A High-Precision, All-Rectangle-Based Method Linearly Concave Hydropower Output in Long-Term Reservoir Operation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Nonlinearity in Hydropower Scheduling Problem
2.2. Linear Concaving Models
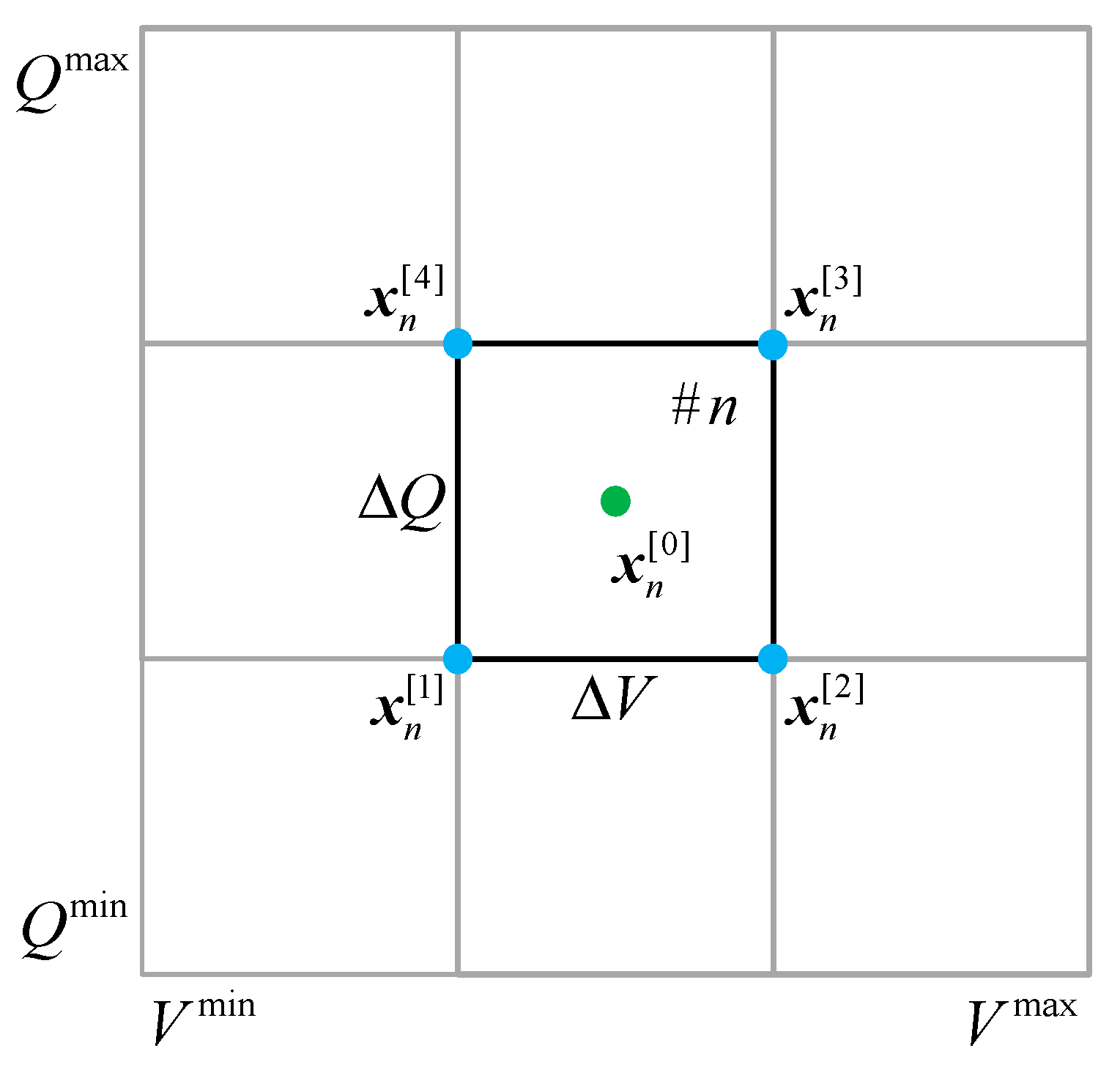
2.2.1. Gridding and Definition
2.2.2. Piecewise Linearization with SOS1 (PWL1)
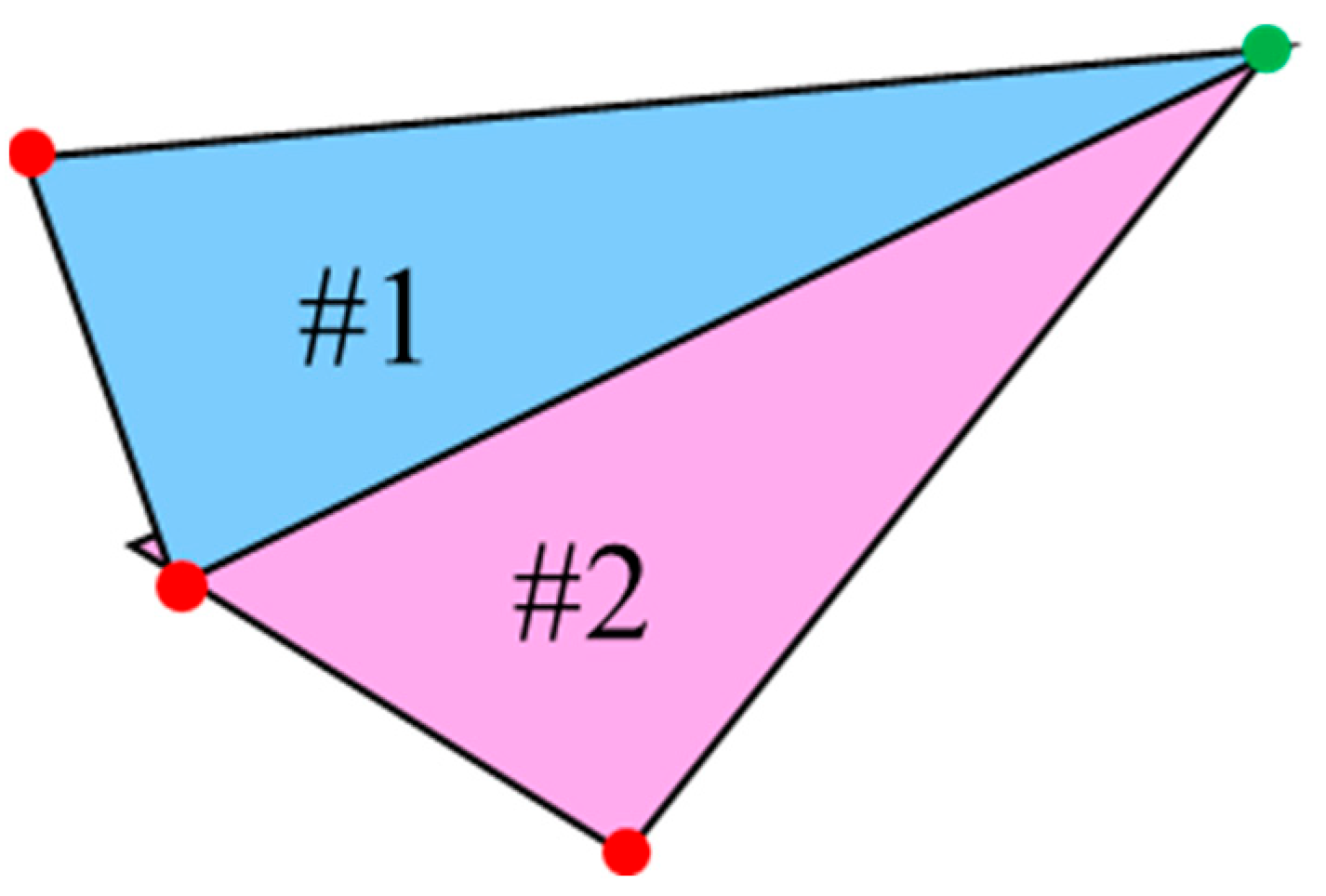
2.2.3. Three-Triangle-Based Linear Concaving (TTBLC)
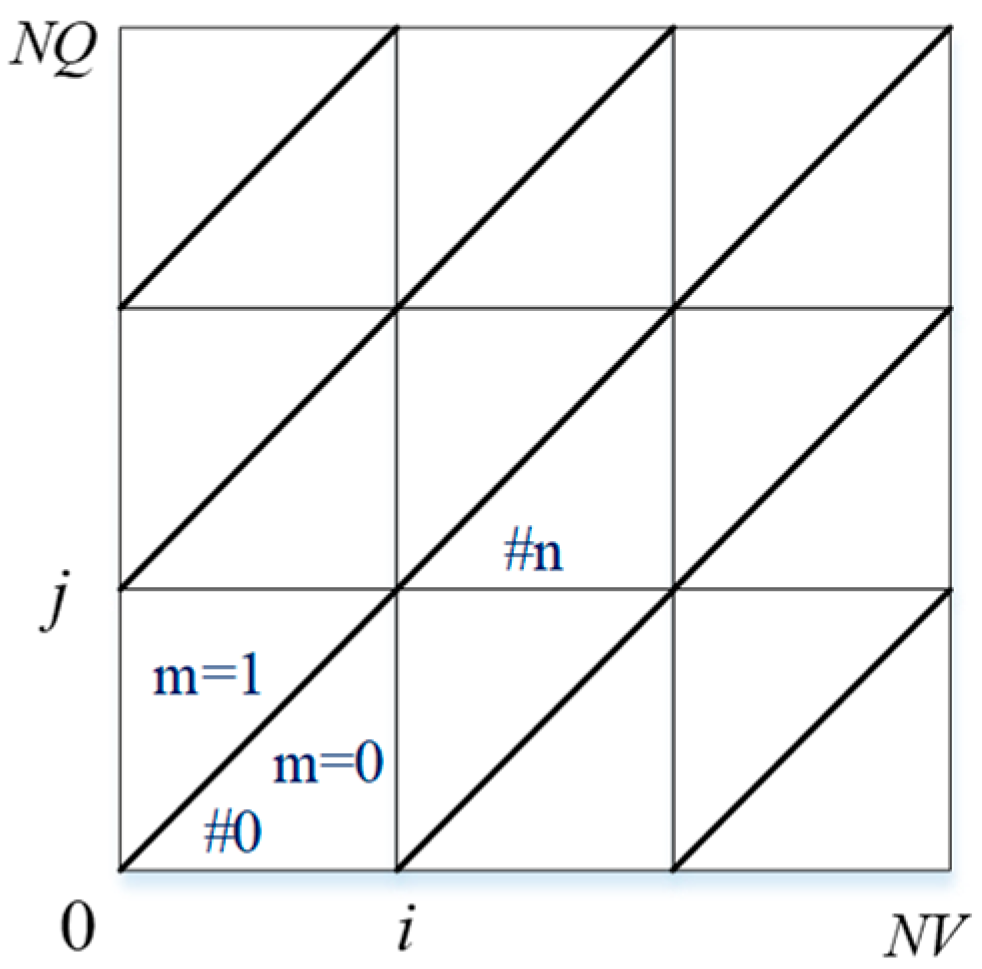
2.2.4. All Rectangle Based Linear Concaving (ARBLC)
2.2.5. Summary of Three Models
3. Convergence Proof
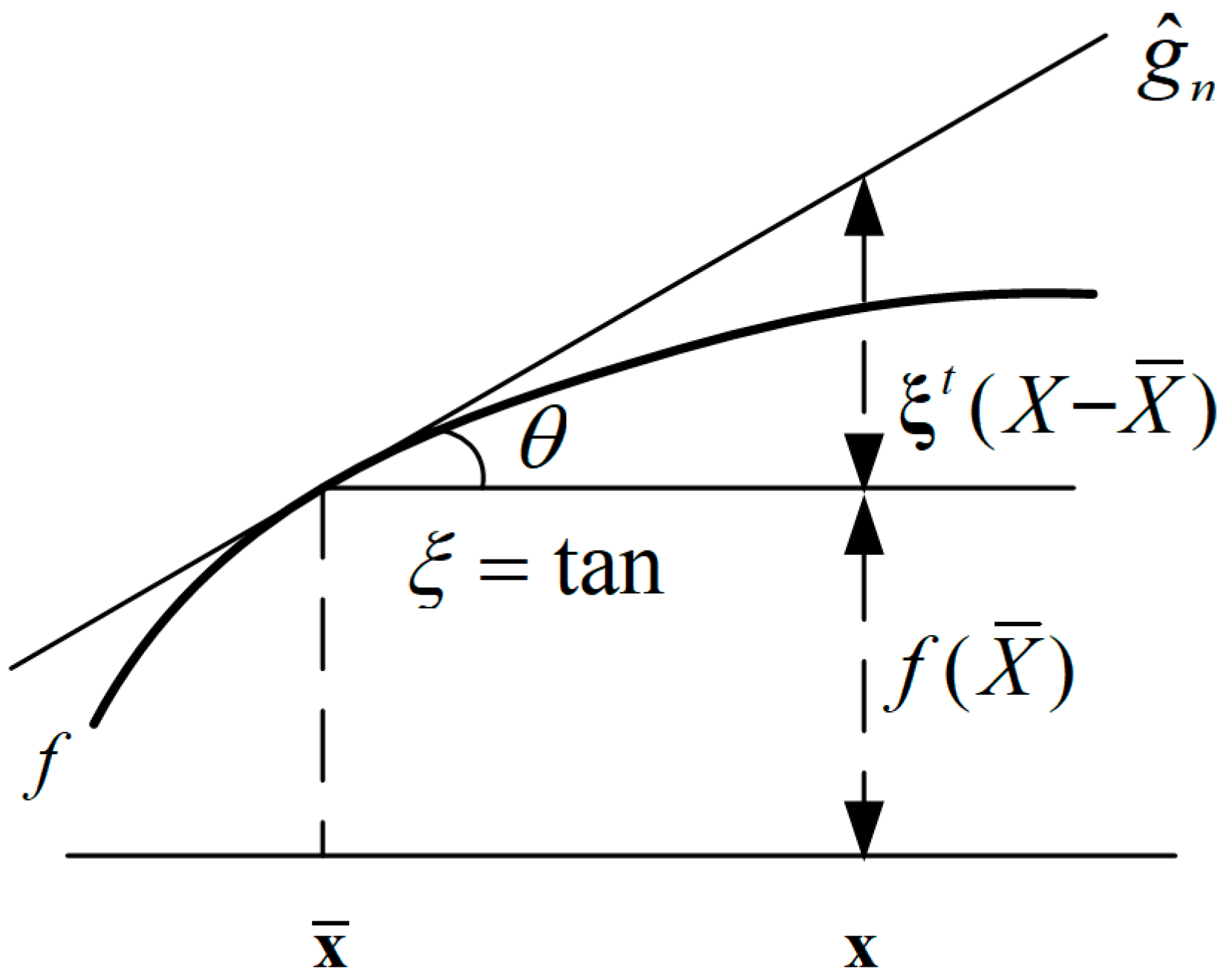
3.1. Mathematical Proof
3.2. The Missing Part in TTBLC
3.3. Numerical Tests
3.3.1. Testing Function
3.3.2. Error Assessment
3.3.3. Three Models for Testing Function
3.3.4. Convergence of ARBLC for Testing Function
4. Numerical Examples
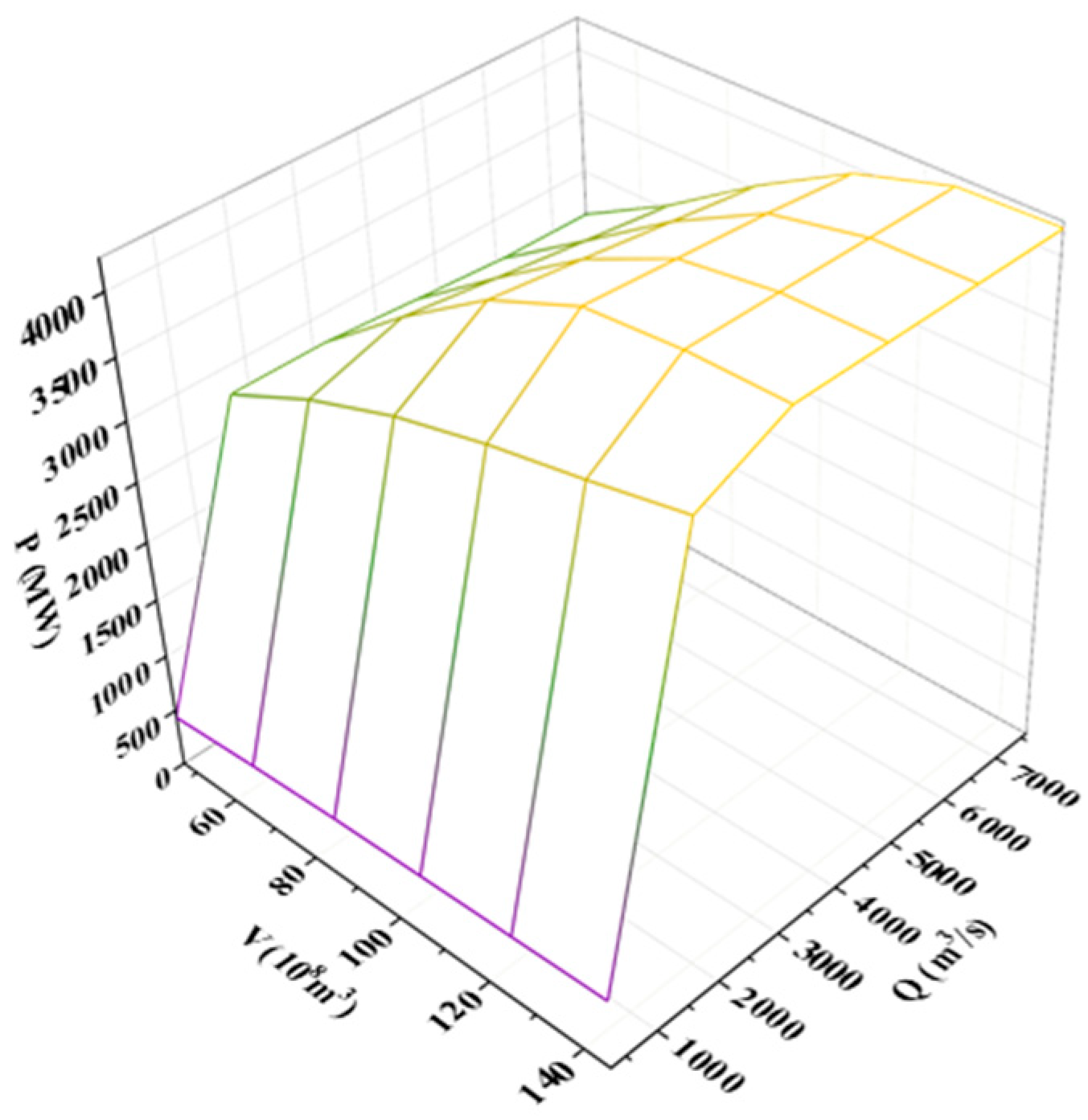
4.1. Engineering Background
4.2. Concavity Based on Original Data
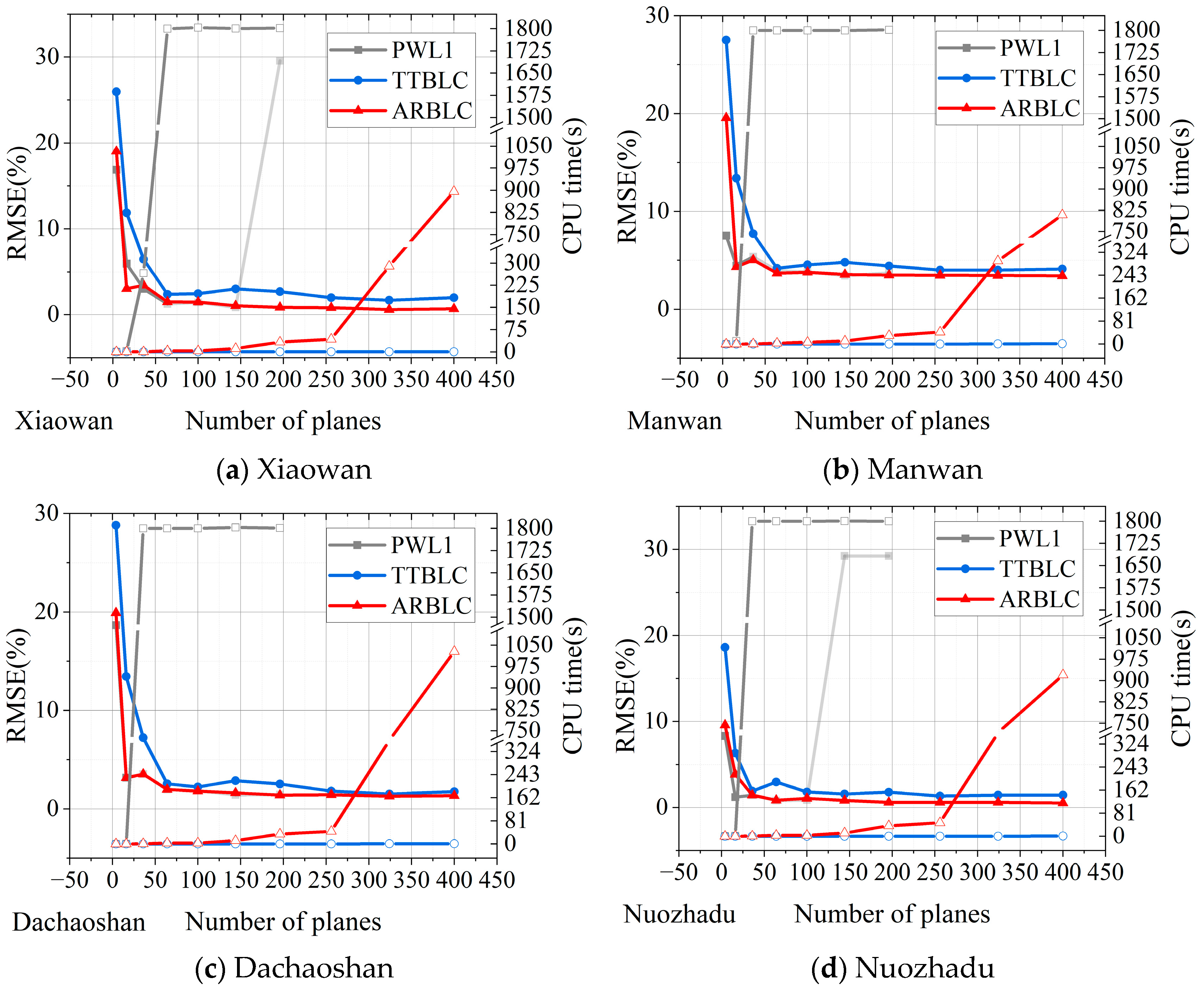
4.3. Comparison Between the Three Models
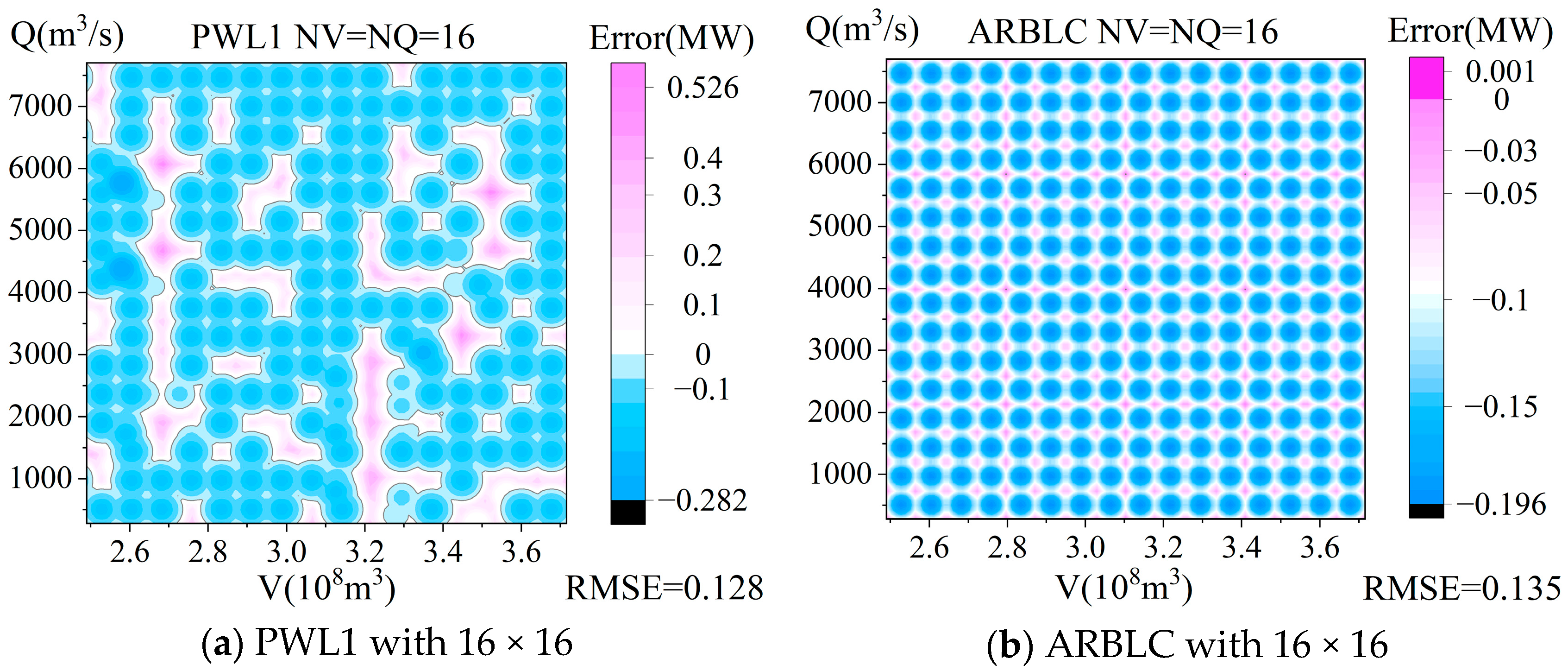
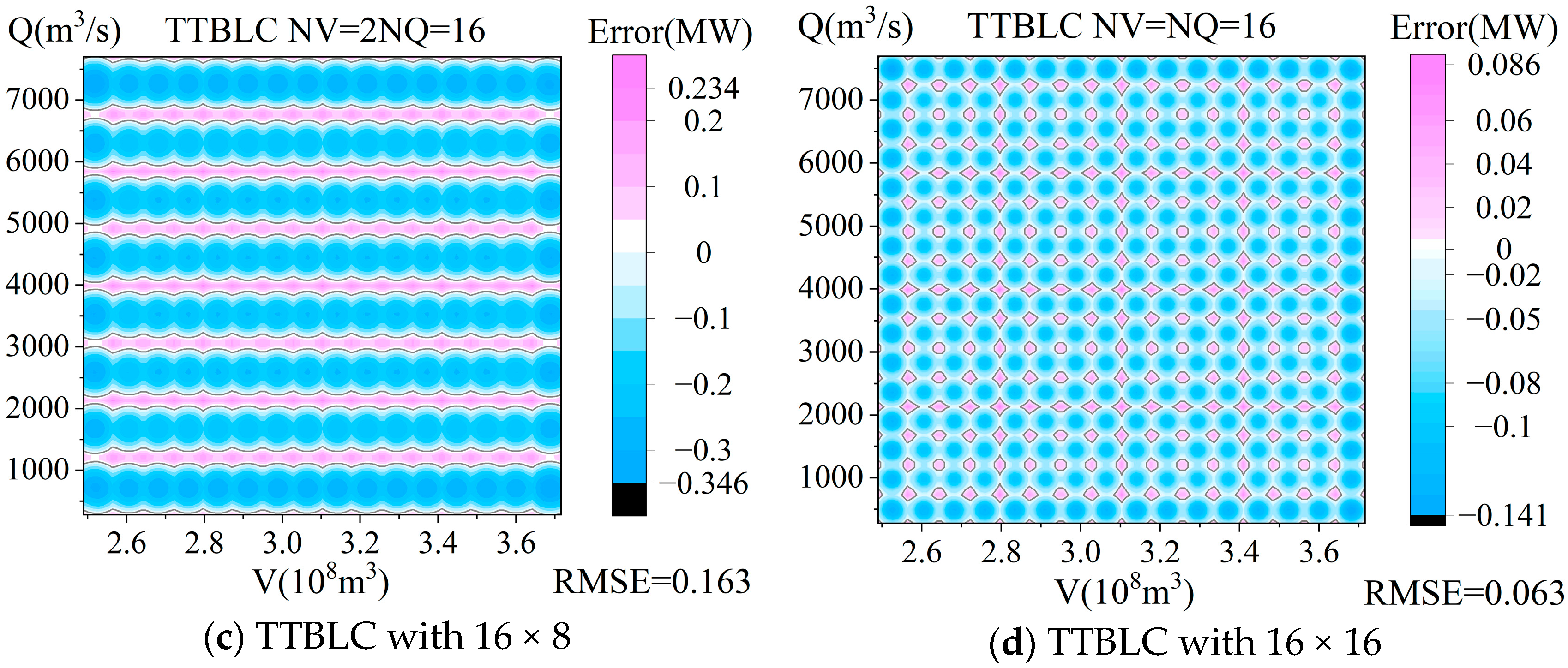
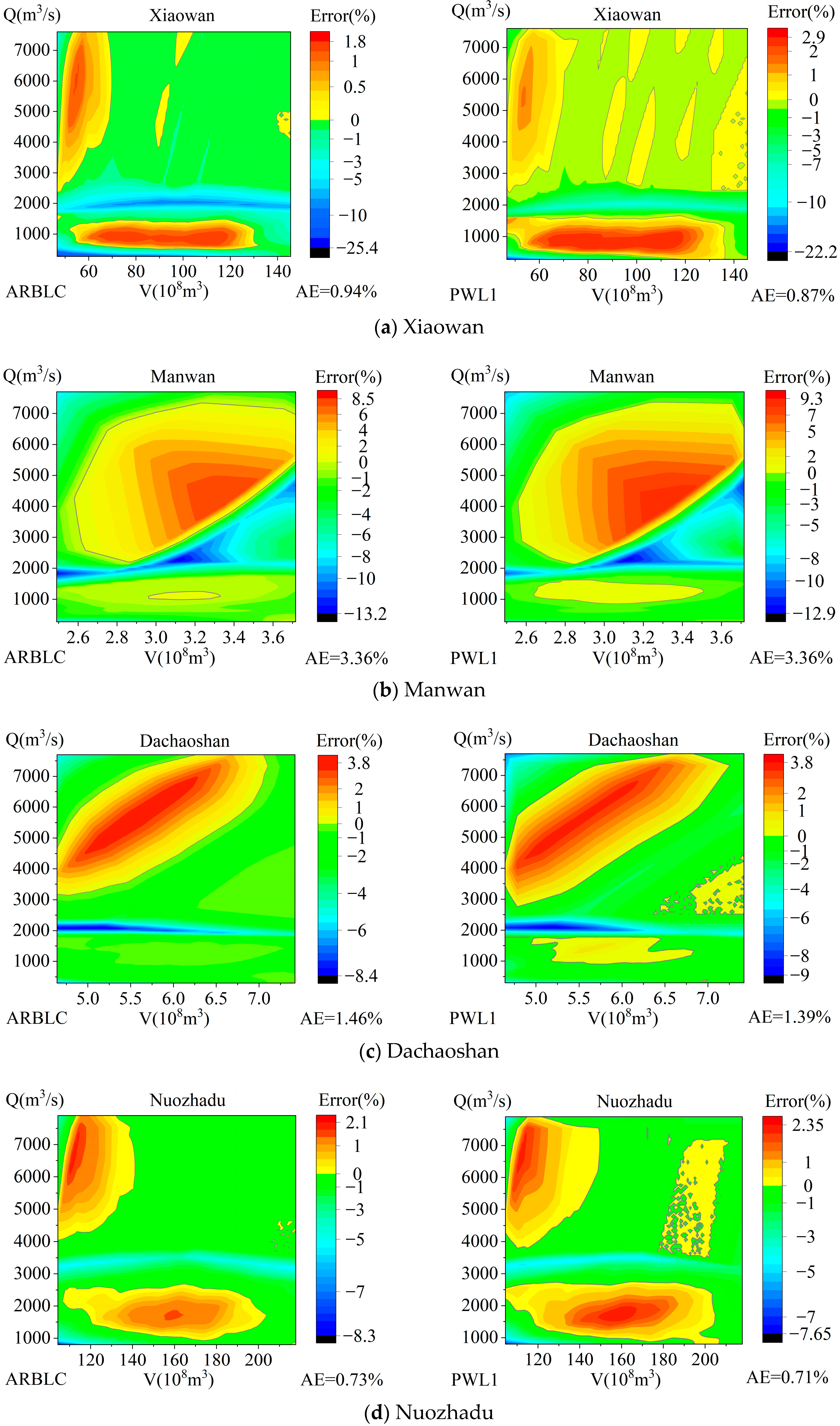
4.4. Distribution of Fitting Errors
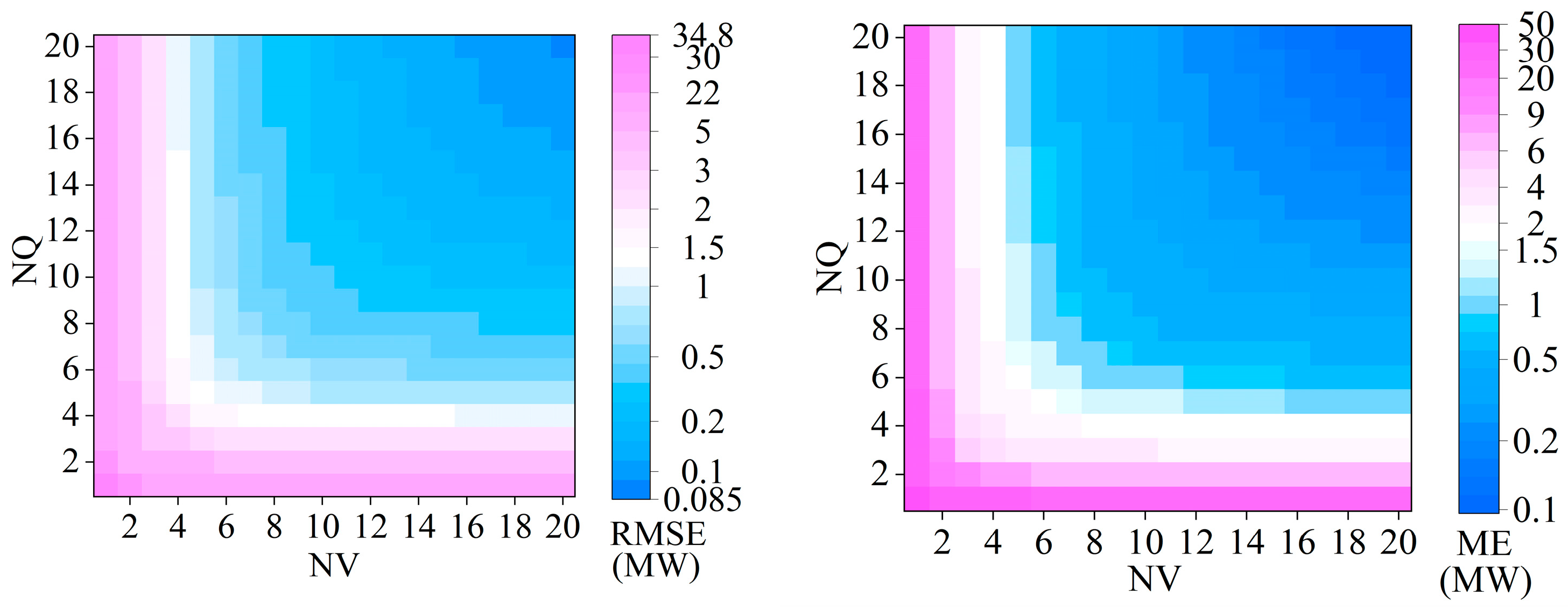
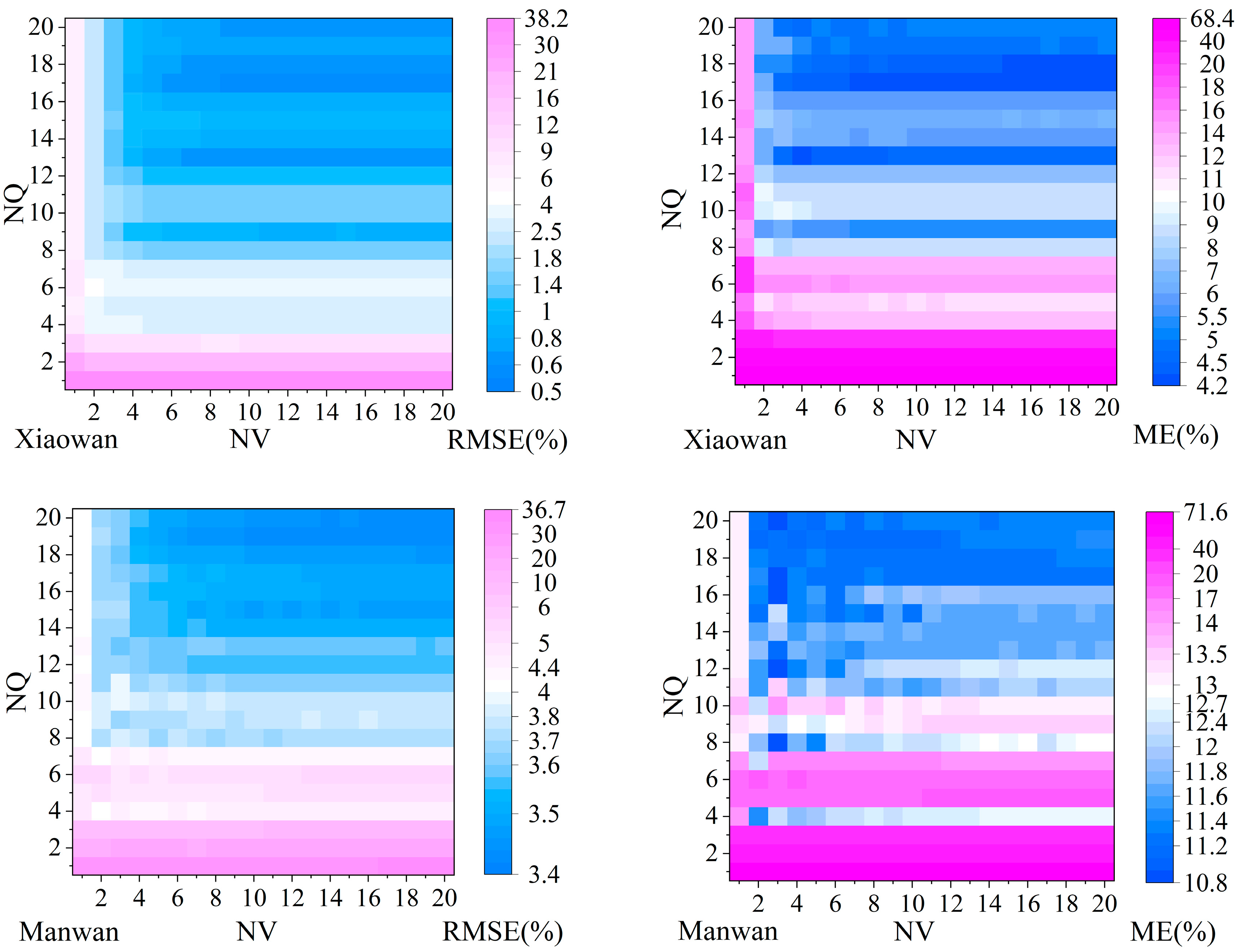
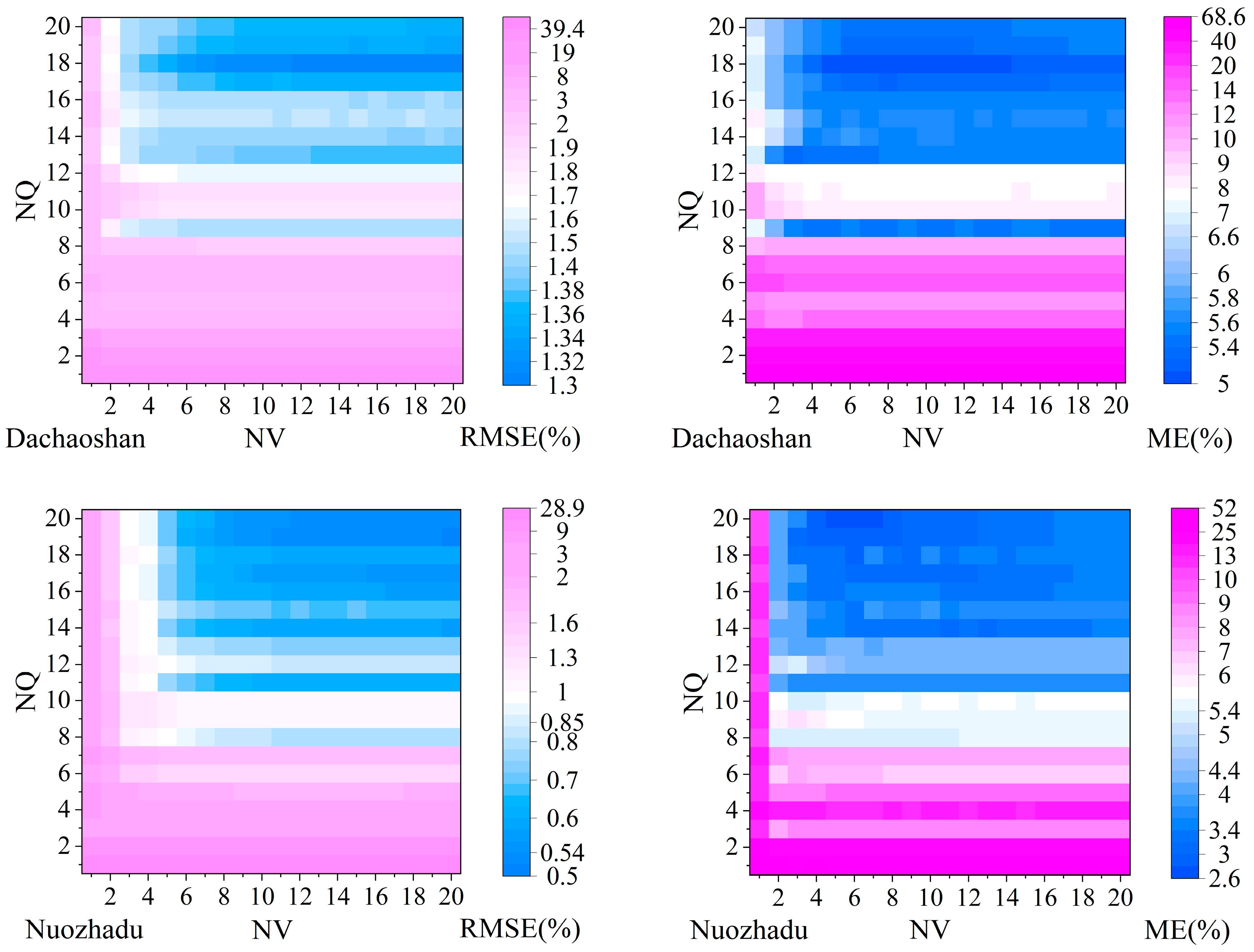
4.5. Convergence of ARBLC for Hydroplants
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Feng, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. A stochastic linear programming model for maximizing generation and firm output at a reliability in long-term hydropower reservoir operation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, J. Investigation on Water Levels for Cascaded Hydropower Reservoirs to Drawdown at the End of Dry Seasons. Water 2023, 15, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, C.; Yan, L. An efficient and accurate Mixed-integer linear programming model for long-term operations of large-scale hydropower systems. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2021, 15, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisández, I.; Pérez-Díaz, J.I. Mixed integer linear programming formulations for the hydro production function in a unit-based short-term scheduling problem. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 128, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zheng, H.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Weekly hydropower scheduling of cascaded reservoirs with hourly power and capacity balances. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela-Ripoll, I.; Otaola-Arca, P.; García-González, J.; Rivero-Honegger, C.; Mariño-Lizuain, F. Optimal discretization of net head dependency in heterogeneous multi-reservoir hydroelectric systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech 2021, Madrid, Spain, 28 June–2 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Ouyang, S.; Ding, X.; Chen, L. Improved decomposition–coordination and discrete differential dynamic programming for optimization of large-scale hydropower system. Energy Conv. Manag. 2014, 84, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.T.; Oliveira, A.R.L.; Soares, S. Interior point method for long-term generation scheduling of large-scale hydrothermal systems. Ann. Oper. Res. 2008, 169, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalao, J.P.S.; Mariano, S.J.P.S.; Mendes, V.M.F.; Ferreira, L.A.F.M. Scheduling of Head-Sensitive Cascaded Hydro Systems: A Nonlinear Approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhndorf, N.; Wozabal, D.; Minner, S. Optimizing Trading Decisions for Hydro Storage Systems Using Approximate Dual Dynamic Programming. Oper. Res. 2013, 61, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, H. Dynamic programming with successive approximation and relaxation strategy for long-term joint power generation scheduling of large-scale hydropower station group. Energy 2021, 222, 119960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. An Efficient Linearization Method for Long-Term Operation of Cascaded Hydropower Reservoirs. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-K.; Niu, W.-J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, C.-T.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Qin, H.; Liu, Y. Developing a successive linear programming model for head-sensitive hydropower system operation considering power shortage aspect. Energy 2018, 155, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilich, N. Shortcomings of linear programming in optimizing river basin allocation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W02426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörensen, K. Metaheuristics—The metaphor exposed. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2015, 22, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, C.G.; Camacho-Gómez, C.; Jiménez-Fernández, S.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Optimal Generation Scheduling in Hydro-Power Plants with the Coral Reefs Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2021, 14, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Lu, P.; Yuan, L. Long-term scheduling of large cascade hydropower stations in Jinsha River, China. Energy Conv. Manag. 2015, 90, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, F.; Gao, J.; Lu, P. Medium to long-term optimization model for cascade hydropower plants under high penetration of variable renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2025, 254, 123739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, A.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Jing, Z.; Peng, Z. How to achieve optimal photovoltaic plant capacity in hydro-photovoltaic complementary systems: Fully coupling long-term and short-term operational modes of cascade hydropower plants. Energy 2024, 313, 134161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baima, D.; Qian, G.; Luo, J.; Wang, P.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J. Monthly hydropower scheduling of cascaded reservoirs using a genetic algorithm with a simulation procedure. Energies 2024, 17, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, J.I.; González-Martínez, J. Comparison between plant-based and unit-based production functions for the day-ahead energy and reserve scheduling of a hydropower plant with common waterways. Energy Syst. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubost, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Lemaréchal, C. A Primal-Proximal Heuristic Applied to the Unit-Commitment Problem; INRIA: Le Chesnay, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Harou, J.J.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Rosenberg, D.E.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Lund, J.R.; Howitt, R.E. Hydro-economic models: Concepts, design, applications, and future prospects. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmeland, M.N.; Zou, J.; Helseth, A.; Ahmed, S. Nonconvex Medium-Term Hydropower Scheduling by Stochastic Dual Dynamic Integer Programming. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 10, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, A.; Hug, G.; Rosinski, S. Real-Time Optimization of the Mid-Columbia Hydropower System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Anjos, M.F.; Cote, P.; Desaulniers, G. MILP Formulations for Generator Maintenance Scheduling in Hydropower Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goor, Q.; Kelman, R.; Tilmant, A. Optimal-multipurposemultireservoir-operation-model-with-variable-productivity-of-hydropower-plants. Water Resour. Plann Manag. 2011, 137, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.; Lü, Q.; Wang, Y. Long-term multi-objective optimal scheduling for large cascaded hydro-wind-photovoltaic complementary systems considering short-term peak-shaving demands. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 301, 118063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Abreu, D.L.; Finardi, E.C. Continuous Piecewise Linear Approximation of Plant-Based Hydro Production Function for Generation Scheduling Problems. Energies 2022, 15, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Wu, S.; Gul, E.; Yu, X.; Ren, P. A 1D linearization–based MILP–NLP method for short-term hydrothermal operation. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2022, 17, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo, A.J.; Arroyo, J.M.; Contreras, J.; Villamor, F.A. Self-scheduling of a hydro producer in a pool-based electricity market. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 17, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, A.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Lodi, A.; Martello, S. An MILP approach for short-term hydro scheduling and unit commitment with head-dependent reservoir. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisández, I.; Périz-Diáz, J.I. Linear Programming Formulations for the Hydro Production Function in a Water Value Calculation. Renew. Energy 2025, 243, 122571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, E.M.L. Branch and bound methods for numerical optimization of non-convex functions. Comput. Stat. 1980, 80, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Belloni, A.; Lima, A.D.; Maceira, M.P.; Sagastizábal, C.A. Bundle Relaxation and Primal Recovery in Unit Commitment Problems. The Brazilian Case. Ann. Oper. Res. 2003, 120, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.V.; Finardi, E.C. Piecewise linear approximations for hydropower production function applied on the hydrothermal unit commitment problem. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 135, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, A.L.; Maceira, M.E.P. A Four-Dimensional Model of Hydro Generation for the Short-Term Hydrothermal Dispatch Problem Considering Head and Spillage Effects. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredo, G.L.M.; Finardi, E.C.; de Matos, V.L. Assessing solution quality and computational performance in the long-term generation scheduling problem considering different hydro production function approaches. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Feng, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. A new three-triangle based method to linearly concave hydropower output in long-term reservoir operation. Energy 2022, 250, 123784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Souza, H.G.; Finardi, E.C.; Brito, B.H.; Takigawa, F.Y.K. Partitioning approach based on convex hull and multiple choice for solving hydro unit-commitment problems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 211, 108285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, J. Short-Term Hydrothermal Scheduling Using a Two-Stage Linear Programming with Special Ordered Sets Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3329–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchette, J.; Vielma, J.P. Nonconvex piecewise linear functions: Advanced formulations and simple modeling tools. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1708.00050v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaraa, M.S.; Sherali, H.D.; Shetty, C.M. Nonliear Programming: Theory and Algorithms, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
| Model | Constraints | Variables | Constraints | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous | Binary | |||
| PWL1 | (24), (26), (27) | |||
| TTBLC | (29)–(32) | 0 | ||
| ARBLC | (24), (35) | 0 | ||
| Models | Resolutions | 4 | 16 | 36 | 64 | 100 | 144 | 196 | 256 | 324 | 400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWL1 | RMSE | 8.676 | 2.168 | 0.915 | 0.534 | 0.340 | 0.226 | 0.165 | 0.128 | X | X |
| MAE | 12.50 | 3.12 | 1.97 | 2.22 | 1.50 | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.53 | X | X | |
| Time | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 3.33 | 11.44 | 12.45 | 293.12 | 856.76 | X | X | |
| TTBLC | RMSE | 14.597 | 3.048 | 1.273 | 0.691 | 0.433 | 0.295 | 0.214 | 0.163 | 0.127 | 0.104 |
| MAE | 22.69 | 5.53 | 2.49 | 1.39 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.22 | |
| Time | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 0.48 | |
| ARBLC | RMSE | 8.676 | 2.168 | 0.964 | 0.542 | 0.346 | 0.241 | 0.177 | 0.135 | 0.107 | 0.085 |
| MAE | 12.50 | 3.12 | 1.39 | 0.78 | 0.50 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| Time | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.58 | 1.31 | 3.20 | 9.73 | 19.33 | 36.24 | 66.28 | 576.60 |
| Characteristics | Xiaowan | Manwan | Dachaoshan | Nuozhadu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operability | Over-year | yearly | yearly | Over-year |
| Minimum storage (108 m3) | 46.62 | 2.49 | 4.64 | 104.425 |
| Maximum storage (108 m3) | 145.57 | 3.716 | 7.42 | 217.776 |
| Minimum release (m3/s) | 270 | 280 | 300 | 800 |
| Maximum release (m3/s) | 7600 | 7700 | 7700 | 7900 |
| Installed capacity (MW) | 4200 | 1670 | 1350 | 5850 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, S.; Wang, J. A High-Precision, All-Rectangle-Based Method Linearly Concave Hydropower Output in Long-Term Reservoir Operation. Energies 2025, 18, 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195102
Zheng H, Huang Y, Wang Y, Hou F, Xu Y, Chen C, Feng S, Wang J. A High-Precision, All-Rectangle-Based Method Linearly Concave Hydropower Output in Long-Term Reservoir Operation. Energies. 2025; 18(19):5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195102
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Hao, Yan Huang, Yongqiang Wang, Feixiang Hou, Yong Xu, Cheng Chen, Suzhen Feng, and Jinwen Wang. 2025. "A High-Precision, All-Rectangle-Based Method Linearly Concave Hydropower Output in Long-Term Reservoir Operation" Energies 18, no. 19: 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195102
APA StyleZheng, H., Huang, Y., Wang, Y., Hou, F., Xu, Y., Chen, C., Feng, S., & Wang, J. (2025). A High-Precision, All-Rectangle-Based Method Linearly Concave Hydropower Output in Long-Term Reservoir Operation. Energies, 18(19), 5102. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195102






