Federated Learning for Decentralized Electricity Market Optimization: A Review and Research Agenda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Foundations and Taxonomies
2.1. Degree of Heterogeneity
2.2. Coordination Architectures
2.3. Optimization Scope
- (a)
- Typical forecasting problems addressed with FL include short-term load prediction, photovoltaic (PV) output forecasting, and electricity price evolution [19].
- (b)
- Economic optimization tasks addressed with FL include the construction of bidding curves, portfolio allocation across diverse assets, and the development of hedging strategies to mitigate market risks.
- (c)
- Operational coordination tasks in FL include generation dispatch, renewable curtailment management, and the activation of reserves to ensure grid reliability [20].
2.4. Relation to Classical Distributed Optimization
3. Federated Learning Architectures in Power Systems
3.1. Centralized Aggregation: The Classical FedAvg Lineage
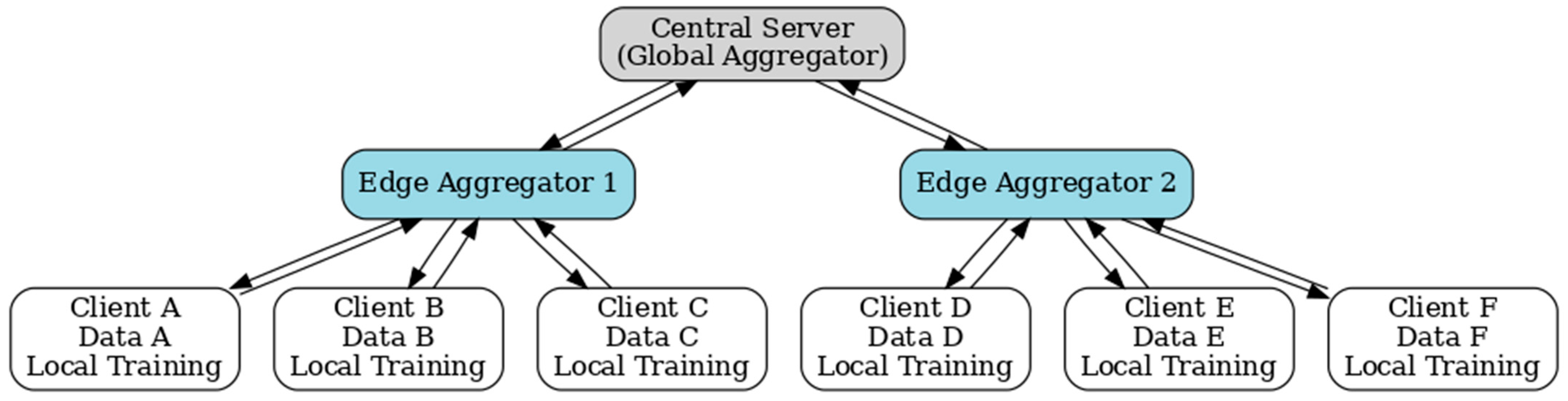
3.2. Hierarchical Federated Learning: Structuring the Grid as a Learning Tree
3.3. Peer-to-Peer and Gossip-Based FL: Architectures Without a Center
3.4. Blockchain-Enabled FL and Smart Contract Aggregation
3.5. Event-Driven and Asynchronous FL
4. Application Domains in Energy Markets
4.1. Load Forecasting and Demand Curve Estimation
4.2. Federated Reinforcement Learning for Bidding and Pricing
4.3. Real-Time Balancing and Ancillary Service Coordination
4.4. Grid Congestion and Voltage Control with FL
4.5. Predictive Maintenance and Asset Health Monitoring
5. Evaluation Practices and Reproducibility
6. Regulatory, Ethical, and Interoperability Aspects
6.1. Privacy Regulations and Their Ambiguities
6.2. Ethical Considerations Beyond Privacy
6.3. Interoperability: The Forgotten Constraint
6.4. Incentive Mechanisms and Participation Dilemmas
6.5. Policy and Regulatory Framework
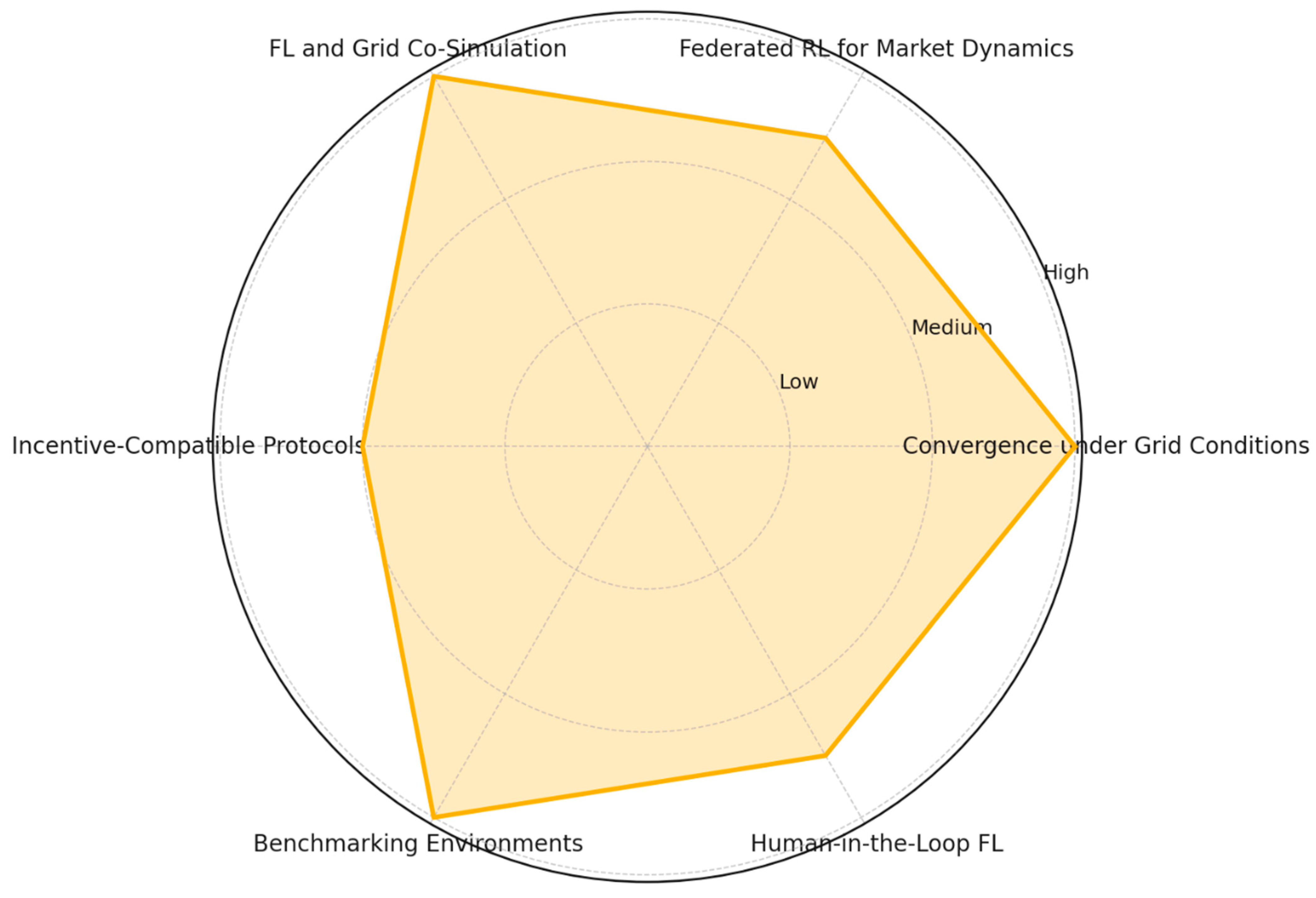
7. Research Agenda and Open Challenges
7.1. Formal Convergence Under Real Grid Conditions
7.2. Federated Reinforcement Learning for Market Dynamics
7.3. Co-Simulation of FL with Grid Control Systems
7.4. Incentive-Compatible Protocols for Participation
7.5. Benchmarking Environments and Open Federated Datasets
7.6. Human-in-the-Loop and Operator Interpretability
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| FL | Federated Learning |
| FRL | Federated Reinforcement Learning |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| Safe RL | Safe Reinforcement Learning |
| Q-learning | Q-learning (value-based RL algorithm) |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient |
| PPO | Proximal Policy Optimization |
| Actor-Critic | Actor-Critic methods in RL |
| CNN-LSTM | Convolutional Neural Network—Long Short-Term Memory hybrid |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory neural network |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| Autoencoder | Autoencoder neural network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| One-Class SVM | One-Class Support Vector Machine (anomaly detection) |
| Isolation Forest | Isolation Forest (ensemble anomaly detection) |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| FedAvg | Federated Averaging algorithm |
| FedSGD | Federated Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| ADMM | Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resources |
| PV | Photovoltaics |
| VPP | Virtual Power Plant |
| DSO | Distribution System Operator |
| TSO | Transmission System Operator |
| ENTSO-E | European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity |
| ESS | Energy Storage System |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| PMU | Phasor Measurement Unit |
| PDC | Phasor Data Concentrator |
| DR | Demand Response |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| DP | Differential Privacy |
| DLT | Distributed Ledger Technology |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | International Standard for Information Security Management |
| NIS2 | EU Directive on Security of Network and Information Systems (NIS2 Directive) |
| NERC CIP | North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection standards |
References
- Mammen, P.M. Federated Learning: Opportunities and Challenges 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.05428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, F.; Hu, Z.; Huang, H. Faster Adaptive Federated Learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 10379–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, J.; Guan, X.; Hassan, M.M.; Alelaiwi, A. Privacy-aware service placement for mobile edge computing via federated learning. Inf. Sci. 2019, 505, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, H.B.; Ramage, D.; Talwar, K.; Zhang, L. Learning Differentially Private Recurrent Language Models 2018. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1710.06963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonawitz, K.; Ivanov, V.; Kreuter, B.; Marcedone, A.; McMahan, H.B.; Patel, S.; Ramage, D.; Segal, A.; Seth, K. Practical Secure Aggregation for Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, TX, USA, 30 October 2017; pp. 1175–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Liu, X. A Review of Federated Learning in Energy Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/IAS Industrial and Commercial Power System Asia (I&CPS Asia), Shanghai, China, 8 July 2022; pp. 2089–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.; Sumper, A.; Aragüés-Peñalba, M.; Galceran-Arellano, S. Advancing Power System Services with Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Techniques: A Review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 76753–76780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. A study of data heterogeneity in federated learning. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 40, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grataloup, A.; Jonas, S.; Meyer, A. A review of federated learning in renewable energy applications: Potential, challenges, and future directions 2023. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, C. A Review of Federated Learning Methods in Heterogeneous Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 5983–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zou, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, H.; Zeng, Z. Spatio–Temporal Aware Personalized Federated Learning for Load Forecasting in Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Wang, J.; Malik, K.; Sanjabi, M.; Rabbat, M. Where to Begin? On the Impact of Pre-Training and Initialization in Federated Learning 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.08090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bosch, J.; Olsson, H.H. Federated Learning Systems: Architecture Alternatives. In Proceedings of the 2020 27th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC), Singapore, 1–4 December 2020; pp. 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Domini, D.; Aguzzi, G.; Esterle, L.; Viroli, M. FBFL: A Field-Based Coordination Approach for Data Heterogeneity in Federated Learning 2025. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, A.M.; Coleri, S.; Papazafeiropoulos, A.K.; Kourtessis, P.; Chatzinotas, S. A Hybrid Architecture for Federated and Centralized Learning. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafid, A.; Hocine, R.; Guezouli, L.; Abdessemed, M.R. Centralized and Decentralized Federated Learning in Autonomous Swarm Robots: Approaches, Algorithms, Optimization Criteria and Challenges: The Sixth Edition of International Conference on Pattern Analysis and Intelligent Systems (PAIS’24). In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Pattern Analysis and Intelligent Systems (PAIS), El Oued, Algeria, 24 April 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Liang, H.H.; Han, X.M.; Liu, B.A.; Cheng, D.Z.; Wang, D. Spread: Decentralized Model Aggregation for Scalable Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 51st International Conference on Parallel Processing, Bordeaux, France, 29 August 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z. Short-Term Load Forecasting of Power System. In Proceedings of the Advances in Materials, Machinery, Electrical Engineering (AMMEE 2017); Atlantis Press: Tianjin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krad, I.; Gao, D.W.; Ela, E.; Ibanez, E.; Wu, H. Analysis of Operating Reserve Demand Curves in Power System Operations in the Presence of Variable Generation. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovajsova, L.; Hluchý, L.; Staňo, M. A Review of Multi-Objective and Multi-Task Federated Learning Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 23rd World Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI), Stará Lesná, Slovakia, 23 January 2025; pp. 000035–000040. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, R.; Costantini, G.; Gorges, D. ADMM-based distributed model predictive control: Primal and dual approaches. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Melbourne, Australia, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 6598–6603. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadimi, E.; Teixeira, A.; Shames, I.; Johansson, M. Optimal Parameter Selection for the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM): Quadratic Problems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2015, 60, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, D.P. Mung Chiang Alternative decompositions and distributed algorithms for network utility maximization. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM ’05. IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 28 November–2 December 2005; pp. 6–2568. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, T.-H.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Sun, D. Beyond ADMM: A Unified Client-variance-reduced Adaptive Federated Learning Framework 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.01519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bennani, I.L.; Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Y. Electricity Consumer Characteristics Identification: A Federated Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3637–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, Y.; Chen, K.; Fan, L.; Yang, Q. Trading Off Privacy, Utility, and Efficiency in Federated Learning. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023, 14, 3595185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, M.; Sikdar, S.; Nejdl, W.; Fisichella, M. FairTrade: Achieving Pareto-Optimal Trade-Offs between Balanced Accuracy and Fairness in Federated Learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 10962–10970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Bao, W.; Zomaya, A.; Nguyen, M.N.H.; Hong, C.S. Federated Learning over Wireless Networks: Optimization Model Design and Analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, G.A.; Shin, J.; Payani, A.; Lee, M.; Kompella, R.R. Not All Federated Learning Algorithms Are Created Equal: A Performance Evaluation Study 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sanjabi, M.; Beirami, A.; Smith, V. Fair Resource Allocation in Federated Learning 2020. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1905.10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y. FedModule: A Modular Federated Learning Framework 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.04849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, D.J.; Topal, T.; Mathur, A.; Qiu, X.; Fernandez-Marques, J.; Gao, Y.; Sani, L.; Li, K.H.; Parcollet, T.; de Gusmão, P.P.B.; et al. Flower: A Friendly Federated Learning Research Framework 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2007.14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrangeli, E.; Tonellotto, N.; Vallati, C. Performance Evaluation of Federated Learning for Residential Energy Forecasting. IoT 2022, 3, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Agarwal, P.; Gupta, K.; Baliarsingh, S.; Vyas, O.P.; Puliafito, A. FedGrid: A Secure Framework with Federated Learning for Energy Optimization in the Smart Grid. Energies 2023, 16, 8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ma, J.; Zhu, J. Hierarchical Federated Learning for Power Transformer Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 3196736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Yue, D. A Heterogeneity-Aware Adaptive Federated Learning Framework for Short-Term Forecasting in Electric IoT Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 15388–15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.; Khan, A.N.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, Q.W.; Kim, D.H. Personalized hierarchical heterogeneous federated learning for thermal comfort prediction in smart buildings. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z. Federated Graph Learning for EV Charging Demand Forecasting with Personalization Against Cyberattacks 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.00742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. H-FL: A Hierarchical Communication-Efficient and Privacy-Protected Architecture for Federated Learning 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.00275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharanarthi, T. Asynchronous Hierarchical Federated Learning: Enhancing Communication Efficiency and Scalability. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Computers and Artificial Intelligence Technology (CAIT), Hangzhou, China, 20 December 2024; pp. 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Arafa, A. Delay Sensitive Hierarchical Federated Learning with Stochastic Local Updates. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2025, 1, 3527699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, X. FedDual: Pair-Wise Gossip Helps Federated Learning in Large Decentralized Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnoo, M.A.; Anwar, A.; Haque, M.E.; Mahmood, A.N. Decentralized Federated Anomaly Detection in Smart Grids: A P2P Gossip Approach 2025. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2407.15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z. Decentralized Federated Learning: A Segmented Gossip Approach 2019. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.G.; Siddiqui, S.; Pölsterl, S.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. BrainTorrent: A Peer-to-Peer Environment for Decentralized Federated Learning 2019. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.06731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, D.; Grace, P.; Naik, N.; Jenkins, P.; Mishra, D.; Prajapat, S. An Introduction to Gossip Protocol Based Learning in Peer-to-Peer Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on ICT in Business Industry & Government (ICTBIG), Indore, India, 8 December 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Verma, A.; Zhu, Z.; Gadekallu, T.R. Federated Edge Computing for Edge-Assisted Consumer Electronics. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2025, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian Cardenas, D.; Mukherjee, M.; Ramirez, J. A Review of Privacy in Energy Applications; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Saroj, S.K.; Chauhan, S.K.; Saini, S.K. Sybil attack prevention and detection in vehicular ad hoc network. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 29–30 April 2016; pp. 594–599. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Gao, L.; He, C.; Zhang, M.; Krishnamachari, B.; Avestimehr, A.S. Federated learning for the internet of things: Applications, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2022, 5, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamedy, F.H.; El-Haggar, N.; Alsumayt, A.; Alfawaer, Z.; Alshammari, M.; Amouri, L.; Aljameel, S.S.; Albassam, S. Unlocking a Promising Future: Integrating Blockchain Technology and FL-IoT in the Journey to 6G. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 115411–115447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Loke, S.W.; Trujillo-Rasua, R.; Jiang, F.; Xiang, Y. Applications of Distributed Ledger Technologies to the Internet of Things: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 52, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.; Moustafa, N.; Turnbull, B. BFL-SC: A blockchain-enabled federated learning framework, with smart contracts, for securing social media-integrated internet of things systems. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2025, 169, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapaaking, A.P.; Khalil, I.; Yi, X.; Lam, K.-Y.; Huang, G.-B.; Wang, N. Auditable and Verifiable Federated Learning Based on Blockchain-Enabled Decentralization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jing, B.; Dou, D. Enhancing trust and privacy in distributed networks: A comprehensive survey on blockchain-based federated learning. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2024, 66, 4377–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Khan, A.F.; Zawad, S.; Anwar, A.; Angel, N.B.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, F.; Butt, A.R. Tokenized Incentive for Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence; AAAI: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, W.; Moustafa, N.; Turnbull, B.; Sohrabi, N.; Tari, Z. Blockchain-Based Federated Learning for Securing Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Alrajeh, N.A.; Muhammad, G. Secure and Provenance Enhanced Internet of Health Things Framework: A Blockchain Managed Federated Learning Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 205071–205087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, F.; Zeydan, E.; Mangues-Bafalluy, J.; Dev, K.; Blanco, L. Blockchain for Federated Learning in the Internet of Things: Trustworthy Adaptation, Standards, and the Road Ahead 2025. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.23823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chang, S.; Dai, M.; Li, D.; Zhao, H. Bridging Data Silos in Finance via Federated Learning. IEEE Netw. 2025, 1, 3584806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Cui, N.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Ding, Y. ChainFL: A Simulation Platform for Joint Federated Learning and Blockchain in Edge/Cloud Computing Environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 3572–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T. The Energy Web: Concept and challenges to overcome to make large scale renewable and distributed energy resources a true reality. In Proceedings of the 2009 7th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Cardiff, UK, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shan, H.; Wang, W.; Quek, T.Q.S. Asynchronous Federated Learning Over Wireless Communication Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 6961–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wen, C.; Wen, T. An Asynchronous and Real-Time Update Paradigm of Federated Learning for Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 8531–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tu, A.; Chen, Y.; Reddi, V.J. FedStaleWeight: Buffered Asynchronous Federated Learning with Fair Aggregation via Staleness Reweighting 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.02877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Chitnis, M. Momentum Approximation in Asynchronous Private Federated Learning 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.09247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Belatreche, A.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H. Event-Driven Learning for Spiking Neural Networks 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.00270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X.; Sun, H. A Federated Learning Framework for Smart Grids: Securing Power Traces in Collaborative Learning 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gooi, H.B. Distribution-Balanced Federated Learning for Fault Identification of Power Lines. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, K.; Metaxiotis, K.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Tavanidou, E. A first approach to e-forecasting: A survey of forecasting Web services. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2003, 11, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolik, M.S. An overview of the National Weather Service’s centralized statistical quantitative precipitation forecasts. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 306–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Chen, C.; Mei, C.; Jing, Y.; Sun, H. A Wind Speed Combination Forecasting Method Based on Multifaceted Feature Fusion and Transfer Learning for Centralized Control Center. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 213, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Purushwalkam, S.; Cogswell, M.; Crandall, D.; Batra, D. Why M Heads are Better than One: Training a Diverse Ensemble of Deep Networks 2015. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, H.M.; Pan, S.B.; Kim, P. A Deep Bidirectional GRU Network Model for Biometric Electrocardiogram Classification Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 145395–145405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.; Baladron, C.; Aguiar, J.M.; Carro, B.; Sanchez-Esguevillas, A.J.; Lloret, J.; Massana, J. A Survey on Electric Power Demand Forecasting: Future Trends in Smart Grids, Microgrids and Smart Buildings. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1460–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekri, M.N.; Grolinger, K.; Mir, S. Asynchronous adaptive federated learning for distributed load forecasting with smart meter data. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 153, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ho, S.; Wang, M.; Gao, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H. Federated Learning Meets Natural Language Processing: A Survey 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, Q.; Xiao, D. Application of LSTM-LightGBM Nonlinear Combined Model to Power Load Forecasting. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2294, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivazhagan, M.G.; Aggarwal, V.; Singh, A.K.; Choudhary, S. Federated Learning with Personalization Layers 2019. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.00818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.; Fan, Z.; Andras, P. Federated Learning for Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting. IEEE Open Access J. Power Energy 2022, 9, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, H. Efficient Large-Scale Personalizable Bidding for Multiagent Auction-Based Federated Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 26518–26530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, H. A Cost-Aware Utility-Maximizing Bidding Strategy for Auction-Based Federated Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 12866–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Mudi, R.; Rahman, S.; Rabie, K.M.; Li, X. Federated Reinforcement Learning for Wireless Networks: Fundamentals, Challenges and Future Research Trends. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2024, 5, 1400–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qiu, G.; Guan, Z.; Zhao, W.; He, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Sponsored Search Real-time Bidding. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19 July 2018; pp. 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, Z. Accelerating Federated Learning with Model Segmentation for Edge Networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2025, 9, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyato, D. Editorial: First Quarter 2023 IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, i–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Liu, A.; Xiong, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Dong, M. TD-MDB: A Truth-Discovery-Based Multidimensional Bidding Strategy for Federated Learning in Industrial IoT Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 4274–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Huang, F.; Chen, T.; Zhong, H.; Chen, Q. Reinforcement Learning Based Bidding Framework with High-dimensional Bids in Power Markets 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zang, T.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y. Reinforcement Learning-Based Dual-Identity Double Auction in Personalized Federated Learning. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 4086–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Yin, C.; Poor, H.V. Convergence Time Minimization for Federated Reinforcement Learning over Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 56th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 9 March 2022; pp. 246–251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cui, T.; Yang, K.; Yuan, R.; He, L.; Li, M. Demand Forecasting of E-Commerce Enterprises Based on Horizontal Federated Learning from the Perspective of Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kang, J. Accelerated Federated Learning via Greedy Aggregation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 2919–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ding, X.; Li, M.; Jin, H. Differentially Private Federated Learning with Importance Client Sampling. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 3635–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, Z. Federated Multiagent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach via Physics-Informed Reward for Multimicrogrid Energy Management. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 5902–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman Taheri, S.; Davoodi, M.; Ali, M.H. A modified modeling approach of virtual power plant via improved federated learning. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 158, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Pasupuleti, J.; Raveendran, S.K.; Basir Khan, M.R. Performance Evaluation of Solar PV Inverter Controls for Overvoltage Mitigation in MV Distribution Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kekatos, V.; Jin, M. Controlling Smart Inverters Using Proxies: A Chance-Constrained DNN-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Bai, D.; Yao, D.; Dai, Y.; Gu, L.; Yu, C.; Sun, L. Personalized Edge Intelligence via Federated Self-Knowledge Distillation. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2023, 34, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achouch, M.; Dimitrova, M.; Ziane, K.; Sattarpanah Karganroudi, S.; Dhouib, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Adda, M. On Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0: Overview, Models, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kea, K.; Han, Y.; Kim, T.-K. Enhancing anomaly detection in distributed power systems using autoencoder-based federated learning. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, R.; Nguyen, D.C. Improved Modulation Recognition Using Personalized Federated Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 19937–19942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasson, M.; Malchiodi, D. Support Vector Based Anomaly Detection in Federated Learning. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 274–287. ISBN 978-3-031-62494-0. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Beheshti, A.; Qi, L.; Hong, Y.; Dou, W. Federated Learning-Based Anomaly Detection with Isolation Forest in the IoT-Edge Continuum. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiser, M.; Zinnikus, I. A Survey on the Use of Synthetic Data for Enhancing Key Aspects of Trustworthy AI in the Energy Domain: Challenges and Opportunities. Energies 2024, 17, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, C.M.; Torralba, A.; Guibas, L.; DiCarlo, J.; Chellappa, R.; Hodgins, J. Next-generation deep learning based on simulators and synthetic data. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2022, 26, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.R.; Dan, G.; Miorandi, D.; Chlamtac, I. Smart Meter Data Privacy: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2820–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Nag, A.; Roy, N.; Dey, A.R.; Ahmed Fahim, S.F.; Ghosh, A. An Investigation into the Prediction of Annual Income Levels Through the Utilization of Demographic Features Employing the Modified UCI Adult Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computing, Communication, and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS), Greater Noida, India, 3–4 November 2023; pp. 1080–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, S.; Hinson, S. Enabling Technologies and Technical Solutions for the Energy Internet. In The Energy Internet; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 203–221. ISBN 978-0-08-102207-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jumar, R.; Maaß, H.; Hagenmeyer, V. Comparison of lossless compression schemes for high rate electrical grid time series for smart grid monitoring and analysis. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 71, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.L.; Chuang, S.J.; Fyfe, C. Power Load Forecasting Using Neural Canonical Correlates. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Barcelona, Spain, 3–7 September 2020; Volume 2, pp. 455–458. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Qian, Q. Privacy Preserving Machine Learning with Homomorphic Encryption and Federated Learning. Future Internet 2021, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidooni, H.; Marchal, S.; Miettinen, M.; Mirhoseini, A.; Mollering, H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Rieger, P.; Sadeghi, A.-R.; Schneider, T.; Yalame, H.; et al. SAFELearn: Secure Aggregation for private FEderated Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 May 2021; pp. 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, N.; Musilek, P. Federated learning with hyperparameter-based clustering for electrical load forecasting. Internet Things 2022, 17, 100470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Friebe, E. Large Resistance Change on Magnetic Tunnel Junction based Molecular Spintronics Devices. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 453, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, S.; So, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Vepakomma, P.; Singh, A.; Qiu, H.; et al. FedML: A Research Library and Benchmark for Federated Machine Learning 2020. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururaj, H.L.; Kayarga, T.; Flammini, F.; Dobrilovic, D. Federated Learning Techniques and Its Application in the Healthcare Industry; World Scientific: Singapore, 2024; ISBN 978-981-12-8793-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Kalathil, D.; Begovic, M.; Xie, L. PyProD: A Machine Learning-Friendly Platform for Protection Analytics in Distribution Systems 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.05802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, V.; Kaza, S.; Annaswamy, A.M. DER Forecast Using Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamala, S.R.; Kummari, N.K.; Singh, A.K.; Saibewar, A.; Chalavadi, K.M. Federated learning to comply with data protection regulations. CSI Trans. ICT 2022, 10, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Shokri, R.; Houmansadr, A. Comprehensive Privacy Analysis of Deep Learning: Passive and Active White-box Inference Attacks against Centralized and Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 739–753. [Google Scholar]
- Ouadrhiri, A.E.; Abdelhadi, A. Differential Privacy for Deep and Federated Learning: A Survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 22359–22380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, J.; Ding, M.; Ma, C.; Yang, H.H.; Farokhi, F.; Jin, S.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Vincent Poor, H. Federated Learning with Differential Privacy: Algorithms and Performance Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inform. Forensic Secur. 2020, 15, 3454–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.; Takeshita, J.; Jung, T.; Niemier, M.; Hu, X.S. Computing-in-Memory for Performance and Energy-Efficient Homomorphic Encryption. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2020, 28, 2300–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K. Ethical Implications and Accountability of Algorithms. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 160, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Zhu, K.; Luong, N.C.; Niyato, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Incentive Mechanisms for Federated Learning: From Economic and Game Theoretic Perspective. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1566–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Bai, H.; Yu, B.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. A survey on federated learning. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 216, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 3652.1-2020; Guide for Architectural Framework and Application of Federated Machine Learning. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020.
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, B.; Brunner, C.; Yip, T.; Chen, Y. IEC 61850 Configuration Solution to Distributed Intelligence in Distribution Grid Automation. Energies 2017, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Zeng, C.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chu, X. Incentive Mechanisms in Federated Learning and A Game-Theoretical Approach. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; Makkar, A.; Conway, M. A Comprehensive Review of Open-Source Federated Learning Frameworks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 260, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Electricity Market Design—Overview and Reforms. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/markets-and-consumers/electricity-market-design_en (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2022/2555 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 December 2022 on Measures for a High Common Level of Cybersecurity across the Union (NIS2 Directive). Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, L333, 80–152. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022; Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection—Information Security Management Systems—Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ENISA Cybersecurity Roles and Skills for NIS2 Essential and Important Entities. European Union Agency for Cybersecurity. 2023. Available online: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/cybersecurity-roles-and-skills-for-nis2-essential-and-important-entities (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Qi, J.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, L.; Zheng, K. Federated Reinforcement Learning: Techniques, Applications, and Open Challenges. Intell. Robot. 2021, 1, 18–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Hossain, R.R.; Mohiuddin, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; Adetola, V.; Jinsiwale, R.A.; Huang, Q.; Yin, T.; Singhal, A. Resilient Control of Networked Microgrids Using Vertical Federated Reinforcement Learning: Designs and Real-Time Test-Bed Validations. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, F.; Saric, M.; Hivziefendic, J.; Dzemic, Z. Hosting capacity in smart distribution systems using OpenDSS tool and Monte Carlo-based methodology. Sci. Technol. Energy Transit. 2025, 80, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Nair, V.; Dias, B.; Morais, H.; Annaswamy, A. Federated learning forecasting for strengthening grid reliability and enabling markets for resilience. IET Conf. Proc. 2025, 2024, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.S.; Lim, W.Y.B.; Xiong, Z.; Cao, X.; Niyato, D.; Leung, C.; Kim, D.I. A Hierarchical Incentive Design Toward Motivating Participation in Coded Federated Learning. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Yao, Y.; Han, S.; Gu, J.; Joe-Wong, C.; Ravi, S.; Avestimehr, S.; He, C. FedML-HE: An Efficient Homomorphic-Encryption-Based Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning System 2024. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xygkis, T.C.; Löfberg, J.; Korres, G.N. Investigation of Optimal Phasor Measurement Selection for Distribution System State Estimation Under Various Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 9006616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakatos, N.P.; Babu, R. Hybrid Optimization Strategies for Global Optimality in Non-Convex Programming Using SQP and IPMs: Avoiding the Maratos Effect in PMU Placement—A Case Study. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3027, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanis, N.; Brodimas, D.; Plakas, K.; Birbas, M.; Birbas, A. Optimal Relocation of Virtualized PDC in Edge-Cloud Architectures Under Dynamic Latency Conditions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), Prague, Czech Republic, 20–22 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufyan, M.A.; Zuhaib, M.; Anees, M.A.; Khair, A.; Rihan, M. Implementation of PMU-Based Distributed Wide Area Monitoring in Smart Grid. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 140768–140778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Use Case | Typical Models | FL Architecture | Key Challenges | Search Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Forecasting | LSTM, GRU, CNN-LSTM hybrids | Centralized or Hierarchical | Data sparsity, personalization, multi-horizon alignment | federated learning load forecasting energy LSTM smart grid |
| Federated RL for Bidding | DDPG, PPO, Actor-Critic RL | Peer-to-Peer, Hierarchical | Strategic behavior, non-stationarity, policy lag | federated reinforcement learning electricity market bidding PPO DDPG |
| Balancing and Ancillary Services | Feedforward DNN, Safe RL, MPC + FL | Hierarchical, Event-Driven | Latency, physical constraints, regulatory compatibility | federated learning ancillary services grid balancing smart inverter |
| Voltage Control and Congestion Management | Safe RL, Q-learning, Constraint-aware DNNs | Hierarchical, Blockchain-enabled | Grid stability, topology opacity, multi-agent coordination | federated learning voltage control congestion smart grid reactive power |
| Predictive Maintenance | Autoencoders, One-Class SVM, Isolation Forest | Centralized (Edge Aggregation) | Sensor heterogeneity, privacy, communication efficiency | federated learning predictive maintenance substations anomaly detection |
| Dimension | Current State | Challenges | Urgency Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy Compliance | Partially addressed (DP, secure aggregation); legal ambiguity remains | Gradient leakage, legal definitions of personal data, trade-offs with accuracy | High |
| Fairness and Bias | Largely ignored; no fairness metrics or adjustments in FL updates | Skewed representation, asynchronous bias, economic marginalization | Medium–High |
| Interoperability | Low; device and protocol heterogeneity hinder model exchange | Lack of standards (APIs, model formats), legacy systems, model alignment | High |
| Incentive Mechanisms | Theoretical only; no standard reward or reputation mechanisms | Free-riding, model poisoning, cost of compute, lack of trust incentives | Medium |
| Research Area | Key Questions/Needs | Open Challenges | Urgency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convergence under Grid Conditions | Formalize behavior under heterogeneity, asynchrony, staleness | No general theory under non-IID, dynamic nodes | High |
| Federated RL for Market Dynamics | Coordinate strategic agents; link policies to market equilibria | Lack of theory at RL–FL–game theory intersection | Medium–High |
| FL and Grid Co-Simulation | Simulate full loop with control systems and power flows | No existing end-to-end FL + grid simulation pipeline | High |
| Incentive-Compatible Protocols | Design reward systems for honest and useful participation | Lack of auditability, fairness, or verifiable rewards | Medium |
| Benchmarking Environments | Create realistic federated datasets and environments | No standard scenarios for federated benchmarking | High |
| Human-in-the-Loop FL | Enable explainability and operator override of FL systems | Explainability methods not adapted for FL aggregation | Medium–High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, T.; Durlik, I.; Kostecka, E.; Kozlovska, P.; Nowak, A. Federated Learning for Decentralized Electricity Market Optimization: A Review and Research Agenda. Energies 2025, 18, 4682. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174682
Miller T, Durlik I, Kostecka E, Kozlovska P, Nowak A. Federated Learning for Decentralized Electricity Market Optimization: A Review and Research Agenda. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4682. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Tymoteusz, Irmina Durlik, Ewelina Kostecka, Polina Kozlovska, and Aleksander Nowak. 2025. "Federated Learning for Decentralized Electricity Market Optimization: A Review and Research Agenda" Energies 18, no. 17: 4682. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174682
APA StyleMiller, T., Durlik, I., Kostecka, E., Kozlovska, P., & Nowak, A. (2025). Federated Learning for Decentralized Electricity Market Optimization: A Review and Research Agenda. Energies, 18(17), 4682. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174682







