Identification of Key Parameters and Construction of Empirical Formulas for Isentropic and Volumetric Efficiency of High-Temperature Heat Pumps Based on XGBoost-MLR Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
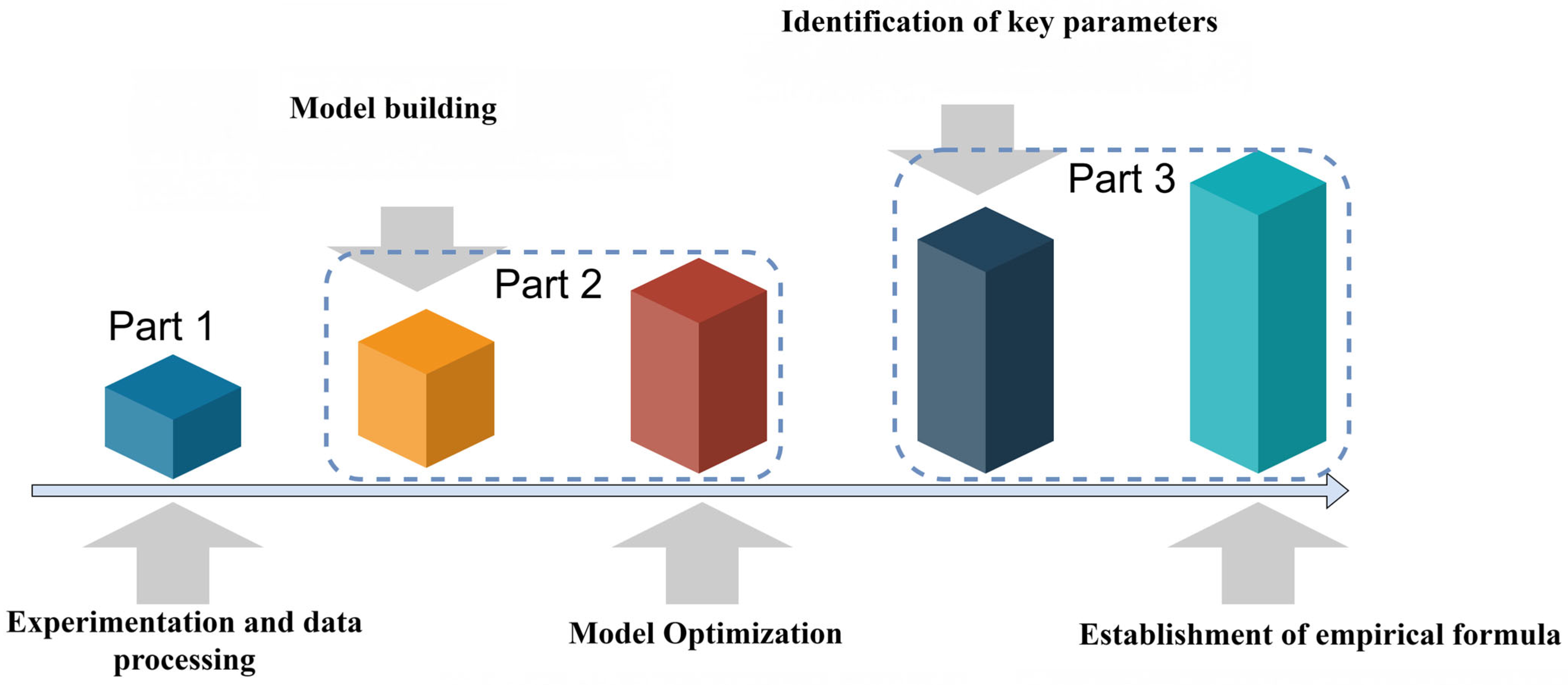
2. Methodology
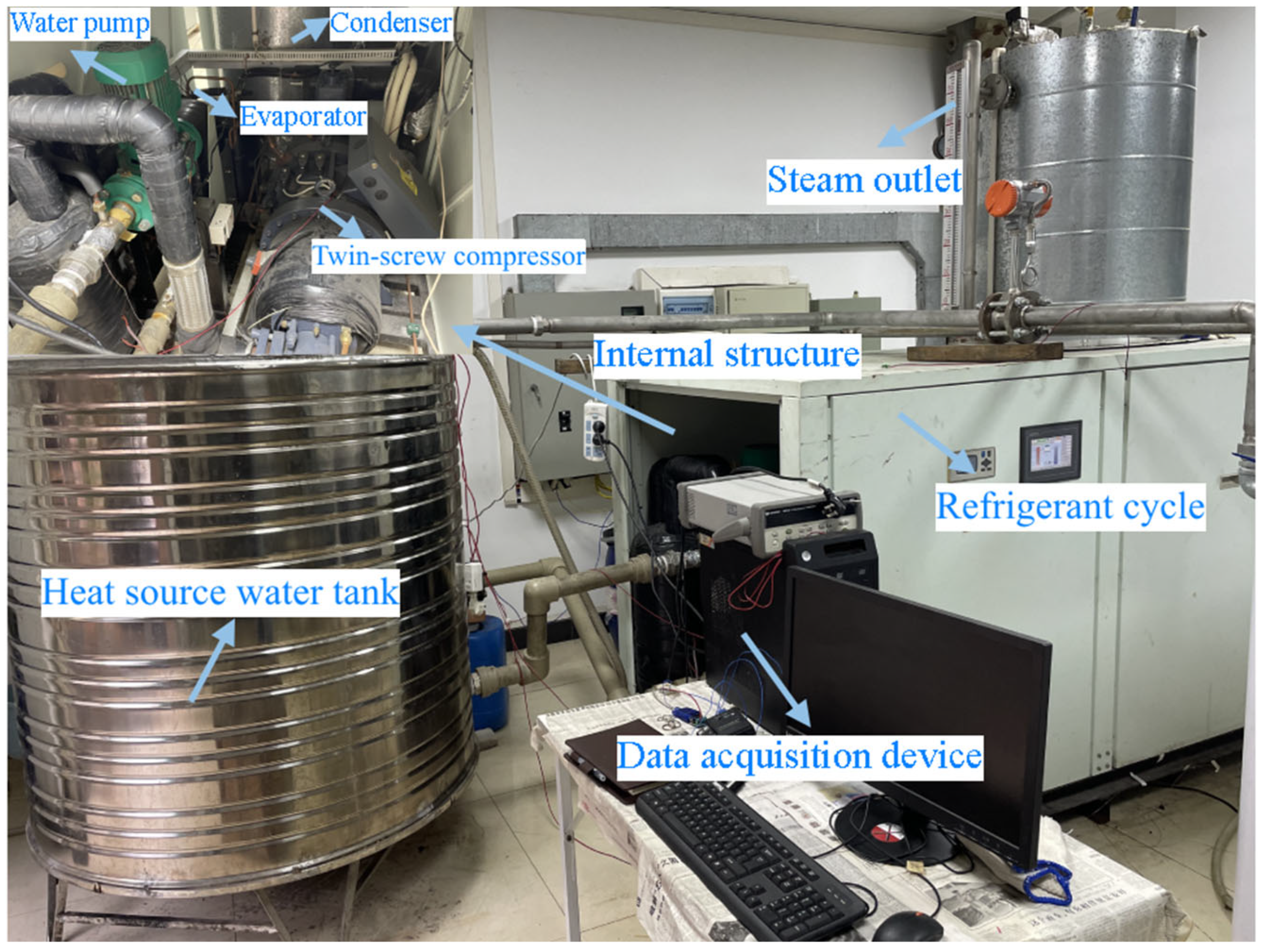
2.1. Experiments and Data Processing
2.1.1. Heat Source Cycle
2.1.2. Refrigerant Cycle
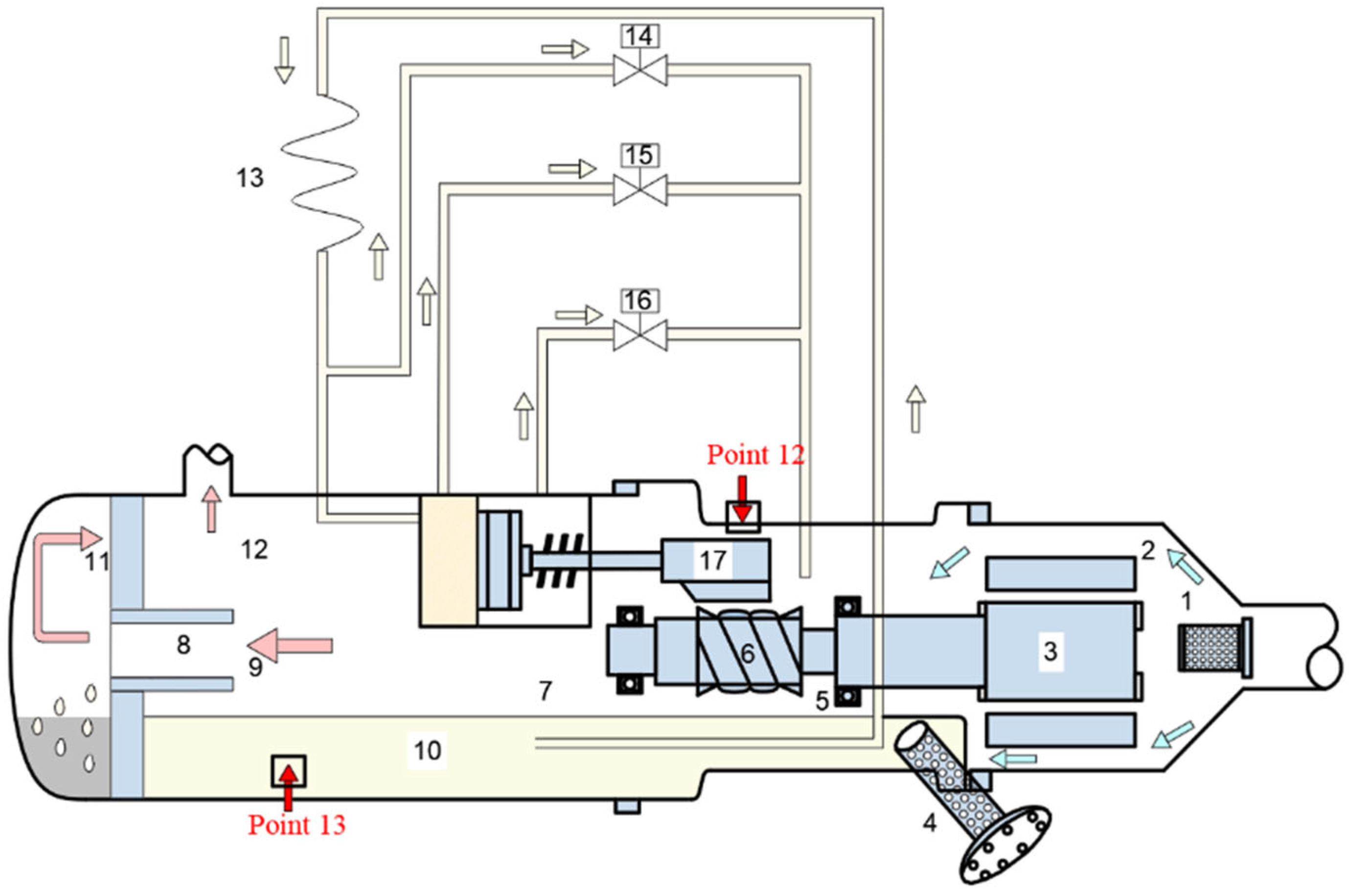
2.1.3. Semi-Hermetic Twin-Screw Compressor Oil Cooling Cycle
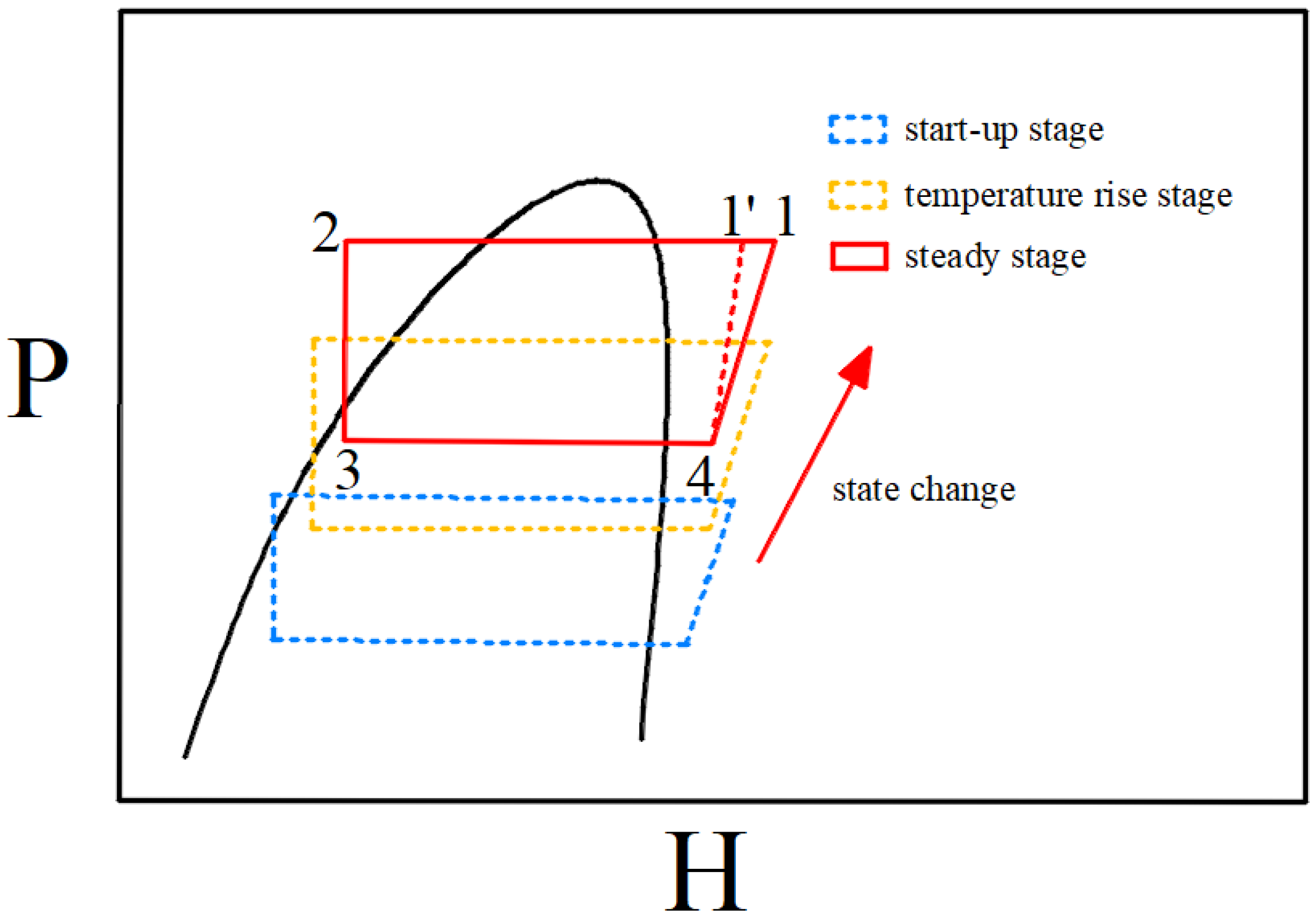
2.1.4. Experimental Procedure
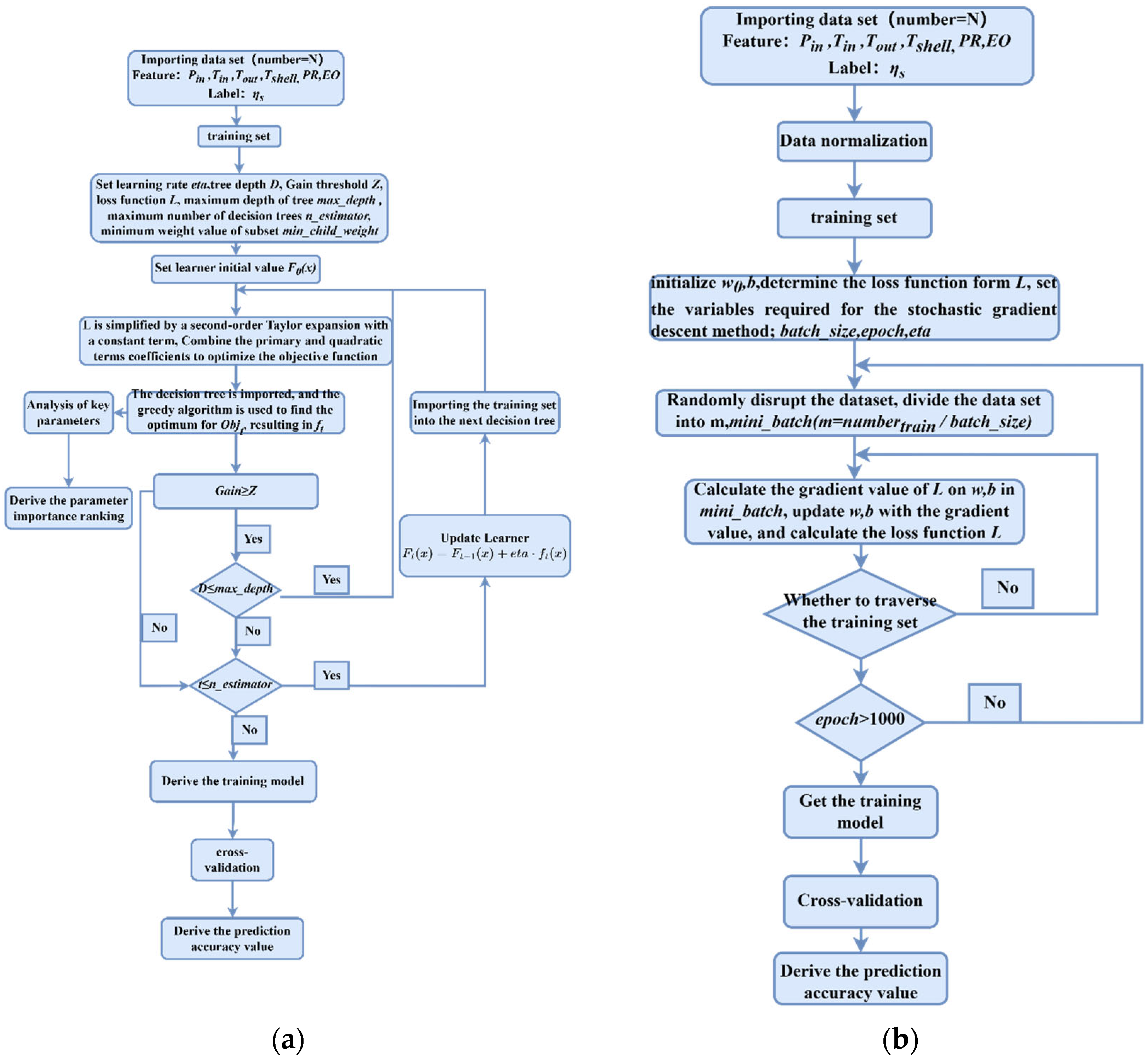
2.2. Model Building and Optimization
2.2.1. Model Building
- (i)
- Thermodynamic modeling building
- (ii)
- Prediction model building
2.2.2. Model Optimization
2.3. Key Parameter Identification and Isentropic Efficiency Empirical Formula Construction
3. Results and Discussion
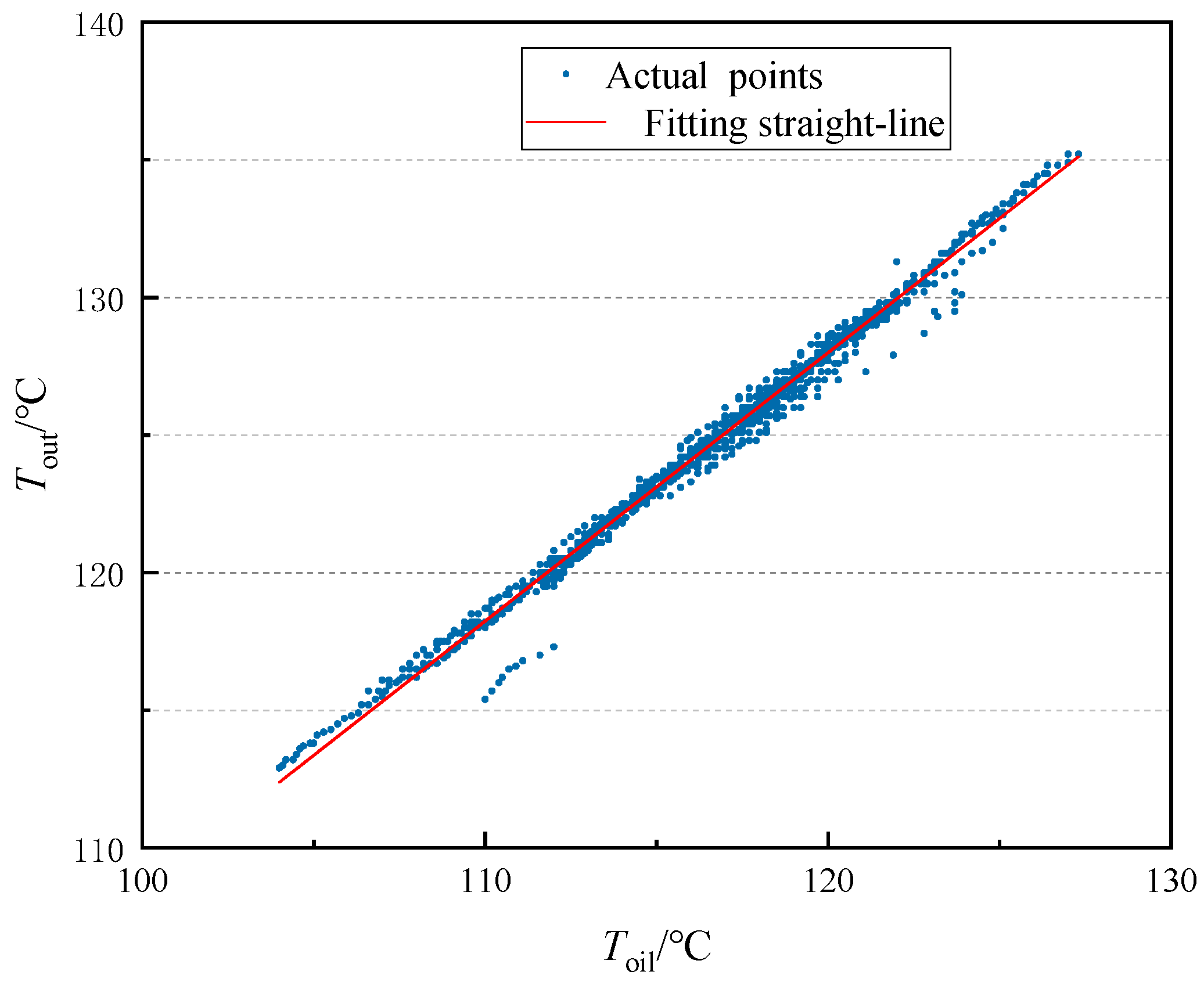
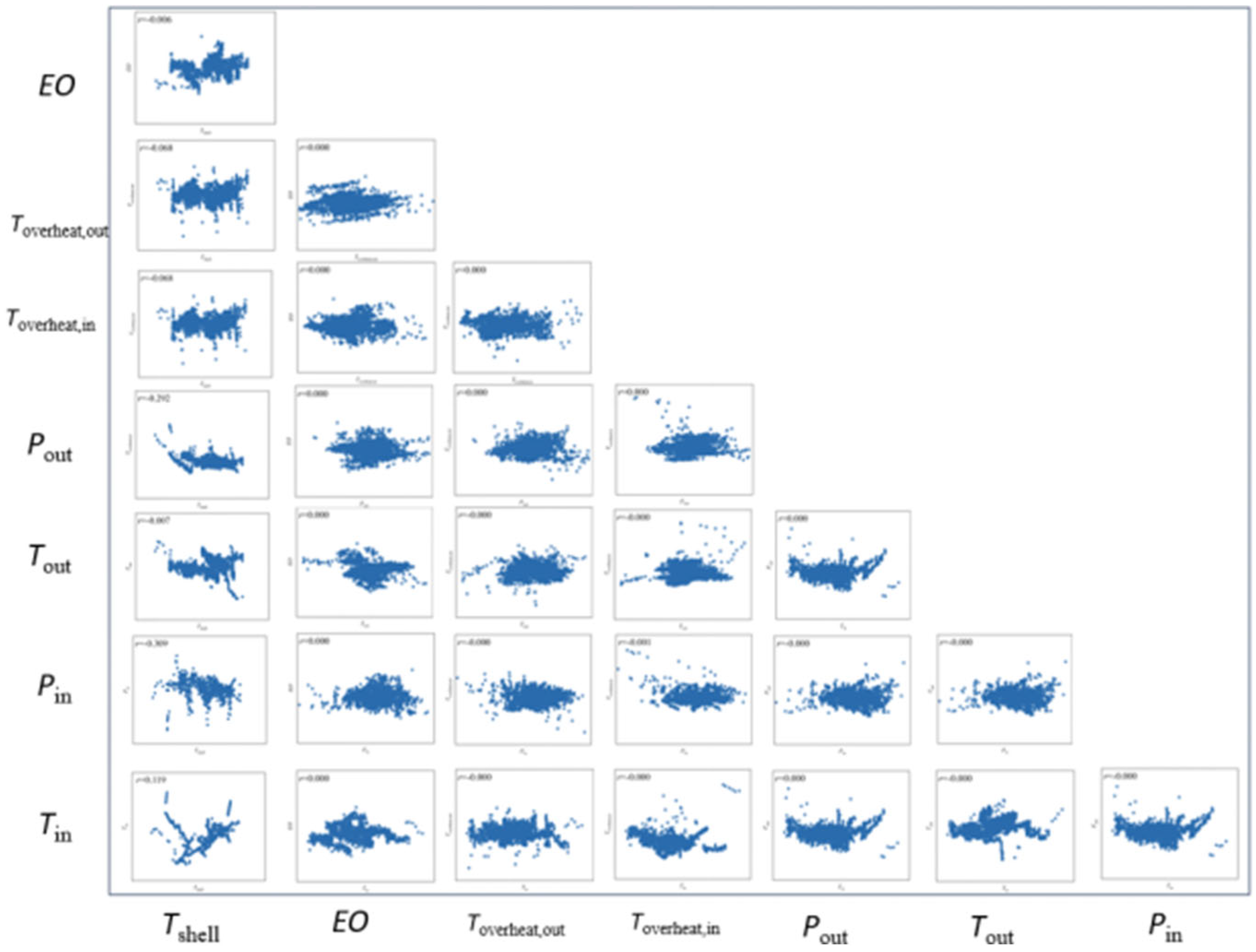
3.1. Data Processing and Parameter Screening
3.2. Optimization of Model
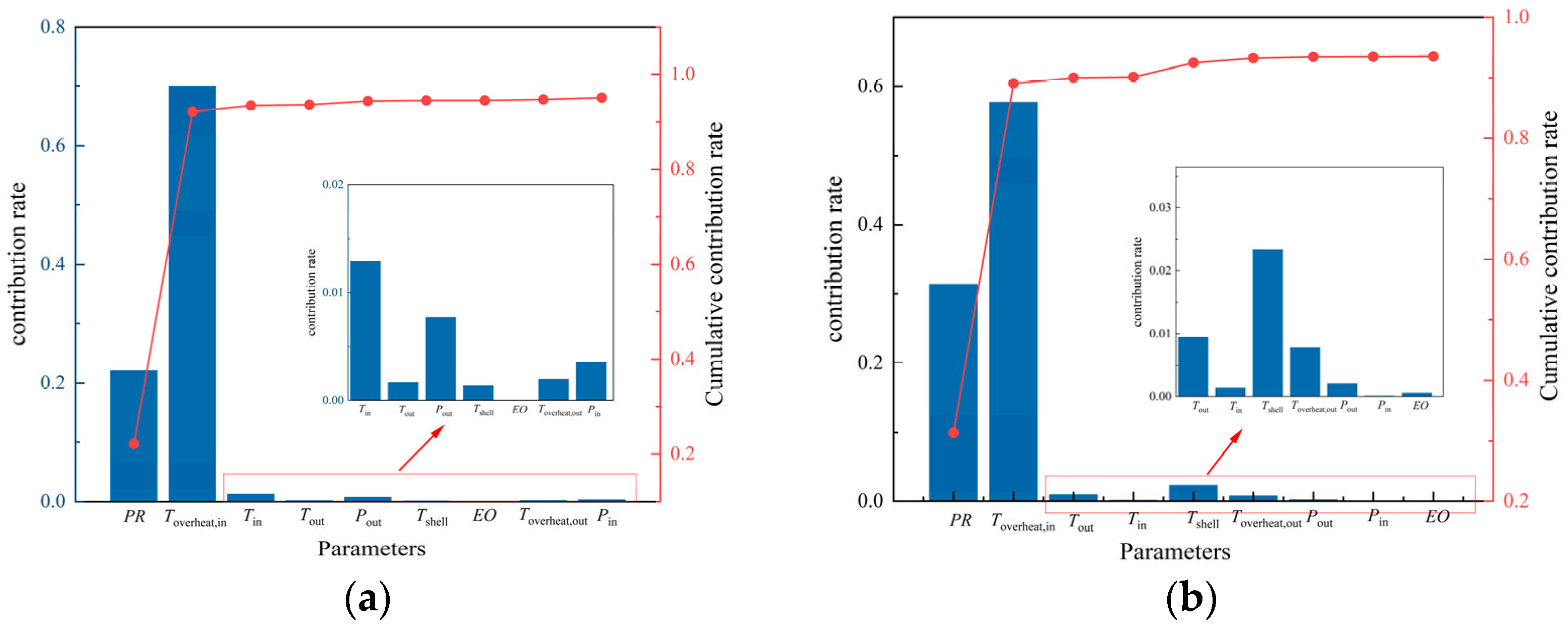
3.3. Key Parameters of XGBoost-MLR Algorithm Analysis
3.4. Fitting and Analysis of Empirical Equation Based on Key Parameters
- (1)
- The compressor used was a semi-hermetic twin-screw compressor.
- (2)
- The process complied with the operating range of data determined in Table 9.
- (1)
- Within a limited range of PR, the system ηs and ηv basically decrease with increasing PR, which is consistent with the trend obtained by the previous researcher. When PR is less than 4, the isentropic efficiency does not change significantly with PR. For example, when the compression ratio is changed from 3.5 to 4, the change in system isentropic efficiency is only 0.006301. The isentropic efficiency increases the decay rate with increasing compression ratio. On the contrary, the volumetric efficiency decreases the decay rate with increasing compression ratio.
- (2)
- Within a limited range of Toverheat,in, the system ηs and ηv increase with increasing Toverheat,in. Toverheat,in has a contributory effect on system performance. Changes in performance parameters due to changes in Toverheat,in can be explained from a physical point of view: the increase in Toverheat,in makes the inhaled gas more stable and reduces the liquid component in it. The actual suction volume of the compressor is closer to the theoretical value. As a result, volumetric efficiency losses due to gas–liquid mixtures are reduced, and compressor power consumption due to liquid strikes in the compressor is minimized.
3.5. Validation of the Generalizability of the Empirical Formulas and Explanation of Method Generalizability
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The model established by the XGBoost-MLR algorithm can accurately identify the key parameters of HTHPs in a limited temperature range. Using the OT algorithms can effectively optimize the input parameter collinearity problem. CV and BO algorithms can improve the prediction model accuracy and make the model R2 stable above 0.95.
- (2)
- In the specified high-temperature range of 90~132 °C, the key parameters of isentropic and volumetric efficiency are PR, Toverheat,in, which can be used to achieve high prediction accuracy. Deleting the key parameters will lead to a significant decrease in the accuracy of the prediction model.
- (3)
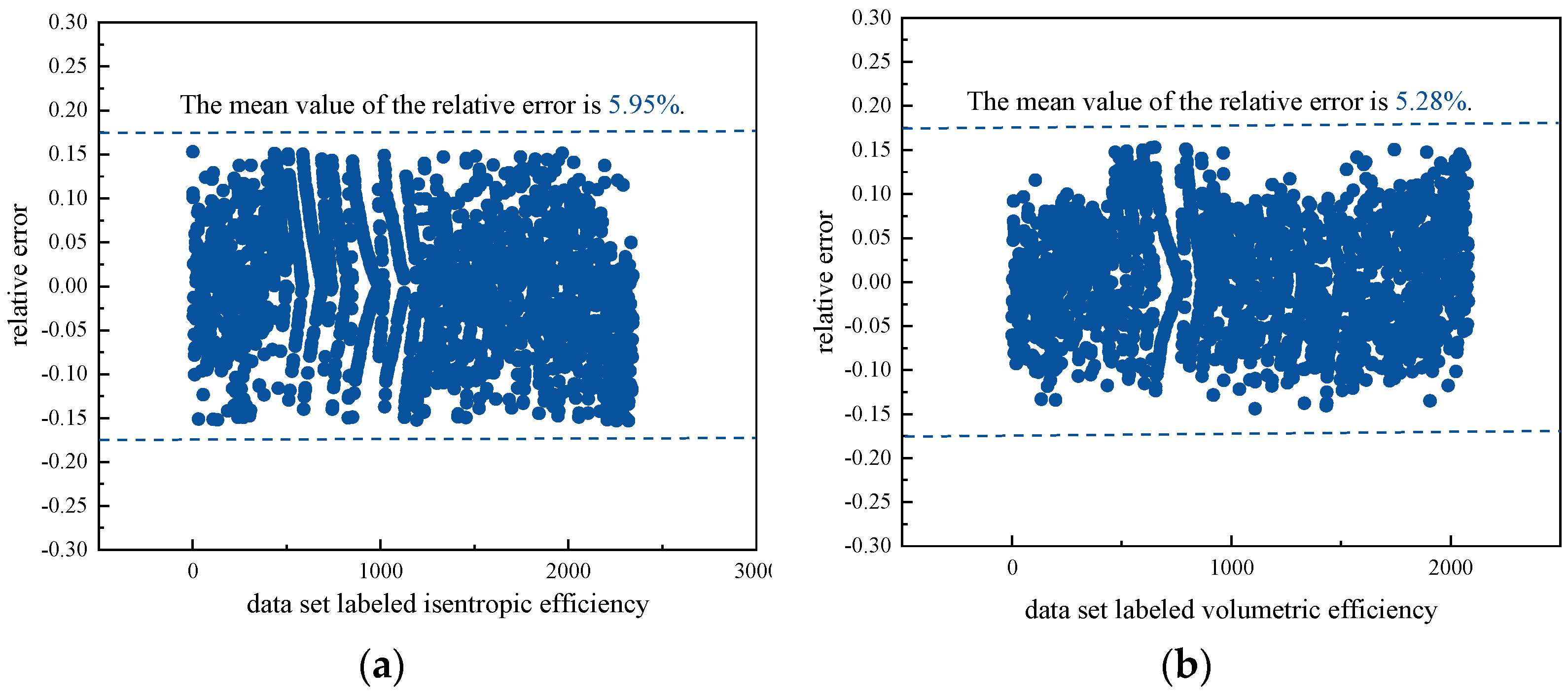
- The empirical formulas of the isentropic and volumetric efficiency constructed based on the key parameters have high accuracy in the temperature range. The relative error of isentropic efficiency empirical formula is between −15.3% and 15.2%. The mean value of the relative errors is 5.95%. The relative error of the volumetric efficiency empirical formula is between −14.4% and 15.3%. The mean value of the relative errors is 5.28%.
- (4)
- The system ηs and ηv basically decrease with increasing PR. However, when PR is less than 4, the isentropic efficiency does not change significantly with PR. The system ηs and ηv increase with increasing Toverheat,in.
- (5)
- The proposed empirical formulas have a clear range of applicability. Twin-screw compressors have the highest applicability. The relative error of the experimental data of scroll compressors and reciprocating compressors is more than 15%. The applicability of the empirical formula for volumetric efficiency is unstable in compressors of different sizes. In contrast, the empirical equations for isentropic efficiency are more widely applicable. The method is generalizable when analyzed in terms of the whole process, which includes the selection of input parameters, the algorithms, and the optimization methods.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| T | Temperature (°C) |
| Q | Instantaneous flow (m3 h−1) |
| q | Heat production value (J kg−1) |
| h | Specific enthalpy (J kg−1) |
| D | Mahalanobis distance |
| r | Correlation coefficient |
| max_depth | Maximum depth of decision tree |
| n_estimator | Number of decision trees |
| Gain | Branch point gain |
| gamma | Minimal loss of branching points |
| min_child_weight | The sum of the minimum instance weights required in the subsections |
| F | Decision Tree Learner |
| batch_size | Number of random samples |
| epoch | Total number of training sessions |
| n_iter | Number of iterations of Bayesian optimization algorithm |
| W | power consumption |
| M | mass flow |
| V | volumetric flow |
| c | constant-pressure specific heat capacity |
| Abbreviations | |
| HTHP | High-temperature heat pump |
| PR | Pressure Ratio |
| COP | Coefficient of Performance |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| RF | Random Forest |
| R2 | Determination coefficient |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
| MLR | Multivariable Linear Regression |
| OT | orthogonal transformation |
| GS | Grid Search |
| BO | Bayesian optimization |
| EO | expansion valve opening |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosting Decision Tree |
| Obj | Objective function |
| L | Loss function |
| Subscripts | |
| 1–12 | Specific state points |
| in | Compressor inlet |
| out | Compressor outlet |
| oil | Compressor lubricants |
| shell | Compressor shell |
| steam | Vapors generated |
| heat | Heat production process |
| ref | Circulating refrigerant |
| stan | Standardized situation |
| source | heat source |
| source,in | Evaporator inlet heat source |
| source,out | Evaporator outlet heat source |
| com | Compressor |
| Greek | |
| ηs | Isentropic efficiency |
| ηv | Volumetric efficiency |
| ρ | density |
| Ω | Regular terms |
References
- United Nations Bureau. National Statistical Yearbook 2022 [EB/OL]. 13 October 2022. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2022/indexch.htm (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Yan, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, R. Air-source heat pump for distributed steam generation: A new and sustainable solution to replace coal-fired boilers in China. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 2000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpagaus, C.; Bless, F.; Uhlmann, M.; Schiffmann, J.; Bertsch, S.S. High-temperature heat pumps: Market overview, state of the art, research status, refrigerants, and application potentials. Energy 2018, 152, 985–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, R.; Deng, N.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.-C. A review and perspective on industry high-temperature heat pumps. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaida, T.; Sakuraba, I.; Hashimoto, K.; Hasegawa, H. Experimental performance evaluation of heat pump-based steam supply system. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Compressors and their Systems, London, UK, 5–9 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, K. High-temperature heat pumps for waste heat recovery. In Proceedings of the 8th EHPA European Heat Pump Forum, Brussels, Belgium, 8 May 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zauner, F. Hochtemperatur-Wärmepumpen zur energetischen Nutzung industrieller (Niedertemperatur-) Abwärme, Ochsner Energie Technik GmbH. In Proceedings of the Highlights der Energieforschung 2016, Die Rolle der Wärmepumpe im zukünftigen Energiesystem, Vienna, Austria, 22 June 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.K.; Ommen, T.; Markussen, W.B.; Reinholdt, L.; Elmegaard, B. Technical and economical working domains of industrial heat pumps: Part 2–Ammonia-water hybrid absorption-compression heat pumps. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 55, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, W.; Fredrich, O. GEA Grasso Heat Pumps Using Ammonia—The Megawatt Range; Achema: Frankfurt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, M.; Rislå, H.N.; Kontomaris, K. Measured performance of a novel high-temperature heat pump with HFO-1336mzz (Z) as the working fluid. In Proceedings of the 12th IEA Heat Pump Conference, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 15–18 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Cao, F.; Xing, Z. Development and experimental validation of a high-temperature heat pump for heat recovery and building heating. Energy Build. 2009, 41, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xing, Z.; Hou, F.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, S. Theoretical and experimental investigation of a novel high-temperature heat pump system for recovering heat from refrigeration system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, F.; Comakli, O.; Lesani, A.; Karagoz, S. Characterization of lubricating oil effects on the performance of reciprocating compressors in air–water heat pumps. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 74, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jiang, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, R. Experimental investigation on the performance of a very high temperature heat pump with water refrigerant. Energy 2020, 190, 116427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, M.; Rulliere, R.; Haberschill, P.; Peureux, J.-L. Modelica-based modeling and simulation of a twin screw compressor for heat pump applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 58, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Experimental performance of moderately high temperature heat pump with working fluid R1234ze(Z). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 144, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, A.Y.; Cotter, D.F.; Le, K.X.; Huang, M.J.; Hewitt, N.J. Thermodynamic analysis of subkey High-Temperature heat pump using low GWP Refrigerants: A theoretical evaluation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Wang, H.-X.; Guo, T.; Chen, C. Performance Simulation and Experimental Testing of Moderately High Temperature Heat Pump Using Non-azeotropic Mixture for Geothermal District Heating. In Proceedings of the 2010 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Chengdu, China, 28–31 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X. Thermoeconomic analysis of optimization potential for CO2 vapor compression cycle: From transkey to superkey operation for waste heat recovery from the steam condenser. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, M.; Rulliere, R.; Haberschill, P.; Peureux, J.-L. Experimental and numerical investigations of a new high temperature heat pump for industrial heat recovery using water as refrigerant. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 44, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, Z.; LI, X.; Feng, L.; Song, M. Study on characteristics of high-temperature hybrid heat pump system for boiling water heater with different refrigerants. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2022, 21, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, T.; Atakan, B. Semi-empirical model of a variable speed scroll compressor for R-290 with the focus on compressor efficiencies and transferability. Int. J. Refrig. 2023, 146, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Liang, J. Research on Dynamic Modeling of a High Temperature Steam Heat Pump. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC 2020), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskosch, D.; Venzik, V.; Atakan, B. Thermodynamic model for reciprocating compressors with the focus on fluid dependent efficiencies. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 84, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, C.O.; Erthal, R.H.; Andrade, D.E.; da Silva, L.W. A semi-empirical model for the unsteady-state simulation of reciprocating compressors for household refrigeration applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlkeld, J.L. Thermal Environmental Engineering; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Simplified steady-state modeling for variable speed compressor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.K.; Demirezen, G.; Fung, A.S.; Janssen, E. The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) in predicting the energy consumption of air-source heat pump in retrofit residential housing. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Xiamen, China, 11–19 November 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z. Intelligent control system for the electric vehicle heat pump air conditioner based on machine learning. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noye, S.; Martinez, R.M.; Carnieletto, L.; De Carli, M.; Aguirre, A.C. A review of advanced ground source heat pump control: Artificial intelligence for autonomous and adaptive control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Identifying the key system parameters of the organic Rankine cycle using the principal component analysis based on an experimental database. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 240, 114252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Ahmad, T. A novel energy demand prediction strategy for residential buildings based on ensemble learning. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 3411–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maesschalck, R.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Massart, D.L. The mahalanobis distance. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2000, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Bao, S. Experimental research on the cyclic Performance of High-Temperature Heat Pump with R134a/R245fa in comparison with R245fa. J. Qingdao Univ. Technol. 2020, 41, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Shi, P.; Shao, X.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y. Experimental Study on High Temperature Heat Pump Unit Based on R245fa Working Fluid. Mech. Electr. Inf. 2020, 25, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Cycle performance evaluation of HFC245fa for high-temperature heat pump systems. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2010, 31, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Yu, X.; Li, X.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Performance analysis of a cascade high temperature heat pump using R245fa and BY-3 as working fluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 140, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Researcher | Compressor Types | Refrigerants | The Empirical Formula for Isentropic Efficiency | Condensing Temperature/°C | Conformity of Data for This Work (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulaiman [17] | Piston compressors | R245fa, R1233Zzd(E) | 80~120 | 0.2136 | |
| Zhang [18] | Piston compressors | R245fa/R152a | 70~90 | 0.2803 | |
| Wang [19] | Twin-Screw Compressors | R744 | 70~90 | 0.2766 | |
| Marwan [20] | Twin-Screw Compressors | R718 | 100~130 | 0.3079 | |
| Wang [21] | Scroll compressors | R245fa | 80~100 | 0 |
| Number | Component | Number | Component |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intake filter | 10 | Lubricating oil tank |
| 2 | Inlet gas (low-pressure) | 11 | Oil filter |
| 3 | Electric machine | 12 | Outlet gas (high-pressure and non-oil) |
| 4 | Oil strainer | 13 | Capillary |
| 5 | Suction end bearing | 14 | Solenoid valve (25%) |
| 6 | Male rotor | 15 | Solenoid valve (50%) |
| 7 | Discharge end bearing | 16 | Solenoid valve (75%) |
| 8 | Muffler | 17 | Capacity control slide valve |
| 9 | Outlet gas (high-pressure and oily) |
| Tsource (°C) | Tsteam,set (°C) |
|---|---|
| 40~75 | 105 |
| 50~75 | 110 |
| 50~75 | 115 |
| 50~75 | 120 |
| Parameter Name | Range (°C) | Control Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor inlet superheat | 3~10 | The suction superheat temperature is controlled by the opening of the electronic expansion valve, so that it is maintained at a level of about 5 °C. |
| Condenser outlet subcooling | 2~10 | Control of subcooling at about 4 °C by regulating the flow of water to the subcooler. |
| Lubricating oil temperature (Toil) | <130 | When the oil temperature is greater than 120 °C, open the oil cooler valve to keep the lubricating oil temperature below 130 °C. |
| Shell temperature (Tshell) | >30 | When not started, the electric heating unit maintains the case temperature at 30 °C or more. After start-up, the electric heating unit is switched off and the shell temperature varies with the operating temperature. |
| Pin (bar) | Pout (bar) | Tin (°C) | Tout (°C) | Toil (°C) | Tshell (°C) | EO (%) | ΔToverheat,in | ΔToverheat,out | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 4.9 | 21.9 | 68.5 | 131.7 | 123.7 | 68.0 | 100 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Min | 2.3 | 11.5 | 42.1 | 96 | 88.2 | 40.2 | 25 | 10.5 | 9.4 |
| Test Point | Point 6 | Point 7 | Point 6 | Point 7 | Point 13 | Point 12 | Point 4 | Point 6 | Point 7 |
| Measurement Sensors | Measurement Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure sensor | 0~4 MPa | ±0.01 MPa |
| Temperature sensor | −200~200 °C | ±0.5 °C |
| Inductive sensor | 0~1 | ±0.5% |
| Electromagnetic flowmeter | 0~25 m3/h | ±0.5% |
| ηs | ηv | |
|---|---|---|
| maximum | 0.0243 | 0.0296 |
| minimum | 0.0226 | 0.0266 |
| average | 0.0232 | 0.0277 |
| relative measurement uncertainty | 0.0558 | 0.0587 |
| Pin (bar) | Pout (bar) | Tin (°C) | Tout (°C) | EO (%) | Tshell (°C) | ΔToverheat,in | ΔToverheat,out | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 2.4 | 11.6 | 42.1 | 96.4 | 29.8 | 41.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Max | 4.8 | 21.9 | 68.5 | 131.7 | 100.0 | 67.9 | 10.5 | 8.5 |
| Parameters | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Range Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tout/°C | 95 | 135 | 40 |
| PR | 3 | 8 | 5 |
| Tin/°C | 40 | 70 | 30 |
| Toverheat,in/°C | 1 | 10 | 9 |
| Toverheat,out/°C | 1 | 8 | 7 |
| ηs | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| ηv | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| Number of Orders | First-Order Equation | Second-Order Equation | Third-Order Equation | Fourth-Order Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula type | ||||
| Isentropic efficiency formula (R2) | 0.9212 | 0.9510 | 0.9547 | 0.9587 |
| Volumetric efficiency formula (R2) | 0.8905 | 0.9129 | 0.9138 | 0.9157 |
| Researchers | Refrigerant | Compressor Type | Exhaust Temperature Range (°C) | Relative Error of Isentropic Empirical Formula (%) | Relative Error of Volumetric Empirical Formula (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhao [12] | R717 | Twin-Screw Compressors | 75~90 | 5.25 | 9.43 |
| Zhuang [35] | R245fa | Twin-Screw Compressors | 90~105 | 1.92 | 15.9 |
| Zhang [36] | R245fa | Twin-Screw Compressors | 90~115 | 4.16 | 2.84 |
| Ma [37] | R245fa | Reciprocating Compressors | 80~102 | 28.7 | N/A |
| Ma [38] | R245fa | Scroll Compressors | 110~147 | 16.53 | 6.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Wu, F.; Lin, W.; Song, W.; Feng, Z. Identification of Key Parameters and Construction of Empirical Formulas for Isentropic and Volumetric Efficiency of High-Temperature Heat Pumps Based on XGBoost-MLR Algorithm. Energies 2025, 18, 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164454
Li S, Wu F, Lin W, Song W, Feng Z. Identification of Key Parameters and Construction of Empirical Formulas for Isentropic and Volumetric Efficiency of High-Temperature Heat Pumps Based on XGBoost-MLR Algorithm. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164454
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuaiqi, Fengming Wu, Wenye Lin, Wenji Song, and Ziping Feng. 2025. "Identification of Key Parameters and Construction of Empirical Formulas for Isentropic and Volumetric Efficiency of High-Temperature Heat Pumps Based on XGBoost-MLR Algorithm" Energies 18, no. 16: 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164454
APA StyleLi, S., Wu, F., Lin, W., Song, W., & Feng, Z. (2025). Identification of Key Parameters and Construction of Empirical Formulas for Isentropic and Volumetric Efficiency of High-Temperature Heat Pumps Based on XGBoost-MLR Algorithm. Energies, 18(16), 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164454






