Hierarchical Distributed Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch Strategy for Regional Integrated Energy System Based on ADMM
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
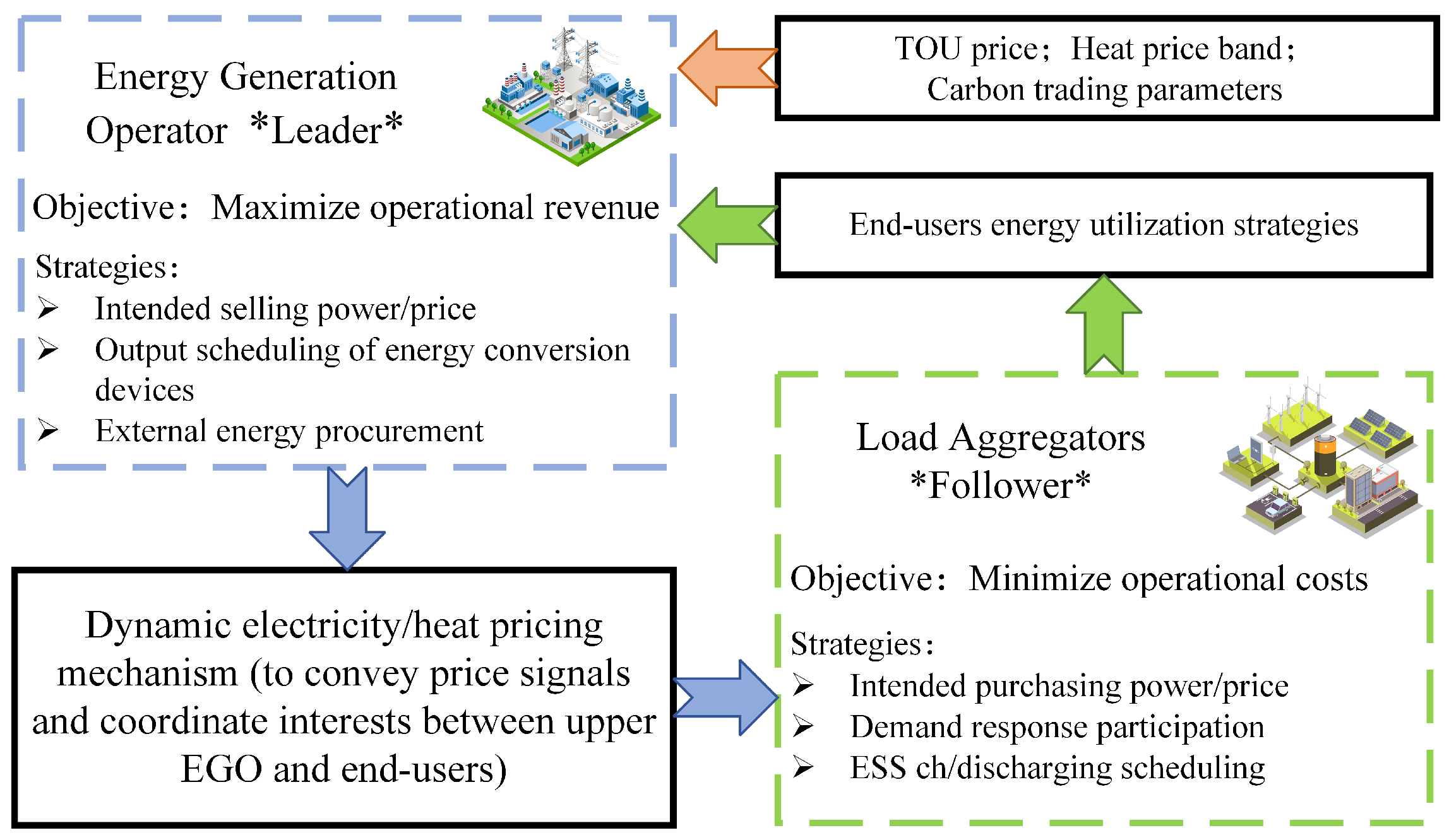
- A low-carbon operation framework for RIES incorporating EGO and LAs has been established, proposing a hierarchical distributed low-carbon economic dispatch strategy for RIESs. Conflicting EGO and LAs are embedded in a Stackelberg game framework to ensure optimal energy trading strategies for both parties. In the energy trading process, EGO acts as the upper-level leader while LAs serve as lower-level followers.
- 2.
- To meet the low-carbon requirements of RIESs, P2G-CCS equipment has been introduced into the RIES operation framework to achieve energy recycling. During the establishment of optimal operation models for EGO and LAs, a stepwise carbon trading mechanism (SCTM) and the PMV index have been incorporated, respectively, further enhancing the system’s low-carbon economic operation capability.
- 3.
- Based on the proven existence of the Stackelberg equilibrium solution in the multi-agent master–slave game transaction model, an ADMM-based approach is proposed to decouple the energy–power and energy–price balance coupling constraints between the leader and followers. Using the McCormick envelope relaxation method, operators’ optimization subproblems are transformed into convex optimization problems to solve the Stackelberg game transaction model, improving solution efficiency. Since only marginal power–price information needs to be exchanged between the leader and followers, the issue of information leakage among energy trading operators is avoided.
2. Bi-Level Optimization Scheduling Framework
2.1. Stackelberg Game Framework
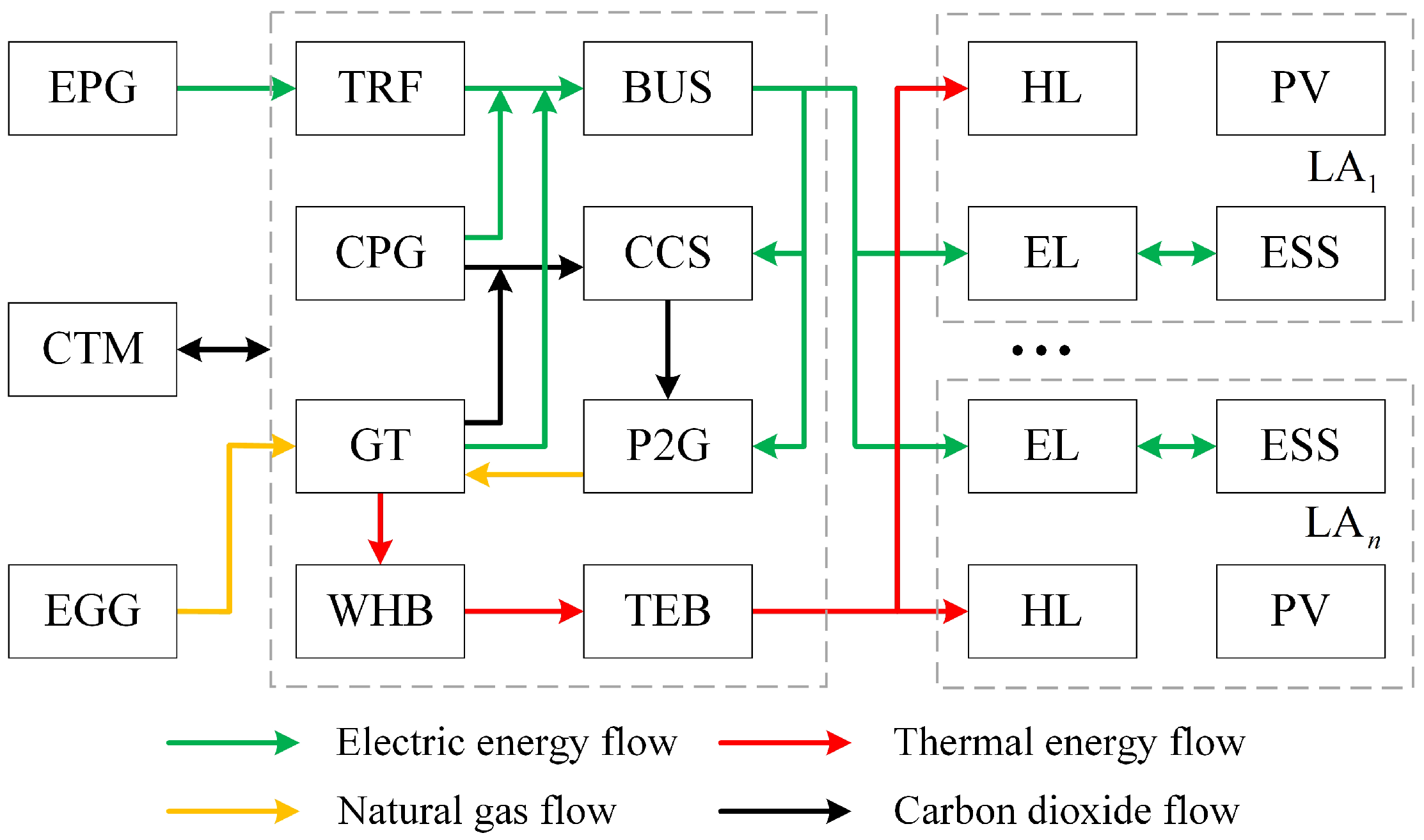
2.2. RIES Architecture Incorporating EGO and LAs
3. Optimization Models for Operators
3.1. Energy Generation Operator
3.1.1. Objective Function
3.1.2. Constraints
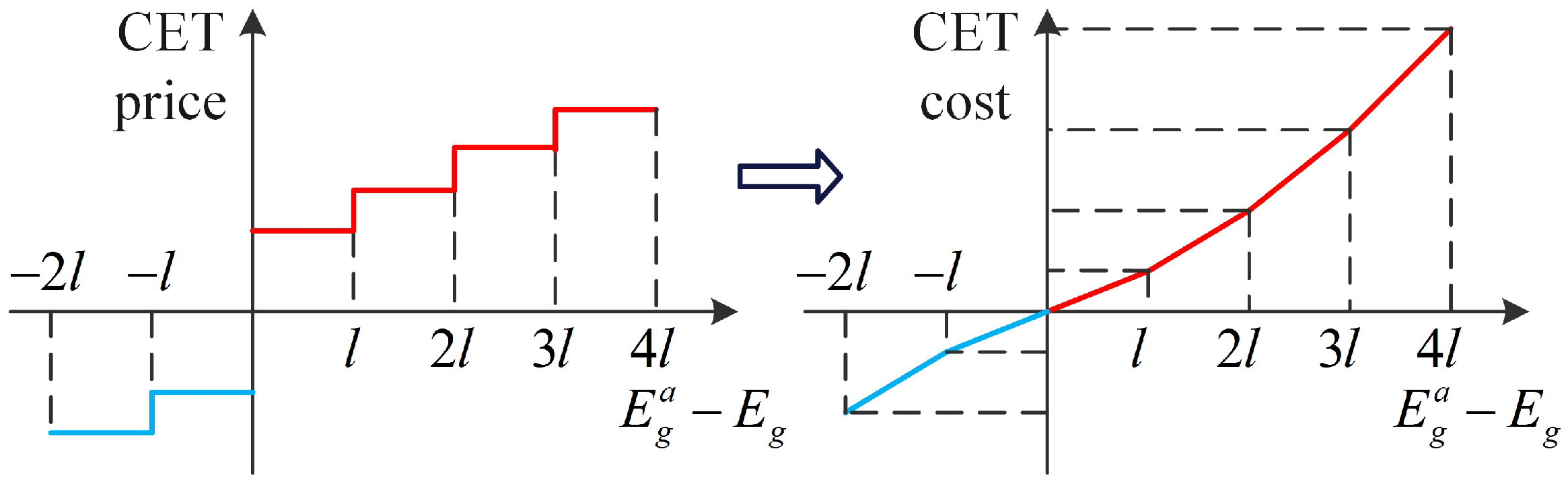
3.2. Stepwise Carbon Trading Mechanism
3.2.1. Carbon Emission Quota
3.2.2. Actual Carbon Emissions
3.2.3. Carbon Trading Costs
3.3. Load Aggregator
3.3.1. Objective Function
3.3.2. Thermal Energy Purchase Strategy Based on Thermal Inertia and PMV
3.3.3. Constraints
4. Distributed Optimization Problem Solving
4.1. Proof of the Stackelberg Game Model
4.1.1. Analysis of the Stackelberg Game Model
4.1.2. Existence Proof of Game Equilibrium
- 1.
- The leader’s strategy set is a non-empty, convex, and bounded subset of the Euclidean space.
- 2.
- The leader’s objective function is a non-empty continuous function on its strategy set .
- 3.
- The follower’s objective function is a non-empty continuous function on its strategy set .
- 4.
- The follower’s objective function is a quasi-convex function with respect to its own strategy.
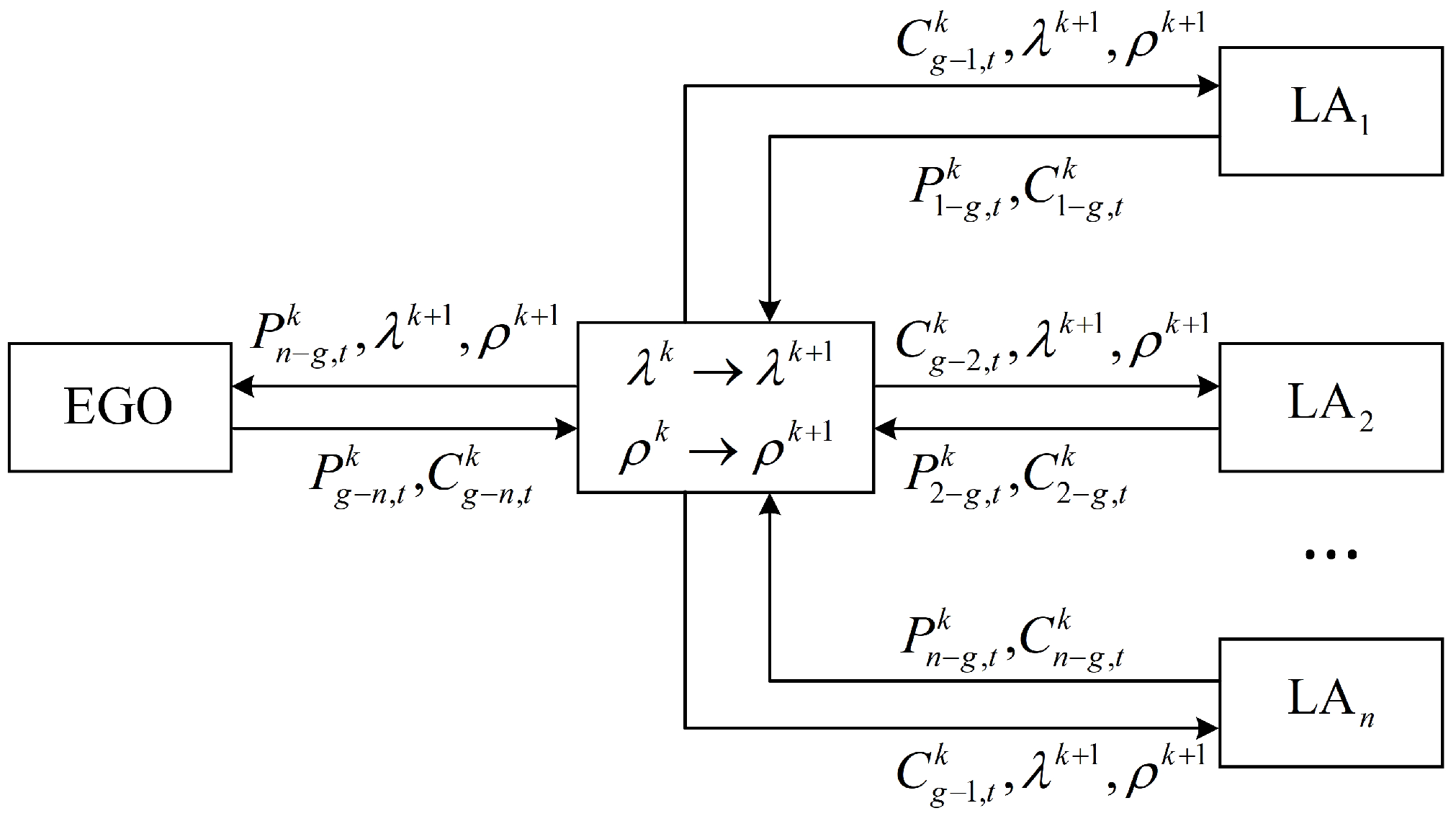
4.2. Distributed Optimization Problem
4.3. Nonlinear Term Processing
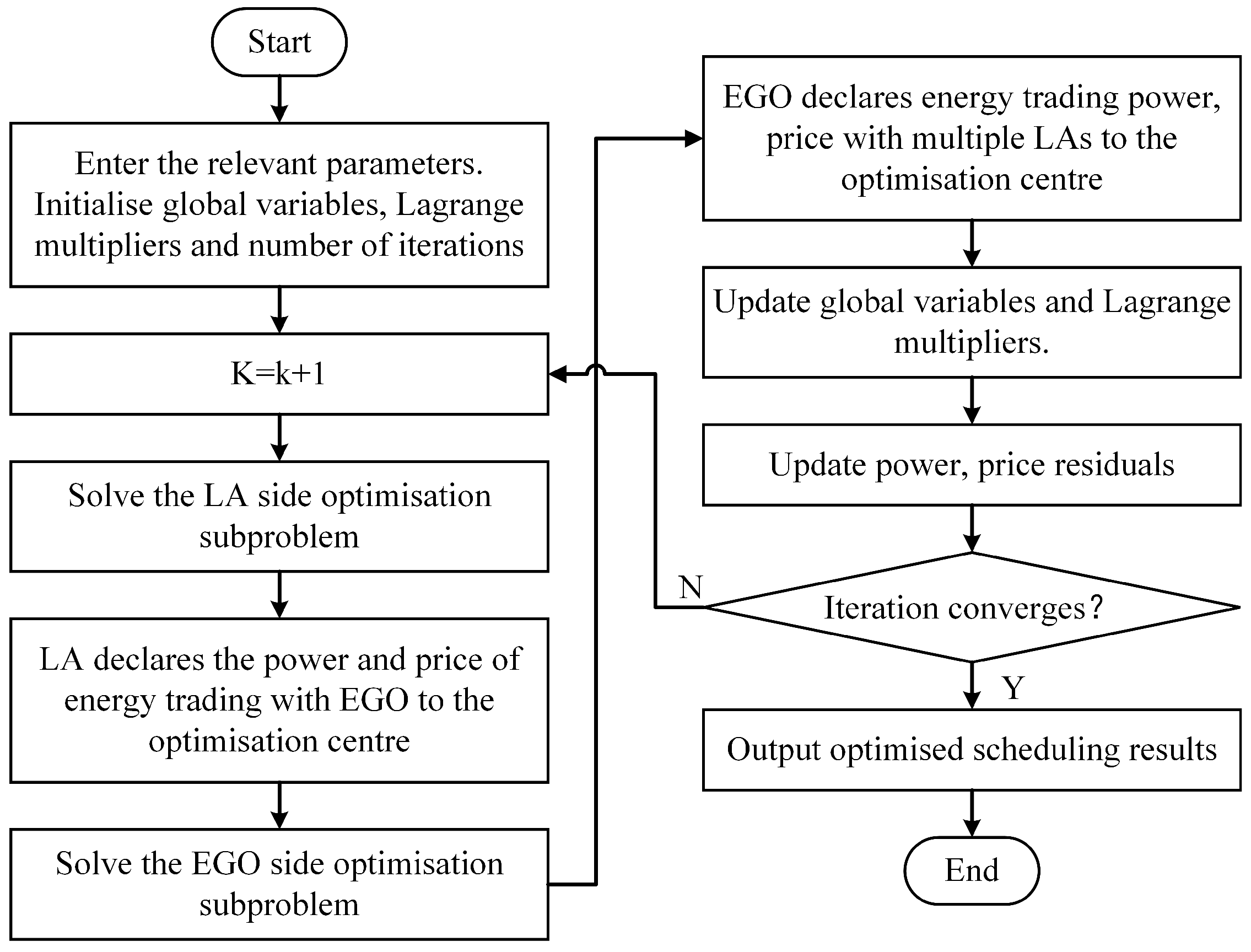
4.4. Optimization Problem Solving Procedure
- (1)
- Set the number of iterations and the convergence margin value, set the initial values of the global variables, the Lagrange multiplier, the penalty factor, the power residual, and the price residual, and set the number of iterations k to zero.
- (2)
- .
- (3)
- Solving subproblems.The upper and lower subproblems are solved separately and in parallel by the corresponding computational bodies.
- (4)
- Updating parameters.Update global variables, Lagrange multipliers, power residuals, and price residuals. Update the global variables according to Equation (61).Update power residuals and price residuals according to Equations (64) and (65).where and are the residual sets for the sold and purchased electricity power; and are the residual sets for the sold and purchased thermal power; and are the residual sets for the sold and purchased electricity price; and and are the residual sets for the sold and purchased thermal price.
- (5)
- Determine whether the current residuals satisfy the ADMM convergence determination condition according to Equation (66).where and are the sum of power residuals and price residuals; and are the convergence margins of power residuals and price residuals.
5. Calculus Analysis
- Modeling stage: Construct the optimal operation model of the EGO and LAs.
- Digital simulation: Verify the convergence of the algorithm and the speed of solving the optimization problem on the PSCAD/MATLAB platform.
- Hardware-in-the-loop testing: Connect the real controller with the real-time grid simulation equipment through the RT-LAB platform to test the communication delay and control response time.
- On-site validation: The strategy is implemented through a layered distributed architecture (physical layer–edge layer–cloud): the terminal equipment collects data, the edge controllers perform local fast response (demand management, energy storage control), and the virtual power plant platform in the cloud coordinates the global optimization to ensure that the regulation delay meets the requirements by combining the 5G/fiber optic hybrid communication.
5.1. Case Configuration
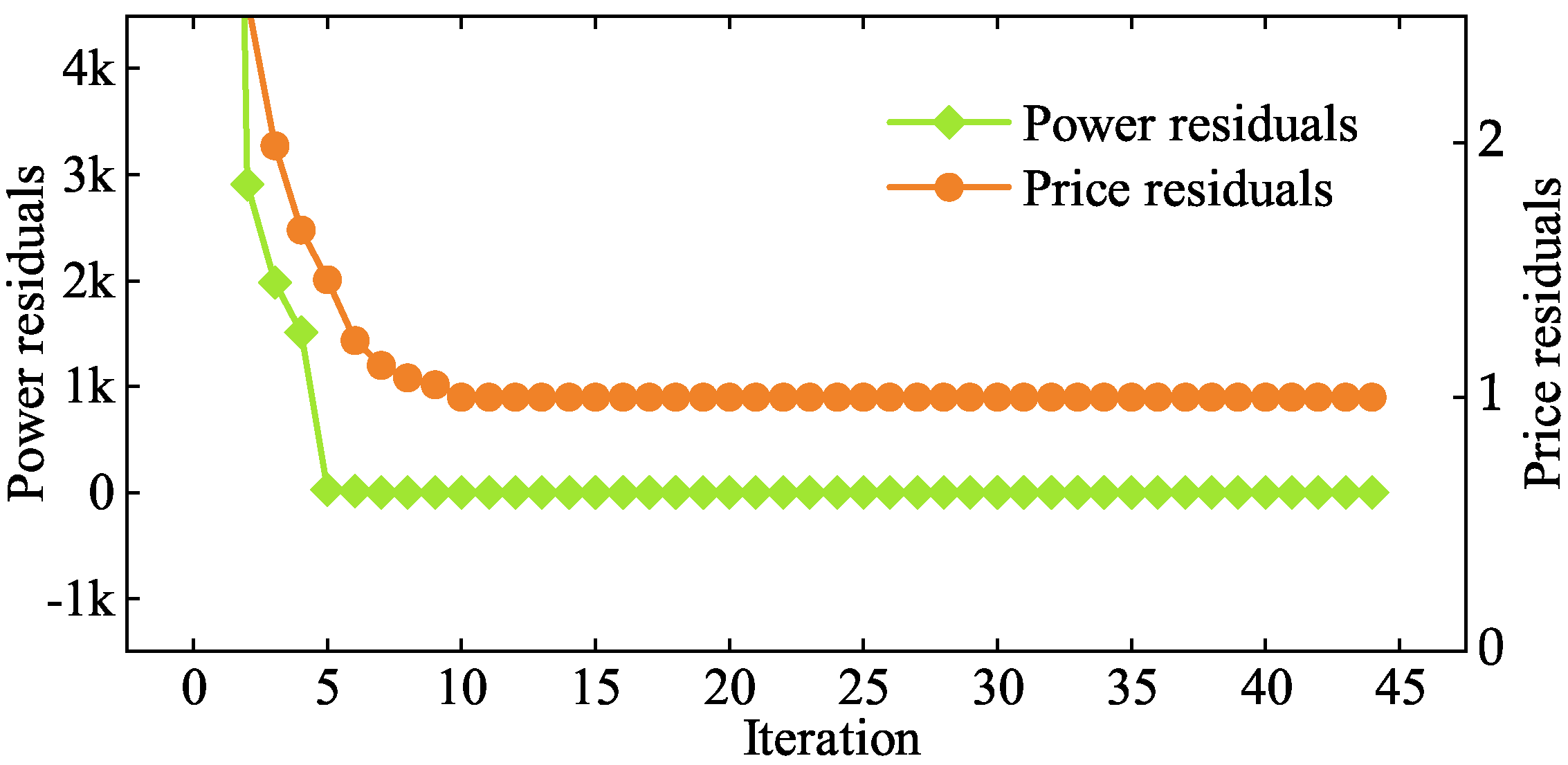
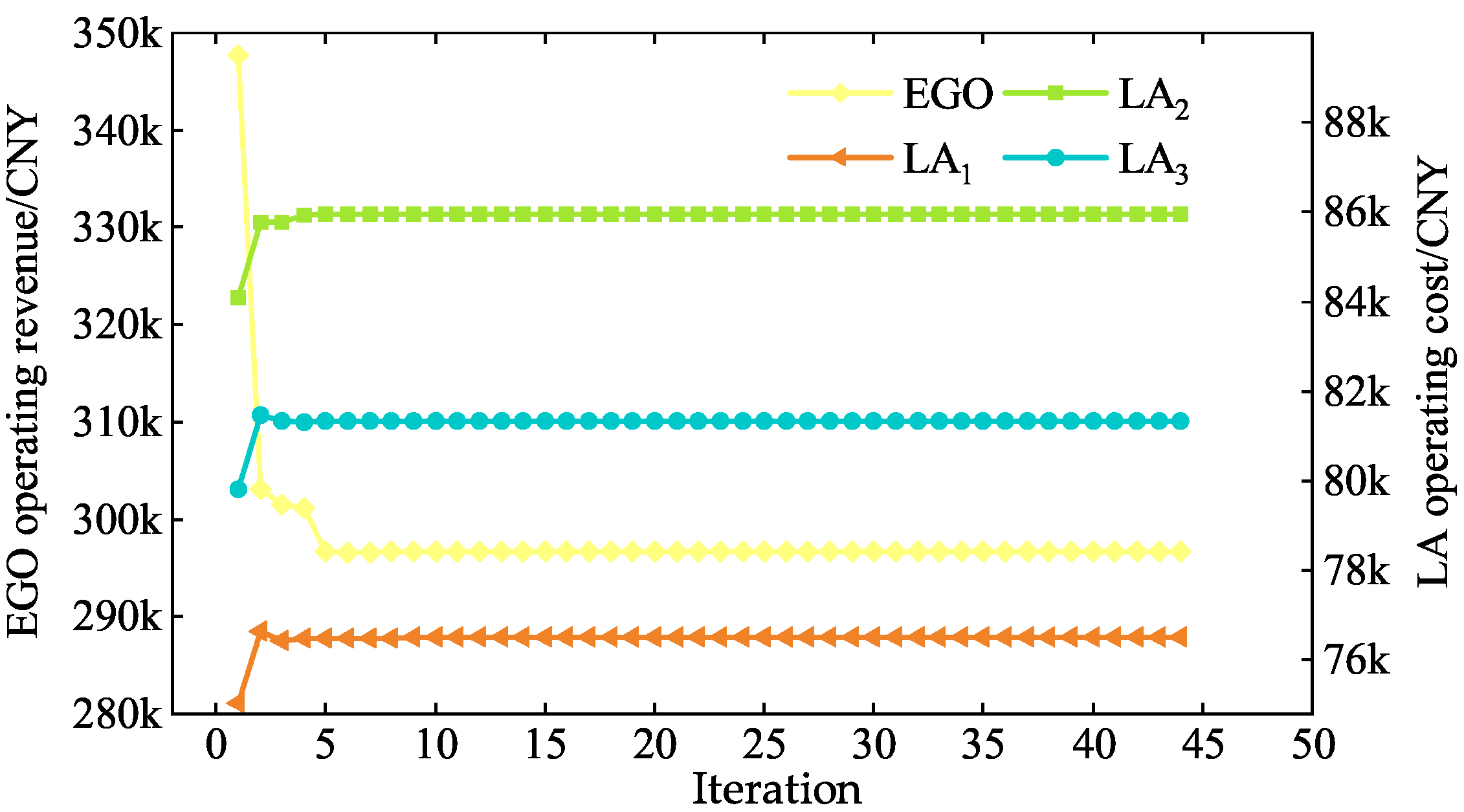
5.2. Optimal Dispatch Results
5.2.1. EGO Operating Optimization Analysis
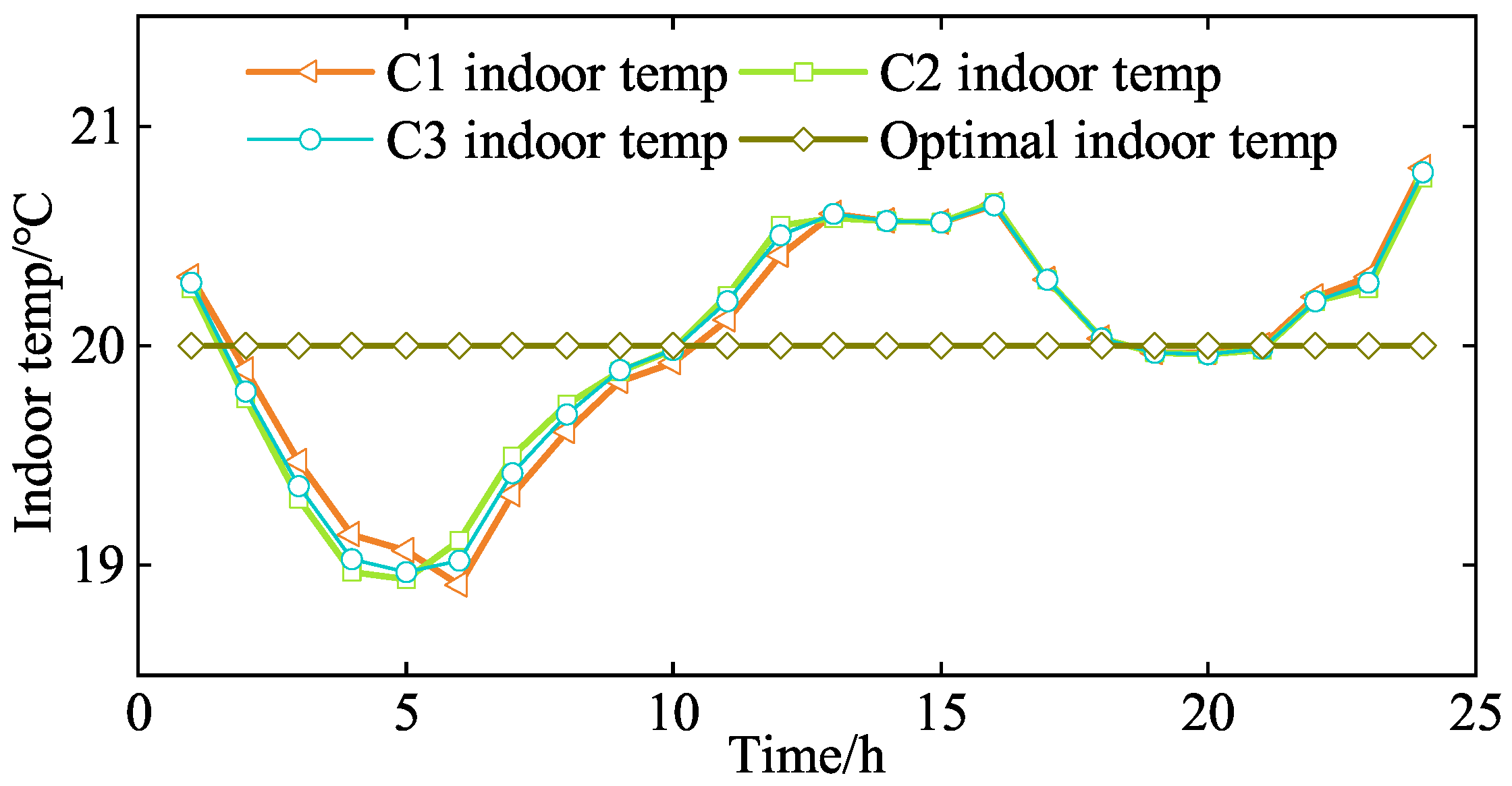
5.2.2. LAs Operating Optimization Analysis
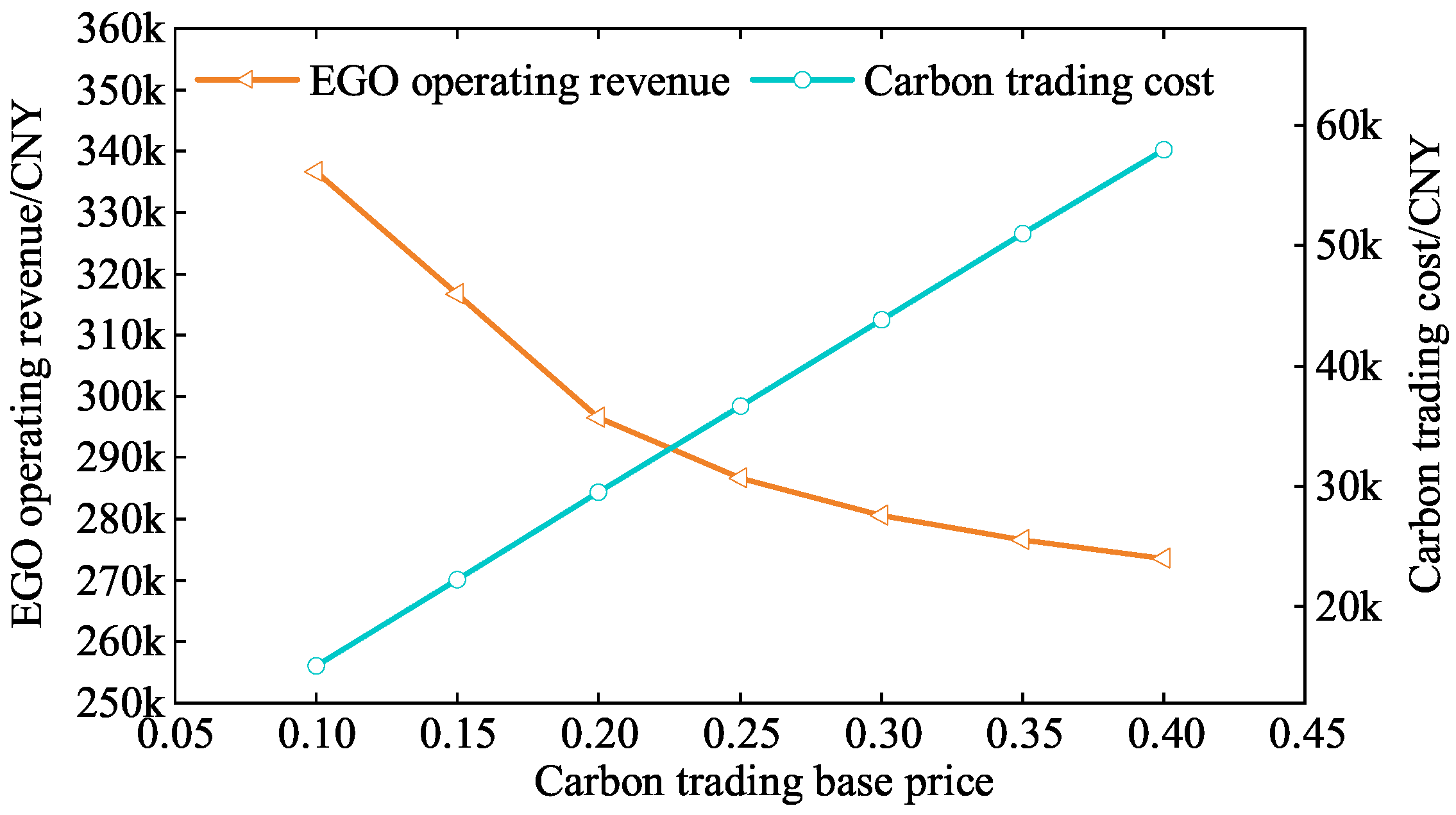
5.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5.4. Scalability Analysis
- Algorithmic level: Firstly, strengthen the distributed algorithm, adopt asynchronous ADMM algorithm to reduce the communication waiting time, and dynamically adjust the parameters to accelerate the convergence; secondly, implement the hierarchical optimization strategy, divide the LA group into multiple sub-systems according to the region, and optimize locally first and then realize the global synergy through the coordination layer.
- Model structure level: Modular design can be used to encapsulate the LA and EGO functional modules, and only the corresponding modules need to be added when adding new LAs. Secondly, the parameters can be dynamically adjusted to establish the mapping relationship between the parameters and the system scale and LA characteristics, such as optimizing the load forecast coefficients according to user types. Finally, robust optimization can be extended to incorporate load and new energy uncertainty into interval constraints to improve anti-interference capability.
- Communication architecture level: Optimize topology, adopt hierarchical distributed communication, use tree topology between the EGO and LA, and design redundant links; choose MQTT lightweight protocol, customize message format and compress data, and encrypt for security.
5.5. Comparative Case Analysis
6. Conclusions
- Effectiveness of the RIES distributed optimal dispatch: The proposed hierarchical distributed low-carbon economic dispatch strategy for the RIES, based on the ADMM, effectively coordinates the interests of the energy trading parties, achieving efficient and economic system operation. Case studies demonstrate that this strategy exhibits significant advantages in enhancing the economic benefits for all stakeholders and improving user energy consumption flexibility.
- Positive impact on system emission reduction: The introduction of SCTM, P2G-CCS, and user thermal energy demand response leads to a significant reduction in the system’s actual carbon emissions. This indicates that the series of measures proposed in this study, including carbon emission pricing and carbon management via P2G-CCS, prompts enterprises to pay greater attention to their carbon emission behaviors. Consequently, these mechanisms effectively promote a broader societal shift towards a low-carbon lifestyle. This approach not only contributes to achieving the “Dual Carbon” goals but also provides economic incentives for enterprises, fostering a win–win outcome for both environmental protection and economic benefits.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IES | Integrated energy system |
| RIES | Regional integrated energy system |
| ADMM | Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers |
| EGO | Energy generation operator |
| LA | Load aggregator |
| SCTM | Stepwise carbon trading mechanism |
| CHP | Combined heat and power |
| TOU | Time-of-use |
| FIT | Feed-in tariff |
| CTM | Carbon trading mechanism |
| SCTP | Stepwise carbon trading price |
| P2G | Power to gas |
| CCS | Carbon capture and storage |
| PMV | Predicted Mean Vote |
| CPG | Coal-fired power generator |
| WHB | Waste heat boiler |
| GT | Gas turbine |
| TRF | Transformer |
| BUS | Electrical bus |
| TEB | Thermal energy bus |
| ESS | Energy storage system |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| EPG | External power grid |
| CBP | Carbon trading base price |
| CGR | Carbon trading price growth rate |
| CET | Carbon emission trading |
| SOC | States of charge |
References
- Nadeem, T.B.; Siddiqui, M.; Khalid, M.; Asif, M. Distributed energy systems: A review of classification, technologies, applications, and policies. Energy Strategy Rev. 2023, 48, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, A.; Sijm, J.; Faaij, A. A systemic approach to analyze integrated energy system modeling tools: A review of national models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Meng, W.; Dong, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, L. A critical survey of integrated energy system: Summaries, methodologies and analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Gao, X. Research on Multi-Objective Parameter Matching and Stepwise Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Energy Storage Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Pan, H. Multi-Objective Optimization of Daylighting–Thermal Performance in Cold-Region University Library Atriums: A Parametric Design Approach. Energies 2025, 18, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Fan, H. Optimization Scheduling of Hydrogen-Integrated Energy Systems Considering Multi-Timescale Carbon Trading Mechanisms. Energies 2025, 18, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ni, G.; Jin, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, G. Multi-Timescale Battery-Charging Optimization for Electric Heavy-Duty Truck Battery-Swapping Stations, Considering Source–Load–Storage Uncertainty. Energies 2025, 18, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Chung, C.Y.; Wen, F. Coordinated Planning Strategy for Integrated Energy Systems in a District Energy Sector. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, N. A two-stage distributed robust optimal control strategy for energy collaboration in multi-regional integrated energy systems based on cooperative game. Energy 2024, 305, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, W.; Song, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, D. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Bi-layer Optimal Scheduling for Microgrids Considering Flexible Load Control. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Soares, J. Multi-agent system consistency-based cooperative scheduling strategy of regional integrated energy system. Energy 2024, 295, 130904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gao, C.; Meng, J.; Abbes, D. An analytical target cascading method-based two-step distributed optimization strategy for energy sharing in a virtual power plant. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Allahham, A.; Walker, S.L. Investment decisions in a liberalised energy market with generation and hydrogen-based vector coupling storage in Integrated Energy System: A game-theoretic model-based approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 166, 110518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, K. Multi-perspective collaborative planning of DN and distribution energy stations with stepped carbon trading and adaptive evolutionary game. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 166, 110522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Shi, P. Equilibrium Interaction Strategies for Integrated Energy System Incorporating Demand-Side Management Based on Stackelberg Game Approach. Energies 2024, 17, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wu, Q.; Guo, H.; Bai, J. Low-Carbon Optimization Scheduling of Integrated Energy Systems Based on Bilateral Demand Response and Two-Level Stackelberg Game. Energies 2024, 17, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Hierarchical stochastic scheduling of multi-community integrated energy systems in uncertain environments via Stackelberg game. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fedorovich, K.S. Optimal operation of multi-integrated energy system based on multi-level Nash multi-stage robust. Appl. Energy 2024, 358, 122557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wei, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, B. Blockchain-Enabled Intelligent Dispatching and Credit-Based Bidding for Microgrids. Electronics 2023, 12, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Dai, Z. Federated Reinforcement Learning for smart and privacy-preserving energy management of residential microgrids clusters. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, B.; Kang, C.; Xi, W.; Feng, M. Low-Carbon Operation of Multiple Energy Systems Based on Energy-Carbon Integrated Prices. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Li, Q.; Pu, Y.; Xie, S.; Chen, W. Low carbon dispatch method for hydrogen-containing integrated energy system considering seasonal carbon trading and energy sharing mechanism. Energy 2024, 308, 132794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Low carbon optimal operation of integrated energy system based on carbon capture technology, LCA carbon emissions and ladder-type carbon trading. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhu, R.; Kong, D.; Guo, H. Considering the Tiered Low-Carbon Optimal Dispatching of Multi-Integrated Energy Microgrid with P2G-CCS. Energies 2024, 17, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Geng, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, X. Low-carbon economic dispatch for electricity and natural gas systems considering carbon capture systems and power-to-gas. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Calautit, J.K.; Wei, S.; Tien, P.W. Real-time clothing insulation level classification based on model transfer learning and computer vision for PMV-based heating system optimization through piecewise linearization. Build. Environ. 2024, 253, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, L. Optimal Dispatching of Combined Heat-power System Considering Characteristics of Thermal Network and Thermal Comfort Elasticity for Wind Power Accommodation. Power Syst. Technol. 2019, 43, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xie, F. Low-carbon oriented planning of shared photovoltaics and energy storage systems in distribution networks via carbon emission flow tracing. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 160, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Huang, L.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X. Decentralized Dispatch of Multi-area Integrated Energy Systems With Carbon Trading. Proc. CSEE 2018, 38, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Gu, W.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Z.Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Ding, S. Unlock the Thermal Flexibility in Integrated Energy Systems: A Robust Nodal Pricing Approach for Thermal Loads. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 2734–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Energy Sharing Management for Microgrids With PV Prosumers: A Stackelberg Game Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xiang, Y. ADMM-Based Differential Privacy Learning for Penalized Quantile Regression on Distributed Functional Data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Shen, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhang, R.; Parisio, A.; Li, X.; Kou, X. Solution to Coordination of Transmission and Distribution for Renewable Energy Integration into Power Grids: An Integrated Flexibility Market. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

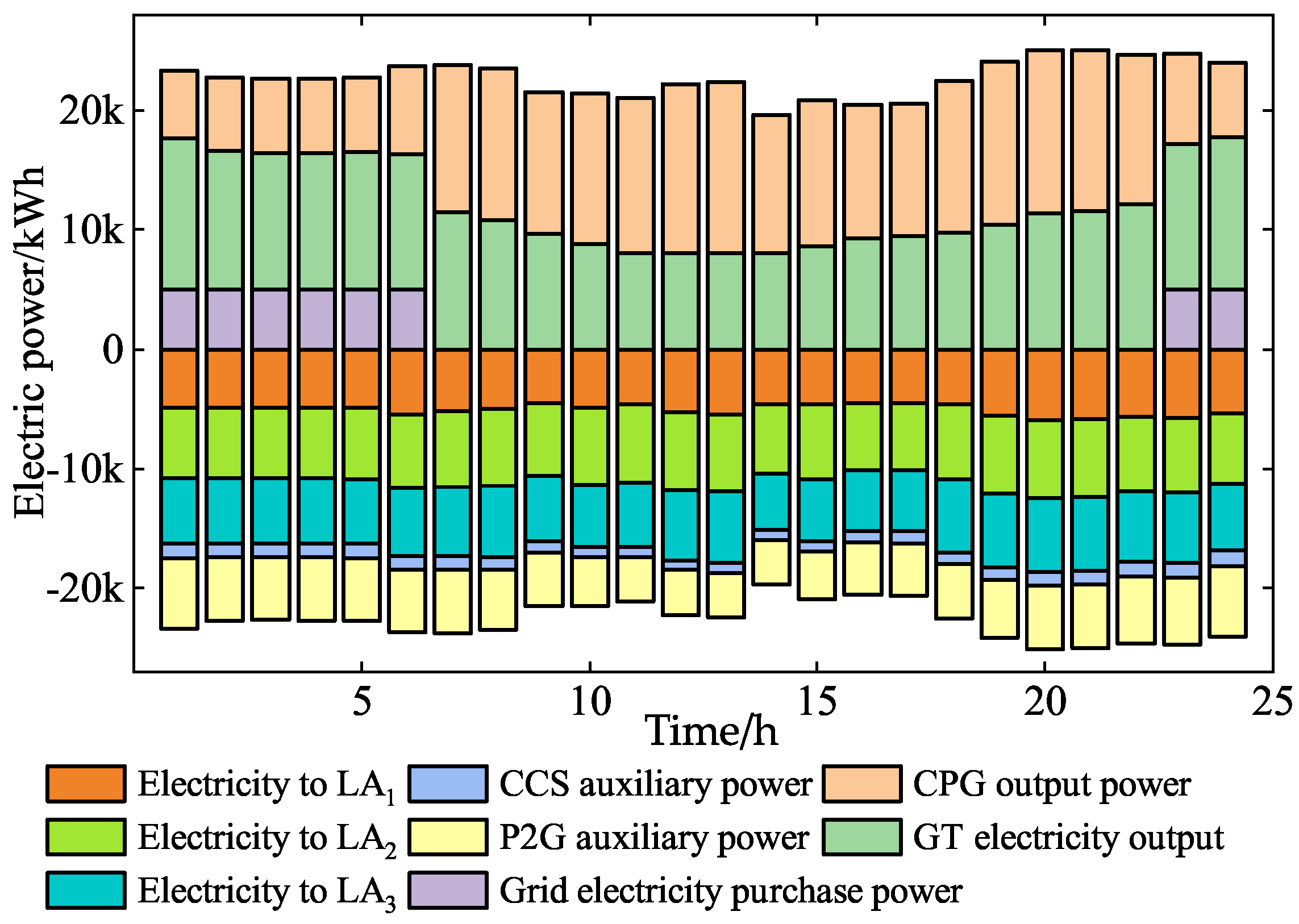
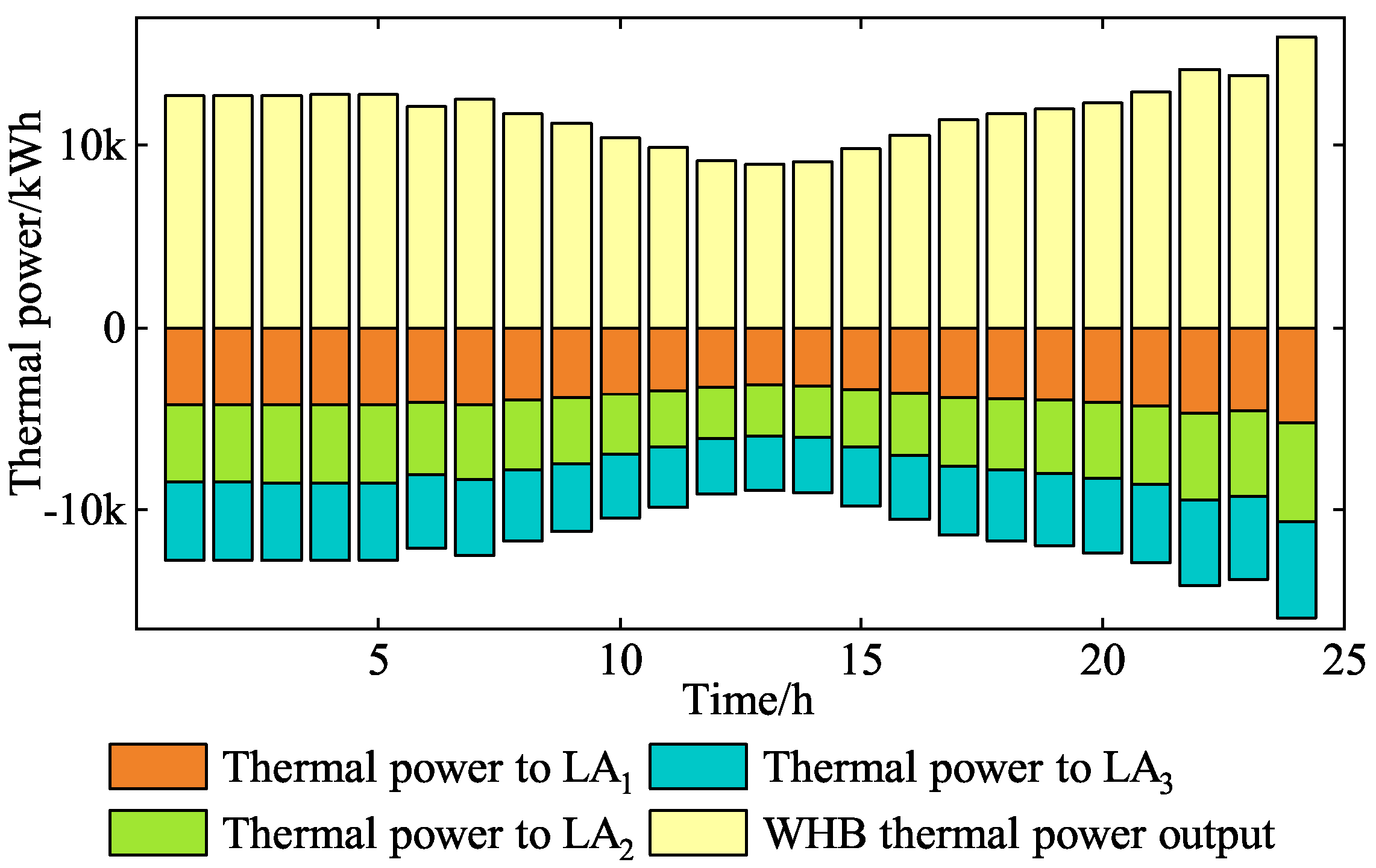
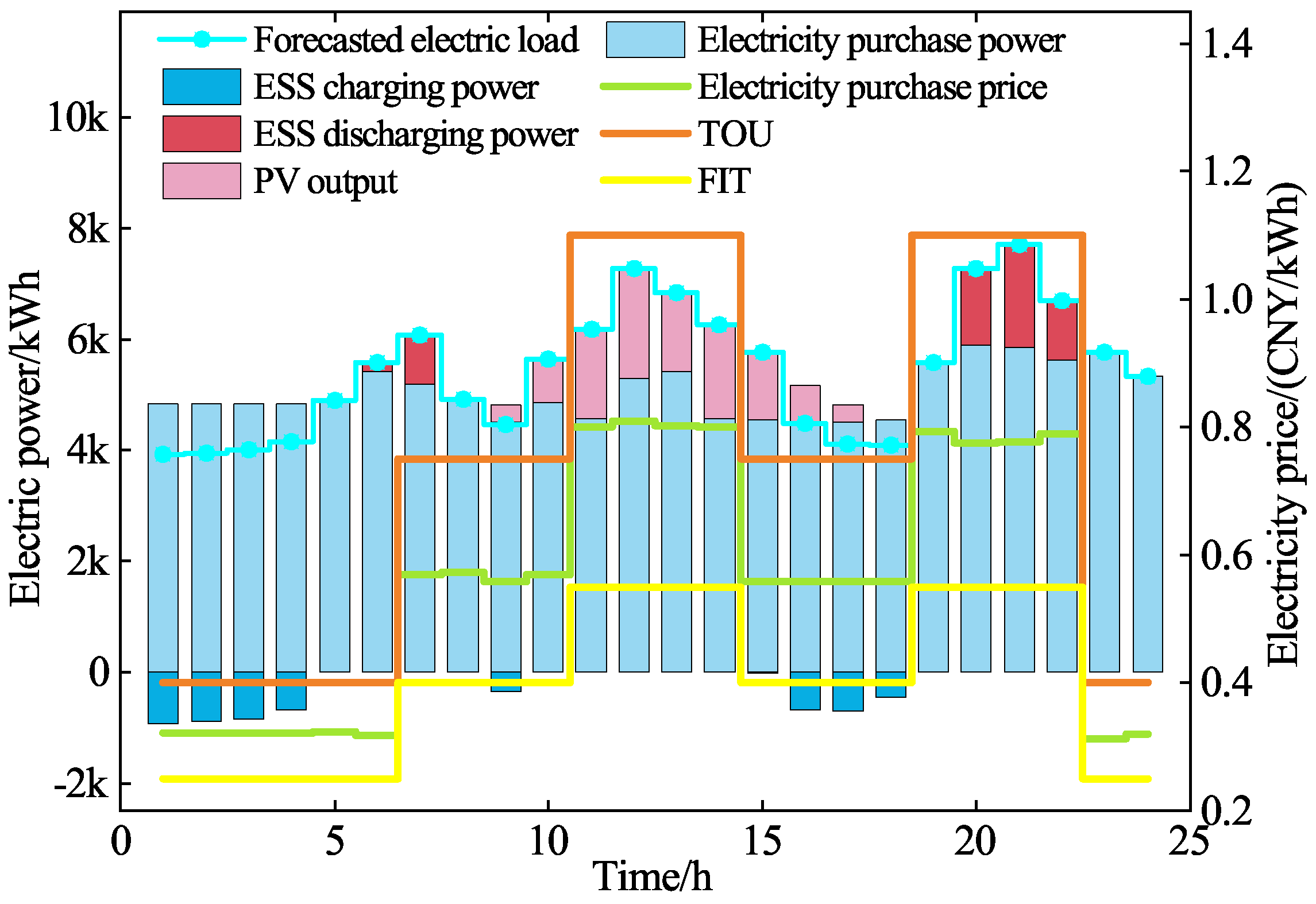
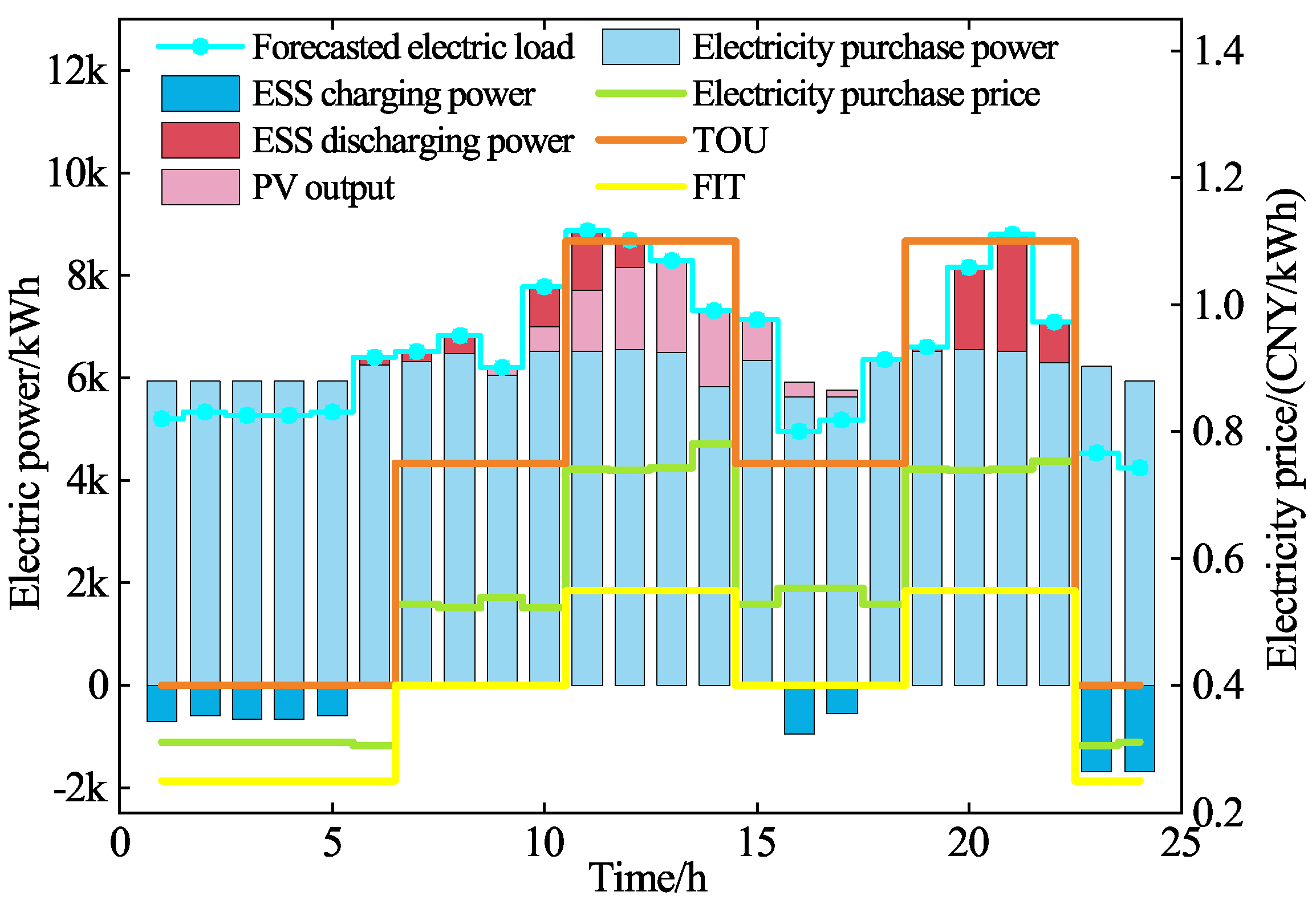
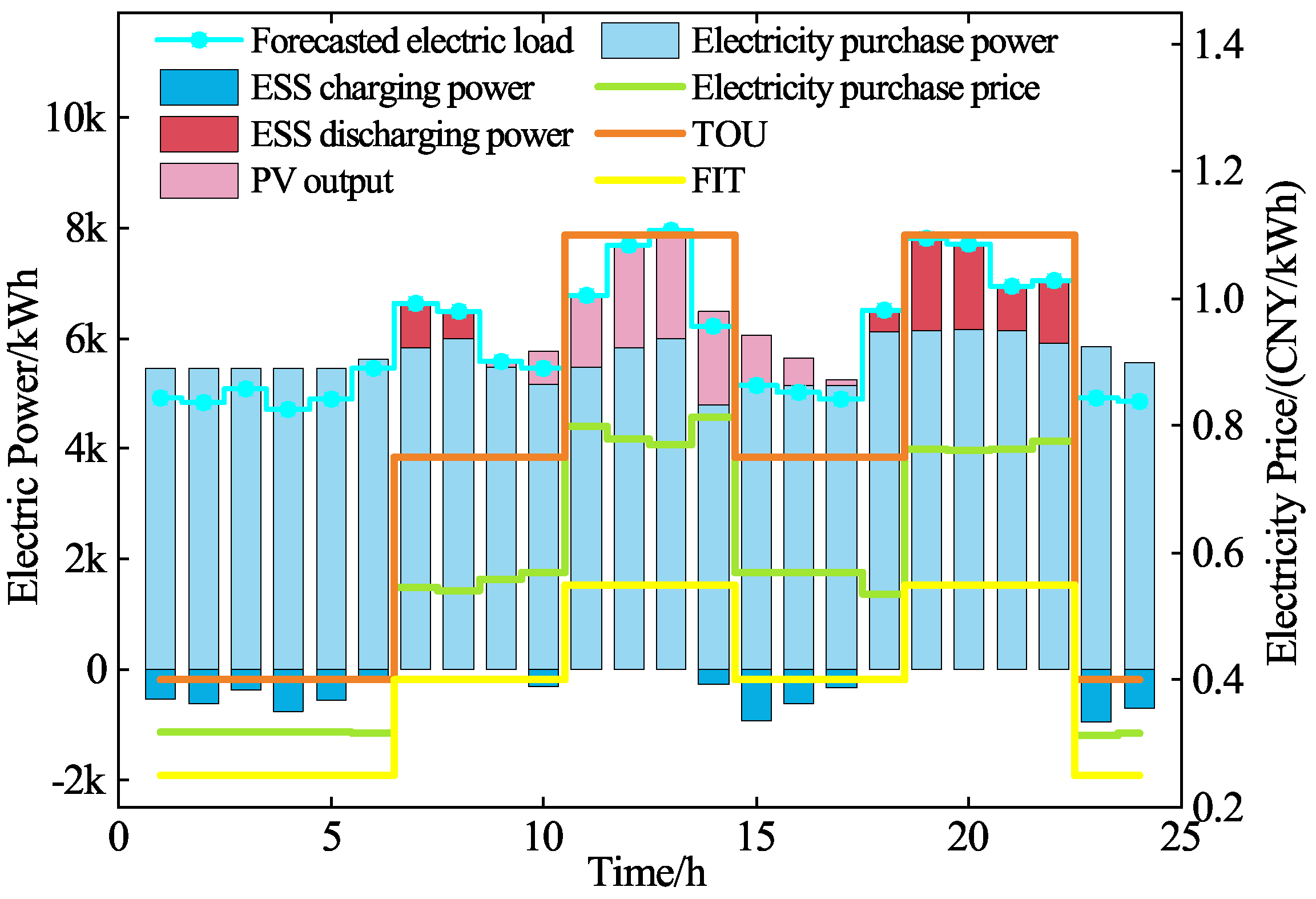
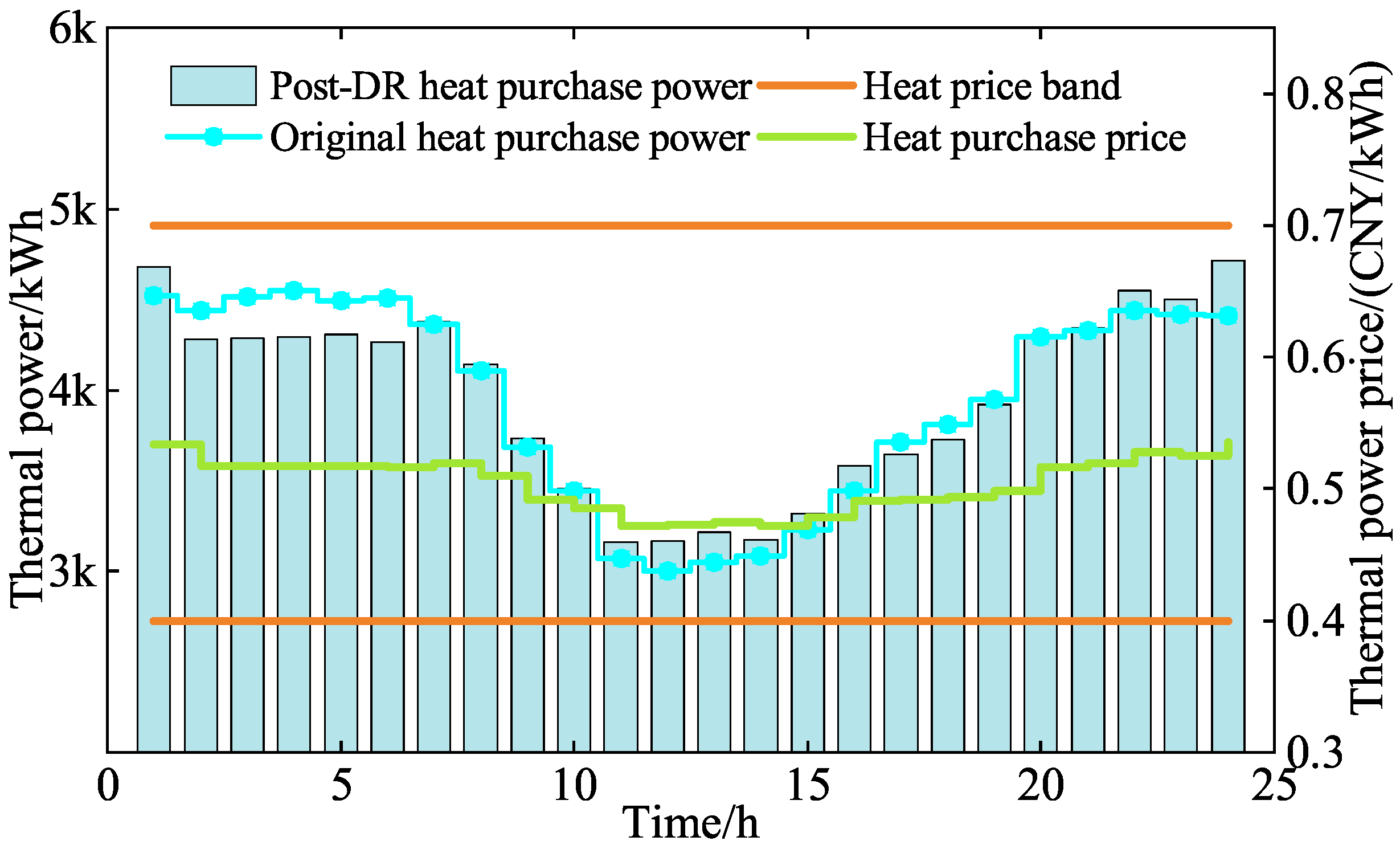
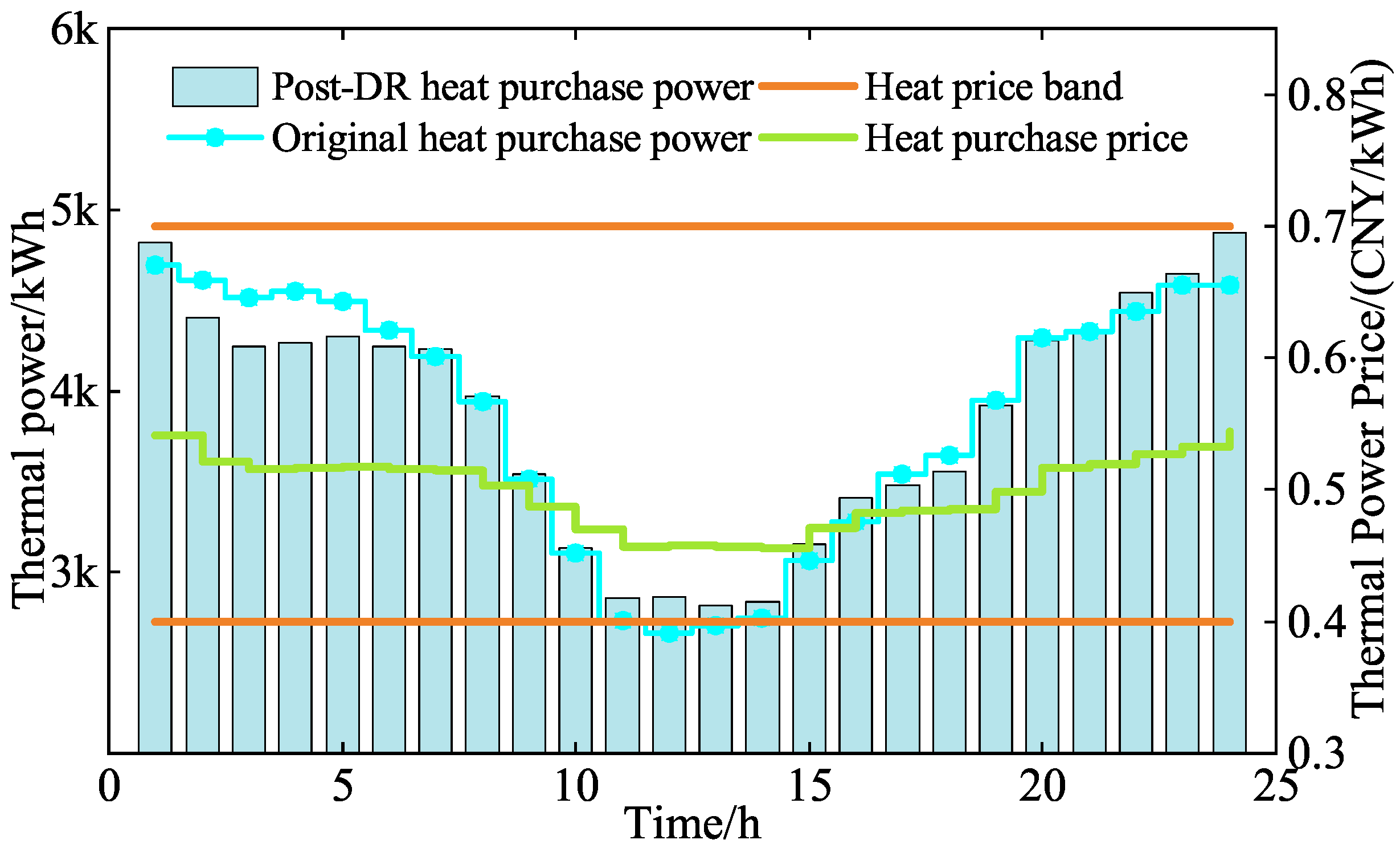
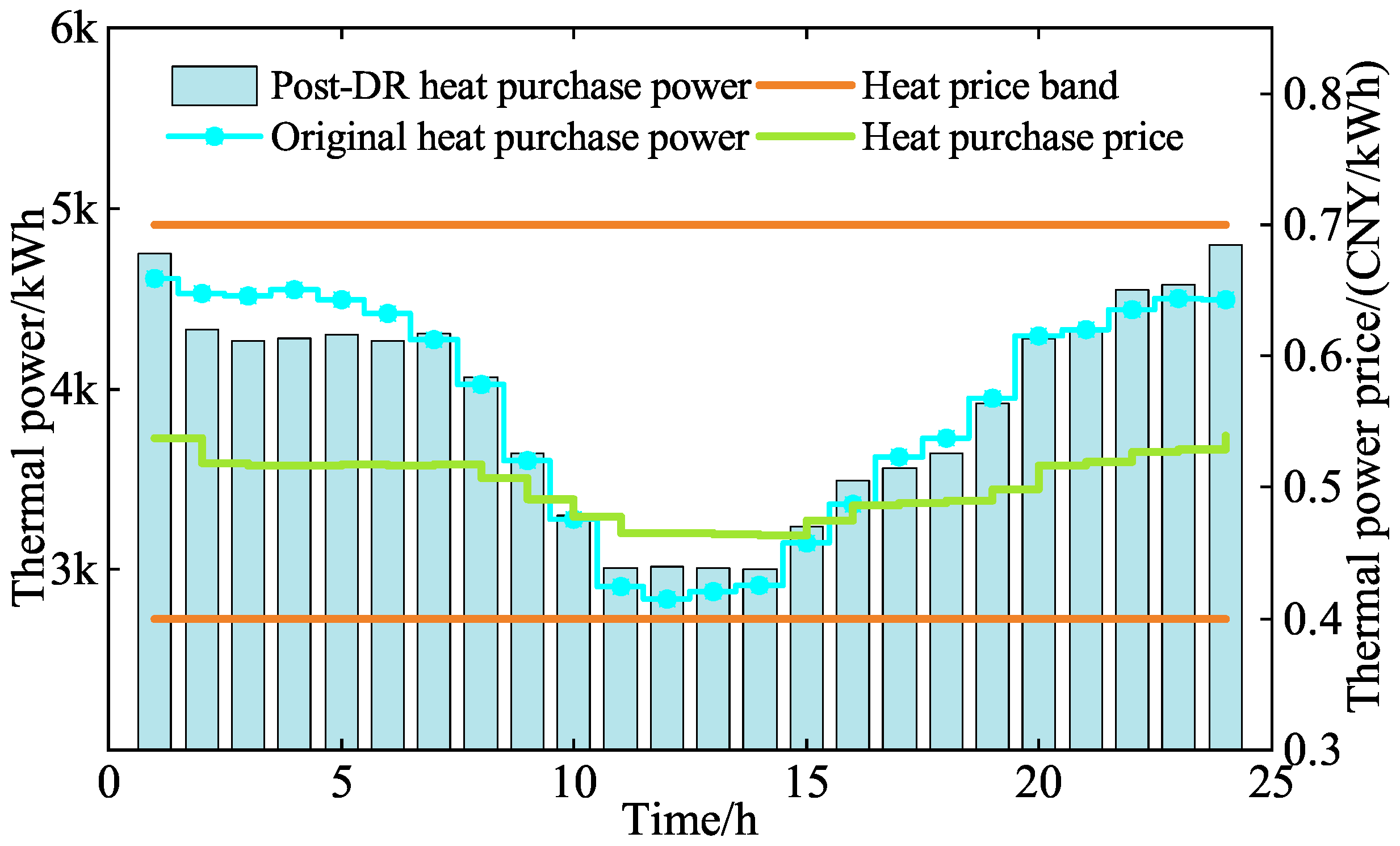
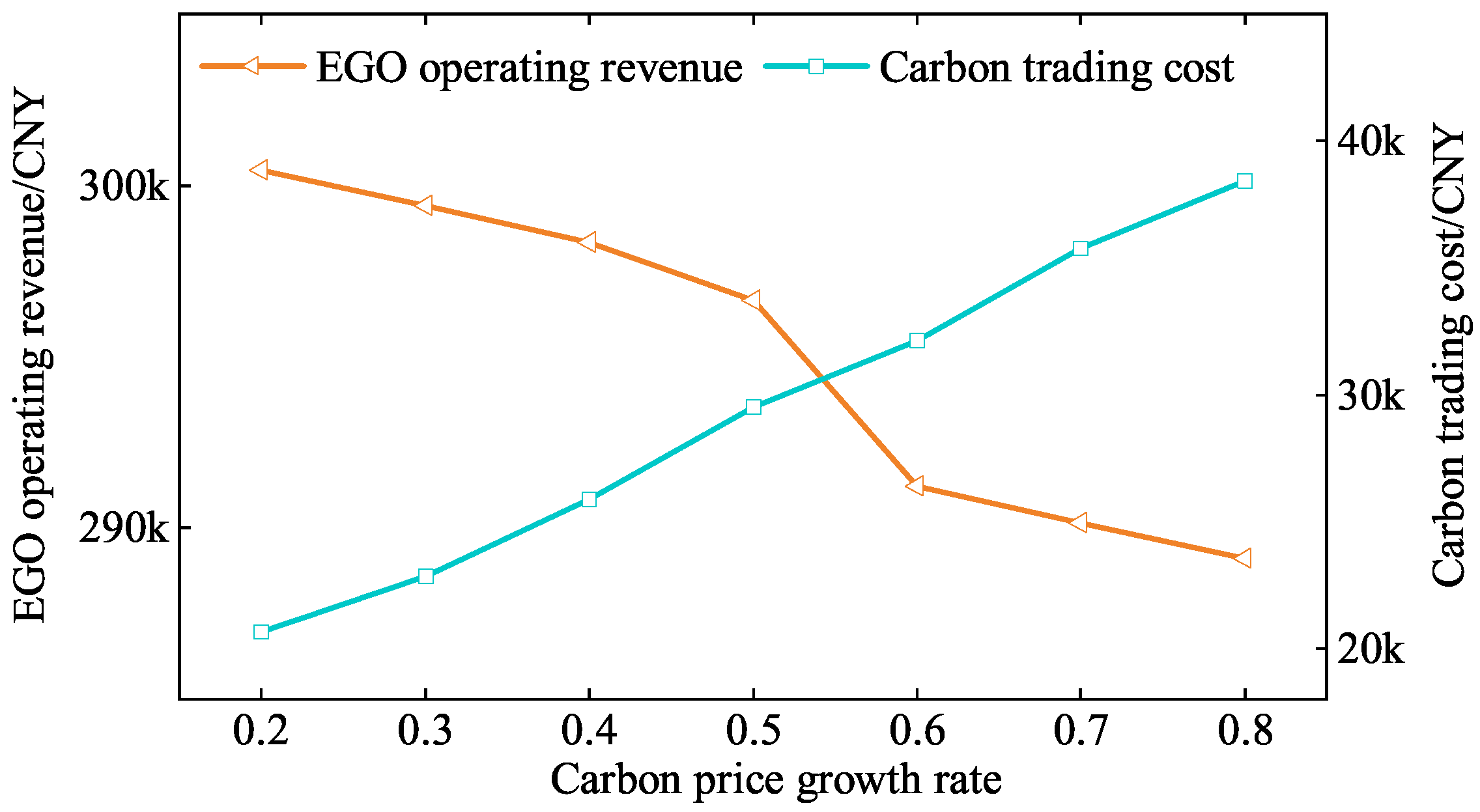
| Types of Electricity Price | Periods | Value (CNY/kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| TOU | Peak (11:00–14:00), (19:00–22:00) | 1.20 |
| Flat (7:00–10:00), (15:00–18:00) | 0.75 | |
| Valley (1:00–6:00), (23:00–24:00) | 0.40 | |
| FIT | Peak (11:00–14:00), (19:00–22:00) | 0.65 |
| Flat (7:00–10:00), (15:00–18:00) | 0.45 | |
| Valley (1:00–6:00), (23:00–24:00) | 0.25 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2 CNY/m3 | 0.234 | ||
| 0.001 | 1.08 | ||
| 0.43 | 0.2 CNY/kg | ||
| 1000 | 50% | ||
| 0.4 | l | 10,000 kg | |
| 0.45 | 0.1 CNY/kWh | ||
| 9.7 | 100 CNY/°C | ||
| 20 MWh | 20 °C | ||
| 2 MWh | 0.66 | ||
| 20 MWh | 0.03 | ||
| 2 MWh | 0.34 | ||
| 0.95 | 33.5 °C | ||
| 0.7 | M | 80 | |
| 0.55 | 0.11 | ||
| 0.4 | 0.98 | ||
| 0.8 CNY/kWh | 0.98 | ||
| 0.3 CNY/kWh | 0.1 | ||
| 0.728 | 0.9 | ||
| 0.367 | 10 MWh | ||
| 0.728 | 0 | ||
| 1.67 | 10 MWh | ||
| 0.756 | 0 |
| Scenario | SCTM | P2G-CCS | ESS | PMV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 2 | × | √ | √ | √ |
| 3 | √ | × | √ | √ |
| 4 | √ | √ | × | √ |
| 5 | √ | √ | √ | × |
| Scenario | EGO Operating Revenue/CNY | Operating Cost/CNY | Operating Cost/CNY | Operating Cost/CNY | RIES Emissions /kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 296,639 | 76,493 | 85,950 | 81,326 | 388,835 |
| 2 | 305,350 | 76,411 | 85,799 | 81,219 | 434,447 |
| 3 | 243,382 | 76,040 | 85,418 | 80,787 | 328,298 |
| 4 | 305,622 | 78,419 | 89,630 | 83,815 | 397,736 |
| 5 | 297,568 | 77,640 | 88,098 | 83,033 | 388,936 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Tong, B.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Hierarchical Distributed Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch Strategy for Regional Integrated Energy System Based on ADMM. Energies 2025, 18, 4638. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174638
Jiang H, Tong B, Yao Z, Zhao Y. Hierarchical Distributed Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch Strategy for Regional Integrated Energy System Based on ADMM. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4638. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174638
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, He, Baoqi Tong, Zongjun Yao, and Yan Zhao. 2025. "Hierarchical Distributed Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch Strategy for Regional Integrated Energy System Based on ADMM" Energies 18, no. 17: 4638. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174638
APA StyleJiang, H., Tong, B., Yao, Z., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Hierarchical Distributed Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch Strategy for Regional Integrated Energy System Based on ADMM. Energies, 18(17), 4638. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174638






