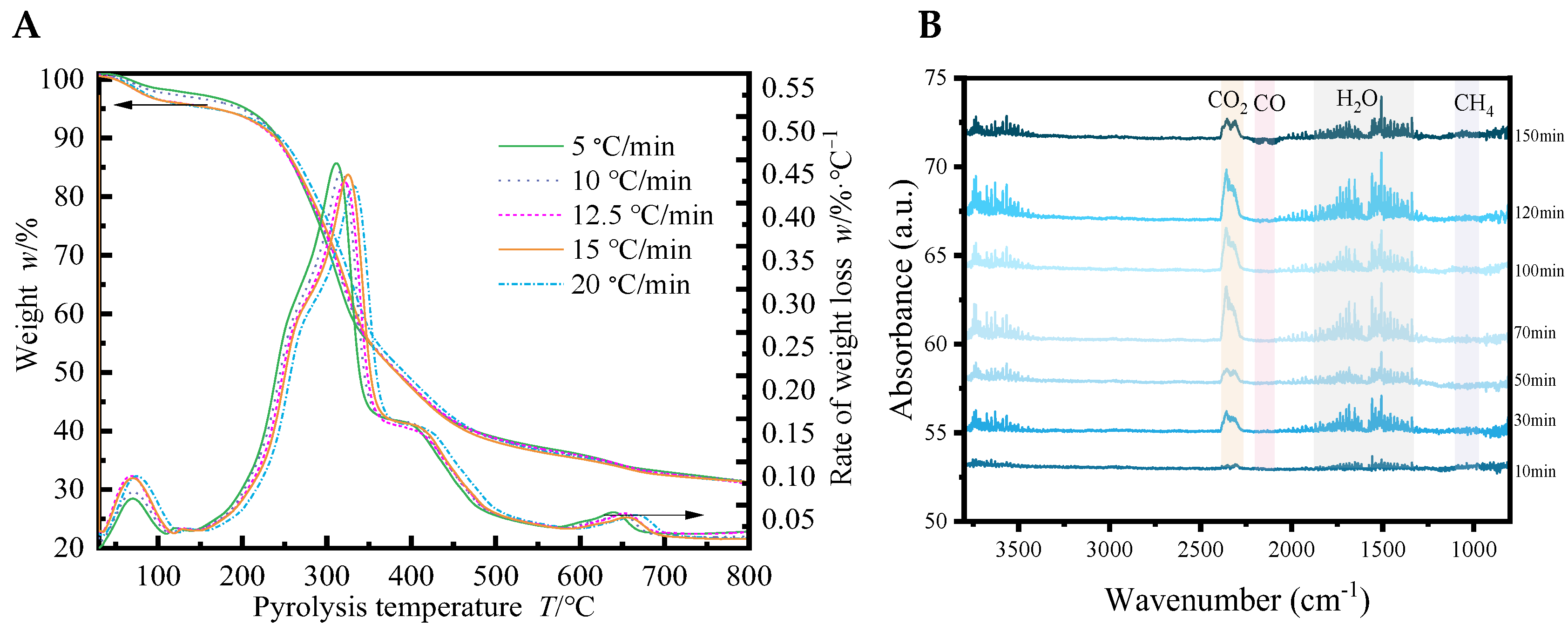
3.5. In Situ Observation and Supposed Mechanism of Tung Seed Shells Pyrolysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSS | Tung seed shell |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| TG–FTIR | Thermogravimetric Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| Ea | Apparent activation energies |
| Tmax | Decomposition temperature |
| A | Pre-exponential factors |
| R | Linear correlation coefficients |
| Tmax0 | Equilibrium decomposition temperature |
| Tp | Peak temperature |
| β | Heating rate |
| n | Reaction order |
| α | Reaction progresses |
References
- Wang, S.; Zhang, A.; Li, N.; Shah, T.A.; Li, Z.; Yi, W. Biomass Pyrolysis and Clean Energy Production. In Advanced Technology for Smart Environment and Energy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, J.; Yang, W.; Chang, C.; Pang, S. Research progress on the preparation of high-value carbon materials by biomass pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 193, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaq, W.A.; Golonka, M.; Scholz, M.; Białowiec, A. Opportunities and challenges of high-pressure fast pyrolysis of biomass: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Pradhan, R.; Naik, S.; Bhatnagar, N.; Singh, S. Evaluation of a centrifugal impaction-type decorticator for shelling tung fruits. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornitta, N.; Nadaleti, W.C.; Bariccatti, R.A.; dos Santos, R.F.; Zornitta, R.L.; Nogueira, C.E.C. Evaluation of the Tung’s fruits as a possible source of sustainable energy. Acta Scientiarum. Technol. 2017, 39, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Salvi, B.; Kumar, V. Thermal degradation and gasification characteristics of Tung Shells as an open top downdraft wood gasifier feedstock. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttibak, S.; Saengmanee, C.; Chuntanapum, A. Production of bio-oil from Tung seed residues in a fluidized-bed reactor. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga, J.F.; Aguado, R.; Pablos, A.; Amutio, M.; Olazar, M.; Bilbao, J. Fast characterization of biomass fuels by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Fuel 2015, 140, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Tariq, R.; Hameed, Z.; Ali, I.; Naqvi, M.; Chen, W.-H.; Ceylan, S.; Rashid, H.; Ahmad, J.; Taqvi, S.A. Pyrolysis of high ash sewage sludge: Kinetics and thermodynamic analysis using Coats–Redfern method. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. A new method for evaluating the sewage sludge pyrolysis kinetics. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-Y.; Huang, X.; Fleischmann, C.; Rein, G.; Ji, J. Pyrolysis of medium-density fiberboard: Optimized search for kinetics scheme and parameters via a genetic algorithm driven by Kissinger’s method. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 6130–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lian, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Hao, X.; Huang, W.; Guan, G. Simulation of pyrolysis in low rank coal particle by using DAEM kinetics model: Reaction behavior and heat transfer. Fuel 2017, 207, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.W.; Redfern, J. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 1964, 201, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, C.D. Kinetic analysis of thermogravimetric data. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1961, 5, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Variation of peak temperature with heating rate in differential thermal analysis. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1956, 57, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevich, S.V.; Mitrofanov, A.V. A Kinetic Study of the Nonisothermal Pyrolysis of Wood. Kinet. Catal. 2024, 65, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaymia, I.; Bedjaoui, A.; Belaadi, A.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Ghernaout, D.; Al-Khawlani, A. Slow Pyrolysis of Agave americana L. Fibers: Analysis of Kinetics and Thermodynamics Using the Coats–Redfern Method at Different Heating Rates. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, O.; Lemaire, R.; Bensakhria, A. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Kinetic Modeling of the Pyrolysis of Different Biomass Types by Means of Model-Fitting, Model-Free, and Network Modeling Approaches. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 10941–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferfari, O.; Belaadi, A.; Bourchak, M.; Ghernaout, D.; Ajaj, R.M.; Chai, B.X. Thermal Decomposition of Syagrus romanzoffiana Palm Fibers: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Studies Using the Coats–Redfern Method. Renew. Energy 2024, 231, 120928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yang, W.; Cong, X.; Dong, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, X. Thermogravimetric Analysis and Reaction Kinetics of Lignocellulosic Biomass Pyrolysis. Energy 2020, 201, 117537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shang, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Qin, S.; Tian, Y. Comparative Study on Pyrolysis Kinetics Behavior and High-Temperature Fast Pyrolysis Product Analysis of Coastal Zone and Land Biomasses. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 10144–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. Pyrolysis Kinetics of Waste Ryegrass under Nitrogen and Air Atmosphere. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Gu, S.; Luo, K.; Bridgwater, A.V.; Fang, M. Kinetic study on thermal decomposition of woods in oxidative environment. Fuel 2009, 88, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Chen, H. TG study on pyrolysis of biomass and its three components under syngas. Fuel 2008, 87, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolina-Jury, F.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. Mechanism of low pressure plasma-assisted CO2 hydrogenation over Ni-USY by microsecond time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Nešumajev, D.; Konist, A. Thermal Decomposition Behaviors and Kinetic Parameter Calculations during Common Reed and Its Components Pyrolysis. Renew. Energy 2025, 248, 123130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisen, D.; Chouhan, A.P.S.; Sarma, A.K.; Rajamohan, S.; Elumalai, P.V.; Balasubramanian, D.; Cherie, A. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Rice Husk and Low-Density Polyethylene Co-Pyrolysis: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Parameters. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Maciejewski, M.; Vyazovkin, S.; Nomen, R.; Sempere, J.; Burnham, A.; Opfermann, J.; Strey, R.; Anderson, H.L.; Kemmler, A.; et al. Computational Aspects of Kinetic Analysis. Part A: The ICTAC Kinetics Project—Data, Methods, and Results. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 355, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescu, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee Recommendations for Performing Kinetic Computations on Thermal Analysis Data. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, N.; Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Favergeon, L.; Muravyev, N.V.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Saggese, C.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E. ICTAC Kinetics Committee Recommendations for Analysis of Thermal Decomposition Kinetics. Thermochim. Acta 2023, 719, 179384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, C. Modeling Chemical and Physical Processes of Wood and Biomass Pyrolysis. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 47–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, C.; Albano, A.; Di Blasi, C. Critical Evaluation of Global Mechanisms of Wood Devolatilization. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 429, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.Q.; You, T.T.; Wang, W.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C. Synergistic Benefits of Ionic Liquid and Alkaline Pretreatments of Poplar Wood. Part 2: Characterization of Lignin and Hemicelluloses. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Qiao, Y.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Liu, Q. Investigation on the Effect of Particle Size and Heating Rate on Pyrolysis Characteristics of a Bituminous Coal by TG–FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 121, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyam, S.; Al-Ansari, T.; McKay, G. Particle Size Impact on Pyrolysis of Multi-Biomass: A Solid-State Reaction Modeling Study. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 7088–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.E.; Catallo, W.J.; Legendre, B.L. Biomass Pyrolysis Kinetics: A Comparative Critical Review with Relevant Agricultural Residue Case Studies. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin Pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecha, M.B.; Montoya Arbelaez, J.I.; Garcia-Perez, M.; Chejne, F.; Ciesielski, P.N. Progress in Understanding the Four Dominant Intra-Particle Phenomena of Lignocellulose Pyrolysis: Chemical Reactions, Heat Transfer, Mass Transfer, and Phase Change. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2868–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Size/μm | Ultimate Analysis/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | |
| ≥380 | 50.67 | 6.19 | 42.38 | 0.30 |
| 250–380 | 54.99 | 6.16 | 38.12 | 0.30 |
| 180–250 | 48.35 | 6.28 | 44.38 | 0.30 |
| 150–180 | 52.48 | 5.99 | 38.36 | 0.77 |
| 120–150 | 52.12 | 6.13 | 39.21 | 0.62 |
| 109–120 | 51.69 | 6.07 | 39.24 | 0.80 |
| 96–109 | 50.75 | 6.05 | 37.39 | 1.34 |
| 80–96 | 51.16 | 6.02 | 37.22 | 1.28 |
| 75–80 | 50.57 | 6.01 | 37.49 | 1.37 |
| ≤75 | 51.67 | 6.16 | 37.49 | 0.97 |
| Particle Size/μm | Tmax/°C | Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C/min | 40 °C/min | 50 °C/min | 60 °C/min | 70 °C/min | Tmax = aβ + b | |
| ≥380 | 365.26 | 371.74 | 379.37 | 386.82 | 389.15 | a = 0.6286, b = 347.04 R = 0.9771 |
| 250–380 | 366.01 | 371.61 | 380.59 | 385.77 | 390.78 | a = 0.6370, b = 347.10 R = 0.9885 |
| 180–250 | 364.27 | 371.16 | 378.10 | 384.48 | 389.65 | a = 0.6408, b = 345.49 R = 0.9968 |
| 150–180 | 360.99 | 368.78 | 374.73 | 379.65 | 384.77 | a = 0.5843, b = 347.04 R = 0.9904 |
| 120–150 | 358.05 | 366.66 | 371.14 | 376.62 | 383.42 | a = 0.6070, b = 340.83 R = 0.9898 |
| 109–120 | 358.41 | 367.13 | 372.49 | 376.24 | 380.77 | a = 0.5383, b = 344.09 R = 0.9704 |
| 96–109 | 347.71 | 356.73 | 362.31 | 368.36 | 371.98 | a = 0.6017, b = 331.33 R = 0.9774 |
| 80–96 | 349.23 | 355.69 | 363.70 | 369.16 | 374.45 | a = 0.6391, b = 330.49 R = 0.9937 |
| 75–80 | 346.68 | 355.85 | 361.81 | 367.04 | 371.10 | a = 0.6003, b = 330.48 R = 0.9754 |
| ≤75 | 352.78 | 362.65 | 369.34 | 373.05 | 377.97 | a = 0.6078, b = 336.77 R = 0.9635 |
| Particle Size/μm | A/min−1 | R |
|---|---|---|
| ≥380 | 3.0676 × 103 | −0.9962 |
| 250–380 | 9.3746 × 102 | −0.9996 |
| 180–250 | 9.4402 × 103 | −0.9992 |
| 150–180 | 1.1530 × 103 | −0.9998 |
| 120–150 | 1.2927 × 103 | −0.9997 |
| 109–120 | 1.1064 × 103 | −0.9999 |
| 96–109 | 3.7174 × 102 | −0.9941 |
| 80–96 | 9.7586 × 102 | −0.9996 |
| 75–80 | 1.8563 × 103 | −0.9997 |
| ≤75 | 9.0325 × 102 | −0.9998 |
| Particle Size/μm | A/min−1 | R |
|---|---|---|
| ≥380 | 4.1305 × 108 | 0.9789 |
| 250–380 | 3.6636 × 108 | 0.9809 |
| 180–250 | 3.6665 × 108 | 0.9921 |
| 150–180 | 2.6269 × 109 | 0.9987 |
| 120–150 | 8.7734 × 108 | 0.9812 |
| 109–120 | 1.2891 × 1010 | 0.9913 |
| 96–109 | 6.8004 × 108 | 0.9958 |
| 80–96 | 2.2314 × 108 | 0.9906 |
| 75–80 | 6.7291 × 108 | 0.9963 |
| ≤75 | 5.0796 × 108 | 0.9871 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Huang, K. Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Tung Seed Shells and In Situ Characterization by Using TG–FTIR Analysis. Energies 2025, 18, 5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215842
Liao Y, Huang K. Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Tung Seed Shells and In Situ Characterization by Using TG–FTIR Analysis. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yiju, and Kai Huang. 2025. "Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Tung Seed Shells and In Situ Characterization by Using TG–FTIR Analysis" Energies 18, no. 21: 5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215842
APA StyleLiao, Y., & Huang, K. (2025). Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Tung Seed Shells and In Situ Characterization by Using TG–FTIR Analysis. Energies, 18(21), 5842. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215842







