Tuning the Activity of NbOPO4 with NiO for the Selective Conversion of Cyclohexanone as a Model Intermediate of Lignin Pyrolysis Bio-Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Catalytic Reactions of Cyclohexanone and Product Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.2. C-C Coupled Adducts in Relation to NiO Loading on NbOPO4
3.3. Coke Formation in Relation to NiO Loading on NbOPO4
3.4. Gas, Coke, and Liquid Products Distribution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAFs | Sustainable Aviation Fuels |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goal |
| HVO | Hydroprocessed Vegetable Oil |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analyser |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Elumalai, S.; Arumugam, B.; Kundu, P.; Kumar, S. Phenol derivatives of lignin monomers for aromatic compounds and cycloalkane fuels. In Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 459–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gu, X. A review on lignin pyrolysis: Pyrolytic behavior, mechanism, and relevant upgrading for improving process efficiency. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Zeng, K.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; Flamant, G.; Nzihou, A.; Vladimirovich, V.S.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Characteristics and evolution of heavy components in bio-oil from the pyrolysis of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaghat, H.; Rezaei, P.S.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of simulated phenolic bio-oil to cycloalkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons over bifunctional metal/acid catalysts of Ni/HBeta, Fe/HBeta and NiFe/HBeta. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Yin, L.; Shao, S.; Li, G. Recent progress on selective hydrogenation of phenol toward cyclohexanone or cyclohexanol. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 072003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Weng, L.; Wu, L.; Tan, L.; Tang, Y. Hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone catalyzed by isolated Pd cations in the micropores of zeolite. Appl. Catal. O Open 2024, 193, 206977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, T.R. Net Zero Aviation Fuels: Resource Requirements and Environmental Impacts; Royal Society: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/net-zero-aviation/net-zero-aviation-fuels-policy-briefing.pdf (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- World Economic Forum. Financing Sustainable Aviation Fuels: Case Studies and Implications for Investment; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Holladay, J.; Abdullah, Z.; Heyne, J. Sustainable Aviation Fuel: Review of Technical Pathways Report; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gundekari, S.; Manupathi, A.; Chandu, S.; Varkolu, M.; Kumar, P.; Karmee, S.K. Catalytic hydroconversion of lignin-based aromatics to aviation fuels—A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 15, 6557–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.B.; Iisa, K.; Dutta, A.; Chen, X.; Wrasman, C.J.; Mukarakate, C.; Yung, M.M.; Nimlos, M.R.; Tuxworth, L.; Baucherel, X.; et al. Opening pathways for the conversion of woody biomass into sustainable aviation fuel via catalytic fast pyrolysis and hydrotreating. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 9768–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevdokimova, O.; Shcherban, N.; Martinez-Klimov, M.; Weydisch, R.; Cueto, J.; Giner, E.A.; Eränen, K.; Peuronen, A.; Lastusaari, M.; Russo, V.; et al. Synthesis of jet-fuel precursors from renewable biomass through aldol condensation of cyclopentanone and furfural on base catalysts. Catal. Today 2025, 443, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.; Patel, H.; Yildirir, E.; Onwudili, J.A. Influence of surface acidity/basicity of selected metal oxide catalysts and reaction atmospheres on the ketonisation of propionic acid to produce 3-pentanone as a liquid biofuel precursor. Renew. Energy 2025, 250, 123386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Hafenstine, G.R.; Nguyen, H.H.; Vardon, D.R. Kinetics and Reactor Design Principles of Volatile Fatty Acid Ketonization for Sustainable Aviation Fuel Production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 2997–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kuang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Qi, F. Efficient Synthesis C12 Biojet Fuel Precursors from Cyclohexanone via Self-Condensation. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 8339–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.; Patel, H.; Onwudili, J.A. Sustainable Aviation Fuel-range Intermediates from Self-aldol Condensation of Cyclohexanone Using Low-cost Niobium Phosphate Catalyst. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 508, 145597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-F.; Paragian, K.; Sadula, S.; Rangarajan, S.; Vlachos, D.G. Sustainable Aviation Fuel Molecules from (Hemi)Cellulose: Computational Insights into Synthesis Routes, Fuel Properties, and Process Chemistry Metrics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 12927–12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Shao, S.; Hu, X.; Cai, Y. Aldol condensation/hydrogenation for jet fuel from biomass-derived ketone platform compound in one pot. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 215, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Arribas-Yuste, E.; Paniagua, M.; Morales, G.; Melero, J.A. Efficient Self-Condensation of Cyclohexanone into Biojet Fuel Precursors over Sulfonic Acid-Modified Silicas: Insights on the Effect of Pore Size and Structure. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 10175–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, J.-J.; Xie, J. Superhydrophobic and superacid magnetic catalyst induced highly selective aldol condensation and alkylation for high-density biofuels. Fuel 2024, 378, 132930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.; Onwudili, J.A.; Yildirir, E.; Hashemnezhad, S.E. Energy-dense sustainable aviation fuel-range hydrocarbons from cyclohexanone as a biomass-derived feedstock via sequential catalytic aldol condensation and hydrodeoxygenation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, I.; Nazir, M.H.; Chiang, K.; Christo, F.; Ameen, M. Current outlook on sustainable feedstocks and processes for sustainable aviation fuel production. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 49, 100959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, S.; Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y. Balancing Intermediates Formation on Atomically Pd-Bridged Cu/Cu2O Interfaces for Kinetics-Matching Electrocatalytic C─N Coupling Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2025, 64, e202503011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yani, F.T.; Husin, H.; Muhammad, S.; Abnisa, F.; Nasution, F. Palm oil hydrodeoxygenation into green diesel over NiO/NbOPO4 catalyst: A novel approach of synthesizing NbOPO4 from NbCl5. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Wan, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. Synergistic catalysis of mesoporous Cu/Co3O4 and surface oxygen vacancy for CO2 fixation to carbamates. J. Catal. 2023, 418, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdollers, A.R.; Schlexer, P.; Tosoni, S.; Pacchioni, G. Increasing Oxide Reducibility: The Role of Metal/Oxide Interfaces in the Formation of Oxygen Vacancies. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6493–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Rich Oxygen Vacancies in Bimetallic MnCo2O4.5 Spheres for Enhancing Lean Methane Catalytic Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, L.; Xu, W.; Liang, J. Ultrahigh selectivity self-condensation of cyclohexanone over TiO2/Al2O3 catalysts and kinetics study. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2023, 136, 2071–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, C.; An, L.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Shao, X.; Li, Z. Research progress of catalysts for aldol condensation of biomass based compounds. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9466–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudi, I.; Hart, A.; Ingram, A.; Wood, J. Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation of Vanillin, a Bio-Oil Model Compound over Renewable Ni/Biochar Catalyst. Catalysts 2023, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwudili, J.A.; Scaldaferri, C.A. Catalytic upgrading of intermediate pyrolysis bio-oil to hydrocarbon-rich liquid biofuel via a novel two-stage solvent-assisted process. Fuel 2023, 352, 129015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, K.; Soria, F. On the detection and size classification of nanometer-size metal particles on amorphous substrates. Ultramicroscopy 1986, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y. Mesoporous niobium phosphate: An excellent solid acid for the dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.T.; Scates, R.; Twigg, M.V. X-ray diffraction study of nickel oxide reduction by hydrogen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 246, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zeb, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, Y.; Sun, G. Highly selective self-condensation of cyclohexanone: The distinct catalytic behaviour of HRF5015. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikhtyanin, O.; Kadlec, D.; Velvarská, R.; Kubička, D. Using Mg-Al Mixed Oxide and Reconstructed Hydrotalcite as Basic Catalysts for Aldol Condensation of Furfural and Cyclohexanone. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z.; Mao, C. Kinetics of the reversible dimerization reaction of cyclohexanone over γ-alumina catalyst. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2011, 102, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Xia, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Aldol condensation of biomass-derived aldehydes and ketones followed by hydrogenation over Ni/HZSM-5 to produce aviation fuel: Role of acid sites. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 250, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, T.; Jing, Z.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Zuo, C. Enhancing aldol condensation with coupling oxygen storage materials and VPO catalysts: Impact of oxygen, kinetics and mechanism. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2025, 693, 120136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Catalysts with metal-acid dual sites for selective hydrodeoxygenation of lignin derivatives: Progress in regulation strategies and applications. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2023, 662, 119266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, C.A.; Rabelo-Neto, R.C.; de Lima, J.R.; Mattos, L.V.; Resasco, D.E.; Noronha, F.B. The Effect of Metal Type on Hydrodeoxygenation of Phenol Over Silica Supported Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Y.; Ye, T.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Ju, S. Cu/Mg/Al hydrotalcite-like hydroxide catalysts for o-phenylphenol synthesis. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Nie, G.; Pan, L.; Zou, J.-J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Highly selective self-condensation of cyclic ketones using MOF-encapsulating phosphotungstic acid for renewable high-density fuel. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4473–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, Y.S.; Kamath, R.S.; Kumbhar, P.S.; Mahajani, S.M. Self-Condensation of Cyclohexanone over Ion Exchange Resin Catalysts: Kinetics and Selectivity Aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, D.; Santos, A.; Simón, E.; Romero, A. Kinetic of Alkali Catalyzed Self-Condensation of Cyclohexanone. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.; Leeke, G.; Greaves, M.; Wood, J. Down-hole heavy crude oil upgrading by CAPRI: Effect of hydrogen and methane gases upon upgrading and coke formation. Fuel 2014, 119, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. Synthesis of branched alkane fuel from biomass-derived methyl-ketones via self-aldol condensation and hydrodeoxygenation. Fuel 2021, 299, 120889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikhtyanin, O.; Chlubná, P.; Jindrová, T.; Kubička, D. Peculiar behavior of MWW materials in aldol condensation of furfural and acetone. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10628–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, B.N.; Skarlos, L.; Kushner, D.J. Simultaneous Determination of Oil and Coke Contents in Spent Hydroprocessing Catalyst by Thermogravimetry. Energy Fuel 1997, 11, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Epelde, E.; Valecillos, J.; Izaddoust, S.; Aguayo, A.T.; Bilbao, J. Coke deactivation and regeneration of HZSM-5 zeolite catalysts in the oligomerization of 1-butene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 120076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M.; Magnoux, P. Organic chemistry of coke formation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 212, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
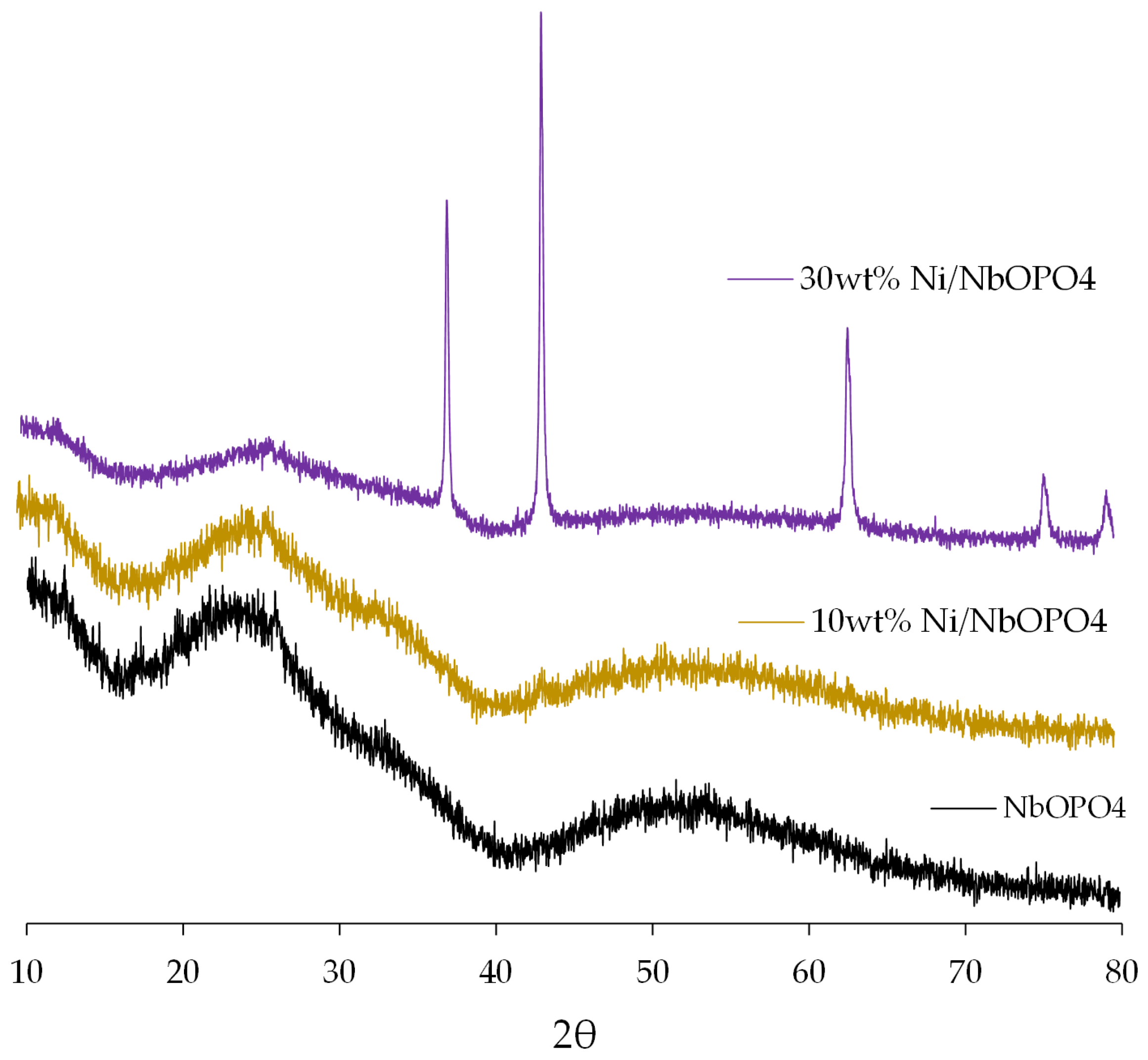
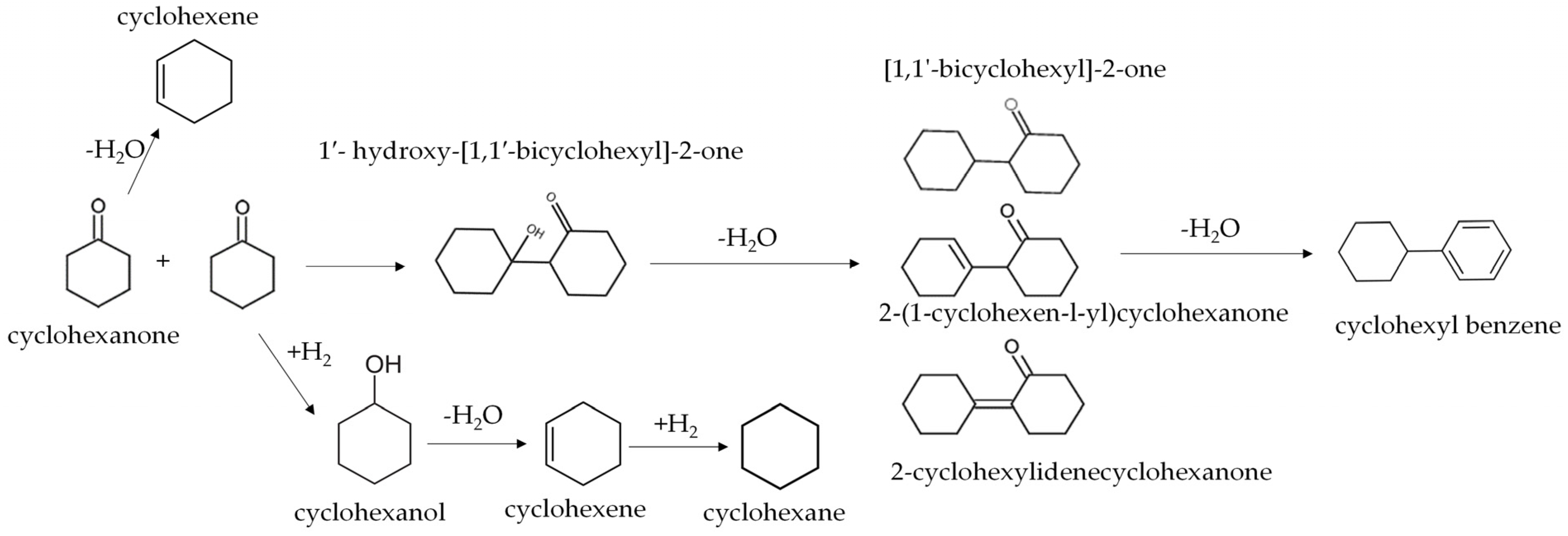


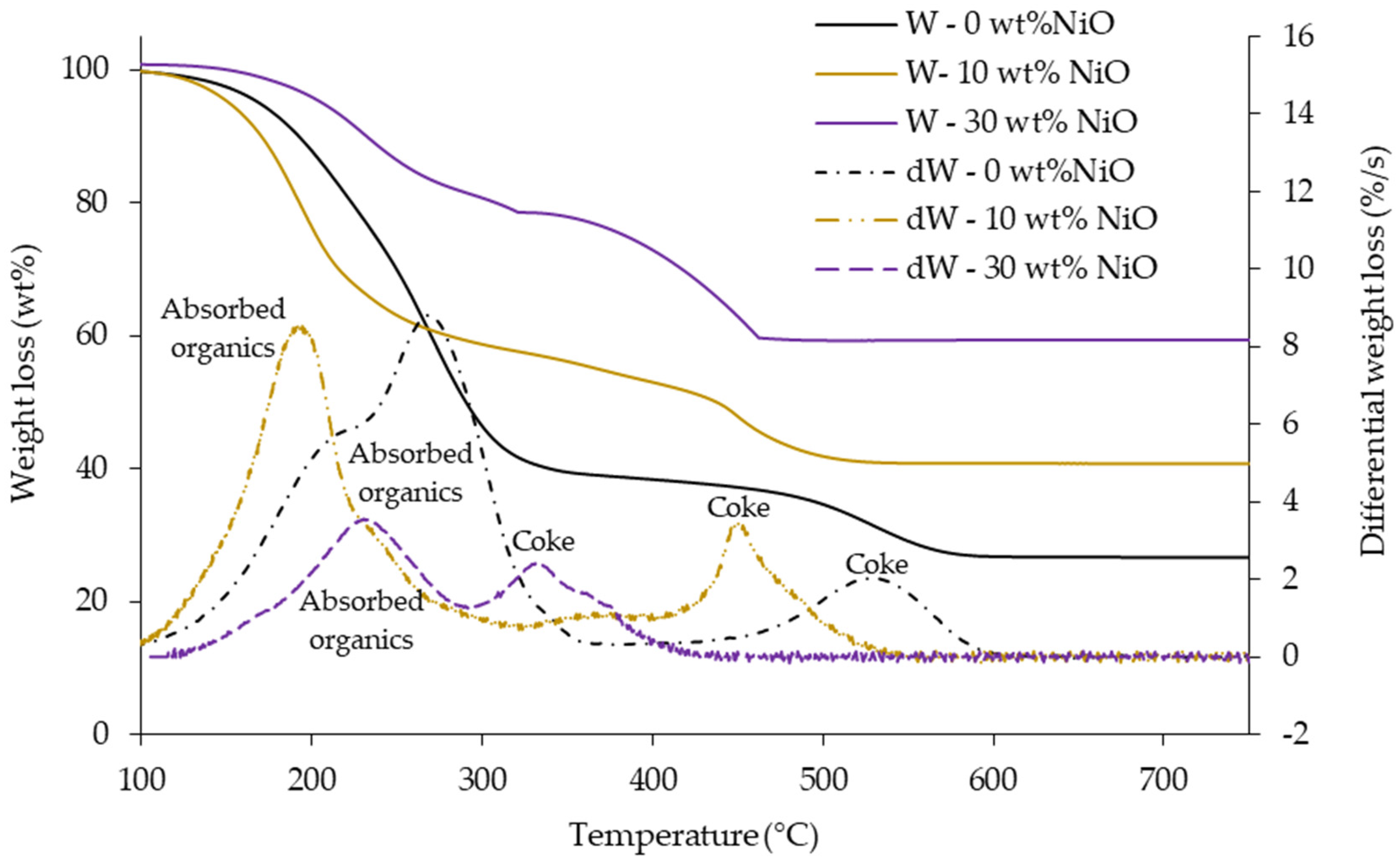
| Parameter | NbOPO4 | 10wt% NiO/NbOPO4 | 30wt% NiO/NbOPO4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2·g−1) | 411 | 272 | 125 |
| Pore volume (cm3·g−1) | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.35 |
| Average pore diameter (nm) | 3.43 | 3.41 | 3.41 |
| Lewis acid (mmol) | 39.4 | 33.0 | 26.6 |
| Brønsted acid (mmol) | 23.5 | 19.7 | 16.0 |
| Brønsted + Lewis acid (mmol) | 68.2 | 58.0 | 47.9 |
| NiO loading (wt%) | NA | 9.2 | 28.5 |
| Catalyst | Conversion (%) | Selectivity Towards C12 (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amberlyst-15 and Amberlyst-70 resins, SO3H-SBA-3, SO3H-SBA-16, and SO3H-FDU-12 | 25–40 | 95 | Ref. [19] |
| SO3H-SBA-15, SO3H-LP-SBA-15, and SO3H–SiNF | 20–22 | 95 | Ref. [19] |
| Ion exchange resin and T-63 | 28–40 | 90–92 | Ref. [44] |
| NbOPO4 | 68–96 | 53–70 | Ref. [16] |
| ZSM, Pd/ZSM, and PdFe/hierarchical-ZSM | 8.3–55 | 52–97 | Ref. [15] |
| Fe3O4, Fe3O4@SiO2, and Fe3O4@SiO2@F-SO3H | 4.2–78 | 22–94.2 | Ref. [20] |
| Amberlyst 15 | 50 | 90 | Ref. [45] |
| Phosphotungstic acid (PTA), MIL-100, PTA@MIL-100 | 8–48 | 10–97 | Ref. [43] |
| TiO2/Al2O3 | 29.11 | 100 | Ref. [28] |
| 10 wt% NiO/NbOPO4 | 66.8 | 96.8 | This study |
| Catalyst | Gas (wt%) | Coke (wt%) | Liquid (wt%) | Balance (wt%) |
| NbOPO4 | 5.22 ± 0.12 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 89.71 ± 1.24 | 95.65 ± 0.62 |
| 10 wt% NiO/NbOPO4 | 6.50 ± 0.02 | 0.66 ± 0.11 | 89.52 ± 0.96 | 96.68 ± 0.43 |
| 30 wt% NiO/NbOPO4 | 6.26 ± 0.07 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 89.71 ± 1.05 | 96.61 ± 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hart, A.; Onwudili, J.A. Tuning the Activity of NbOPO4 with NiO for the Selective Conversion of Cyclohexanone as a Model Intermediate of Lignin Pyrolysis Bio-Oils. Energies 2025, 18, 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154106
Hart A, Onwudili JA. Tuning the Activity of NbOPO4 with NiO for the Selective Conversion of Cyclohexanone as a Model Intermediate of Lignin Pyrolysis Bio-Oils. Energies. 2025; 18(15):4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154106
Chicago/Turabian StyleHart, Abarasi, and Jude A. Onwudili. 2025. "Tuning the Activity of NbOPO4 with NiO for the Selective Conversion of Cyclohexanone as a Model Intermediate of Lignin Pyrolysis Bio-Oils" Energies 18, no. 15: 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154106
APA StyleHart, A., & Onwudili, J. A. (2025). Tuning the Activity of NbOPO4 with NiO for the Selective Conversion of Cyclohexanone as a Model Intermediate of Lignin Pyrolysis Bio-Oils. Energies, 18(15), 4106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154106







