Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AFPMSM Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening
2.1. Cogging Torque Calculation with the Magnetic Field Energy Method
2.2. Rotor MMF Distribution
2.3. Stator Permeance Function
2.4. Magnetic Energy Integration Considering the Axial Direction
3. Reconstruction of MMF and Air Gap Permeability via FEA Post-Processing
3.1. MMF Approximation via Field Difference
- slotted (realistic) stator model;
- smooth (idealized) stator model.
3.2. Permeance Approximation via Field Ratio
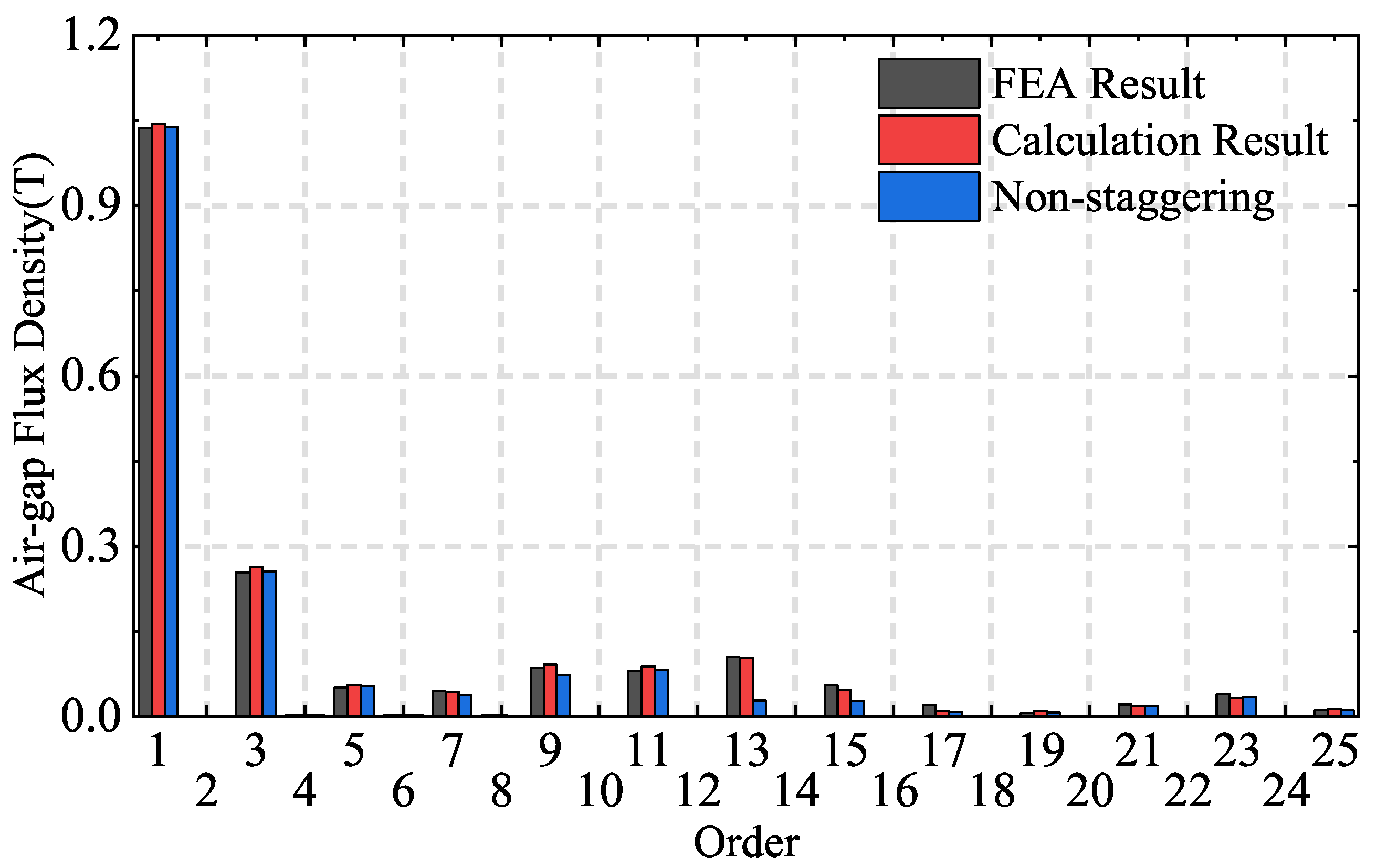
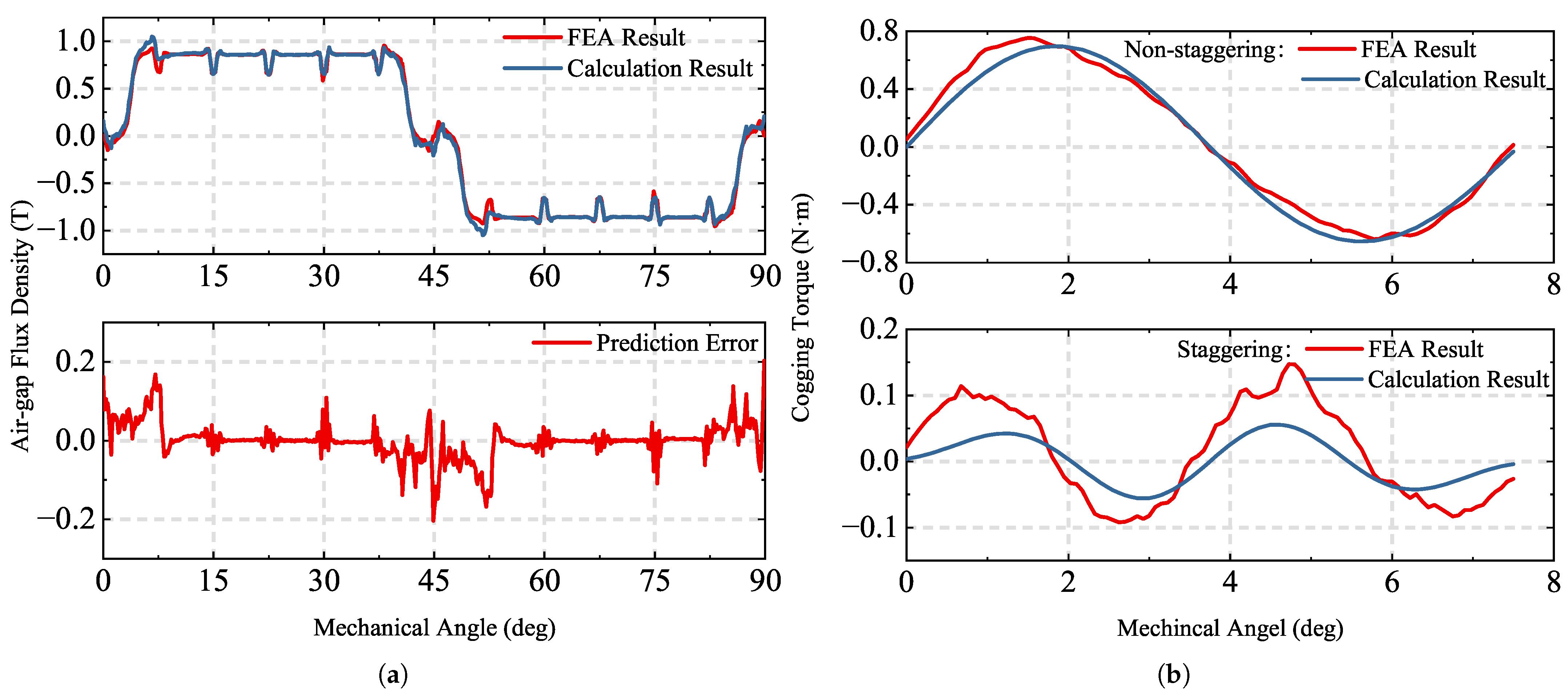
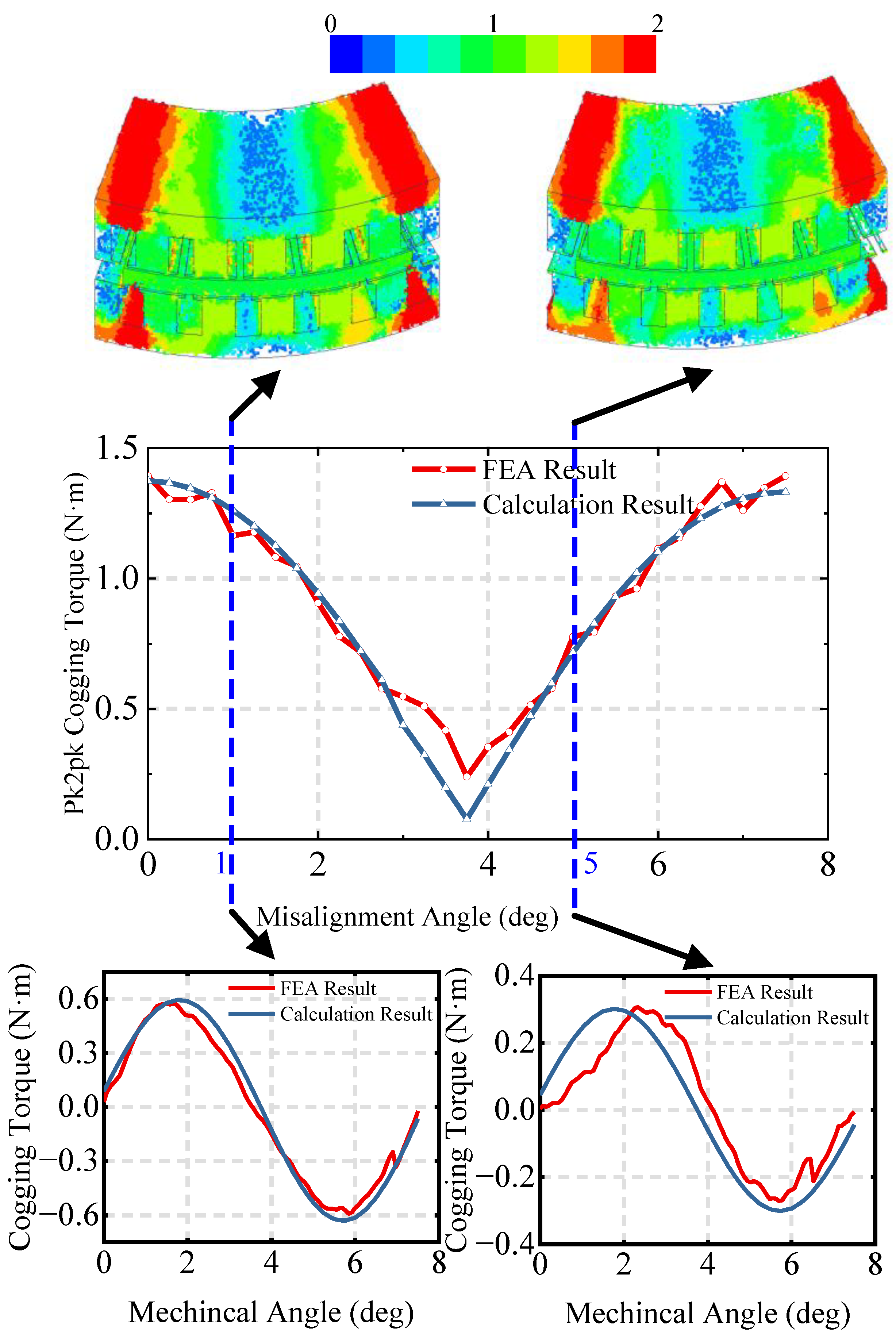
4. Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Effects of Stator Staggering
4.2. Efficiency of Calculations and Accuracy
5. Conclusions
- The proposed harmonic screening-based method provides accurate and efficient prediction of cogging torque in AFPMSMs. Compared with conventional FEA, it achieves a 91.75% reduction in computation time without demanding excessive hardware resources and reaches over 0.9 of the waveforms’ similarity. This makes it particularly suitable for rapid evaluation of motor performance during the early design phase;
- The method establishes a clear relationship between cogging torque and the harmonic frequencies and amplitudes of key electromagnetic parameters, offering valuable insights for future studies aimed at cogging torque reduction;
- The approach reveals the connection between the harmonics of air gap magnetic density and stator staggering, thereby laying a solid foundation for further research into the effects of stator staggering on other motor performance types;
- It is necessary to further analyze the torque fluctuations of AFPMSM under load conditions using the energy method. The results of this study contribute to enriching the application of the energy method in torque prediction and calculation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, A.; Dieterich, D.; Urschel, S. Comparison of Eddy Current Loss Calculation Techniques for Axial Flux Motors with Printed Circuit Board Windings. Energies 2025, 18, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zha, X.; Qu, R. Pulsating Torque Suppression of Flux Reversal Machines Based on Specific Harmonic Contributions of Rotor Permeance and PM MMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strączyński, P.; Różowicz, S.; Baran, K. Automated Laboratory Stand for Determining the Cogging Torque of a Small Permanent Magnet Electric Machine Using the MATLAB Environment. Energies 2025, 18, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, M.H.; Rahideh, A.; Faradonbeh, V.Z. Analytical Cogging Torque and Unbalanced Magnetic Force Calculations in Slotted Surface-PM Machines Assuming Finite Iron Permeability. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2024, 10, 9088–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee-Alam, F. On-Load Cogging Torque Calculation in Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Motors Using Hybrid Analytical Model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2024, 60, 8200110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; Lu, D. Investigation of Post-Demagnetization Torque Ripple in Integer-Slot Surface-Mounted PM Wind Power Generators after Short-Circuit Faults. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Niu, S.; Gao, J.; Huang, S. Harmonic Interaction Model for Fast and Accurate Cogging Torque Calculation in Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2025. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeida, A.; Lehikoinen, A.; Rasilo, P.; Vansompel, H.; Belahcen, A.; Arkkio, A.; Sergeant, P. A Simple and Efficient Quasi-3D Magnetic Equivalent Circuit for Surface Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8318–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, J. Investigation and Analysis of Cogging Torque for Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Fukuoka, Japan, 26–29 November 2024; pp. 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, J.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Pang, X.; Liu, W.; Kong, Z. Study of Electromagnetic Characteristics of Brushless Reverse Claw Pole Electromagnetic and Permanent Magnet Hybrid Excitation Generator for Automobiles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tong, W.; Hou, M.; Wu, S.; Tang, R. Analytical Model for No-Load Electromagnetic Performance Prediction of V-Shape IPM Motors Considering Nonlinearity of Magnetic Bridges. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.N. Analytical Prediction of Cogging Torque in Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Design and Analysis of Permanent Magnets in a Negative-Salient Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 182249–182259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Fang, S.; Xu, Q.; Pan, Z. Detent Torque Analysis of Multi-Stator-Module Permanent Magnet Arc Machine Based on a Hybrid Analytical Model Considering Asymmetric Stator and Rotor Eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, C.; Kou, B.; Wei, J.; Wang, W. A Novel Rapid Optimization Design Method for the Reverse-Salient Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2024, 10, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüner, E.; Çolak, Y. Experimental Investigation of Magnet Grouping Technique in Reduction of Cogging Torque and Total Harmonic Distortions in the Axial Flux PM Generator for Direct Drive Wind Turbine. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2023, 51, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Li, S.; Nie, R.; Wang, P.; Xu, S.; Gan, C. A Dual-Rotor Axial-Flux PM Motor with Equidirectional Toroidal Winding and 3-Slot/4-Pole Unit Block for Torque Density Improvement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 16200–16211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiku, J.; Khan, M.A.; Barendse, P.S.; Pillay, P. Influence of Slot Openings and Tooth Profile on Cogging Torque in Axial-Flux PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7578–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Pan, G.; Mao, Z. Analytical Calculation and Optimization of the Segmented-Stator Dual-Rotor Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 8101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Pan, Y.; Huang, S. Cogging Torque Suppression of Permanent Magnet Homopolar Inductor Machine Based on Tooth Combination Method. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2024, 10, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Niu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, S.; Chan, W.L. Diverse Slot-Opening Designs for Cogging Torque and Performance Optimization in PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2025, 11, 8414–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Outer diameter (mm) | 110 |
| Inner diameter (mm) | 80 |
| Airgap length (mm) | 1 |
| Magnet thick(mm) | 8 |
| Slot opening width (mm) | 0.86 |
| Slot opening height (mm) | 0.6 |
| FEA | Harmonic Screening | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Model | i7-9750H | R5 3500U |
| CPU Threads | 12 | 8 |
| CPU Frequency (GHz) | 2.6 | 2.4 |
| RAM Capacity (GB) | 32 | 20 |
| System Version | Windows 10 Enterprise 21H2 | |
| Software Version | Maxwell 2023R2 | MATLAB R2023b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.-K.; Zou, X.-P.; Guo, Q.-C.; Zhu, L.-K. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening. Energies 2025, 18, 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143779
Zhao X-K, Zou X-P, Guo Q-C, Zhu L-K. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening. Energies. 2025; 18(14):3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143779
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiao-Kun, Xin-Peng Zou, Qi-Chao Guo, and Liang-Kuan Zhu. 2025. "Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening" Energies 18, no. 14: 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143779
APA StyleZhao, X.-K., Zou, X.-P., Guo, Q.-C., & Zhu, L.-K. (2025). Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening. Energies, 18(14), 3779. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143779






