A Less-Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Machine with Hybrid Magnet Configuration for Electric Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design Approach and Specifications of the Proposed Machine
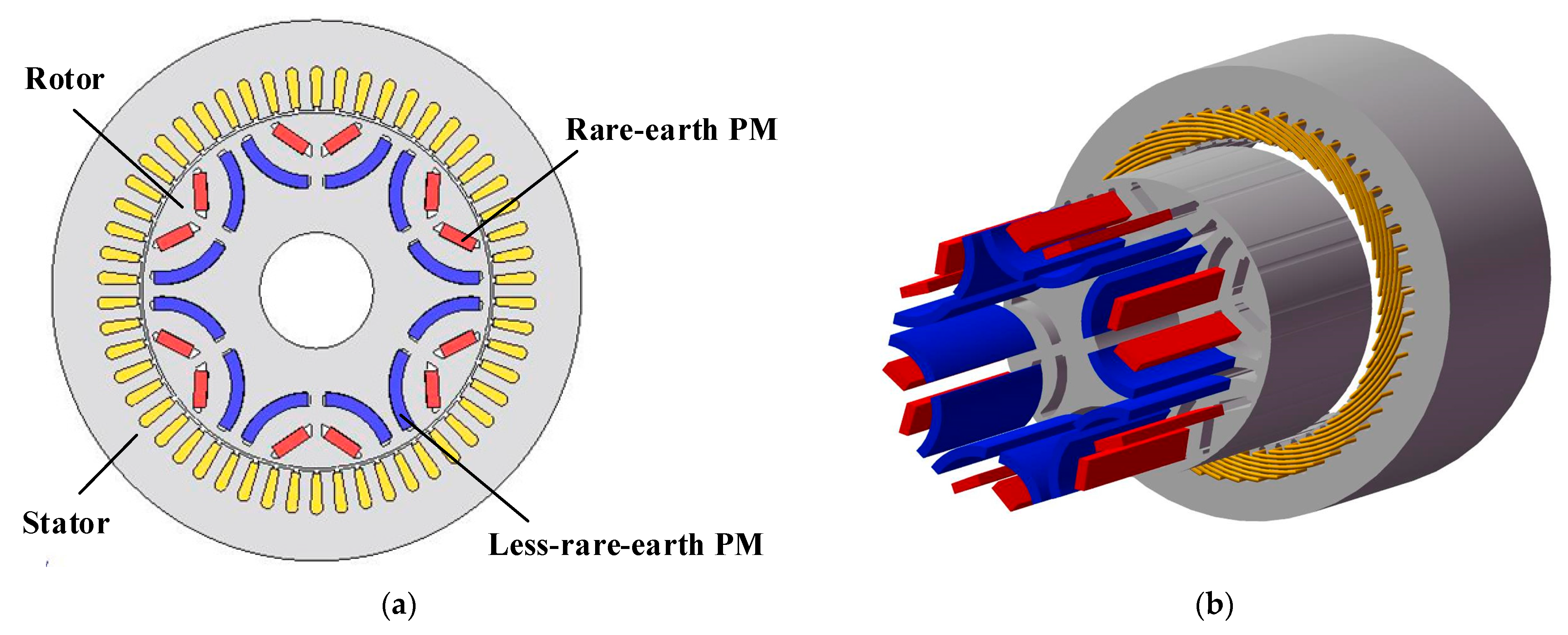
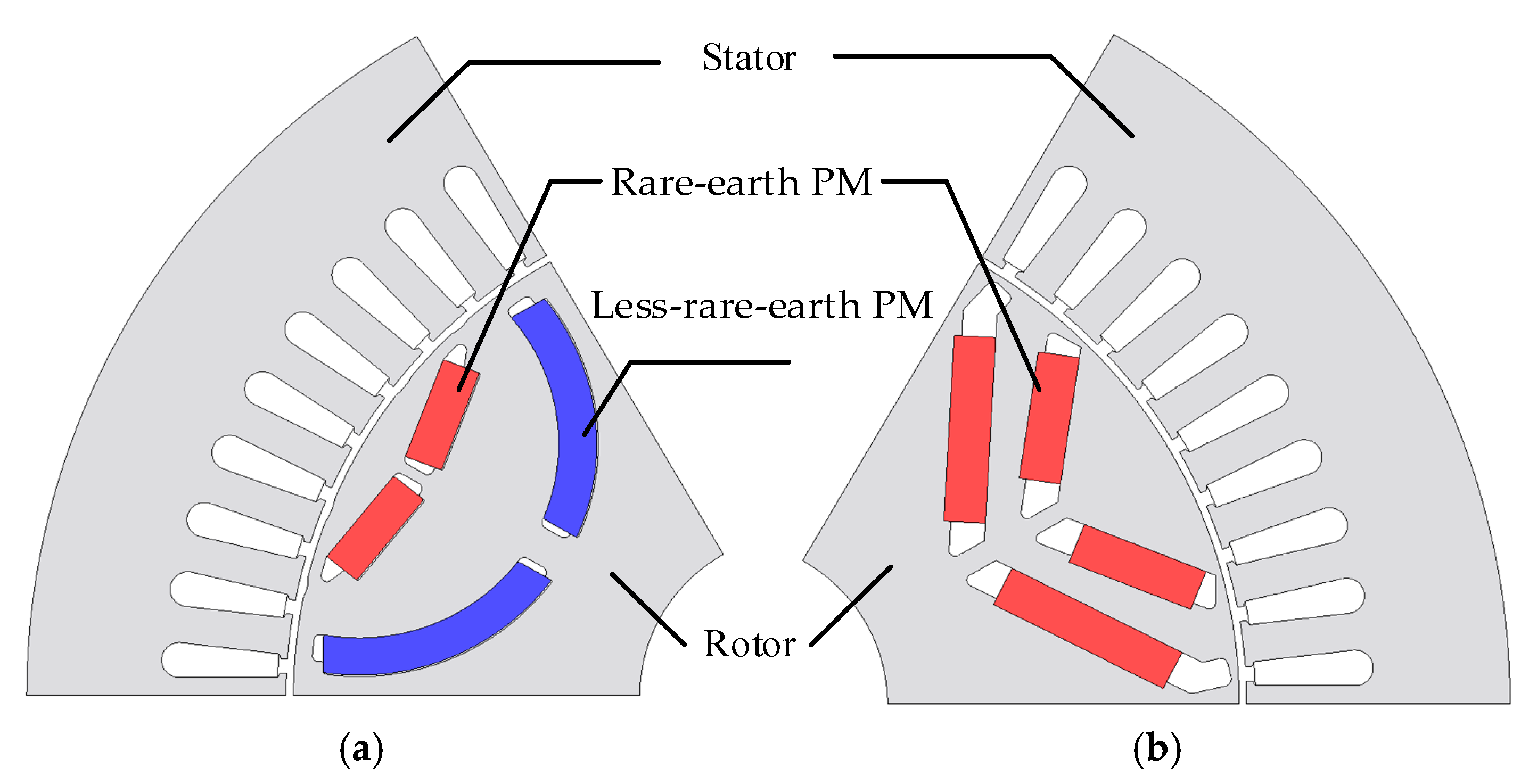
2.1. Propose Topology
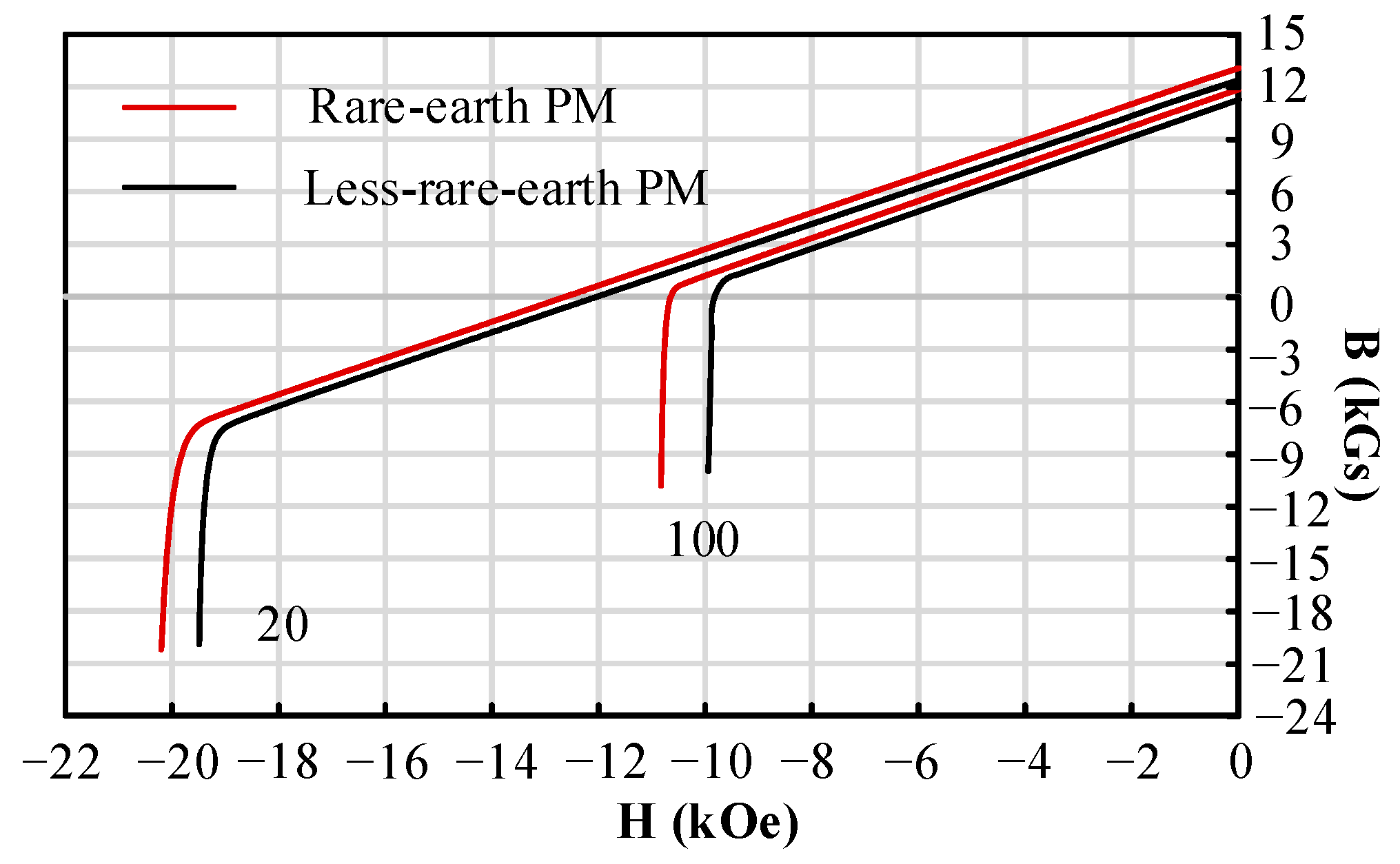
- The first layer employs a V-shaped rare-earth PM, primarily providing a high torque output capability and protecting the second layer of magnets from demagnetization currents particularly under ASC conditions, thereby enhancing their anti-demagnetization capability.
- The second layer incorporates an arc-shaped less-rare-earth PM, which increases the saliency ratio and significantly enhances the flux-focusing effects, thereby improving torque density. Additionally, the cost of this design is approximately one-third compared to traditional PM machines.
- The proposed HLEPM machine meets high torque output requirements, exhibits high efficiency from medium- to high-speed ranges, and effectively mitigates the risk of accidental demagnetization of PMs under ASC conditions.
2.2. Specifications and Dimensions
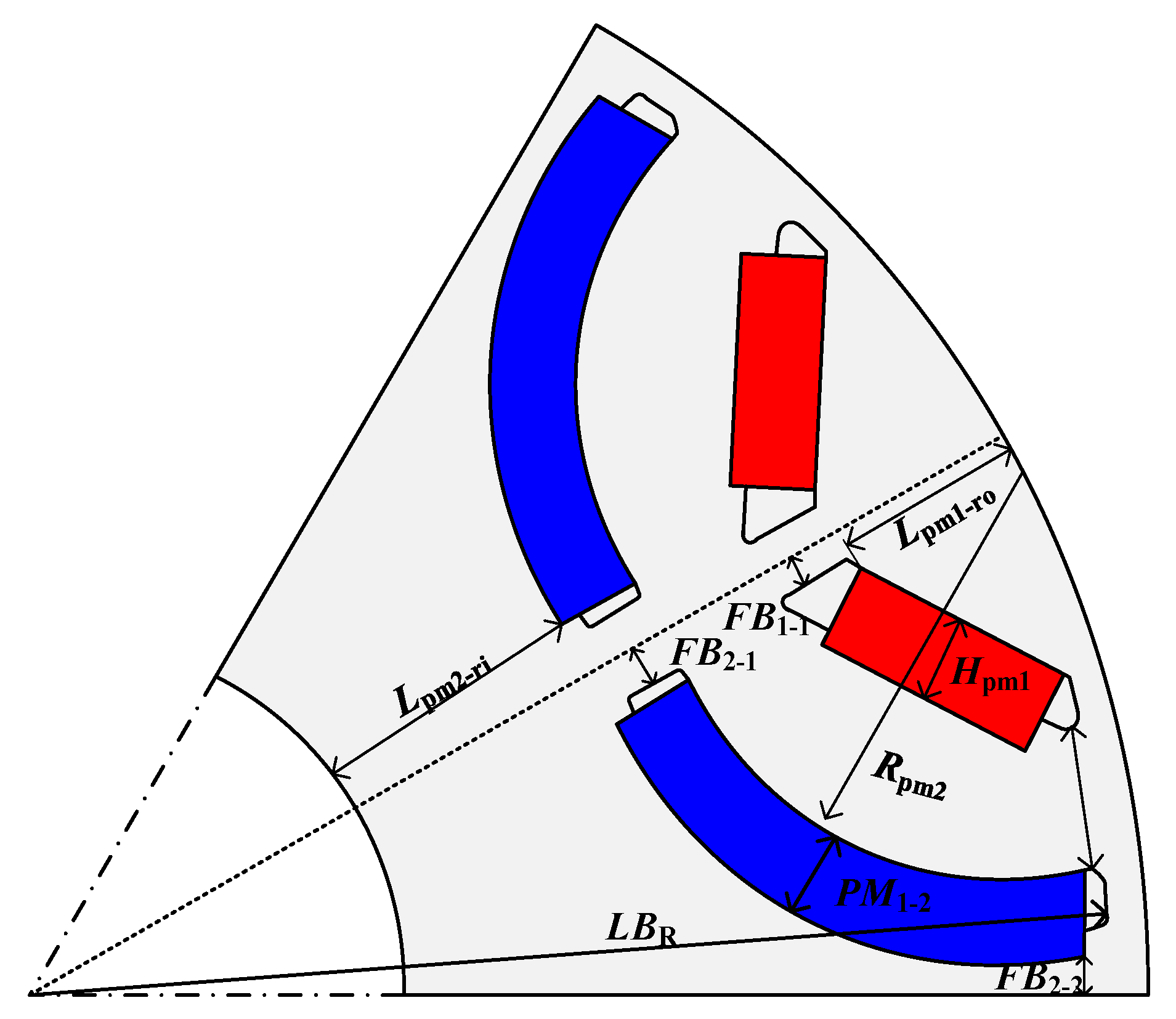
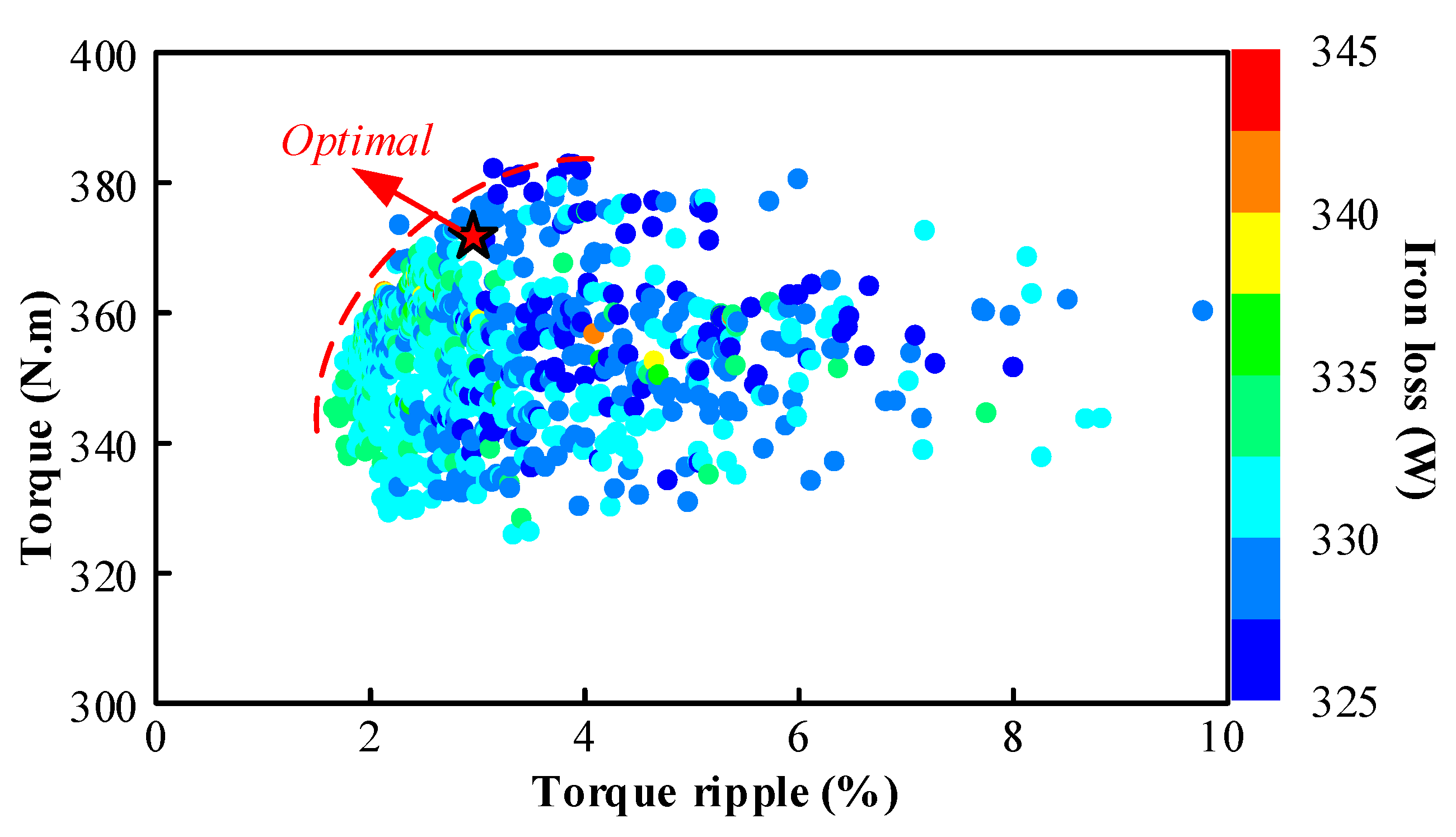
2.3. Optimization
3. Electromagnetic Performance of Electric Machine
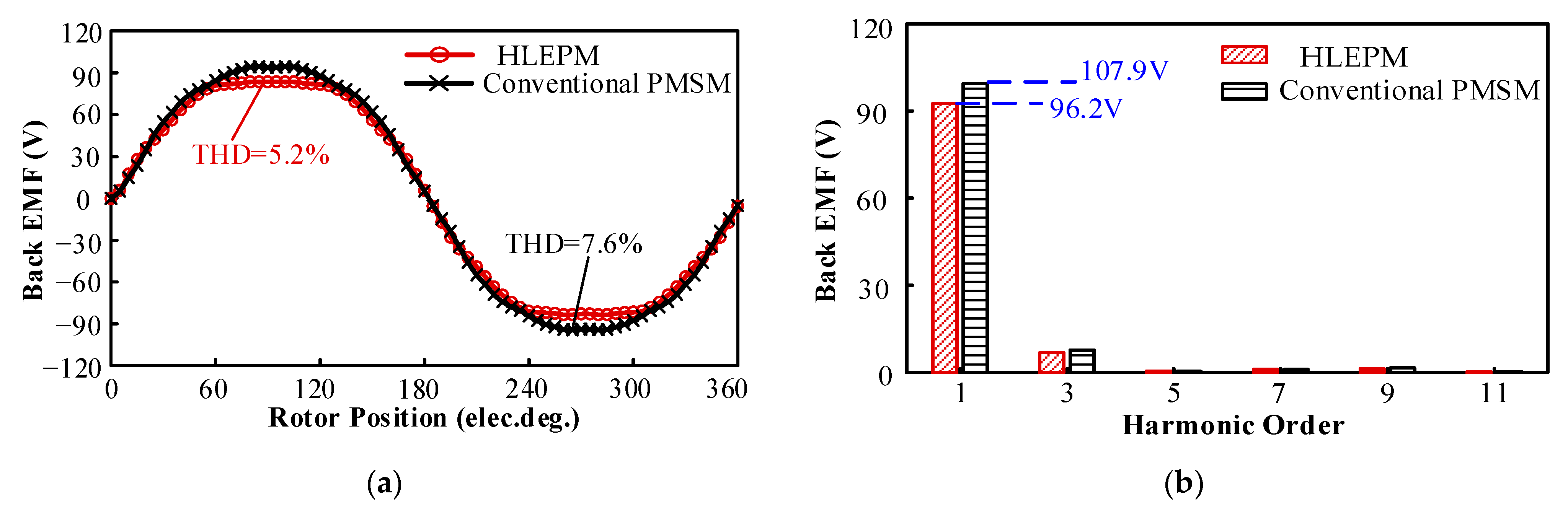
3.1. No-Load Performance
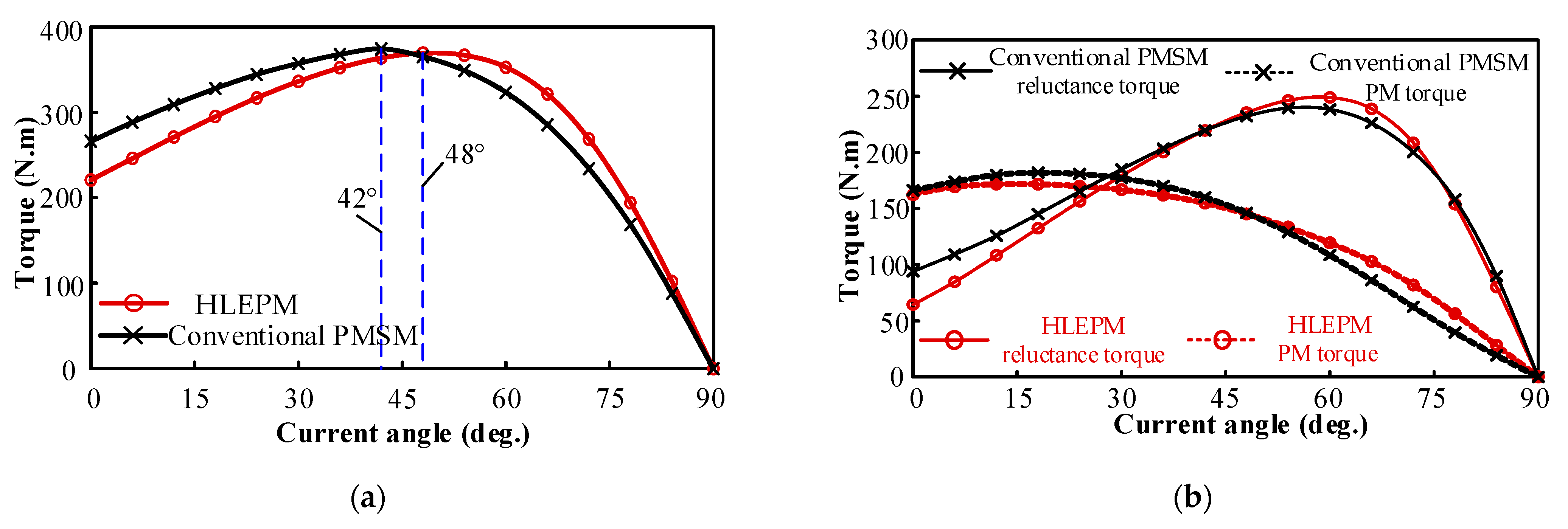
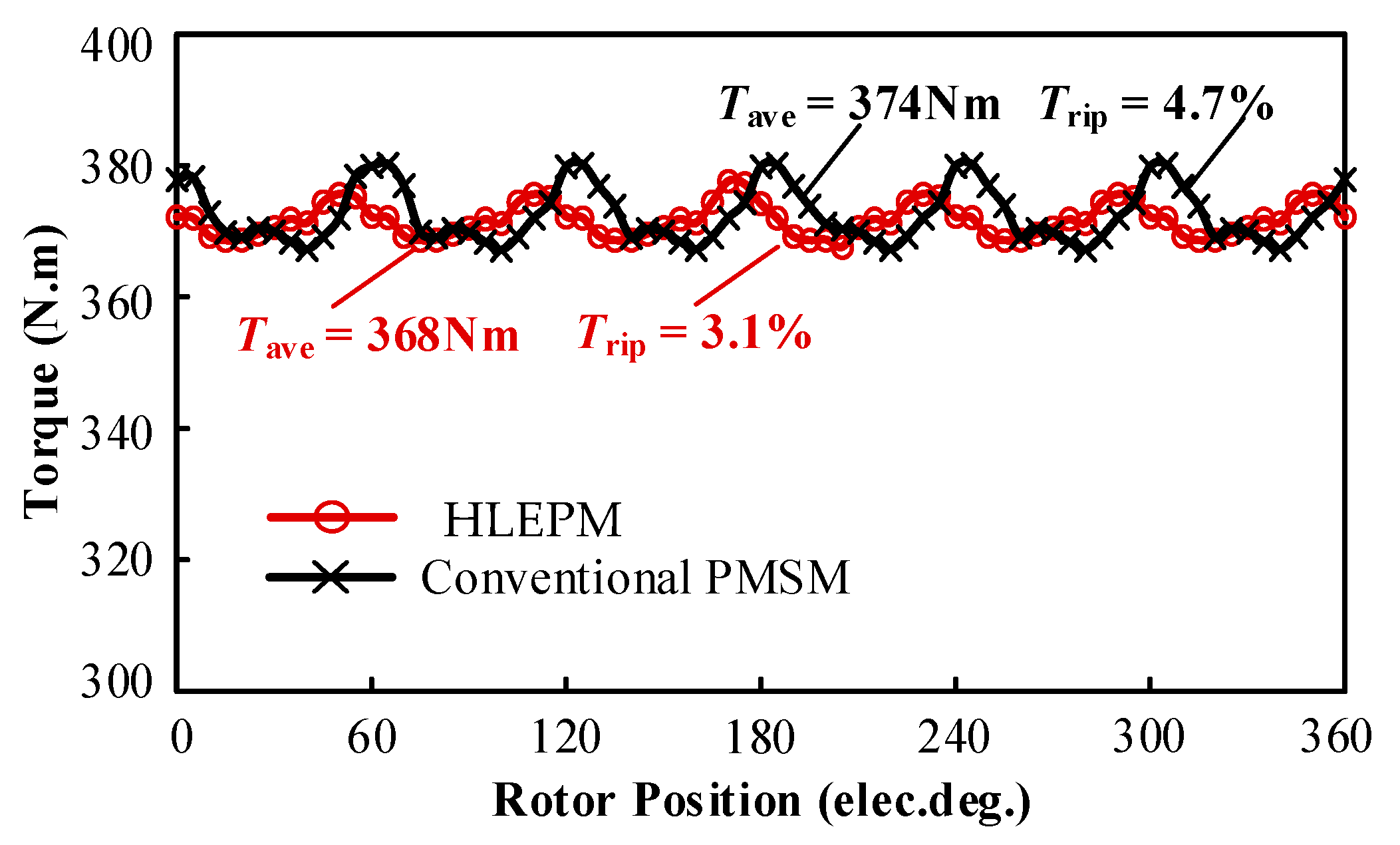
3.2. Load Performance
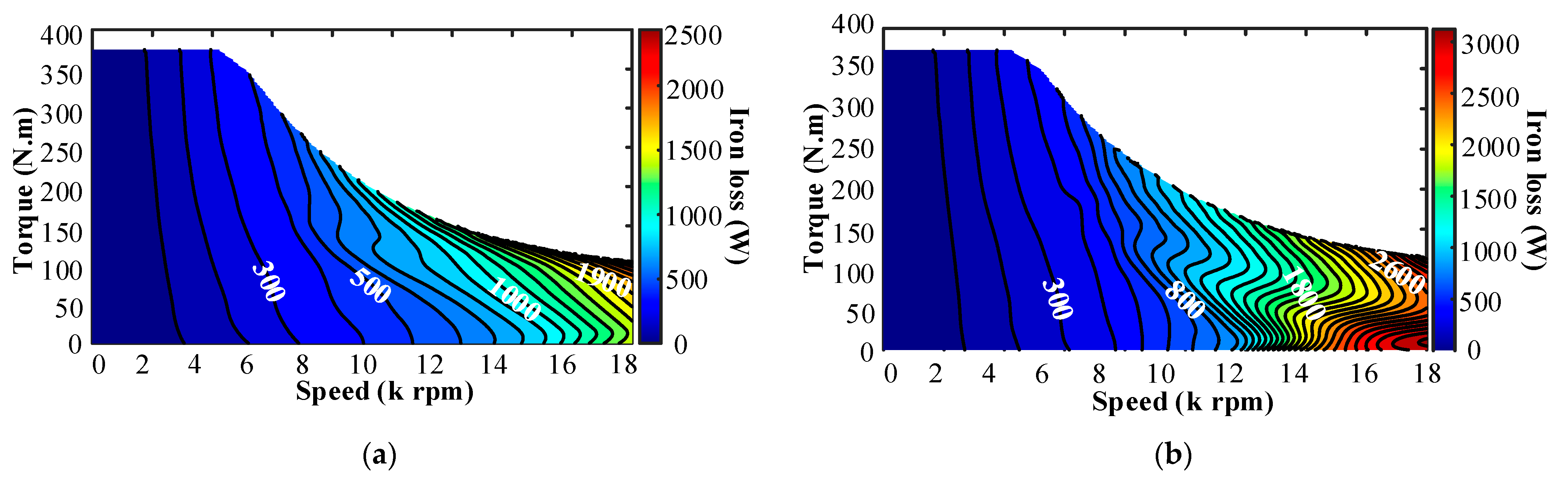
3.3. Loss Characteristics
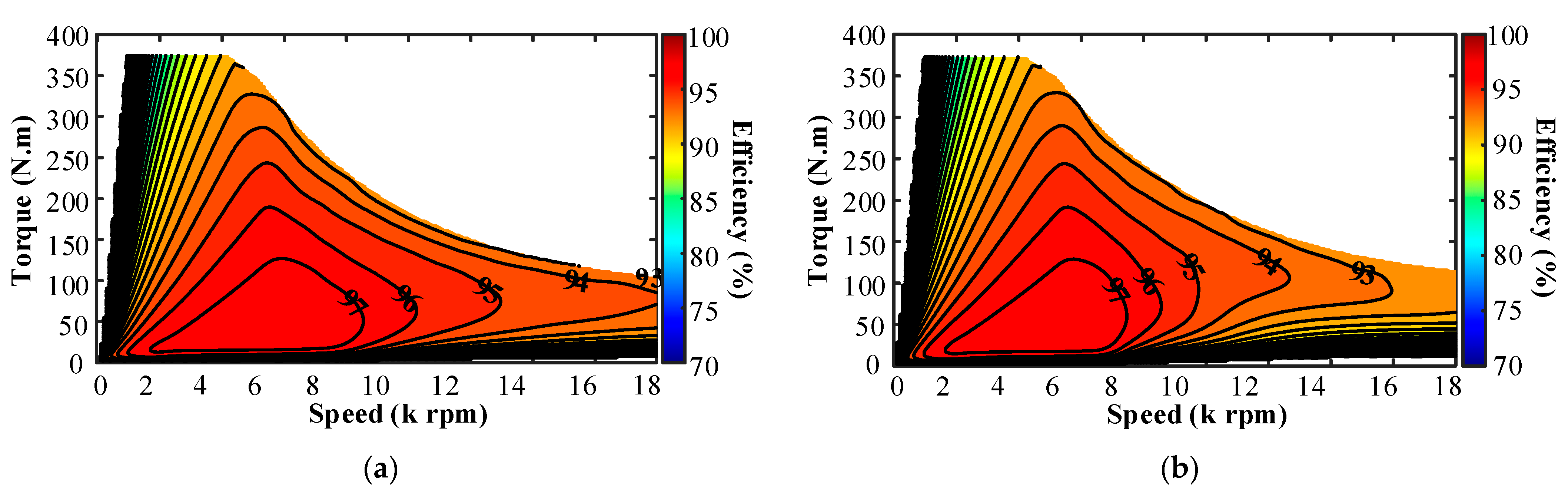
3.4. Efficiency
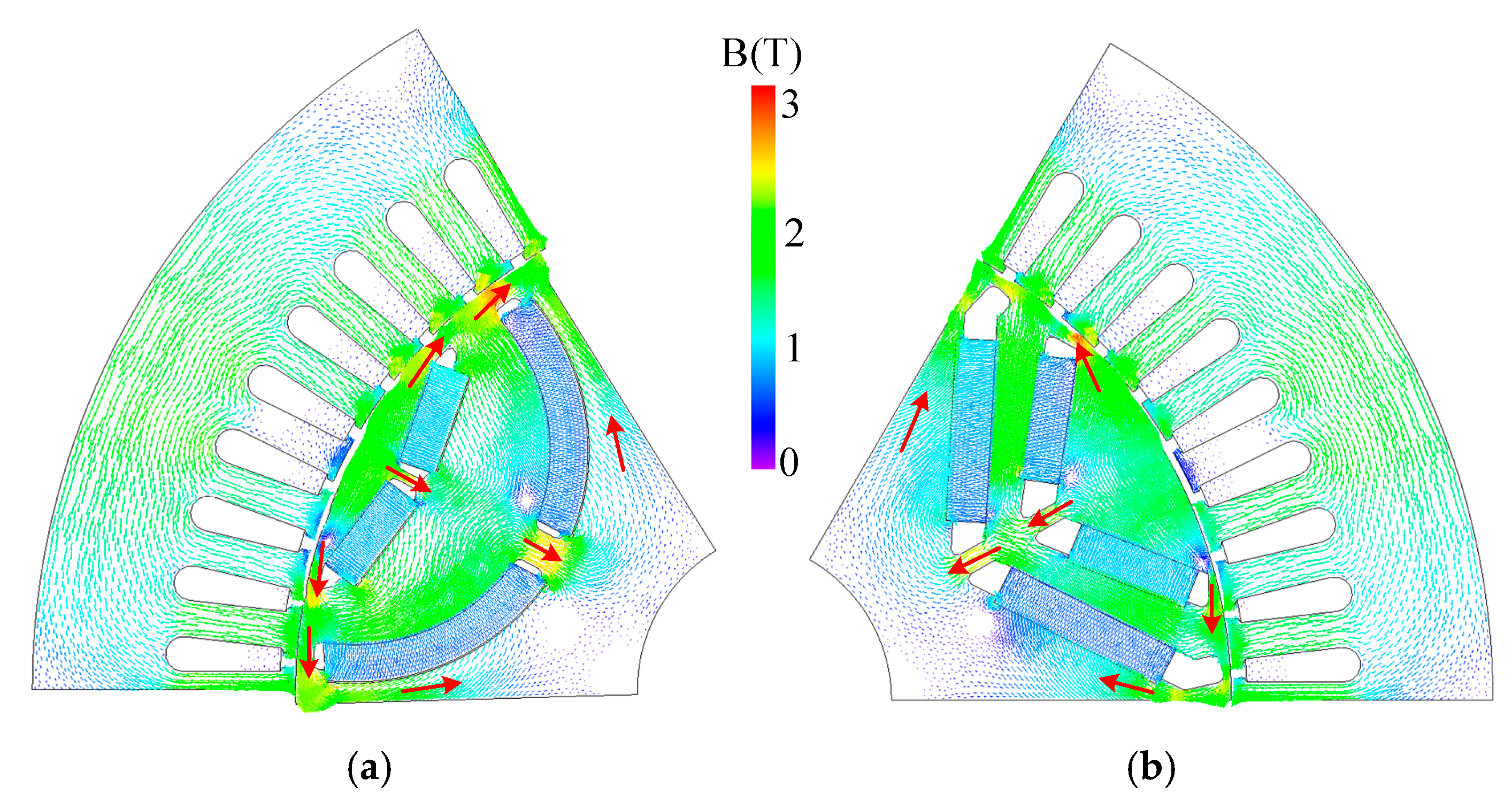
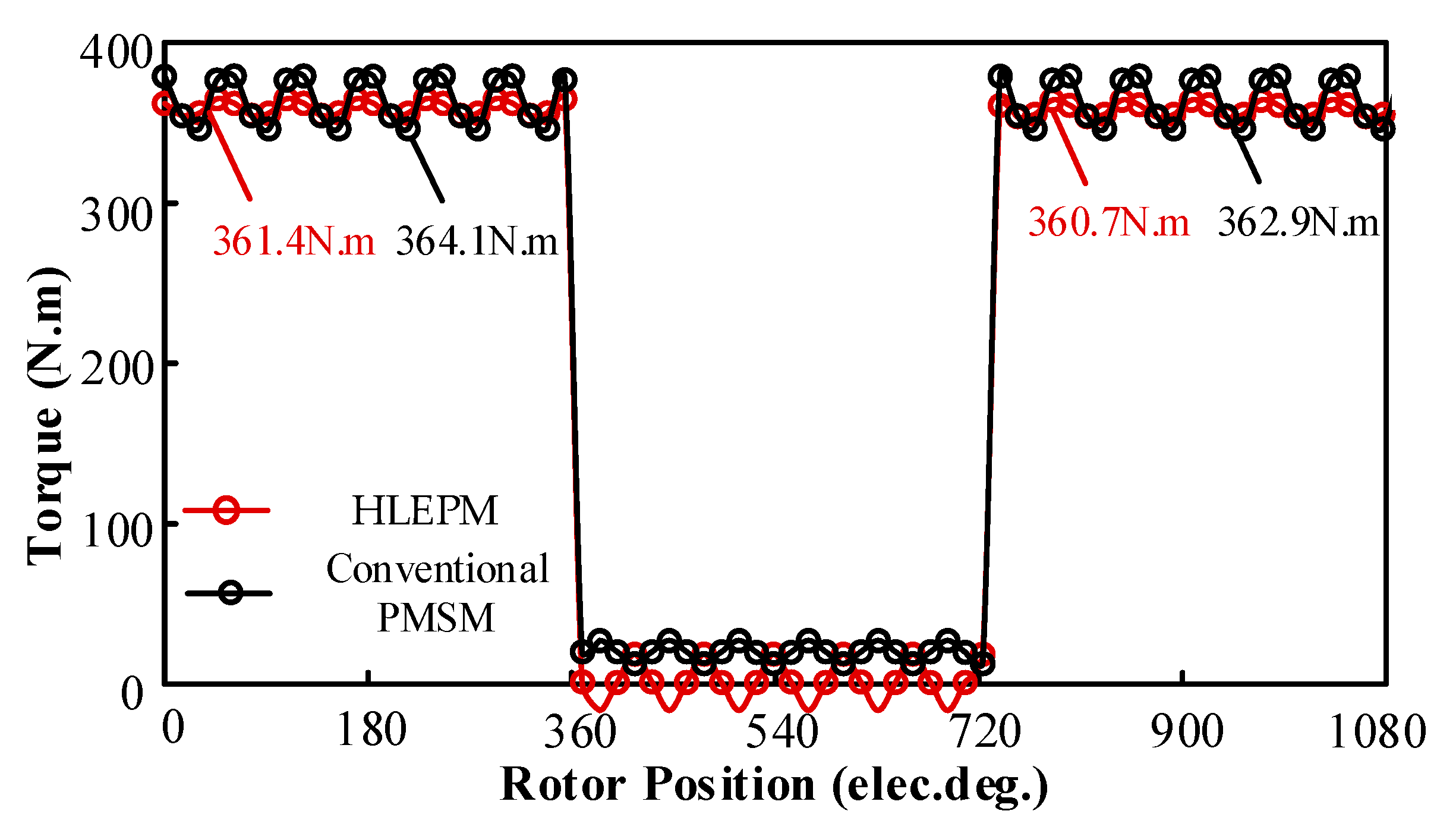
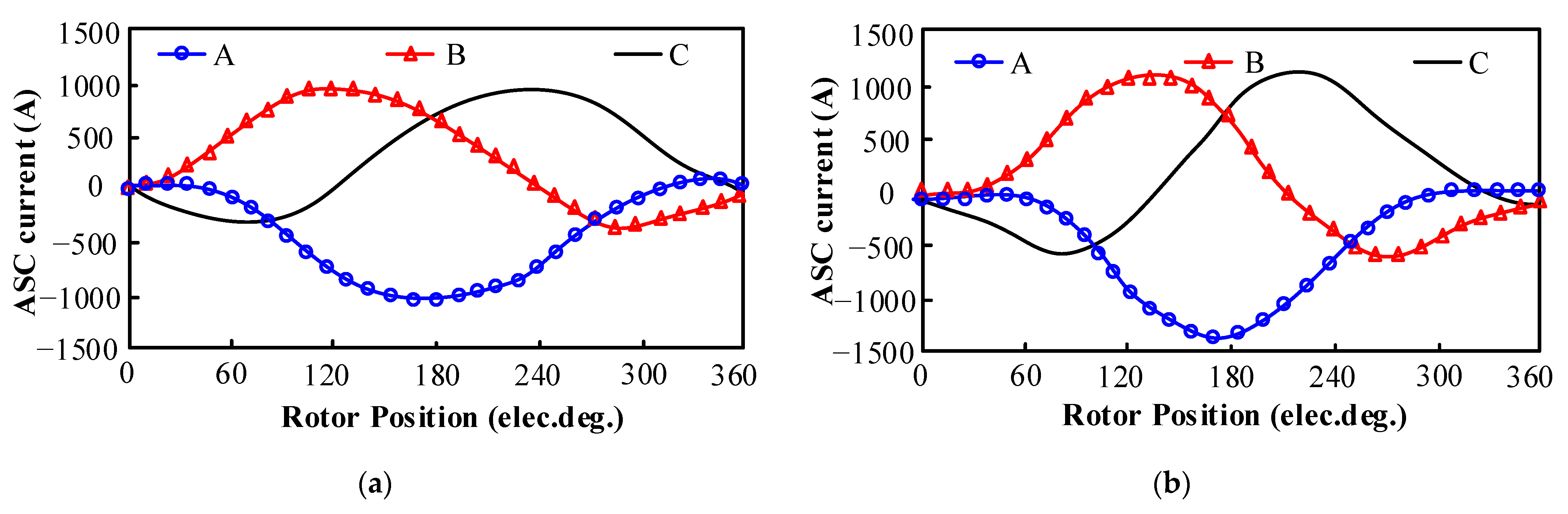
4. Demagnetization Analysis Under ASC Operating Condition
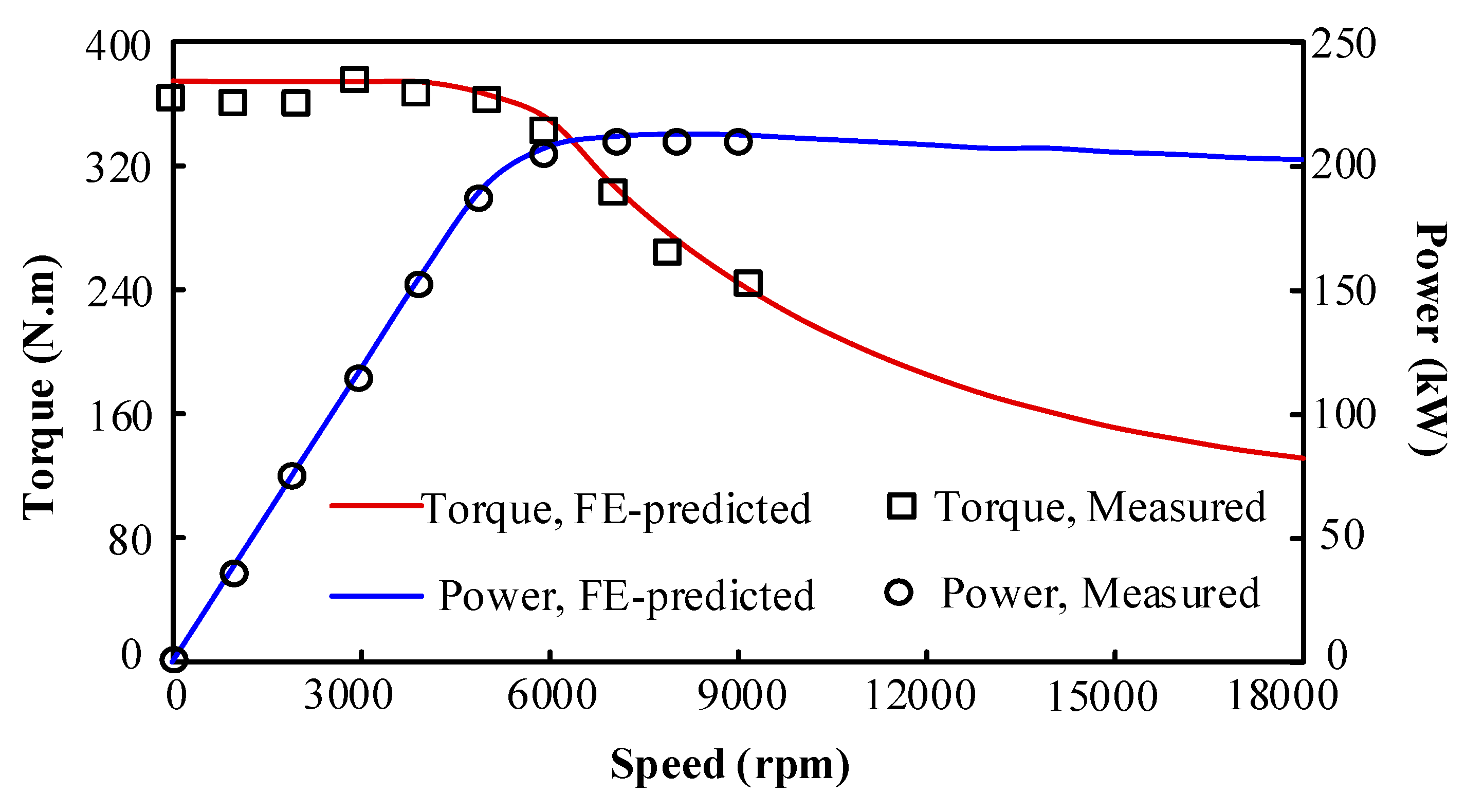
5. Experimental Validation
6. Conclusions
- Design Optimization: Strategic placement of hybrid PMs to enhance electromagnetic performance.
- Material Innovation: Reduction in dysprosium content or adoption of novel grain boundary diffusion processes to minimize rare-earth usage and lower motor costs.
- Multidisciplinary Optimization: Consideration of cost factors and multi-physical field couplings to improve overall performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khooban, M.H.; Gheisarnejad, M.; Vafamand, N.; Boudjadar, J. Electric vehicle power propulsion system control based on time-varying fractional calculus: Implementation and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2019, 4, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, I.; Ozpineci, B.; Islam, M.S.; Gurpinar, E.; Su, G.J.; Yu, W. Electric drive technology trends, challenges, and opportunities for future electric vehicles. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Zuo, Y.; Xie, S.; Hoang, C.C.; Han, B.S.; Lee, H.T. Comparative study of permanent-magnet vernier machine and interior permanent-magnet machine for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 6601–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen, F.; Rahman, K.; Son, Y. Electrical propulsion system design of chevrolet bolt battery electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Amiri, E.; Rastgoufard, P.; Mirafzal, B. Toward less rare-earth permanent magnet in electric machines: A review. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 900119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, T.; Zhu, X.; Fan, D.; Wang, Q. Analysis and design of a new type of less-rare-earth hybrid-magnet machine with different rotor topologies. IEEE Trans. Appl. Superconduct. 2020, 30, 5200406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, W.; Quan, L.; Xiang, Z.; Gu, W. Design and multi-objective stratified optimization of a less-rare-earth hybrid permanent magnets machine with high torque density and low cost. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Bang, Z.Y.; Cheng, L.Z.; Yu, L.; Jie, Z.H.; Xu, S.H. Energy-saving design and research of high-speed permanent magnetic synchronous motor under the development of rare earth resources. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 19, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Tahanian, H.; Aliahmadi, M.; Faiz, J. Ferrite permanent magnets in electrical machines: Opportunities and challenges of a non-rare-earth alternative. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 900120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xu, G.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z. A high torque density ferrite STPM machine using flux-leakage utilized rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 15393–15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrievskii, V.; Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Goman, V. Improved design of synchronous homopolar machine with ferrite magnets with increased resistance to irreversible demagnetization for subway train. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 100725–100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, Z.; Fan, D.; Quan, L.; Xu, L. Robust optimization of a rare-earth-reduced high-torque-density PM machine for electric vehicles based on parameter sensitivity region. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 10269–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y. Design and investigation of flux-reversal permanent-magnet motor with less rare-earth magnet for low-cost application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 4133–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Cost-effective high torque density Bi-magnet machines utilizing rare earth and ferrite permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, G.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. A new hybrid excitation flux switching machine using low-cost ferrites with flux regulation capability. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fan, D.; Xiang, Z.; Quan, L.; Hua, W.; Cheng, M. Systematic multi-level optimization design and dynamic control of less-rare-earth hybrid permanent magnet machine for all-climatic electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouiabadi, M.M.; Aliabad, A.D.; Mousavi, S.M.; Amiri, E. Design and analysis of E-core PM-assisted switched reluctance machine. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Kim, K.O.; Lim, M.S. Performance improvement of rare-earth free high-speed multilayer IPMSM using dual-phase magnetic material. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 59, 8205105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hao, X.; Gao, C.; Jiang, Z. An effective nontransient active short-circuit method for PMSM in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 3571–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, G.F.; Bojoi, A.; Pescetto, P.; Ferrari, S.; Peretti, L.; Pellegrino, G. Active short-circuit strategy for PMSMs enabling bounded transient torque and demagnetization current. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 109001–109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, Y. Discontinuous active short circuit strategy for improved safe state of PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhan, H.; Fang, Y. Influence of dimensional parameters on three-phase short circuit and demagnetization in surface-mounted PM machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2514–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhan, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, K.; Yu, L. Investigation of post-demagnetization torque ripple in fractional-slot surface-mounted PM wind power generators after short circuit faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Peng, F. A novel delta-type hybrid-magnetic-circuit variable flux memory machine for electrified vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 3512–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



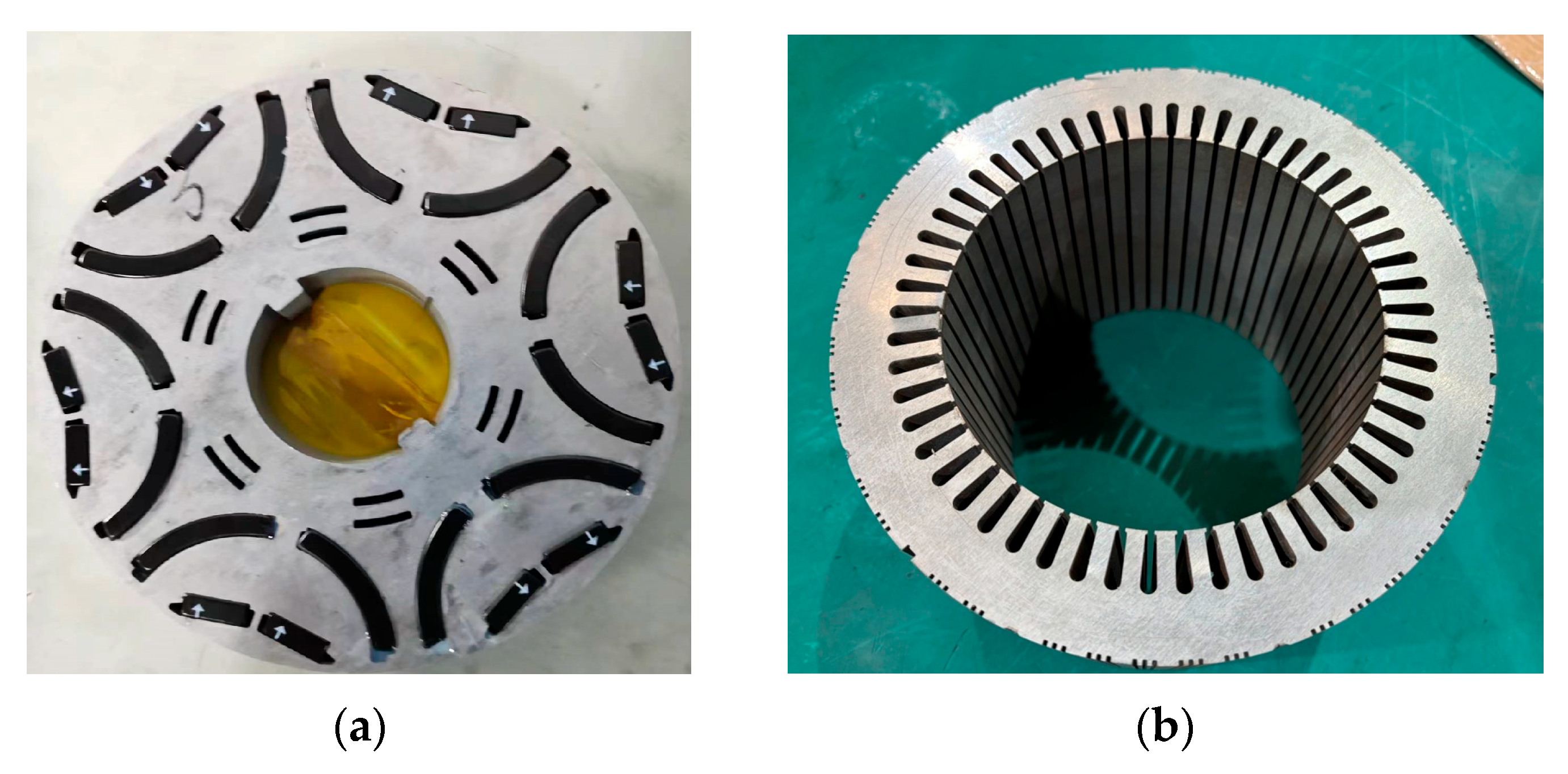

| Materials | Brand | Cost | Percentage of Dy | Percentage of Tb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare-earth PM | N42UH | 63–90 USD/kg | 3–6% | 0.25% |
| Less-rare-earth PM | N38UH | 48–70 USD/kg | 1.2–3.5% | 1% |
| Sator/Rotor core | 25SW1300 | 8–20 USD/kg | / | / |
| Item | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sator outer diameter | mm | 210 |
| Rotor outer diameter | mm | 138 |
| Air gap length | mm | 1 |
| Maximum speed | r/min | 18,000 |
| Maximum efficiency | % | ≥94 |
| DC bus voltage | V | 360 |
| Maximum current | Arms | 630 |
| Number of turns | / | 5 |
| Parallel branches | / | 3 |
| Objective | Value | Weights |
|---|---|---|
| Torque | Maximum | 0.8 |
| Torque ripple | Minimum | 0.6 |
| Iron loss | Minimum | 1 |
| Parameter | Unit | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hpm | mm | 4.5~6.5 |
| FB1-1 | mm | 1~3 |
| FB2-1 | mm | 1.5~4 |
| FB2-2 | mm | 2~4 |
| Lpm1-ro | mm | 4~12 |
| Lpm2-ri | mm | 14~18 |
| Rpm2 | mm | 24~28 |
| LBR | mm | 65~67 |
| PM1-2 | mm | 5~9 |
| Parameter | HLEPM | Conventional PMSM |
|---|---|---|
| Winding cost (USD) | 66.2 | |
| Silicon steel cost (USD) | 63.8 | |
| PM weight (kg) | 0.84(V-shaped)/1.85(arc-shaped) | 2.65 |
| PM cost (USD) | 139.2 | 166.95 |
| Total cost (USD) | 269.2 | 296.95 |
| Relative cost (%) | 90.7 | 100 |
| Machine Topology | Copper Loss (W) | Iron Loss (W) |
|---|---|---|
| HLEPM | 14,000 | 346 |
| Conventional PMSM | 14,000 | 360 |
| Machine Topology | Maximum Efficiency (%) | Maximum Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| HLEPM | 97.94 | 218 |
| Conventional PMSM | 97.95 | 213 |
| Efficiency (%) | Speed Range (rpm) | Increase Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 95 | 10,600~13,800 | 30 |
| 94 | 13,500~18,000 | 33 |
| Item | Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
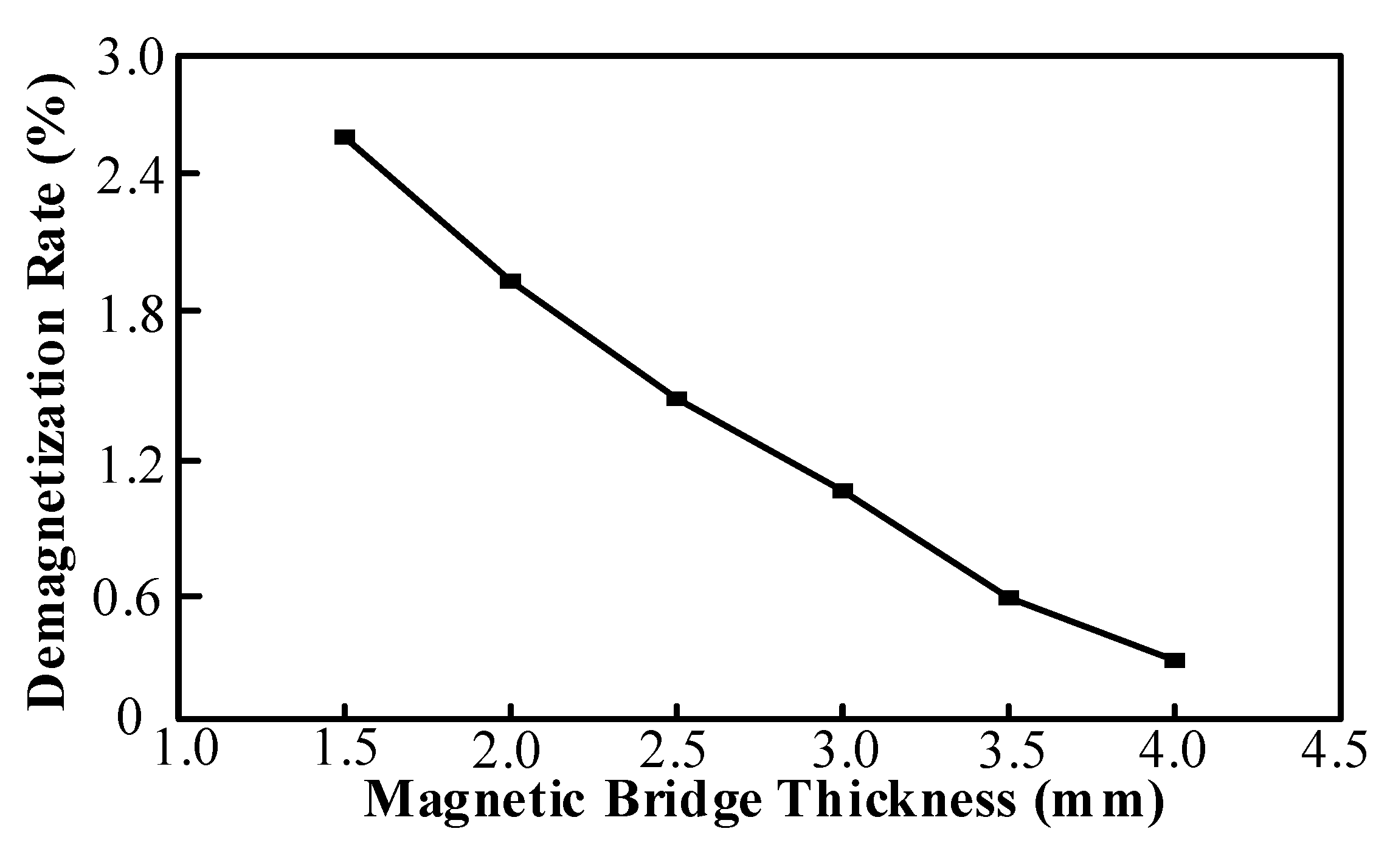
| Magnetic bridge (mm) | 4 | 3.5 | 3 | 2.5 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Demagnetization rate (%) | 0.76 | 0.93 | 1.22 | 1.47 | 1.79 | 2.18 |
| Machine Topology | Demagnetization Rates Exceeding 5% (%) | Torque Reduction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| HLEPM | 1.34 | 0.19 |
| Conventional PMSM | 2.28 | 0.32 |
| Item | FE-Predicted | Experiment | Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line-line voltage | 166.6 V | 165.4 V | 0.72% |
| Maximum power | 218 kW | 204.5 kW | 6.19% |
| Maximum efficiency | 97.94% | 97.11% | 0.83% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, S.; Lin, H. A Less-Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Machine with Hybrid Magnet Configuration for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2025, 18, 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123051
Yang H, Wu P, Liu D, Zhu Y, Fang S, Lin H. A Less-Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Machine with Hybrid Magnet Configuration for Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123051
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hui, Peng Wu, Dabin Liu, Yuehan Zhu, Shuhua Fang, and Heyun Lin. 2025. "A Less-Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Machine with Hybrid Magnet Configuration for Electric Vehicles" Energies 18, no. 12: 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123051
APA StyleYang, H., Wu, P., Liu, D., Zhu, Y., Fang, S., & Lin, H. (2025). A Less-Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet Machine with Hybrid Magnet Configuration for Electric Vehicles. Energies, 18(12), 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123051








