Variable Dimensional Bayesian Method for Identifying Depth Parameters of Substation Grounding Grid Based on Pulsed Eddy Current
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electromagnetic Forward Model of Substation Grounding Grid
2.1. Construction of Electromagnetic Forward Model
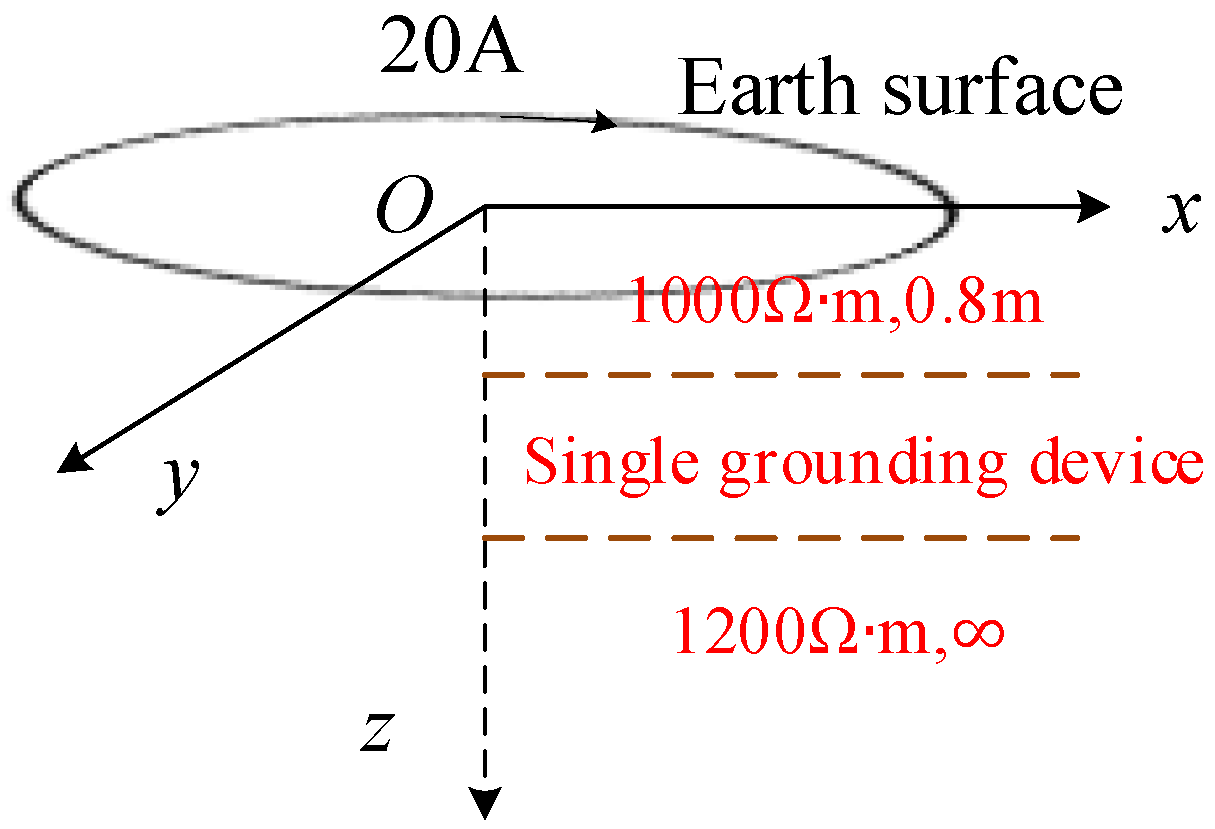
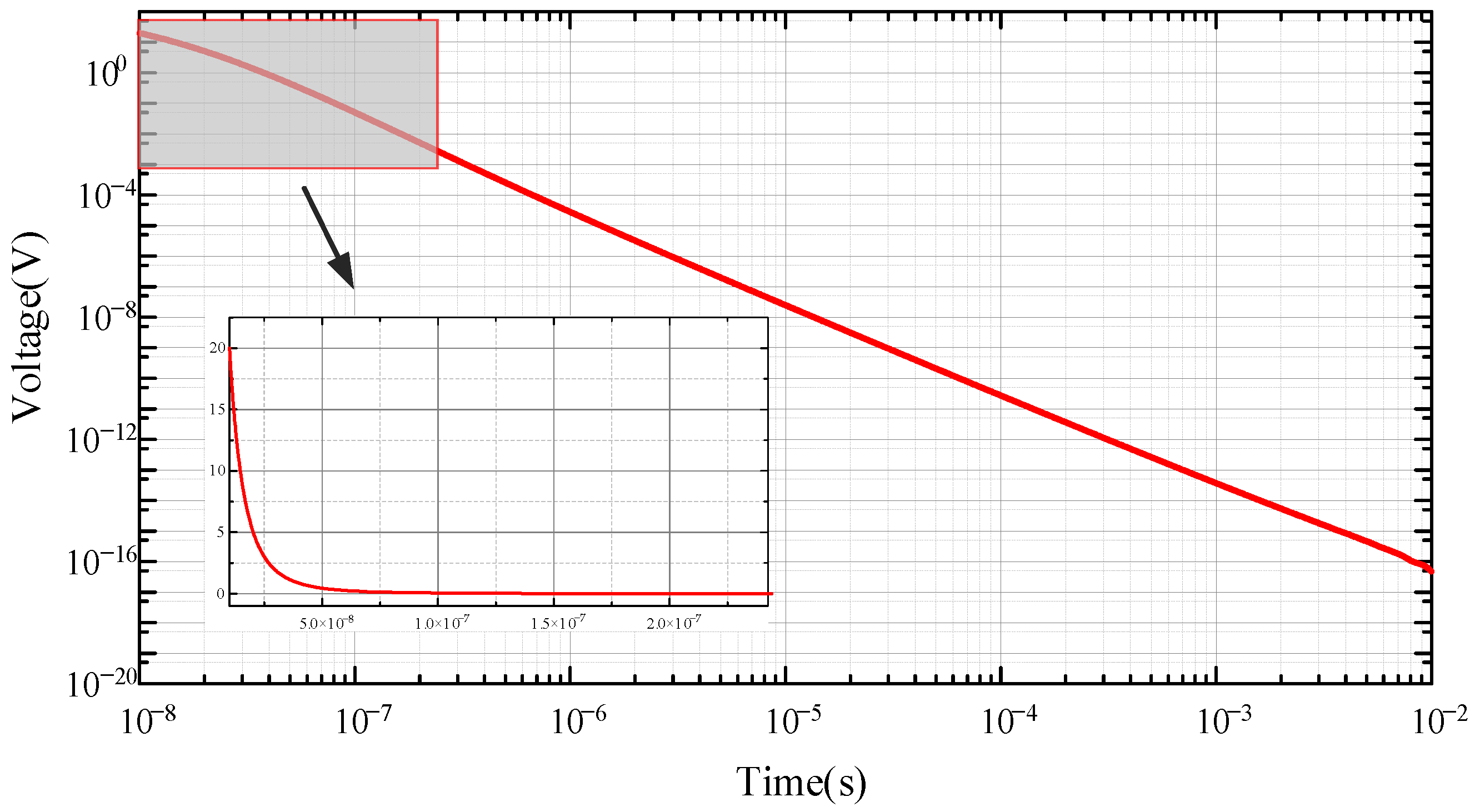
2.2. Verification of Forward Model
3. Substation Grounding Grid Parameter Identification Method
3.1. Model Parameter Initialization
3.2. Prior Function and Likelihood Function Generation
- (1)
- Prior Function
- (2)
- Likelihood Function
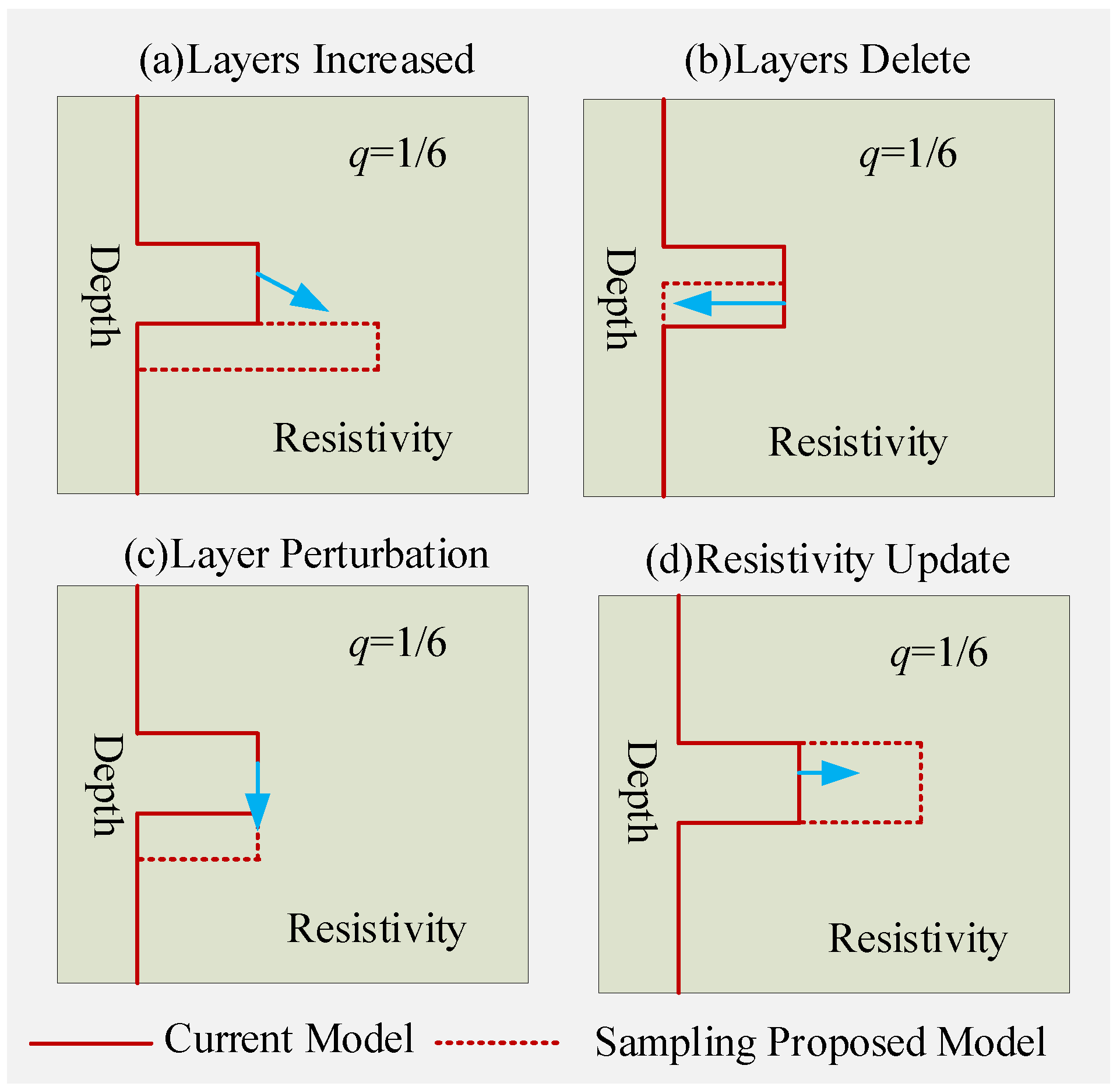
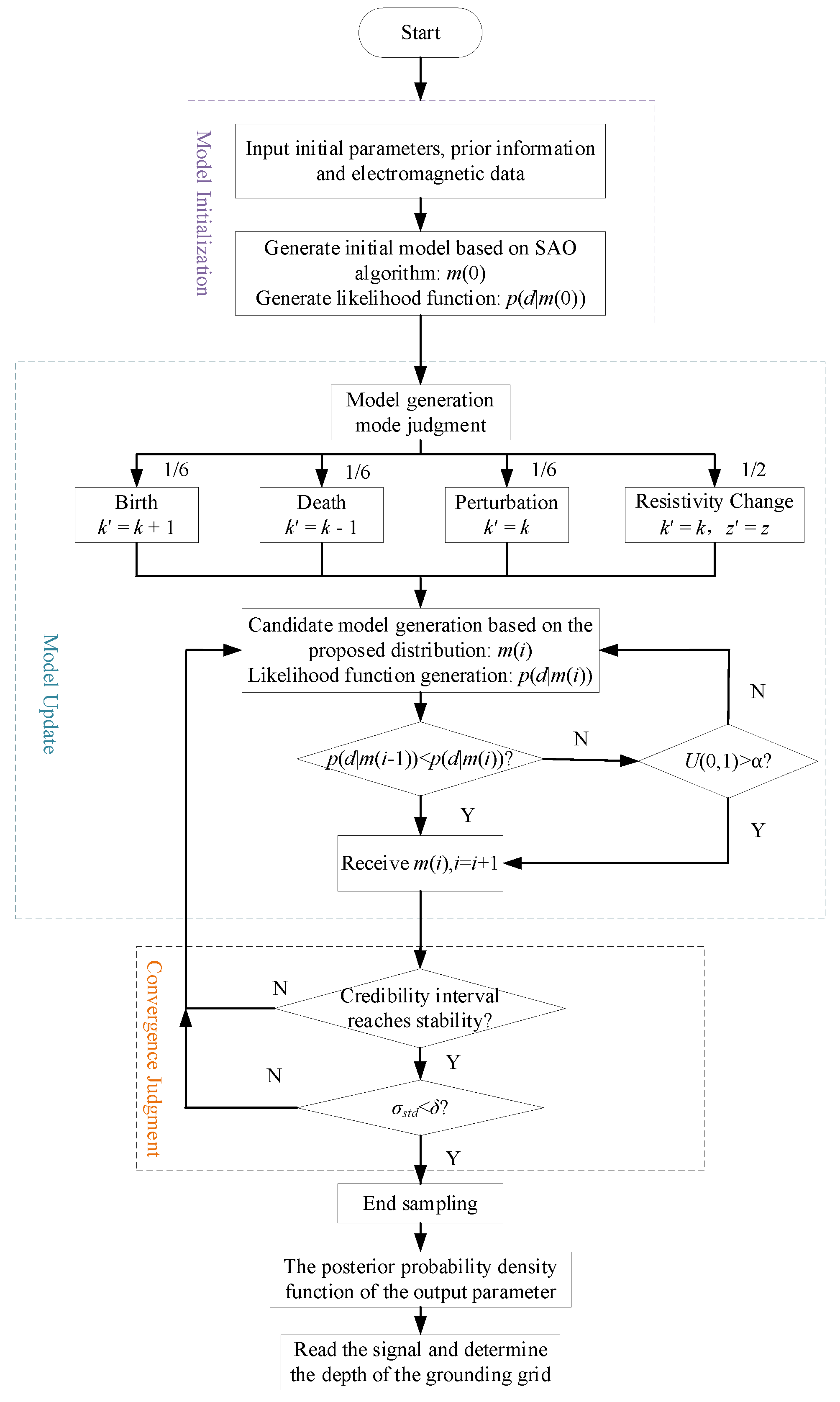
3.3. RJMCMC Method Improvement
- (1)
- Model Generation Based on Dual-Factor Control
- (2)
- Model Acceptance Probability Setup
3.4. Convergence Criterion for Uncertainty Assessment
4. Simulation Model Verification of Parameter Identification
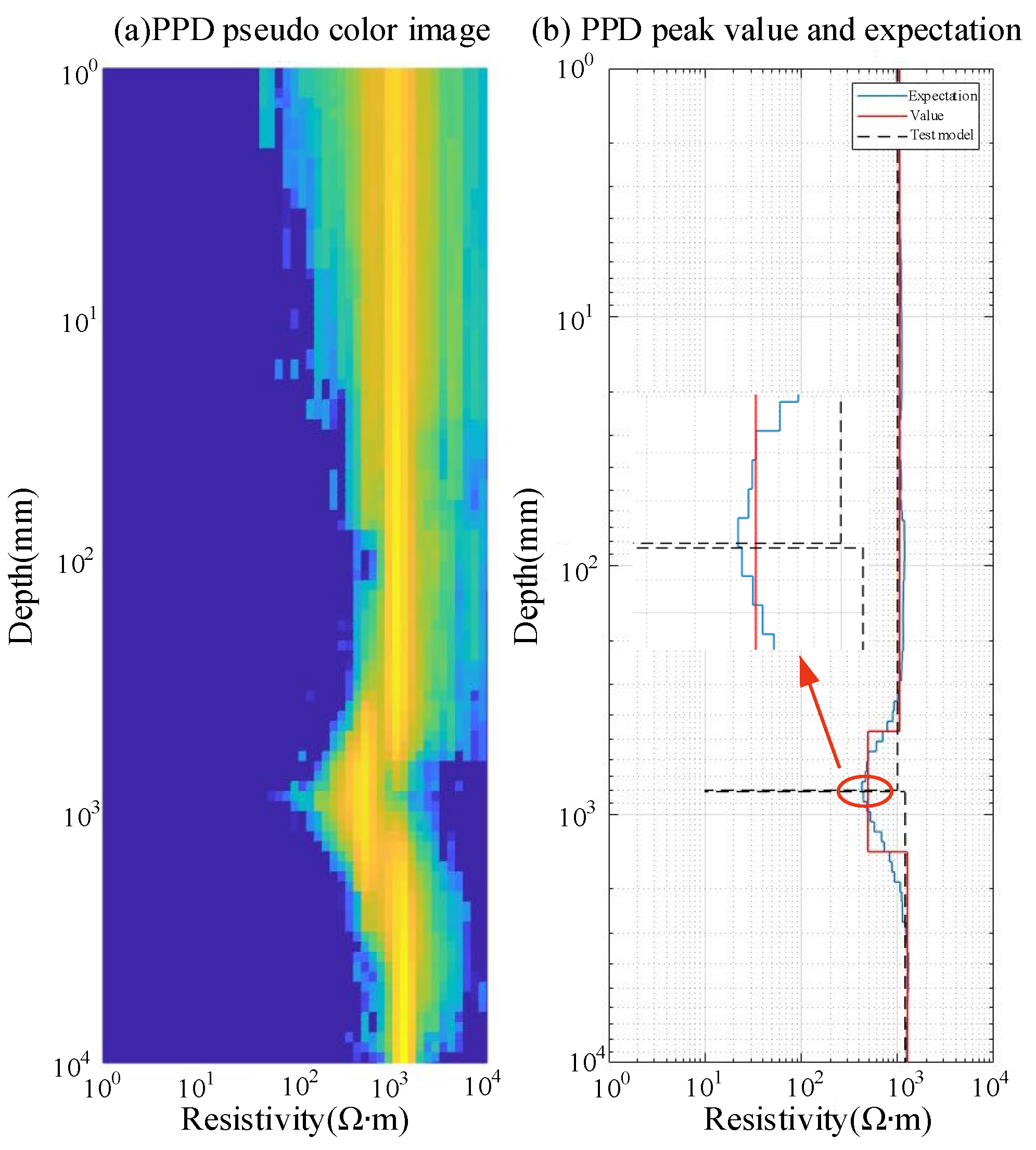
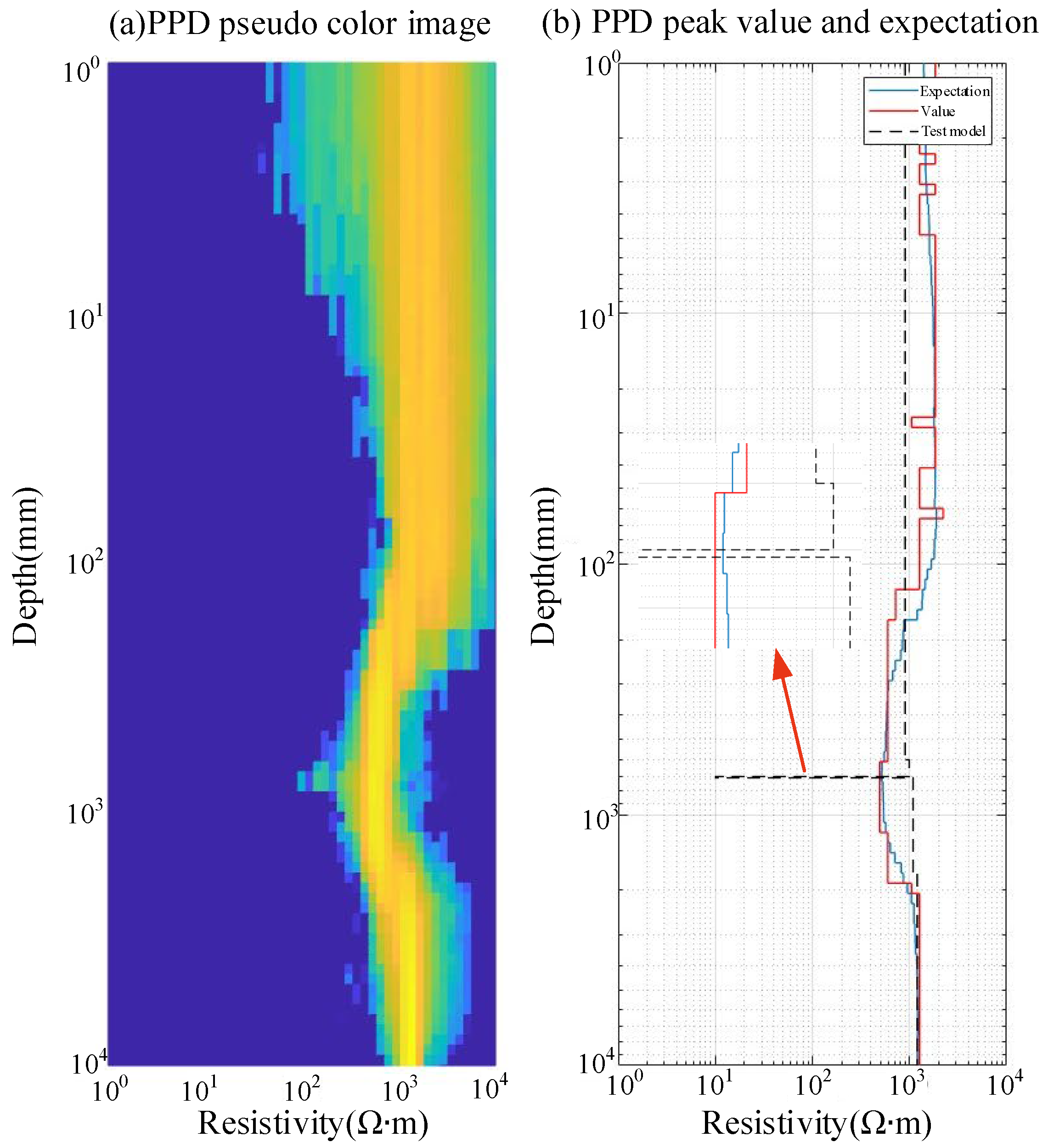
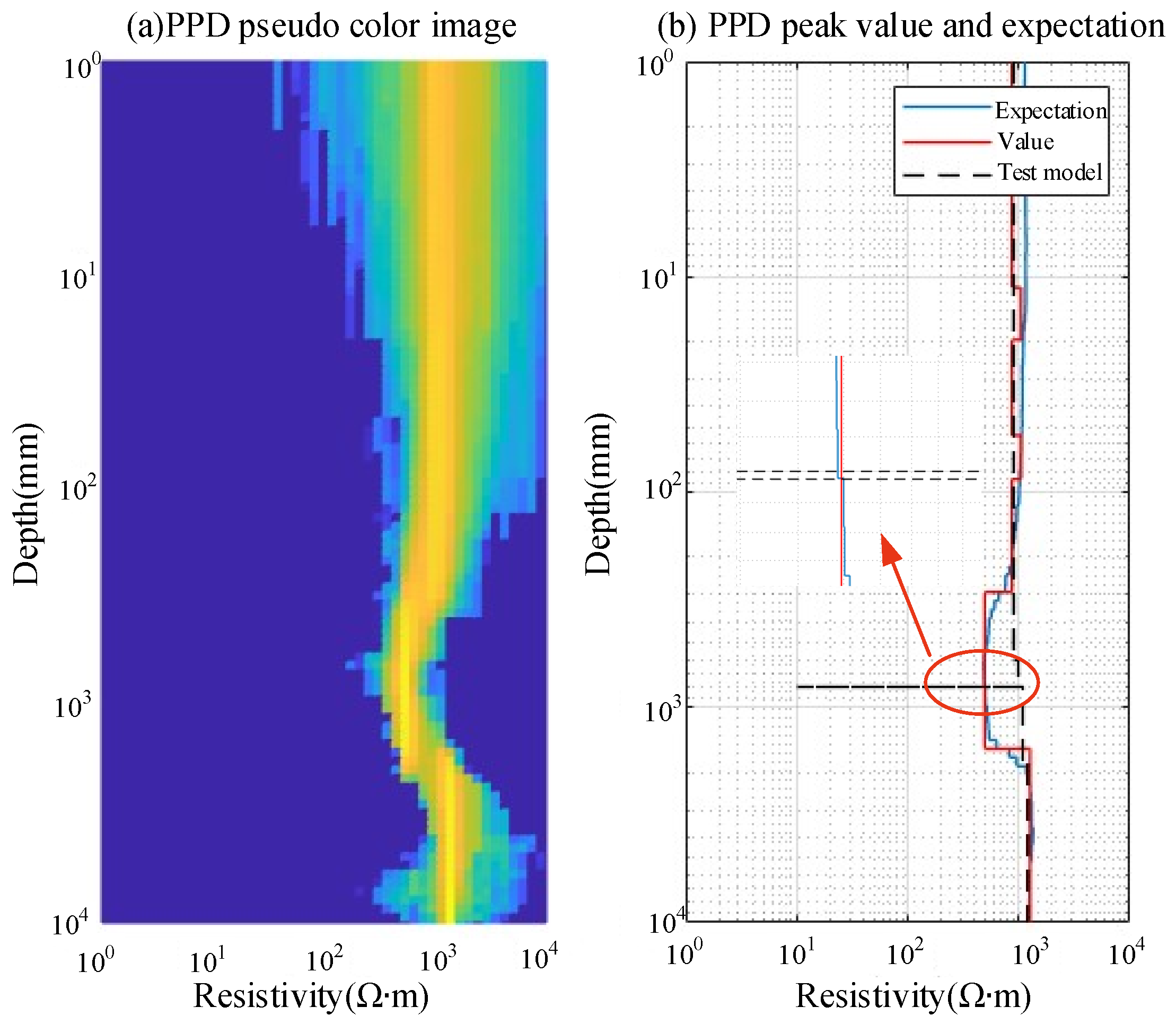
4.1. Parameter Identification Results for the H-Type Grounding Grid Model
4.2. Parameter Identification Results for Grounding Grid Depth Variation
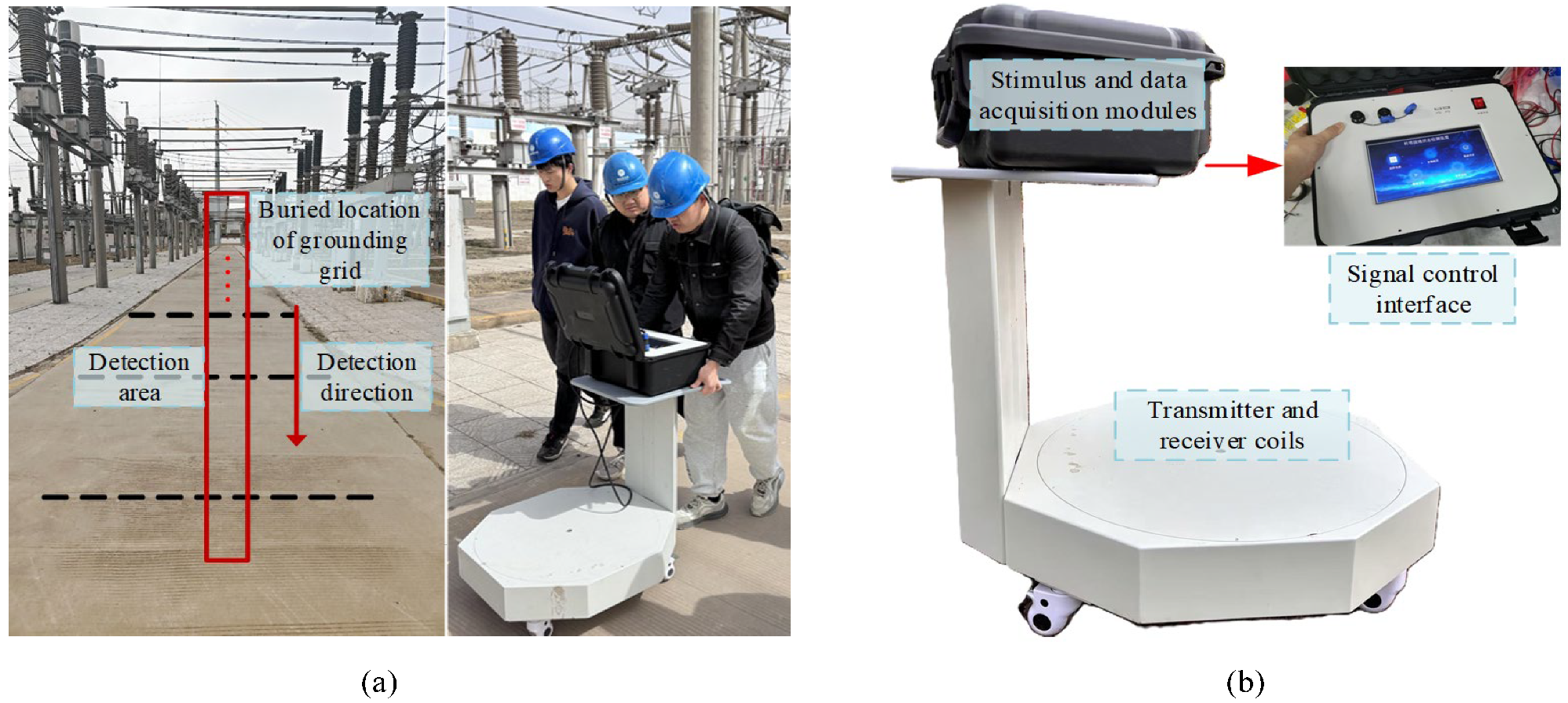
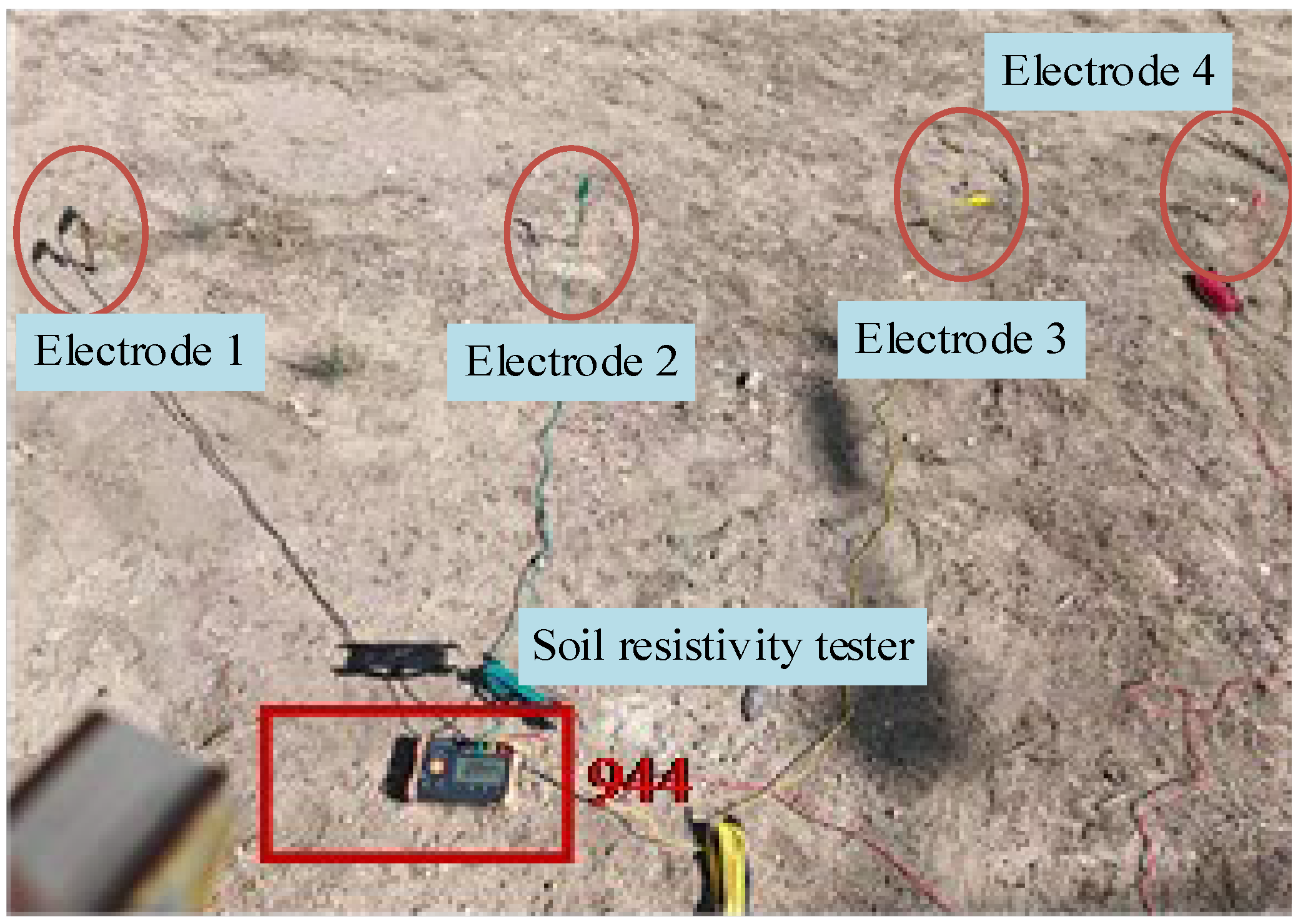
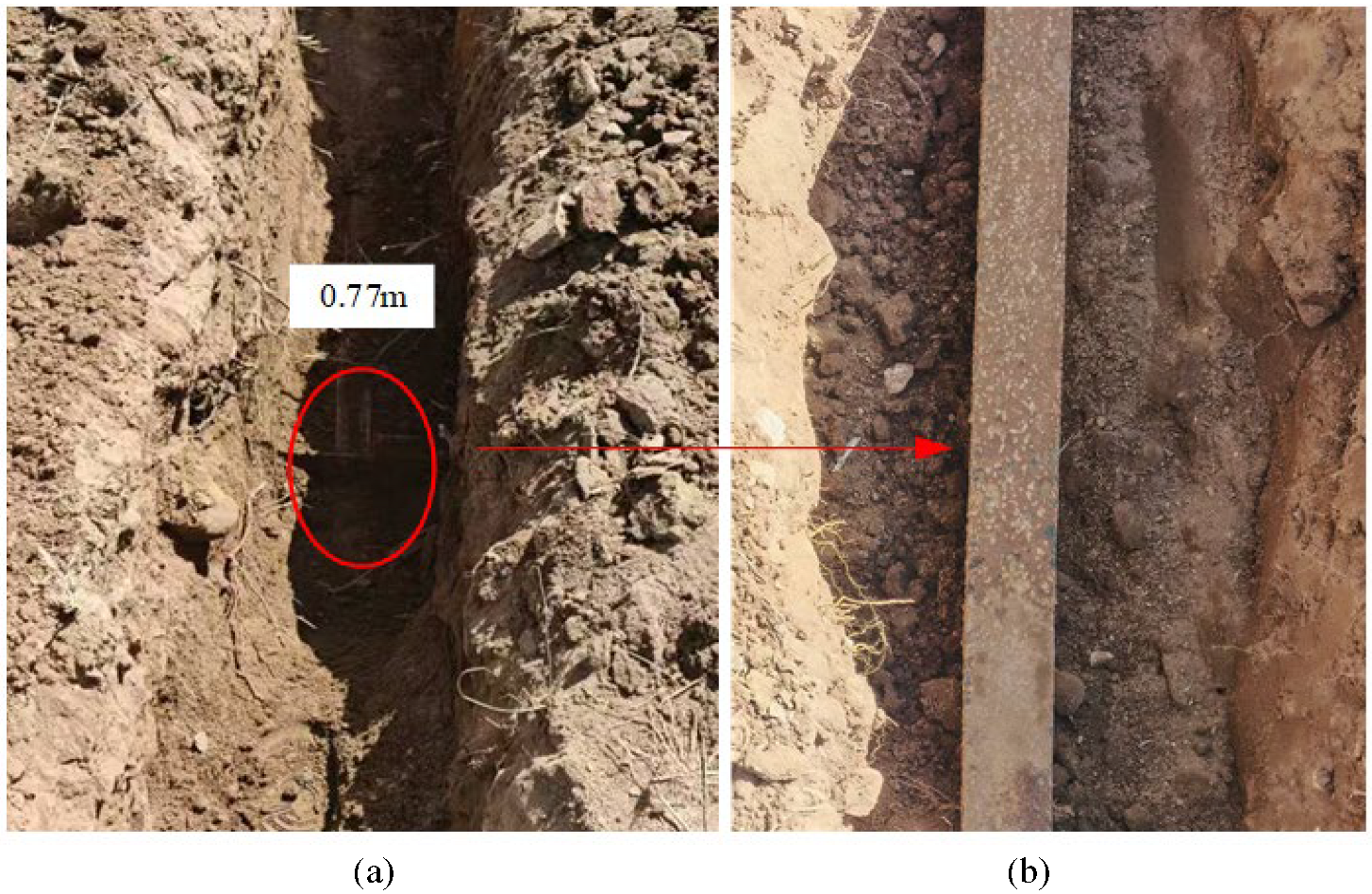
5. Experimental Validation
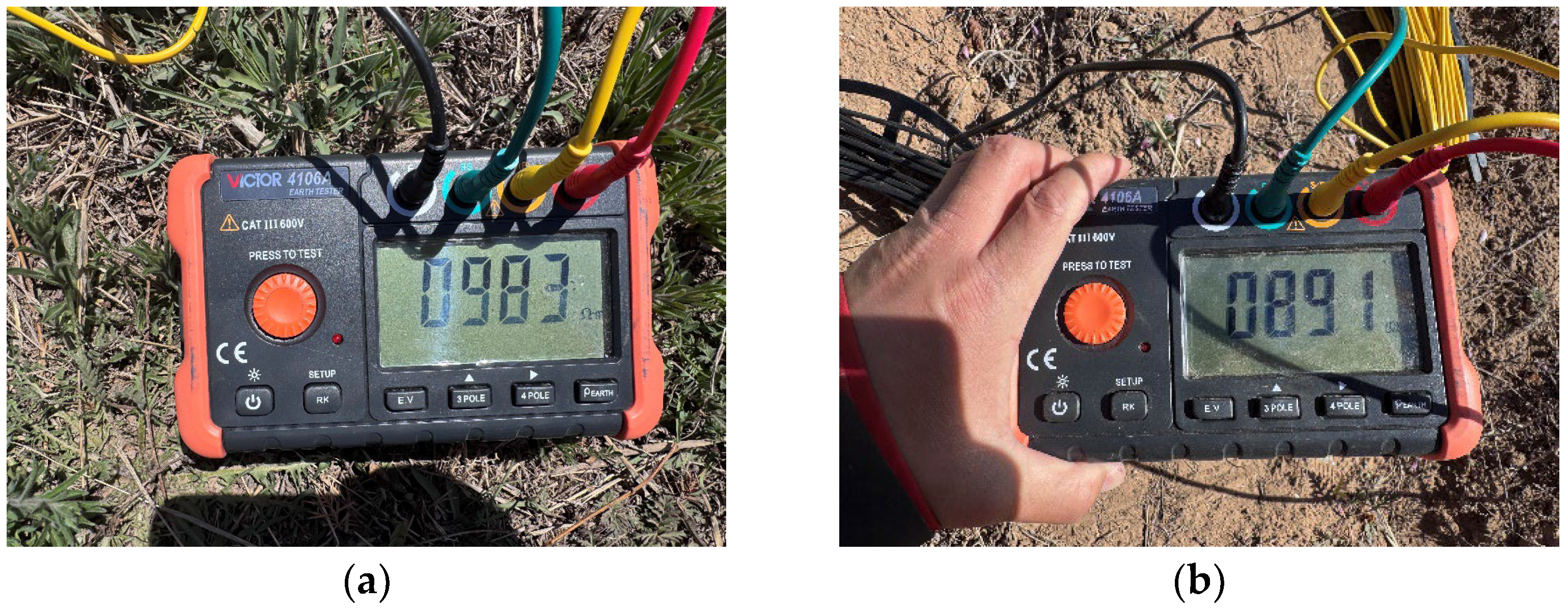
5.1. Experimental Process
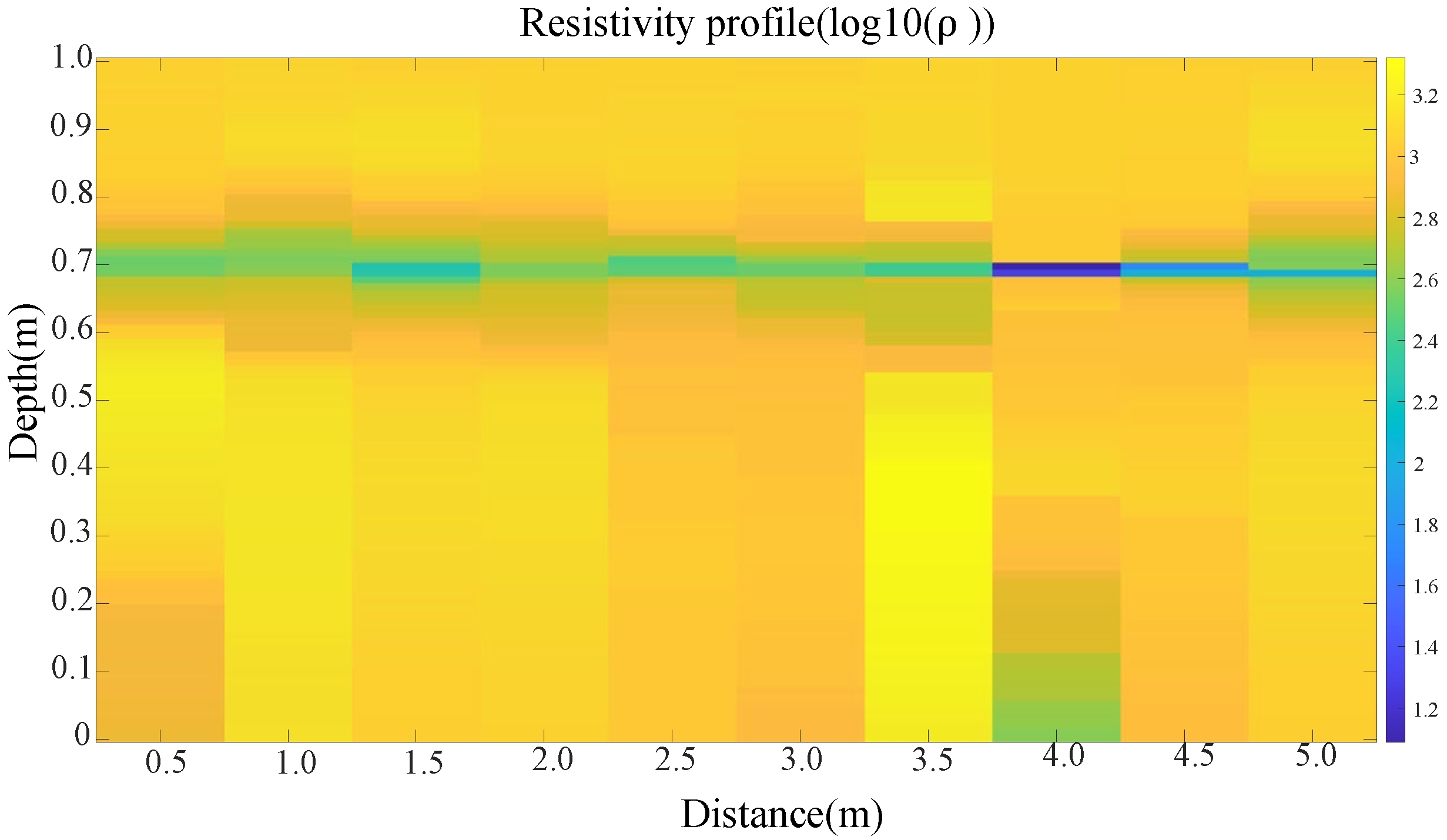
5.2. Parameter Identification Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; He, J.L.; Zeng, R. State of art and prospect of grounding technology in power system. High Volt. Eng. 2015, 41, 2569–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y. Research on Fault Diagnosis for Grounding Grid in Substation Based on Tikhonov Regularized Principle. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Luo, B.; Yan, F.; Zhang, H. Study on numerical simulation of electromagnetic response of intelligent substation grounding grid based on multi-grid partitioning technology. Electr. Meas. Instrum. 2024, 61, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.S.; Sun, H.Y.; Li, S.S.; Wang, S.; Huang, S.L. Mix-frequency SH guided wave corrosion defects detection method for high voltage transmission tower grounding electrode. Trans. China Electrotechn. Soc. 2025, 40, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liao, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, N.; Fu, Z. Research on Small-Loop Transient Electromagnetic Method Forward and Nonlinear Optimization Inversion Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Lei, Y.Z. Analytical expressions of induced coil voltages generated by pulsed eddy currents for metal pipe testing. Proc. CSEE 2012, 32, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Fu, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, X.; Bao, M. Configuration Detection of Substation Grounding Grid Using Transient Electromagnetic Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6475–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, S. Thickness measurement and surface-defect detection for metal plate using pulsed eddy current testing and optimized Res2Net network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J. Modelling and experimental study on pipeline defect characterisations using a pulsed eddy current measurement. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2024, 40, 4024–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.W.; Guo, Z.; Gan, F.; Zuo, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Array coil design and experimental verification for separation of tower grounding pulsed eddy current excitation and response magnetic field signals. Energies 2025, 18, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, P.; Huang, L.; Meng, C. A Time-Domain Calibration Method for Transient EM Field Sensors. Measurement 2021, 168, 108368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tai, H.-M.; Chen, W. On-Site Calibration of Air-Coil Sensor for Transient Electromagnetic Exploration. Geophys. Prospect. 2019, 67, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Q.; Yan, L.; Lu, Y. Fault detection method of substation ground grid based on transient electromagnetic method. In International Conference of Electrical, Electronic and Networked Energy Systems; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Xue, G.; Lei, K.; Song, W. Transient electromagnetic smoke ring due to a grounded-wire source. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiarowski, A.; Hodges, G. Transient electromagnetic smoke rings in a half-space during active transmitter excitation. Geophysics 2021, 86, E199–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasion, L.R. Detecting Unexploded Ordnance with Time Domain Electromagnetic Induction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Jiang, H. Fast localization of underground targets by magnetic gradient tensor and Gaussian-Newton algorithm with a portable transient electromagnetic system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 148469–148478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fang, D.; Zhu, J. A high-performance portable transient electromagnetic sensor for unexploded ordnance detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Luan, X. Accurate measurement of characteristic response for unexploded ordnance with transient electromagnetic system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Luan, X.; Liu, Z. Improved differential evolution algorithm for multi-target response inversion detected by a portable transient electromagnetic sensor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 208107–208119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimić, M.; Ambruš, D.; Bilas, V. Rapid object depth estimation from position-referenced EMI data using machine learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimić, M. Machine Learning Based OBJECT classification from Pulse Induction Metal Detector Data. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Xing, K.; Zheng, Y. Fast inversion of subsurface target electromagnetic induction response with deep learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Applicability of transient electromagnetic fast forward modeling algorithm with small loop. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2020, 98, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptasarma, D. New digital linear filters for Hankel J0 and J1 transforms. Geophys. Prospect. 2010, 45, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
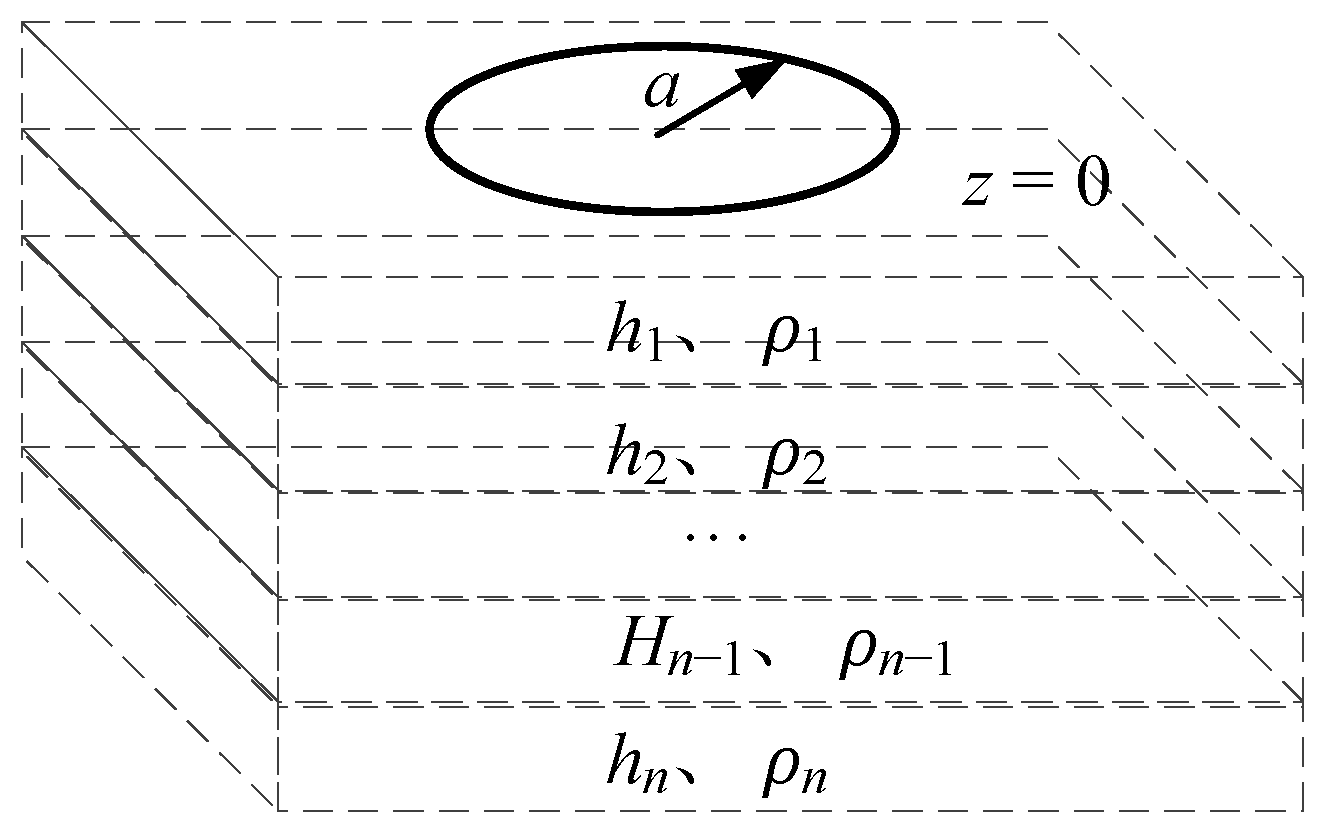


| Resistivity | Unit (Ω∙m) | Thickness | Unit (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ1 | 900 | h1 | 0.8 |
| ρ2 | 1/(5.6 × 106) | h2 | 0.012 |
| ρ3 | 1000 | h3 | ∞ |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Minimum Number of Model Layer Interfaces | 3 |
| Maximum Number of Model Layer Interfaces | 10 |
| Number of Burn-in Phases | 10,000 |
| Total Number of Samples | 1,000,000 |
| Number of Markov Chains | 1 |
| Resistivity Update Step Size σchange | 4 |
| Layer Interface Perturbation Step Size σmove | 10 |
| New Layer Generation Step Size σbirth | 4 |
| ρ (Ω∙m) | 100 < ρ ≤ 500 | 500 < ρ ≤ 1000 | 1000 < ρ ≤ 2000 | >2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | ≥0.6 | ≥0.5 | ≥0.5 | ≥0.3 |
| Maximum Length (m) | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| Measuring Point | Measured Value z (m) | True value zreal (m) | Error Err |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 7.89% |
| 2 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 6.41% |
| 3 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 7.79% |
| 4 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 8.00% |
| 5 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 10.13% |
| 6 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 7.89% |
| 7 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 8.97% |
| 8 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 6.49% |
| 9 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 6.76% |
| 10 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 8.97% |
| 11 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 6.67% |
| Measuring Point | Measured Value z (m) | True Value zreal (m) | Error Err |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 8.16% |
| 2 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 7.92% |
| 3 | 1.01 | 1.11 | 9.01% |
| 4 | 1.05 | 0.96 | 9.38% |
| 5 | 0.94 | 1.02 | 7.84% |
| 6 | 1.04 | 0.96 | 8.33% |
| 7 | 1.06 | 0.97 | 9.28% |
| 8 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 7.77% |
| 9 | 0.94 | 1.04 | 9.62% |
| 10 | 0.97 | 1.06 | 8.49% |
| Measuring Point | Measured Value z (m) | True Value zreal (m) | Error Err |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.29 | 1.18 | 9.32% |
| 2 | 1.31 | 1.19 | 10.08% |
| 3 | 1.11 | 1.21 | 8.26% |
| 4 | 1.12 | 1.20 | 6.67% |
| 5 | 1.32 | 1.20 | 10.00% |
| 6 | 1.27 | 1.16 | 9.48% |
| 7 | 1.09 | 1.18 | 7.63% |
| 8 | 1.12 | 1.23 | 8.95% |
| 9 | 1.11 | 1.21 | 8.26% |
| 10 | 1.10 | 1.19 | 7.56% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, X.; Li, Z.; Hou, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Variable Dimensional Bayesian Method for Identifying Depth Parameters of Substation Grounding Grid Based on Pulsed Eddy Current. Energies 2025, 18, 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174649
Kang X, Li Z, Hou J, Xu S, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Wang J. Variable Dimensional Bayesian Method for Identifying Depth Parameters of Substation Grounding Grid Based on Pulsed Eddy Current. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174649
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Xiaofei, Zhiling Li, Jie Hou, Su Xu, Yanjun Zhang, Zhihao Zhou, and Jingang Wang. 2025. "Variable Dimensional Bayesian Method for Identifying Depth Parameters of Substation Grounding Grid Based on Pulsed Eddy Current" Energies 18, no. 17: 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174649
APA StyleKang, X., Li, Z., Hou, J., Xu, S., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Z., & Wang, J. (2025). Variable Dimensional Bayesian Method for Identifying Depth Parameters of Substation Grounding Grid Based on Pulsed Eddy Current. Energies, 18(17), 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174649







