The Application of a New Microbial Biosurfactant to Remove Residual Oil from Electric Power Plant and to Inhibit Metal Corrosion in a Salty Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Biosurfactant Production
2.3. Biosurfactant Extraction
2.4. Toxicity Test with Artemia Salina
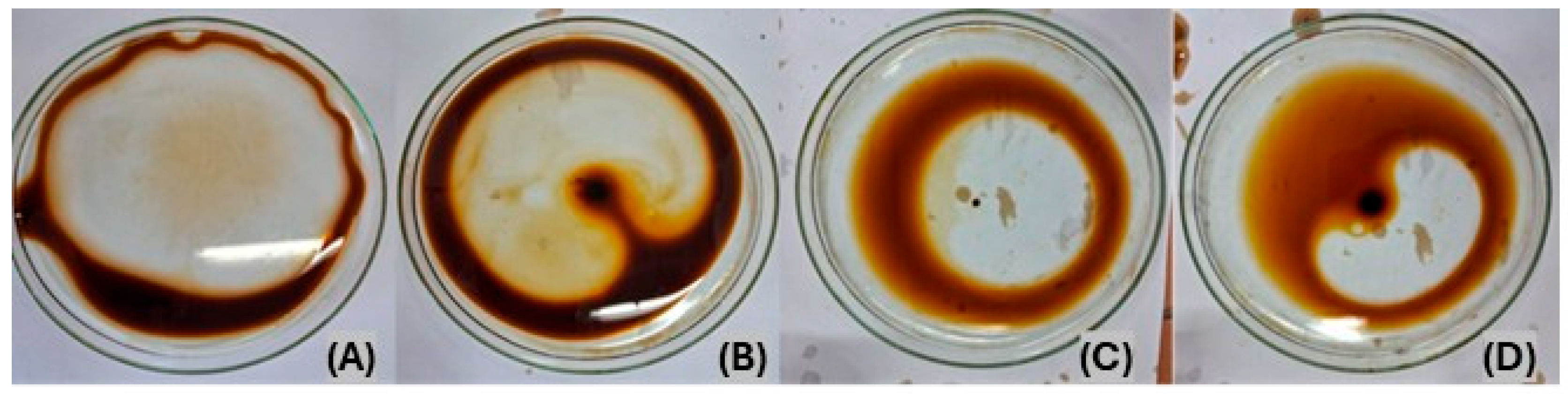
2.5. Dispersion of Engine Oil in Seawater
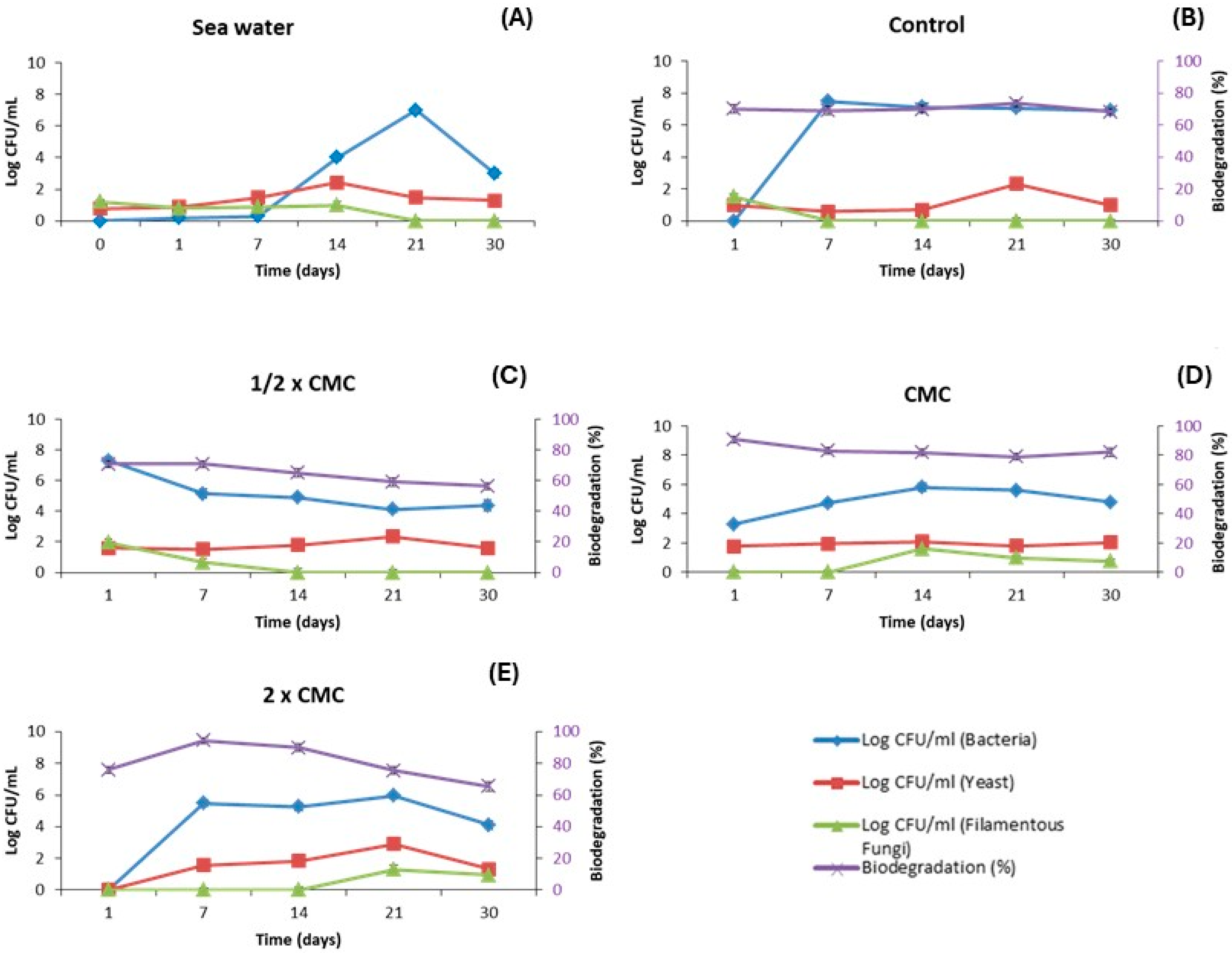
2.6. Tests of Bioremediation of Oil Spill in Seawater
2.7. Inhibition of Metal Corrosion in Seawater Using the Isolated Biosurfactant
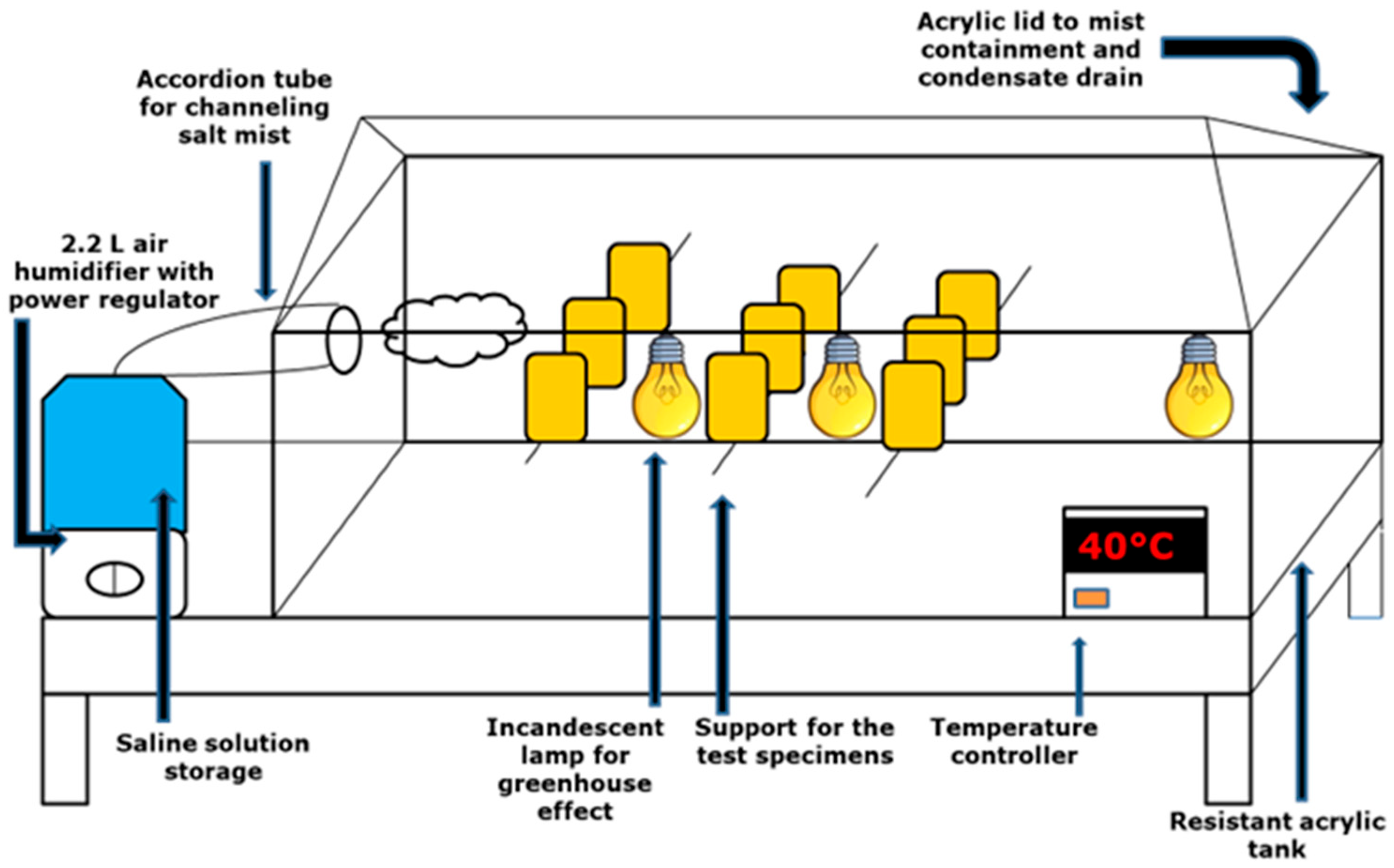
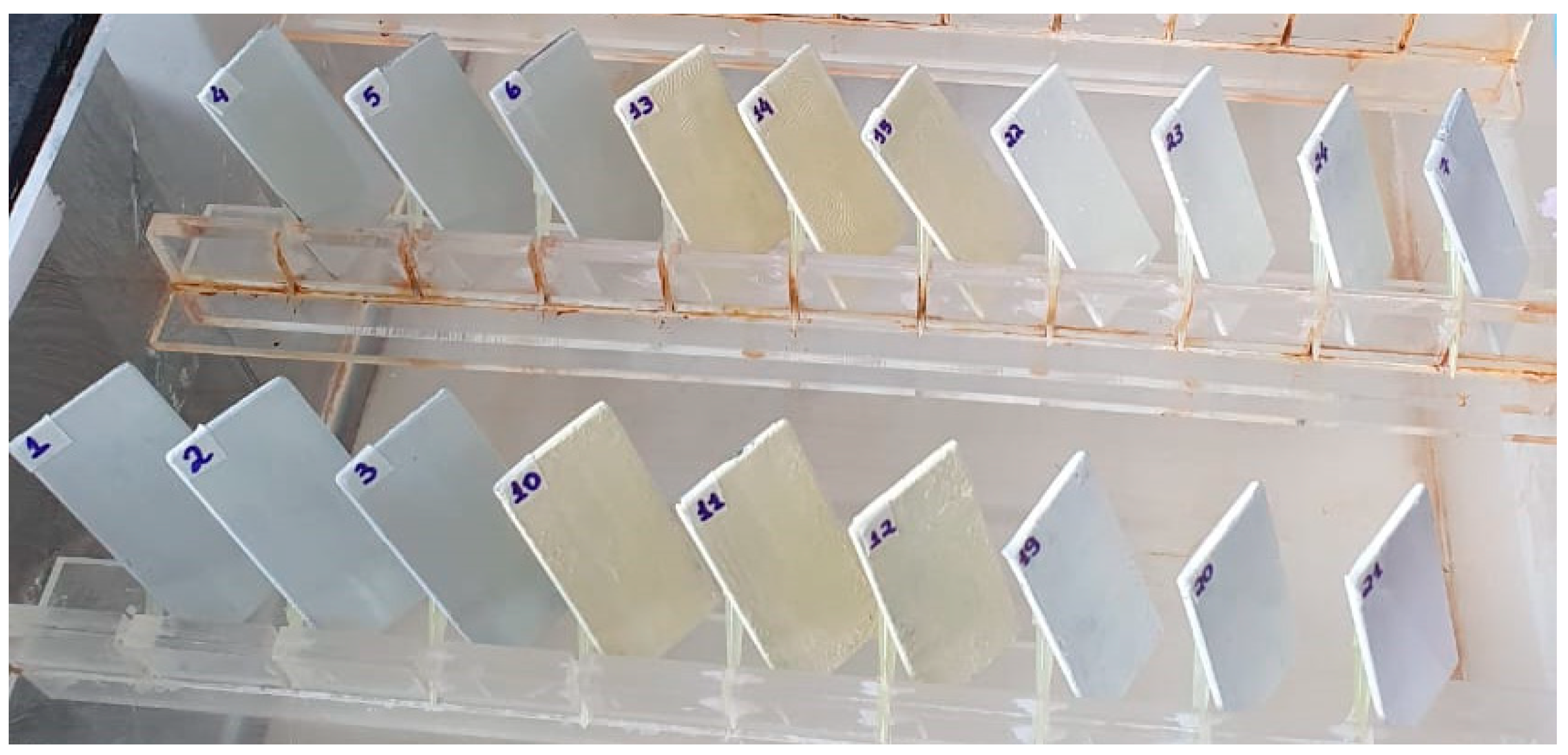
2.8. Evaluation of Biosurfactant Incorporated into Biodegradable Matrix as an Inhibitor of Corrosion Due to Atmospheric Physical Factors on Metal Surfaces
2.9. Biosurfactant’s Incorporation into Synthetic Enamels
2.10. Application of Biosurfactant as an Additive in Synthetic Enamels to Inhibit Metal Corrosion Due to Atmospheric Physical Factors
2.11. Statistical Analysis of Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Toxicity of the Biosurfactant to Artemia Salina
3.2. Dispersion of Engine Oil in Seawater
3.3. Bioremediation of Oil Spills in Seawater
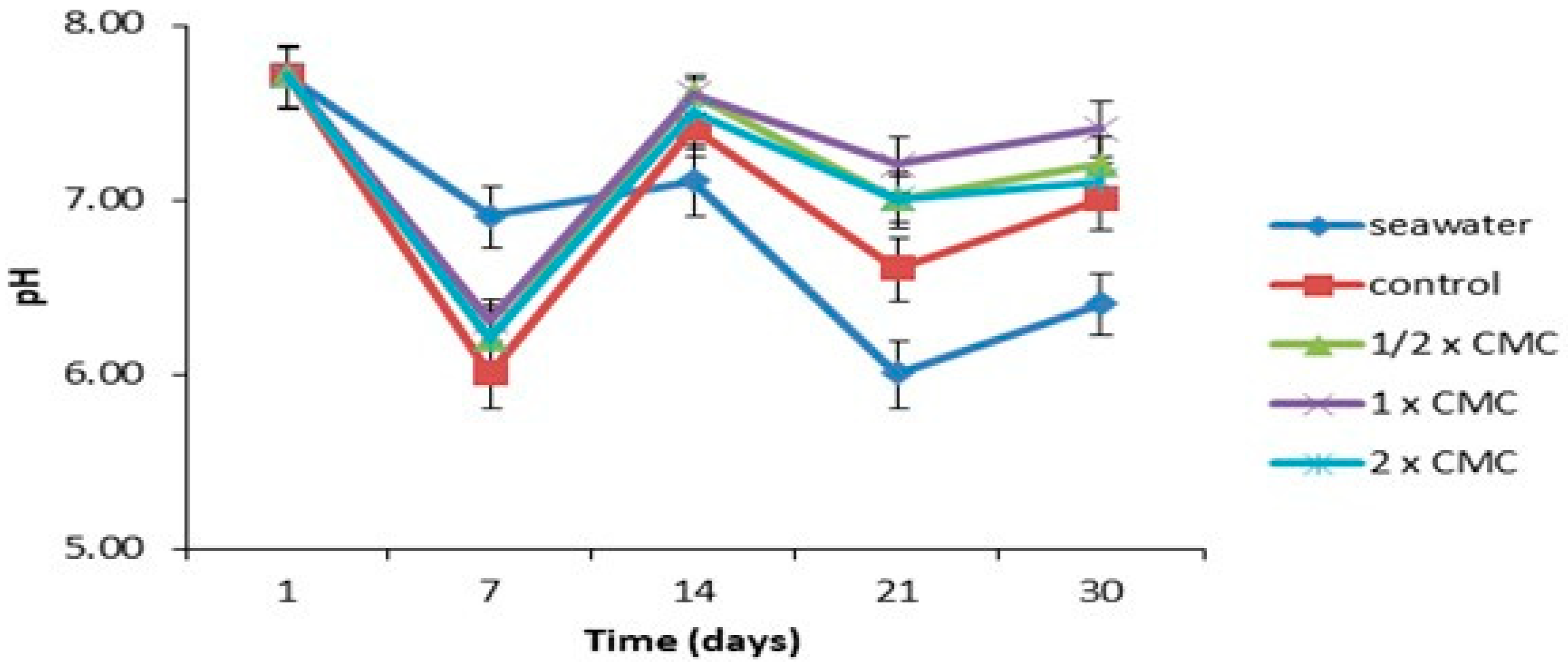
3.4. Inhibition of Metal Corrosion by the Isolated Biosurfactant in Seawater
3.5. Biosurfactant in Biodegradable Matrix as an Inhibitor of Corrosion Due to Atmospheric Physical Factors
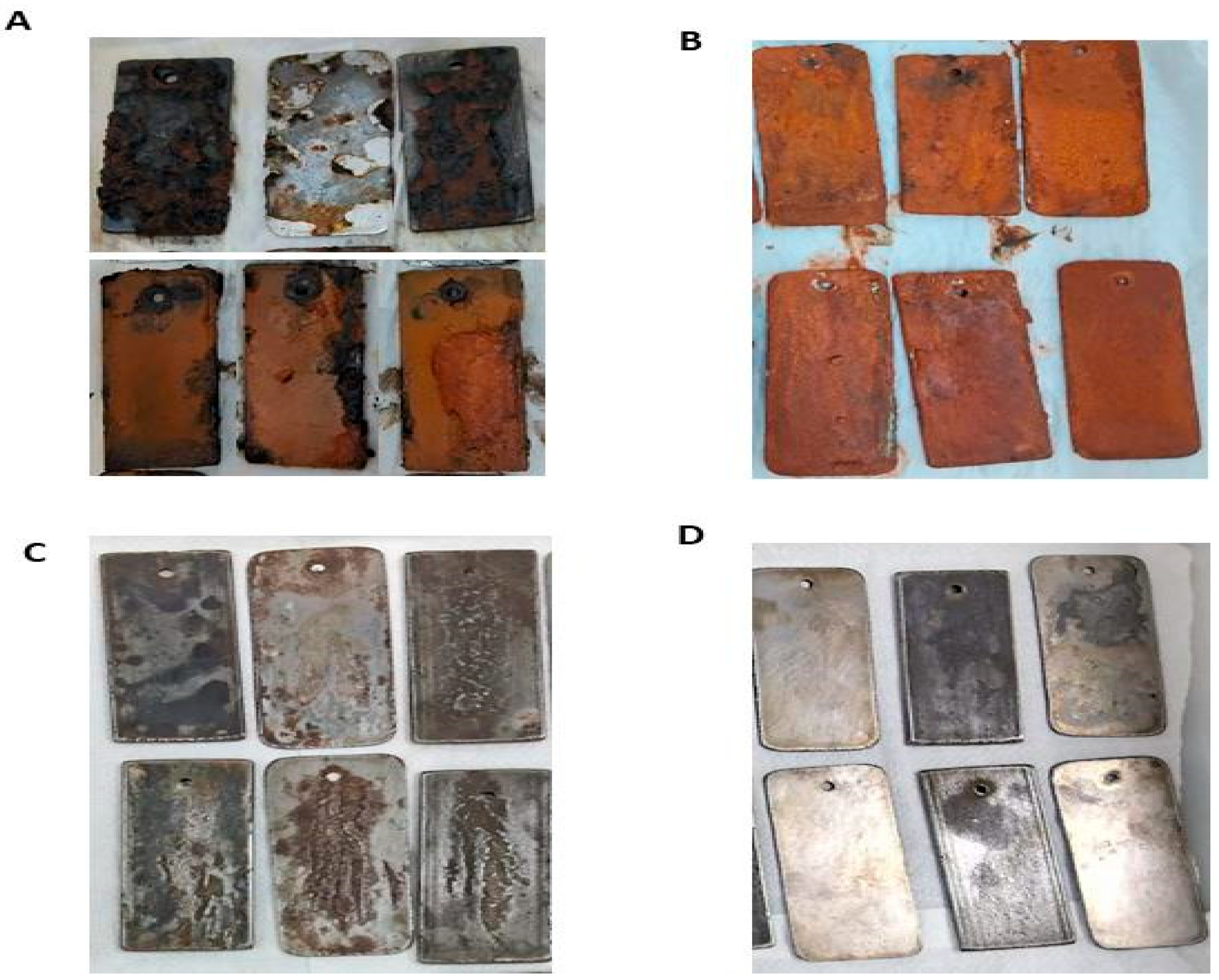
3.6. Use of Synthetic Enamels with Biosurfactant to Inhibit Corrosion Due to Atmospheric Physical Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, R.; Rathore, D. Effects of fertilization with textile effluent on germination, growth and metabolites of chilli (Capsicum annum L.) cultivars. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossai, I.C.; Ahmed, A.; Hassan, A.; Hamid, F.S. Remediation of soil and water contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbon: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elijah, A.A. A review of the petroleum hydrocarbons contamination of soil, water and air and the available remediation techniques, taking into consideration the sustainable development goals. Earthline J. Chem. Sci. 2022, 7, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Maddela, N.R.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K. Fate of total petroleum hydrocarbons in the environment. In Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons: Environmental Fate, Toxicity, and Remediation; Kuppusamy, S., Maddela, N.R., Megharaj, M., Venkateswarlu, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccioli, Y.E.S.; Oliveira, K.W.; Campos-Guerra, J.M.; Converti, A.; Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: Chemical properties, ecofriendly environmental applications, and uses in the industrial energy sector. Energies 2024, 17, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormare, R.; Kumar, M.A. Environmental health and risk assessment metrics with special mention to biotransfer, bioaccumulation and biomagnification of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 2020, 302, 134836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.F.; Vieira, K.S.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Lima, L.S.; Azevedo-Netto, A.; Delgado, J.F.; Corrêa, T.R.; Baptista Neto, J.A.; Fonseca, E.M. Heavy metal and hydrocarbons bioaccumulation by two bivalve’s species from Santos Bay, Brazil. Stud. Neotrop. Fauna Environ. 2024, 59, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of different industrial activities on soil heavy metal pollution, ecological risk, and health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigil, T.N.; Felton, S.M.; Fahy, W.E.; Kinkeade, M.A.; Visek, A.M.; Janiga, A.R.; Jacob, S.G.; Berger, B.W. Biosurfactants as templates to inspire new environmental and health applications. Front. Synth. Biol. 2024, 2, 1303423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, S.; Yousaf, S.; Khan, I. A review on the synthesis of bio-based surfactants using green chemistry principles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 30, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtode, V.S.; Cardoza, C.; Yasin, H.K.A.; Mali, S.N.; Tambe, S.M.; Roy, P.; Singh, K.; Goel, A.; Amin, P.D.; Thorat, B.R.; et al. Green surfactants (biosurfactants): A petroleum-free substitute for sustainability─ Comparison, applications, market, and future prospects. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11674–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahed, M.A.; Matinvafa, M.A.; Azari, A.; Mohajeri, L. Biosurfactant, a green and effective solution for bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. Discov. Water 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, H.; Verma, J.S.; Ashish. Biosurfactants for oil pollution remediation. In Microbial Biosurfactants: Preparation, Properties and Applications; Inamuddin, Ahamed, M.I., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Z.; Anas, M.; Khatoon, K.; Malik, A. Biosurfactant-producing bacteria as potent scavengers of petroleum hydrocarbons. In Microbiomes and the Global Climate Change; Lone, S.A., Malik, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.K.; Gupta, S.; Pandey, A. Evolution in mitigation approaches for petroleum oil-polluted environment: Recent advances and future directions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61821–61837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumanatharayil, J.J. Exploring the Effectiveness of Biosurfactant in Enhancing Oil Recovery and Reducing Environmental Impact in Oil and Gas Industry. Master’s degree dissertation, Technische Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, R.; Bodratti, A.M.; Tsianou, M.T.; Alexandridis, P. Biosurfactants, natural alternatives to synthetic surfactants: Physicochemical properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakontis, C.E.; Amin, S. Biosurfactants: Formulations, properties, and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 48, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, R.; Déziel, E.; Soberón-Chávez, G. Microbial biosurfactants: Updates on their biosynthesis, production and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1433035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, S.A.; Naughton, P.J.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Microbial biosurfactants in cosmetic and personal skincare pharmaceutical formulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Trybala, A.; Starov, V.; Pinfield, V.J. Effect of synthetic surfactants on the environment and the potential for substitution by biosurfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markande, A.R.; Patel, D.; Varjani, S. A review on biosurfactants: Properties, applications and current developments. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinelli, D.R.; Cespi, M.; Lorusso, N.; Palmieri, G.F.; Bonacucina, G.; Blasi, P. Surfactant self-assembling and critical micelle concentration: One approach fits all? Langmuir 2020, 36, 5745–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, X. Treatment of surfactants with concentrations below critical micelle concentration by ultrafiltration: A mini-review. Water Cycle 2022, 3, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldes, A.B.; Álvarez-Chaver, P.; Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M. Purification of lipopeptide biosurfactant extracts obtained from a complex residual food stream using Tricine-SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1199103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Rajendran, D.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.N.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Extraction, purification and applications of biosurfactants based on microbial-derived glycolipids and lipopeptides: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradighadi, N.; Lewis, S.; Olivo, J.D.; Young, D.; Brown, B.; Nešić, S. Determining critical micelle concentration of organic corrosion inhibitors and its effectiveness in corrosion mitigation. Corrosion 2021, 77, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Liao, G.; Luan, H.; Chen, Q.; Nie, X.; Liu, D.; Feng, Y. Oil solubilization in sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate micelles: New insights into surfactant enhanced oil recovery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 569, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehal, N.; Sonal; Jaiswar, S.; Singh, P. Extensive studies on fermentative production of biosurfactants from extremophilic marine microbes. In Marine Surfactants: Preparations and Applications; Kim, S., Shin, K., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 375–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, D.; Ramasamy, R.; Thiagarajan, Y.R.; Thirumalairaj, B.; Krishnamoorthy, U.; Siddiqui, M.I.H.; Lakshmaiya, N.; Kumar, A.; Shah, M.A. Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview. Open Chem. 2024, 22, 20240036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthipan, P.; Cheng, L.; Rajasekar, A.; Karthikeyan, O.P.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Editorial: Biosurfactants-next-generation biomolecules for enhanced biodegradation of organic pollutants, volume II. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1513087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, I.; Karpenko, O.; Banya, A.; Lubenets, V.; Shapovalenko, S.; Pengxiang, G. New environmentally friendly compositions as inhibitors of metal corrosion. Sci. Stud. Res. Chem. Chem. 2023, 24, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Barxanadjyan, A.; Hakimov, R.; Ibragimov, B. Research of the possibility of using waste of paint and varnish materials for anti-corrosion protection of metal parts of transport equipment. J. Tashkent Inst. Railw. Eng. 2020, 16, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.N.; Kassab, E.; Pandoli, O.G.; Oliveira, J.L.; Quintela, J.P.; Bott, I.S. Corrosion behaviour of an epoxy paint reinforced with carbon nanoparticles. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Hegazy, M.M.; Awad, M.K.; Shawky, M. Chemical, electrochemical, theoretical (DFT & MEP), thermodynamics and surface morphology studies of carbon steel during gas and oil production using three novel di-cationic amphiphiles as corrosion inhibitors in acidic medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Farhadian, A.; Berisha, A.; Deyab, M.A.; Chen, J.; Iravani, D.; Rahimi, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, D. Novel biosurfactants for effective inhibition of gas hydrate agglomeration and corrosion in offshore oil and gas pipelines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 11, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Kudbanov, A.; Rezaeisadat, M.; Nurgaliev, D.K. Waterborne polymers as kinetic/anti-agglomerant methane hydrate and corrosion inhibitors: A new and promising strategy for flow assurance. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 77, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płaza, G.; Achal, V. Biosurfactants: Eco-friendly and innovative biocides against biocorrosion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshin, T.A.; Fakinle, B.S.; Oyewole, O. The role of microbes in the inhibition of the atmospheric corrosion of steel caused by air pollutants. Corros. Rev. 2023, 41, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Cao, M. Application of surfactants in corrosion inhibition of metals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 73, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; Prasad, S.; Rtimi, S. Preparation, characterization and application of biosurfactant in various industries: A critical review on progress, challenges and perspectives. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, A.; Rehman, R.; Fuwad, A.; Shahid, M.K.; Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Jamal, A.; Aftab, M.N.; Mainali, B.; Choi, Y. Current advances in the classification, production, properties and applications of microbial biosurfactants–A critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 306, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Koul, Y.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Chang, J.; Wong, J.W.C.; Bui, X. A critical review on various feedstocks as sustainable substrates for biosurfactants production: A way towards cleaner production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Mehl, A.; Mach, E.; Couto, P.; Mansur, C.R.E. Application of biosurfactants in enhanced oil recovery ex-situ: A review. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3117–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Ping, Y.; Alikhani, M.A. A review on biosurfactant applications in the petroleum industry. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5477185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathiri, E.; Prakash, P.; Karmegam, N.; Varjani, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Ravindran, B. Biosurfactants: Potential and eco-friendly material for sustainable agriculture and environmental safety—A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga, E.B.; Celik, P.A.; Cabuk, A.; Banat, I.M. Biosurfactants: Opportunities for the development of a sustainable future. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Abdallah, M.; Alfakeer, M.; Altass, H.M.; Althagafi, I.I.; El-Ossaily, Y.A. Performance of unprecedented synthesized biosurfactants as green inhibitors for the corrosion of mild steel-37-2 in neutral solutions: A mechanistic approach. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 14, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, Z. Potential of biosurfactants in corrosion inhibition. In Industrial Applications of Biosurfactants and Microorganisms: Green Technology Avenues from Lab to Commercialization; Aslam, R., Aslam, J., Hussain, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Hussain, C.M.; Quraishi, M.A.; Alfantazi, A. Green surfactants for corrosion control: Design, performance and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 311, 102822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, S.; Mobin, M.; Aslam, R. Application of biosurfactants as anti-corrosive agents. In Advancements in Biosurfactants Research; Aslam, R., Mobin, M., Aslam, J., Zehra, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.; Yan, Z. Application of biomass corrosion inhibitors in metal corrosion control: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeve, M.D.; Maeseneire, S.L.D.; Roelants, S.L.K.W.; Soetaert, W. Starmerella bombicola, an industrially relevant, yet fundamentally underexplored yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selva Filho, A.A.P.; Faccioli, Y.E.S.; Converti, A.; Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Maximization of the production of a low-cost biosurfactant for application in the treatment of soils contaminated with hydrocarbons. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Soares da Silva, R.D.C.F.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Removal of heavy oil from contaminated surfaces with a detergent formulation containing biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas spp. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.N.R.L.; Farias, C.B.B.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Glycerol as substrate for the production of biosurfactant by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UCP0992. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Sasaki, M.; Komatsu, K.; Miura, A.; Matsuda, H. Oil spill remediation by using the remediation agent JE1058BS that contains a biosurfactant produced by Gordonia sp. strain JE-1058. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Walter Works Association, Walter Environmental Federation (S.I.): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, D.K.F.; Meira, H.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactant production from Candida lipolytica in bioreactor and evaluation of its toxicity for application as a bioremediation agent. Process Biochem. 2017, 54, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccioli, Y.E.S.; Oliveira da Silva, G.; Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Application of a biosurfactant from Pseudomonas cepacia CCT 6659 in bioremediation and metallic corrosion inhibition processes. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 351, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Selva Filho, A.A.P.; Faccioli, Y.E.S.; Silva, Y.K.; Oliveira, K.W.; Araujo, G.P.; Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Application of Pseudomonas cepacia CCT 6659 biosurfactant as a metal corrosion inhibitor in a constructed Accelerated Corrosion Chamber (ACC). Fermentation 2024, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Material Metálico Revestido e Não Revestido: Corrosão Por Exposição à Névoa Salina; NBR 8094; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, E. Geração de Vapor e Água de Refrigeração, 2nd ed.; Ecolab Química Ltda: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1988; pp. 1–305. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, S.H. Estudo da Utilização da Xantana e Hipoclorito de Sódio Como Estratégia Para Controle da Biocorrosão. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pontes, J.F.R.; Bendinelli, E.V.; Amorim, C.C.; Sá, M.M.; Ordine, A.P. Effect of corrosion inhibitor used in surface treatment on the anticorrosive performance of an epoxy paint system. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2016, 7, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durval, I.; Rufino, R.; Sarubbo, L. Biosurfactant as an environmental remediation agente: Toxicity, formulation, and application in the removal of petroderivate in sand and rock walls. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussin, N.B.A.; Shivanand, P.; Lim, L.H. Biosurfactant production by Trichoderma sp. MK116452 and its possible application in oil recovery. Res. Sq. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deivakumari, M.; Sanjivkumar, M.; Suganya, A.M.; Prabakaran, J.R.; Palavesam, A.; Immanuel, G. Studies on reclamation of crude oil polluted soil by biosurfactant producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa (DKB1). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.M.S.; Lira, I.R.A.S.; Pinto, M.I.S.; Almeida, F.C.; Almeida, D.G.; Rufino, R.D.; Sarubbo, L.A.; Luna, J.M. Formulation of the biosurfactant produced by Candida sphaerica for application as a bioremediation agent. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; Rodríguez, D.M.; Ferreira, I.N.S.; Almeida, S.M.; Takaki, G.M.C.; Lima, M.A.B. Novel production of biodispersant by Serratia marcescens UCP 1549 in solid-state fermentation and application for oil spill bioremediation. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sivapragasam, M.; Talukder, M.M.R.; Yusup, S.B.; Goto, M. A binary mixture of a biosurfactant and an ionic liquid surfactant as a green dispersant for oil spill remediation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Yusup, S.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Ionic liquid-biosurfactant blends as effective dispersants for oil spills: Effect of carbon chain length and degree of saturation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebede, G.; Tafese, T.; Abda, E.M.; Kamaraj, M.; Assefa, F. Factors influencing the bacterial bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminants in the soil: Mechanisms and impacts. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9823362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Sarubbo, L.A. Ecotoxicity of the formulated biosurfactant from Pseudomonas cepacia CCT 6659 and application in the bioremediation of terrestrial andaquatic environments impacted by oil spills. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 154, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.G.; Soares da Silva, R.C.F.; Meira, H.M.; Brasileiro, P.P.F.; Silva, E.J.; Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Sarubbo, L.A. Production, characterization and commercial formulation of a biosurfactant from Candida tropicalis UCP 0996 and its application in decontamination of petroleum pollutants. Process 2021, 9, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneeswari, R.; Swathi, K.V.; Sekaran, G.; Ramani, K. Microbial-induced biosurfactant-mediated biocatalytic approach for the bioremediation of simulated marine oil spill. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D.; Wang, F. Rhamnolipid as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for microbiologically influenced corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2022, 204, 110390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, N.; El-Gammal, B.; Fargaly, T.A.; Mohammed, A.A.K.; Fawzy, A. Experimental and computational explorations for the inhibitive performances of synthesized green surfactants against the corrosion of copper in nitric acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1319, 139439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyab, M.A.; Ibrahim, I.Z.; El-Shamy, O.A.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Awad, A.F.; Alghamdi, M.M.; El-Zahhar, A.A.; Abo-Riya, M.A. Synthesis, surface activity, and corrosion inhibition capabilities of new non-ionic gemini surfactants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
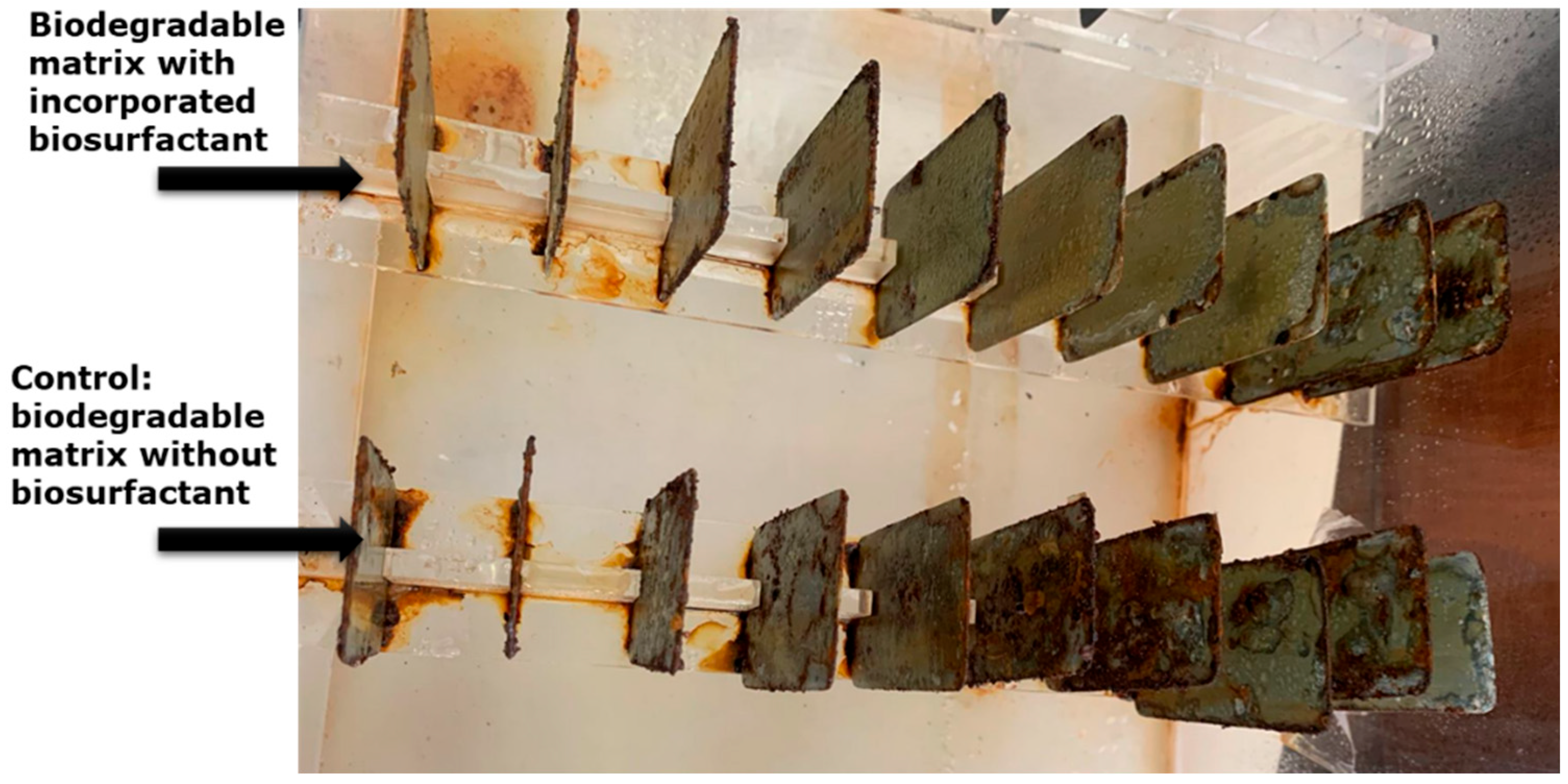

 ).
).
 ).
).

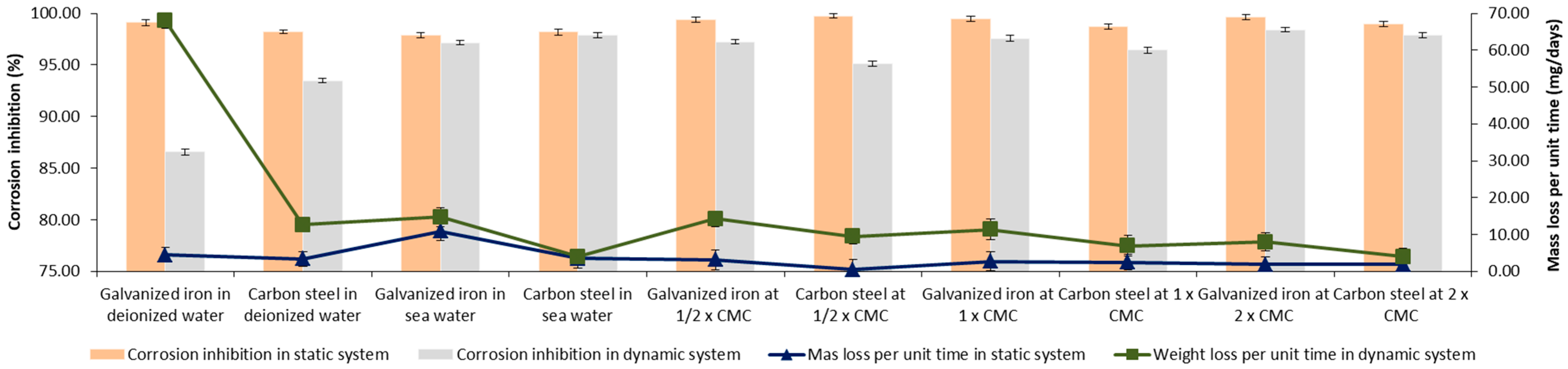
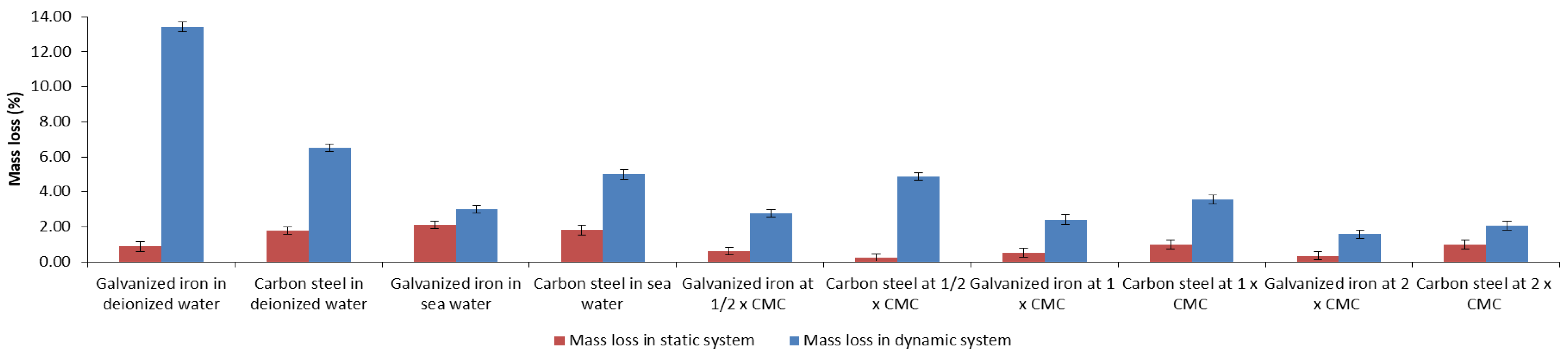

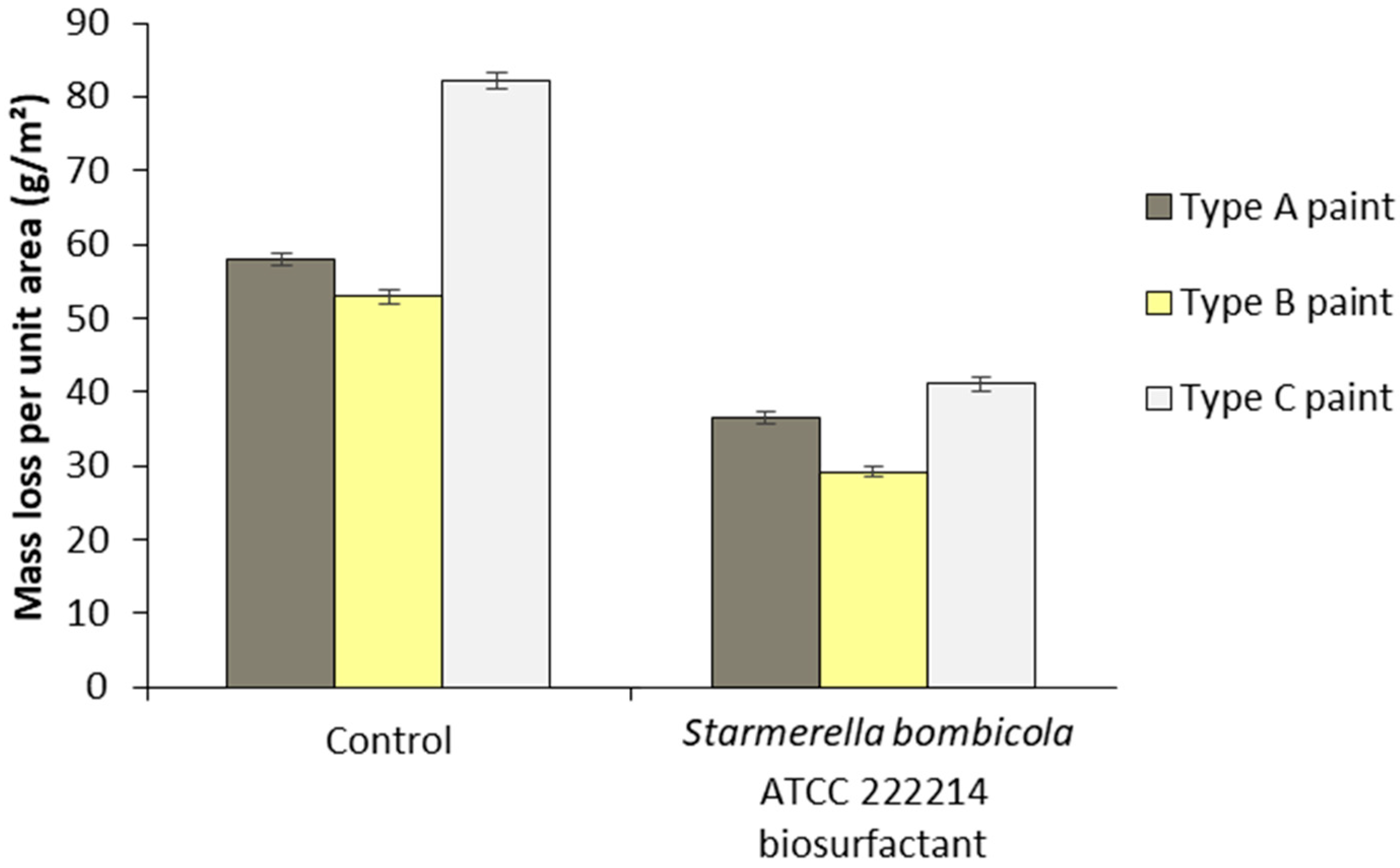
| Paint | Characteristics | Composition | Color | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Easy-to-apply alkyd resin-based enamel with quick drying and good coverage, 900 mL | Resin consisting of polyalcohols, polyacids, aliphatic solvent, active pigments, additives, drying oils, and turpentine | Ice white | Covering of external and internal surfaces of wood, metal, and masonry |
| Type B | Quick-drying satin synthetic enamel, 900 mL | Resin containing polyacids, polyalcohols, pigments, solvents, additives, and oils | Bright ivory | External covering of wood, metal, galvanized steel, and aluminum |
| Type C | Premium quick-drying synthetic enamel, 900 mL | Hydrated light petroleum distillates, xylene, toluene, cobalt octoate, manganese octoate, and methyl ethyl ketoxime | Snow white | Covering of wood, aluminum, ferrous metals, galvanized steel, and masonry surfaces |
| Biosurfactant Concentration with Deionized Water as Solvent | Artemia salina Mortality Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| 1% Biosurfactant Solution in Sea Water | 2% Biosurfactant Solution in Sea Water | |
| ½ × CMC | 3.0% ± 0.8 | 10.0% ± 0.3 |
| CMC | 13.0% ± 0.2 | 17.0% ± 0.2 |
| 2 × CMC | 17.0% ± 0.2 | 30.0% ± 0.4 |
| Biosurfactant/Oil Ratio (v/v) | Oil Dispersion Rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 × CMC | CMC | 2 × CMC | Crude Biosurfactant | |
| 1:2 | 23.3 ± 0.9 | 25.6 ± 0.6 | 28.9 ± 0.8 | 73.0 ± 0.7 |
| 1:8 | 25.6 ± 0.9 | 45.0 ± 0.7 | 52.3 ± 0.8 | 77.6 ± 0.5 |
| 1:25 | 22.2 ± 0.6 | 37.5 ± 0.6 | 46.7 ± 0.6 | 70.1 ± 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selva Filho, A.A.P.; Faccioli, Y.E.S.; Converti, A.; Casazza, A.A.; Soares da Silva, R.d.C.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. The Application of a New Microbial Biosurfactant to Remove Residual Oil from Electric Power Plant and to Inhibit Metal Corrosion in a Salty Environment. Energies 2025, 18, 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133359
Selva Filho AAP, Faccioli YES, Converti A, Casazza AA, Soares da Silva RdCF, Sarubbo LA. The Application of a New Microbial Biosurfactant to Remove Residual Oil from Electric Power Plant and to Inhibit Metal Corrosion in a Salty Environment. Energies. 2025; 18(13):3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133359
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelva Filho, Alexandre Augusto P., Yslla Emanuelly S. Faccioli, Attilio Converti, Alessandro Alberto Casazza, Rita de Cássia F. Soares da Silva, and Leonie A. Sarubbo. 2025. "The Application of a New Microbial Biosurfactant to Remove Residual Oil from Electric Power Plant and to Inhibit Metal Corrosion in a Salty Environment" Energies 18, no. 13: 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133359
APA StyleSelva Filho, A. A. P., Faccioli, Y. E. S., Converti, A., Casazza, A. A., Soares da Silva, R. d. C. F., & Sarubbo, L. A. (2025). The Application of a New Microbial Biosurfactant to Remove Residual Oil from Electric Power Plant and to Inhibit Metal Corrosion in a Salty Environment. Energies, 18(13), 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18133359









