Adaptive Maximum Power Capture Control for Wind Power Systems with VRB Storage Using SVR-Based Sensorless Estimation and FPNN-IPSO Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
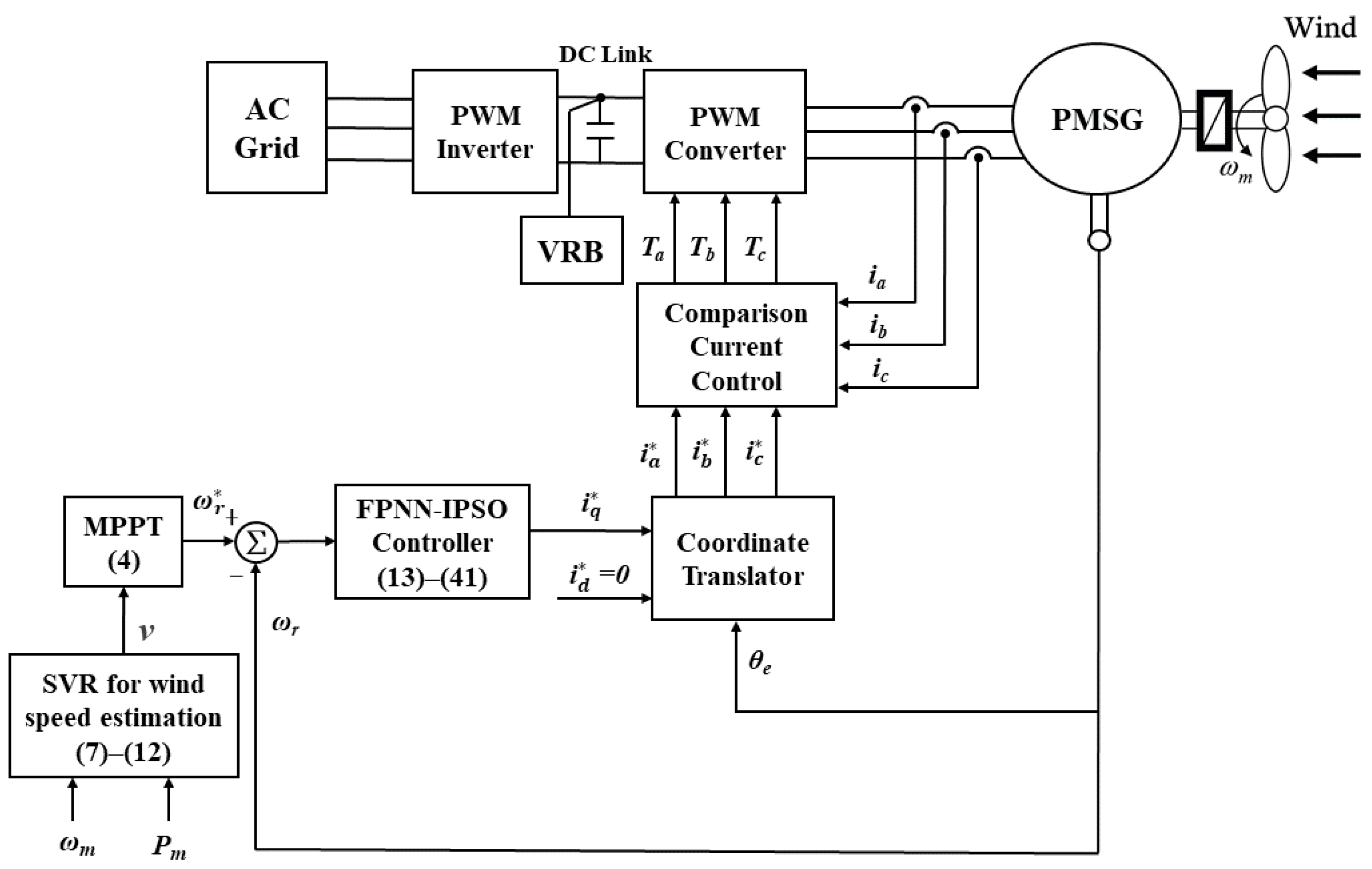
2. Analytical Evaluation of the Wind Power Generation System
2.1. Wind Turbine Characteristics and Modeling
2.2. PMSG
2.3. Principle of a Vanadium Redox Battery
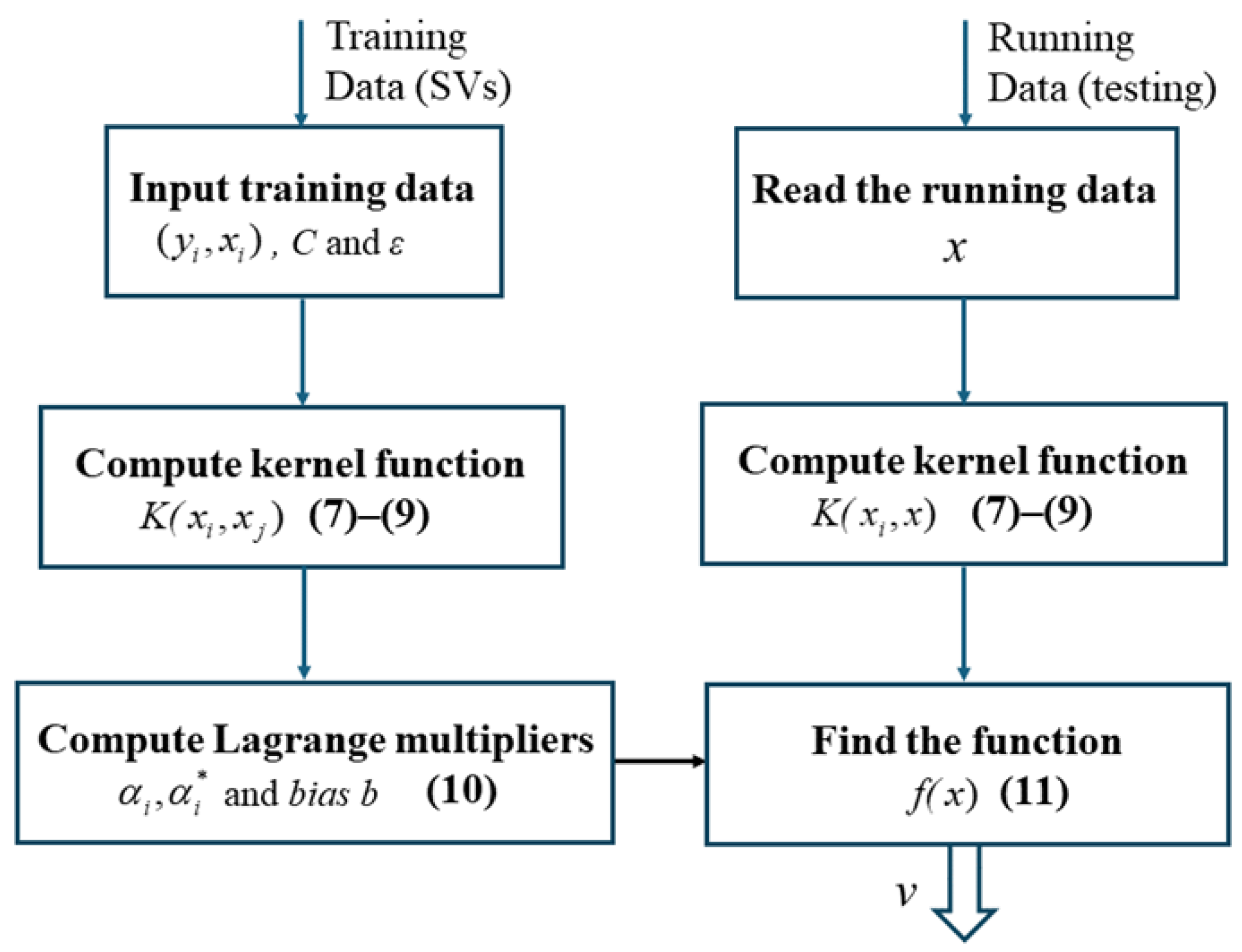
3. An SVR Approach for Wind Speed Estimation
4. Proposed FPNN with IPSO Control System
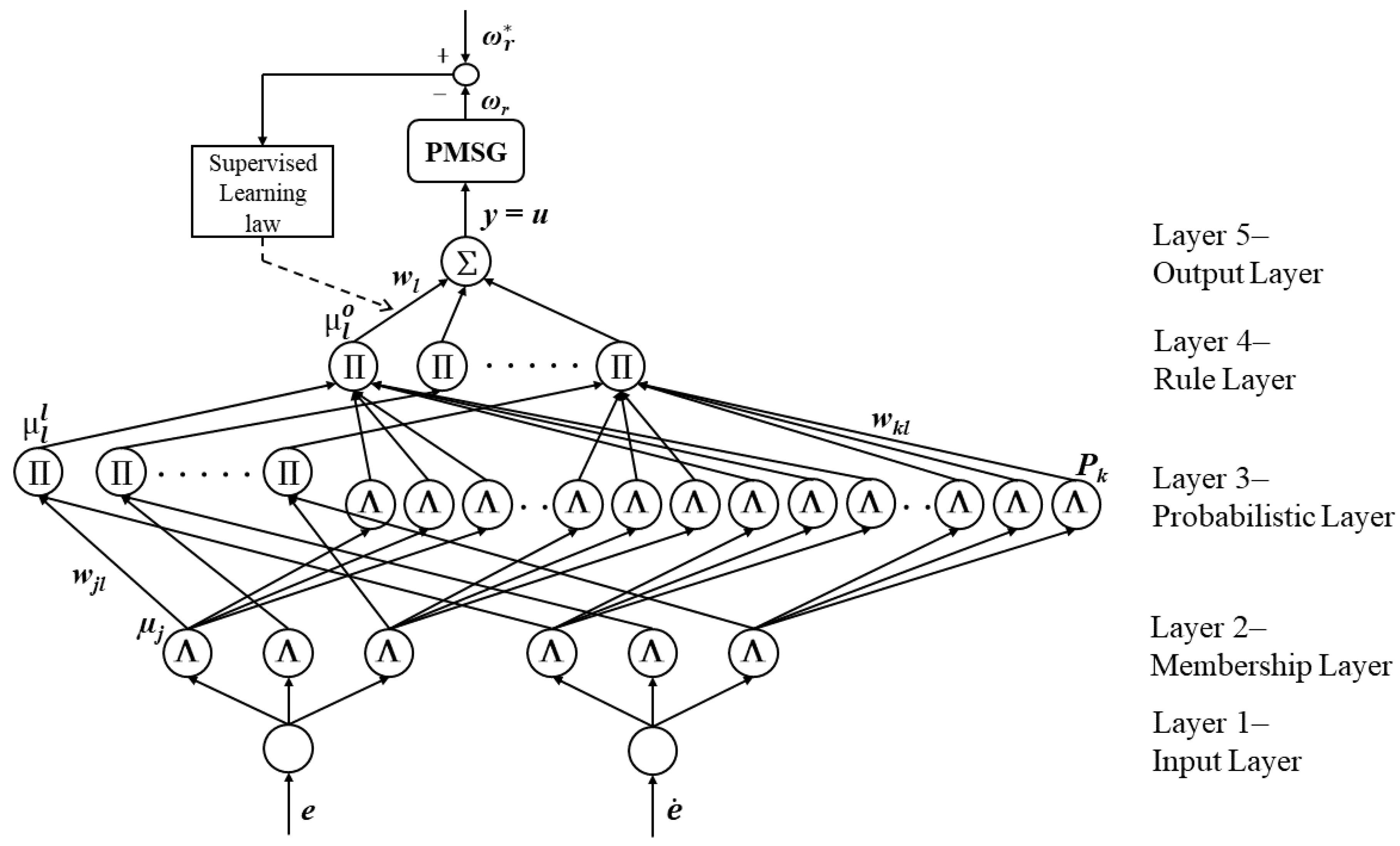
4.1. Fuzzy Probabilistic Neural Network (FPNN)
4.2. Online Supervised Learning and Training Process
- (1)
- Layer5: The propagated error term is defined as follows:
- (2)
- Layer4: The error term to be propagated is given:
- (3)
- Layer2: The following expression defines the error term that is propagated through the network:
4.3. Convergence Analysis
4.4. Composite Stability of Estimator–NN–MPC
4.5. Adjustment of Learning Rates Using IPSO
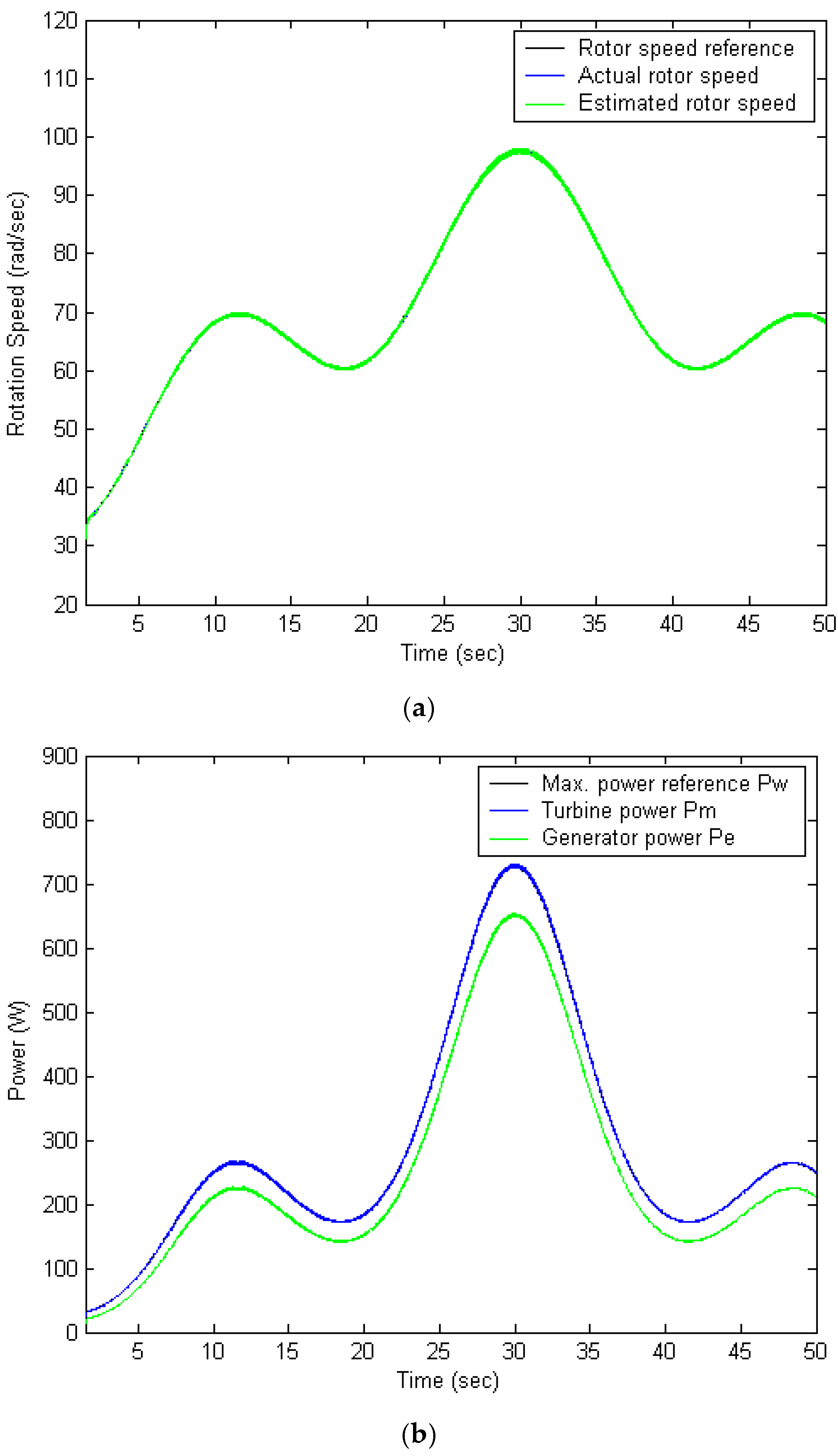
5. Case Studies and Simulation Results
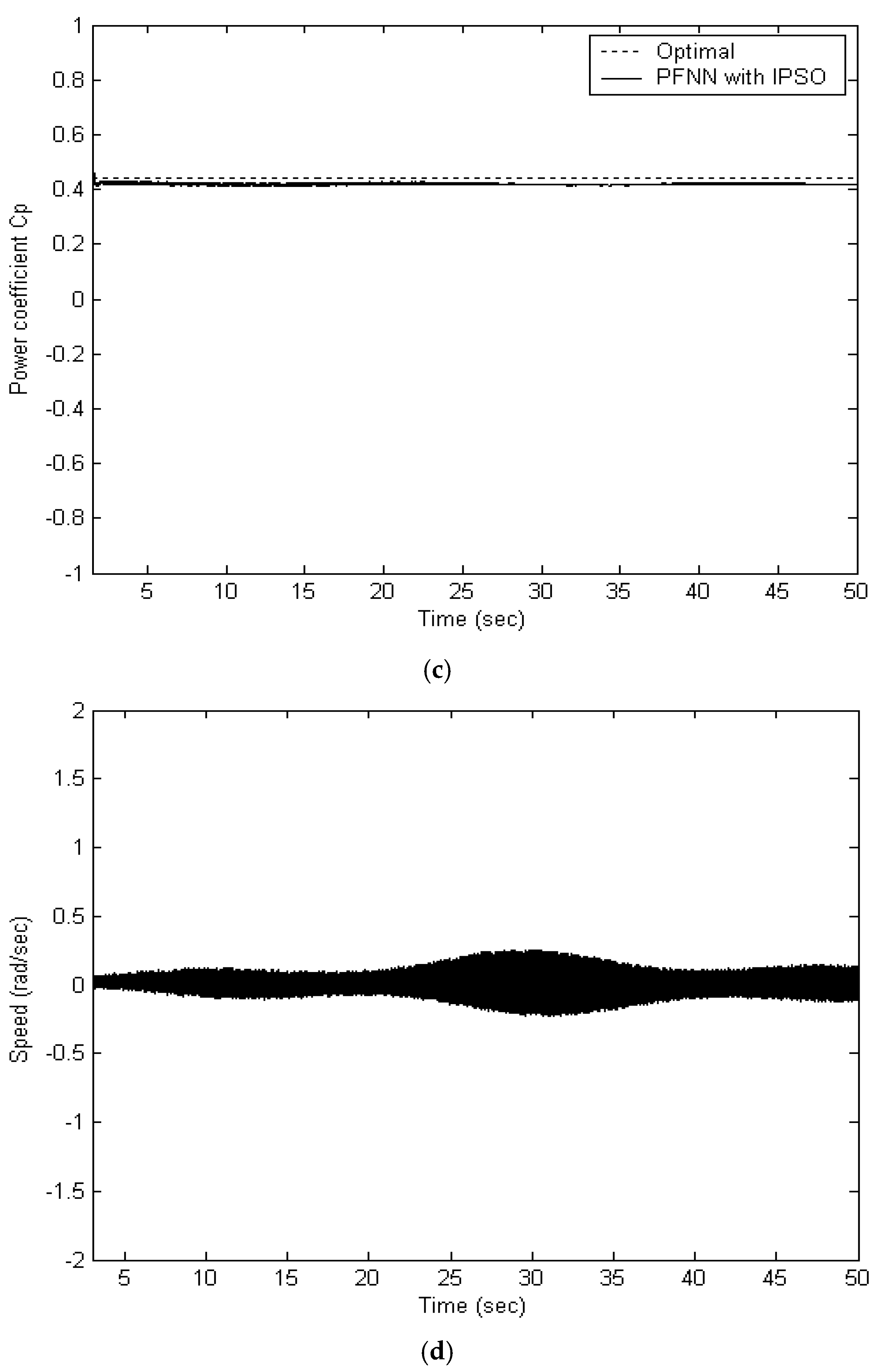
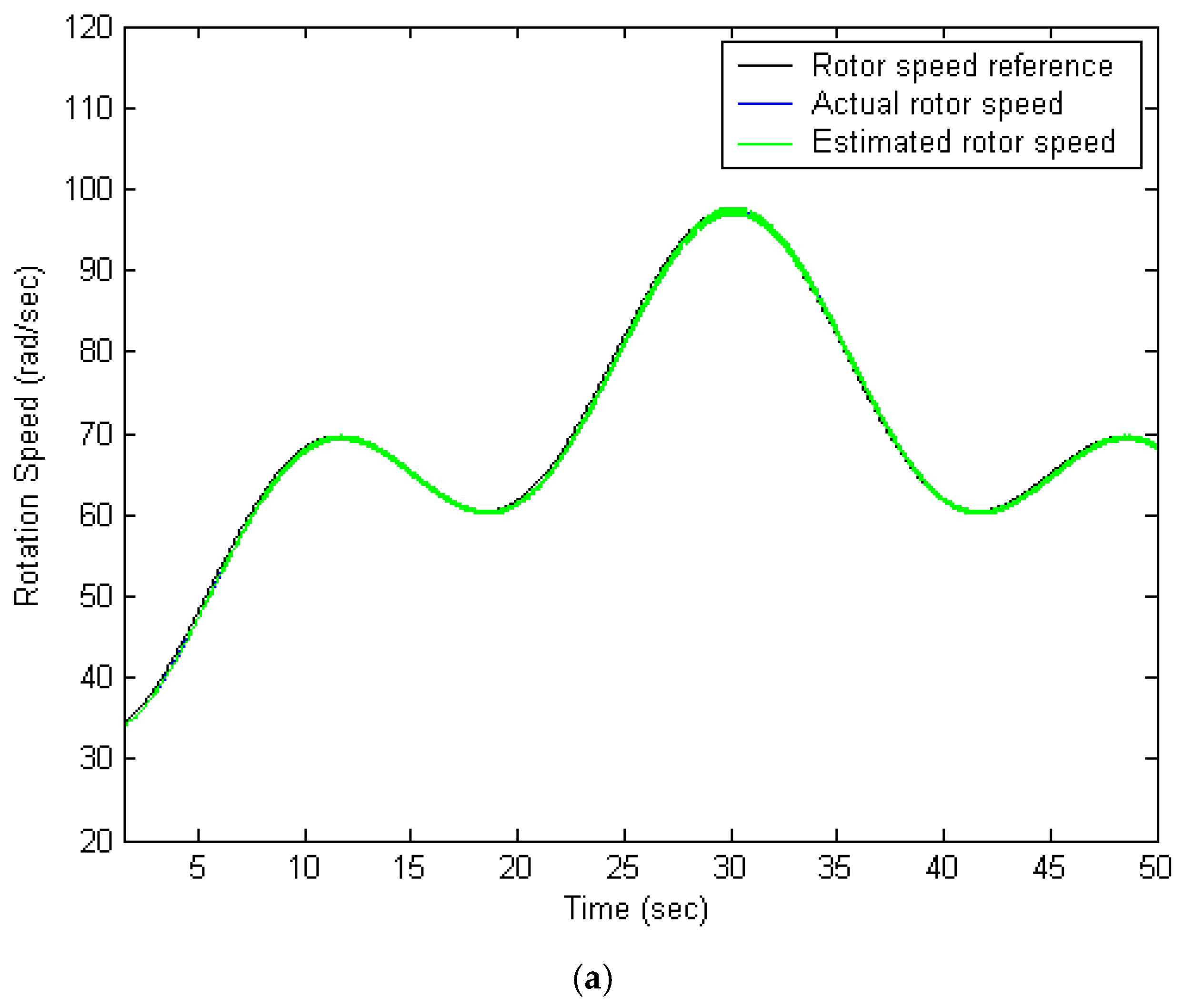
5.1. FPNN with IPSO Algorithm
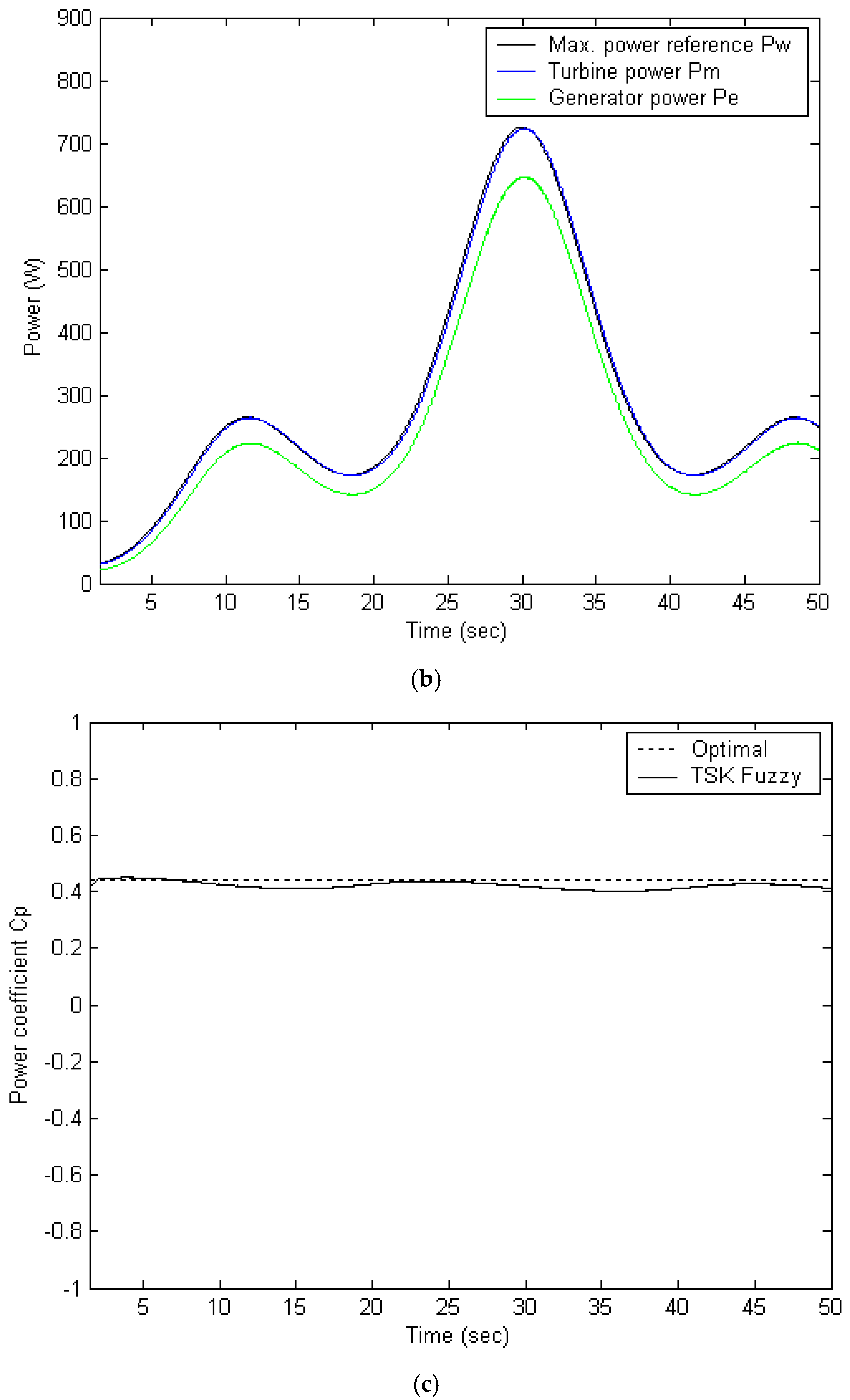
5.2. TSK Fuzzy-Based Algorithm
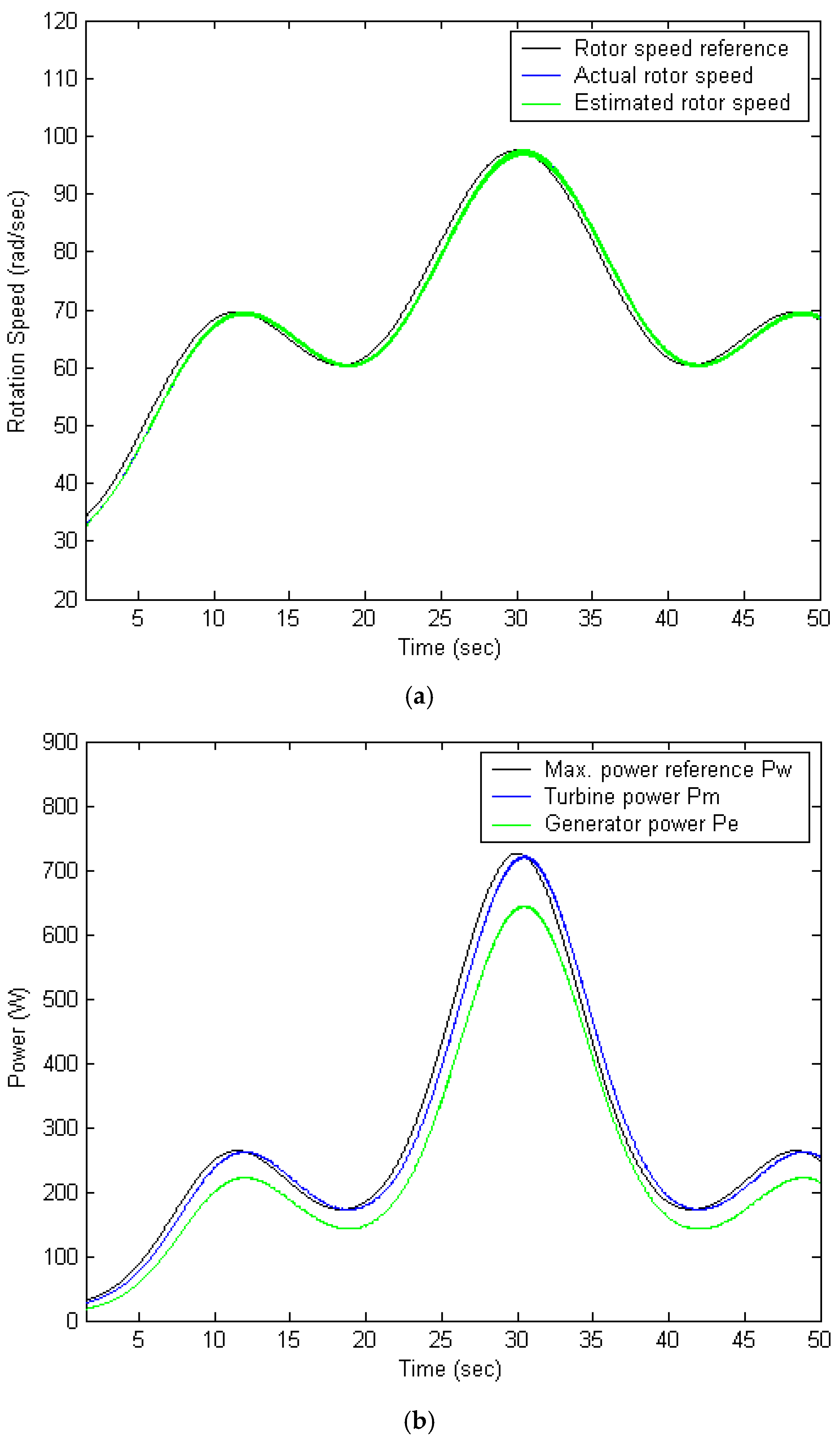
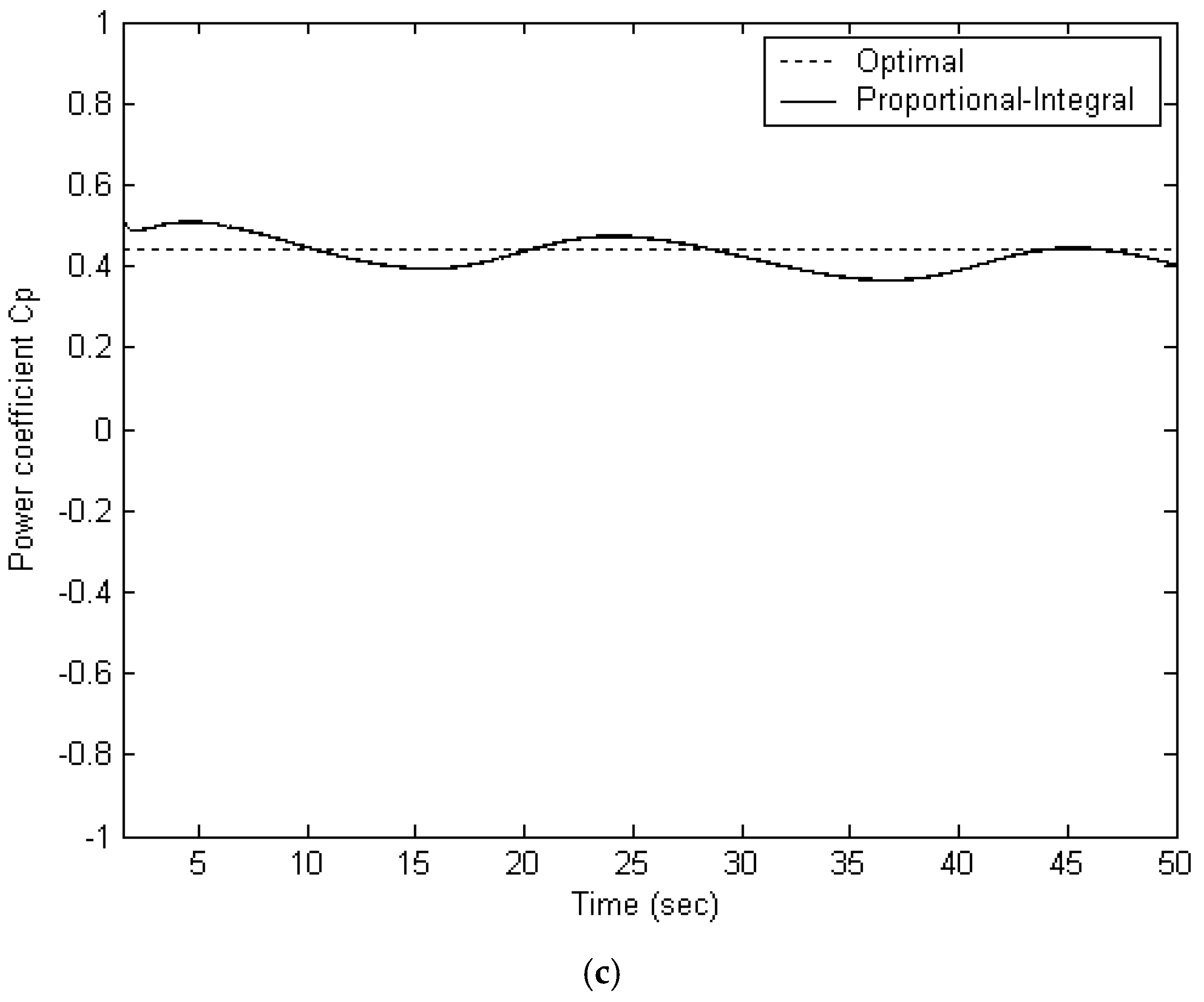
5.3. PI Controller
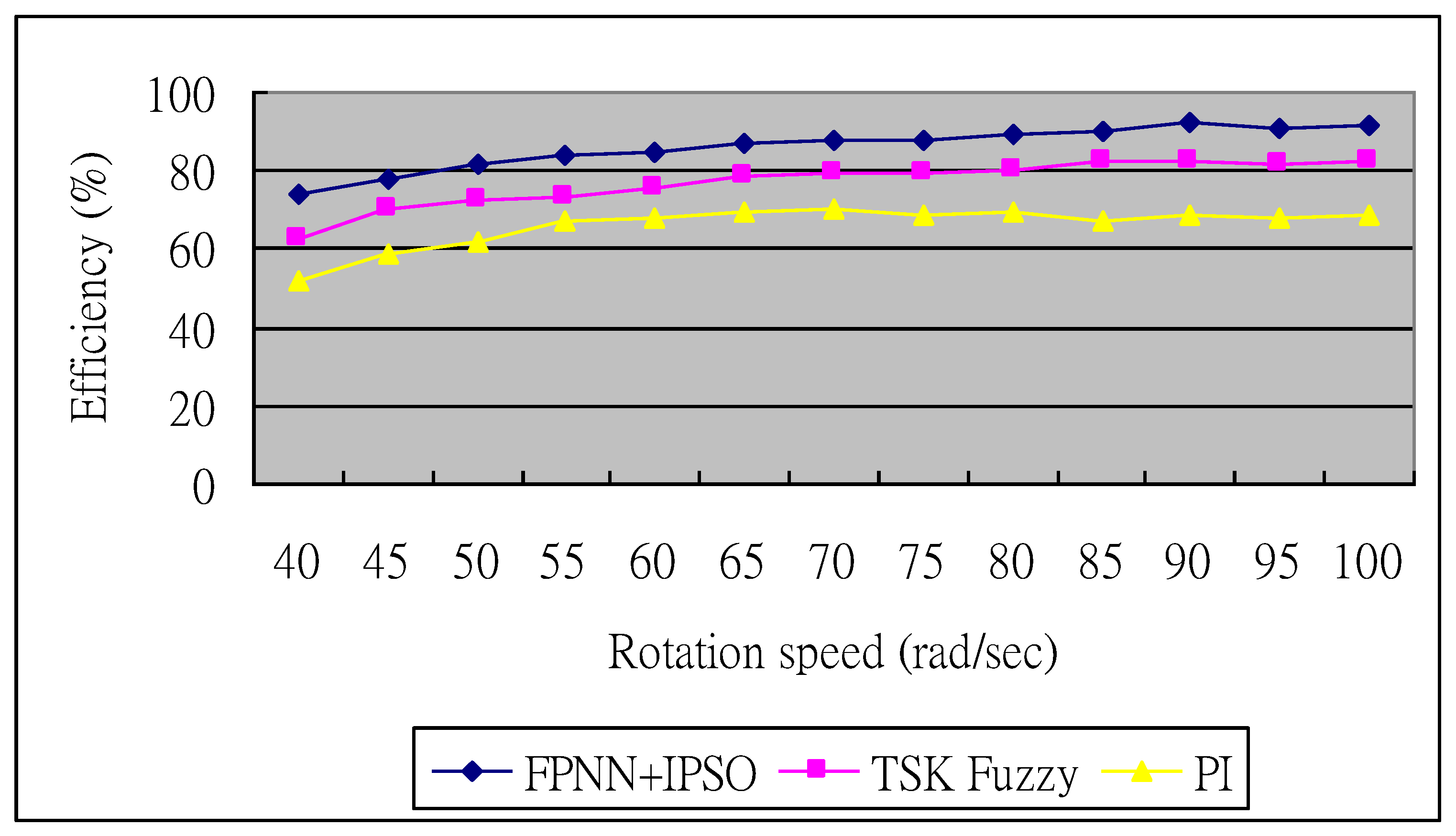
5.4. Performance Comparison
| Method | Average Power (Pm) (W) | Increasing Power Percentage (%) | Max. Power Coefficient (%) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPNN with IPSO method | 271 | 9.71 | 2.53 | 86.11 |
| [43] | 267 | 8.09 | 2.57 | 85 |
| TSK Fuzzy method | 259 | 4.85 | 9.33 | 76.97 |
| PI method | 247 | reference | 13.32 | 66.03 |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Composite Stability Proof
Appendix A.1. Error Model
Appendix A.2. Lyapunov Candidate
Appendix A.3. Derivative Bound for the Plant Part
Appendix A.4. Neural Adaptation Term
Appendix A.5. Estimator and Disturbance Contributions
Appendix A.6. Conclusions
References
- Klement, E.P.; Mesiar, R.; Pap, E. A universal integral as common frame for choquet and Sugeno integral. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Wang, M.H.; Hagras, H. A type-2 fuzzy ontology and its application to personal diabetic-diet recommendation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Park, J.B.; Joo, Y.H. Improvement on nonquadratic stabilization of discrete-time Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems: Multiple parameterization approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Sutikno, T.; Subrata, A.C.; Elkhateb, A. Evaluation of Fuzzy Membership Function Effects for Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique of Photovoltaic System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 109157–109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Sun, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, H.; Qiao, J. Self-Organizing Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Neural Network Using Information Aggregation Method. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 6428–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Wu, C.H. Robust optimal reference-tracking design method for stochastic synthetic biology systems: T-S fuzzy approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Statist. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Chang, J.H. Robust Localization Method Based on Non-Parametric Probability Density Estimation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 61468–61480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridi, M.; Kargas, N.; Sidiropoulos, N.D. Low-Rank Characteristic Tensor Density Estimation Part I: Foundations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 2654–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Integral Aggregations of Continuous Probabilistic Hesitant Fuzzy Sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ying, H. Modeling and Control of Probabilistic Fuzzy Discrete Event Systems. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2022, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Bi, L.; Yang, Z.; Fei, W. A Novel Control Framework of Brain-Controlled Vehicle Based on Fuzzy Logic and Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 21777–21789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzayed, M.; Farajpour, Y.; Chaoui, H. Simplified Current Sensorless Maximum Power Extraction for Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 104686–104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Ding, Z. Surrogate-Assisted Cooperation Control of Network-Connected Doubly Fed Induction Generator Wind Farm with Maximized Reactive Power Capacity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, F.E.Z.; Hasanien, H.M.; Sabry, W.; Ullah, Z.; Alkuhayli, A.; Yakout, A.H. Mountain Gazelle Algorithm-Based Optimal Control Strategy for Improving LVRT Capability of Grid-Tied Wind Power Stations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 129479–129492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, R.I.; Ronilaya, F.; Rifa’i, M.; Jasa, L.; Priyadi, A.; Mauridhi Hery, P. Sensorless Optimum Power Extraction for Small Scale Stand Alone Wind Turbine Based on Fuzzy Controller. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Electromagnetic Technology (AEMT), Lombok, Indonesia, 9–12 April 2018; pp. 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, S.; Nakayama, H.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Sensorless output maximization control for variable-speed wind generation system using IPMSG. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid Hamad, Y.; Nasser Hussain, A.; Lafta, Y.N.; Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Multi-Objective Optimization of Renewable Distributed Generation Placement and Sizing for Technical and Economic Benefits Improvement in Distribution System. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 164226–164247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, L.K.; Verma, M.K.; Joshi, P. Novel Real Valued Improved Coral-Reef Optimization Algorithm for Optimal Integration of Classified Distributed Generators. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 80623–80638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cruz, R.; Sanchez, E.N.; Ornelas-Tellez, F.; Loukianov, A.G. Particle Swarm Optimization for Discrete-Time Inverse Optimal Control of a Doubly Fed Induction Generator. IEEE Trans. Power Cybern. 2013, 43, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.N.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.H. Large-Scale Structured Output Classification via Multiple Structured Support Vector Machine by Splitting. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 2112–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Baldick, R. Ramp Event Forecast Based Wind Power Ramp Control with Energy Storage System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.; Zheng, J.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Man, Z.; Liang, B. Barrier Function Based Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Uncertain Systems with Input Saturation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 4258–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.M.; Chen, C.H.; Tu, C.S. Maximum Power Point Tracking-Based Control Algorithm for PMSG Wind Generation System without Mechanical Sensors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, R.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, Y.R. Novel maximum-power-extraction algorithm for PMSG wind generation system. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2007, 1, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutari, H.; Ibrahim, T.; Nor, N.B.M.; Abdulrab, H.Q.A.; Saad, N.; Al-Tashi, Q. Coordination of Enhanced Control Schemes for Optimal Operation and Ancillary Services of Grid-Tied VSWT System. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 43520–43535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, A.; Pugach, M.; Polyakov, A.; Osinenko, P.; Bolychev, A.; Terzija, V.; Parsegov, S. Optimal Flow Factor Determination in Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Control. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 19277–19284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Crow, M.L.; Elmore, A.C. A Balance-of-Plant Vanadium Redox Battery System Model. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.R.; Seok, J.K.; Lee, D.C. Mechanical parameter identification of servo systems using robust support vector regression. IEEE PESC Conf. 2004, 5, 3425–3430. [Google Scholar]
- Aghakashkooli, M.R.; Jovanovic, M.G. A Sensorless Parameter Independent Controller for Brushless Doubly-Fed Reluctance Wind Generators. In Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems (PEDS) 2023, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–10 August 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H. Three-phase induction motor operation trend prediction using support vector regression for condition-based maintenance. In Proceedings of the World Congress on intelligent control and automation (WCICA) 2006, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 7878–7881. [Google Scholar]
- Asaly, S.; Gottlieb, L.A.; Reuveni, Y. Using Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Ionospheric Total Electron Content (TEC) Data for Solar Flare Predictions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrabgoun, O.; Daneshkhah, A.; Esmaeilbeigi, M.; Sohrabi Safa, N.; Alenezi, A.H.; Rahman, A. Predicting Primary Sequence-Based Protein-Protein Interactions Using a Mercer Series Representation of Nonlinear Support Vector Machine. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 124345–124354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkassky, V.; Miller, F. Learning from Data Concept Theory and Methods; John. Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, J. Semi-Supervised Concept Learning by Concept-Cognitive Learning and Concept Space. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.J.; Wai, R.J.; Lee, C.C. Fuzzy neural network position controller for ultrasonic motor drive using push-pull DC-DC converter. IET Proc. Control Theory Appl. 1999, 146, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H. Dynamic Optimization of Rotor-Side PI Controller Parameters for Doubly-Fed Wind Turbines Based on Improved Recurrent Neural Networks Under Wind Speed Fluctuations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 102713–102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Rehman, O.U.; Rehman, S.U.; Ullah, S.; Waqas, M.; Zhu, R. A Novel Quantum Inspired Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Electromagnetic Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 21909–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, S.; Srivastava, L.; Pandit, M. Optimal location and sizing of STATCOM for voltage security enhancement using PSO-TVAC. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy Systems, Chennai, India, 22–24 December 2011; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Le, K.H.; Cao, M.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Le, M.V. Determining Optimal Location and Sizing of STATCOM Based on PSO Algorithm and Designing Its Online ANFIS Controller for Power System Voltage Stability Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Green Technology and Sustainable Development (GTSD) 2020, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 27–28 November 2020; pp. 272–279. [Google Scholar]
- Munnu, M.K.; Choudhary, J. Optimal Placement and Sizing of Custom Power Devices using PSO and APSO Optimization in Radial Distribution Network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Energy, Power and Environment: Towards Flexible Green Energy Technologies (ICEPE) 2023, Shillong, India, 15–17 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.M.; Mulla, M.A. Rotor Position-Sensorless Algorithms for Direct Power Control of Rotor-Tied DFIG. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 6213–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.M.; Hong, C.M.; Ou, T.C.; Chiu, T.M. Hybrid Intelligent Control of PMSG Wind Generation System Using Pitch Angle Control with RBFN. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, K.-H.; Hong, C.-M.; Cheng, F.-S. Adaptive Maximum Power Capture Control for Wind Power Systems with VRB Storage Using SVR-Based Sensorless Estimation and FPNN-IPSO Optimization. Energies 2025, 18, 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205461
Lu K-H, Hong C-M, Cheng F-S. Adaptive Maximum Power Capture Control for Wind Power Systems with VRB Storage Using SVR-Based Sensorless Estimation and FPNN-IPSO Optimization. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205461
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Kai-Hung, Chih-Ming Hong, and Fu-Sheng Cheng. 2025. "Adaptive Maximum Power Capture Control for Wind Power Systems with VRB Storage Using SVR-Based Sensorless Estimation and FPNN-IPSO Optimization" Energies 18, no. 20: 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205461
APA StyleLu, K.-H., Hong, C.-M., & Cheng, F.-S. (2025). Adaptive Maximum Power Capture Control for Wind Power Systems with VRB Storage Using SVR-Based Sensorless Estimation and FPNN-IPSO Optimization. Energies, 18(20), 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205461








