Wave Prediction Error Compensation and PTO Optimization Control Method for Improving the WEC Power Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
- By optimizing the control of the charge and discharge of the accumulators in the PTO system, the poor power quality caused by wave prediction errors is improved.
- The operation efficiency and stability of the hydraulic PTO system are increased by controlling the torque of the generator.
2. Problem Statement and Overview of Control Method
3. Modeling Analysis
3.1. Dynamic Modeling of Floating Pendulum
3.2. Hydraulic System Modeling
3.2.1. Hydraulic Motor Analysis
3.2.2. Accumulators Analysis
3.2.3. Simplification Analysis
3.3. MPC Control System Design
4. Case Study
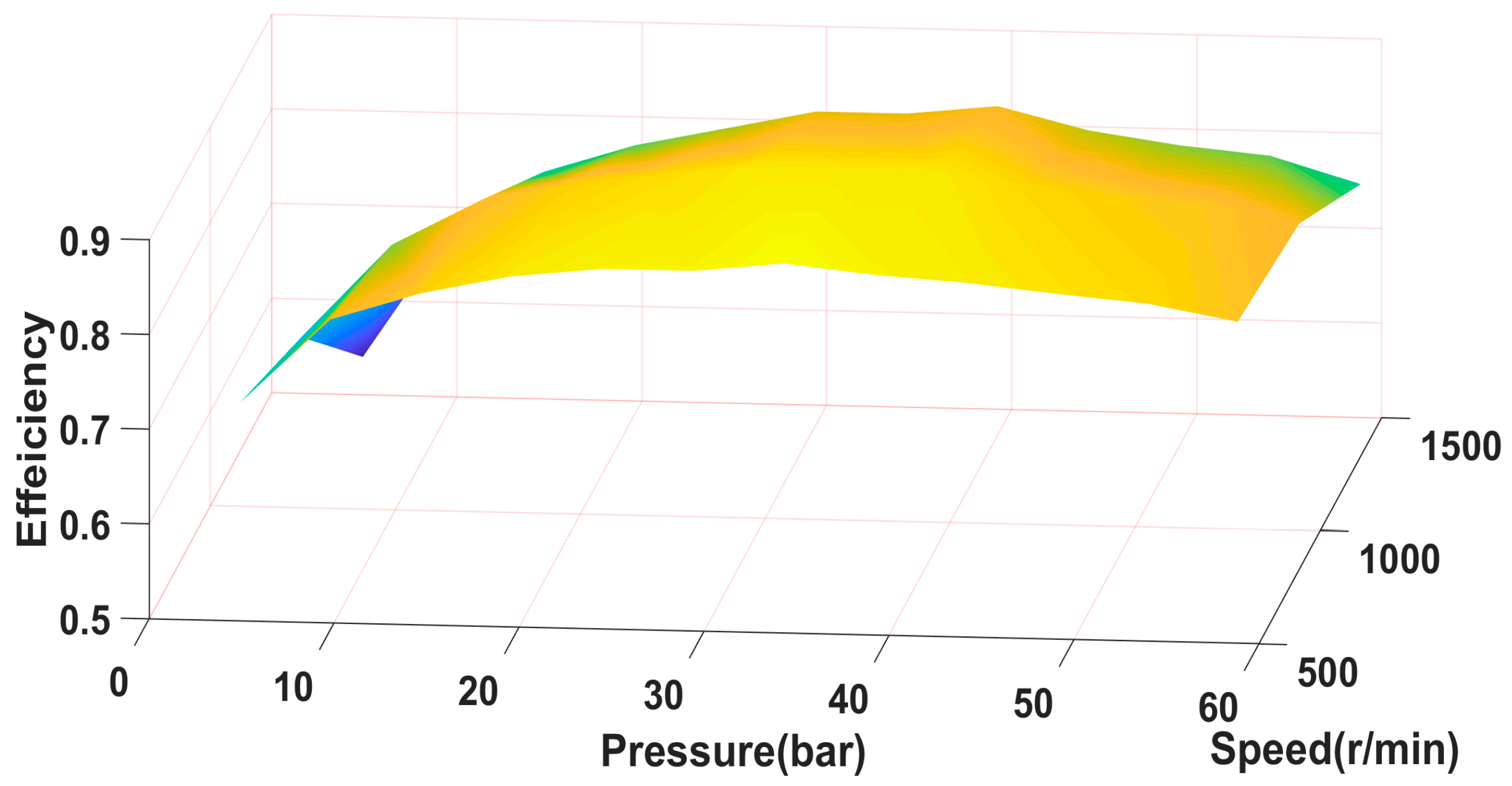
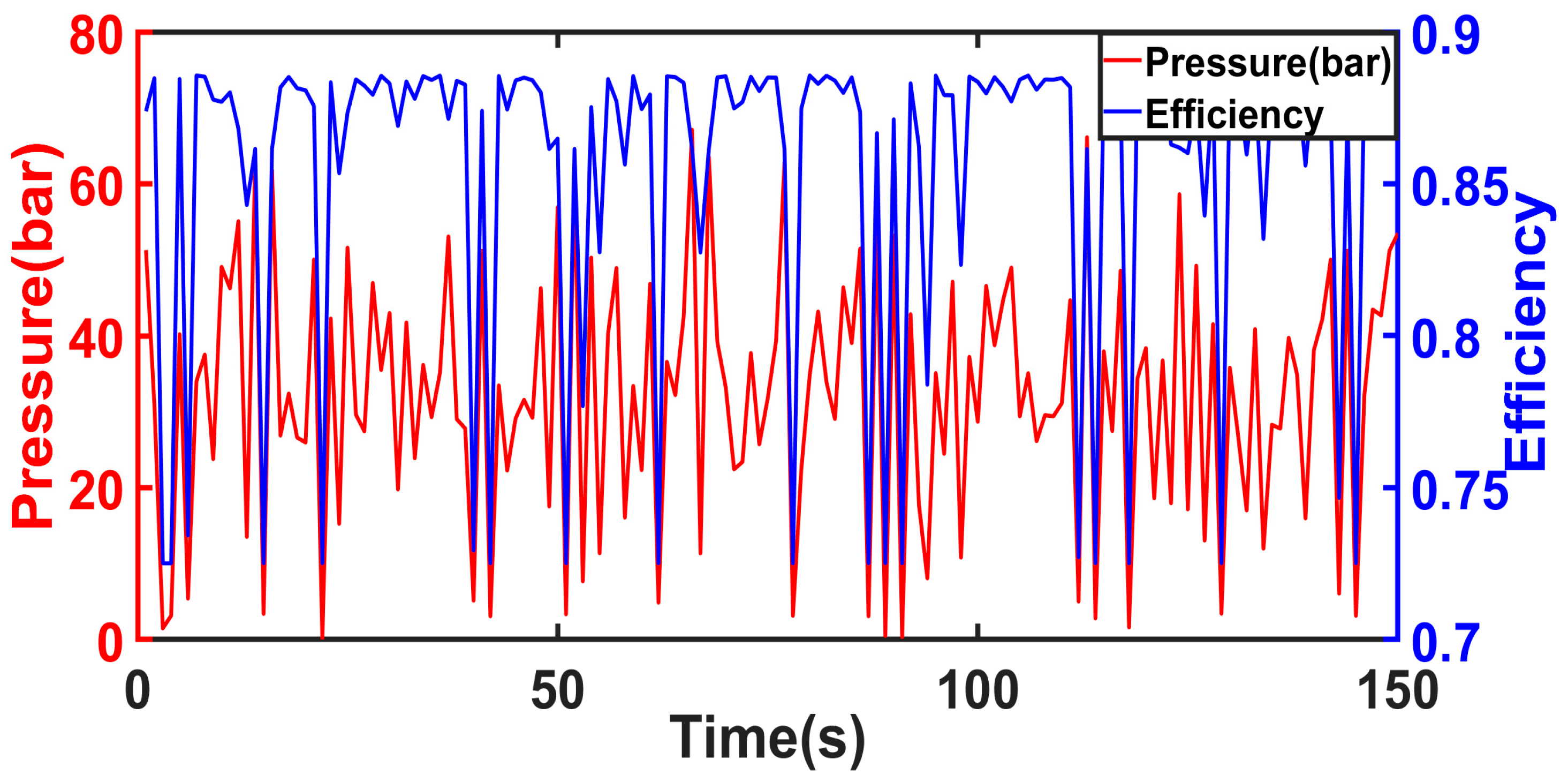
4.1. Hydraulic Efficiency Optimization Verification
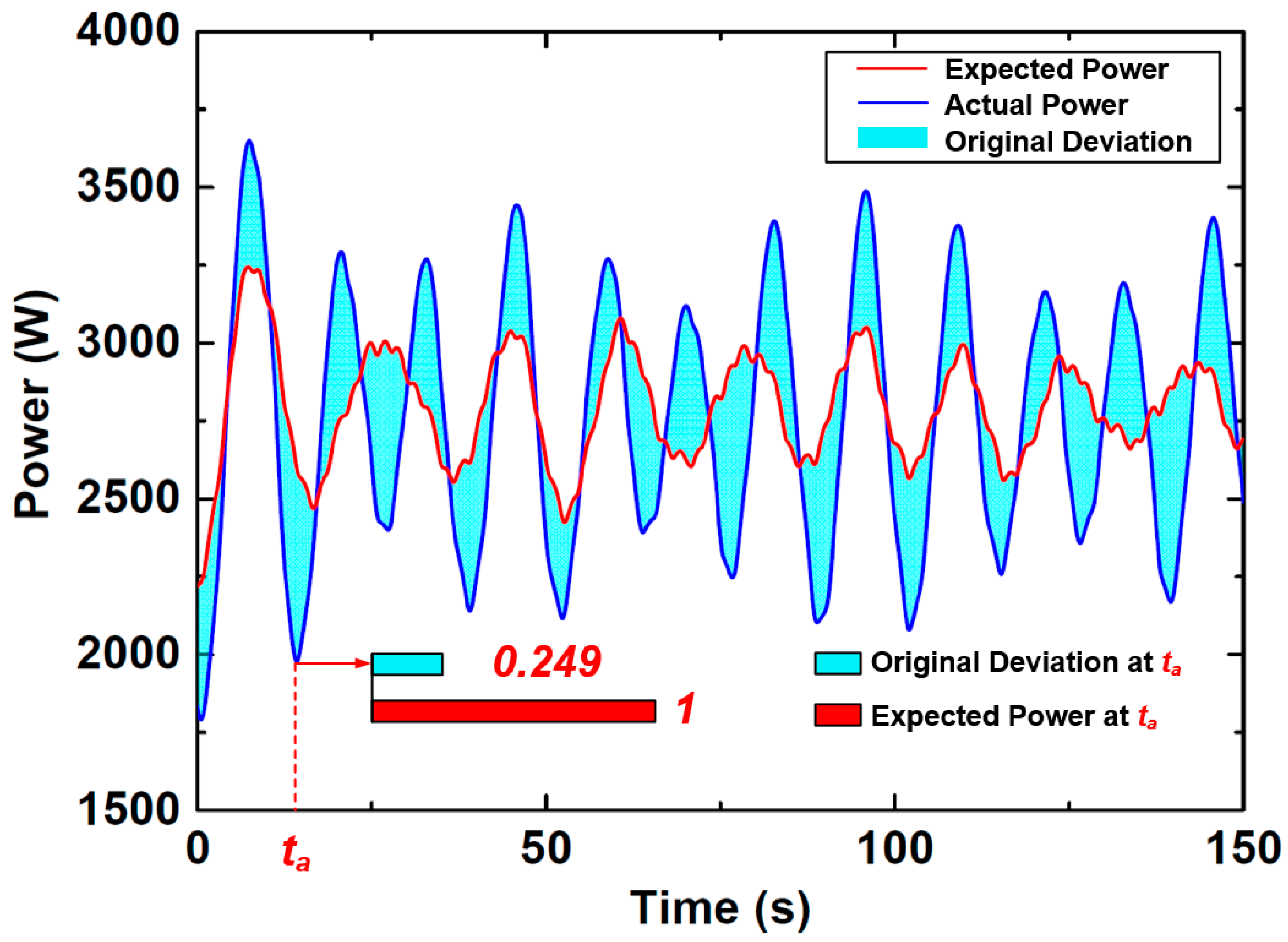
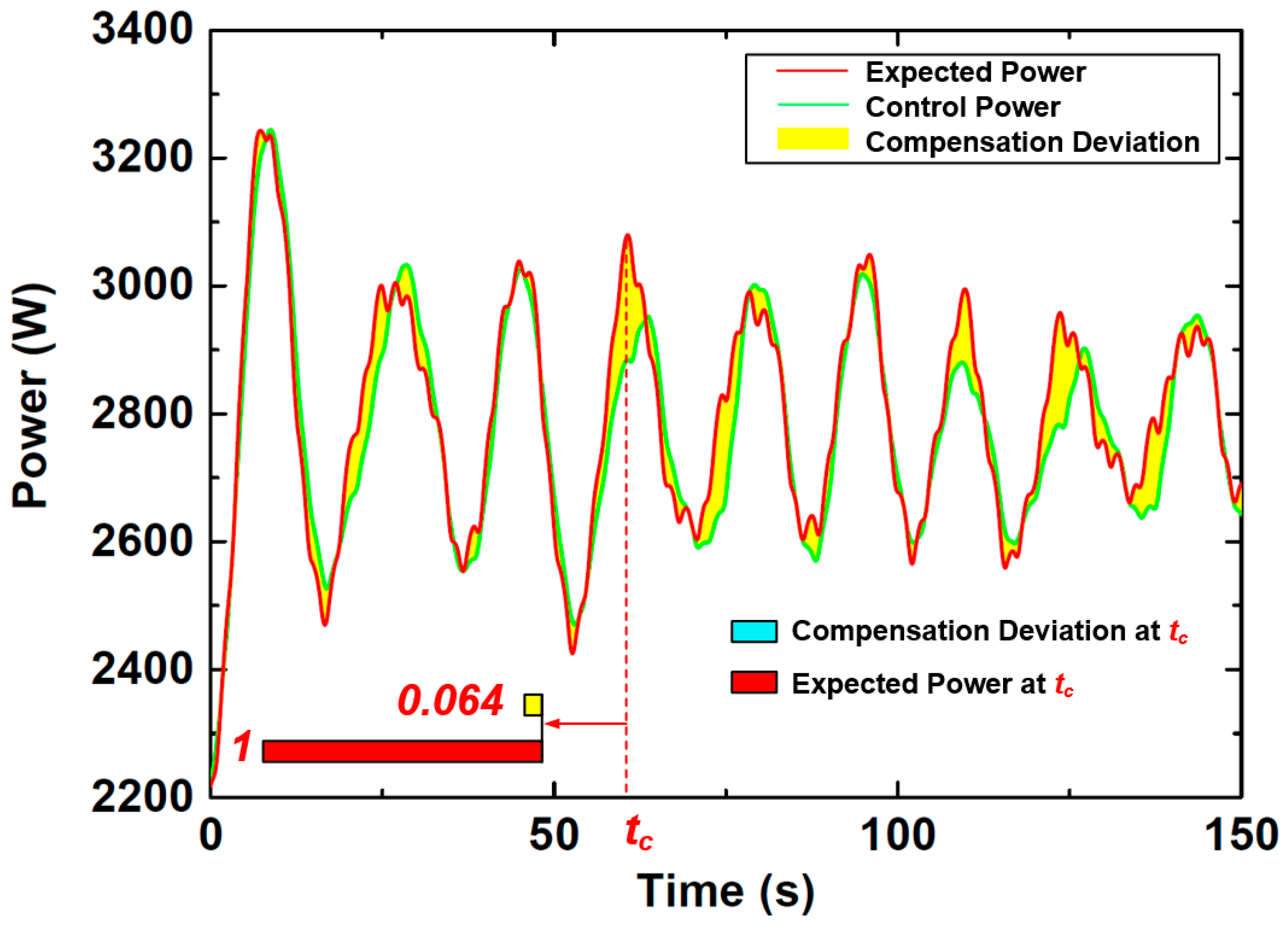
4.2. Prediction Deviation Compensation Verification
5. Conclusions
5.1. Overall Conclusions
5.2. Limitations and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Astariz, S.; Iglesias, G. The economics of wave energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, A.; McCullen, P.; Falcão, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Gardner, F.; Hammarlund, K.; Lemonis, G.; Lewis, T.; Nielsen, K.; Petroncini, S.; et al. Wave energy in Europe: Current status and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, W. A Comprehensive Review on the Development of Sustainable Energy Strategy and Implementation in China. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2010, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.d.O. Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W. Wave energy conversion and hydrodynamics modelling technologies: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, D.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F. On the potential synergies and applications of wave energy converters: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ning, D.; Gou, Y.; Zhou, Z. Wave energy converter optimization based on differential evolution algorithm. Energy 2022, 246, 123433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretel, J.A.M.; Lightbody, G.; Thomas, G.P.; Lewis, A.W. Maximisation of Energy Capture by a Wave-Energy Point Absorber using Model Predictive Control. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 3714–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Gai, N.; Stansby, P.; Li, G. Linear Non-Causal Optimal Control of an Attenuator Type Wave Energy Converter M4. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Helmy, W.; Turky, R.A.; Abdel Aleem, S.H.E. Transient stability improvement of wave energy conversion systems connected to power grid using anti-windup-coot optimization strategy. Energy 2022, 245, 123321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J. Optimization of Energy Storage Configuration for Error Compensation of Wind Power Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Shanghai, China, 2–4 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Pan, W.-X.; Li, X. Energy storage scheduling design on friendly grid wind power. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshirband, S.; Amir, M.; Timon, R.; Narjes, N.; Chau, K.-W. Prediction of significant wave height; comparison between nested grid numerical model, and machine learning models of artificial neural networks, extreme learning and support vector machines. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Ma, X. Prediction of Wave Power Generation Using a Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Inputs. Energies 2018, 11, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uihlein, A.; Magagna, D. Wave and tidal current energy—A review of the current state of research beyond technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, A.; Holst, U.; Holst, J. Forecasting near-surface ocean winds with Kalman filter techniques. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminezhad, M.H.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Mousavi, S.J. Application of fuzzy inference system in the prediction of wave parameters. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, M.C.; Kumar, N.K. Interpolation of wave heights. Ocean Eng. 2000, 27, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, M.R.; Horwood, J.M.K.; Thurley, R.W.F.; Baker, J. Filters for linear sea-wave prediction. Ocean Eng. 2006, 33, 2332–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liang, H.; Dinavahi, V. Direct Interval Forecast of Uncertain Wind Power Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liao, H.-y. An intelligent method for wind power forecasting based on integrated power slope events prediction and wind speed forecasting. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 13, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.Y. An overview of medium- to long-term predictions of global wave energy resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Bussar, C.; Stöcker, P.; Moraes, L.; Magnor, D.; Leuthold, M.; Sauer, D.U. Application of Battery Storage for Compensation of Forecast Errors of Wind Power Generation in 2050. Energy Procedia 2015, 73, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.P.; Dhar, S.; Dash, P.K. An effective battery management scheme for wind energy systems using multi Kernel Ridge regression algorithm. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, F.; Riahy, G.H. MPC-based approach for online demand side and storage system management in market based wind integrated power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 106, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Ni, T.; Cheng, P.; Lei, S. Wind Power Prediction Based on LS-SVM Model with Error Correction. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R. Design, simulation, and testing of a novel hydraulic power take-off system for the Pelamis wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, R.; McKee, K.; Howard, I. Advancements of wave energy converters based on power take off (PTO) systems: A review. Ocean Eng. 2020, 204, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargo, C.J.; Hillis, A.J.; Plummer, A.R. Optimisation and control of a hydraulic power take-off unit for a wave energy converter in irregular waves. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2014, 228, 462–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasberger, J.; Yang, L.; Bacelli, G.; Zuo, L. Control co-design and optimization of oscillating-surge wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2024, 225, 120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargo, C.J.; Plummer, A.R.; Hillis, A.J.; Schlotter, M. Determination of optimal parameters for a hydraulic power take-off unit of a wave energy converter in regular waves. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2012, 226, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Q.; Bao, G. Influence of hydraulic power take-off unit parameters on power capture ability of a two-raft-type wave energy converter. Ocean Eng. 2018, 150, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, A.F.d.O. Phase control through load control of oscillating-body wave energy converters with hydraulic PTO system. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Bao, J.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Tu, L.; Zhang, D. Review of hydraulic transmission technologies for wave power generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Andreu, J.; Ceballos, S.; Martínez de Alegría, I.; Kortabarria, I. Review of wave energy technologies and the necessary power-equipment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Mu, A.; Ma, T. Design and control of a point absorber wave energy converter with an open loop hydraulic transmission. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 121, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.F.; Calvário, M.; Kamarlouei, M.; Soares, C.G. Design tradeoffs of an oil-hydraulic power take-off for wave energy converters. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, G.; Pasta, E.; Carapellese, F.; Bonfanti, M. Energy-maximising model predictive control for a multi degree-of-freedom pendulum-based wave energy system. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Li, G. Model predictive control of a wave-to-wire wave energy converter system with non-linear dynamics and non-linear constraints using a tailored pseudo-spectral method. Energy 2024, 304, 132060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadmani, A.; Nikoo, M.R.; Gandomi, A.H.; Wang, R.-Q.; Golparvar, B. A review of machine learning and deep learning applications in wave energy forecasting and WEC optimization. Energy Strategy Rev. 2023, 49, 101180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacelli, G.; Coe, R.G. Comments on Control of Wave Energy Converters. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2021, 29, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.G.; Patel, A.I.; Singh, R.G. Real time implementation of MPC in bottle washer machine for small scale beverage industry. In Proceedings of the 2017 6th International Conference on Computer Applications In Electrical Engineering-Recent Advances (CERA), Roorkee, India, 5–7 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gallutia, D.; Tahmasbi Fard, M.; Gutierrez Soto, M.; He, J. Recent advances in wave energy conversion systems: From wave theory to devices and control strategies. Ocean Eng. 2022, 252, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, E.; Carapellese, F.; Mattiazzo, G. Deep Neural Network Trained to Mimic Nonlinear Economic Model Predictive Control: An Application to a Pendulum Wave Energy Converter. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 August 2021. [Google Scholar]







| RMSE of Wave Prediction Error | Deviation | RMSE of Power Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0500 | 351.99 | 0.1123 | 0.0964 | |
| 58.14 | 0.0159 | |||
| 0.1499 | 437.20 | 0.1405 | 0.1199 | |
| 74.14 | 0.0206 | |||
| 0.2871 | 642.80 | 0.1943 | 0.1277 | |
| 219.40 | 0.0666 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, T.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Qian, P.; Zhang, D.; Feng, B. Wave Prediction Error Compensation and PTO Optimization Control Method for Improving the WEC Power Quality. Energies 2025, 18, 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154043
Lan T, Wang J, He L, Qian P, Zhang D, Feng B. Wave Prediction Error Compensation and PTO Optimization Control Method for Improving the WEC Power Quality. Energies. 2025; 18(15):4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154043
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Tianlong, Jiarui Wang, Luliang He, Peng Qian, Dahai Zhang, and Bo Feng. 2025. "Wave Prediction Error Compensation and PTO Optimization Control Method for Improving the WEC Power Quality" Energies 18, no. 15: 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154043
APA StyleLan, T., Wang, J., He, L., Qian, P., Zhang, D., & Feng, B. (2025). Wave Prediction Error Compensation and PTO Optimization Control Method for Improving the WEC Power Quality. Energies, 18(15), 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18154043






