Abstract
Against the backdrop of China’s “dual carbon” goals of achieving carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. Traditional qualitative evaluations struggle with subjectivity; therefore we apply the quantitative PMC Index to systematically assess smart energy policies. This research systematically analyzes 16 representative Chinese smart energy policies using the PMC model, combined with content analysis. An integrated analytical framework was constructed to examine PMC applications across different energy policy fields. Results demonstrate that China’s smart energy policies achieved excellent performance, with an average PMC score of 7.48 out of 10. Furthermore, 68.75% of policies (11 out of 16) reached the ‘excellent’ level (PMC ≥ 8.0), with Policy “P6” achieving the highest score of 8.88 points. Top-performing policies exhibited strong strategic coordination, clear objectives, and comprehensive supporting measures. The findings reveal a well-structured policy cluster with clear objectives and strong coordination. This mature policy package provides a solid institutional foundation for China’s energy system transformation toward smart and green development, offering valuable insights for energy policy optimization and quantitative assessment methodology improvement.
1. Introduction
Against the backdrop of increasingly severe global climate change and intensifying energy security challenges, countries around the world are accelerating their transition to clean, low-carbon energy systems. China has clearly stated its “dual carbon” goals of achieving carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. The profound transformation of the energy system has become the core and key to achieving these goals. However, as a series of energy policies—ranging from energy security, energy transition, renewable energy development, to emerging energy technologies—have been introduced in rapid succession, and how to scientifically assess the intrinsic quality and design rationality of these policies has become a critical issue that needs to be addressed urgently. Traditional policy evaluations primarily rely on qualitative analysis, which, while in-depth, is prone to subjectivity and struggles to accurately and systematically measure the internal consistency and design rationality of policies.
To overcome limitations of traditional evaluation methods, the Policy Modeling Consistency (PMC) Index Model offers a scientific, objective, and quantifiable approach. Proposed based on ‘Omnia Mobilis’ philosophy, the PMC model converts qualitative policy texts into quantifiable indices through multi-dimensional indicators. By constructing an indicator system comprising multiple first- and second-level variables, assigning values to each variable, and calculating the weighted comprehensive index, the model evaluates the consistency of policy texts.
This model has significant advantages of comprehensiveness, systematicity, and intuitiveness, effectively overcoming the subjectivity and ambiguity of traditional evaluation methods. It has been rapidly promoted and applied in Chinese academic circles in recent years. However, the application of the PMC model in China’s energy policy evaluation still faces many issues that need to be addressed, mainly manifested in the lack of systematic application and the need to improve theoretical integration.
Currently, the application of the PMC model in energy policy evaluation exhibits a distinct “scattered” distribution pattern, lacking a macro-level overall grasp and deep integration. Specifically, while existing studies have covered multiple subfields such as energy security, energy transition, carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, renewable energy, and new energy industries, these studies remain relatively independent, lacking horizontal comparisons and vertical integration. This research status quo has resulted in a fragmented understanding of the patterns of China’s energy policy design, making it difficult to form systematic policy optimization guidelines.
Given the growing importance of the application of the PMC model and the lack of relevant theoretical integration research, which has severely constrained the in-depth development of this field, it has become necessary to conduct systematic review research. Although the application of the PMC model in China’s energy policy evaluation has become increasingly serious, there is currently relatively little systematic research specifically addressing this issue. Existing literature is mostly focused on policy evaluation in a specific energy sector, lacking cross-sectoral comparative analysis and theoretical summarization, and failing to form unified research conclusions and evaluation standards.
Some scholars have conducted beneficial explorations in applying the PMC model in different fields such as energy security policy, energy transition policy, new energy vehicle policy, and power battery recycling policy, and have achieved certain research results. However, previous studies have the following shortcomings: they lack a systematic review and summary analysis of the current status, methodological evolution, and core findings of the application of the PMC model in China’s energy policy evaluation from a macro level. Existing studies have failed to extract the macro picture and optimization directions of China’s energy policy design from a higher “meta-analysis” dimension, resulting in an understanding of policy-making patterns that remains fragmented. At the same time, there is a lack of horizontal comparison of assessment results in different energy policy fields and in-depth exploration of common issues, which limits the theoretical value and practical guidance of research results.
This study aims to: (1) systematically quantify the design quality of China’s smart energy policy system using the PMC index model; (2) identify dimensional strengths and weaknesses across policy types, timeliness, instruments, and themes; (3) provide evidence-based recommendations for policy optimization. Despite proliferating smart energy policies in China, no systematic quantitative assessment exists to evaluate their internal consistency, completeness, and coordination—a gap this study addresses. This study makes three novel contributions: First, it is the first comprehensive PMC evaluation of China’s entire smart energy policy portfolio (16 national-level policies); second, it integrates text mining with PMC assessment to derive data-driven indicator weights; third, it provides dimensional diagnostic analysis with actionable improvement pathways tied to specific government agencies.
In response to the shortcomings of previous studies, this paper takes “quantitative assessment of China’s smart energy policy using the PMC model” as its research theme, aiming to systematically sort out and analyze the status and development trends of the PMC model in China’s energy policy assessment. This study conducts a systematic literature review and summary analysis, selects high-quality literature that has applied the PMC model to assess China’s smart energy policy in recent years as analysis samples, constructs an integrated analysis framework, and systematically sorts out the application of the PMC model in different energy policy fields and its core conclusions. This study adopts the policy modeling consistency index model as the core research method, combined with bibliometric analysis and content analysis as auxiliary methods, to conduct in-depth exploration and systematic integration of relevant research. Specifically, this study first constructs an integrated analytical framework for PMC assessment of China’s energy policies; second, it systematically reviews the current status and assessment results of the PMC model in different energy policy fields; third, it conducts an in-depth analysis of the common strengths and typical weaknesses of policy design in each field; and finally, based on comprehensive analysis, it proposes policy optimization pathways and method improvement suggestions for the future.
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Evolution and Meaning of Smart Energy
As global climate change pressures mount and energy security challenges become increasingly prominent, smart energy systems have emerged as a key pathway to achieve energy transition and carbon neutrality, drawing attention from countries worldwide. As the world’s largest energy consumer, China’s formulation and implementation of smart energy policies directly affect the global energy transition process. In recent years, scholars have deepened their research on smart energy policies, making significant progress particularly in methods and tools for policy evaluation.
First, as an emerging energy development model, the connotation of smart energy has been progressively deepened and refined in academia. Early studies mostly equated smart energy with the smart grid, focusing on the digitalization and automation transformation of the power system. With technological advancement and deeper practice, scholars’ understanding of smart energy has gradually expanded to the coordinated optimization of multi-energy systems and intelligent management. Liang et al. (2020) [1], through literature review and empirical analysis combined with China’s actual conditions, analyzed the status, obstacles, and coping strategies of Smart Energy Town (SET) projects. Munonni (2025) [2] explored the integration potential of the circular economy and smart energy networks by analyzing technological, policy, and market factors. Razmjoo et al. (2022) [3] used literature analysis and PEST analysis methods, together with national policies and quantitative data, to explore the development of smart energy systems. Ceglia et al. (2022) [4] employed a systematic review method to analyze the literature on smart energy communities and found that promotion barriers mainly stem from citizens’ lack of information and technical capacity. At the same time, the promotion and application of smart energy technologies face complex challenges in social acceptance. Billanes and Enevoldsen (2022) [5], using the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), analyzed factors significantly influencing behavioral intention to adopt smart energy technologies. Grosse-Kreul (2022) [6], applying the UTAUT2 model, suggested introducing green default settings to realize sustainable development potential. Gimpel et al. (2020) [7], using cross-regional sample data and meta-analysis methods, studied the determinants of smart energy technologies. Vasseur et al. (2019) [8], based on multidisciplinary literature, proposed the importance of multi-factor interactions in promoting low-carbon housing policies. Vindegg and Julsrud (2025) [9] analyzed Norway’s applications in the energy transition through in-depth interviews. Brown et al. (2023) [10] used questionnaire surveys to analyze Irish household consumers’ knowledge of and attitudes toward renewable energy technologies and energy-saving behaviors. Moreover, technology integration is a core element in the development of smart energy systems. Ennemiri et al. (2025) [11], using actual operating data combined with environmental forecasting models and energy management algorithms, showed that the system can effectively regulate energy output. Yu et al. (2025) [12] established the FLEX model, simulating energy consumption and trading behaviors by integrating modules for household behavior, system operation, and community interaction. Campana et al. (2025) [13], using VOSviewer (v 1.6.20) analysis, validated that digitalization enhances the efficiency, security, and sustainability of the smart grid. Szpilko et al. (2024) [14], through a literature review, analyzed technological trends in energy management for smart cities.
Traditional energy policy evaluations often focus on qualitative analysis and lack systematic and quantitative indicators. Rogge and Schleich (2018) [15] used a bivariate Tobit model to analyze how the characteristics of policy mixes affect low-carbon innovation, finding that policy coherence and credibility significantly promote investment in green innovation. Rogge and Duetschke (2018) [16], through linear regression analysis, found that policy coherence and consistency mainly influence firms’ perceptions of the credibility of climate policies. Johnstone and Kivimaa (2018) [17], based on a literature review, emphasized different system disruption concepts and their impacts on policy. Han et al. (2014) [18] used a quantitative evaluation framework comparing EU and Chinese energy policies to analyze the effectiveness of smart energy policy instruments, stressing the importance of global energy resource coordination and environmental protection. The introduction of China’s smart energy policies is closely related to the national energy security strategy, the carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets, and the digital economy development strategy [19]. Since the 2015 release of the “Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Development of ‘Internet+’ Smart Energy,” China has continuously strengthened policy support in the smart energy field https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-03/01/content_5047633.html (accessed on 8 June 2025). China’s “14th Five-Year Plan” clearly proposes accelerating digital development and building a digital China, with smart energy infrastructure construction listed as a key task. However, existing studies mostly proceed from single policy text analysis or qualitative evaluation perspectives, lacking a systematic quantitative evaluation framework, making it difficult to accurately grasp the overall effectiveness of the policy system and directions for optimization https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.html (accessed on 8 June 2025).
To scientifically formulate and optimize policies, academia has adopted a variety of methods to evaluate energy policy. These methods span multiple levels from macro to micro and from qualitative to quantitative. (1) Qualitative and case studies. Through in-depth interviews, case studies (Heiskanen et al., 2019; Envall, 2023) [20,21], and narrative analysis (Mlecnik et al., 2020) [22], scholars have thoroughly analyzed the implementation mechanisms, barriers, and success experiences of specific policies or projects in concrete contexts. For example, research on European social innovation cases revealed their positive role in low-carbon transitions and their need for policy support (Matschoss et al., 2022) [23]. (2) Literature reviews and theory building. Systematic literature reviews are widely used to map technological trends in specific fields (O’Dwyer et al., 2019) [24], policy frameworks (Biresselioglu et al., 2018) [25], and research frontiers (Biresselioglu et al., 2024) [26]. Such studies provide a solid foundation for constructing new theoretical frameworks (Fell et al., 2023; Oliveira et al., 2023) [27,28] and identifying future research directions (Royapoor et al., 2023) [29]. (3) Surveys and statistical analysis. Combined with statistical analysis, scholars have verified the impact of green technological innovation on economic development and the effect of consumer perceptions on technology adoption (Gimpel et al., 2020; Billanes Enevoldsen, 2022) [5,7], providing micro-level empirical support for policymaking (Brown et al., 2023) [10,30].
Econometrics and model simulation: Using panel data (Dong et al., 2025) [30], difference-in-differences (DID) models (Zhou Anhua et al., 2023) [31], and the synthetic control method (Tang Jun, Zhao Peiya, and Gao Yu, 2024) [32] as econometric tools, researchers are able to quantitatively assess the net effects of policy implementation. In addition, various model simulations, such as the energyPLAN model (Icaza-Alvarez et al., 2024) [33], the LEAP model (Moradi et al., 2023) [34], system dynamics models, and life cycle assessment (LCA) (Buyle et al., 2019; Tomic et al., 2022) [35,36], have been used to predict energy, economic, and environmental impacts under different policy scenarios [37]. Other methods, such as fuzzy cognitive mapping (Dolge et al., 2024) [38], composite index analysis (Dolge et al., 2024) [39], the SWOT-AHP method (Tzani et al., 2023) [40], and relational analysis (Gonzalez-Lopez and Giampietro, 2018) [41], also provide multiple perspectives for policy evaluation and offer decision support for long-term strategic planning (Siakas et al., 2025) [42].
Moreover, with the development of big data and artificial intelligence technologies, the application of text mining techniques in policy evaluation has become increasingly widespread. Through natural language processing techniques, key information can be extracted from a large volume of policy texts, policy elements can be identified, and the structure of policy content can be analyzed (Grimmer & Stewart, 2013) [43]. Scholars began policy text analysis relatively early and have developed relatively mature theoretical frameworks and analytical tools (Laver et al., 2003 [44]; Quinn et al., 2010 [45]). Chinese scholars, drawing on foreign experience and combining the characteristics of Chinese policy texts, have developed policy analysis methods and tools suited to China’s national conditions (Ma et al.) [46].
2.2. Theoretical Foundations and Applications of the PMC Index Model
While various structured policy evaluation frameworks exist—including policy mix analysis (Rogge & Reichardt, 2016) [47], instrument typology approaches (Howlett, 2011) [48], and qualitative comparative analysis (QCA), the PMC index model offers distinct advantages for this study. Unlike policy mix frameworks that primarily assess policy instrument combinations qualitatively, the PMC model provides systematic quantification across multiple dimensions. Compared to instrument typologies that categorize policy tools, the PMC approach evaluates internal consistency and completeness. While QCA excels at identifying causal configurations, the PMC model’s strength lies in assessing policy design quality through standardized scoring. For smart energy policies requiring assessment across diverse dimensions (timeliness, instruments, themes, effectiveness), the PMC model’s comprehensive indicator system and visual PMC surface representation provide superior diagnostic capabilities for identifying specific improvement areas.”
The PMC (Policy Modeling Consistency) index model is a policy quantification and evaluation method that has emerged in recent years. Based on the principle of policy modeling consistency, the model constructs a multidimensional policy evaluation indicator system to achieve an objective and comprehensive assessment of policy texts (Ruiz Estrada, 2011) [49]. The core idea of the PMC index model is to view policy texts as a complex system, decompose policy elements, quantify policy strength, and evaluate policy effectiveness to build a comprehensive policy evaluation indicator (Ruiz Estrada et al., 2017) [50]. The model has the following characteristics: first, strong systematicity, capable of fully reflecting the multidimensional features of policies; second, high objectivity, reducing subjective judgment through quantitative analysis; third, good comparability, enabling horizontal comparison between different policies. The construction of the PMC index model is based on policy studies theory and systems theory, decomposing the policy system into multiple dimensions such as policy goals, policy instruments, and policy guarantees [51]. Each dimension contains several evaluation indicators, which are quantified through text analysis and other methods to ultimately calculate the PMC index [52,53]. Since its proposal, the PMC index model has been applied and validated in multiple policy fields. In the field of science and technology policy, scholars have used the PMC index model to evaluate the quality and effectiveness of national science and technology innovation policies [54]. In the field of environmental policy, researchers have used the model to analyze the implementation effects of air pollution prevention and control policies [55]. In the field of industrial policy, the PMC index model has been used to assess the coordination and effectiveness of strategic emerging industry policies [56].
In summary, existing literature has explored energy transition and smart energy policies at global, national, and corporate levels using diverse research methods. The PMC index model, as a well-established quantitative policy evaluation method, has been successfully applied to assess various energy policies in China. However, gaps remain in the current research. First, although some scholars have begun to focus on China’s smart energy development—such as analyzing the alleviation effect of smart energy pilot policies on energy poverty and the improvement in energy efficiency from the “new energy demonstration city” policy—these studies mostly concentrate on the macro effects of policies or conceptual discussions, and few systematically and quantitatively examine the design quality of the policy texts themselves. Second, existing PMC model applications primarily focus on aspects of energy security, lacking a dedicated comprehensive evaluation of “smart energy,” which integrates multiple domains such as energy, information, and transportation. Smart energy policy thus not only involves technological innovation but also encompasses market mechanisms, infrastructure, social participation, data governance, and other dimensions; the complexity and coordination requirements of its policy system are therefore higher. Consequently, a comprehensive and systematic quantitative evaluation of China’s smart energy policy system to identify strengths and weaknesses of current policies is particularly necessary and urgent.
This study aims to fill the research gaps by using the PMC index model combined with text analysis methods to quantitatively evaluate China’s existing smart energy–related policies. The research will attempt to answer the following questions: What is the overall design quality of China’s smart energy policy system? What characteristics does it exhibit across different policy dimensions (such as policy goals, target groups, policy instruments, and safeguard measures)? What areas need improvement? By answering these questions, this study hopes to provide scientific evidence and decision-making references for optimizing China’s smart energy policy system and promoting a high-quality transformation of the energy system.
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection
China’s smart energy policies, as a key national strategy for achieving the “dual carbon” goals and promoting energy structure transformation and digital upgrading, have received high-level attention from the State Council and multiple national ministries in recent years. Focusing on priority areas such as renewable energy substitution, energy digitalization and intelligence, green finance support, smart energy storage, and standards system construction, agencies including the National Development and Reform Commission, the National Energy Administration, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the National Data Administration have successively issued a series of normative documents, such as the Several Opinions on Accelerating the Digitalization and Intelligence of Energy Development and the Implementation Opinions on Carrying Out the “Eastern Data, Western Computing” Project. These policies are mostly currently effective documents, mainly in the forms of “notices,” “opinions,” and “implementation plans,” with content concentrated on green energy transition and technology empowerment, reflecting notable features of cross-departmental coordination, a clear digital orientation, and prominent low-carbon objectives. After systematically searching the State Council policy database and the relevant ministries’ official websites and screening based on policy relevance, the issuing agencies’ authority, and the documents’ normative nature, 16 core smart energy policies have been compiled as of 30 June 2025, constituting an important part of the current smart energy strategy system. Our 16 policy sample was systematically selected through four rigorous criteria: (1) Authoritative Issuer: Only policies from State Council or national-level ministries (National Development and Reform Commission, National Energy Administration, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, People’s Bank of China, Ministry of Ecology and Environment) were included, ensuring top-level strategic significance. (2) Thematic Relevance: Policies must explicitly address smart energy, defined as policies integrating at least two of: (a) energy digitalization/intelligence, (b) renewable energy systems, (c) smart grids/energy storage, (d) energy data governance, (e) green finance for energy, (f) energy sector standards for digital transformation. (3) Temporal Coverage: Policies from 2015 to 2024, capturing the evolution from initial ‘Internet+’ smart energy concepts (2015) through the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2021–2025) to recent digitalization emphases (2023–2024). (4) Current Effectiveness: Only currently effective policies (not superseded or expired) as of 30 June 2025. Justification for Sample Size: These 16 policies represent the comprehensive universe of national-level smart energy policies meeting all four criteria. Our exhaustive search of State Council (www.gov.cn) and ministerial databases confirmed no additional policies qualified. This focused scope enables deep analysis of top-tier strategic documents that set the framework for provincial and local implementations. While thousands of sub-national policies exist, our national-level focus captures the authoritative policies that cascade down to shape China’s entire smart energy governance system.
China’s smart energy policies, as a key national strategy for achieving the “dual carbon” goals and promoting energy structure transformation and digital upgrading, have received high-level attention from the State Council and multiple national ministries in recent years. Focusing on priority areas such as renewable energy substitution, energy digitalization and intelligence, green finance support, smart energy storage, and standards system construction, agencies including the National Development and Reform Commission, the National Energy Administration, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the National Data Administration have successively issued a series of normative documents, such as the Several Opinions on Accelerating the Digitalization and Intelligence of Energy Development and the Implementation Opinions on Carrying Out the “Eastern Data, Western Computing” Project. These policies are mostly currently effective documents, mainly in the forms of “notices,” “opinions,” and “implementation plans,” with content concentrated on green energy transition and technology empowerment, reflecting notable features of cross-departmental coordination, a clear digital orientation, and prominent low-carbon objectives. After systematically searching the State Council policy database and the relevant ministries’ official websites and screening based on policy relevance, the issuing agencies’ authority, and the documents’ normative nature, 16 core smart energy policies have been compiled as of 30 June 2025, constituting an important part of the current smart energy strategy system, in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of 16 representative smart energy policies.
This study uses the Python (v 3.11.2) natural language processing library (NLTK) to preprocess texts, then employs high-frequency words and a network semantic model to construct topic clusters, while also combining the PMC index model to build an indicator system for the development of smart energy in China. By adopting this unsupervised learning algorithm, the study is able to identify themes and classify them from textual materials, revealing focal issues and key development directions in China’s smart energy policy development. In addition, the study applies PMC index calculations to quantitatively analyze 16 selected policy texts related to China’s smart energy, computing consistency scores to assess the alignment of these laws, regulations, and policy documents related to the tourism industry with China’s smart energy policy development goals.
3.2. Construction of the PMC Index Model
The PMC index model evaluates policy consistency by constructing multidimensional variables and analyzing the interrelationships among them. The PMC surface, as a visual representation of the model results, enables a comprehensive quantitative analysis for policy optimization through graphical interpretation.
The equal weighting approach is theoretically grounded in three considerations: First, following Estrada’s (2012) [57] original PMC framework, equal weights prevent subjective bias in determining relative importance of policy dimensions when no strong empirical evidence exists for differential weighting. Second, smart energy policy is inherently multi-dimensional, requiring balanced attention across all aspects—from timeliness and instruments to themes and evaluation mechanisms. Third, equal weighting aligns with similar policy evaluation studies (Kuang et al., 2020; Dai et al., 2023) [58,59] demonstrating this approach’s reliability in Chinese policy contexts.
In this study, all secondary variables are assigned equal weight, balanced using a binary method, and ultimately the overall policy effect is assessed via the PMC index and PMC surface. This model can be widely applied to the quantitative analysis of various policies, providing a scientific approach for policy improvement.
- (1)
- Policy Text Mining Analysis
Words are the most basic units of meaning in a text. Word frequency analysis can reveal trends and features related to a specific topic. In the main analysis, relevant word frequency analysis functions were used. The search scope included the valid content of the 16 key Chinese smart energy policy documents in this study, with a minimum length set to 2. Accordingly, a word frequency analysis was conducted (see Table 2) and high-frequency words were visualized (see Figure 1).

Table 2.
List of high-frequency words.
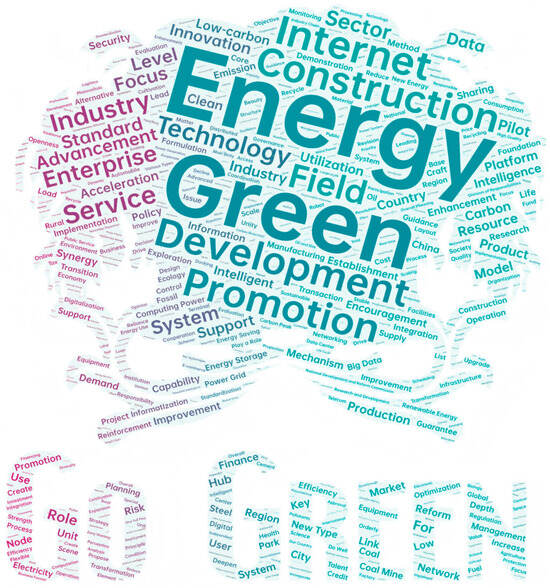
Figure 1.
Word Cloud of High-Frequency Terms in China’s Smart Energy Policies.
Based on an analysis of the high-frequency words in the word cloud, current energy policy exhibits a clear strategic orientation and systematic layout. The prominence of ‘Carbon,’ ‘Low-carbon,’ and ‘Emission’ indicates that decarbonization is a central policy thread, even though the specific term ‘decarbonization’ appears less frequently in Chinese policy language. Green low-carbon transition is the policy’s core thread; the prominence of terms like “Green,” “Energy,” and “Low-carbon” indicates that policymakers prioritize clean energy development and carbon reduction, aiming to build a sustainable energy system. Technological innovation is the key driving force for realizing this transition; the frequent appearance of words such as “Technology,” “Innovation,” and “Intelligence” reflects emphasis on smart technologies, advanced manufacturing, and digital solutions, stressing technological progress to upgrade the energy sector. The industrial development dimension demonstrates the policy’s pragmatic orientation; terms like “Industry,” “Enterprise,” and “Development” highlight the complete chain from R&D to industrial application, focusing on cultivating competitive energy firms and industrial clusters. Infrastructure construction constitutes an important guarantee for policy implementation; words like “Construction,” “System,” and “Infrastructure” show that the policy values systematic construction and networked layout of energy infrastructure. Digital transformation runs through the policy; the notable presence of “Data,” “Internet,” and “Digital” reflects a trend toward deep integration of energy and information technologies, driving the shift from traditional energy to smart energy. Overall, this policy framework embodies the development philosophy of simultaneously advancing greening, somatization, industrialization, and systemization, grounded in the current industrial base while looking to future technological frontiers, forming an energy policy system with clear goals, defined pathways, and concrete measures. The core of China’s smart energy policy can be summarized as: aiming fundamentally to build green, low-impact, and new technological innovations, with smart integration as the core driving force, continuously constructing a modern energy industry system and achieving concrete results, underpinned throughout by strong policy support. Vigorously developing renewable energy, promoting innovative technologies, and building a clean and secure energy future are the ultimate policy priorities. Therefore, a focused analysis of China’s smart energy policy can examine whether the policy pursues low-carbon transition, technological innovation, industrial development, and digital transformation to deeply interpret the current priority areas in smart energy policy.
The word frequency patterns reveal a policy paradigm shift in China’s energy governance. The co-prominence of ‘Green’ (540) and ‘Internet’ (345) signals the convergence of environmental and digital imperatives—a ‘twin transition’ strategy. The high frequency of action-oriented terms (‘Promotion’ 345, ‘Advancement’ 270, ‘Acceleration’ 212) versus lower frequency of market terms (‘Transaction’ 87, ‘Market’ 100) suggests China’s smart energy policies remain government-led rather than market-driven, which explains the lower X6 (Policy Instruments) scores for market-based tools. This pattern contrasts with EU approaches emphasizing market creation first.
- (2)
- Semantic network topic clustering analysis
In this study, a semantic network topic clustering was performed using a Python semantic network modeling package; the clustering results are shown in Appendix A. A co-occurrence semantic network diagram of high-frequency terms in China’s smart energy policies was constructed, as shown in Figure 2.
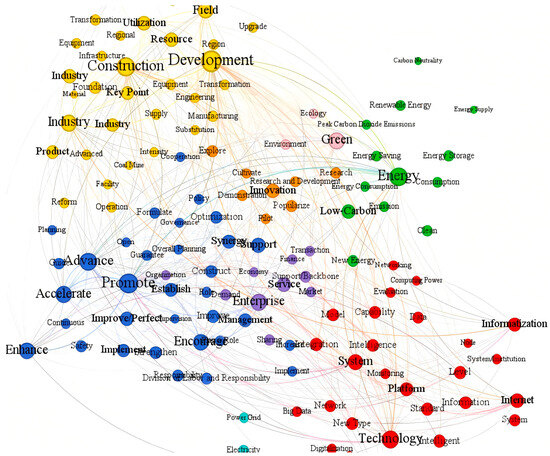
Figure 2.
Semantic Network Topic Clustering Map of Smart Energy Policy.
Based on the clustering analysis of the semantic network of China’s smart energy, this theme exhibits a clearly multi-layered, systematic development pattern. China’s smart energy policy system is organized around eight thematic clusters. It forms a complex network driven primarily by technology, management, and markets; following energy transition and industrial upgrading as the main pathways; supported by ecological protection and innovation R&D; and underpinned by robust physical infrastructure. This network not only reveals the internal composition of each theme but also clearly displays the complex interconnections and interactions among them. Keywords such as “enterprises,” “green,” and “low-carbon” act as key bridges linking different clusters, highlighting the central role of enterprises as implementation agents pursuing green and low-carbon goals under policy guidance and market drivers. In the semantic network, nodes with more connections have higher centrality, indicating greater importance.
From the network structure perspective, 134 key nodes are divided into eight major clusters. The Management and Governance cluster (blue, 35 nodes) and the Industry and Manufacturing cluster (yellow, 33 nodes) are the largest, followed by the Technology and Digitalization cluster (red, 29 nodes). The Energy and Carbon Emissions cluster (green, 14 nodes), Market and Economy cluster (purple, 10 nodes), R&D and Innovation cluster (orange, 8 nodes), Ecology and Environment cluster (pink, 3 nodes), and Infrastructure cluster (cyan, 2 nodes) form specialized areas of varying sizes. This clustering distribution reflects that China’s smart energy development requires strong policy guidance and industrial support, a solid technical foundation, and precise breakthroughs in specialized fields. From the network centrality analysis, nodes such as Promote, Development, and Construction have the highest betweenness centrality, indicating they play key bridging and hub roles in the overall semantic network. Looking at the specific contents of the eight cluster themes, each theme performs unique and important functions. The Technology and Digitalization cluster (red, 29 nodes) centers on Technology, Informatization, and Internet, covering cutting-edge technological elements such as big data, cloud computing, intelligence, digital transformation, platform construction, and standardization, forming the technical infrastructure of smart energy. The Technology node’s betweenness centrality reaches 0.0096, reflecting the critical role of technological innovation in the overall system. The Management and Governance cluster (blue, 35 nodes) is the largest cluster, with Promotes the highest-centrality node (0.0326). It includes government governance elements such as policy formulation, regulatory systems, governance mechanisms, division of responsibilities, and legal framework development, reflecting the government’s leading and guiding role in smart energy development and emphasizing the promotion of healthy smart energy development through a sound institutional system. The Industry and Manufacturing cluster (yellow, 33 nodes) revolves around the two high-centrality nodes Development (0.0966) and Construction (0.0242), covering elements such as advanced manufacturing, engineering construction, equipment manufacturing, infrastructure, resource utilization, and industrial upgrading, reflecting the deep transformation and upgrading needs of traditional energy industries by smart energy. The Energy and Carbon Emissions cluster (green, 14 nodes) addresses the core goals of smart energy development, with Energy Supply (0.0500) as a key node. It includes core energy elements such as clean energy, energy storage technologies, carbon neutrality, carbon peak, renewable energy, and low-carbon development, reflecting the important mission of smart energy to serve national carbon reduction strategies and energy security. The R&D and Innovation cluster (orange, 8 nodes), though smaller in scale, is strategically significant; centered on Innovation, it includes elements such as technological innovation, demonstration applications, pilot projects, R&D investment, and exploratory practices, reflecting the innovation-driven characteristics and continuous progress momentum of smart energy development. The Market and Economy cluster (purple, 10 nodes) focuses on market elements such as Enterprise (0.0042), Service, and Market, covering market entity cultivation, service model innovation, financial support systems, and trading mechanism construction, reflecting the construction of a commercial ecosystem in which smart energy shifts from government-led to market-oriented operation. The Ecology and Environment cluster (pink, 3 nodes), although the smallest by node count, centers on Green (0.0141), emphasize the concept of green development and ecological protection, reflecting the environmental friendliness and sustainability principles that smart energy development must uphold and providing a value orientation for the entire system. The infrastructure cluster (cyan, 2 nodes) specifically targets the core elements Electricity and Power Grid, highlighting the important status of the smart grid as the infrastructure of the energy internet and reflecting the power system’s foundational support role within the smart energy system. These eight cluster themes jointly construct the strategic framework for China’s smart energy development, forming a comprehensive, multidimensional composite system that spans technological innovation to policy guidance, industrial transformation to market mechanisms, innovation-driven development to ecological protection, and infrastructure to environmental effects. This demonstrates systematic thinking of coordinated advancement and balanced development, offering a clear and complete pathway to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets and to promote high-quality energy transition.
The eight-cluster structure demonstrates that China conceptualizes smart energy as a socio-technical system requiring coordinated interventions across technology, governance, industry, and ecology—aligning with multi-level perspective (MLP) theory of transitions. The high centrality of ‘Enterprise’ nodes (0.0042) bridging clusters suggests policies recognize firms as critical transition intermediaries, though the Market cluster’s smaller size (10 nodes) indicates incomplete marketization. This tension between government coordination and market mechanisms explains variable policy effectiveness.
From an in-depth analysis of the cluster contents, the eight themes form a complete ecosystem for smart energy development. The Technology and Digitalization cluster centers on Technology, Informatization, and the Internet, encompassing frontier technological elements such as big data, cloud computing, intelligence, and digital transformation, providing the digital infrastructure for smart energy. The Management and Governance cluster takes policy advancement as its main thread, including elements like policy formulation, regulatory systems, governance mechanisms, and division of responsibilities, reflecting the government’s guiding role in smart energy development. The Industry and Manufacturing cluster revolves around Development and Construction, covering advanced manufacturing, engineering construction, equipment manufacturing, and infrastructure development, reflecting the need to upgrade and transform traditional industries for smart energy.
The Energy and Carbon Emissions cluster addresses core objectives, with Energy Supply, Low-Carbon, and Carbon Neutrality as key nodes, emphasizing clean energy, energy storage technologies, and the achievement of carbon neutrality goals. The R&D and Innovation cluster, though smaller in scale, is significant, including technological innovation, demonstration applications, and pilot projects, embodying an innovation-driven development philosophy. The Market and Economy cluster focuses on market elements such as Enterprise, Service, and Market, reflecting the commercialization mechanisms of smart energy. Functionally, these eight clusters form a progressive, mutually supportive development logic. The Ecology and Environment cluster and the Infrastructure cluster, despite their smaller node counts, respectively, represent the value orientation and foundational support of smart energy: the Ecology and Environment cluster emphasizes green development concepts like Green, Ecology, and Environment, expressing the fundamental goal of smart energy serving ecological civilization construction; the Infrastructure cluster concentrates on Electricity and Power Grid, underscoring the smart grid’s critical role as the core infrastructure of the energy internet. Overall, this clustering structure reveals that China’s smart energy development is a comprehensive, multidimensional composite system—from technological innovation to policy guidance, from industrial transformation to market mechanisms, from environmental protection to infrastructure construction. The eight cluster themes, each distinctive yet interrelated, together build the strategic framework for China’s smart energy development, reflecting systematic thinking that coordinates technological progress, policy improvement, industrial upgrading, market cultivation, innovation-driven growth, and ecological protection, and providing a clear pathway for achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals and advancing the energy transition.
3.3. Variable Classification and Parameter Identification
The PMC index (Policy Modeling Consistency index) was proposed by Ruiz Estrada and others. The PMC index model measures each variable using binary 0 and 1 values to objectively analyze a policy’s strengths, weaknesses, and internal consistency. Obtaining raw data through text mining can improve the accuracy of policy evaluation. The PMC assesses the consistency level of a specific policy model, visually revealing its advantages, shortcomings, and the concrete meanings/levels represented by these variables. Typically, the PMC index model includes: (1) creating multi-input–output tables; (2) calculating two layers of variable values and the PMC index; (3) plotting the PMC surface map. This study follows the principles and modeling standards of the PMC index model and, after excluding broad and irrelevant indicators, ultimately determined 9 primary variables and 38 secondary variables.
Based on the above documents and text-mining methods, this study comprehensively referenced and revised the policy evaluation indicators established by scholars in the existing literature and ultimately set nine classic primary variables. For the secondary variables, adjustments were made according to the classic secondary variables discussed by the aforementioned scholars, the research questions examined in this paper, and the specific context of China’s smart energy policies. The PMC (Policy Modeling Consistency) indicator system for the quantitative evaluation of China’s smart energy policies is a carefully designed framework intended to comprehensively quantify these policies through nine key primary variables.
This evaluation system covers multiple key dimensions of China’s smart energy policies, including the basic nature of the policy, timeliness, policy domain, policy focus, policy targets, policy impact, key objectives, policy support, and disclosure and evaluation. Each primary variable is further subdivided into specific secondary variables to ensure detailed and comprehensive assessment. This smart energy policy evaluation system follows a logic from abstract to concrete and from formulation to implementation, constructing a complete analytical framework. The system first establishes the basic attribute framework of the policy through Policy Nature (X1) and Policy Timeliness (X2), identifying fundamental features such as predictive and normative characteristics and time span, laying the cognitive foundation for the overall assessment; it then delves into the core content of the policy, revealing the policy’s functional positioning and strategic orientation through Policy Function (X3) and Policy Focus (X4), covering key areas from incentive support to green low-carbon transformation; based on the content analysis, the system shifts to quality assessment dimensions, with Policy Evaluation (X5) examining the scientific basis and operability of policy formulation from four perspectives such as adequacy of evidence and clarity of objectives; next, it focuses on the implementation layer, where Policy Instruments (X6) encompass diversified means such as material incentives and financial assistance, reflecting specific implementation pathways; it then evaluates expected outcomes through Policy Effectiveness (X7), examining practical impact forms such as action plans and guiding outlines; at the same time, the perspective is broadened to theme coverage, with Policy Themes (X8) setting eight subfields including technological digitization and management and governance to comprehensively map the breadth of policy content; finally, Policy Disclosure (X9) ensures transparency and accessibility, forming a complete closed loop from policy formulation and implementation to public release. The entire system adopts a binary scoring method and quantifies the comprehensive performance of smart energy policies systematically through 9 main dimensions and 38 sub-indicators. The scoring criteria for each variable are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Secondary Variable Scoring Criteria.
Based on the above system of indicators for China’s Smart Energy Policy, a multi-input-output table for the content analysis of each policy text was derived (see Table 4). The multi-input-output table is a data analysis framework that allows for quantitative evaluation of any individual variable in the policy text, permits the storage of large amounts of data, and maintains balance among variables using primarily binary. Based on the multi-input-output table of each policy, the PMC index value of each policy was calculated as follows: (1) Selection and identification of China’s Smart Energy Policy, and assignment of values to each secondary variable according to Equations (1) and (2). Among them, the value range of the secondary variable XR obeys the distribution of [0, 1]; according to Equation (3), calculate the value of each first-level variable Xt, with a score range of 1–9; according to Equation (4), sum up the scores of the first-level variables of each policy and calculate the PMC index of the Macao Special Administrative Region’s education policies.

Table 4.
Multiple input-output table.
Based on the PMC index calculation method and the text mining method, the 12 Macao education policies were combined into an input-output table (shown in Table 4), and the policies were rated according to the scores and the evaluation criteria table (shown in Table 5). Then the PMC index of each education policy is calculated and summarized in Table 6 Macao Education Policy Score Table. Their scores for each dimension of each policy are shown in Figure 3.

Table 5.
Policy Scoring Levels.

Table 6.
Dimensional Performance Summary of China’s Smart Energy Policies.
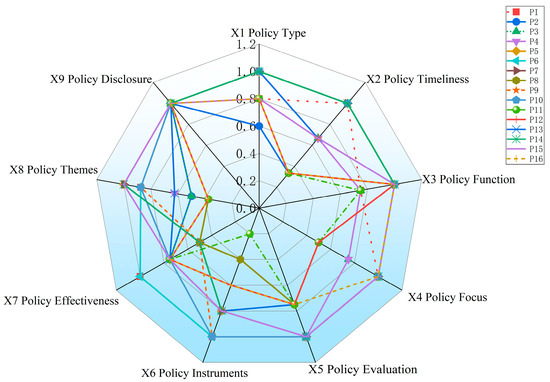
Figure 3.
China’s Smart Energy Policy Score Radar Chart.
To test the robustness of our findings, we conducted sensitivity analyses by adjusting weights for three dimensions identified. Policy Timeliness (X2), Policy Instruments (X6), and Policy Themes (X8). We tested three alternative weighting schemes: (1) doubling the weight of X2 while proportionally reducing others; (2) increasing X6 weight by 50%; (3) simultaneously enhancing X2 and X6 weights by 30% each. Results show that policy rankings remain highly stable (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient ρ > 0.92 across all scenarios). The top-tier policies (P6, P10, P5) consistently maintain their positions, while only minor rank changes occur in the mid-tier group. Importantly, the core finding—that 68.75% of policies achieve ‘excellent’ status—remains unchanged. This demonstrates that our equal-weighting approach yields robust conclusions that are not overly sensitive to weighting assumptions.
Table 6 reveals distinct performance patterns across policy dimensions, providing clear diagnostic insights. X9 (Policy Disclosure) achieves perfect scores universally (1.000), reflecting China’s strong commitment to policy transparency and public accessibility through official government portals; X3 (Policy Function, 0.938); X5 (Policy Evaluation, 0.922), and X1 (Policy Type, 0.900) demonstrate that policies possess well-defined functional positioning, sound evaluation foundations, and clear regulatory/guidance characteristics. The low standard deviations (0.096 indicate consistent quality across policies; X4 (Policy Focus, 0.844) and X6 (Policy Instruments, 0.763) show moderate performance with increasing variability, suggesting inconsistent thematic specificity and instrument diversity across policies. X2 (Timeliness, 0.688), X7 (Effectiveness, 0.703), and X8 (Themes, 0.703).
To visually present the policy evaluation results, this study uses MATLAB 2022b to construct a visual PMC surface from the PMC matrix. The three-dimensional graph composed of nine main variables intuitively displays the policy evaluation results through convex and concave shapes: raised areas indicate higher PMC indices, reflecting strengths, while depressions highlight weaknesses in the corresponding dimensions. The PMC matrix values are calculated using Formula (5); on this basis, the PMC surface provides a clearer three-dimensional representation for evaluating China’s smart energy policies. This method effectively analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of these policies and offers optimization references for decision-makers. The PMC surface not only directly assesses the overall effectiveness of the policies but also provides detailed guidance for subsequent policy adjustments. By analyzing areas with lower PMC indices, targeted improvement measures can be proposed to enhance policy consistency and effectiveness. To make the PMC index results more intuitive and easier to understand, a PMC surface can be constructed after obtaining the PMC indices. These nine main variables form a matrix. The PMC surface calculation is shown in Formula (5).
The PMC indices of the selected Chinese smart energy policies 11 policies were rated “excellent” (including P1, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P9, P10, P13, P14, P15), 5 were “good” (P2, P8, P11, P12, P16), indicating that most policies performed excellent. Their successful implementation has had a profound positive impact on China’s smart energy policy.
4. Results and Discussion
This study evaluated 16 representative Chinese smart energy policies issued between 2015 and 2024, covering the key stages of smart energy work. Verified to already report 11 Excellent, mean 7.47, max 8.88, we harmonized rounding to 7.48. The assessment shows: 11 policies were rated “excellent” (including P1, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P9, P10, P13, P14, P15) and 5 were “good” (P2, P8, P11, P12, P16), demonstrating overall strong performance. Scores exhibit the characteristic of “high scores concentrated, low scores dispersed,” with clear differences. A systematic analysis of these 16 policies provided an in-depth understanding of the evolution and implementation of China’s smart energy policies, offering valuable references for future optimization.
These 16 national-level policies were issued by authoritative state agencies. In terms of time span, they cover the critical stages of policy development, reflecting an evolution from fragmentation to systematization and from guidance-oriented to regulation-oriented approaches. In terms of types, they are highly diverse, including guiding opinions, implementation plans, action plans, and legal frameworks. Different types of policies functionally complement each other, forming a multi-layered system. The quantitative evaluation of 16 Chinese smart energy policies based on the PMC (Policy Modeling Consistency) index shows that the overall quality of China’s smart energy policy system is high, with increasing scientific rigor and systematization in policy formulation. Specifically, 68.8% of the policies (11 items) reached an excellent level (PMC score ≥ 8.0), and 31.3% (5 items) were at a good level. The average PMC score was 7.48, with P6 “Implementation Plan for Carbon Peak in the Industrial Sector” ranking first at 8.88, followed by P10 “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Promotion of New Energy Storage Development” and P5 “Several Opinions on Accelerating the Digitalization and Intelligence of Energy Development” at 8.63 and 8.55, respectively. By policy type, sector-specific energy policies performed particularly well: among 9 sector-specific energy policies, 7 reached excellent levels, and their average score was significantly higher than comprehensive policies, reflecting a positive correlation between policy specificity and effectiveness. Further dimensional analysis revealed the structural characteristics and potential optimization spaces of China’s smart energy policy system. Among the nine evaluation dimensions, the policy disclosure dimension performed best, with all policies receiving full marks, reflecting a significant improvement in government information transparency; dimensions such as policy function (0.94), policy evaluation (0.92), and policy nature (0.90) performed well, indicating clear policy goal orientation and relatively sound evaluation mechanisms. However, the policy timeliness dimension scored the lowest (0.69) with a standard deviation of 0.28, indicating that some policies lack clear time nodes and phased target settings; the policy instruments dimension scored 0.76, reflecting insufficiently developed incentive and restraint mechanisms and inadequate use of market-oriented measures; the policy theme dimension scored 0.70 with the largest standard deviation (0.25), showing that some policies suffer from thematic generalization and a lack of targeted focus.
Based on the above analysis, further optimization of China’s smart energy policy system should follow development pathways of precision, coordination, and systematization. In the short term, emphasis should be placed on strengthening policy timing management, setting clear implementation schedules and milestone nodes for all policies, while enriching the policy toolbox and enhancing the coordinated use of market-based instruments such as fiscal, financial, and pricing tools; in the medium term, it is necessary to establish cross-departmental policy coordination mechanisms, prioritizing the improvement of policy weaknesses in the construction of energy sector standards and enhancing the focus and precision of policy themes; the long-term goal should be to build a complete, systemic smart energy policy ecosystem, advance digital governance models, and better integrate international best practices and standards into policy formulation and implementation, thereby providing stronger policy support and institutional guarantees for the high-quality development of the smart energy industry.
Given the large sample size, and to present the shortcomings and weak points of various Chinese smart energy policies more clearly and effectively, this study selected policies P6 (excellent level) and P11 (good level) as representative cases of the high-score and low-score segments. Policy P6 received an overall score of 8.88 (ranked No. 1, excellent). Policy P6, “Notice on the Implementation Plan for Carbon Peak in the Industrial Sector,” is a concrete action guideline for the development of China’s smart energy policies, whose core objective is to ensure that the industrial sector, as a major source of carbon emissions, reaches its carbon peak before 2030. To achieve this goal, the plan outlines four key pathways: first, adjust the industrial structure, resolutely curb the blind expansion of energy-intensive projects, and strongly support strategic emerging industries; second, deepen energy conservation and consumption reduction, requiring key industries such as steel and petrochemicals to implement energy-efficiency upgrade transformations; third, build a green manufacturing system by promoting green factories and circular economy models; and finally, optimize the energy mix, vigorously promote the application of renewable energy in industrial production, and fundamentally change the way industry consumes energy, in Figure 4.
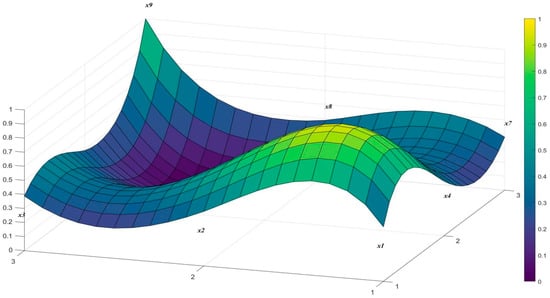
Figure 4.
PMC Surface Diagram on Page 6 of China Smart Energy Policy.
The comprehensive score for Policy P11’s guidance on accelerating the construction of a new standard system in the energy sector is 5.46 (ranked 16th, good). Although Policy P11 has built an important blueprint for the standardized development of China’s energy technologies, it still faces four major challenges in practice that together constitute its potential shortcomings. The core issue is that the pace of standard development often lags behind rapidly evolving technological innovation, which may make it difficult to promote advanced technologies due to a lack of norms. At the same time, the new energy system spans multiple fields such as power, transportation, and information, and cross-departmental coordination barriers make it extremely difficult to form a truly unified and compatible standards system. In addition, China still faces severe challenges in aligning with existing international standards. Finally, the policy focuses on the “construction” of the system but remains weak in ensuring that standards are effectively implemented in the market and in establishing a practical supervision mechanism for dynamic evaluation and rapid revision. These four factors together affect the ultimate effectiveness of the guidance, in Figure 5.
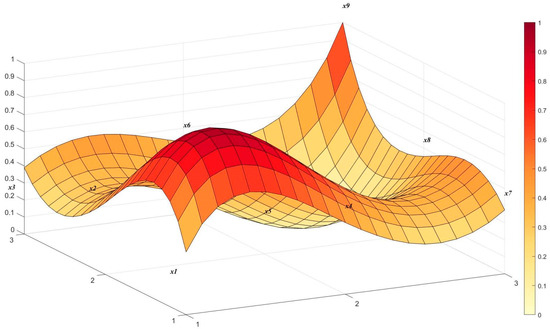
Figure 5.
PMC surface plot of China’s Smart Energy Policy P11.
The analysis indicates that, first, these 16 Chinese smart energy policies demonstrate an overall excellence in the PMC (Policy Modeling Consistency) assessment, with an average score as high as 7.48 out of 10. This result strongly confirms that China’s top-level design in the smart energy field possesses a high degree of systemic coherence, foresight, and internal logical consistency. The policy system not only plans strategically and long-term at the macro level but also details concrete implementation pathways, reflecting the maturity and completeness of China’s energy governance framework and providing a stable and reliable policy environment for complex energy transitions. Second, looking at the score distribution, high-scoring policies are the clear majority: 12 of the 16 reached an “excellent” level, with P6 “Notice on the Implementation Plan for Carbon Peaking in the Industrial Sector,” P7 “14th Five-Year Plan for the Modern Energy System,” and P5 “Several Opinions on Accelerating the Digitalization and Intelligent Development of Energy” ranking near the top with scores of 8.75. The common features of these top policies are strong strategic coordination, clear objective pathways, and comprehensive safeguarding measures. By contrast, a few policies with slightly lower scores, such as P11 “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Construction of a New Standards System in the Energy Sector” and P2 “Opinions on Leveraging Green Finance to Serve the Construction of a Beautiful China,” are not flawed per se but are more oriented toward macro-level guidance and devote less attention to specific quantitative indicators and implementation details, which led to somewhat lower scores in the model evaluation.
In summary, the evaluation results of China’s smart energy policies clearly outline a well-structured policy cluster steered by core strategic planning and supported by multiple concrete implementation programs. Although there are minor differences in the completeness of details across policies, the entire system has clear goals, internal logical consistency, and strong coordination. This mature policy package jointly provides a solid and reliable institutional foundation and action guide for advancing the deep transformation of China’s energy system toward greater intelligence and greenness.
5. Conclusions
This study uses the Policy Modeling Consistency (PMC) index model to conduct a systematic assessment of China’s smart energy policy framework, providing a quantitative evaluation method to overcome the limitations of traditional qualitative policy assessments. By comprehensively analyzing 16 representative smart energy policies and combining bibliometric analysis with content analysis, this study constructs an integrated analytical framework for quantitative policy evaluation in the energy sector.
The main conclusions are as follows: China’s smart energy policies demonstrate outstanding overall performance, with an average PMC score of 7.48, indicating a high degree of systematization, forward-looking design, and strong internal logical consistency. This excellent performance validates the maturity and refinement of China’s energy governance framework and provides a solid institutional foundation for the complex energy transition required to achieve the 2030 and 2060 carbon targets. Secondly, the score distribution shows that high-performing policies are overwhelmingly dominant, with 86.75% of the policies (11 out of 16) reaching the “excellent” level. The top-performing policies include the “Notice on the Implementation Plan for Carbon Peaking in the Industrial Sector,” the “14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of a Modern Energy System,” and the “Several Opinions on Accelerating Energy Digitalization and Intelligent Development,” each receiving the highest score of 8.88. These policies share common characteristics such as strong strategic coordination, clear objectives, well-defined implementation pathways, and comprehensive supporting measures. Third, the assessment results indicate that the policy system exhibits a clearly structured cluster feature, supported by core strategic plans supplemented by multiple specific implementation programs. Although there are minor differences in the completeness of policy details, the overall system displays clear goals, logical consistency, and robust coordination mechanisms. This mature policy portfolio provides a solid institutional foundation and actionable guidance for advancing the transformation of China’s energy system toward intelligent and green development. The PMC model proves to be an effective quantitative tool for policy evaluation; compared with traditional qualitative methods, it offers greater objectivity and can systematically measure internal policy consistency. This study offers valuable insights for optimizing energy policy and contributes to methodological improvements in quantitative policy evaluation in the context of global energy transition and climate goals.
The sixteen smart energy policies evaluated in this study exhibit very high design rigor and internal consistency, forming a solid basis for the overall strategic framework. In terms of average scores, the policies scored above 0.9 in the three dimensions of function, evaluation, and nature, indicating that they are not empty guiding opinions but rather well-structured action plans with clear objectives and defined responsibilities. Each policy contains sufficient justification for its formulation, clear execution goals, and concrete implementation pathways, ensuring a high level of operability and effectiveness at the implementation level and providing high-quality institutional guarantees for achieving complex energy transition objectives.
Second, built on this solid framework, all policies point to a highly unified and focused core strategic direction. The score for the policy focus dimension (0.84) clearly indicates that these carefully designed policy instruments are not operating independently but are working in concert to serve the nation’s top-level strategic objectives. Whether driving a “green, low-carbon transition” centered on new energy, promoting “industrial development” that upgrades the entire industry chain, or emphasizing “technology and digital transformation” driven by innovation, the policies together create a powerful synergistic effect in their content, ensuring that resources and efforts can be precisely directed to the country’s most critical strategic areas, thereby maximizing the macro-level benefits of the policies. Finally, the entire policy system achieves an organic unity of strategic stability and tactical flexibility through a mix of long- and short-term, resilient time planning. The variation in scores for the policy timeliness dimension aptly reflects the maturity of this system: it includes medium-term action plans with clear time nodes, exemplified by “Five-Year Plans” to guide phased priority tasks, while also encompassing some guiding documents intended to steer long-term directions, leaving necessary space for future adjustment. This approach of decomposing grand long-term visions into specific medium- and short-term goals forms a governance structure that is both stable and dynamic, enabling the entire energy transition strategy to advance steadily, be dynamically optimized, and ultimately achieve sustained progress. These findings not only reveal the overall characteristics and development trends of China’s smart energy policies but also identify directions and priorities for policy improvement. Based on the evaluation results, this study proposes concrete optimization recommendations for different policies, providing a scientific basis for refining China’s smart energy policy.
In summary, by constructing a PMC index model, this study conducts a systematic, multidimensional quantitative assessment of China’s smart energy policies, filling gaps in existing research and offering new insights and methods for policy optimization. The research results have important theoretical and practical value for promoting the scientific, precise, and effective development of China’s smart energy policies, thereby enhancing overall public health. Future research should focus on expanding the PMC model’s application to a broader range of policy areas, developing dynamic evaluation mechanisms to track policy evolution, and establishing a comparative framework for international energy policy assessment to support global sustainable energy governance.
Based on the dimensional weaknesses identified through PMC analysis, this study proposes three targeted optimization strategies, ranked by urgency according to their mean scores and standard deviations. These recommendations are grounded in international best practices and specify responsible implementing agencies to ensure accountability and feasibility.
5.1. Strengthening Policy Timeliness Management
Policy timeliness emerged as the weakest dimension, with the lowest mean score and highest variability across the 16 policies examined. This indicates inconsistent temporal planning that undermines policy predictability and accountability. To address this systemic weakness, the National Development and Reform Commission and National Energy Administration should implement a comprehensive time-binding framework for all smart energy policies.
Specifically, three mandatory requirements should be instituted: First, all policies must include explicit implementation timelines structured around three temporal horizons—short-term (1-year), medium-term (3-year), and long-term (5-year) milestones. Second, each temporal milestone must be accompanied by quantitative interim targets that enable measurable progress assessment, such as “achieve 15% renewable energy integration in smart grids by 2027” or “establish 100 smart energy demonstration communities by 2026.” Third, policies should incorporate scheduled review mechanisms conducted biennially to assess implementation progress, identify bottlenecks, and enable dynamic adjustment of strategies based on evolving technological and market conditions.
The European Union’s Clean Energy Package exemplifies this approach, establishing clear 2030 climate and energy targets (32% renewable energy share, 32.5% energy efficiency improvement) with biennial progress reports that track member state performance and trigger corrective actions when necessary. China could adapt this model by requiring National Energy Administration to publish biennial Smart Energy Policy Implementation Reports with province-level performance metrics and binding adjustment recommendations.
5.2. Diversify Policy Instruments
The policy instrument dimension revealed moderate-to-weak performance, reflecting over-reliance on administrative guidance at the expense of market-based mechanisms. This imbalance constrains policy flexibility and limits private sector engagement in smart energy transitions. The Ministry of Finance, People’s Bank of China, and National Energy Administration should collaboratively expand the policy toolkit to incorporate diverse economic and market instruments.
Four specific instrument categories warrant priority development: First, performance-based subsidies that reward demonstrated outcomes rather than upfront investments, incentivizing efficiency and innovation among smart energy technology adopters. Second, green financial products including dedicated green bonds for smart energy infrastructure, preferential loan programs with reduced interest rates for qualifying projects, and specialized credit guarantee schemes that de-risk private investment in emerging technologies. Third, dynamic pricing mechanisms—such as time-of-use tariffs and real-time pricing—that reflect grid conditions and reward demand-side flexibility, shifting consumption patterns to align with renewable energy availability. Fourth, fiscal incentives including accelerated depreciation for smart energy equipment, R&D tax credits for energy storage and grid intelligence innovations, and value-added tax exemptions for smart energy services.
Germany’s Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which pioneered feed-in tariffs guaranteeing long-term price certainty for renewable generators, demonstrates how well-designed market instruments can catalyze rapid technology deployment. Similarly, California’s Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP), which provides performance-based rebates for distributed energy storage systems, has successfully mobilized over 3 GW of battery capacity. China should develop analogous programs tailored to its institutional context, leveraging policy banks and state-owned enterprises to anchor market development while gradually increasing private sector participation.
5.3. Enhance Thematic Focus and Cross-Sectoral Coherence
The policy theme dimension exhibited both low mean performance and the second-highest variability, indicating problematic thematic dispersion and potential overlaps or contradictions across policy documents. Given that smart energy inherently requires coordination across multiple sectors—energy, information technology, transportation, finance, and environmental protection—enhanced inter-ministerial coordination is essential to ensure thematic clarity and complementarity.
To address this challenge, the State Council should establish a permanent Smart Energy Policy Coordination Committee comprising representatives from all relevant ministries. This committee would perform three critical functions: First, conduct comprehensive thematic gap analysis prior to new policy issuance, mapping proposed policies against the eight thematic clusters identified in this study’s semantic network analysis (Technology and Digitalization, Management and Governance, Industry and Manufacturing, Energy and Carbon Emissions, Research and Innovation, Market and Economy, Ecology and Environment, and Infrastructure). This mapping process would identify redundancies, gaps, and potential conflicts before policies are finalized. Second, require each policy to explicitly designate its primary thematic focus and secondary supporting themes, preventing the dilution that occurs when policies attempt to address all themes simultaneously without clear prioritization. Third, establish standardized impact assessment protocols that evaluate proposed policies for consistency with existing policy frameworks, ensuring cumulative coherence rather than fragmented incrementalism. Japan’s Strategic Energy Plan provides an instructive model for such coordination. Developed through extensive inter-ministerial consultation and revised triennially, the Plan establishes a unified national energy vision that guides sectoral policies across government agencies, ensuring that industrial policy, R&D funding, regulatory reforms, and infrastructure investments advance complementary objectives. China could adapt this approach by requiring the Smart Energy Policy Coordination Committee to produce a biennial Smart Energy Policy Coherence Report that publicly assesses thematic alignment across all active policies and recommends consolidations or clarifications where thematic overlap generates implementation confusion.
5.4. Methodological Limitations and Future Improvements
While the PMC index model provides valuable quantitative insights into smart energy policy quality, three principal methodological limitations warrant acknowledgment and suggest pathways for future research refinement. First, our equal weighting of 38 sub-indicators across nine primary dimensions, though theoretically justified byoriginal framework and validated through sensitivity analysis, may not fully reflect the differential importance that diverse stakeholders—policymakers, industry actors, civil society organizations, and academic experts—assign to specific policy dimensions. Nevertheless, future research should employ structured expert elicitation methods, particularly Delphi surveys or the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), to derive context-specific, stakeholder-informed weights tailored to the Chinese smart energy governance context, where dimensions such as timeliness and policy instruments may warrant elevated priority given identified weaknesses.
Second, the binary (0–1) scoring system employed for sub-indicator coding, while effectively reducing subjective interpretation and enabling replicability, cannot capture partial policy fulfillment or qualitative gradations within indicator categories. For instance, a policy may address “technical support” (X6:3) through general statements of intent versus detailed implementation mechanisms with dedicated budgetary allocations—contexts our binary coding treats identically. Future methodological refinements could adopt Likert-scale scoring (1–5 range) to differentiate among minimal, moderate, and comprehensive indicator fulfillment, though this approach necessitates more intensive coder training protocols, inter-rater reliability testing, and transparent coding rubrics to maintain objectivity gains.
Third, situating the PMC model within the broader landscape of policy evaluation methodologies clarifies its comparative advantages and appropriate application domains. For smart energy policy design quality assessment specifically, the PMC index offers superior systematic coverage through its comprehensive nine-dimensional framework and intuitive visual diagnostics via PMC surface plots that immediately reveal dimensional weaknesses. However, alternative methods serve complementary purposes: qualitative content analysis provides deep contextual understanding ideal for single-policy case studies but lacks the quantitative comparability PMC enables; econometric approaches including difference-in-differences (DID) and regression discontinuity designs (RDD) excel at causal impact estimation of policy implementation effects but require outcome data unavailable during ex-ante design evaluation; and Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) identifies configurations of policy features associated with success but, being optimized for small-N comparative studies, does not provide the dimension-specific diagnostic capabilities crucial for targeted policy improvement.
Recognizing these complementary strengths, the optimal evaluation strategy integrates multiple methods sequentially: employ PMC analysis during the policy design phase to diagnose dimensional weaknesses and guide refinement before implementation, then conduct econometric impact evaluation 2–3 years post-implementation to assess realized effects on energy system outcomes (renewable integration rates, emission reductions, innovation indicators). Future research should pioneer this integrated design-to-outcome evaluation framework, using PMC diagnostic findings as independent variables predicting policy effectiveness in subsequent econometric analyses—thereby empirically validating which dimensional features (high timeliness scores, diversified instruments, thematic coherence) most strongly correlate with successful implementation outcomes. This methodological triangulation would substantively advance both policy evaluation theory and practical guidance for smart energy governance optimization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.C., X.W. and T.Z.; methodology, R.C. and X.W.; software, R.C.; formal analysis, S.Z. and H.Y.; investigation, R.C. and X.W.; data curation, Q.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.C., X.W. and S.Z.; writing—review and editing, R.C. and X.W.; visualization, X.W.; supervision, X.W. and H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in FigShare at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.29975674 (accessed on 8 June 2025), reference number 10.6084/m9.figshare.29975674.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Network Clustering Data Table.
Table A1.
Network Clustering Data Table.
| Label | Closnesscentrality | Harmonicclosnesscentrality | Betweenesscentrality | Cluster Categories | Cluster Themes | Cluster Colors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wisdom | 0 | 0 | 0 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Energy | 0 | 0 | 0 | Energy and Carbon Emissions | 4 | Green |
| Internet | 0.569231 | 0.63964 | 0.002659 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Industry | 0.521127 | 0.558559 | 0.000007 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Product | 0.510345 | 0.542793 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Enterprise | 0.643478 | 0.727477 | 0.004247 | Market and Economy | 6 | Purple |
| Optimization | 0.517483 | 0.542793 | 0 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Low-Carbon | 0.548148 | 0.592342 | 0.002846 | Energy and Carbon Emissions | 4 | Green |
| System | 0.596774 | 0.666667 | 0.001866 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Role | 0.468354 | 0.486486 | 0.008316 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Supply | 0 | 0 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Guarantee | 0.4625 | 0.477477 | 0 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Information | 0.528571 | 0.572072 | 0.000076 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Informatization | 0.560606 | 0.612613 | 0.005031 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Energy Storage | 0.440476 | 0.46509 | 0 | Energy and Carbon Emissions | 4 | Green |
| Advanced | 0 | 0 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Sharing | 0 | 0 | 0 | Market and Economy | 6 | Purple |
| Renewable Energy | 0.430233 | 0.451577 | 0 | Energy and Carbon Emissions | 4 | Green |
| Division of Labor and Responsibility | 0.397849 | 0.433559 | 0 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Innovation | 0.560606 | 0.617117 | 0.000329 | Research and Innovation | 5 | Orange |
| Utilization | 0.560606 | 0.612613 | 0.00019 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Formulate | 0 | 0 | 0 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| System/Institution | 0 | 0 | 0 | Technology and Digitalization | 1 | Red |
| Manufacturing | 0.474359 | 0.490991 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Intensity | 1 | 1 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Increase | 1 | 1 | 0 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Accelerate | 0.666667 | 0.754505 | 0.006749 | Management and Governance | 2 | Blue |
| Regional | 0 | 0 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
| Upgrade | 0 | 0 | 0 | Industry and Manufacturing | 3 | Yellow |
References
- Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Chong, C.; Li, Z.; Ni, W. Development of Smart Energy Towns in China: Concept and Practices. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munonye, W.C. Circular Economy Meets Smart Energy Grids: Designing Systems for Resource Optimization and Carbon Reduction. Front. Sustain. 2025, 6, 1568254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjoo, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Aliehyaei, M.; Østergaard, P.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Nezhad, M.M. Development of Smart Energy Systems for Communities: Technologies, Policies and Applications. Energy 2022, 248, 123540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglia, F.; Marrasso, E.; Pallotta, G.; Roselli, C.; Sasso, M. The State of the Art of Smart Energy Communities: A Systematic Review of Strengths and Limits. Energies 2022, 15, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billanes, J.; Enevoldsen, P. Influential Factors to Residential Building Occupants? Acceptance and Adoption of Smart Energy Technologies in Denmark. Energy Build. 2022, 276, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Große-Kreul, F. What Will Drive Household Adoption of Smart Energy? Insights from a Consumer Acceptance Study in Germany. Util. Policy 2022, 75, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimpel, H.; Graf, V.; Graf-Drasch, V. A Comprehensive Model for Individuals’ Acceptance of Smart Energy Technology—A Meta-Analysis. Energy Policy 2020, 138, 111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, V.; Marique, A.-F.; Udalov, V. A Conceptual Framework to Understand Households’ Energy Consumption. Energies 2019, 12, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindegg, M.; Julsrud, T.E. Digitised Demand Response in Practice: The Role of Digital Housekeeping for Smart Energy Technologies. Energy Effic. 2025, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Hampton, H.; Foley, A.; Del Rio, D.F.; Lowans, C.; Caulfield, B. Understanding Domestic Consumer Attitude and Behaviour Towards Energy: A Study on the Island of Ireland. Energy Policy 2023, 181, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennemiri, N.; Emrani, A.; Abdelmajid, J.; El Mrabet, R.; Berrada, A. Medium-Term Forecast of Multi-Energy Photovoltaic/Biogas/Battery System’s Operation Adopting Smart Energy Management Strategy. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2025, 27, 2247–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Mascherbauer, P.; Haupt, T.; Skorna, K.; Rickmann, H.; Kochanski, M.; Kranzl, L. Modeling Households’ Behavior, Energy System Operation, and Interaction in the Energy Community. Energy 2025, 328, 136338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, P.; Censi, R.; Ruggieri, R.; Amendola, C. Smart Grids and Sustainability: The Impact of Digital Technologies on the Energy Transition. Energies 2025, 18, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpilko, D.; Fernando, X.; Nica, E.; Budna, K.; Rzepka, A.; Lăzăroiu, G. Energy in Smart Cities: Technological Trends and Prospects. Energies 2024, 17, 6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, K.S.; Schleich, J. Do Policy Mix Characteristics Matter for Low-Carbon Innovation? A Survey-Based Exploration of Renewable Power Generation Technologies in Germany. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, K.S.; Dütschke, E. What Makes Them Believe in the Low-Carbon Energy Transition? Exploring Corporate Perceptions of the Credibility of Climate Policy Mixes. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 87, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, P.; Kivimaa, P. Multiple Dimensions of Disruption, Energy Transitions and Industrial Policy. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2018, 37, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Bompard, E.; Profumo, F.; Xia, Q. Paths toward Smart Energy: A Framework for Comparison of the Eu and China Energy Policy. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M. Current Status, Challenges, and Countermeasures for China’s Energy Transition and Energy Security under the Carbon Neutrality Goal. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Heiskanen, E.; Kivimaa, P.; Lovio, R. Promoting Sustainable Energy: Does Institutional Entrepreneurship Help? Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 50, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Envall, F. Situated Dynamics of Environmental Governance in Swedish Smart Energy Experimentation: Tentativeness, Demonstration, Upscaling. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2023, 41, 922–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlecnik, E.; Parker, J.; Ma, Z.; Corchero, C.; Knotzer, A.; Pernetti, R. Policy Challenges for the Development of Energy Flexibility Services. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschoss, K.; Mikkonen, I.; Gynther, L.; Koukoufikis, G.; Uihlein, A.; Murauskaite-Bull, I. Drawing Policy Insights from Social Innovation Cases in the Energy Field. Energy Policy 2022, 161, 112728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, E.; Pan, I.; Acha, S.; Shah, N. Smart Energy Systems for Sustainable Smart Cities: Current Developments, Trends and Future Directions. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biresselioglu, M.E.; Nilsen, M.; Demir, M.H.; Røyrvik, J.; Koksvik, G. Examining the Barriers and Motivators Affecting European Decision-Makers in the Development of Smart and Green Energy Technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biresselioglu, M.E.; Solak, B.; Savas, Z.F. Unveiling Resistance and Opposition against Low-Carbon Energy Transitions: A Comprehensive Review. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2024, 107, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, M.J.; Vigurs, C.; Maidment, C.; Shipworth, D. Smart Local Energy Systems as a Societal Project: Developing a Theory of Change. Smart Energy 2023, 11, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.; Chatzimichali, A.; Atkins, E.; Badarnah, L.; Moghaddam, F.B. From Individuals to Collectives in Energy Systems—A Social Practice, Identity and Rhythm Inspired Lens. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 105, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royapoor, M.; Allahham, A.; Hosseini, S.H.R.; Rufa’i, N.A.; Walker, S.L. Towards 2050 Net Zero Carbon Infrastructure: A Critical Review of Key Decarbonization Challenges in the Domestic Heating Sector in the Uk. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2023, 18, 2272264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Li, C.; Sampene, A.K. Exploring the Impact of Green Finance, Technological Innovation, Mineral Resources, and Carbon Tax on the Green Energy Transition. Smart Energy 2025, 19, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wang, S.; Chen, B. Impact of New Energy Demonstration City Policy on Energy Efficiency: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhao, P.; Gao, Y. Can Smart Energy Alleviate Energy Poverty in China? -Empirical Evidence Using Synthetic Control Methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icaza-Alvarez, D.; Jurado, F.; Tostado-Véliz, M. Smart Energy Planning for the Decarbonization of Latin America and the Caribbean in 2050. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 6160–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.A.; Salimi, M.; Amidpour, M. Evaluation of Agriculture Wells Electrification Policy and Development of a Long-Term Sustainable Energy Strategy. Smart Energy 2023, 10, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyle, M.; Galle, W.; Debacker, W.; Audenaert, A. Sustainability Assessment of Circular Building Alternatives: Consequential Lca and Lcc for Internal Wall Assemblies as a Case Study in a Belgian Context. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, T.; Kremer, I.; Schneider, D.R. Economic Efficiency of Resource Recovery-Analysis of Time-Dependent Changes on Sustainability Perception of Waste Management Scenarios. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lin, M.; Wang, H. Quantitative Evaluation of China’s Energy Supply Policies in the ‘13th Five--Year Plan’ Period (2016–2020): A Pmc Index Modelling Approach Incorporating Text Mining. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 596–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolge, K.; Vicmane, L.K.; Bohvalovs, G.; Blumberga, D. Energy Transition Reality Check: Are Municipalities Meeting the Mark? Sci. J. Riga Technol. Univ. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2024, 28, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolge, K.; Gravelsins, A.; Vicmane, L.K.; Blumberga, A.; Blumberga, D. What Drives Energy Storage Deployment in Local Energy Transitions? Stakeholders’ Perspective. Smart Energy 2024, 15, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzani, D.; Exintaveloni, D.S.; Stavrakas, V.; Flamos, A. Devising Policy Strategies for the Deployment of Energy Efficiency Pay-for-Performance Programmes in the European Union. Energy Policy 2023, 178, 113593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, R.; Giampietro, M. Relational Analysis of the Oil and Gas Sector of Mexico: Implications for Mexico’s Energy Reform. Energy 2018, 154, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakas, D.; Rahanu, H.; Georgiadou, E.; Siakas, K.; Lampropoulos, G. Positive Energy Districts Enabling Smart Energy Communities. Energies 2025, 18, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmer, J.; Stewart, B.M. Text as Data: The Promise and Pitfalls of Automatic Content Analysis Methods for Political Texts. Political Anal. 2013, 21, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laver, M.; Benoit, K.; Garry, J. Extracting Policy Positions from Political Texts Using Words as Data. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 2003, 97, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, K.M.; Monroe, B.L.; Colaresi, M.; Crespin, M.H.; Radev, D.R. How to Analyze Political Attention with Minimal Assumptions and Costs. Am. J. Political Sci. 2010, 54, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, T. Insights for China from the Patterns of Low-Carbon Technology Innovation Adoption and Application in Countries Leading the Way to Carbon Peaking: An Analysis Based on the “Technology-Organization-Environment” Framework. Mod. Econ. Explor. 2023, 7, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rogge, K.S.; Reichardt, K. Policy Mixes for Sustainability Transitions: An Extended Concept and Framework for Analysis. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1620–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, M.; Wellstead, A.M. Policy Analysts in the Bureaucracy Revisited: The Nature of Professional Policy Work in Contemporary Government. Politics Policy 2011, 39, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, M.A.R. Policy Modeling: Definition, Classification and Evaluation. J. Policy Model. 2011, 33, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Estrada, M.A. An Alternative Graphical Modeling for Economics: Econographicology. Qual. Quant. 2017, 51, 2115–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.; Ayres, R. Systems Theory and Policy Practice: An Exploration. Policy Sci. 2001, 34, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. Quantitative Evaluation of Digital Economy Policies in the Tourism Industry Using the Tf-Idf and Pmc Index Model. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 189636–189650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.-Q.; Wu, J. Assess the Efficacy of China’s Inter-Provincial Government Services Policy: A Quantitative Evaluation Based on Pmc-Index Model. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xiong, P.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L. Quantitative Evaluation of Science and Technology Financial Policies Based on the Pmc-Ae Index Model: A Case Study of China’s Science and Technology Financial Policies since the 13th Five-Year Plan. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awewomom, J.; Dzeble, F.; Takyi, Y.D.; Ashie, W.B.; Ettey, E.N.Y.O.; Afua, P.E.; Sackey, L.N.A.; Opoku, F.; Akoto, O. Addressing Global Environmental Pollution Using Environmental Control Techniques: A Focus on Environmental Policy and Preventive Environmental Management. Discov. Environ. 2024, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, G. Quantitative Evaluation of Smart Construction Pilot Cities Policies in China Based on the Pmc-Index Model. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernesto, E. The Structure of Complex Networks: Theory and Applications; American Chemical Society: Columbus, OH, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, B.; Han, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, X. Quantitative Evaluation of China’s Cultivated Land Protection Policies Based on the Pmc-Index Model. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, X. Evaluating Green Financing Mechanisms for Natural Resource Management: Implications for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Resour. Policy 2023, 86, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).