Multi-Area Wind Power Planning with Storage Systems for Capacity Credit Maximization Using Fuzzy-Based Optimization Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Contributions
- We develop a fuzzy optimization GEP framework that represents wind uncertainty using membership functions, enhancing CC estimation beyond deterministic approaches.
- We present the first integration of a CAESS into multi-area GEP, demonstrating its critical role in mitigating wind intermittency and boosting CC.
- A case study demonstrates the model’s effectiveness for a multi-area power system. It provides valuable lessons on strategic wind resource allocation and energy storage, which can increase system resilience and capacity credit.
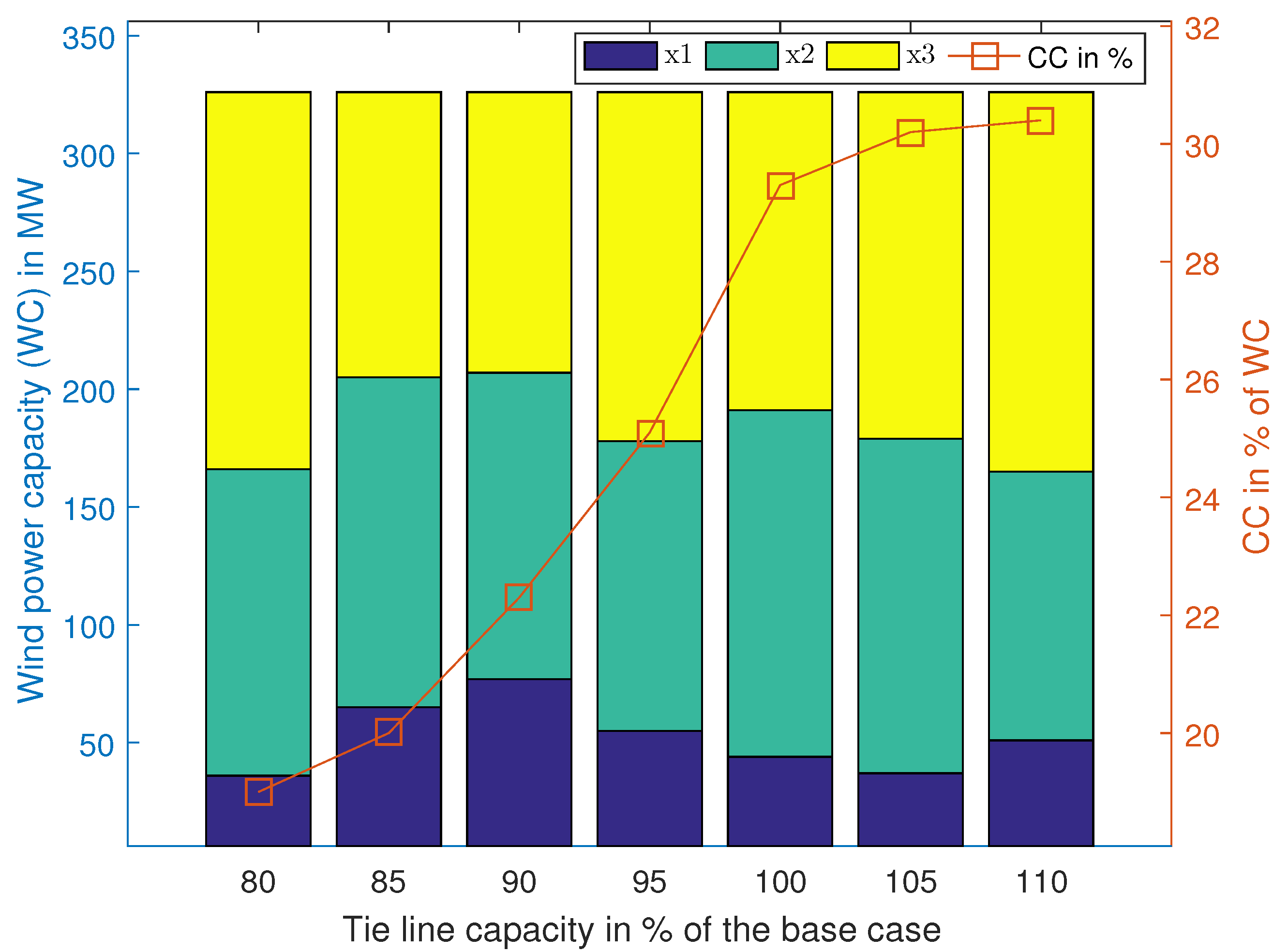
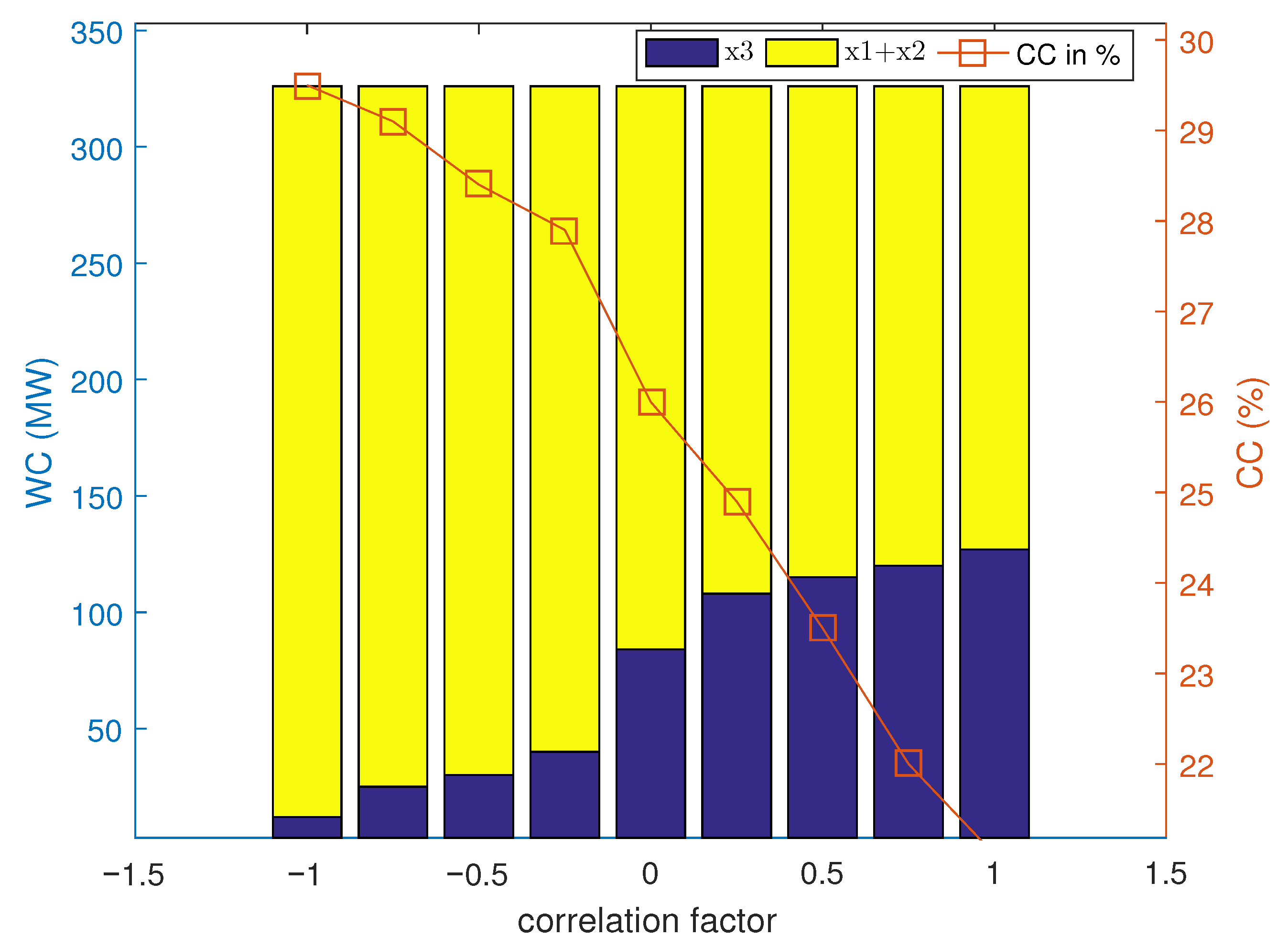
- A detailed sensitivity analysis reveals the importance of tie-line capacity and wind-profile correlation in improving power-system efficiency.
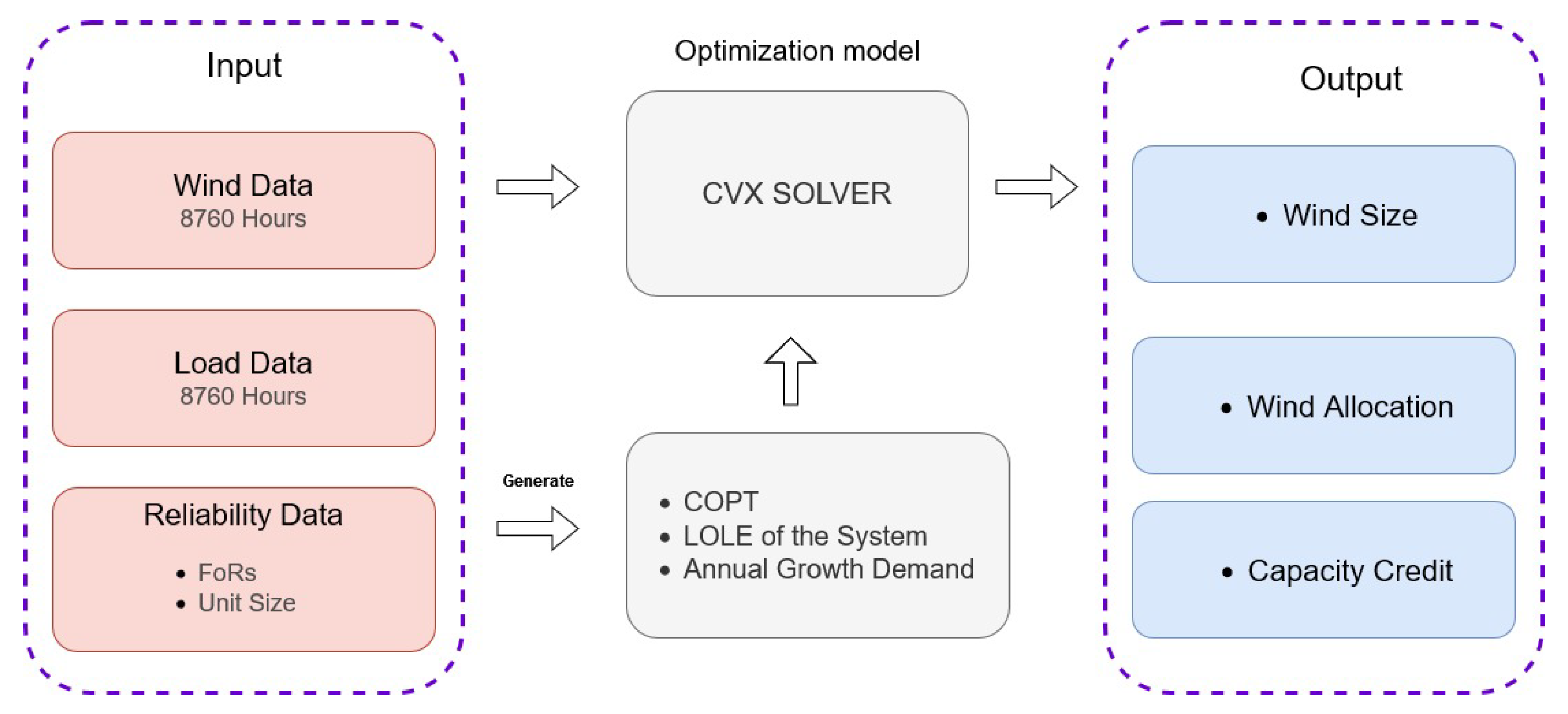
2. Methodology
2.1. Operating Principle
2.2. Decision and Dependent Variables
2.3. Assumptions
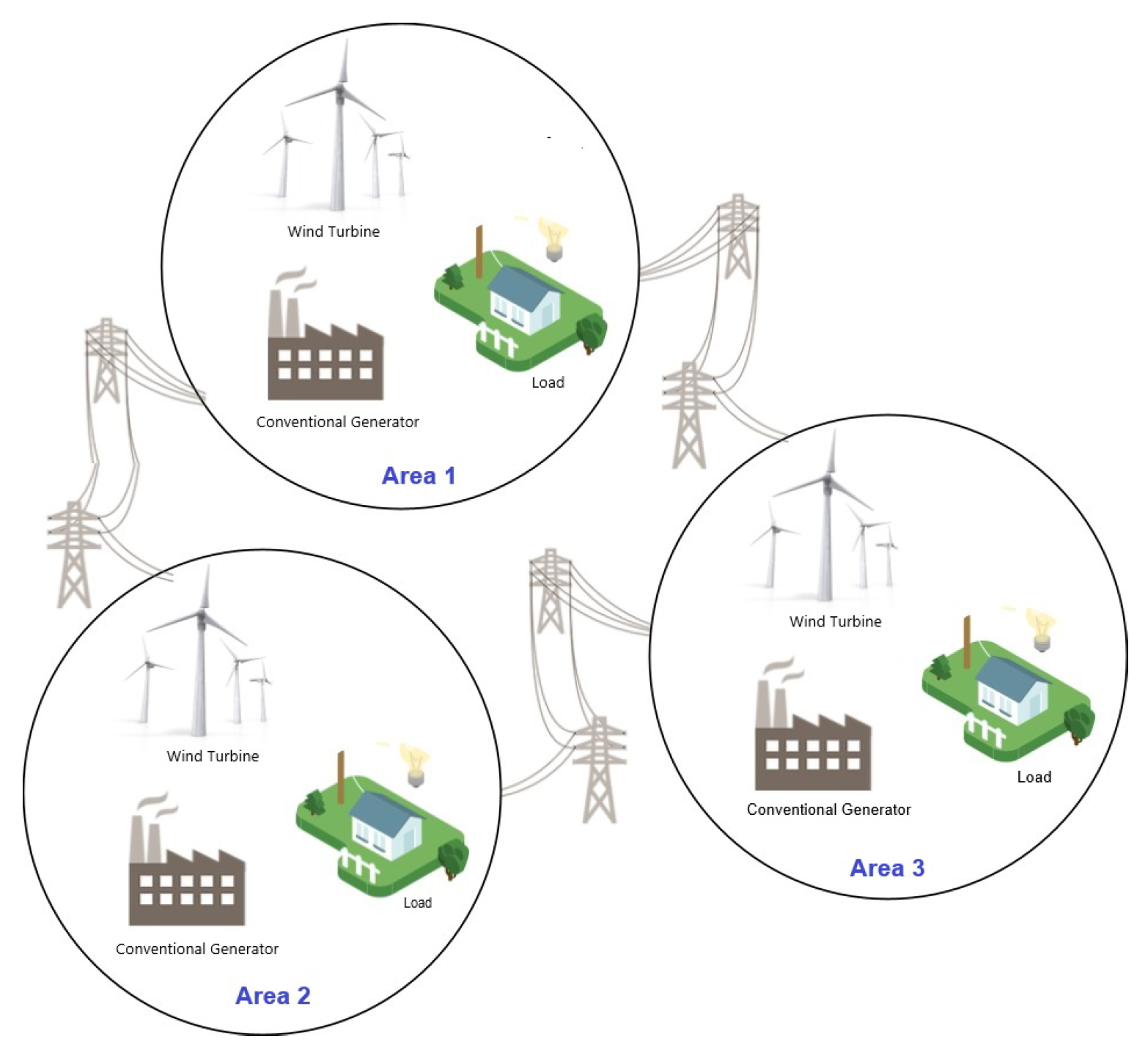
2.4. System Configuration
2.5. Load Model
2.6. Wind Model
2.7. Compressed-Air Energy Storage System (CAESS)
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Deterministic Model Formulation
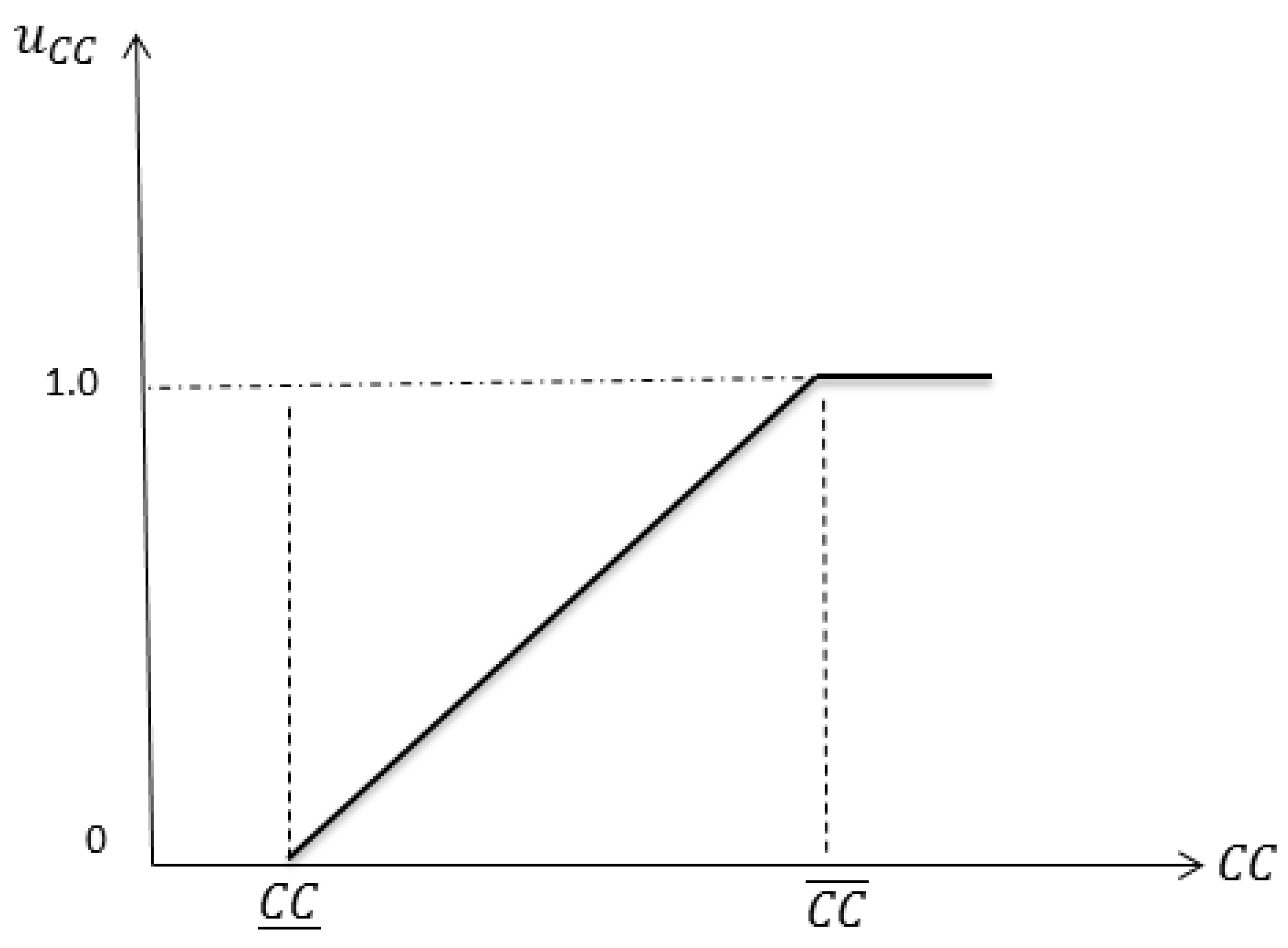
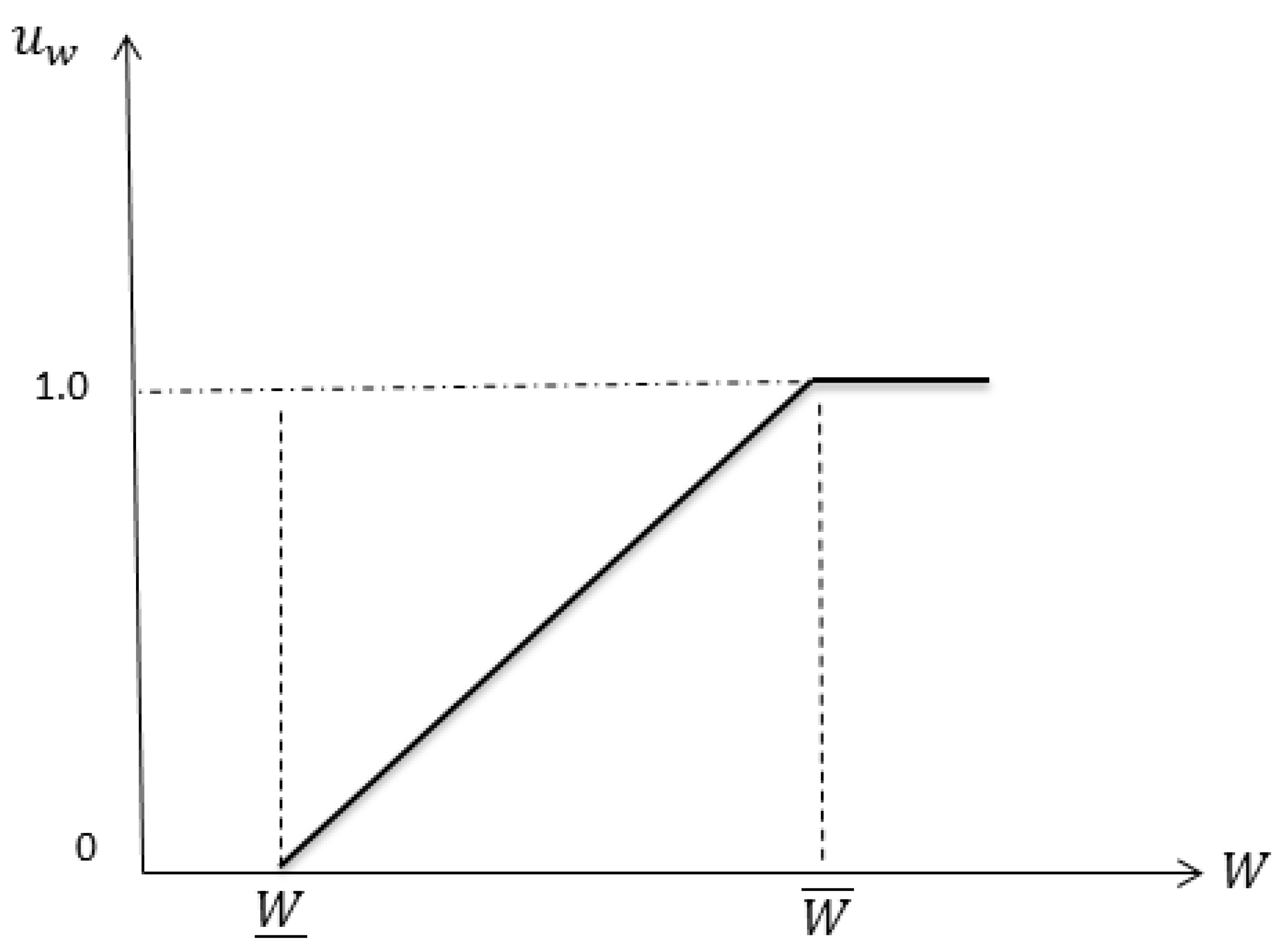
3.2. Fuzzy Optimization
3.2.1. Fuzzy Objective Model
3.2.2. Fuzzy Model of Wind Power
3.2.3. Complete Fuzzy Model of Proposed GEP
4. Case Study
4.1. Deterministic Model
4.1.1. System Configuration
4.1.2. System Parameters and Data
4.1.3. Case Study Scenarios
- Base case: estimated the original system’s reliability to find the original system’s LOLE.
- Scenario 1: Even distribution in Areas 1 and 2; wind capacity is evenly divided (163 MW each), with no wind in Area 3. We examined the effect on capacity credit (CC).
- Scenario 2: even distribution in Areas 2 and 3; 163 MW of wind capacity in each area with no wind in Area 1.
- Scenario 3: even distribution across all areas; each area received an equal share of 109 MW of wind capacity.
- Optimal case: In the optimal case, wind capacity allocation was optimized to maximize the capacity credit (CC). After successfully solving the optimization problem using the CVX toolbox, the results indicated the following allocations: 44 MW for Area 1, 147 MW for Area 2, and 135 MW for Area 3.
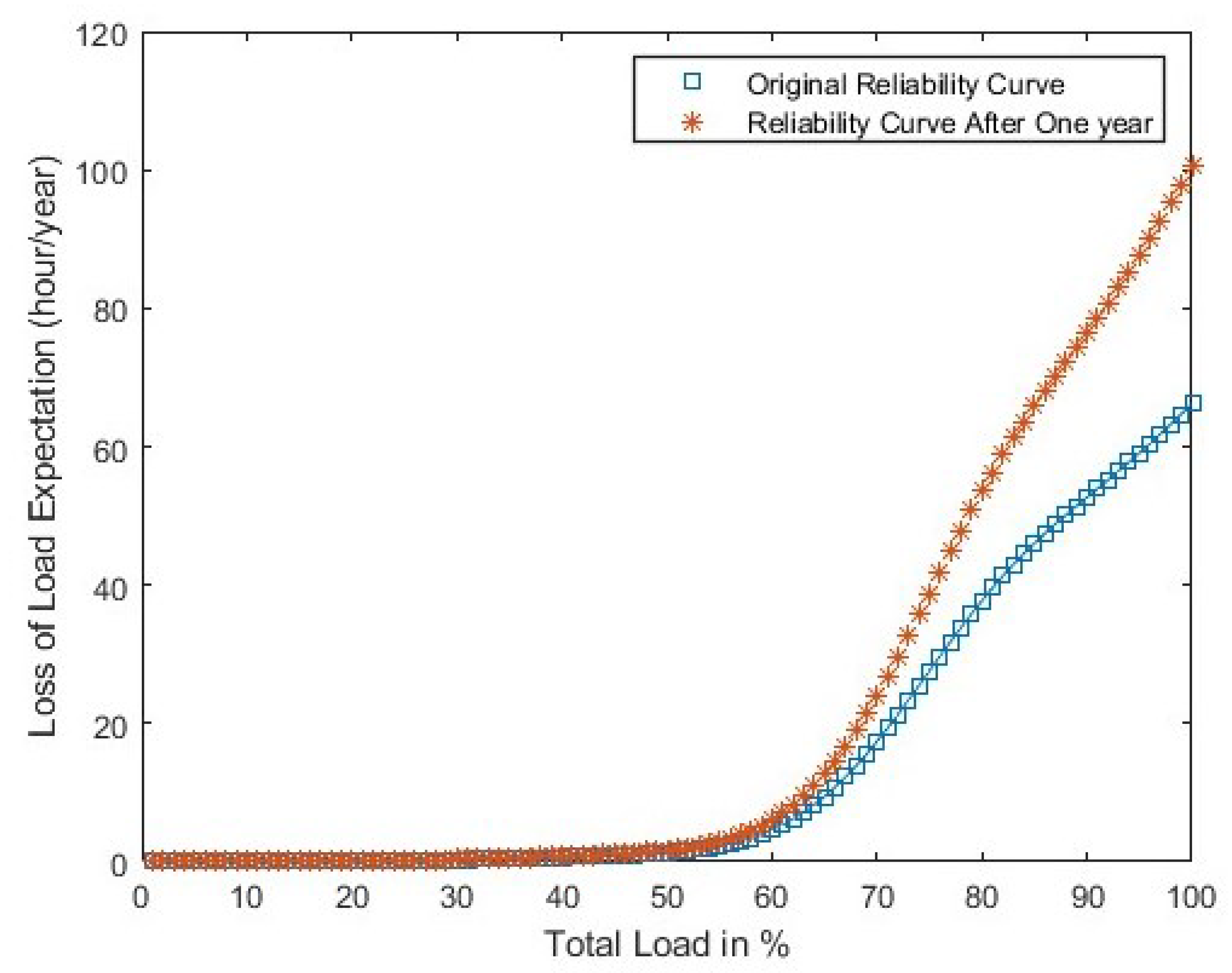
4.1.4. Findings and Discussion
- Base case reliability assessment
- 2.
- Impact of wind power allocation
- 3.
- Impact of CAESS integration
- Capacity credit optimization: we proposed a capacity-credit-centric approach that explicitly tackled the issues arising from renewable integration.
- CAESS’s advantage: we showed that storage systems could overcome issues related to integrating renewable energy sources.
- Optimal wind allocation and policy implications: distributing wind power optimally across interconnected areas maximized capacity credit, minimized the system’s loss of load expectation (LOLE), and enhanced the system’s resilience and reliability.
4.1.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4.2. Fuzzy Optimization
5. Conclusions
- (i)
- Developing a fuzzy-based optimization strategy that directly maximizes capacity credit while considering wind uncertainty;
- (ii)
- Integrating a compressed-air energy storage system (CAESS) into a multi-area generation expansion planning framework;
- (iii)
- Emphasizing capacity credit enhancement rather than cost minimization, which sets our study apart from most previous research.
- Improve compressed-air energy storage system (CAESS) capacity and power limitations:
- 2.
- Refining transmission network models:
- 3.
- Assessing the economic implications of the CAESS and wind allocation for cost–benefit optimization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Indices of areas | |
| Upper limitation of wind allocation in area i | |
| t | Hour index |
| J | Set of all area receiving power |
| I | Set of all area of wind farm |
| T | Set of all hours in the study |
| Decision variable of wind allocation | |
| Total installation of wind capacity | |
| Capacity outage probability table | |
| Hourly conventional capacity of area i | |
| Hourly wind data of area i | |
| Capacity credit of area i | |
| Tie-line capacity between areas i and j (MW) | |
| Hourly power flow from area i to area j | |
| Hourly load data for area i | |
| Penetration level of wind power plant | |
| Fuzzy sets for the capacity credit | |
| Fuzzy sets for the wind power parameter | |
| Upper/lower limit for the capacity credit | |
| Upper/lower limit for the wind parameter | |
| Membership function of the capacity credit | |
| Membership function of the wind parameter | |
| Efficiency of charging | |
| Efficiency of discharging | |
| Binary variable to allow only one mode charge or discharge | |
| CAES capacity MWh | |
| CAES charge power at time t and area i | |
| CAES discharge power at time t and area i |
References
- Global Wind Energy Council. Global Wind Report 2024; Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC): Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- WindEurope, Wind Energy in Europe 2023—Statistics and the Outlook for 2024–2030, Feb. 2024. Available online: https://windeurope.org/intelligence-platform/product/wind-energy-in-europe-2023-statistics-and-the-outlook-for-2024-2030/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, W. Overview of Power System Planning under Uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Control Science (IC2ECS), Nanjing, China, 16–18 December 2022; pp. 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Billinton, R.; Gao, Y.; Karki, R. Application of a Joint Deterministic-Probabilistic Criterion to Wind Integrated Bulk Power System Planning. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, C.A.; Lazaroiu, G.C.; Dumbrava, V.; Roscia, M. Deterministic Approach for Generation and Transmission Expansion Planning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on ENERGY and ENVIRONMENT (CIEM), Prague, Czech Republic, 23–27 July 2018; pp. 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Vafamehr, A.; Khodayar, M.E.; Manshadi, S.D.; Ahmad, I.; Lin, J. A Framework for Expansion Planning of Data Centers in Electricity and Data Networks Under Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Sun, K.; Lane, D.; Gu, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F. A Novel Generation Rescheduling Algorithm to Improve Power System Reliability with High Renewable Energy Penetration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Ela, A.A.; El-Sehiemy, R.A.; Shaheen, A.M.; Shalaby, A.S.; Mouafi, M.T. Reliability constrained dynamic generation expansion planning using honey badger algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Ela, A.A.; El-Sehiemy, R.A.; Shaheen, A.M.; Shalaby, A.S.; Mouwafi, M.T. Robust generation expansion planning in power grids under renewable energy penetration via honey badger algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 7923–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cao, M.; Yang, Y. Capacity Credit Evaluation of Correlated Wind Resources Using Vine Copula and Improved Importance Sampling. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Vrakopoulou, M.; Mancarella, P. Assessment of the Capacity Credit of Renewables and Storage in Multi-Area Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, Y.; Fang, C.; Su, Y.; Kang, C. Power System Adequacy with Variable Resources: A Capacity Credit Perspective. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 73, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hu, P.; Liu, G.; Mancarella, P. Capacity Credit Evaluation Framework of Wind, Solar and Pumped Hydro Storage Considering Generation Adequacy and Flexibility. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES), Perth, WA, Australia, 10–12 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Zeng, P.; Xu, X. Capacity Credit Assessment of Wind Power Considering Energy Storage. In Proceedings of the 2014 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Shenzhen, China, 23–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Garver, L.L. Effective Load Carrying Capability of Generating Units. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1966, PAS-85, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, C.; Chung, Y.; Kim, Y.J. ELCC-based capacity credit estimation accounting foruncertainties incapacity factors and its application to solar power in Korea. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V. Integration of compressed air energy storage with wind turbine to provide energy source for combustion turbine generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Europe, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Calero, F.; Cañizares, C.A.; Bhattacharya, K.; Anierobi, C.; Calero, I.; de Souza, M.F.Z.; Farrokhabadi, M.; Guzman, N.S.; Mendieta, W.; Peralta, D.; et al. A Review of Modeling and Applications of Energy Storage Systems in Power Grids. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 806–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, N.; Li, P.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W.; Yang, W. Methodology for Capacity Credit Evaluation of Physical and Virtual Energy Storage in Decarbonized Power System. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-F.; Oh, U.-J.; Choi, J.-S. Power System Reliability Evaluation Including Capacity Credit Considering Wind Energy with Energy Storage Systems in China. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, U.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.-H. Capacity credit and reasonable ESS evaluation of power system including WTG combined with BESS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems (PMAPS), Beijing, China, 16–20 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saket, R.K.; Sanjeevikumar, P. (Eds.) Reliability Analysis of Modern Power Systems, 1st ed.; Wiley Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Makvand, S.B. Probabilistic evaluation and planning of power transmission system reliability. Iet Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Review of Uncertainty Modeling for Optimal Operation of Integrated Energy System. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 641337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Soroudi, A. Uncertainty Management in Power System Operation Decision Making. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.N.; Billinton, R. Probabilistic Assessment of Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1978, PAS-97, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.S.; Quan, H.; Wen, K.Y.; Srinivasan, D. Probabilistic risk and severity analysis of power systems with high penetration of photovoltaics. Sol. Energy 2021, 230, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, U.; Gürcan, Ö.F.; Güldeş, M.; Şahin, C. A Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Method for Selection of Biomass Power Plant Location. In Optimization and Decision-Making in the Renewable Energy Industry; Balo, F., Topal, A., Demir, E., Ulutaş, A., Eds.; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Xu, J.; Da, L.; Hashim, M. Ahp and Fuzzy Topsis Methods for Green Supplier Selection and Evaluation. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 5, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.S.; Souza, J.D.F.; Lima, E.L. An Industrial Maintenance Decision Support System based on Fuzzy Inference to Optimize Scope Definition. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 51, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Liao, H.; Zavadskas, E.K. An overview of fuzzy techniques in supply chain management: Bibliometrics, methodologies, applications and future directions. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2021, 27, 402–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Zheng, X.-J. Enhancing smart city assessment: An advanced MCDM approach for urban performance evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 105930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, F.J.; Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M. Fuzzy logic-based energy management system for grid-connected residential DC microgrids with multi-stack fuel cells: A multi-objective approach. Sustain. Energy, Grids Netw. 2022, 32, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.-T.; Nguyen, N.-A.-T.; Nguyen, V.-T.-T.; Dang, L.-T.-H. A Two-Stage Multi-Criteria Supplier Selection Model for Sustainable Automotive Supply Chain under Uncertainty. Axioms 2022, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, M.; Shaabani, A.; Santos-Arteaga, F.J.; Valaei, N. An integrated fuzzy sustainable supplier evaluation and selection framework for green supply chains in reverse logistics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, F.J.; Segura, F.; Andújar, J.M.; Palacio, A.; Saenz, J.L.; Isorna, F.; López, E. Multi-Objective Fuzzy Logic-Based Energy Management System for Microgrids with Battery and Hydrogen Energy Storage System. Electronics 2020, 9, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-Barrios, M.; Jaramillo-Rueda, N.; Gul, M.; Yucesan, M.; Jiménez-Delgado, G.; Alfaro-Saíz, J.-J. A Fuzzy Hybrid MCDM Approach for Assessing the Emergency Department Performance during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.; Saraiva, J.T. Fuzzy Modeling of Power System Optimal Load Flow. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1992, 7, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shahidehpour, S.M.; Adapa, R. A fuzzy Set Approach to Tie Flow Computation in Optimal Power Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the American Power Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–25 April 1992; pp. 1443–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Guan., X.; Luh, P.; Prasannn, B. Power System Scheduling with Fuzzy Reserve Requirements. In Proceedings of the IEEE/PES 1995 Summer Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awami, A.T.; Amleh, N.A.; Muqbel, A.M. Optimal Demand Response Bidding and Pricing Mechanism with Fuzzy Optimization: Application for a Virtual Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5051–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Al-Awami, A.T.; Sortomme, E.; Abido, M.A. Coordinated bidding of ancillary services for vehicle-to-grid using fuzzy optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Chen, Q.; Dong, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, L. Power System Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets and Incidence Matrices. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2023, 38, 3924–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masteri, K.; Venkatesh, B.; Freitas, W. A Fuzzy Optimization Model for Distribution System Asset Planning With Energy Storage. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 5114–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Feng, X.; Wu, Q. Optimal Stochastic Deployment of Heterogeneous Energy Storage in a Residential Multienergy Microgrid with Demand-Side Management. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Xu, G.; Fei, Z.; Li, Z.; Du, L.; Guerrero, J.M.; Li, Z. Two-Stage Coordinated Robust Planning of Multi-Energy Ship Microgrids Considering Thermal Inertia and Ship Navigation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Renewable Electricity Futures Study Data Explorer. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/analysis/re-futures.html (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Potter, C.W.; Lew, D.; McCaa, J.; Cheng, S.; Eichelberger, S.; Grimit, E. Creating the Dataset for the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (U.S.A.). Wind. Eng. 2008, 32, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschen, D.S.; Strbac, G. Fundamentals of Power System Economics, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.K.; Jha, A.V.; Appasani, B.; Srinivasulu, A.; Bizon, N.; Thounthong, P. Load Frequency Control Using Hybrid Intelligent Optimization Technique for Multi-Source Power Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, C.; Wong, P.; Albrecht, P.; Allan, R.; Bhavaraju, M.; Billinton, R.; Singh, C. The IEEE Reliability Test System-1996. A report prepared by the Reliability Test System Task Force of the Application of Probability Methods Subcommittee. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1999, 14, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia. Load Data for Belgium Electricity. Available online: https://www.elia.be/en/grid-data/load-and-load-forecasts (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Ghazal, H.M. Wind Power Generation Expansion Planning Based on Capacity Credit Maximization. Master’s Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, May 2018. [Google Scholar]


| Ref. | Scope | Uncertainty Handling | Storage Type | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5] | GEP | Deterministic | None | Minimize cost |
| [48] | Residential microgrid | Stochastic | Heterogeneous | Cost and demand-side management |
| [49] | Ship microgrid | Robust optimization | Thermal | Cost and navigation |
| This Study | Multi-area GEP | Fuzzy optimization | CAESS | Maximize CC |
| MAPE Results | |
|---|---|
| Area i | MAPE |
| 1 | 13.3% |
| 2 | 11.1% |
| 3 | 15.21% |
| Average | 13.2% |
| Location | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional capacity | 560 MW | 696 MW | 751 MW |
| Peak load | 445 MW | 550 MW | 600 MW |
| Wind profile | NREL data for location A | NREL data for location B | NREL data for location C |
| Line Capacity | |
|---|---|
| Line No. | Capacity |
| L12 | 40 MW |
| L13 | 45 MW |
| L23 | 45 MW |
| Line Capacity | |
|---|---|
| Parameter | Value |
| 25 MW | |
| 25 MW | |
| CAES capacity in each area | 50 MWh |
| C-rate | 0.5 C |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| Generating Unit Reliability Data | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Size | Area 1 | Unit Size | Area 2 | Unit Size | Area 3 | |||
| No. Units | FOR | No. Units | FOR | No. Units | FOR | |||
| 12 | 5 | 0.02 | 12 | 3 | 0.02 | 20 | 3 | 0.1 |
| 50 | 4 | 0.01 | 20 | 2 | 0.1 | 50 | 2 | 0.02 |
| 100 | 3 | 0.04 | 155 | 4 | 0.04 | 197 | 3 | 0.05 |
| New Peak Load | |
|---|---|
| Area i | Peak Load |
| 1 | 471.7 MW |
| 2 | 583 MW |
| 3 | 636 MW |
| Loss of Load Expectation (h/y) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area i | Base Case | After One Year | LOLE (h/y) of Each Case | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Optimal | |||
| 1 | 5.58 | 10.57 | 6 | 8.9 | 6.4 | 5.2 |
| 2 | 18 | 32.9 | 26.35 | 22 | 23.7 | 17.6 |
| 3 | 41 | 57 | 52.3 | 43.7 | 39 | 41.28 |
| Total | 64.58 | 100.5 | 84.65 | 74.6 | 69.1 | 64.1 |
| Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area i | Deterministic Results | ||
| Wind | WC | CC | |
| Allocation | MW | ||
| 1 | 44 | 326 | 29.3% |
| 2 | 147 | ||
| 3 | 135 | ||
| Comparison Among Cases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area i | Wind Installation Cases | |||
| Case | Case | Case | Optimal | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Case | |
| 1 | 163 | 0 | 109 | 44 |
| 2 | 163 | 163 | 109 | 147 |
| 3 | 0 | 163 | 109 | 135 |
| CC | 16% | 19% | 24% | 29.3% |
| Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area i | Deterministic Results Using CAES | ||
| Wind | WC | CC | |
| Allocation | MW | ||
| 1 | 51 | 273 | 35% |
| 2 | 90 | ||
| 3 | 132 | ||
| Comparison Result | ||
|---|---|---|
| Without CAES | With CAES | |
| Expected CC | 29.3% | 35% |
| Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area i | Fuzzy Results | ||
| Wind | WC | CC | |
| Allocation | MW | ||
| 1 | 36 | 286 | 33.4% |
| 2 | 109 | ||
| 3 | 141 | ||
| Comparison Results | ||
|---|---|---|
| Deterministic | Fuzzy | |
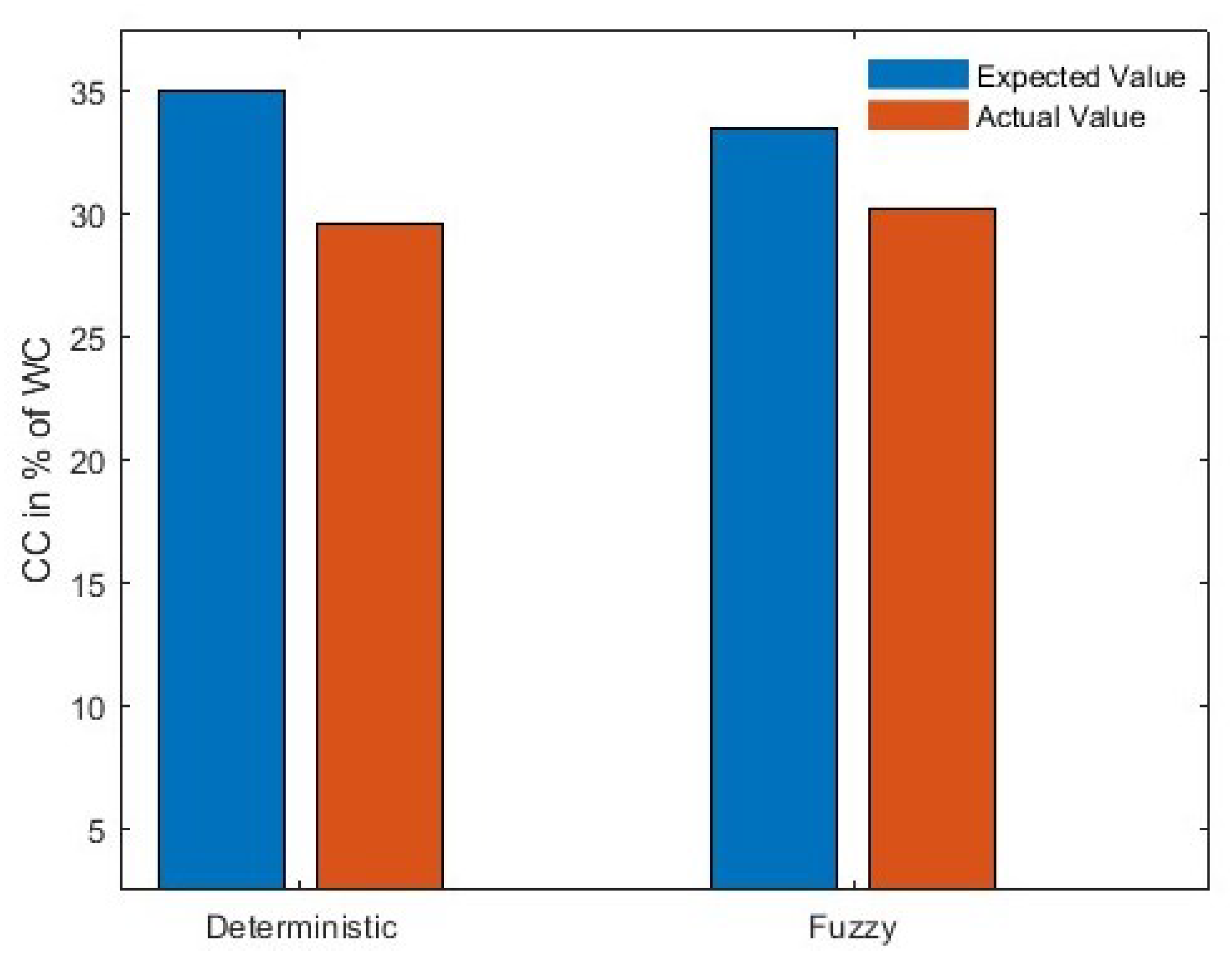
| Expected CC | 35% | 33.4% |
| Actual CC | 29.5% | 30.2% |
| Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deterministic | Fuzzy | |||
| ±5 | ±9 | ±13 | ||
| Expected CC | 35% | 32.8% | 33.4% | 32.5% |
| Actual CC | 29.5% | 29.3% | 30.2% | 29% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghazal, H.M.; Khan, U.A.; Alismail, F. Multi-Area Wind Power Planning with Storage Systems for Capacity Credit Maximization Using Fuzzy-Based Optimization Strategy. Energies 2025, 18, 5628. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215628
Ghazal HM, Khan UA, Alismail F. Multi-Area Wind Power Planning with Storage Systems for Capacity Credit Maximization Using Fuzzy-Based Optimization Strategy. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5628. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215628
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhazal, Homod M., Umer Amir Khan, and Fahad Alismail. 2025. "Multi-Area Wind Power Planning with Storage Systems for Capacity Credit Maximization Using Fuzzy-Based Optimization Strategy" Energies 18, no. 21: 5628. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215628
APA StyleGhazal, H. M., Khan, U. A., & Alismail, F. (2025). Multi-Area Wind Power Planning with Storage Systems for Capacity Credit Maximization Using Fuzzy-Based Optimization Strategy. Energies, 18(21), 5628. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215628







