Abstract
Digital Twin (DT) technology has emerged as a valuable tool for researchers and engineers, enabling them to optimize performance and enhance system efficiency. This paper presents a comprehensive Systematic Literature Review (SLR) following the PRISMA framework to explore current applications of DT technology in the power generation sector while highlighting key advancements. A new framework is developed to categorize DTs in terms of time-scale horizons and applications, focusing on power plant types (emissive vs. non-emissive), operational behaviors (including condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, fault detection, power generation prediction, and optimization), and specific components (e.g., power transformers). The time-scale is subdivided into a six-level structure to precisely indicate the speed and time range at which it is used. More importantly, each category in the application is further subcategorized into a three-level framework: component-level (i.e., fundamental physical properties and operational characteristics), system-level (i.e., interaction of subsystems and optimization), and service-level (i.e., value-adding service outputs). This classification can be utilized by various parties, such as stakeholders, engineers, scientists, and policymakers, to gain both a general and detailed understanding of potential research and operational gaps. Addressing these gaps could improve asset longevity and reduce energy consumption and emissions.
1. Introduction
There is no doubt that electricity is the fundamental foundation powering homes, industries, and technology, while also enabling modern conveniences. In other words, it is an integral part of everyday life, supporting healthcare and driving economic growth worldwide [1]. The journey of electricity from generation to consumption can be summarized across four overlapping sectors: generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization. During the generation phase, energy sources (e.g., fossil fuels, hydro, wind, or solar) are converted into electricity. Transmission involves high-voltage lines that transport electricity over long distances, while distribution uses substations to deliver electricity at various voltage levels to meet different demands. Finally, in the utilization sector, end-users consume electricity for various applications; indeed, approximately 66% of electricity is consumed by induction motors [2,3]. Among these sectors, generation, as the starting point of the electricity supply chain, has increasingly captured the attention of researchers. This study focuses specifically on this critical sector, considering the power generation phase from synchronous generators to the connection point to transmission lines, which includes the power transformer.
There are several types of power generation systems, which can be categorized into two main classes: (1) emissive power plants, which rely heavily on fossil fuels to drive turbines connected to generators, and (2) non-emissive power plants, which utilize renewable energy sources (RES) such as solar, wind, hydro, biomass, and geothermal energy. Although emissive power plants are reliable and contribute to meeting baseload demand, they emit greenhouse gases and pollutants. These plants consist of various components, including generator machines, step-up transformers, cooling systems, and rotational components like pumps and bearings. It is important to note that some of these components, particularly the rotational ones, are absent in photovoltaic (PV) systems.
Efficient management and control of the power generation system, which encompasses various micro sectors, presents significant challenges in power system operation and planning. Several tools and technologies contribute to addressing these challenges; however, each has its own limitations. For instance, one study focused on the SCADA system [4], while another developed a low-cost, real-time IoT-SCADA system for monitoring and controlling PV systems [5]. However, this system is hindered by cybersecurity risks and a high dependency on cloud servers. Energy Management Systems (EMS) are another approach used for managing power grids, but are limited by their lack of adaptability and reliance on data quality [6]. Similarly, Distributed Energy Resource Management Systems (DERMS) offer solutions for efficiently managing power systems ranging from fully centralized to fully decentralized models, yet they face challenges like complex implementation and high computational workloads [7]. Optimal Power Flow (OPF) models are employed to optimize power flow and ensure cost-effective, reliable operation; however, they are limited by non-linear complexity and scalability issues [8]. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models have emerged as innovative solutions that analyze large datasets to improve the precision of demand predictions, thereby facilitating more efficient power generation management [9]. Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS) use real-time monitoring and communication infrastructure for data transmission, making them highly applicable for power systems, yet they face challenges such as data management issues and dependence on communication networks [10]. While these technologies offer significant benefits for managing, optimizing, and controlling power systems, their adoption is often hindered by high costs, complexity, and integration difficulties. As a result, technological innovations are crucial to overcoming these challenges and enhancing the efficiency and reliability of modern power systems.
In this context, Digital Twin (DT) technology has emerged as a transformative solution, integrating the strengths of various models into a cohesive framework. The concept of a Digital Twin can be traced back to NASA’s Apollo 13 mission in the 1970s, when a twin spacecraft was used for security purposes [11]. The term “Digital Twin” was first officially proposed by Dr. Grieves in 2002 [12], who defined it as a digital representation of a physical entity connected through a data layer. This technology was later implemented by NASA in 2010 [13] and 2011 [14] for space vehicles and has since been further developed for various other applications. In the power systems sector, researchers have explored the application of DT technology to create a “digital twin” of the physical power grid and the online power grid, supporting the enhancement of power grid operations [15]. The integration of DT in power systems for monitoring, fault detection, and optimization was discussed in [16]. To improve cybersecurity within power grids, particularly in microgrids, scientists proposed a framework in [17]. Fault detection for power plants using vector autoregressive and deep learning algorithm techniques is another notable application of DT technology explored in [18].
Following the globally widespread adoption of DT technology in the power system, particularly in the generation sector, as discussed in Section 2.2, the need for a comprehensive review, investigation, and categorization of relevant studies has become evident. To address this necessity, we adopted a systematic literature review (SLR) approach, following the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) framework, to collect and review existing research. Additionally, this review examines DT’s functionality in the power generation sector by answering the following key questions:
- How can a balance be achieved between the trade-offs of transitioning to RES while maintaining existing power plants?
- How can the efficiency of both fossil-fuel-based power plants and RES be improved?
- How can faults be detected in both non-emissive and emissive power plants?
- How can energy systems, including power generation, microgrids, and associated equipment, be effectively managed?
Several existing classification frameworks fail to incorporate the full scope of system-level interactions or rely too heavily on static models that do not capture the dynamic nature of power plant operations and cannot address the challenges mentioned above. Our three-tier application framework offers a systematic approach that integrates real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization, ensuring that both operational and strategic objectives are met. Furthermore, the six-tier temporal scale provides a more nuanced approach than traditional models, as it explicitly considers multiple timescales of DT applications, from real-time control to long-term predictive modeling, allowing for a more comprehensive and adaptive approach to power generation management.
This review serves as a valuable resource for future researchers by compiling numerous references related to DT applications and time horizons in the power generation sector. However, it does not delve deeply into the mathematical models and algorithms used in these studies. The primary objective is to map out DT-driven strategies in the power generation sector and streamline access to relevant methodologies. Given the extensive body of literature across multiple databases, every effort has been made to include the most significant contributions. Nonetheless, while the possibility of inadvertently omitting some studies is minimal, it cannot be entirely ruled out. The key contributions of this paper are as follows:
- Quantitative Analysis—A systematic review of existing DT-driven research in the power generation sector, gathered from diverse sources, following the PRISMA protocol.
- Qualitative Assessment and Review—A comprehensive review of influential studies to identify trends and highlight the most common applications of DT technology in power generation.
- Categorization of DT Applications—An organized classification of DT applications in the power generation sector based on the reviewed literature.
The rest of the study is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the quantitative review and the methodology used to conduct it. Section 3 presents a qualitative review of the literature, which is conducted by classifying DT in terms of time-scale and applications and providing a comprehensive review of relevant studies across different defined subcategories. Finally, Section 4 discusses the conclusions, research challenges, and future directions.
2. Quantitative Review
The quantitative review systematically analyzes the literature based on variables such as title relevance, citation counts, authorship patterns, and geographical trends. First introduced in 1969 as a bibliometric analysis, this approach offers a multidisciplinary framework for examining research evolution over time [19]. It maps the development of a field by identifying key authors, publications, and emerging trends [20,21]. The methodology and results of the systematic literature review (SLR) on the applications of DT technologies in power generation are presented here.
2.1. Methodology
The SLR follows PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines, ensuring a structured and unbiased review [22,23]. PRISMA’s four phases: Identification, Screening, Eligibility, and Inclusion, are summarized below:
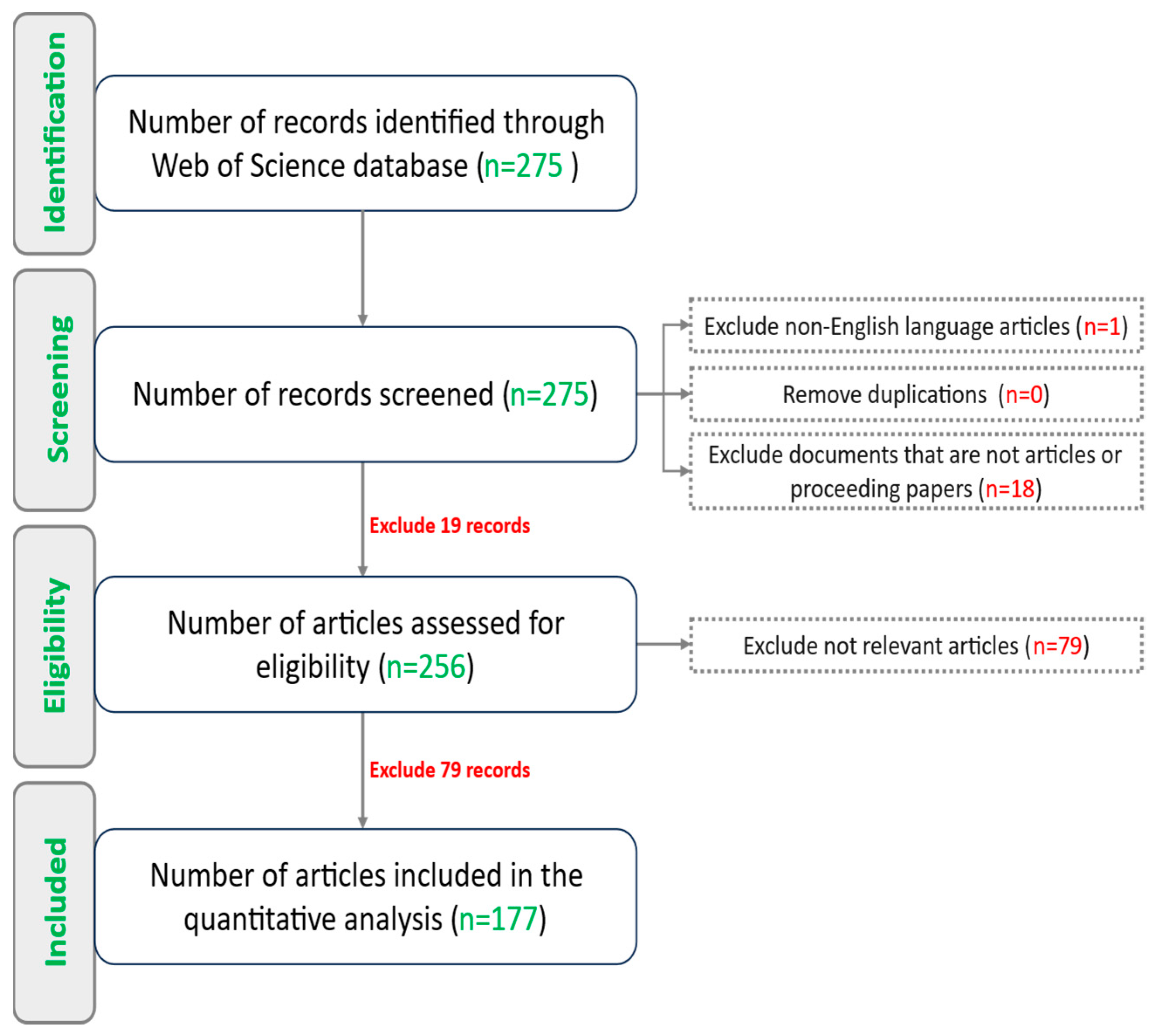
- Identification: To ensure a thorough review, multiple databases and search queries were evaluated to identify the most suitable source for this study. After comparing their scope and relevance, the Web of Science is selected as the primary database due to its broad inclusion of high-impact research from various fields, making it well-suited for an in-depth review. A comprehensive search was conducted in November 2024 using the Web of Science database. A tailored search query targeted titles, keywords, and abstracts related to DT and power generation technologies (Search query: “digital twin*” AND (“power plant” OR “power generation” OR “main shaft” OR “transformer*”)). Boolean operators and wildcard symbols enhanced precision. This search yielded 275 studies.
- Screening: Non-English articles (1) and non-article documents (18) were excluded, leaving 256 records.
- Eligibility: A detailed assessment excluded 79 irrelevant studies, reducing the dataset to 177 articles.
- Inclusion: The final dataset of 177 articles represents the most relevant research. Figure 1 summarizes this process using a PRISMA flowchart.
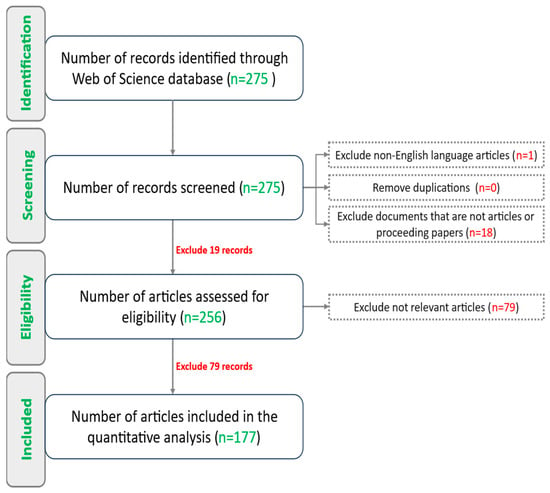 Figure 1. PRISMA Flowchart for Systematic Review Process.
Figure 1. PRISMA Flowchart for Systematic Review Process.
The review is conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines, and the completed PRISMA 2020 checklist is provided as Supplementary Material.
2.2. Results of Quantitative Analysis
Following the refinement of identified studies using the PRISMA method, as outlined in Section 2.1, a total of 177 articles were deemed eligible for the final quantitative analysis. The bibliometric analysis is conducted using the Biblioshiny package in RStudio-1.1.456 [24], which facilitates a comprehensive examination of publication trends and other relevant metrics. The search query yielded 177 distinct studies across 119 scientific sources, with the main details of this collection summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Key details about the dataset.
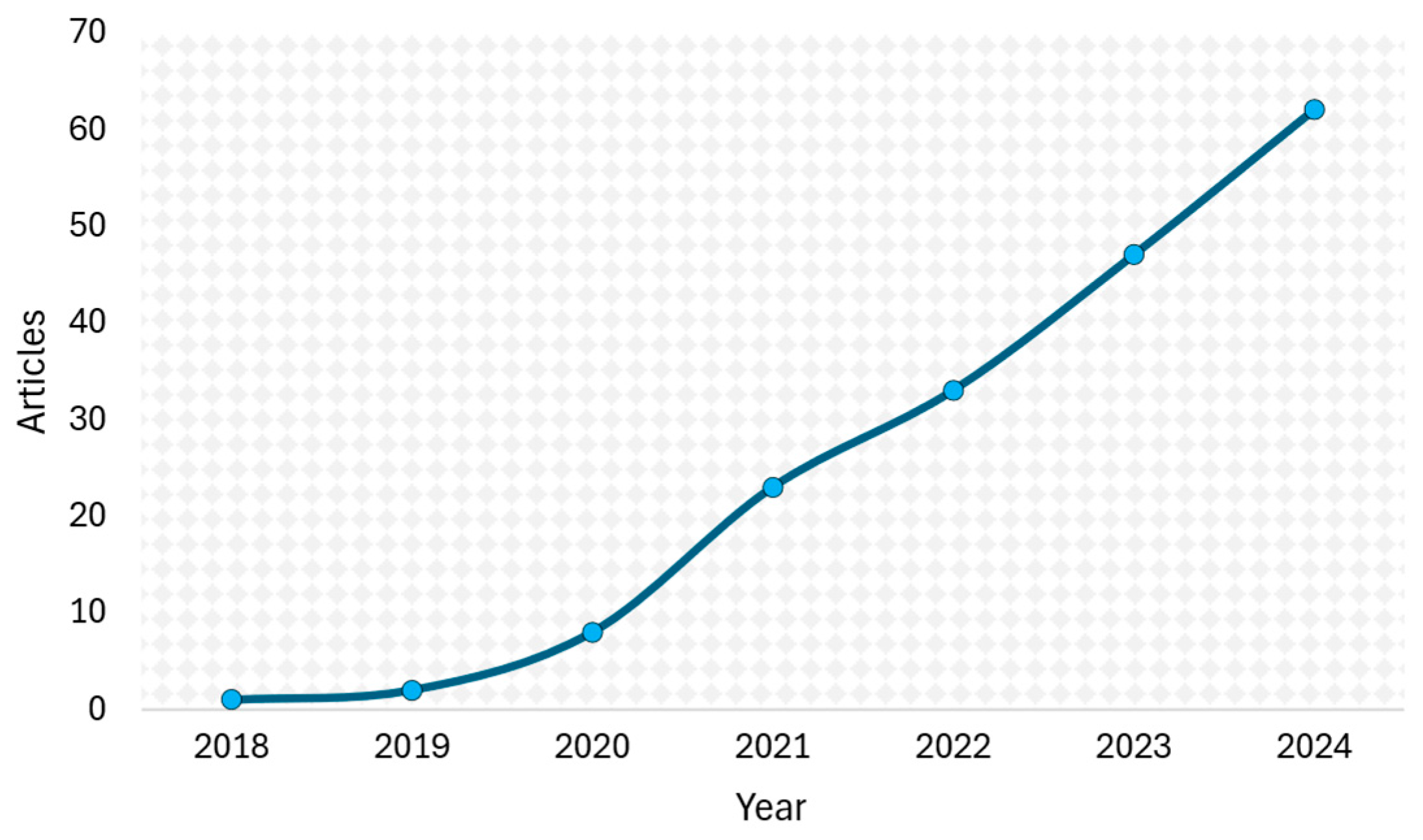
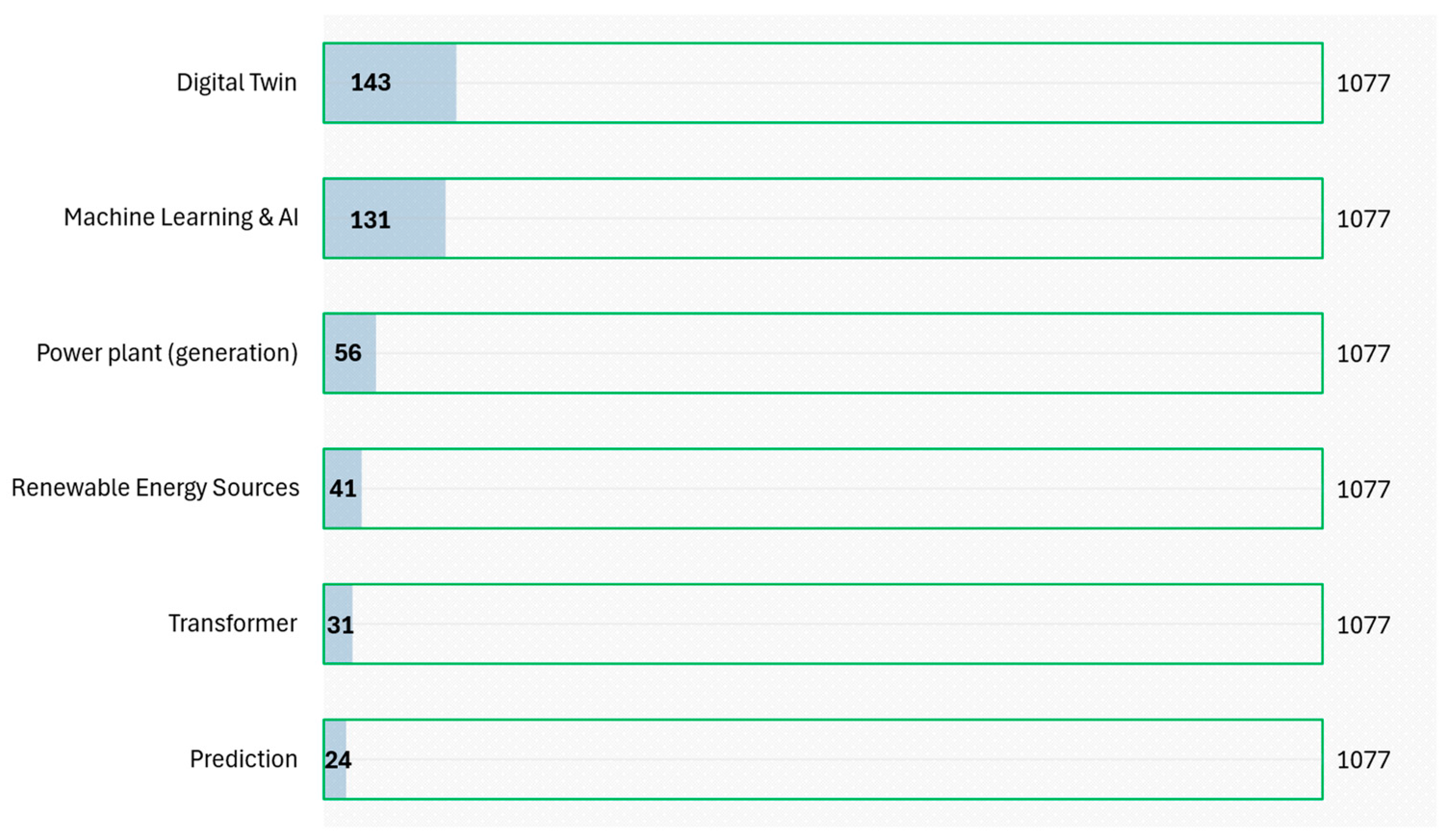
From 2018 to 2024, research on DT in power generation grew steadily, with an average annual growth rate of 99% (Figure 2). This trend reflects increasing interest in the field. Figure 3 displays the categorization of frequent words in the keywords defined by authors (1077 keywords), with each category representing different forms and synonyms for similar concepts. For instance, the “Renewable Energy Sources” category consolidates terms such as “renewable energy,” “wind energy”, and “photovoltaic systems”. This figure highlights prominent themes, such as “Digital Twin” (143 mentions), “Machine Learning & AI” (131 mentions), “Power Plant” (56 mentions), and “Renewable Energy Sources” (41 mentions).
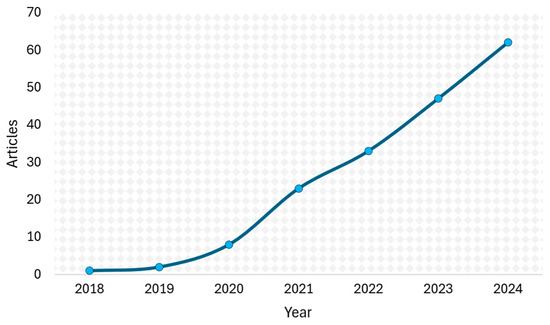
Figure 2.
Annual scientific production.

Figure 3.
The 6 Most Frequent Words (Phrases) in Authors’ Keywords.
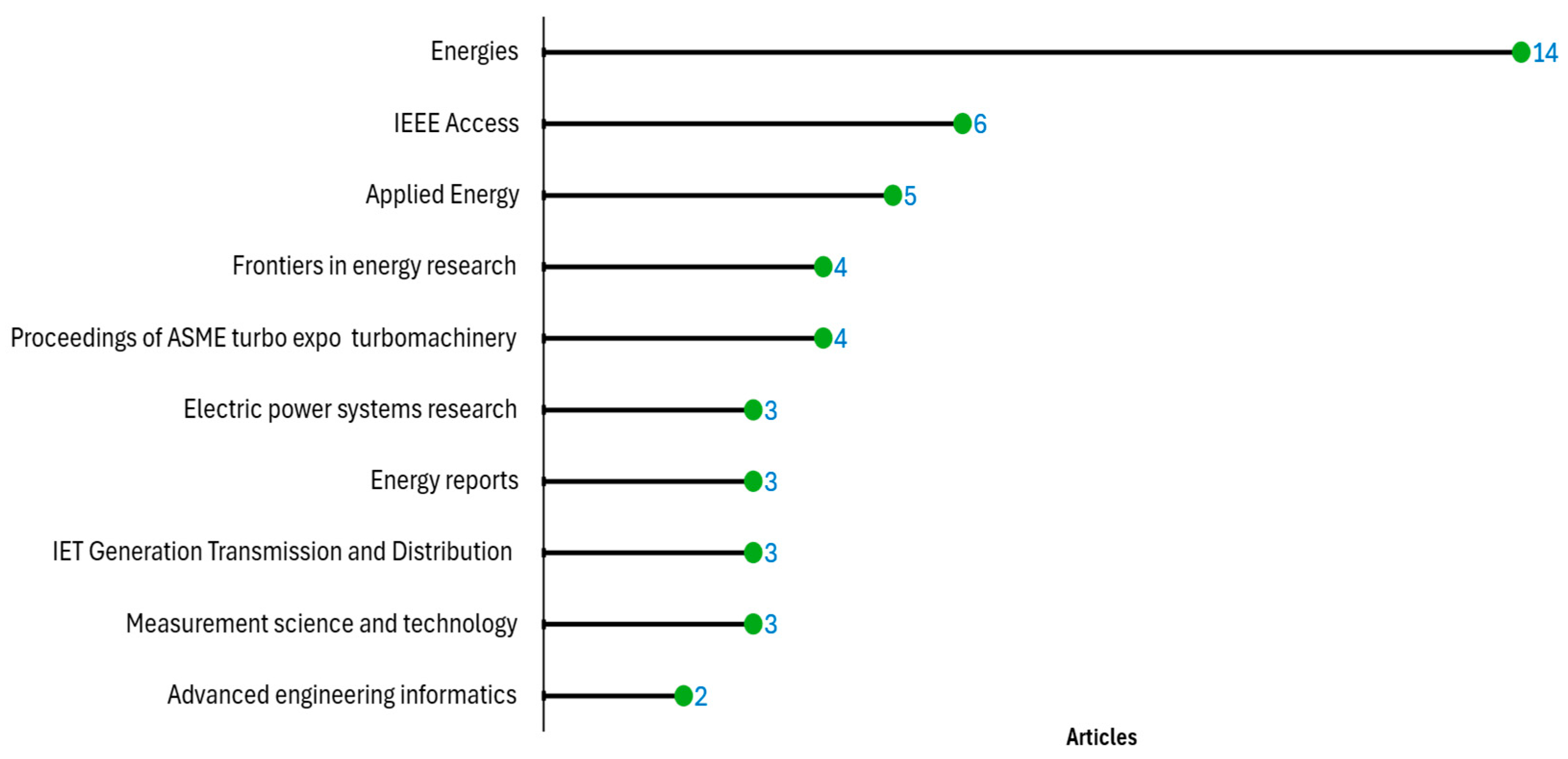
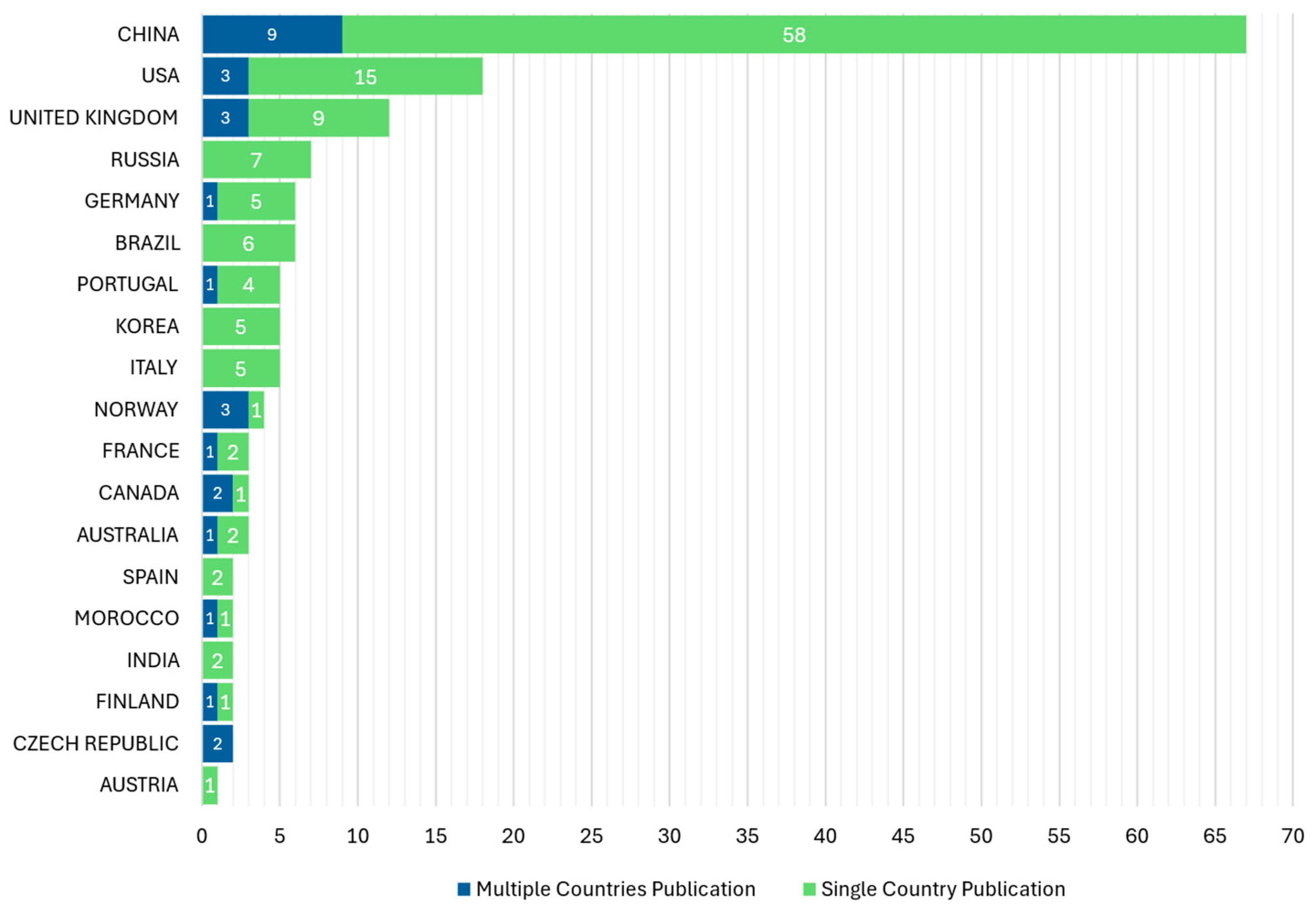
Among the 119 sources, Energies leads with 14 publications, followed by IEEE Access (6) and Applied Energy (5) (Figure 4). The growth trends of the top five sources reveal increasing publication counts, particularly in Energies (Figure 5). This demonstrates the expanding focus on DT applications within power generation. Figure 5 illustrates the number of scientific publications categorized by the nationality of the corresponding author, distinguishing between Single Country Publications (SCP) and Multiple Countries Publications (MCP). China has the highest single-country publications (58) and multi-country collaborations (9). Norway (75%) and Canada (67%) show high international collaboration rates.
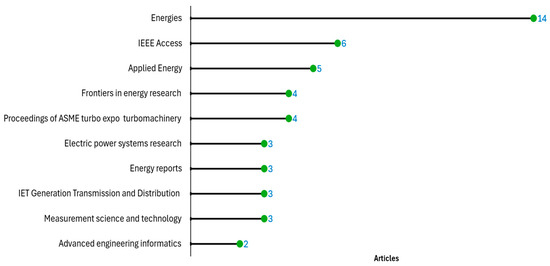
Figure 4.
The 10 most relevant sources.
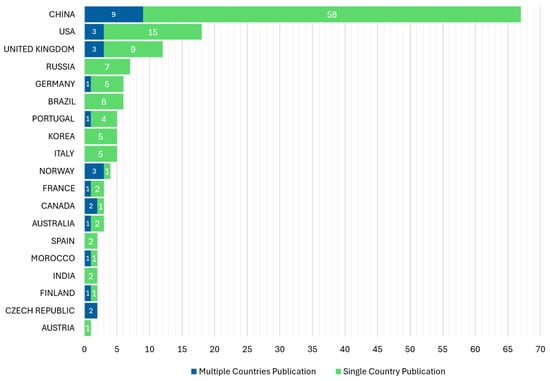
Figure 5.
Number of scientific productions based on the corresponding author’s country.
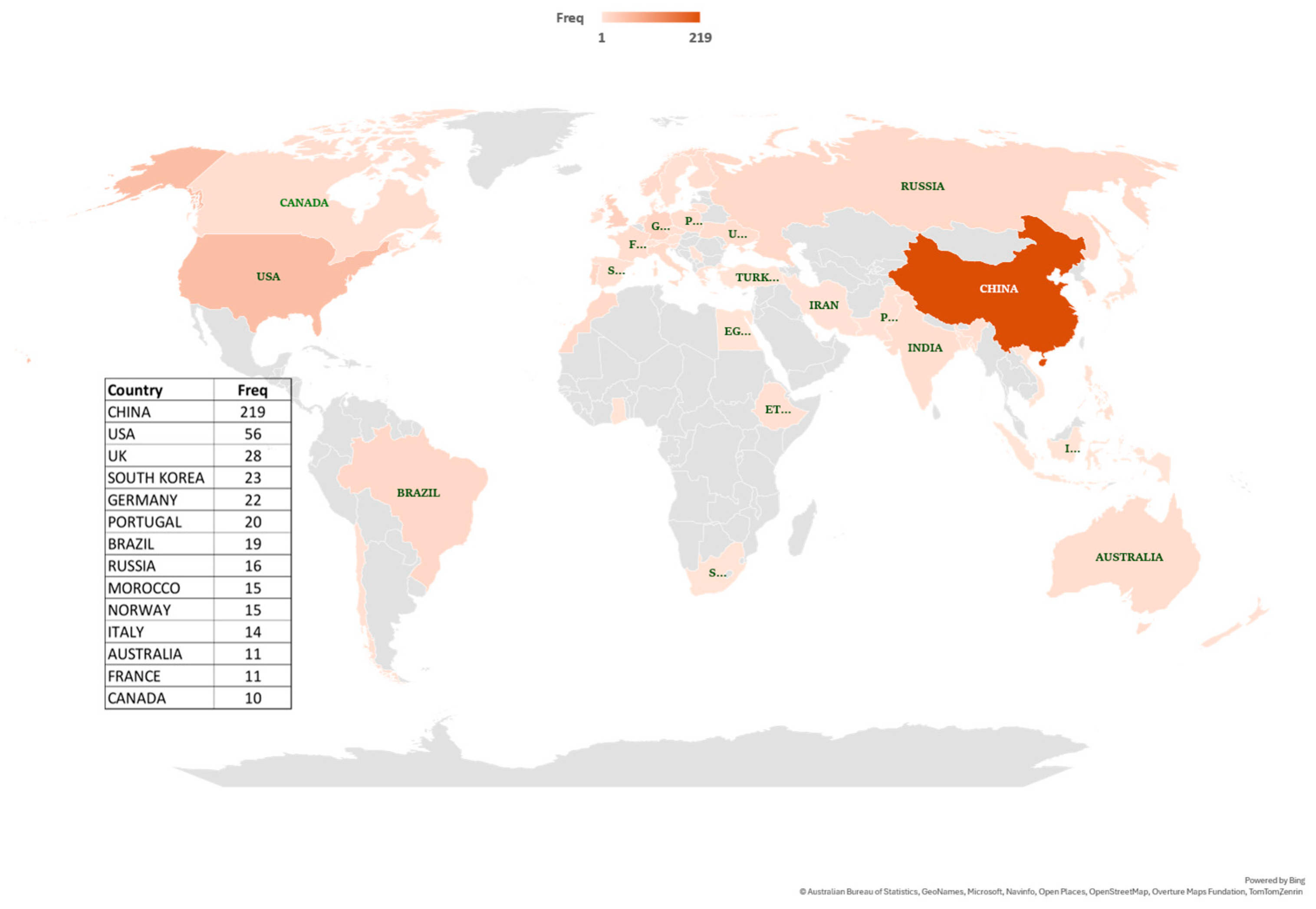
The global geographic distribution of scientific output in this research area is presented in Figure 6. It is worth mentioning that this index counts each occurrence of a country’s affiliation, rather than counting unique papers. China leads in contributions (219 records), followed by the USA (56) and the UK (28). Research output is limited in many African nations. It is worth mentioning that papers with multiple authors from the same country are counted multiple times, as each author’s affiliation contributes separately to the country’s scientific production.
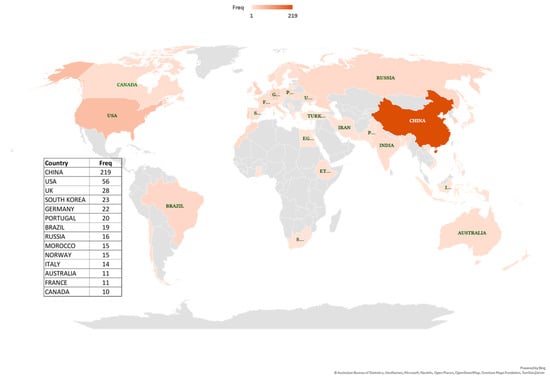
Figure 6.
Distribution of scientific output by country (grey areas indicate countries with no published articles in the retrieved literature).
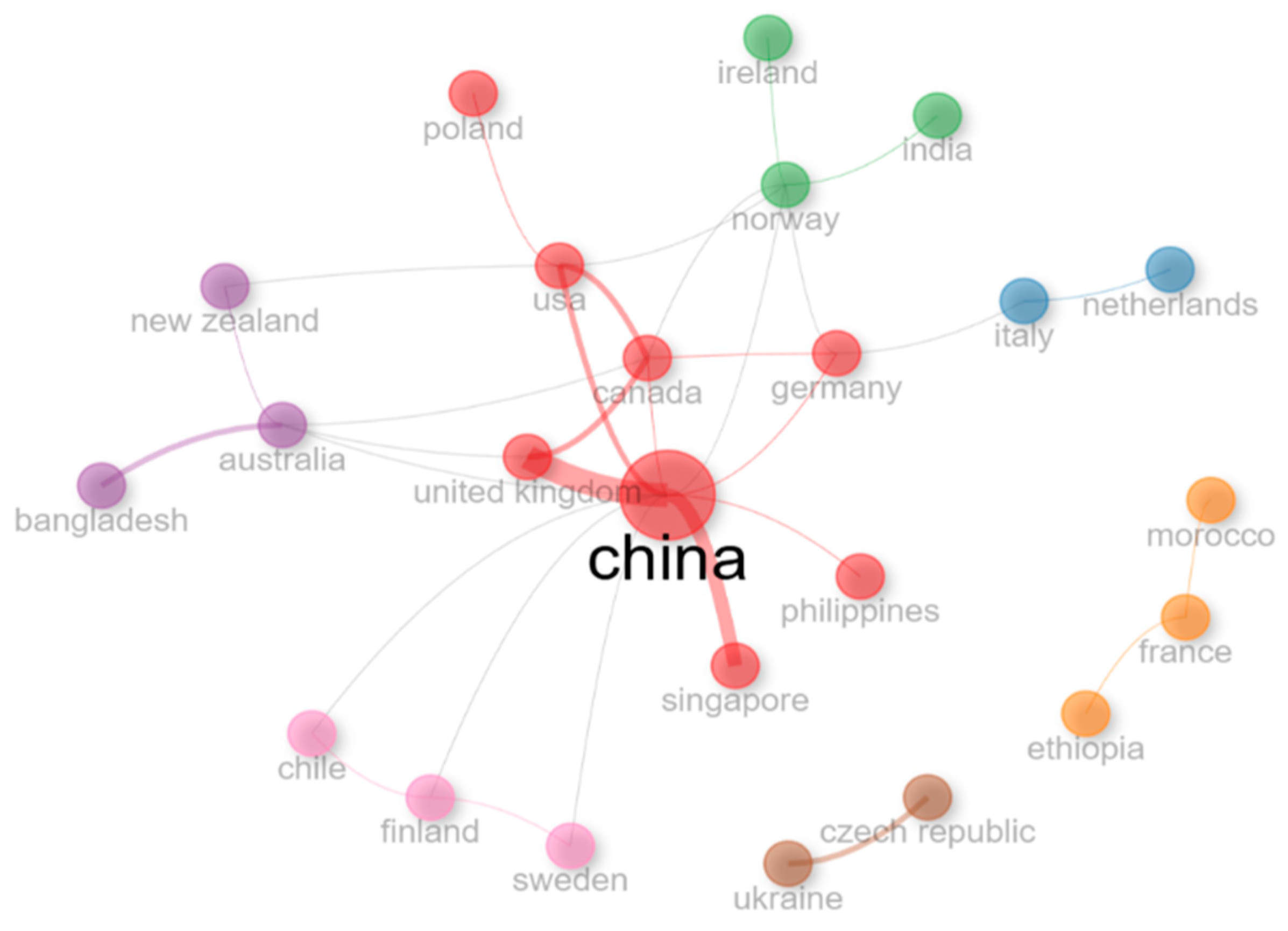
Figure 7 illustrates a country-level collaboration network, showcasing global research partnerships. Collaborative networks highlight China and the UK as pivotal players in global partnerships. This visualization underscores the global scope of research partnerships, with clusters representing groups of countries that frequently collaborate on common research topics.
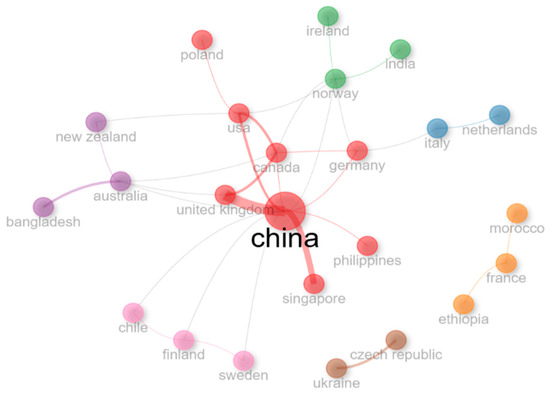
Figure 7.
Country-level collaboration network.
2.3. Selection of the Most Appropriate Documents
To automatically filter out low-quality studies and select the most relevant research for the qualitative review, two indices are used: the similarity index and the SJR (SCImago Journal Rank) scores, which serve as scientific indicators for journals.
2.3.1. Similarity Index
To measure the similarity between the provided keywords and the abstracts, the abstracts of 177 documents are first extracted and preprocessed. This process includes converting text to lowercase, eliminating numbers and punctuation, tokenization, removing stopwords, and stemming using Python’s Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library [25] implemented in version 3.10.11. These preprocessing tasks normalize the text and facilitate the creation of a Vector Space Model. A TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) vectorizer is then used to develop a term-document matrix, with rows representing terms, columns representing documents, and cell values representing term frequency (or 0 if absent). In this framework, the TF-IDF vectorizer transforms each abstract into a numerical representation that captures the weight of terms based on both their frequency in the document and rarity across the corpus. Cosine similarity is then applied to these TF-IDF vectors to measure the angle () between documents and the search query, as provided in Equation (1) [26]. In this approach, TF-IDF defines the textual importance of words while cosine similarity quantifies their alignment, and together, they indicate how semantically close a paper is to the research topic.
These similarity scores are then normalized to a range between 0 and 1.
2.3.2. SJR Score
To identify high-quality publications, the SJR scores are obtained from the SJR website [27]. The SCImago Journal & Country Rank is a free portal providing scientific indicators of journals and countries, developed from data in the Scopus® database (Elsevier B.V.). The indicators are needed to assess scientific fields in order to compare journals. The SJR scores are normalized between 0 and 1. By averaging the normalized similarity scores and normalized SJR scores, a new metric called ‘Cosine_SJR’ is computed. Cosine similarity quantifies the textual closeness between a paper’s content and the defined search scope, ensuring topical relevance. Conversely, the SJR score reflects the scientific reputation and citation impact of the publishing journal, representing publication quality. Averaging these normalized indicators yields a composite index, Cosine_SJR, that prioritizes papers both semantically aligned with the research topic and published in reputable journals. Other weighting alternatives are also applicable; however, in this study, to keep the relevance and quality of the selected papers equally weighted, the average value has been considered.
Finally, based on the Cosine_SJR scores, the top 87 papers were selected, providing a strong and representative set of high-quality, relevant research papers for qualitative analysis.
2.4. Discussion on Quantitative Analysis
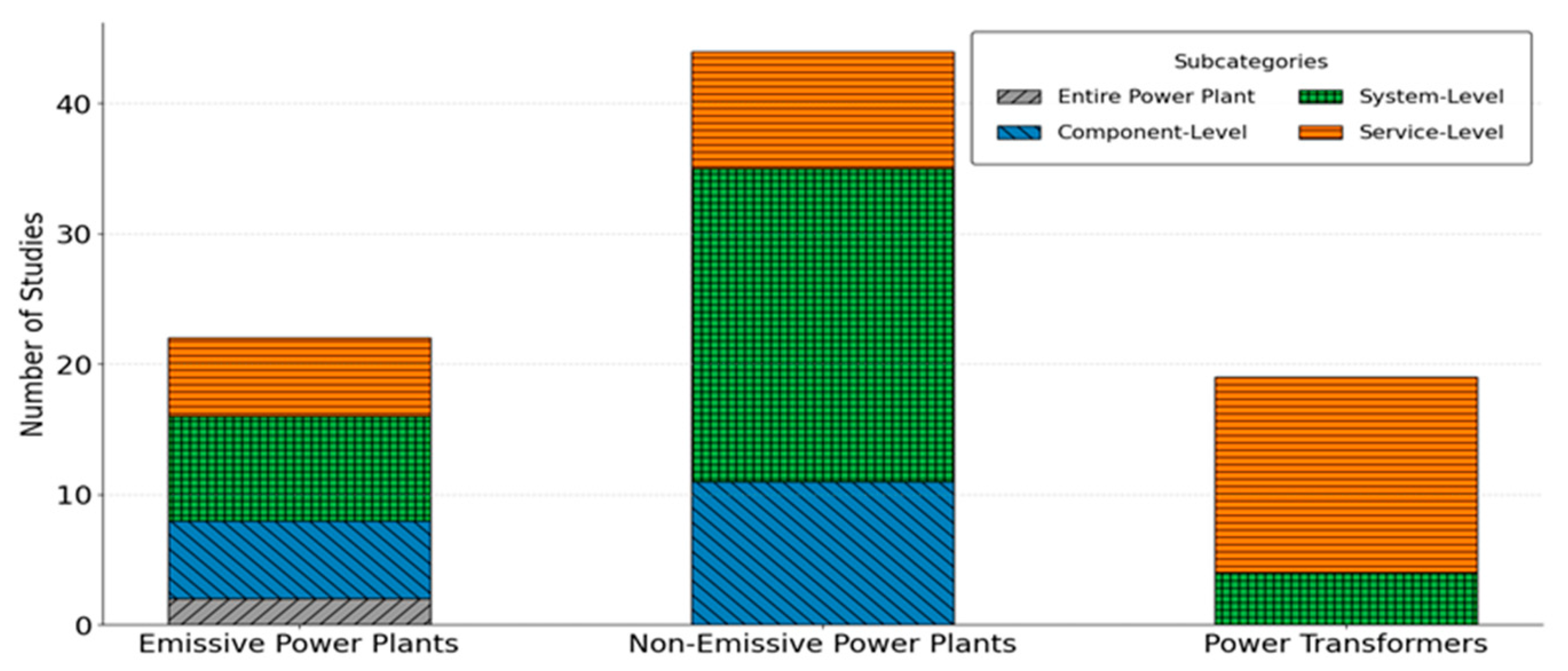
After selecting the top 87 papers using Cosine_SJR scores, each paper’s application was analyzed and classified into different categories. Based on foundational knowledge and an intuitive approach, we classified the application of DT technology in the power generation sector into three main categories: (1) emissive power plants, (2) non-emissive power plants, and (3) power transformers. Each category was subsequently subdivided into subcategories, creating a three-level framework. Figure 8 graphically represents the distribution of studies classified by application. As shown in the figure, a significant number of studies (44 out of 87) focus on non-emissive power plants, compared to emissive power plants (22 out of 87), indicating a growing interest in and priority toward renewable energy systems. Studies within the non-emissive power plants category cover various aspects, including photovoltaic (PV) systems (optimization, fault detection), wind energy generation (wind turbines and their condition monitoring), microgrids, and other RESs (e.g., geothermal, biomass, and hydroelectric power). Power transformers (19 out of 87) also receive significant attention, with the majority of studies focusing on fault detection and condition monitoring (CM). A detailed classification of studies by application, along with a list of papers in each category and their main focus, is provided in the qualitative review section. It is worth mentioning that, after evaluating all 87 papers, we found that two papers focused on general power systems, transmission lines, and busbar protection inside substations; these were excluded from the review.
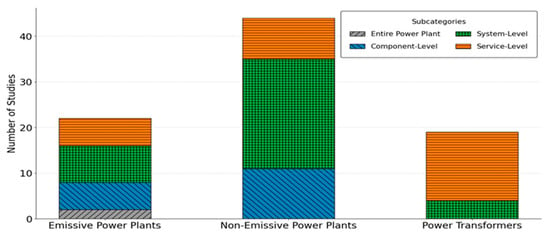
Figure 8.
Distribution of the studies classified by application.
As illustrated in Figure 8, each class is subdivided into various subclasses. Two papers focused on the entire power plant, while the other subcategories are as follows:
- Component-Level: This subcategory includes studies that focus on the individual components of the power plant, such as turbines, rotors, blades, and cooling systems. These papers typically analyze the performance and behavior of specific parts of the system, including their material properties and operational characteristics.
- System-Level: The system-level subcategory involves papers that examine the interaction and optimization of multiple components within the power generation system. These studies often explore how different subsystems (e.g., turbines, generators, and transformers) work together to achieve optimal performance, such as reducing losses or increasing output power. Papers in this category typically focus on system-wide control, efficiency improvements, and integrated operations, sometimes including modeling and simulation of various system configurations.
- Service-Level: This subcategory focuses on the value-added services provided by DTs for the operational management of power plants. Services such as condition monitoring (CM), predictive maintenance (PM), fault detection, and other maintenance management functions directly impact the overall performance of power plants, leading to improved asset longevity and reduced potential failures.
The quantitative analysis provided a structured overview of research trends, geographical distributions, and thematic focuses, offering a data-driven snapshot of how Digital Twin applications in power generation have evolved. Building upon these findings, the next section complements the statistical perspective with a qualitative analysis that delves into the content of selected studies. This qualitative review interprets the technical depth, methodologies, and thematic orientations of the most relevant papers, providing contextual understanding that numerical indicators alone cannot capture.
3. Qualitative Review
The qualitative review provides a comprehensive assessment of influential studies to identify trends and highlight the most common applications of DT technology in the power generation sector. In the first part of this qualitative review, various definitions of DT technology from the literature are presented and subsequently classified based on their application and timescale, as shown in Figure 9. The classification methodology based on application is described in Section 2.4, and the results of this classification will be explored in the subsequent sections. Additionally, the time-scale classification methodology will be discussed in Section 3.2. This review focuses on the application of DT technology in emissive power plants, non-emissive power plants, and power transformers, following an intuitive classification approach. Based on the detailed bibliometric analysis presented in this section, the next section offers a comprehensive qualitative review of the selected articles.
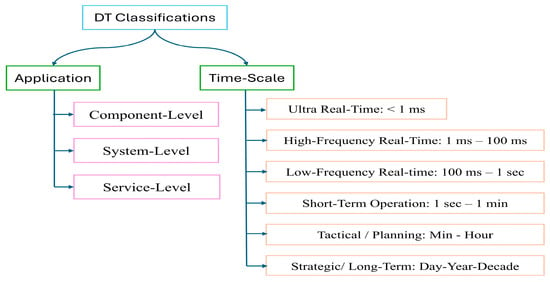
Figure 9.
Hierarchical classification of DT types based on application level and time-scale horizons.
3.1. DT Technology: Definitions
This section contrasts and compares several recently used DT definitions from both industrial and academic sources, directly quoted from the reference literature. The goal is to propose a more generic DT definition that is suitable for widespread application across various domains. To support this detailed literature review, 20 definitions from academia and 4 from industry are presented in Table 2. Each definition in this table shares the same foundational concept as Grieves’s original definition [12], but has been refined to better suit specific application sectors. Definitions from an industrial perspective (e.g., Microsoft) have reformulated their language to emphasize the benefits of the DT platform they provide, rather than offering a broad definition. Numerous definitions of DT technology exist in studies across various applications, including transportation [28], health [29], marine [30], energy [31], manufacturing [32], and remanufacturing [33], with variations based on the nature of each industry and its specific features. Inspired by several definitions from different sectors, this study proposes a comprehensive and generic DT definition for the power generation sector, which encompasses all relevant aspects, devices, and technologies: DT is defined as a technology that can accurately portray and simulate the behavior of physical entities as digital representations in the real world, using real-time data from sensors to continuously adapt to changes for various purposes such as monitoring, optimization, prediction, and detection.

Table 2.
Definitions of DT in both academia and industry.
3.2. DT Technology: Time-Scale Classifications
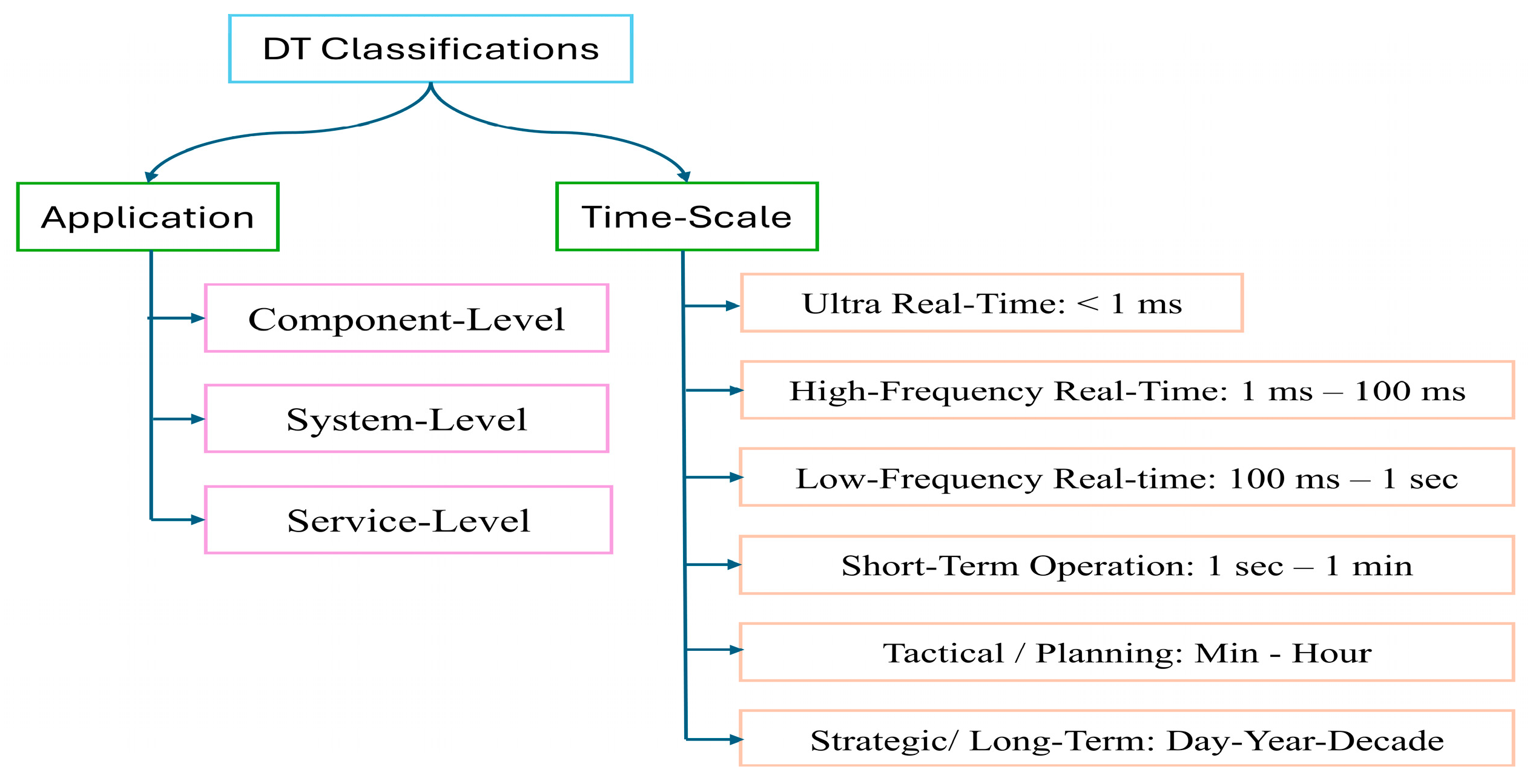
In this part of the review, we describe the six time horizons (a six-level structure) that define outcome time scales in industrial systems, particularly in the power generation sector, as shown in Figure 10.
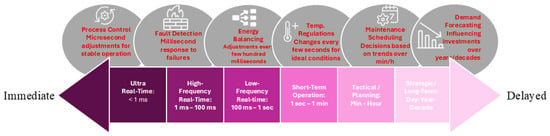
Figure 10.
Time-scales of several DT purposes in the power generation sector.
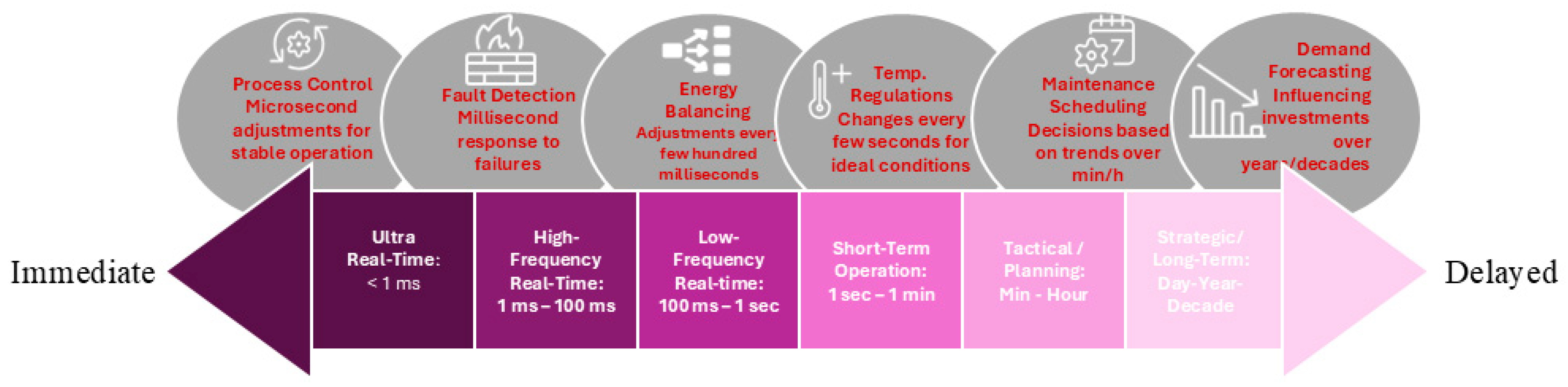
This figure visually represents a timeline with six key operational time scales, ranging from immediate responses to delayed decisions. This classification is crucial because it aligns the operational needs, data processing speeds, and decision-making cycles of DT systems with the appropriate time scales, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and timely responses in industrial applications.
The figure illustrates how these time scales range from ultra-fast control loops, measured in microseconds or milliseconds, to long-term strategic planning, which can span years or even decades. Implementing DTs in the energy industry requires a thorough understanding of these time scales, which are widely recognized in both the literature and industry standards. They can be categorized as follows: Ultra Real-Time (<1 ms), High-Frequency Real-Time (1 ms to 100 ms), Low-Frequency Real-Time (100 ms to 1 s), Short-Term Operational (1 s to 1 min), Tactical/Planning (minutes to hours), and Strategic/Long-Term (days to years or decades).
Next, all selected literature is categorized according to their time-scale horizons in Table 3.

Table 3.
Classification of Papers Based on Time-Scale Horizons explains the methodology of time-scale.
In this classification, each study in our literature pool (87 papers) is divided into distinct sections, with each section evaluated separately to determine its classification within a specific time-scale. As a result, a paper may encompass multiple time-scale horizons rather than being restricted to just one. To illustrate the time-scale classification methodology, we analyze [119] as a case study. This work demonstrates how a single study can span multiple time horizons:
- High-Frequency Real-Time (1–100 ms): The vibration signal analysis for OLTC (Online Tap-Changer) operation is conducted using a high sampling rate of 10,240 Hz.
- Low-Frequency Real-Time (100 ms−1 s): Vibration signals generated by OLTC operations are recorded over approximately 0.2 s.
- Short-Term Operational (1 s−1 min): The study applies dynamic model updating and optimization-based estimation after each OLTC operation.
- Strategic/Long-Term (Days–Years–Decades): It also tracks degradation trends such as spring looseness and delays in diverter switching due to wear.
This study illustrates how a single work can span four distinct time scale horizons, each associated with a different aspect of the analysis. Table 4 provides a synoptic view of the classification of studies on DT applications in power generation systems. The following sections will comprehensively investigate the main categories.

Table 4.
Classification of studies on digital twin applications in power generation systems: a synoptic view.
3.3. Digital Twin Applications in Emissive Power Plants
For decades, emissive power plants (e.g., coal-fired, natural gas, and oil) have been a fundamental component of power systems. Although the penetration of RES is increasing, emissive power plants remain essential due to their ability to provide inertia, given the current state of technology. In these plants, the DT serves as a vital element of cyber-physical systems, integrating real-time data processing, process visualization, and control system interactions. To evaluate and optimize power plant performance, various modeling approaches, such as white-box, black-box, and gray-box models, are utilized in the literature. White-box models rely on known physics, equations, and first principles (e.g., thermodynamics) to describe plant operations. Black-box models use AI or ML to identify patterns from data without understanding the system’s internal workings. Gray-box models combine physics-based equations with real-world data, enhancing accuracy and flexibility for performance prediction and optimization while accounting for uncertainties [125].
DT technology is commonly applied to various components, systems, and services in emissive power plants, including turbines, rotors, diesel engines, cooling systems, CM, and PM. In the following subsections, the application of DT in each of these components will be explored using a three-level structure classification. However, it is important to note that the use of DT is not limited to individual components; recent advancements have expanded its scope to encompass the entire power plant. For example, to achieve plant-wide performance optimization, researchers in [34] developed a DT for an entire thermal power plant, a 1000 MW ultra-supercritical (USC) unit, which is accessible via the web. Mathematical models and reinforcement learning were employed to simulate the dynamic behaviors of the plant’s processes, such as the combustion process, air and flue gas systems, and the distributed control system (DCS). This approach improved energy efficiency to 46%, which is 10% higher than sub-critical coal power plants. Additionally, scientists in [35] introduced a hybrid modeling approach that combines physical mechanisms with operational data to enhance gray-box models of thermal systems in service, such as boilers, steam turbines, steam pipes, feedwater pumps, and regenerative heaters, in a 660 MW ultra-supercritical double reheat power plant. The primary focus was on creating high-precision models of thermal systems in operational power plants to support the development of DTs. This model reduced power losses by up to 0.91%, and heat consumption increased by 0.54% due to a decline in steam turbine performance.
3.3.1. Component-Level Digital Twins
Turbines play a crucial role in the power generation sector by converting heat energy from steam into mechanical energy, which powers a generator to produce electricity. Steam turbines are widely used in thermal power plants due to their high efficiency and ability to produce large amounts of power. Their reliability and continuous operation make them the backbone of many power systems [126]. A DT model for the steam turbine system (STS) is created to monitor in real time parameters such as high- and low-pressure turbines (HPT, LPT), feedwater pump turbine (FPT), pumps (condensate, booster, and feedwater), and regenerative heaters (No. 1 to No. 8) [59]. The study results in an average energy efficiency increase of 0.35% in the STS of a 1030 MW ultra-supercritical power plant. Mark Baker and Budimir Rosic provide two detailed studies on power turbines. In the first paper [60], a comprehensive DT framework is designed to accurately simulate the dynamics of steam turbine systems in thermal power plants, bridging the gap between real-time operational data and high-fidelity system modeling. In the second paper [61], they address the challenges of real-time thermal field prediction in power turbines, including advanced data transfer techniques, hybrid modeling strategies, and their application in enabling DTs for power turbine systems. The study introduces spatial Kriging methods and a new coordinate-based process of hash mapping for fast and accurate data transfer. This combines low-order models, high-fidelity simulations, and real-time sensor data. The turbine is equipped with 64 thermocouples installed on the outer casing. Data is sampled once per minute over a 500 h period, covering ramp-up, part-load, and gland heating conditions, which are used to construct a 3D model of the turbine geometry for a 1030 MW thermal power plant. The number of sensors was reduced from 64 to 32, while still capturing critical thermal gradients for accurate monitoring, thereby reducing the required number of thermal measurements by 50%, while still accurately reconstructing the full thermal field.
In thermal power plants, the rotor is a massive shaft that holds the turbine blades and rotates. Specifically, for steam turbines, the rotor is designed to withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses [127]. In [36], researchers improved the accuracy of fault diagnosis for four common rotor faults: unbalance, misalignment, friction, and bearing loosening, while reducing uncertainty. Additionally, a novel monitoring system was integrated with the DT model, which is dynamically updated with real-time sensor data, enabling continuous data flow. Rotor thermal stress increased slightly from 446.24 to 464.72 MPa; however, efficiency improved, and the start-up time was reduced by 5.3% (32 min saved).
Without a proper cooling system, a generator can overheat, leading to damage or shutdowns. This system removes excess heat, typically using water, to ensure smooth and efficient operation [128,129,130]. Scientists in [37] employ fuzzy inference systems to replicate the decision-making behavior of human operators (as part of the DT structure) to determine the optimal number of cooling fans required under varying operational conditions, thereby improving energy efficiency. A significant contribution of this work is the automatic extraction of fuzzy rules from historical data obtained via the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system of a 320 MW thermoelectric power plant in Brazil. The optimized fan operation reduced energy consumption by 1.44 MWh per day per radiator, decreased fan usage by up to 3 units per radiator, and improved predictive accuracy by 7.5% through dynamic fuzzy rule updates. In [123], the effectiveness of fault management in heat exchange systems is examined. The authors focus on a closed-loop water system consisting of a water pump, an air cooler (a one-dimensional single-tube heat exchanger), and a heater, all equipped with sensors for measuring mass flow, pressure, and temperature. Faults such as leaks, clogged inlets, and thinned pipes are simulated, along with sensor failures and multiple combined faults. The DT-based framework improved the accuracy and timeliness of fault detection by 96% and 35%, respectively, and reduced unplanned downtime due to faults by 18.5%.
3.3.2. System-Level Digital Twins
In [93], the authors present an approach to improve the control and optimization of power plants that integrate combustion engines, battery storage, and grid connectivity. Reference vibration signals for each operational state of the machine are collected in this system, using various control and data acquisition layers to extract features with fast Fourier transform (FFT), statistical time analysis, and short-time Fourier transform (STFT) for combustion control. The model achieved significant computation speed improvements (94% faster simulation times) while maintaining high accuracy (within 4% to 8% of real measurements). In [121], the researchers suggest a platform to enhance the reliability and efficiency of marine diesel engines through the implementation of a Performance Digital Twin (PDT). The framework is calibrated using test results from a diesel engine across 27 different operating modes to measure both static parameters (e.g., intake and exhaust temperatures, engine power) and dynamic parameters (e.g., in-cylinder pressure, fuel injection pressure). This structure improved fuel consumption prediction by 10.5%, NOx emission accuracy by 48.4%, and smoke opacity prediction by 57.2%, thereby enhancing engine efficiency and emission forecasting. In [73], an architecture with five layers is introduced: web interface, server cluster, real-time data, controller, and equipment layer. The DT continuously monitors the diesel generator’s operational parameters, such as current, voltage, speed, and temperature, and provides real-time feedback and control of the excitation system and speed regulation of the generator through a PI controller. The system architecture supports both MATLAB/Simulink R2022b and an open-source alternative (M2PLink). Ref. [110] discusses a smarter way to predict the performance of a combined cycle power plant (CCPP), particularly the gas turbine units (CCGUs). This model utilized 20,000 pieces of raw operating data from two 376.4 MW CCGUs over one week. The DT framework, using Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (NODEs), significantly improved CCGU performance prediction with exceptionally high accuracy (R2 = 0.993, MAPE = 0.325%), compared to traditional models like Random Forest, BP Neural Networks, and LSTM.
Advanced solutions, such as DT, can enable real-time fault detection. For instance, a framework explored in [74] applies to any type of power plant, though it is more applicable to district heating power plants, to manage the resilience of the plant and its associated heating network. The integration of DT with resilience management allows for comprehensive and timely preparation and response to emerging threats, while also enhancing the resilience of Critical Infrastructure Systems and Organizations (CISOs). The scenario to be validated involves a major fire at a district heating power plant caused by a technical defect that went undetected, leading to the shutdown of heating for hospitals, elderly homes, schools, and 15,000 households. This method achieved a 35% reduction in response time, an 18% decrease in economic losses, and a 22.8% improvement in failure prediction accuracy. Scientists in [98] design a DT-based platform for Combined Heat and Power (CHP) cogeneration, with a steam extraction rate of 350 tonnes/h, replicating the thermodynamic behavior in a 320 MW coal power plant. It evaluates potential optimization strategies, estimating up to a 3.5 g/kWh reduction in coal consumption. The researchers in [38] combine mechanism-based models with data-driven methods to capture both known physical dynamics and unmodeled behaviors of the boiler system, including the pulverizing system, furnace, and drum. By employing this model, heat transfer efficiency improved by 9.8%, unburned carbon content in fly ash was reduced by 5.4%, and boiler thermal efficiency increased by 4.6%. The management of power plants, specifically through the predictive maintenance (PM) of Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), is discussed in [97]. In this study, DT serves as a digital replica of the physical RTU connected to a large power generator. The framework achieved 100% anomaly detection accuracy and improved forecasting accuracy with XGBoost (5.6 s execution time), which was 15 times faster than LSTM.
3.3.3. Service-Level Digital Twins: Reliability and Maintenance
Over time, components like bearings, blades, and seals in machinery naturally degrade due to constant use, heat, and pressure. CM identifies early signs of wear (e.g., unusual vibrations, noise, or temperature fluctuations), allowing for timely repairs before component failure. Additionally, CM detects performance issues, such as dirty filters, misaligned components, or damaged parts, which can lead to increased fuel or energy consumption while maintaining the same power output [131]. Finding a scalable and intelligent solution for CM in thermal power plants is crucial. In [62], the authors present a Hybrid Twin Thermal Power Plant (HT-TPP) architecture that combines physical models (white-box) with data-driven models (black-box) to create a comprehensive digital representation of thermal power plant systems. The model is fully aligned with the ISO 13374:2015 standard [132] for CM and diagnostics of machines. Downtime due to turbine malfunctions decreased by 20%, anomaly detection speed increased by 40%, computational load dropped by 35%, and early fault detection enabled maintenance 30% sooner than traditional methods. In [63], a DT-based subspace model predictive control (DTSMPC) scheme is introduced. To accurately estimate critical parameters in real time, an online data assimilation method based on the Cubature Kalman Filter (CKF) is proposed. This structure was implemented on a 600 MW thermal power plant to accurately reflect the plant’s fuel combustion and vapor-water dynamics behavior, achieving 29% faster load adjustment, reducing overshoot by 29%, and cutting power overshoot by 36%.
The study [64] discusses a hybrid modeling method to correct the inherent mismatches and errors in thermal system models by utilizing online measured data through a grey-box strategy. This method was validated on an in-service 660 MW ultra-supercritical double-reheat power plant, where shaft work output uncertainty decreased by 36.55% (from 6.21 to 3.94 MW), while heat consumption rate uncertainty reduced by 43.82% (from 52.57 to 29.53 kJ/kW·h). In [65], the authors explore a novel solution to integrate three distinct flow systems—material, energy, and information—to provide a more accurate representation of the plant’s operations. It reflects actual operating conditions and adjusts parameters such as turbine efficiency, heat transfer coefficients, and pump efficiency based on historical data. Adjusting the condenser model reduced heat loss by 14%, optimizing steam turbine efficiency decreased energy losses by 9.5%, and lowering the cooling water pressure drop improved heat exchanger efficiency by 12.3%.
PM actions in power plants ensure that all in-service systems remain in a healthy condition, meeting objectives such as enhancing operational reliability, reducing maintenance costs and downtime, and improving energy efficiency. By forecasting equipment failures and performance degradations, PM allows for timely interventions, reducing unplanned downtimes and optimizing the plant’s overall efficiency [133,134]. In [66], the authors develop a DT model for a 342 MW thermal power plant (TPP) to address mechanical issues such as air filter failures, fuel leaks, valve malfunctions, oil leakage, and turbocharger faults. This model uses wavelet transforms and gradient boosting algorithms to categorize failures into six subsystems: air intake, exhaust, fuel, water cooling, lubrication, and mechanical systems. The DT model detected failures up to 2 days earlier, and real-time monitoring reduced maintenance downtime by 25%. In [99], the research focuses on three distinct operating scenarios for a cogeneration plant: (1) the plant supplies energy solely to the sugar factory, (2) the plant provides energy exclusively to the electricity grid, and (3) the plant simultaneously supplies energy to both the sugar factory and the electricity grid. Using a DT model created with ProSimPlus® v. 3.7.6 process simulation software, the researchers simulate these scenarios to assess their performance. The analysis revealed that Mode 3 resulted in the highest profitability and potential exergy loss reductions of up to 9.63 MW. By optimizing the interaction between different energy flows within the plant, a 15% heat recovery potential was identified.
3.4. Non-Emissive Power Plants
Non-emissive power plants, including wind turbines, solar panels, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy, produce clean and sustainable power. The use of DT technology enhances the efficiency of RESs, enabling their integration into modern smart grids that align with global zero-carbon emission goals, paving the way for a greener future [135,136].
3.4.1. Component-Level Applications
Blades are the most critical components of a wind turbine, as they capture wind energy and convert it into mechanical power. Their aerodynamic design is essential, since well-optimized blades can harvest more energy and operate efficiently over a wide range of wind speeds [137]. In [100], a comprehensive methodology to assess blade reliability is applied to the IEA-15 MW offshore reference wind turbine rotor blade. The study employs high-fidelity Fluid–Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations, serving as the foundation of a DT, to capture the dynamic response of the rotor blade. The model was 400 times faster in predicting blade deflection than full-scale FSI simulations, completing the same task in about one minute instead of seven hours, corresponding to a 99.5% reduction in computational cost.
The drivetrain system in a wind turbine transfers the energy captured by the blades to the generator and includes key components such as shafts, gears, and bearings that operate together to ensure smooth turbine performance. In [101], a novel method for fault detection is introduced, optimizing the placement and number of vibration sensors. To reduce data volume while maintaining detection accuracy, a combined Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) approach is used to process vibration data. Before optimization (ISO standards), multiple sensors were required; after optimization using the DT approach, only two sensors were sufficient.
A methodology for the real-time stability assessment of wind power plants (WPPs) is discussed in [75]. It combines reverse-time trajectory analysis, used to evaluate nonlinear stability, with a reduced-order modeling technique that identifies the boundary of nonlinear stability for a WPP coupled to the AC power grid via a long HVAC cable. The model analyzes system responses to small frequency disturbances (±5 Hz from nominal). The stability margin increased by 18%, preventing instability under high wind speed conditions, and the assessment time was reduced by 77%.
DT technology contributes significantly to environmental sustainability. In [117], a simulation for geothermal power plants (GPPs) is developed using UniSim Design® software version R460 to evaluate the environmental and energy performance of different configurations. The model assesses the environmental impact of GPPs, particularly the emissions of pollutants such as Hg, H2S (reduced by up to 77%), NH3, and SO2. Four alternative configurations of a 40 MW GPP in Tuscany, Italy, were simulated and compared. Two additional studies investigate boiler performance in a 200 MW biomass-fired power plant in Ontario, Canada. The first work [67] predicts operating-variable set points that optimize performance under uncertainty. The DT model provides optimized quantities of interest (QOIs) while continuously learning and quantifying uncertainty in those variables. Efficiency increased by 3.5%, NOx emissions were reduced by 8.7%, and unscheduled downtime decreased by 12%. The second study [68] analyzes data from December 2019, including 35 different measurements such as oxygen concentration, electrical power from the grid, boiler outlet conditions, and several gas temperatures. The DT improved efficiency by 4.2%, reduced power fluctuations by 6.5%, and decreased unplanned downtime by 15%.
Hydroelectric power plants are essential for sustainable energy generation, and their inertia plays a critical role in maintaining power system stability, particularly under high penetration of photovoltaic and wind sources. The DT framework in [69] compares live PLC-based sensor data with model-generated predictions to identify (1) malfunctions in the plant’s physical components and (2) errors or inaccuracies in sensor measurements. If a sensor fails or provides unreliable data, the DT generates accurate virtual measurements from its internal model, ensuring uninterrupted operation. Predictive maintenance (PM) scheduling improved by 40%, unplanned shutdowns caused by sensor failures were reduced by 85%, and energy loss due to unnecessary stoppages decreased by 12%. In [46], the authors propose creating a digital shadow using a system of equations that models the physical behavior of the plant integrated with a SCADA system. The simulation considers both normal operation and two fault conditions: excessive generator shaft vibration (mechanical fault) and rapid degradation of stator copper insulation (electrical fault). The mechanical fault was detected after 18–26 observations, while the electrical fault was properly identified after 24–34 observations. A DT-based computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model in [118] investigates the environmental and ecological impacts of the Water Vortex Power Plant (WVPP), particularly its influence on aquatic life, such as fish migration and behavior. The system was designed for a head of 1 m and achieved a 4% water height prediction accuracy, demonstrating the applicability of DT to both technical optimization and ecological assessment.
There is a growing trend toward integrating renewable energy systems with electrolyzers to produce hydrogen and oxygen while simultaneously providing heating. Recent studies, such as [138], explore the integration of Power-to-X systems using DT to optimize hydrogen production, improving both efficiency and economic feasibility. The main findings of [102] include the development of a DT to simulate and optimize various configurations of PV array size, hydrogen storage capacity, and the hydrogen-to-methane ratio. The study reports annual CO2 savings of 155 tons and demonstrates economic viability with a 16-year payback period for full hydrogen combustion. Excess electricity from PV cells in [43] is converted to hydrogen through electrolysis, stored, and later used by SOFCs to generate power when solar input is insufficient. The model dynamically balances global exploration and local exploitation during optimization, improving convergence speed and parameter identification accuracy. The system’s lifespan was extended by 14%, while energy curtailment and frequency fluctuations were reduced by 9.6% and 11.4%, respectively.
3.4.2. System-Level Applications
Due to the significant uncertainties and fluctuations of renewable energy systems, accurately predicting power generation, which is a crucial factor for electricity pricing and system reliability, remains a major challenge [139,140]. In [70], Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins infrastructure is employed to create a five-dimensional platform that replicates the physical operations of a 1.5 MW wind turbine power plant (WTPP). A Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) is used to predict wind power generation, achieving a 9% improvement in prediction accuracy compared with traditional statistical models and an 18–22% reduction in forecasting errors. In [39], the authors propose a DT-based forecasting method for both wind and photovoltaic power generation. The deep learning model, WPNet, trained and tested using data from the Elia Open Data Portal, achieved a 12–15% improvement in prediction accuracy and reduced forecasting errors by up to 15%.
In PV systems, one major challenge lies in accurately computing shading patterns for Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) arrays. In [103], researchers employ an artificial neural network (ANN) trained with high-resolution shading data derived from Digital Surface Models (DSMs) generated by Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) technology. The ANN predicts AC output power and meteorological variables at 5 min intervals with a Mean Relative Error (MRE) between 6% and 15%. The study in [112] addresses parameter discrepancies arising from the bifacial nature of PV modules by introducing a bifacial correction coefficient validated with operational data and TensorFlow-based simulations. A DT model using bidirectional gated recurrent units (Bi-GRU) processes historical and meteorological data to predict power output under various weather conditions, achieving up to a 72% reduction in forecasting errors.
To mitigate data contamination in PV datasets, ref. [40] applies Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to restore historical data and improve physical-digital mapping accuracy, yielding an 18.2% improvement in prediction precision using data from 2016 to 2018. The PV framework in [104] is optimized to balance two objectives: maximizing panel absorption and maintaining suitable ground absorption for agricultural purposes. The DT system, based on a reduced-order formulation of Maxwell’s equations, improves panel absorption efficiency by 23.5%. The study in [113] investigates a dual-system three-phase inverter (DSPI) to enhance the efficiency of on-grid PV systems, achieving a 0.911% rise in annual energy production and 0.9259% higher revenue compared with conventional inverters.
Paper [76] focuses on reducing PV output variability to enhance grid stability through DT-based energy storage optimization, achieving steady power output for 87% of the year, a 0.9259% increase in annual energy generation, and 88.5% storage efficiency. The mathematical model in [71] optimizes control of normal-mode parameters in power systems with high renewable integration, reducing energy curtailment by 9.6% and increasing renewable utilization by 7.2%. Through improved solar irradiance forecasting, ref. [124] integrates multiple tree-based ensemble learning models to capture temporal variability in irradiance, achieving a 7.8% rise in solar energy utilization and a 5.2% decrease in power curtailment.
Controlling distributed energy generation systems that simultaneously produce heat and electricity, such as PV-powered combined heat and power (CHP) units, presents significant challenges due to the complexity and inefficiencies of managing DERs. In [44], researchers demonstrate that integrating a solar collector to adjust the pump’s switching set points increases pump activation frequency, reducing the coolant’s cooling time within the pipes. The implementation of the DT framework resulted in 10% energy savings, a 12% increase in efficiency, and 95% accuracy in energy optimization. In [77], a solar PV system supplies energy to a residential building, where a decentralized fuzzy logic controller manages the load based on solar power availability, battery state of charge, and tariff rates, without the need for communication between residential units. The study, conducted on the rooftop of a nine-story building, achieved a 60 kW load reduction through DT-enabled load shedding and shifting.
The integration of DT technology with VPPs enhances the operation, control, and management of DERs [141]. Real-world data are used to capture daily load patterns, water usage, and energy storage capacity to precisely control demand response (DR). The DT simulates the aggregated performance of water heaters, and switching from electric water heaters (EWHs) to heat pump water heaters (HPWHs) reduced electricity consumption by approximately 70%. Study [47] investigates how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can be integrated into VPPs. The DT simulates real-time HVAC behavior using one physical and twenty-nine virtual systems, improving monitoring, control, and optimization. This approach reduced energy consumption by 12.3% and improved power prediction accuracy by 9.6%. Integrating DT technology with RESs also creates new opportunities in electricity markets. In [105], a novel framework is proposed for managing energy resources in Renewable Energy Communities (RECs) through Collaborative Virtual Power Plant Ecosystems (CVPP-E) and Cognitive Household Digital Twins (CHDTs). The model, consisting of 100 CHDTs implemented in the AnyLogic platform (without specifying further details), increased household engagement in energy-saving behaviors by 15%. To enable secure and decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) energy transactions among consumers and prosumers in smart grids (SGs), ref. [48] develops a sustainable energy trading system combining VPP, DT, and blockchain technologies. The framework employs Ethereum smart contracts for automated, fair payments and applies cooperative game theory for transaction optimization, while the DT simulates VPP performance to identify potential issues and assess alternative scenarios.
DT technology revolutionizes microgrid management by creating virtual replicas of physical systems for real-time monitoring, optimization, and predictive analysis. By integrating IoT sensors, ML, and advanced simulation models, DERs can be controlled more efficiently [142], particularly in the presence of battery energy storage systems (BESS) [143,144,145,146]. This section focuses on the integration of DT with the power generation sector. The DT was developed on Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS) [94], which optimizes power generation and introduces self-healing capabilities, achieving a 5.8% increase in efficiency, an 18.3% reduction in downtime, and an 87% faster fault-response time. Various ML algorithms—polynomial regression for modeling, logistic regression for fault classification, and gradient descent for optimization—support this framework. Study [78] demonstrates the effectiveness of a layered DT for Industry 5.0 power grid management, reducing forecasting error by 5.21% and computational time for anomaly detection by 27%.
Ref. [79] presents a web-based DT for Deakin University’s microgrid, which supplies 50–55% of the university’s electricity demand and reduces CO2 emissions by 12,000 tonnes annually. In [58], a hybrid model predictive control (MPC) strategy for renewable-powered microgrids with seasonal hydrogen storage combines energy production and consumption modeling with a DT-based optimizer to determine the optimal 24 h management strategy. This model cut CO2 emissions by 7.8%, reduced unplanned downtime by 15%, and achieved 42% faster decision-making. The DT in [95] simulates and optimizes component scheduling, increasing renewable utilization by 15% and lowering operational expenses by 18.7%. An intrusion detection system (IDS) is also incorporated to identify and mitigate cyber threats such as Sybil and masquerading attacks in the microgrid’s cyber layer.
For building-level energy management, researchers in [80] develop a DT-based energy management system (EMS) using a microgrid modeled with OPAL-RT 5700, RT-Lab 2019.3, and MATLAB 2018b, with components interconnected through the IEC 60870-104 communication protocol. This framework increased renewable energy penetration by 17.3%, and reduced electricity costs and CO2 emissions by 23.7% and 9.5%, respectively. Reference [53] introduces a microgrid digital twin (MGDT) model capable of estimating the cycle count and stress levels of a BESS, improving accuracy by 14.6%. Predictive maintenance using the MGDT lowered maintenance costs by 22.8% and battery downtime by 17.3%. Finally, study [81] applies DT technology to manage small productive processes (SPPs) as electrical loads; validated in a solar-drying case study in Chile, it reduced microgrid operating costs by approximately 5%.
3.4.3. Service-Level Digital Twins: Reliability and Maintenance
For the efficient operation of wind turbines (WTs), it is essential to implement fault detection, lifetime estimation, stability assessment, and, more broadly, CM. In [106], researchers propose a strategy to identify the root causes of anomalies in a 5 MW WT under three scenarios: (1) active power deviation ≥ 500 kW, (2) overheating in two of the three control cabinets, and (3) filter plate temperature exceeding 100 °C. The framework was validated using field fault data collected from a sugar factory, a thermal power plant, and a wind farm, resulting in a 25% reduction in downtime, 96.66% fault detection accuracy, and a 40% reduction in false alarms. To overcome the challenge of limited direct measurements in offshore environments, ref. [111] proposes a framework based on recursive Bayesian inference for a WT at the Block Island Wind Farm (BIWF) in the United States. By utilizing output-only measurements, the DT model simultaneously estimates structural parameters and unmeasured inputs, achieving substantial computational efficiency by processing 1000 data points in just 10 steps, compared to 1000 separate iterations required by traditional Kalman filtering.
PV power plants often experience faults such as broken connections, damaged panels, or partial shading, which reduce output and may cause further damage if left unaddressed. In [115], by assessing each PV array’s current ratio within a DT framework, fault detection and localization are achieved with a classification accuracy of 98.55% in just 1.02 ms. For classification, the authors employ a Shifted Window (Swin) Transformer, capable of detecting multiple fault types, including line-to-line (L-L) faults, open or shorted modules and strings, and partial shading conditions. Paper [41] introduces a deep learning approach using a Convolutional Mixer (ConvMixer) that processes two-dimensional images generated from PV DC array power data, achieving an overall accuracy of 97%. To transmit classified and detected faults, the study integrates a LoRa (long-range) notification system optimized for low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs). The DT model is validated using an Opal-RT eMegasim simulator (without specifying further details) on a 49 kW PV farm.
In [42], an advanced Fault Detection and Diagnosis (FDD) framework is implemented to evaluate PV system performance through unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with RGB and thermal cameras for inspection and monitoring. The approach differentiates between short-lived anomalies (e.g., dust, temporary shading, minor circuit faults) and permanent ones (e.g., aging degradation), prompting dynamic DT model updates. Study [107] employs Microsoft’s AirSim simulator to emulate aerial robot flights within a DT environment, modeling robot dynamics and simulating sensor data. Custom APIs execute scenarios such as boundary detection, path planning, and fault detection. The system processed aerial images 3.5 times faster than conventional models and achieved a bird-dropping detection accuracy of 95.2%. Paper [116] addresses the interpretability challenge of data-driven PV inverter models by incorporating DT technology to bridge physical and analytical domains. This framework reduced fault detection time by 47.2% and achieved a 96.8% accuracy in identifying capacitor degradation trends.
Rolling bearings support the rotating shafts in pumps, turbines, generators, and other auxiliary equipment. By reducing friction, they ensure smooth operation even under high temperatures, pressures, and dynamic conditions [147]. Fault diagnosis in rolling bearings, particularly under conditions of limited labeled data in industrial environments, is examined in [108], where DT is employed to generate simulated fault data for network training, achieving an accuracy of 84.21%. A dynamic model of the rolling bearing with five degrees of freedom is developed to replicate operating conditions and fault modes. In [109], a vision transformer (ViT)-based network combined with a short-time Fourier transform (STFT) is pre-trained on a large dataset to improve diagnostic capability. The model generates simulated bearing acceleration vibration signals under various fault conditions, supplementing limited real measurements and increasing fault diagnosis accuracy to 91.33%.
3.5. Power Transformer
Power transformers in power plants play a critical role in stepping up voltage for efficient long-distance electricity transmission. As one of the most expensive and vital components of the power system, their continuous monitoring and timely maintenance are essential to ensure reliability. This section reviews recent advances in DT applications for power transformers, focusing on improvements in fault detection, temperature prediction, CM, PM, and electrodynamic force analysis.
3.5.1. System-Level Applications
The DT framework presented in [82] serves as the foundation for thermal hydraulic network modeling (THNM) and error analysis, developed using COMSOL Multiphysics version 5.6 to predict temperature distributions in disc-type transformer windings. This study addresses non-uniformities in the entry and exit of vertical oil ducts by comparing THNM results with CFD simulations, improving transformer thermal management, and reducing computational time from 34 h to 35 s. Paper [83] introduces an Online Extreme Learning Machine with Kernels (OL-ELMK) approach, enabling the DT model to continuously learn from new data and maintain high predictive accuracy as the transformer’s thermal behavior evolves. Unlike static models, this method adapts in real time, achieving 99.8% prediction accuracy and reducing unplanned maintenance interventions by 15%. In [84], the integration of reduced-order modeling based on Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) and finite element (FE) methods allows a DT to analyze a 500 kVA transformer’s temperature field 192 times faster than conventional models. Similarly, the DT-based approach in [85] enhances hotspot formation analysis in a 500 kVA oil-immersed transformer, reducing computation time from 300 s to 0.07 s using fewer training samples.
3.5.2. Service-Level Digital Twins: Reliability and Maintenance
Given the complexity of power transformers and their dependence on interdisciplinary principles from physics, chemistry, and electrical engineering, effective fault detection across components requires a high degree of expertise, which DT technology can facilitate through accurate and efficient diagnostics. In [49], a DT model replicating a 110 kV oil-immersed transformer employs vibration signals collected from the oil tank surface using Printed Circuit Board (PCB) sensors, a collector, and a PC configured for a 2860 Hz sampling frequency and 200 ms sampling time. Under varying load conditions (40%, 50%, and 70%), the model achieved 95% accuracy in identifying transformer winding faults. Study [50] addresses the limitations of traditional relay protection systems in detecting early-stage faults such as inter-turn short circuits. A DT-based microthermal field model using finite element analysis (FEA), combined with multisensor data fusion and Bayesian inference, improves accuracy in hotspot detection, achieving 35% faster fault diagnosis, an 18% reduction in unplanned maintenance, and a 96% confidence level in detecting mild faults. The DT framework in [51] integrates data from dissolved gas analysis (DGA) and acoustic vibration signals to provide a holistic condition assessment for a 400 kV oil-immersed transformer, enhancing diagnostic accuracy to 98.10%, reducing false alarms by 7.8%, and lowering unplanned maintenance by 15%.
Paper [86] develops a DT model to simulate inter-turn faults at varying locations and severities, trained and tested with 550 sets of real fault data, achieving 95.24% fault identification accuracy. DT monitoring enables early fault detection before reaching critical thermal thresholds; for instance, winding hotspot temperature rose from 42.2 °C to 80.1 °C under a 1% inter-turn fault. In [87], researchers employ COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5 to simulate 105 scenarios under varying load factors (0.5–1.1), ambient temperatures (10–30 °C), and fault conditions (1–5% inter-turn faults), achieving 92.9% detection accuracy and an 18% reduction in unplanned maintenance. A DT-based vibration analysis framework in [88] using four PCB sensors on a 400 kVA transformer achieved 98% diagnostic accuracy, a 31% faster fault detection time, and a 12.4% reduction in maintenance costs. Authors in [89] apply a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) trained with frequency response analysis (FRA) indices to locate disk space variation (DSV) faults, outperforming the support vector machine (SVM) method with 96.33% localization accuracy, a 28% reduction in classification time, and 14.6% less unplanned downtime. Finally, in [122], a DT-based approach for power electronic transformers (PETs) simulates five fault scenarios—including blocked modes and four types of overcurrent (O/C) faults—achieving 96% detection accuracy, 35% faster diagnosis, and an 18.5% reduction in downtime.
CM in power transformers continuously evaluates temperature, oil levels, and electrical performance to enable early detection of anomalies such as overheating and insulation degradation. This proactive approach enhances maintenance strategies, minimizes downtime, and extends service life [148,149]. To assess CM in ±800 kV ultra-high-voltage (UHV) bushings, study [148,149]. Study [90] employs a fuzzy clustering algorithm based on similarity matching, incorporating maximum and minimum temperatures inside and outside the bushing. Using COMSOL Multiphysics, components such as aluminum and copper tubes, insulator skirts, and capacitor cores are modeled. The DT accurately predicted bushing overheating and impedance rise with an error margin ≤ 5%. In [119], the mechanical state of On-Load Tap Changers (OLTCs) is analyzed using vibration signals sampled at 10,240 Hz with a window size of 400 samples. This approach reduced fault detection time by 27% and unplanned maintenance by 18%.
Reference [96] presents a large-scale CM of 40 transformers, equipped with sensors for current, voltage, and ambient temperature, transmitting data through a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) to the cloud. The approach achieved an 18% reduction in unplanned maintenance, a 25% faster diagnostic response, and a 9% decrease in energy loss. Paper [91] evaluates insulation degradation and overall transformer lifespan by analyzing insulation classes (105–220 °C), cooling systems (air-forced, AF), mean winding temperature rise (100–140 K), and ambient conditions (20–40 °C). The results show that lower insulation classes, forced-air cooling, and cooler environments reduce thermal stress. The study reported a 77.8% reduction in thermal degradation with AF cooling and a 6644% increase in aging rate under extreme ambient conditions.
Asset management plays a crucial role in maintaining a sustainable power grid. Study [72] investigates transformer asset health using Hydran M2-X units for real-time dissolved gas analysis (DGA) and moisture monitoring in insulating oil, providing updates every 15 s. The DT model enhanced asset availability by 30–40%, reliability by 12%, and reduced unplanned maintenance by 15%. In [92], a DT framework is introduced to simulate and evaluate electrodynamic forces acting on three-phase high-voltage disconnectors, extendable to transformers. The DT enables real-time simulation of short-circuit events, using finite element modeling (FEM) to solve complex electromagnetic field equations. The method reduced simulation time by 99.7% (from 12 h to 2 min), accurately matched force measurements up to 1.74 kN, and lowered testing costs by 50–70%.
PM of power transformers is vital for maintaining power system stability. Undetected faults in these assets can disrupt continuous power supply, cause cascading failures, and result in costly repairs [150]. In [52], a DT framework for power system stability is developed and validated through several case studies, including voltage stability analysis, dynamic stability assessment, and optimization of renewable energy integration. The model uses real-time data from the transformer, such as oil quality, temperature, and load, to predict potential failures through machine learning algorithms for early fault detection. The DT-based framework reduced transformer maintenance costs by 25%, extended lifespan by 5–8 years, decreased downtime by 40%, improved fault detection speed by 60%, and reduced power losses by 15%.
4. Conclusions and Challenges
This systematic literature review presented a comprehensive analysis of the integration of DT technology in the power generation sector, examining both functional roles and application contexts. The introduction outlined the need for digitalization across emissive and non-emissive plants, surveyed emerging technologies, and clarified the concept of DT from multiple perspectives. To advance research, we proposed a framework that categorizes applications by plant type (emissive vs. non-emissive), operational behavior (e.g., CM, PM, fault and anomaly detection, power/temperature prediction, optimization), and component scope (e.g., transformers, rolling bearings). As summarized in Table 4, 83 papers were analyzed. In addition, by decomposing study objectives, we derived a six-level set of time scales for DT purposes, reported in Table 3.
Key findings and conclusions regarding the application of DT across various categories are summarized below.
In summary, the research questions outlined in the introduction are addressed in various sections of the manuscript, providing key insights into the application and evolution of DT technologies in power generation systems.
RQ#1: How can a balance be achieved between the trade-offs of transitioning to RES while maintaining existing power plants? We explored the role of DT technologies in optimizing conventional power plants and integrating RES. DTs enhance both the flexibility of existing plants and the predictability of RES, facilitating a smoother transition to a more sustainable energy system.
RQ#3: How can faults be detected in both non-emissive and emissive power plants? We showed how DT technologies improve efficiency and reduce downtime through enhanced fault detection (CM and PM), with notable improvements in rotor fault diagnostics, sensor failure detection, and predictive accuracy across different plant types.
RQ#4: How can energy systems, including power generation, microgrids, and associated equipment, be effectively managed? This question is answered by detailing how DTs improve the optimization of power generation, microgrids, and DERs. Key benefits include enhanced plant-wide efficiency, real-time optimization, and smarter integration of RES, all contributing to more effective energy system management.
4.1. Emissive Power Plants
In emissive power plants, DT technology has been applied both to plant-wide operations and to individual components such as turbines, rotors, and cooling systems. CM and PM have emerged as key strategies for optimizing performance and reliability. Studies on diesel generators and coal-fired plants have also demonstrated how real-time data and machine learning techniques contribute to more accurate and comprehensive system modeling. Collectively, this body of research has enhanced operational efficiency, predictive accuracy, and the overall performance of traditional power plants.
4.2. Non-Emissive Power Plants
The application of DT technology in non-emissive power plants has been extensively explored across various renewable energy systems. A substantial portion of the research has focused on wind turbines, with numerous studies analyzing blades, drivetrain systems, condition monitoring, and power generation prediction. In PV systems, many studies have examined power forecasting, output optimization to maximize generation and minimize losses, fault detection, and integration with electrolyzers and CHP systems. Additional research has addressed the integration of RESs with electricity markets and VPPs, underscoring the flexibility and scalability offered by DT implementations.
Research on geothermal, biomass, and HEPPs has further advanced understanding of how DT enhances efficiency and performance in these systems. The application of DT concepts in microgrids has also shown a major impact on long-term planning by supporting optimization, fault detection, power generation prediction, and overall operational management. These models have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of microgrid operations. Collectively, these findings highlight the role of DT in optimizing energy generation, improving system reliability, and enabling more effective management of non-emissive power plants.
4.3. Power Transformer
The integration of DT technology with power transformers has primarily focused on fault detection, with various approaches utilizing real-time data to identify anomalies and incipient failures. In parallel, condition monitoring has been applied to continuously assess transformer health and performance, thereby supporting predictive maintenance and minimizing unplanned outages. Another significant research direction has addressed temperature prediction and the effects of thermal management on transformer lifespan. Collectively, these studies emphasize the essential role of DT in enhancing reliability and extending the operational life of power transformers.
4.4. Future Direction
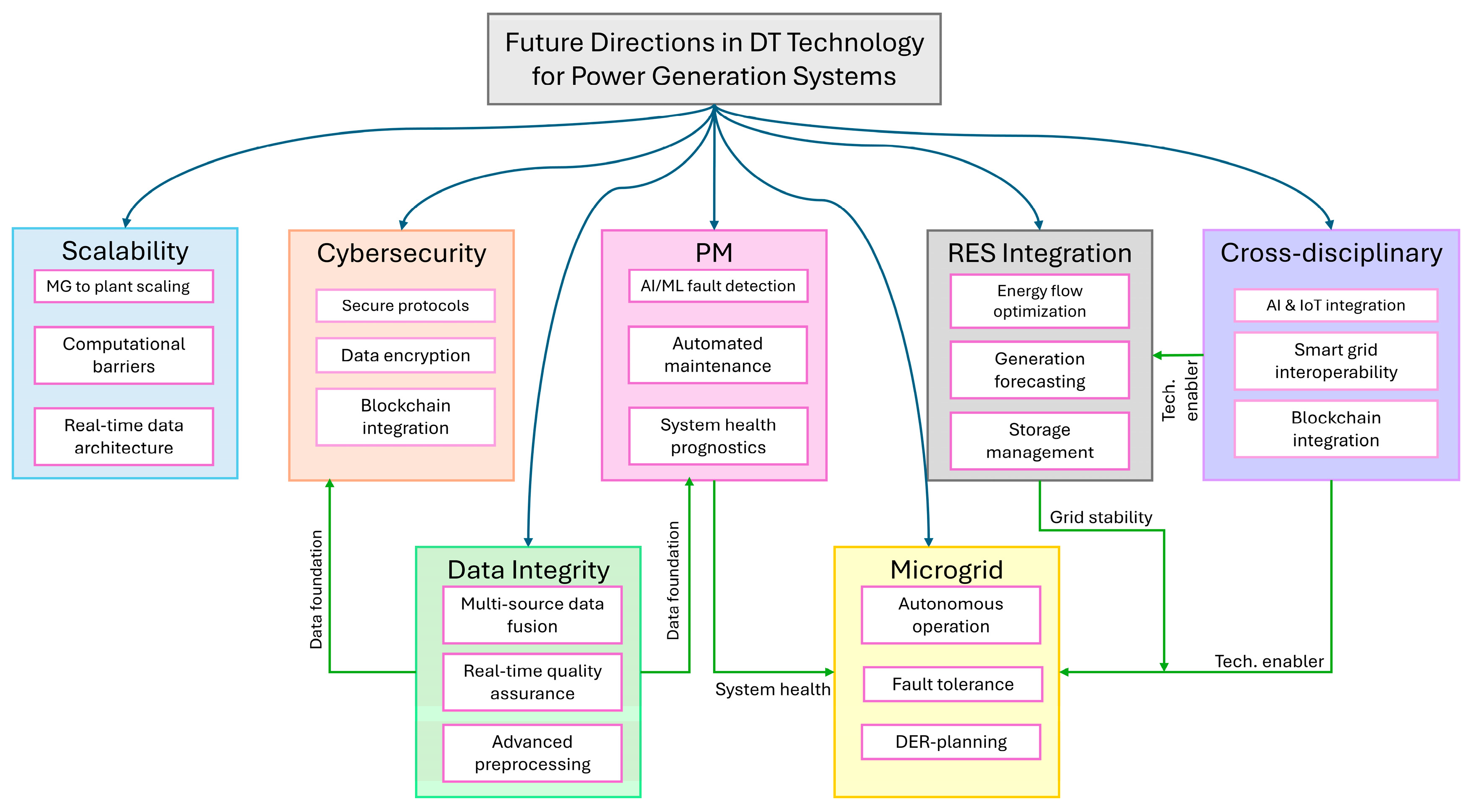
Future research should explore how to scale DT-based optimization effectively for both large- and small-scale power plants (e.g., microgrids) to address the distinct needs and complexities of these systems, shown in Figure 11.
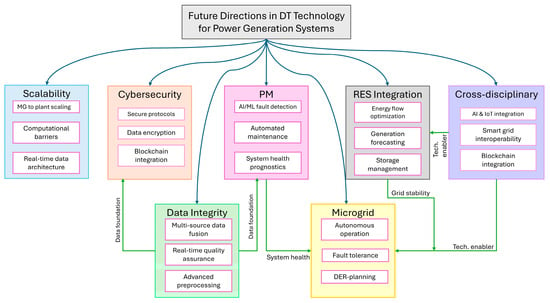
Figure 11.
Strategic research roadmap for advancing Digital Twin technology in power systems.
Data quality and integration remain critical obstacles. Effective real-time monitoring and data acquisition from diverse sensors and systems are essential for accurate DT models. Future investigations should focus on enhancing data-driven DT models, ensuring the integration of real-time data from heterogeneous sources, and improving the accuracy of predictions, particularly in the context of RES. Furthermore, as DTs become more integrated into critical infrastructure, cybersecurity becomes a priority. Research should focus on developing secure DT frameworks for power plants to explore strategies like blockchain or secure communication protocols to safeguard system integrity.
Several research projects will be able to benefit from DT integration:
- Advanced fault detection using AI-driven DT models that improve real-time PM and reduce downtime across both emissive and non-emissive plants.
- Optimization of RES integration through DTs, especially for wind, solar, and energy storage systems, to improve grid stability and minimize curtailment.
- Integration of DTs with microgrids to enable dynamic optimization, ensuring resilience and autonomous operation during grid failures.
- Collaborative DT research for cyber-physical systems to enhance the interoperability and robustness of DERs, smart grids, and VPPs.
The future of DT technology in the power generation sector is vibrant and holds vast potential. Further interdisciplinary research in these areas will be crucial to unlocking the full capabilities of DTs, improving system efficiency, and accelerating the transition to renewable energy systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en18215627/s1, File S1. PRISMA 2020 Checklist. Reference [151] is cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing, and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Saeid Shahmoradi is supported by the project PNRR-NGEU, which has received funding from the MUR-DM 117/2023. 

Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zheng, W.; Chen, P. The political economy of air pollution: Local development, sustainability, and political incentives in China. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 69, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipouya, A.; Ghezelbashan, A.; Shahmoradi, S. Frequency Control in the Presence of Dynamic Model of Induction Motor Based on Virtual Inertia. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives (ICEMD), Tehran, Iran, 20–21 December 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar, V.; Veena, M.B. Cybersecurity and IEC 62351 for SCADA Systems of Power Grid. SSRG Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 11, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Baig, M.J.; Iqbal, M.T. An Internet of Things—Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (IoT-SCADA) Architecture for Photovoltaic System Monitoring, Control, and Inspection in Real Time. Electronics 2025, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischos, S.; Dalagdi, E.; Vrakas, D. Intelligent energy management systems: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 11635–11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strezoski, L. Distributed energy resource management systems—DERMS: State of the art and how to move forward. WIREs Energy Environ. 2023, 12, e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, B.; Wu, M.; Cui, H. Optimal Power Flow in Distribution Network: A Review on Problem Formulation and Optimization Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, A.; Daneshvar, M.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Energy Intelligence: A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence for Energy Management. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, R.; Kande, M. Analysis of Wide Area Monitoring System architectures. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 1269–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Bazmohammadi, N.; Madary, A.; Vasquez, J.C.; Mohammadi, H.B.; Khan, B.; Wu, Y.; Guerrero, J.M. Microgrid Digital Twins: Concepts, Applications, and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 2284–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M. Digital Twin: Manufacturing Excellence Through Virtual Factory Replication; Digital Twin: San Jose, Costa Rica, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Modeling, Simulation, Information Technology & Processing Roadmap; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Tuegel, E.J.; Ingraffea, A.R.; Eason, T.G.; Spottswood, S.M. Reengineering Aircraft Structural Life Prediction Using a Digital Twin. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2011, 2011, 154798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.H.; Wang, L. Application and Development Prospect of Digital Twin Technology in Aerospace. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Dou, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, W.; Lei, X.; Han, D. Digital Twin and Its Application in Power System. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 12–14 September 2020; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Danilczyk, W.; Sun, Y.; He, H. ANGEL: An Intelligent Digital Twin Framework for Microgrid Security. In Proceedings of the 2019 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Wichita, KS, USA, 13–15 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiti, A.K.; Kapat, J.S.; Vesely, L. Digital twin in energy industry: Proposed robust digital twin for power plant and other complex capital-intensive large engineering systems. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3704–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, A. Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. J. Doc. 1969, 25, 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Overlapping Community Discovery for Identifying Key Research Themes. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 68, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manesh, M.F.; Pellegrini, M.M.; Marzi, G.; Dabic, M. Knowledge management in the fourth industrial revolution: Mapping the literature and scoping future avenues. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 68, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, M.H.; Bompard, E.; Colella, P.; Huang, T. Data analytics in the electricity market: A systematic literature review. Energy Syst. 2023, 16, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Klein, E.; Loper, E. Natural Language Processing with Python: Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 0596555717. [Google Scholar]
- vom Scheidt, F.; Medinová, H.; Ludwig, N.; Richter, B.; Staudt, P.; Weinhardt, C. Data analytics in the electricity sector–a quantitative and qualitative literature review. Energy AI 2020, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimago Journal & Country Rank. Available online: https://www.scimagojr.com/journalrank.php (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- González, M.; Salgado, O.; Croes, J.; Pluymers, B.; Desmet, W. A Digital Twin for Operational Evaluation of Vertical Transportation Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 114389–114400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, K.P.; Brito, G.; Kamel Boulos, M.N. Health Digital Twins in Life Science and Health Care Innovation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2024, 64, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madusanka, N.S.; Fan, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiang, X. Digital Twin in the Maritime Domain: A Review and Emerging Trends. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradi, S.; Mazza, A.; Pons, E. Digital Twin Applications in the Energy Sector. In Proceedings of the 2024 AEIT International Annual Conference (AEIT), Trento, Italy, 25–27 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, G.; Li, H.; Cao, Y. Manufacturing Blockchain of Things for the Configuration of a Data- and Knowledge-Driven Digital Twin Manufacturing Cell. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 11884–11894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Zhu, L.; Liu, F. Big data driven Hierarchical Digital Twin Predictive Remanufacturing paradigm: Architecture, control mechanism, application scenario and benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhou, H.; Hu, W.; Liu, G.-P.; Guan, S.; Feng, X. Toward a Web-Based Digital Twin Thermal Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Petersen, N.; Liu, P.; Li, Z.; Wirsum, M. Hybrid modelling and simulation of thermal systems of in-service power plants for digital twin development. Energy 2022, 260, 125088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Xin, Y. Thermal Power Plant Turbine Rotor Digital Twin Automation Construction and Monitoring System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8527281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, C.A.A.d.A.; Villanueva, J.M.M.; de Almeida, R.J.S.; de Medeiros, I.E.A. Digital Twins of the Water Cooling System in a Power Plant Based on Fuzzy Logic. Sensors 2021, 21, 6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H. Recurrent Neural Network-Based Hybrid Modeling Method for Digital Twin of Boiler System in Coal-Fired Power Plant. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Huan, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, B.; Wang, Y. The Wind and Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Method Based on Digital Twins. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Gui, Y.; Sun, Q.; Gao, D.W. Digital Twin Empowered PV Power Prediction. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-Y.; Pula, R.A. Diagnosis of PV faults using digital twin and convolutional mixer with LoRa notification system. Energy Reports 2023, 9, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitouni, S.I.; Abdelmoula, I.A.; Es-sakali, N.; Mghazli, M.O.; Er-retby, H.; Zoubir, Z.; El Mansouri, F.; Ahachad, M.; Brigui, J. Implementing a Digital Twin-based fault detection and diagnosis approach for optimal operation and maintenance of urban distributed solar photovoltaics. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 48, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ye, Z.; Ni, P.; Cao, C.; Wei, X.; Zhao, J.; He, X. Intelligent Digital Twin Modelling for Hybrid PV-SOFC Power Generation System. Energies 2023, 16, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanov, M.M.; Arakelyan, E.K.; Boldyrev, I.A.; Lunenko, V.S.; Menshikov, P.D. Digital twins application in control systems for distributed generation of heat and electric energy. Arch. Thermodyn. 2021, 42, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchiralla, F.M.; Jalo, N.; Thollander, P.; Andersson, M.; Johnsson, S. Energy use categorization with performance indicators for the food industry and a conceptual energy planning framework. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Michalski, M.A.; de Andrade Melani, A.H.; da Silva, R.F.; de Souza, G.F. A Fault Detection Framework Based on Data-Driven Digital Shadows. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncert. Eng. Syst. Part B Mech. Eng. 2024, 10, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-A.; Byeon, G.; Son, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, S. Data-Driven Modeling of HVAC Systems for Operation of Virtual Power Plants Using a Digital Twin. Energies 2023, 16, 7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Houda, Z.A.; Brik, B. Next-power: Next-generation framework for secure and sustainable energy trading in the metaverse. Ad Hoc Netw. 2023, 149, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Diagnostic Research for the Failure of Electrical Transformer Winding Based on Digital Twin Technology. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 17, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, B. Digital Twin-Driven Hot Spot Capture for Power Transformer Interturn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis Based on Microthermal Field. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3532613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Miao, Y.; Guan, S. Fault diagnosis method for oil-immersed transformers integrated digital twin model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Khalil, A.G. Digital twin real-time hybrid simulation platform for power system stability. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmawansa, N.; Gunawardane, K.; Madanian, S.; Than Oo, A.M. Battery Energy Storage Capacity Estimation for Microgrids Using Digital Twin Concept. Energies 2023, 16, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABB. Digital Twin. Available online: https://search.abb.com/library/Download.aspx?Action=Launch&DocumentID=9AKK107046A8849&DocumentPartId=&LanguageCode=en (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- GE. What is Digital Twin? Available online: https://www.gevernova.com/software/blog/what-digital-twin (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Siemens. Digital Twin. Available online: https://www.plm.automation.siemens.com/global/en/our-story/glossary/digital-twin/24465 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Microsoft. Microsoft Azure Digital Twin. Available online: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/digital-twins/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Thaler, B.; Posch, S.; Wimmer, A.; Pirker, G. Hybrid model predictive control of renewable microgrids and seasonal hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 38125–38142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, J. Digital twin modeling and operation optimization of the steam turbine system of thermal power plants. Energy 2024, 290, 129969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Rosic, B. The Hybrid Pathway to Flexible Power Turbines, Part I: Novel Autoencoder Methods for the Automated Optimization of Thermal Probes and Fast Sparse Data Reconstruction, Enabling Real-Time Thermal Analysis. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2024, 146, 031020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Rosic, B. The Hybrid Pathway to Flexible Power Turbines, Part II: Fast Data Transfer Methods Between Varying Fidelity Simulations, to Enable Efficient Conjugate Thermal Field Prediction. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2024, 146, 031021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, M.; Siham, B.; Hicham, M.; Amine, M. HT-TPP: A Hybrid Twin Architecture for Thermal Power Plant Collaborative Condition Monitoring. Energies 2022, 15, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H. Digital twin-based subspace model predictive control for thermal power plant. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2023, 237, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, P.; Li, Z. Data reconciliation-based simulation of thermal power plants for performance estimation and digital twin development. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 168, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Gao, H.; Wang, W.; Cao, J.; Yang, W.; Zeng, R.; He, Y. Application of Three-Flow Fusion Technology Based on Modelica in Thermal Power Digital Twin. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2022, 6, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deon, B.; Cotta, K.P.; Silva, R.F.V.; Batista, C.B.; Justino, G.T.; Freitas, G.C.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Barbosa, A.S.; Loucao, F.L., Jr.; Simioni, T.; et al. Digital twin and machine learning for decision support in thermal power plant with combustion engines. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 253, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinti, J.P.; Smith, P.J.; Smith, S.T. Atikokan Digital Twin: Machine learning in a biomass energy system. Appl. Energy 2022, 310, 118436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinti, J.P.; Smith, P.J.; Smith, S.T.; Diaz-Ibarra, O.H. Atikokan Digital Twin, Part B: Bayesian decision theory for process optimization in a biomass energy system. Appl. Energy 2023, 334, 120625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersan, M.; Irmak, E. Development and Integration of a Digital Twin Model for a Real Hydroelectric Power Plant. Sensors 2024, 24, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Sharma, V.; Cao, T.-V.; Canberk, B.; Duong, T.Q. Machine Learning-Based Digital Twin for Predictive Modeling in Wind Turbines. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 14184–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belik, M.; Rubanenko, O. Implementation of Digital Twin for Increasing Efficiency of Renewable Energy Sources. Energies 2023, 16, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; de Almeida, N.M.; Martins, J.P.; Patricio, H.; Morgado, J.G. Analysing the Value of Digital Twinning Opportunities in Infrastructure Asset Management. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Luo, N.; Hu, W.; Lei, Z. Design and Implementation of Digital Twin Diesel Generator Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichte, D.; Torres, F.S.; Engler, E. Framework for Operational Resilience Management of Critical Infrastructures and Organizations. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, H. Online assessment of multi-parameter stability region and stability margin of wind power plants. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 155, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benato, A.; De Vanna, F.; Stoppato, A. Levelling the Photovoltaic Power Profile with the Integrated Energy Storage System. Energies 2022, 15, 9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzala, M.; Memon, Z.; Hussain, M.I.; Azeem, F.; Shahzad, N.; Kim, J.-T. Fuzzy-Logic-Based Cascaded Decentralized Control and Power Quantification of Residential Buildings for Effective Energy Load Management. Buildings 2024, 14, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Han, D.; Yang, C.; Cai, J.; Liang, W.; Li, K.-C. TS-DP: An Efficient Data Processing Algorithm for Distribution Digital Twin Grid for Industry 5.0. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natgunanathan, I.; Mak-Hau, V.; Rajasegarar, S.; Anwar, A. Deakin microgrid digital twin and analysis of AI models for power generation prediction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 18, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Tjandra, R.; Soh, C.B.; Cao, S.; Soh, D.C.L.; Tan, K.T.; Tseng, K.J.; Krishnan, S.B. Digital Twin of Microgrid for Predictive Power Control to Buildings. Sustainability 2024, 16, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espin-Sarzosa, D.; Palma-Behnke, R.; Valencia-Arroyave, F. Towards Digital Twins of Small Productive Processes in Microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Gao, M.; Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhuo, R. Improved thermal hydraulic network modelling and error analysis in disc-type transformer windings. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2024, 18, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yang, F.; Farooq, U.; Li, X.; Jiang, J. An online learning method for constructing self-update digital twin model of power transformer temperature prediction. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 237, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Jing, L.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B. Research on digital twin modeling method of transformer temperature field based on POD. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, B. Fast calculation of temperature distribution in oil-immersed transformer windings based on U-net neural network. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 035132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Gao, D.; Qin, T.; Wang, W. Identification method for inter-turn faults in transformers based on digital twin concept. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1376306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sheng, G.; Zhou, N.; Ni, Z.; Jiang, X. Incipient interturn fault detection for ONAN power transformers using electrothermal characteristic fusion analysis. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2024, 18, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y. Research on Digital Technology of Mechanical Structure Fault Diagnosis of Power Transformer Based on Comprehensive Feature Extraction and SABO-PNN. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5501204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, C.; Yu, L.; Dong, S.; Liu, Y. Using MLP to locate transformer winding fault based on digital twin. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1175808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Lin, M.; Xin, D.; Tang, H.; Wu, G. A zero-sample state evaluation model for valve-side bushing of UHV converter transformer oriented to digital twin under attribute analysis. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxegarai, A.; Valverde, V.; Eguia, P.; Perea, E. Analysis of Loss of Life of Dry-Type WTSU Transformers in Offshore Wind Farms. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2020, 10, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulborski, M.; Lapczynski, S.; Kolimas, L.; Kozarek, L.; Cichecki, H.; Sul, P.; Owsinski, M.; Berowski, P.; Baczynski, D.; Wesolowski, M. Examination of Electrodynamic Forces in High Voltage Disconnector Related to the Short-Circuit Current Using the Digital Twin Technology. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 75701–75717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderang, E.; Hautala, S.; Mikulski, M.; Storm, X.; Niemi, S. Development of a digital twin for real-time simulation of a combustion engine-based power plant with battery storage and grid coupling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, M.M.H.; Choudhury, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Pota, H.; Yang, F. Novel abstractions and experimental validation for digital twin microgrid design: Lab scale studies and large scale proposals. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, M. Blockchain-Based energy trading in Renewable-Based community based Self-Sufficient Utility: Analysis of Technical, Economic, and regulatory aspects. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 64, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, T.R.; Martins, M.A.I.; Martins, K.A.; de Macedo, A.F.; de Francisci, S. Application Study in the Field of Solutions for the Monitoring Distribution Transformers of the Overhead Power Grid. Energies 2021, 14, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekidis, A.; Georgakis, A.; Dalamagkas, C.; Papageorgiou, E.I. Predictive Maintenance Framework for Fault Detection in Remote Terminal Units. Forecasting 2024, 6, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, Z.; Cui, L.; Liu, X.; Ku, A.Y. A case study of digital-twin-modelling analysis on power-plant-performance optimizations. Clean Energy 2019, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharew, S.S.; Di Pretoro, A.; Yimam, A.; Negny, S.; Montastruc, L. Exploiting exergy and exergoeconomic analysis as decisional tool for cogeneration plant optimal operating mode: A sugar factory case study. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keprate, A.; Bagalkot, N.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Sen, S. Reliability analysis of 15MW horizontal axis wind turbine rotor blades using fluid-structure interaction simulation and adaptive kriging model. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 116138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaj, A.; Gao, Z.; Nejad, A.R. Fault detection of offshore wind turbine drivetrains in different environmental conditions through optimal selection of vibration measurements. Renew. Energy 2023, 203, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martire, M.; Kaya, A.F.; Morselli, N.; Puglia, M.; Allesina, G.; Pedrazzi, S. Analysis and optimization of a hybrid system for the production and use of green hydrogen as fuel for a commercial boiler. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 56, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, J.; Martin-Chivelet, N.; Sanz-Saiz, C. BIPV Modeling with Artificial Neural Networks: Towards a BIPV Digital Twin. Energies 2022, 15, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohdi, T.I. A digital-twin and machine-learning framework for the design of multiobjective agrophotovoltaic solar farms. Comput. Mech. 2021, 68, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Kankam, K.O.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Modeling Collaborative Behaviors in Energy Ecosystems. Computers 2023, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Liu, C.; Jiang, D. Root cause localization for wind turbines using physics guided multivariate graphical modeling and fault propagation analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 295, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahi, M.; Esmailifar, S.M.; Sizkouhi, A.M.M.; Aghaei, M. Digital-PV: A digital twin-based platform for autonomous aerial monitoring of large-scale photovoltaic power plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 118963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.C.; Ren, Z.; Ni, Q.; Gu, F.; Feng, K.; Yu, K.; Ge, J.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Z. Digital twin-driven partial domain adaptation network for intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearing. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 234, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xia, M. Digital twin-assisted intelligent fault diagnosis for bearings. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.; Chenyu, D.U.; Peng, C.; AL-Bukhaiti, K. Predictive modeling of combined cycle power plant performance using a digital twin-based neural ODE approach. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Moaveni, B.; Ebrahimian, H.; Hines, E.; Bajric, A. Joint parameter-input estimation for digital twinning of the Block Island wind turbine using output-only measurements. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 198, 110425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunqiao, L.; Yan, F. An innovative power prediction method for bifacial PV modules. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaicys, J.; Norkevicius, P.; Baronas, A.; Gudzius, S.; Jonaitis, A.; Peftitsis, D. Efficiency Evaluation of the Dual System Power Inverter for On-Grid Photovoltaic System. Energies 2022, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Rooney, T.; Akeyo, O.M.; Branecky, B.; Ionel, D.M. Equivalent Electric and Heat-Pump Water Heater Models for Aggregated Community-Level Demand Response Virtual Power Plant Controls. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141233–141244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-Y.; Pula, R.A. Diagnosis of photovoltaic faults using digital twin and PSO-optimized shifted window transformer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L.; Zhan, G. Enhancing interpretability in data-driven modeling of photovoltaic inverter systems through digital twin approach. Sol. Energy 2024, 276, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, M.; Pannocchia, G.; Tognotti, L.; Paci, M. Rigorous simulation of geothermal power plants to evaluate environmental performance of alternative configurations. Renew. Energy 2023, 207, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powalla, D.; Hoerner, S.; Cleynen, O.; Muller, N.; Stamm, J.; Thevenin, D. A Computational Fluid Dynamics Model for a Water Vortex Power Plant as Platform for Etho- and Ecohydraulic Research. Energies 2021, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Youn, B.D. Digital twin approach for on-load tap changers using data-driven dynamic model updating and optimization-based operating condition estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 181, 109471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, P.; Li, H.; Li, G. Enhanced Detection of Electric Power Facilities Utilizing a Re-Parameterized Convolutional Network. Trait. Signal 2024, 41, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchev, D.; Varbanets, R.; Shumylo, O.; Zalozh, V.; Aleksandrovska, N.; Bratchenko, P.; Truong, T.H. Digital Twin Test-Bench Performance for Marine Diesel Engine Applications. Pol. Marit. Res. 2023, 30, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Ye, H.; Pei, W.; Kong, L.; Huo, Q.; Han, Y. A monitoring and diagnostics method based on FPGA-digital twin for power electronic transformer. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 210, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesely, L.; Fernandez, E.; Kapat, J.; Ghouse, J.H.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Ruscher, C.J.; Rolling, A.J. Fault Management Architecture Based on a Digital Twin Approach. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2022, 144, 032106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, D.; Oh, J.; Leem, S.; Ha, H.; Moon, J. A Hybrid Ensemble Model for Solar Irradiance Forecasting: Advancing Digital Models for Smart Island Realization. Electronics 2023, 12, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahcheraghian, A.; Madani, H.; Ilinca, A. From White to Black-Box Models: A Review of Simulation Tools for Building Energy Management and Their Application in Consulting Practices. Energies 2024, 17, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, E.; Matsuno, N.; Tanaka, K.; Nishimoto, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Imano, S. Latest Technologies and Future Prospects for a New Steam Turbine. Mitsubishi Heavy Ind. Tech. Rev. 2015, 52, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Parlak, M.; Taplak, H. Rotor-Dynamic Analysis of a Small Steam Turbine Using Finite Element Method. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2020, 7, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Pang, H.; He, S.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Gao, M. Evaporative Cooling Applied in Thermal Power Plants: A Review of the State-of-the-Art and Typical Case Studies. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2023, 19, 2229–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60045-1:2021; Steam Turbines—Part 1: Specifications. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Tsou, J.L.; Maulbetsch, J.; Shi, J. Power Plant Cooling System Overview for Researchers and Technology Developers; Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI): Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vilas Boas, F.M.; Borges-da-Silva, L.E.; Villa-Nova, H.F.; Bonaldi, E.L.; Oliveira, L.E.; Lambert-Torres, G.; Assuncao, F.D.; Costa, C.I.; Campos, M.M.; Sant’Ana, W.C.; et al. Condition Monitoring of Internal Combustion Engines in Thermal Power Plants Based on Control Charts and Adapted Nelson Rules. Energies 2021, 14, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13374:2015; Condition Monitoring and Diagnostics of Machines—Data processing, Communication and Presentation—Part 1: General guidelines. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Molęda, M.; Małysiak-Mrozek, B.; Ding, W.; Sunderam, V.; Mrozek, D. From Corrective to Predictive Maintenance—A Review of Maintenance Approaches for the Power Industry. Sensors 2023, 23, 5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 3006.3-2017; IEEE Recommended Practice for Determining the Impact of Preventative Maintenance on the Reliability of Industrial and Commercial Power Systems. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–34. [CrossRef]
- Redi, T. Systematic review of mitigation approaches in Ethiopia’s energy sector: Strategies for sustainable development and climate resilience [version 1; peer review: 1 approved with reservations]. F1000Research 2024, 13, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.B.; Ganesh, P.; Vinay Kumar, K.; Mohanarao, P.A.; Swathi, A.; Manoj, V. Renewable Energy Integration in Modern Power Systems: Challenges and Opportunities. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 591, 03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A.; Hejazi, F. Innovations in Wind Turbine Blade Engineering: Exploring Materials, Sustainability, and Market Dynamics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi, A.; Andresen, B. Power Quality Analysis and Improvement of Power-to-X Plants Using Digital Twins: A Practical Application in Denmark. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Y.; Lai, S.; Zhao, J. Enhancing Integrated Gas and Electricity Networks Operation with Coupling Attention-Graph Convolutional Network Under Renewable Energy Variability. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2025, 12, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariazadeh, A.; Keane, A. Coordinated Planning of Wind Turbines, Batteries and Electrolyzers in Distribution Systems: A Stochastic Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Torino, Italy, 10–12 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Tang, Y.; He, Z.; Lin, W. Research on Digital Twin Modeling for Virtual Power Plant BT–Advances in Wireless Communications and Applications; Jain, L.C., Kountchev, R., Zhang, K., Kountcheva, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaneasan, B.; Tan, K.T.; Zhang, W. Cognitive Digital Twin for Microgrid: A Real-World Study for Intelligent Energy Management and Optimization. IEEE Internet Comput. 2024, 29, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, A.F.; Akbari, E.; Shahmoradi, S.; Pirouzi, S.; Shahbazi, A. Stochastic economic sizing and placement of renewable integrated energy system with combined hydrogen and power technology in the active distribution network. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokar, M.R.; Shahmoradi, S.; Mohammed, A.H.; Foong, L.K.; Le, B.N.; Pirouzi, S. Stationary and mobile storages-based renewable off-grid system planning considering storage degradation cost based on information-gap decision theory optimization. J. Energy Storage 2023, 58, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, A.F.; Akbari, E.; Shahmoradi, S.; Veisi, M.; Pirouzi, S. Flexibility regulation-based economic energy scheduling in multi-microgrids with renewable/non-renewable resource and stationary storage systems considering sustainable computing by hybrid metaheuristic algorithm. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2025, 48, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, A.F.; Akbari, E.; Veisi, M.; Shahmoradi, S.; Pirouzi, S. non-renewable/renewable units. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandel, S.; Bartschat, A.; Glodowski, J.; Bader, N.; Poll, G. Wear Development in Oscillating Rolling Element Bearings. Lubricants 2023, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msane, M.R.; Thango, B.A.; Ogudo, K.A. Condition Monitoring of Electrical Transformers Using the Internet of Things: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std C57.106-2015; IEEE Guide for Acceptance and Maintenance of Insulating Mineral Oil in Electrical Equipment; (Revision IEEE Std C57.106-2006). IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–38. [CrossRef]
- Zare Ghaleh Seyyedi, A.; Armand, M.J.; Shahmoradi, S.; Mahmoudi Rashid, S.; Akbari, E.; Al-Hassanawy, A.J.K. Iterative optimization of a bi-level formulation to identify severe contingencies in power transmission systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 145, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).