Abstract
Urban water distribution systems face growing challenges from energy inefficiencies caused by hydraulic anomalies, such as pipe aging, bursts, demand variability, and suboptimal pump and valve operations. This review systematically evaluates current technologies for energy-efficient management of WDNs under such conditions, structured around both basic and applied technologies. Basic technologies include real-time monitoring, data acquisition, and hydraulic modeling with CFD simulation. Applied technologies focus on demand forecasting, pressure management for energy optimization, and leakage anomaly detection. Case studies demonstrate the practical value of these approaches. Despite recent advances, challenges persist in data interoperability, real-time optimization complexity, scalability, and forecasting uncertainty. Future research should emphasize adaptive AI algorithms, integration of digital twin platforms with control systems, hybrid optimization frameworks, and renewable energy recovery technologies. This review provides a comprehensive foundation for the development of intelligent, energy-efficient, and resilient urban water distribution systems through integrated, data-driven management strategies.
1. Introduction
Water is a vital resource for society, and approximately 7% of global energy consumption is attributed to water distribution systems [1]. Urban water distribution networks (WDNs) constitute a fundamental component of modern urban infrastructure, ensuring the delivery of safe and reliable drinking water to billions of people worldwide. Over the past century, these systems have evolved from simple layouts into complex, pressurized, and interconnected networks. However, rapid urbanization, increasing climate variability, and aging infrastructure have introduced substantial operational challenges [2]. Hydraulic anomaly events, such as pressure transients [3], sudden flow deviations [4], undetected leaks, and mechanical failures [2], pose continuous threats to the continuity of service and the sustainability of water distribution systems. These events not only compromise the reliability of water supply but also lead to increased energy consumption [5].
Energy consumption in WDNs primarily arises from pumping stations, pressure regulation, and leakage management. Much of this energy is wasted due to inefficient pump scheduling, poor zone coordination, and delayed anomaly detection [1]. Improving energy efficiency requires integrating effective anomaly detection and control strategies [6].
In recent years, the advent of smart technologies has revolutionized water system management. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, including pressure sensors, flow meters, and acoustic leak detectors, has enabled real-time, high-resolution monitoring of system performance [7]. When combined with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) or advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) systems, these technologies facilitate the early detection of irregularities and support timely interventions. Additionally, the development of digital twins, which are real-time, physics-based virtual replicas of physical water systems, enables continuous simulation, scenario testing, and predictive maintenance without interrupting actual operations [8].
The increasing availability of sensor-rich data has further catalyzed the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) methods in WDNs [9]. By learning patterns in flow and pressure data, AI algorithms, particularly those based on deep learning architectures, such as long short-term memory (LSTM) networks [10] and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [11], are capable of classifying anomalies, forecasting system behaviors, and recommending energy-optimal control strategies.
Building upon these technological foundations, the convergence of IoT infrastructure, digital twin modeling, and AI-based analytics is gradually opening new frontiers in anomaly management and energy-efficient operation of WDNs. IoT infrastructure lays the groundwork by generating continuous streams of operational data; digital twins offer platforms for model-based reasoning and virtual experimentation; and AI algorithms enable the translation of data and model outputs into actionable insights. Nevertheless, several key challenges remain. Limitations in data quality, computational scalability, and implementation costs continue to hinder the widespread deployment of such integrated frameworks. Future progress may rely on optimizing sensor placement, enhancing the interoperability of real-time digital twins with AI-driven decision systems, and developing scalable, energy-efficient strategies for pressure management and anomaly resolution.
This review aims to provide an overview of current technologies for energy-efficient management of WDNs under hydraulic anomaly conditions, as illustrated in Figure 1. The basic technologies include (1) real-time monitoring and data acquisition, encompassing SCADA and AMI systems, smart sensor networks, and IoT integration, which provide dynamic data support for anomaly detection, and (2) hydraulic modeling and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation, covering the application of EPANET and recent advancements such as digital twin technology, which support network computation. These technologies establish the data and modeling infrastructure necessary for the development and implementation of advanced applications. Based on this foundation, the primary applied technologies include: (1) Demand forecasting techniques, highlighting the role of water demand prediction in energy-efficient operations, contrasting conventional and data-driven approaches, and exploring predictive control applications; (2) Pressure management strategies for energy optimization, including pump scheduling, pump-valve co-optimization, and district metered area (DMA) partitioning; and (3) Leakage anomaly detection technologies, addressing classification methods and early fault detection strategies.
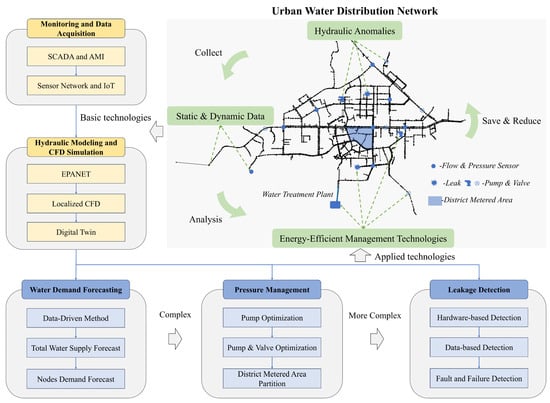
Figure 1.
Technologies for energy-efficient management of urban water distribution networks under hydraulic anomalies.
The structure of the paper is as follows. It begins with an analysis of the causes and impacts of hydraulic anomalies. This is followed by an overview of current technologies for the energy-efficient management of WDNs under such conditions, along with the identification of key research challenges and implementation barriers. Emerging opportunities for future development are also explored. Subsequently, through case studies and a SWOT analysis, the paper highlights the contributions of these technologies to the advancement of intelligent and energy-efficient water distribution system design and operation.
2. Hydraulic Anomalies and Energy Efficiency
Hydraulic anomalies in WDNs are defined as deviations from standard operating conditions, typically manifested through irregularities in pressure levels, flow distributions, or demand-supply dynamics. These anomalies commonly arise from aging infrastructure, fluctuating water demands, pipe bursts, and inefficient pump or valve operations. In practice, a condition is considered anomalous when key hydraulic parameters deviate markedly from normative thresholds. For instance, pressure falling below 15–20 m or exceeding 60–80 m, sudden flow rate variations exceeding 20–30% of predicted values, or the occurrence of abnormal flow reversals and transient disturbances.
2.1. Causes of Hydraulic Anomalies
- (1)
- Aging Infrastructure
As the infrastructure of water distribution networks ages, various components such as pipes, valves, and pumps experience wear and tear, which increases friction losses and resistance within the system [12]. As a result, higher energy is required to pump water to maintain the desired pressure and flow. Furthermore, the deterioration of materials can lead to leakages [2]. These issues are particularly pronounced in older urban areas with infrastructure that is decades old and has not been adequately updated or maintained.
- (2)
- Unexpected Pipe Failures and Bursts
Unforeseen pipe bursts or other failures often result in sudden disruptions to water flow, which directly impact the system’s hydraulic stability [13,14]. These failures cause pressure drops and flow anomalies in the affected areas. Additionally, the energy required to restore the system after a burst, including pumping water to repair or replace the affected infrastructure, leads to further energy inefficiencies [3].
- (3)
- Fluctuating Water Demand
Urban water demand fluctuates significantly over the course of a day, a week, and across different seasons, presenting major challenges for maintaining hydraulic balance in water distribution systems. During periods of high demand, certain areas may experience excessive consumption and low pressure. Conversely, during periods of low demand, energy is often wasted. In addition, sudden and unpredictable changes in water use can lead to abnormal flow distributions and pressure variations, which require additional energy input and can place stress on the system. These fluctuations may also result in hydraulic issues, such as pump inefficiency, inadequate pressure, and potential damage when pumps operate outside their optimal efficiency range [4,15].
- (4)
- Suboptimal Pump and Valve Operations
Pumps and valves play an essential role in regulating flow and pressure in WDNs. However, when these components are not operated efficiently, hydraulic anomalies can emerge [16,17]. For example, pumps that operate at fixed speeds may consume unnecessary energy during periods of low demand. Similarly, improperly adjusted valves can lead to excessive pressure in certain parts of the network, causing leakage in other areas. Suboptimal scheduling and operation of pumps and valves can, therefore, significantly affect the overall energy efficiency of the water distribution system.
- (5)
- Transient Hydraulic Events
In addition to steady-state inefficiencies, dynamic disturbances such as transient hydraulic events pose a critical challenge to energy-efficient operations. These events, most notably water hammer, are typically caused by the abrupt opening or closing of valves, sudden pump shutdowns, or emergency pipe isolations [18]. Rapid changes in flow velocity generate pressure surges that propagate throughout the network and may result in structural damage, including pipe deformation, joint failure, and mechanical fatigue in pumps and valves [19]. These disturbances disrupt system stability and require corrective measures that often involve additional energy input. Furthermore, repeated exposure to transients can accelerate equipment degradation and increase the frequency of maintenance interventions, thereby elevating both energy and operational costs.
2.2. Consequences of Hydraulic Anomalies
- (1)
- Increased non-revenue water losses
High-pressure zones in the network often lead to an increase in the rate of leakage, contributing to non-revenue water (NRW) [20]. The higher the pressure in certain parts of the network, the more likely water will leak through weak spots in the infrastructure, such as joints and valves. These leaks increase the energy required to pump water to compensate for the loss, further increasing operational costs and wasting valuable energy.
- (2)
- Excessive Energy Consumption
Hydraulic anomalies primarily lead to excessive energy consumption by increasing friction losses, reducing pump efficiency, and necessitating additional pumping operations to maintain desired pressure and flow conditions [1]. For example, aging pipes or network leaks increase hydraulic resistance, requiring pumps to work harder. Transient events, such as water hammer, also cause energy spikes due to abrupt pressure changes and the need for compensatory system responses [19]. Moreover, corrective measures, such as installing booster pumps or adjusting valve positions, further elevate energy use.
- (3)
- Decreased Service Reliability
Hydraulic anomalies can undermine service reliability [21]. Areas experiencing inadequate pressure are prone to water shortages and may even face supply disruptions during periods of high demand. Transient pressure fluctuations, including those caused by water hammer, may trigger localized instability or equipment malfunctions, further compromising service continuity [19]. As a result, utilities often need to invest in backup systems to maintain service levels in these zones. However, these additional interventions are typically energy-intensive and often provide only short-term relief for persistent hydraulic anomalies.
- (4)
- Increased Operational Costs
The need for continuous monitoring, maintenance, and corrective measures to address hydraulic anomalies results in higher operational costs. Traditional systems, which rely on manual valve adjustments and fixed pump schedules, require significant operator intervention. Furthermore, water hammer and similar transients can damage valves, joints, and meters over time, increasing the frequency of repairs. The frequent deployment of energy-intensive pumps and valves to restore balance to the system also increases both energy and maintenance costs [1].
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Acquisition
The effective management of hydraulic anomalies relies on the accurate and timely acquisition of real-time data from multiple locations within the WDN. As a basic technology, real-time monitoring and data acquisition is essential for detecting anomalies, evaluating system performance, and implementing corrective measures without delay.
3.1. SCADA and AMI Systems
With the continuous advancement of the water supply industry, SCADA systems have become the technological foundation of modern WDN management, offering continuous monitoring and centralized control of key hydraulic infrastructure, including pipelines, reservoirs, pumping stations, and storage tanks [22,23]. SCADA systems provide operators with real-time access to essential hydraulic parameters, such as pressure, flow rate, tank levels, and pump performance, across the entire distribution network. This real-time insight enables the identification of hydraulic anomalies [24].
Beyond real-time monitoring, SCADA systems also support historical data storage, which is essential for trend analysis and long-term performance evaluation. In practice, SCADA systems in WDNs are typically categorized into SCADA-Q and SCADA-P configurations [25]. SCADA-Q primarily monitors source flows at network inlets, enabling basic operational control (e.g., pump scheduling) and preliminary leak detection. SCADA-P incorporates internal pressure and flow measurements, greatly enhancing the system’s leak detection capabilities and supporting hydraulic model calibration.
Despite their widespread deployment, traditional SCADA systems have notable limitations. The reliance on fixed-point sensors can result in insufficient spatial resolution, hindering the detection of localized anomalies in complex network segments. Additionally, data is typically collected from a limited number of nodes, making it difficult to monitor distributed or decentralized regions effectively. To overcome these challenges, modern utilities are increasingly integrating SCADA systems with emerging technologies such as smart sensor networks, IoT devices, and digital twins, thereby improving spatial coverage, diagnostic capabilities, and system intelligence for real-time monitoring and proactive system management [26,27].
Compared to SCADA systems, AMI is primarily focused on enhancing demand-side monitoring and acquiring consumer-level data [25,28]. AMI systems are capable of automatically recording water usage at high temporal resolution, which reduces the need for manual meter reading and improves data accuracy. These data can be used by utilities to detect abnormal consumption patterns, inform customers of potential issues, and identify possible leaks, thereby contributing to the reduction of non-revenue water. In addition, AMI enables the analysis of consumption behaviors over time, supporting time-of-use assessments and the identification of peak demand periods, which are essential for demand-side management. However, AMI does not provide direct measurements of hydraulic parameters such as pressure or flow, and therefore, it cannot replace SCADA systems and monitor the operational status of the entire distribution network. Instead, AMI complements SCADA by extending data acquisition to locations where SCADA coverage is limited, particularly in residential and commercial areas.
3.2. Smart Sensor Networks and IoT Integration
The integration of IoT technologies into WDNs represents a transformative evolution from conventional supervisory control systems to intelligent and data-driven infrastructure management. Traditional SCADA systems, although historically fundamental to network operations, are often limited by inadequate spatial coverage, low sampling frequency, centralized data processing, and unidirectional communication architecture. These limitations significantly constrain real-time responsiveness and hinder the implementation of adaptive control strategies under the increasingly complex demands of urban water supply systems. In contrast, modern IoT-based smart sensor networks consist of spatially distributed and autonomous sensing units that are capable of continuously monitoring key hydraulic parameters, including pressure and flow rate, with high spatial and temporal resolution [26,29]. These systems integrate embedded microcontrollers, low-power wide-area communication technologies such as Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT), LoRa, and fifth-generation (5G) networks, as well as edge computing architectures that enable localized data processing [24,26]. At the sensor level, tasks such as anomaly detection, signal filtering, and preliminary classification can be performed efficiently. This not only reduces data transmission volumes and network latency but also enhances the overall responsiveness, reliability, and scalability of the monitoring system. A key advantage of IoT frameworks lies in their bidirectional communication capability. This enables dynamic reconfiguration of sensing parameters, remote firmware updates, and adaptive threshold adjustments in response to evolving operational conditions. Such flexibility allows for real-time control strategies and enhances the resilience of water supply systems.
Specifically, pressure transducers are used to monitor hydraulic conditions by capturing pressure transients and deviations from expected values, which are critical for the detection of pipe bursts, valve failures, and other operational anomalies [29,30]. Ultrasonic and electromagnetic flow meters measure flow velocity and volume with high accuracy and minimal interference with the pipeline, facilitating real-time assessment of supply–demand balance [30]. Acoustic sensors installed on pipe surfaces detect high-frequency vibrations generated by leak-induced turbulence. These signals can be analyzed in the spectral or frequency domain to support early leak detection [29]. On the consumer side, smart water meters continuously record water usage at short intervals, providing data that can be used for analyzing consumption behavior, forecasting demand, and identifying localized leakage events [7,31].
IoT-enabled smart sensor networks provide continuous, high-resolution monitoring and intelligent decentralized control, which significantly enhance the detection of hydraulic anomalies and improve the overall energy efficiency of the system. SCADA systems, AMI systems, and IoT-based platforms each play complementary roles in forming a comprehensive smart water infrastructure. SCADA systems provide real-time monitoring and centralized control of key hydraulic components; AMI systems enable high-resolution demand-side data acquisition at the consumer level; and IoT technologies offer flexible, distributed sensing and communication capabilities. The integration of these technologies facilitates enhanced anomaly detection, predictive analytics, and system optimization, collectively contributing to improved hydraulic performance and energy efficiency across the entire water distribution network.
4. Hydraulic Modeling and CFD Simulation
Hydraulic simulation serves as a foundational technology in the analysis and management of WDNs. These simulation tools enable the evaluation of system performance under defined operating conditions and provide a scientific basis for informed decision-making in both routine operations and contingency planning. By simulating different scenarios, utilities can assess the potential impacts of control strategies, infrastructure changes, or demand fluctuations before they are applied in practice.
4.1. EPANET and Its Applications
EPANET, developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), is one of the most widely utilized open-source platforms for hydraulic modeling of WDNs [1,32]. It offers robust simulation capabilities for evaluating both steady-state and extended-period hydraulic behaviors, as well as water quality dynamics in pressurized pipe systems. By incorporating key system parameters, including temporal variations in demand patterns, hydraulic properties of pipes, operational characteristics of pumps and valves, and the complexity of network topology, EPANET facilitates a comprehensive and dynamic understanding of WDN performance across a broad spectrum of operating conditions. A notable advantage of EPANET is its capacity to simulate networks of virtually any size or complexity, as it imposes no software-based limitations on the number of network elements. This scalability makes it particularly suitable for both small-scale local systems and large-scale urban infrastructures. The software supports multiple head loss equations, allowing engineers to select the most appropriate method based on the specific hydraulic characteristics of the network under study.
The flexibility of EPANET extends to the simulation of a wide range of operational scenarios [32]. System operators can evaluate the effects of time-dependent demand fluctuations, structural modifications (including the addition or removal of pipes, pumps, or storage facilities), and emergency events such as pump malfunctions or pipeline failures. These capabilities assist utilities in anticipating system responses, conducting vulnerability assessments, and formulating effective contingency plans. In addition, the platform enables the virtual testing of control strategies, including pressure management through valve regulation and pump operation scheduling, thereby supporting data-driven decision-making prior to the implementation of physical interventions. In terms of energy efficiency, EPANET provides analytical tools for assessing pump performance and estimating energy consumption associated with water conveyance. It allows for the identification of energy-intensive zones and the diagnosis of inefficiencies arising from suboptimal pump operations, excessive pressure conditions, or uneven flow distribution. By simulating alternative operational strategies, utilities can identify cost-effective solutions for minimizing energy losses, improving pump efficiency, and ultimately reducing electricity expenditures. These outcomes are especially valuable in large-scale water supply systems, where energy costs constitute a significant portion of total operational expenses.
Due to its open-source nature, EPANET is supported by a vibrant global user community that actively contributes to its development, maintenance, and enhancement through third-party tools and user interfaces [33]. A wide array of extensions and graphical environments have been created to improve its functionality and accessibility, including toolkits based on programming languages such as Python 3.11 and MATLAB R2023b [33]. These extensions support automated simulations, integration with optimization algorithms, and advanced data analysis, thereby broadening the scope of EPANET’s applications in research and practice. In summary, EPANET serves as a foundational tool for the analysis, planning, and optimization of water distribution systems.
EPANET and similar hydraulic modeling tools are widely used to analyze system behavior and evaluate energy efficiency in WDNs. These tools are particularly suitable for long-term planning and system design as they enable scenario-based simulations to assess network performance under various operating conditions. However, such models are typically run in a static, batch-processing mode, where simulation parameters must be defined in advance and manually input by operators. While this approach is effective for strategic evaluations, it has limitations in supporting real-time operational decisions as it does not reflect continuously changing system states. Furthermore, although EPANET includes functions for estimating energy consumption, the reliability of simulation outputs is strongly influenced by the accuracy and resolution of the input data. To overcome these limitations and improve the responsiveness of network management, the integration of Digital Twin technology has been proposed.
4.2. Localized CFD Analysis
While EPANET provides valuable insights at the network scale, its resolution is insufficient for capturing complex flow phenomena occurring within individual hydraulic components. CFD offers a complementary approach for analyzing localized hydraulic phenomena with high spatial and temporal resolution [34,35]. CFD techniques numerically solve the Navier–Stokes equations to simulate complex transient hydraulic behaviors, including turbulence, pressure fluctuations, and water hammer effects within specific components, such as valves, pumps, elbows, and junctions [36].
CFD is particularly valuable for investigating hydraulic anomalies that are difficult to characterize using network-level models. For example, transient pressure waves caused by rapid valve closures or pump shutdowns, which are common sources of water hammer, can be accurately simulated to evaluate their amplitude, propagation characteristics, and potential structural impacts [37]. Furthermore, CFD facilitates the optimization of hydraulic component geometry and configuration, thereby reducing local energy losses and enhancing hydraulic performance. For instance, simulations can inform the redesign of pump impellers or valve housings to minimize cavitation, turbulence, and head loss under variable operating conditions [35]. These component-level improvements, when incorporated into system design, contribute to overall energy efficiency.
The application of CFD in WDNs is further supported by advances in high-performance computing, which enable the simulation of unsteady three-dimensional flows in complex geometries within practical time constraints. Contemporary CFD platforms, such as ANSYS Fluent 2023 R2 and COMSOL Multiphysics 6.1, provide reliable solvers and advanced meshing tools suitable for modeling pressurized water flow and multiphase interactions [38].
Despite its advantages, CFD modeling requires accurate geometric representations and boundary conditions. The setup process, including mesh generation, turbulence model selection, and parameter calibration, can be computationally demanding and time-consuming. Therefore, CFD is most effective when applied in a targeted manner to complement system-level tools, particularly in the analysis of critical components or high-risk areas identified through EPANET or digital twin simulations. By providing high-resolution insights into localized hydraulic behaviors, CFD supports the diagnosis of anomalies, the mitigation of transient effects such as water hammer, and the design of energy-efficient components. When integrated with network-scale modeling approaches, CFD contributes to a comprehensive and multi-scale framework for the intelligent and resilient operation of urban water distribution systems.
4.3. Digital Twin Technology
Building on the strengths of both EPANET and CFD, digital twin technology offers a comprehensive and real-time framework for modeling, monitoring, and optimizing the performance of WDNs [8,39]. A digital twin functions as a dynamic replica of the physical network, continuously reflecting its behavior, operational dynamics, and performance by assimilating real-time data from field-deployed sensors [27]. In the context of WDNs, digital twins are developed by coupling high-fidelity hydraulic and flow models with real-time data acquired from SCADA systems, smart meters, pressure sensors, and flow monitors. This integration enables the continuous updating of the virtual model as new data becomes available, thus providing a high-resolution, real-time representation of the network’s operational state.
Compared to SCADA systems, Digital Twin technology provides a continuously updated simulation environment that reflects both the real-time state and projected evolution of a WDN. This dynamic modeling capability supports a more comprehensive understanding of system behavior under varying conditions. Digital twins allow operators to evaluate various operational strategies, such as modifying pump schedules, adjusting valve configurations, or implementing network isolation measures, within a risk-free virtual environment prior to field deployment [39]. This reduces the operational risks associated with field-based trial-and-error approaches and supports data-informed decision-making aimed at enhancing performance, reliability, and energy efficiency. Additionally, Digital Twins support continuous anomaly detection by identifying deviations from modeled hydraulic behavior, which may indicate emerging issues such as leaks, pipe bursts, or equipment faults.
Despite these advantages, the implementation of digital twin technology in WDNs presents several challenges. Chief among these is the necessity for precise calibration and validation of the hydraulic model using both historical and real-time data. This process is significantly more complex and data-intensive than the configuration of conventional SCADA systems. In addition, real-time simulation and continuous model updating in large-scale networks demands substantial computational resources, requiring the development of robust data integration frameworks and the deployment of high-performance computing infrastructure. In summary, digital twin technology represents a transformative advancement in the field of hydraulic modeling. By enabling real-time simulation, predictive analytics, and enhanced decision-support capabilities, it overcomes many of the limitations associated with traditional SCADA systems and offers significant potential for the intelligent and proactive management of modern WDNs.
5. Water Demand Forecasting Techniques
Water demand in urban distribution systems exhibits variability across daily to seasonal scales. While such patterns are typically routine, abrupt fluctuations may indicate operational anomalies such as equipment faults or unauthorized consumption, which can lead to pressure imbalances and pipe failures. As an applied technology, demand forecasting is essential for detecting and managing these abnormal variations, thereby enhancing hydraulic stability and reducing energy consumption through more efficient system operation.
5.1. Conventional vs. Data-Driven Forecasting Approaches
Traditionally, water demand has been forecast using statistical methods such as autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models, which assume linearity and require stationarity, as described in Table 1 [40]. While effective at capturing regular seasonal trends, these models often struggle with non-linear dependencies and abrupt behavioral shifts. In contrast, machine learning and deep learning approaches have emerged as robust alternatives, capable of modeling complex temporal dependencies and adapting to heterogeneous influencing factors. Techniques such as random forests (RF) and support vector machine/regression (SVM/SVR) have been widely applied for water demand prediction due to their simplicity and moderate interpretability [41,42]. While these methods can capture non-linear relationships and perform well with structured features, they are typically limited in modeling long-range temporal patterns. To overcome such limitations, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and their variants have demonstrated improved accuracy in water consumption forecasting tasks.
Recently, Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), a simplified variant of RNNs, have been increasingly utilized in water demand forecasting due to their ability to capture long-term temporal dependencies with reduced computational overhead [40]. When combined with attention mechanisms, GRU-based models, similar to LSTM networks, can dynamically assign weights to different time steps in the input sequence, allowing the network to focus on periods with higher predictive significance [10,43]. This integration has been shown to enhance both the accuracy and interpretability of forecasts, particularly in the presence of irregular or abrupt consumption variations. Empirical studies have demonstrated that GRU-Attention architectures outperform conventional statistical and basic machine learning models in daily demand prediction tasks, making them particularly well-suited for real-time control applications in water distribution systems.
To enhance forecasting accuracy, recent models often incorporate exogenous variables such as ambient temperature, rainfall, day-of-week indicators, and holiday markers [44]. These external factors play a significant role in influencing water usage patterns, particularly in residential and mixed-use areas. By integrating these contextual factors, forecasting models can offer a more comprehensive representation of consumption dynamics, leading to more stable and accurate predictions.

Table 1.
Prevailing methodologies in contemporary water demand forecasting.
Table 1.
Prevailing methodologies in contemporary water demand forecasting.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications & Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exponential Smoothing [45] | Simple, effective, easy implementation. | Poor with complex time series patterns. | For data with moderate trends and seasonal effects. |
| Linear Regression [46] | Simple and interpretable. | Only for linear relationships. | Applied in valid linear regression tasks. |
| ARIMA [40] | Simple structure, low computation cost. | Demands accurate data, lacks generalization. | Suited for stationary time series without long-term dependence. |
| SVM/SVR [42] | Effective in high-dimensional spaces, strong generalization. | Sensitive to parameter selection, high computation cost. | Effective for complex, high-dimensional classification tasks. |
| RF [41] | Robust, handles high-dimensional data. | Poor interpretability, computationally costly. | Suitable for classification and regression, resistant to noise and overfitting. |
| Neural Networks [40] | Strong non-linear modeling ability. | Need large data, prone to overfitting. | Widely used in complex regression and classification with large datasets. |
| RNN [47] | Fit for sequential data. | Have gradient issues, hard to capture long-term dependencies. | Useful for time series and sequential data analysis despite training difficulties. |
| GRU [40] | Simplified structure, computationally efficient. | Limited capability to model very long-term dependencies. | Faster alternative to LSTM for real-time apps with limited resources. |
| LSTM [10] | Captures long-term dependencies well. | High computational complexity, many parameters. | Commonly used for sequential data tasks requiring long-term memory. |
5.2. Demand Forecasting as a Tool for Energy-Efficient Operation
In water distribution systems, energy consumption is closely linked to the real-time operation of pumps and valves. A mismatch between actual demand and operational schedules often leads to energy inefficiencies, particularly due to pump operation during low-demand periods [4]. Accurate demand forecasting enables system operators to proactively align pumping schedules with anticipated consumption patterns [48]. Such alignment helps reduce unnecessary pump cycling and prolongs the mechanical lifespan of critical assets. Therefore, demand forecasting forms a fundamental component of energy-efficient system management, supporting both economic savings and operational efficiency.
Unanticipated spikes or drops in consumption can destabilize pressure conditions across the network, leading to a cascade of hydraulic instabilities. When incorporated into real-time monitoring frameworks, demand forecasting models serve as a critical reference for anomaly detection. By continuously comparing real-time consumption data with predicted baselines, the system can identify deviations indicative of leaks, unauthorized usage, or sensor faults.
Beyond prediction, the integration of demand forecasts into control systems forms the foundation for advanced strategies [48,49]. In this approach, forecasted demand serves as input to an optimization routine that calculates the optimal sequence of control actions, such as pump scheduling, valve adjustments, and pressure management, over a future time horizon. This feedback loop allows the system to preemptively adapt to consumption changes, minimize energy use, and maintain service standards by optimizing pressure levels and reducing unnecessary pump operation. The value of demand forecasting lies in its dual utility: it enables proactive, energy-efficient operation while simultaneously serving as a real-time anomaly detection tool. This dual role positions forecasting at the heart of next-generation water distribution management systems. In particular, the combination of machine learning-based forecasts with real-time telemetry data holds significant potential for creating fully adaptive and self-optimizing infrastructure.
6. Pressure Management-Based Energy Efficiency Optimization Strategies
Pressure is a key indicator of energy status in WDNs, and abnormal variations often signal hydraulic inefficiencies or potential failures. As an applied technology, pressure management focuses on identifying and mitigating these anomalies to maintain system stability and improve energy efficiency. It is one of the central strategies for optimizing energy distribution and reducing operational losses across the network.
6.1. Pump Optimization
The hydraulic behavior of pump systems in pump stations is fundamentally determined by the interaction between pump performance curves and system resistance curves [17,50]. In such systems, throttling valves influence the system by altering the shape and slope of the hydraulic resistance curve, which effectively changes the operating point of the pump on its performance curve. Meanwhile, variable-speed pumps (VSPs) achieve flow and pressure modulation by adjusting their rotational speed, thereby shifting their performance curves dynamically.
The overall energy efficiency of these systems is primarily influenced by the following factors [17]:
- (1)
- Pump Efficiency (η): This typically reaches its maximum at the Best Efficiency Point (BEP), which is a specific flow rate and head where the pump operates most effectively. Operating too far from this point leads to energy losses and reduced efficiency.
- (2)
- Valve-Induced Head Losses: When flow is controlled by throttling valves, artificial head losses are introduced into the system. These losses increase nonlinearly with the degree of throttling and contribute to higher energy consumption without improving system output.
- (3)
- Hydraulic and Mechanical Stability: Operating the pump significantly away from its BEP not only lowers efficiency but also induces undesirable effects, such as cavitation, vibration, and excessive mechanical stress, all of which accelerate equipment degradation and reduce service life.
- (4)
- Hydraulic Noise Generation: Excessive hydraulic noise, typically caused by turbulence, cavitation, or rapid valve operations, is often a symptom of inefficient flow conditions [51]. While primarily an acoustic issue, such noise also reflects energy dissipation within the system, indicating areas of suboptimal performance that may warrant operational or design adjustments.
From a control perspective, the optimal scheduling of pumps can be classified into implicit scheduling and explicit scheduling. Implicit scheduling includes parameters such as pump flow rate, pump pressure, and rotational speed of variable-speed pumps, as well as triggering pump condition changes based on tank water levels. These control methods do not directly specify pump operation times but instead rely on system state changes to guide pump behavior. In contrast, explicit scheduling primarily involves direct control of pump on/off states, including determining the pump’s operating status at predefined time intervals, specifying the duration of each pump operation, and setting the exact times for starting or stopping pumps.
From an optimization perspective, the primary goals often include [17]:
- (1)
- Minimizing total power consumption (Psys = ΣPi), especially in configurations where multiple pumps operate in series or parallel.
- (2)
- Reducing the specific energy consumption (Esys = Psys/Qsys), which represents the amount of energy used per unit volume of water delivered.
- (3)
- Extending pump and valve lifespan by maintaining operating conditions within a defined range around the BEP, typically within ±10%.
Furthermore, the methods for optimizing pump-valve operations in WDNs have traditionally relied on heuristic strategies such as throttling control (TC), bypass control (BC), fixed-speed pump scheduling (FSPS), and affinity law-based speed regulation (ALSR), as summarized in Table 2 [17]. While TC and BC are straightforward to implement, they often incur substantial energy losses due to increased hydraulic resistance and recirculation, respectively. FSPS, typically formulated via linear programming (LP), can reduce energy use during low-demand periods but is limited by discrete control granularity. ALSR employs variable frequency drives (VFDs) for continuous speed modulation based on the affinity laws, offering improved efficiency, though accuracy declines under turbulent or non-ideal flow conditions. To overcome these limitations, intelligent optimization methods have been introduced. Model-based approaches, including mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) and gradient-based algorithms such as sequential quadratic programming (SQP), enable the joint optimization of discrete and continuous variables. However, these methods often face challenges related to scalability and the risk of convergence to local optima. Metaheuristic algorithms like genetic algorithms (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) provide robust search capabilities in complex, non-convex solution spaces, achieving notable energy savings [52]. Additionally, ML techniques, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs), SVMs, and reinforcement learning (RL), facilitate nonlinear modeling, classification of optimal operational zones, and adaptive control under dynamic conditions. Furthermore, multi-agent systems (MAS)-based pump-valve control involves autonomous agents that collaborate for system-wide optimization, enhancing distributed decision-making in large systems [53]. Despite their advantages, MAS-based approaches can face communication overhead and scalability issues.

Table 2.
Prevailing methodologies for pump optimization.
6.2. Pump-Valve Co-Optimization
Pumps constitute the primary source of energy input in WDNs, and their operation is fundamental to the system’s energy optimization. However, relying solely on pump scheduling often fails to fully exploit the operational flexibility of the network. This limitation arises from the significant influence of valve operations, particularly those involving pressure-reducing valves (PRVs) and throttling valves, on flow distribution, pressure regulation, and energy dissipation within the system. Consequently, in addition to optimizing pump operations, it is necessary to incorporate localized hydraulic control mechanisms to achieve comprehensive energy efficiency.
Pump-valve co-optimization enhances the decision-making process by integrating both pump-related and valve-related control variables into the operational model [57,58]. This expanded optimization framework improves system adaptability and energy-saving capacity. The valve-related decision variables typically include valve on/off status, valve positioning, valve opening degree, flow rate through the valve, head loss coefficient, and the pressure setting for PRVs. In high-pressure zones, PRVs are extensively applied to maintain appropriate downstream pressure, thereby reducing structural stress, minimizing leakage, and ensuring operational stability.
In the context of valve regulation, particularly with rapid throttling or abrupt closure of pressure-reducing valves (PRVs), transient hydraulic phenomena such as water hammer may be triggered. Water hammer is characterized by sudden pressure surges caused by the rapid deceleration of water columns, which can lead to severe pipe stress, joint failures, and localized cavitation. These pressure transients not only threaten the structural integrity of the distribution system but also result in energy inefficiencies through dissipative pressure fluctuations and non-uniform flow regimes. Therefore, valve operation strategies should incorporate water hammer mitigation measures, including gradual valve actuation protocols, use of surge protection devices (e.g., air chambers or surge tanks), and coordinated pump-valve timing. Co-optimization frameworks that integrate transient-aware control constraints can significantly enhance both energy efficiency and operational safety under dynamic demand conditions.
Compared to pump-only optimization, pump-valve co-optimization enables a more coordinated and balanced distribution of pressure and flow throughout the network. It significantly improves energy efficiency while maintaining the reliability and quality of water service delivery. To address the inherent complexity of incorporating both discrete and continuous control variables, various optimization algorithms such as mixed-integer nonlinear programming, metaheuristic methods, and learning-based approaches have been effectively applied [57,59]. These methods facilitate the integration of pump and valve controls within a unified optimization framework, thereby supporting real-time decision-making and enhancing system adaptability under dynamic operating conditions.
6.3. District Metered Areas Partition
DMAs refer to the subdivision of a WDN into smaller, pressure-controlled zones, typically bounded by flow meters or control valves. By isolating flow paths and monitoring inflows and pressures at the boundaries, DMAs facilitate more granular hydraulic control and enhance the observability of localized system behavior. From the perspective of energy efficiency, DMA partitioning directly contributes to pressure regulation by enabling the application of zone-specific control strategies. In particular, PRVs located at DMA boundaries can be optimally adjusted to maintain stable downstream pressures that align with minimum service requirements. Moreover, DMA-based pressure management complements other energy-efficient strategies by reducing the operational complexity and enhancing the responsiveness of control actions. For instance, demand forecasting within individual DMAs allows predictive pressure adjustment and supports adaptive pump control in upstream facilities. As such, DMA partitioning serves as an enabling framework for distributed, demand-driven energy optimization.
The effectiveness of DMA design relies heavily on the underlying optimization methods, as summarized in Table 3. These methods are particularly suitable for addressing multi-objective problems that involve minimizing pressure variability, balancing water demand across zones, and reducing overall energy consumption. In addition to conventional optimization algorithms, such as genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization, and ant colony optimization, graph theory and network topology analysis are commonly employed to represent the water distribution network as a weighted graph, where nodes represent junctions and edges represent pipes [60,61]. Based on this representation, clustering algorithms including k-means, hierarchical clustering, and spectral clustering are utilized to group nodes into zones that exhibit both hydraulic and topological similarity. Moreover, community detection techniques grounded in modularity optimization, such as the Louvain algorithm, have been applied.

Table 3.
Prevailing methodologies for district metered areas partition.
Table 3.
Prevailing methodologies for district metered areas partition.
| Method Category | Specific Method | Principles | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical Clustering | k-means [62] | Partitions nodes into k clusters by minimizing within-cluster Euclidean distance of hydraulic attributes. | Computationally efficient for mid-sized networks. | Requires predefined cluster count; ignores topological connectivity. |
| Classical Clustering | Hierarchical Clustering [60] | Agglomerative/divisive clustering based on similarity matrices to form dendrograms. | Multi-scale partitioning; interpretable hierarchy. | High computational complexity; scalability issues. |
| Classical Clustering | Spectral Clustering [60] | Utilizes eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix for dimensionality reduction before clustering. | Captures non-convex topological relationships. | Sensitivity to parameters; high memory demand for matrix operations. |
| Community Detection | Louvain Algorithm [61] | Maximizes modularity to identify densely connected subgraphs. | Automatic cluster number determination; scalable. | Potential imbalance in zone sizes. |
7. Leakage Anomaly Detection Technologies
Leakage in WDNs constitutes a major type of hydraulic anomaly, typically categorized into background leakage, hidden or latent leakage, and visible leakage, such as pipe bursts. Background leakage refers to minor yet persistent water loss through pipe walls or joints. Hidden leakage occurs underground without surface manifestation and is usually difficult to detect, while visible leakage leads to noticeable water discharge and service interruptions. Undetected or delayed responses to such leakage events can result in significant water loss, increased energy consumption, infrastructure damage, and reduced service reliability. Existing leakage detection techniques can be broadly classified into three categories: hardware-based methods, model-based methods, and data-driven methods, each offering distinct advantages and facing specific limitations, as summarized in Table 4.
Hardware-based methods detect physical manifestations of leakage by deploying specialized field instruments, such as acoustic sensors, pressure loggers, flow meters, ground-penetrating radar, and vibration detectors [3,63]. Among these, acoustic-based techniques are the most widely used due to their ability to capture sound waves generated by pressurized water escaping through pipe defects. Acoustic emission methods [13], which rely on elastic waves released by leaking fluid, enable the identification and localization of leaks by analyzing signal strength and propagation characteristics along the pipeline. These approaches are particularly effective for direct and localized leak detection in critical zones, although their accuracy may be compromised by environmental noise, pipe material variability, and accessibility constraints. Additionally, their implementation often involves substantial capital and maintenance costs.

Table 4.
Prevailing methodologies for leakage detection approaches.
Table 4.
Prevailing methodologies for leakage detection approaches.
| Category | Subcategory | Typical Techniques | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware-Based | Acoustic Methods [13] | Hydrophones, correlators | High accuracy in localization; Effective for metallic pipes | Affected by environmental noise; Less effective in plastic pipes |
| Hardware-Based | Pressure/Flow Sensors [30] | Pressure loggers, inline flow meters | Real-time monitoring; Suitable for transient analysis | High installation cost; Require dense sensor deployment |
| Hardware-Based | Advanced Sensing [13] | Ground-penetrating radar, fiber-optic cables, vibration sensors | Non-invasive; Applicable in inaccessible areas | Expensive; Limited by depth, soil and pipe material |
| Model-Based | Hydraulic Modeling [64] | EPANET | System-level analysis; Capable of simulating various scenarios | Require detailed and accurate network model |
| Model-Based | Inverse Modeling [65] | Pressure and flow residual analysis, parameter calibration | Can locate leak zones; Integrate with SCADA data | Sensitive to boundary conditions and demand uncertainty |
| Model-Based | Data Assimilation [65] | Kalman filter, particle filter, model predictive control | Combine models with real-time data; Improve forecast accuracy | Computationally intensive; Complex implementation |
| Data-Driven | Supervised Learning [66] | SVM, RF, Decision Trees | Easy to train; High accuracy with labeled data | Require labeled historical data; Limited generalization |
| Data-Driven | Deep Learning [67] | LSTM, GRU, Autoencoders, CNN | Handle nonlinear and temporal patterns; Highly scalable | Black-box models; High data and computation demands |
Model-based leakage detection relies on hydraulic or hydrodynamic simulation models to represent the expected behavior of a water distribution system under normal conditions [64,65]. Leakage is identified by detecting discrepancies between simulated and observed variables, such as pressure and flow rate at specific locations. Tools like EPANET are commonly used in this domain, often integrated with calibration routines, sensitivity analysis, and inverse modeling techniques to improve detection accuracy. Nevertheless, their effectiveness is highly dependent on the accuracy and completeness of the input data, including network topology, demand patterns, and boundary conditions.
The increasing adoption of IoT devices and smart metering technologies in water distribution networks has enabled the development of data-driven approaches for leakage detection. These methods apply AI and ML algorithms to identify anomalies in both historical and real-time operational data. Commonly employed techniques include SVM, RF, LSTM networks, autoencoders, and classical statistical time series models [66,67]. Data-driven methods are particularly advantageous for large-scale systems as they are capable of processing noisy, nonlinear, and high-dimensional datasets. Their scalability and adaptability make them promising tools for complex network environments.
Beyond detecting leakage events after they occur, modern water utilities are increasingly interested in identifying early-stage faults and failures that may precede more severe anomalies [12,68]. This includes detecting subtle changes in operational behavior that suggest pipe material degradation, valve malfunction, or declining pump efficiency [69]. Early fault detection techniques focus on recognizing small but systematic deviations in parameters such as pressure, flow, and energy usage. By identifying faults before they evolve into significant leakage events, water utilities can implement condition-based maintenance strategies, reduce emergency repair costs, and extend infrastructure lifespan.
Generally, leakage detection represents a key applied technology for managing hydraulic anomalies in WDNs. It targets various forms of leakage, including background losses, hidden underground leaks, and visible pipe bursts, through a combination of hardware-based sensing, model-based simulations, and data-driven analytics. Each approach has distinct strengths and limitations, and their integration can significantly enhance the accuracy and timeliness of leak identification. More recently, the focus has shifted toward early fault detection, enabling proactive maintenance and further improving system reliability and energy efficiency.
8. Case Study and SWOT Analysis
Recent advances in smart technologies have significantly improved the capacity of WDNs to manage hydraulic anomalies and optimize energy use. Nevertheless, scaling up these solutions remains challenging due to technical limitations, data constraints, and operational complexities. To better understand their practical applicability, this section presents a real-world case study of D City’s WDN and conducts a structured SWOT analysis. The goal is to assess current capabilities and identify key enablers and barriers to the broader adoption of energy-efficient management strategies.
8.1. Energy-Efficient Management of D City’s WDN Under Hydraulic Anomalies
8.1.1. Basic Technologies: Data Acquisition and Hydraulic Modelling
Taking D City in southern China as a representative case, a comprehensive hydraulic model was developed to support the analysis of its urban WDN, as shown in Figure 2. The modeled network spans an area of 3406 km2 and supplies water to approximately 300,000 residents. As of 2024, a complete survey was conducted for pipelines with diameters of DN300 and above. The city’s water supply infrastructure consists of two clear water reservoirs and four operational pumps located in the main water treatment plant. The plant delivers water through two primary outlet pipelines (DN1000 and DN1200), with a total supply capacity of 100,000 m3/day. The system integrates 22 pressure monitoring points, including newly installed sensors in 2024, as well as 105 flow monitoring points that cover both large consumers and DMA inlets.
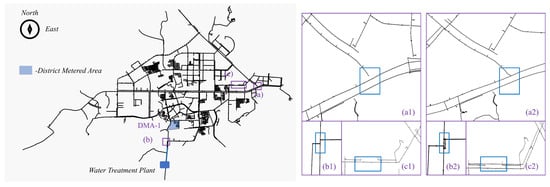
Figure 2.
Hydraulic model and bottleneck locations in D City’s WDN: (a) pipe disconnection; (b) bottleneck pipe; (c) pipe disconnection.
Hydraulic simulation and analysis of the network revealed three key bottleneck areas that limit operational efficiency and pressure balance. These critical sections, requiring urgent optimization and capacity enhancement, are highlighted in Figure 2. A comparative analysis was conducted using the hydraulic model to assess pressure, flow, and head loss before and after the proposed improvements. The simulation results are summarized in Table 5, demonstrating significant enhancements in hydraulic performance following targeted interventions.

Table 5.
Comparison of hydraulic parameters before and after bottleneck renovation.
For Pipeline a, located at the outlet of the water treatment plant, the original system design incorporated two parallel pipelines to accommodate high flow demands and maintain operational redundancy. However, due to system constraints, the configuration was reduced to a single functioning pipeline. This change led to significantly increased flow velocities and head losses, thereby exacerbating mechanical stress within the pipe and elevating the risk of structural failure, such as bursts or leaks. Through the reinstatement of the dual-pipe configuration, the hydraulic load was more evenly distributed, resulting in a substantial reduction in head loss. This intervention not only stabilized pressure fluctuations at the source but also led to a measurable decline in energy consumption associated with water transport, thereby enhancing overall network efficiency.
In the case of Pipeline b, the construction of an additional DN600 pipeline markedly improved the local conveyance capacity. The new infrastructure effectively alleviated hydraulic bottlenecks, reducing the head loss in the existing pipe by approximately 3.87 m. This improvement translated into a more balanced flow distribution and a significant gain in energy efficiency, particularly during peak demand periods. Likewise, Pipeline c benefited from the installation of a DN500 pipeline in parallel with the original conduit. This upgrade resulted in a 0.15-m decrease in head loss, contributing to localized pressure relief and improved hydraulic performance within the surrounding subnetwork.
Collectively, these engineering interventions demonstrate a comprehensive approach to hydraulic optimization within D City’s water distribution network. By mitigating frictional losses and redistributing flow more effectively, the system achieves measurable energy savings. From a broader perspective, these upgrades support the sustainable operation of the water infrastructure by extending asset lifespan, reducing maintenance frequency, and minimizing environmental and financial impacts over time.
8.1.2. Applied Technologies: Pressure Regulation and Leakage Detection
- (1)
- Valve Optimization
DMA-1, located closest to the water treatment plant, experiences elevated water pressure due to its low topographic elevation. As shown in Figure 3, At 1:00 a.m., during low-demand periods, the average network pressure peaks at 39 m. This condition leads to excessive leakage (over 25% by mass balance analysis) and user complaints of high tap pressure, which increases energy consumption and risk of infrastructure failure.
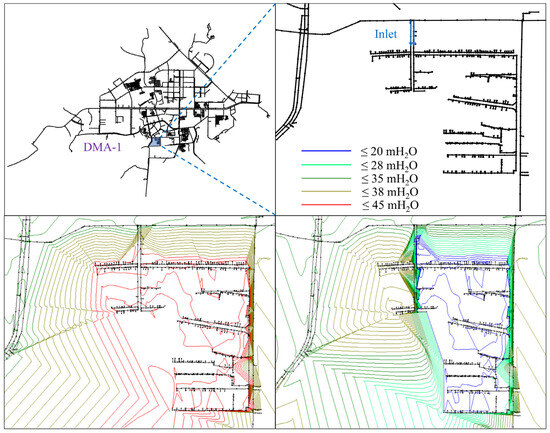
Figure 3.
Valve regulation in DMA-1 for pressure control.
To address this, the inlet gate valve was adjusted, reducing its opening by 50%. Simulation results showed a pressure drop from 39 m to 25 m, which is still sufficient for end-user demands but much safer and more efficient. Using a pressure leakage exponent of 0.5, the background leakage was estimated to decline by approximately 19.94%, indicating notable water and energy savings.
- (2)
- Leakage detection
A model-based leakage detection strategy was implemented using the Darwin Calibrator module within WATERGEMS, targeting high-pressure zones identified through hydraulic simulations. These areas, visually represented in red and yellow in Figure 4(S1), were prioritized due to their elevated risk of leakage under pressure anomalies. To locate potential leak points, artificial demand increments of 10% were systematically applied to each node within the suspect areas. The resulting simulated pressures were then compared with actual field measurements obtained from pressure sensors. The node exhibiting the smallest deviation between simulated and observed values was flagged as the most probable leak location.
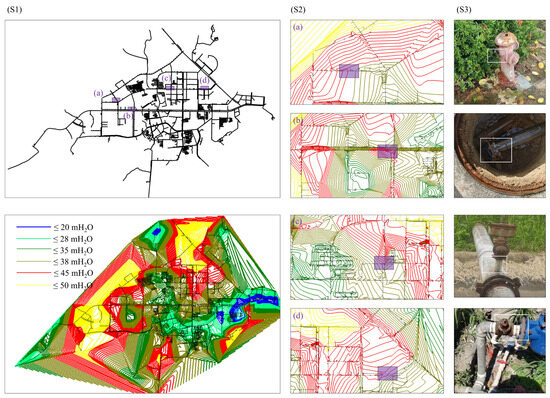
Figure 4.
Model-based leakage detection and field validation: (S1) Simulation results; (S2) Four identified leakage locations (purple boxes); (S3) Field-validated leakage points (white boxes); (a) Leaking hydrant; (b) Pipeline rupture inside a valve chamber; (c) Joint leak between interconnected pipes; (d) Joint leak between interconnected pipes.
This analytical method led to the successful identification of four actual leakage sites, which were subsequently verified through field inspections conducted between June and December 2024. As shown in Figure 4(S2), the confirmed leak locations were highlighted in purple within the hydraulic model. Corresponding field photographs of these leak sites are presented in Figure 4(S3), illustrating various types of failures including a leaking hydrant, a pipeline rupture within a valve chamber, and two joint leaks between interconnected pipes.
The integration of model-based analytics with on-site verification not only improved leak detection accuracy but also enabled timely maintenance interventions. These efforts contributed to enhanced water conservation, improved pressure regulation, and reduced energy losses, underscoring the effectiveness of combining hydraulic modeling with practical field operations in the context of intelligent water distribution network management.
8.2. SWOT Analysis
- (1)
- Strengths
The ongoing advancement of smart technologies has endowed WDNs with several intrinsic strengths that facilitate energy-efficient operation under hydraulic anomalies. A prominent example is the digital twin, a powerful tool for real-time system monitoring, predictive modeling, and decision support, functioning as a dynamic virtual replica of the physical water network [8,27]. By integrating IoT-based sensors and AI-driven analytics, digital twins can provide high-fidelity simulations that reflect the current state of the network and forecast future behavior under different operational scenarios [29,70]. However, several technical challenges remain. These include difficulties in integrating heterogeneous models (e.g., hydraulic, data-driven, and control models), maintaining real-time synchronization with physical assets, and scaling digital twin frameworks across complex and geographically distributed systems [39]. To overcome these issues, future research can focus on the development of open, modular architectures that support interoperability, real-time computation, and seamless data integration. Embedding AI capabilities into digital twins can further enhance their utility in anomaly detection, leak localization, and predictive maintenance.
Effective pressure management is essential for reducing leakage, extending infrastructure lifespan, and minimizing energy consumption in WDNs. Traditional approaches typically rely on global regulation through pump scheduling and PRVs. However, these methods may not be sufficient to handle localized pressure anomalies or dynamic demand variations. A more comprehensive strategy combines global optimization with local pressure control [53,57]. This includes the joint optimization of pumps and valves for system-wide regulation, along with localized devices, such as fixed pressure tanks, mobile pressure regulation vehicles, or local booster stations to address area-specific requirements [53,71].
- (2)
- Weaknesses
The effectiveness of AI-driven optimization and anomaly detection in WDNs is heavily influenced by the quality and completeness of the underlying data. Despite the increasing deployment of SCADA systems, IoT-enabled smart meters, and pressure sensors, real-world datasets often suffer from significant quality issues. One of the most critical challenges is data incompleteness, which may result from sensor malfunctions, communication errors, power outages, or maintenance activities [72,73]. These data gaps can reduce model accuracy, hinder the detection of abnormal patterns, and ultimately compromise the reliability of decision-making processes. Moreover, missing data disrupt the temporal continuity necessary for training and validating machine learning models.
Optimizing hydraulic performance in large-scale WDNs requires handling high-dimensional simulations and complex decision-making processes. These tasks are often computationally demanding, especially when rapid or real-time responses are needed.
Traditional simulation tools like EPANET operate in an extended-period simulation mode, where hydraulic computations at each time step are treated independently [74,75]. This means that the system’s dynamic behavior is not continuously modeled, which limits the ability to accurately capture transient interactions across time steps. Digital twin models often require more detailed input parameters, such as time-varying demand patterns, valve operations, pump schedules, and sensor feedback, which significantly increases the model’s complexity and the computational burden [8,27]. AI-based approaches, including deep learning and reinforcement learning, have the potential to support optimization and anomaly detection in such complex environments. However, these models typically demand large computational resources and can be time-consuming to train and deploy, especially in large and dynamic networks [76]. As a result, there is a trade-off between model accuracy and computational efficiency, particularly when deploying these systems in large-scale and dynamic networks.
- (3)
- Opportunities
Accurate and timely data acquisition is fundamental to the effective management of intelligent WDNs. However, many existing systems face challenges such as insufficient sensor coverage, suboptimal placement, and inconsistent data quality [77,78]. Advanced placement methodologies, such as sensitivity analysis, information entropy-based techniques, and graph-theoretic models, provide systematic approaches for identifying the most informative locations for sensor installation [79,80]. In parallel with deployment optimization, ensuring the reliability of data transmission from these monitoring points is equally important. This necessitates the use of robust communication technologies, including NB-IoT and 5G communication protocols, which are capable of supporting long-distance transmission, low latency, and high data integrity [26]. These technologies are crucial for ensuring stable and continuous data flow from spatially distributed sensors to centralized control systems, particularly in complex urban and subterranean environments.
In WDNs, excess hydraulic pressure, which is typically dissipated through PRVs, represents a significant source of untapped energy. The integration of pumps as turbines (PATs) enables the recovery of this surplus energy in a cost-effective manner by converting pressure losses into electricity [81,82]. Owing to their adaptability to variable flow conditions, low cost, and ease of deployment, PATs are well suited for application in urban WDNs. In addition to energy recovery, PATs assist in pressure regulation, contribute to leakage reduction, and enhance system resilience. When integrated with smart grid technologies, the recovered energy can support demand-responsive power use. Therefore, PAT-based energy recovery offers a sustainable and scalable approach to improving both energy efficiency and operational sustainability in WDNs.
- (4)
- Threats
The implementation of AI-enhanced control systems, digital twins, and smart sensing technologies in WDNs involves considerable financial costs. High initial investments are required to deploy IoT sensors, system integration, and upgrades to existing infrastructure. In addition, ongoing maintenance, data management, and the need for trained technical personnel contribute to long-term operational expenses. These economic constraints pose significant challenges to the large-scale and sustainable adoption of intelligent technologies in WDNs, particularly for utilities with limited budgets and technical capacity. These economic constraints are particularly challenging for utilities in developing regions or small- to medium-sized cities with limited budgets and infrastructure resilience.
In addition to financial barriers, operational uncertainties also pose significant challenges. Accurate water demand forecasting is essential for the efficient operation of water distribution networks, including tasks such as pump scheduling, pressure control, and energy management. However, demand is influenced by a variety of dynamic and external factors, such as climate variability, irregular rainfall, extreme temperatures, urban development, population shifts, and changes in user behavior caused by policies or economic conditions [43,83]. This complexity poses a challenge for conventional forecasting models and increases the need for more flexible and data-driven approaches.
9. Conclusions
This review highlights the critical role of hydraulic anomaly management in enhancing energy efficiency, operational reliability, and sustainability in WDNs. The integration of real-time monitoring technologies, predictive modeling, AI-driven optimization, and digital twin frameworks has significantly improved the detection of hydraulic anomalies, pressure regulation, and energy consumption optimization.
However, several key challenges must be addressed to fully harness the potential of these advanced technologies. Data integration remains a fundamental issue due to the fragmented nature of existing systems, including SCADA platforms, IoT-based sensor networks, and hydraulic simulation tools. Ensuring the seamless flow of high-quality, real-time data across these components is essential. In addition, as optimization models grow increasingly complex, maintaining computational efficiency becomes critical, requiring a careful trade-off between model accuracy and real-time applicability. The scalability and high implementation costs of AI-based systems also present barriers, particularly for utilities with constrained financial and technical capacities. Furthermore, uncertainties in water demand forecasting, which result from climate variability, urban development, and changing consumption patterns, continue to challenge the reliability of operational planning.
To overcome these barriers, future research should focus on developing self-learning AI models capable of dynamically adapting to evolving system conditions. Enhancing the interoperability of digital twin platforms will be essential to seamlessly integrate hydraulic simulations, optimization algorithms, and real-time control strategies. Moreover, the incorporation of renewable energy sources, such as micro-hydropower systems for in-network energy recovery, can further enhance the sustainability of water distribution system operations. The adoption of hybrid optimization frameworks that combine AI-based methods with rule-based heuristics may also offer robust, interpretable, and computationally efficient solutions.
By addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging technologies, the next generation of water distribution systems can evolve into more resilient, energy-efficient, and environmentally sustainable infrastructures. Realizing this vision will require coordinated efforts among academic researchers, industry practitioners, and policymakers to transform conventional water systems into intelligent, data-driven networks capable of meeting the complex demands of future urban environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.G. and B.D.; methodology, H.C. and B.D.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D.; writing—review and editing, S.H.; supervision, H.C. and S.H.; project administration, J.G. and H.C.; funding acquisition, J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by several funding sources: National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3203804); Key Research and Development Program of Heilongjiang Province of China, grant number 2022ZX01A06; State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resource & Environment (Harbin Institute of Technology), (No. 2024TS26); Collaborative Innovation Achievement Project of Heilongjiang Province’s “double world-class project” Disciplines, grant number LJGXCG2023-018.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which greatly improved the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The abbreviations used in this manuscript:
| Full Name | Abbreviation | Full Name | Abbreviation |
| water distribution networks | WDNs | variable-speed pumps | VSPs |
| Internet of Things | IoT | Best Efficiency Point | BEP |
| supervisory control and data acquisition | SCADA | throttling control | TC |
| advanced metering infrastructure | AMI | bypass control | BC |
| artificial intelligence | AI | fixed-speed pump scheduling | FSPS |
| machine learning | ML | affinity law-based speed regulation | ALSR |
| long short-term memory | LSTM | linear programming | LP |
| convolutional neural networks | CNNs | variable frequency drives | VFDs |
| district metered area | DMA | mixed-integer nonlinear programming | MINLP |
| non-revenue water | NRW | sequential quadratic programming | SQP |
| Narrowband IoT | NB-IoT | genetic algorithms | GA |
| fifth-generation | 5G | particle swarm optimization | PSO |
| United States Environmental Protection Agency | EPA | artificial neural networks | ANNs |
| autoregressive integrated moving average | ARIMA | reinforcement learning | RL |
| random forests | RF | multi-agent systems | MAS |
| support vector machine/regression | SVM/SVR | pressure-reducing valves | PRVs |
| recurrent neural networks | RNNs | Computational Fluid Dynamics | CFD |
| Gated Recurrent Units | GRUs | pumps as turbines | PATs |
References
- Coelho, B. Efficiency Achievement in Water Supply Systems—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, R.K.; Salman, A.M.; Li, Y.; Yu, X. Asset Management Decision Support Model for Water Distribution Systems: Impact of Water Pipe Failure on Road and Water Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, E.; Shahrour, I. Water Leak Detection: A Comprehensive Review of Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions. Water 2024, 16, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Sousa, J.; Marques, A.S. Influence of Future Water Demand Patterns on the District Metered Areas Design and Benefits Yielded by Pressure Management. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraka, D.; Kruszyński, W.; Tyniec, J.; Gwoździej-Mazur, J.; Kaźmierczak, B. Practical Aspects of the Energy Efficiency Evaluation of a Water Distribution Network Using Hydrodynamic Modeling—A Case Study. Energies 2023, 16, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Savic, D.; Butler, D. Making Waves: Towards Data-Centric Water Engineering. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hong, T.; Kang, C. Review of Smart Meter Data Analytics: Applications, Methodologies, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3125–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.M.; Morani, M.C.; Carravetta, A.; Fecarrotta, O.; Adeyeye, K.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. New Challenges towards Smart Systems’ Efficiency by Digital Twin in Water Distribution Networks. Water 2022, 14, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounce, S.R.; Boxall, J.B.; Machell, J. Development and Verification of an Online Artificial Intelligence System for Detection of Bursts and Other Abnormal Flows. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 136, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, X. Short-Term Water Demand Forecast Based on Deep Learning Method. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Lansey, K.E. Convolutional Neural Network for Burst Detection in Smart Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 3729–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, R.K.; Salman, A.M.; Li, Y.; Yu, X. Reliability Analysis of Water Distribution Systems Using Physical Probabilistic Pipe Failure Method. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 04018097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.K.; Chin, C.S.; Zhong, X. Review of Current Technologies and Proposed Intelligent Methodologies for Water Distributed Network Leakage Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 78846–78867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpak, D. Method for Determining the Probability of a Lack of Water Supply to Consumers. Energies 2020, 13, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Sá Marques, A.; Sousa, J. Identification of the Optimal Entry Points at District Metered Areas and Implementation of Pressure Management. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, T.; Ribau, J.; Figueiredo, D.; Alves, R. Improving Energy Efficiency in Water Supply Systems with Pump Scheduling Optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Pei, J.; Pavesi, G.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W. Application of Intelligent Methods in Energy Efficiency Enhancement of Pump System: A Review. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11592–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, K.; Bergant, A.; Stosiak, M.; Deptuła, A.; Karpenko, M.; Kubrak, M.; Kodura, A. Water Hammer Simulation Using Simplified Convolution-Based Unsteady Friction Model. Water 2022, 14, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, J.R.; Stoner, M.A.; Hunt, W.A. Water Hammer: Causes and Effects. J. AWWA 1984, 76, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Washali, T.M.; Sharma, S.K.; Kennedy, M.D. Alternative Method for Nonrevenue Water Component Assessment. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisi, A.; Forsyth, M.; Naser, G. Water Distribution Systems Reliability: A Review of Research Literature. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.J.; Muhammed, A.B.; Subramaniam, S.K.; Abdullah, A.; Silva, R.M.; Akram, O.K. A Review on Current and Old SCADA Networks Applied to Water Distribution Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 First International Conference of Intelligent Computing and Engineering (ICOICE), Hadhramout, Yemen, 15–16 December 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dobriceanu, M.; Bitoleanu, A.; Popescu, M.; Enache, S.; Subtirelu, E. SCADA System for Monitoring Water Supply Networks. WTOS 2008, 7, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Kuhanestani, P.K.; Farmani, R.; Keedwell, E. Literature Review of Data Analytics for Leak Detection in Water Distribution Networks: A Focus on Pressure and Flow Smart Sensors. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 03122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Lansey, K.E. Comparison of AMI and SCADA Systems for Leak Detection and Localization in Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, N.K.; Pradeep, P.; Rao, S.N.; Devidas, A.R.; Ramesh, M.V. IoT-Enabled Water Distribution Systems—A Comparative Technological Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 101042–101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.M.; Kuriqi, A.; Besharat, M.; Creaco, E.; Tasca, E.; Coronado-Hernández, O.E.; Pienika, R.; Iglesias-Rey, P. Smart Water Grids and Digital Twin for the Management of System Efficiency in Water Distribution Networks. Water 2023, 15, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCarlo, M.F.; Berglund, E.Z. Using Advanced Metering Infrastructure Data to Evaluate Consumer Compliance with Water Advisories during a Water Service Interruption. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousso, B.Z.; Lambert, M.; Gong, J. Smart Water Networks: A Systematic Review of Applications Using High-Frequency Pressure and Acoustic Sensors in Real Water Distribution Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 410, 137193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Azam, S.; Shanmugam, B.; Mathur, D. A Review on Current Technologies and Future Direction of Water Leakage Detection in Water Distribution Network. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 107177–107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominola, A.; Giuliani, M.; Piga, D.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.E. Benefits and Challenges of Using Smart Meters for Advancing Residential Water Demand Modeling and Management: A Review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 72, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A. An Overview of EPANET Version 3.0. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis, Tucson, AZ, USA, 12–15 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Authors: Klise, K.A. An Overview of the Water Network Tool for Resilience (WNTR): (075). In Proceedings of the WDSA/CCWI Joint Conference Proceedings, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, 23–25 July 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Karpenko, M.; Stosiak, M.; Šukevičius, Š.; Skačkauskas, P.; Urbanowicz, K.; Deptuła, A. Hydrodynamic Processes in Angular Fitting Connections of a Transport Machine’s Hydraulic Drive. Machines 2023, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filo, G.; Lisowski, E.; Rajda, J. Design and Flow Analysis of an Adjustable Check Valve by Means of CFD Method. Energies 2021, 14, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.W.; Van Bloemen Waanders, B.G. High Fidelity Computational Fluid Dynamics for Mixing in Water Distribution Systems. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium 2006, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 March 2006; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.R.A.; Pu, J.H.; Hanmaiahgari, P.R.; Lambert, M.F. Insights into CFD Modelling of Water Hammer. Water 2023, 15, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalgham, W.R.; Seibi, A.C.; Boukadi, F. Simulation of Leak Noise Propagation and Detection Using COMSOL Multiphysics. In Proceedings of the Volume 14: Emerging Technologies; Materials: Genetics to Structures; Safety Engineering and Risk Analysis, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–17 November 2016; p. V014T07A030. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, E.Z.; Shafiee, M.E.; Xing, L.; Wen, J. Digital Twins for Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2023, 149, 02523001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhong, D.; Deng, L.; Ou, C.; Xin, P. An Innovative Hourly Water Demand Forecasting Preprocessing Framework with Local Outlier Correction and Adaptive Decomposition Techniques. Water 2021, 13, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Long, T.; Xiong, J.; Bai, Y. Multiple Random Forests Modelling for Urban Water Consumption Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4715–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebode, O.; Ighravwe, D.E. Urban Water Demand Forecasting: A Comparative Evaluation of Conventional and Soft Computing Techniques. Resources 2019, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zheng, F.; Tao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kapelan, Z. Hourly and Daily Urban Water Demand Predictions Using a Long Short-Term Memory Based Model. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 05020017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y. Anomaly Detection and Classification in Water Distribution Networks Integrated with Hourly Nodal Water Demand Forecasting Models and Feature Extraction Technique. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, J. Performance of Combined Double Seasonal Univariate Time Series Models for Forecasting Water Demand. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, J.F. Peak Daily Water Demand Forecast Modeling Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfei, A.; Brentan, B.M.; Menapace, A.; Righetti, M.; Herrera, M. Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks for Water Demand Forecasting. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR032299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Kapelan, Z. Adaptive Water Demand Forecasting for near Real-Time Management of Smart Water Distribution Systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 60, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, D.J.; Garrote, L.; Sánchez, R.; Santillán, D. Pressure Management in Water Distribution Systems: Current Status, Proposals, and Future Trends. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04015061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimorelli, L.; Covelli, C.; Molino, B.; Pianese, D. Optimal Regulation of Pumping Station in Water Distribution Networks Using Constant and Variable Speed Pumps: A Technical and Economical Comparison. Energies 2020, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Gao, M.; He, S. A Review of the Flow-Induced Noise Study for Centrifugal Pumps. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhong, D.; Wu, R.; Liu, L. Real-Time Scheduling of Pumps in Water Distribution Systems Based on Exploration-Enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning. Systems 2023, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhong, D. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework for Real-Time Scheduling of Pump and Valve in Water Distribution Networks. Water Supply 2023, 23, 2833–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, P.W.; Germanopoulos, G. Optimal Pump Scheduling in Water-Supply Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1992, 118, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhao, A.; Zhou, W.; Xu, H.; Wu, D. Improving Reliability of Pumps in Parallel Pump Systems Using Particle Swam Optimization Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58427–58434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Lucken, C.; Baran, B.; Sotelo, A. Pump Scheduling Optimization Using Asynchronous Parallel Evolutionary Algorithms. CLEI Electron. J. 2004, 7, 2:1–2:20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yu, T.; Chu, S.; Liu, X. Leakage Control and Energy Consumption Optimization in the Water Distribution Network Based on Joint Scheduling of Pumps and Valves. Energies 2019, 12, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Ballesteros, A.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, D.; Perea-Moreno, A.-J. Advances in Leakage Control and Energy Consumption Optimization in Drinking Water Distribution Networks. Energies 2022, 15, 5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bokde, N.; Kulat, K.; Yaseen, Z.M. Nodal Matrix Analysis for Optimal Pressure-Reducing Valve Localization in a Water Distribution System. Energies 2020, 13, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa Bui, X.; Marlim, M.S.; Kang, D. Water Network Partitioning into District Metered Areas: A State-Of-The-Art Review. Water 2020, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Rauch, W. Automated Creation of District Metered Area Boundaries in Water Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Greco, R.; Santonastaso, G.F. Weighted Spectral Clustering for Water Distribution Network Partitioning. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2017, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, M.; Kammoun, A.; Abid, M. Leak Detection Methods in Water Distribution Networks: A Comparative Survey on Artificial Intelligence Applications. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2022, 13, 04022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Sage, P.; Turtle, D. Pressure-Dependent Leak Detection Model and Its Application to a District Water System. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 136, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kulat, K.D. A Selective Literature Review on Leak Management Techniques for Water Distribution System. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3247–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Tan, D.; Shen, D. Review of Model-Based and Data-Driven Approaches for Leak Detection and Location in Water Distribution Systems. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3282–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Pan, H. Leak Detection and Location Based on ISLMD and CNN in a Pipeline. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30457–30464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, P.W.; Xu, C. Predicting Pipe Failure Effects in Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1993, 119, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Farmani, R.; Keedwell, E. Gradual Leak Detection in Water Distribution Networks Based on Multistep Forecasting Strategy. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, S.A.; Maiolo, M.; Brusco, A.C.; Turco, M.; Pirouz, B.; Greco, E.; Spezzano, G.; Piro, P. Smart Technologies for Water Resource Management: An Overview. Sensors 2022, 22, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, K.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Deng, L.; Xin, P. Innovative Water Supply Network Pressure Management Method—The Establishment and Application of the Intelligent Pressure-Regulating Vehicle. Energies 2022, 15, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Yu, T.; Shao, Y. Dealing with Data Missing and Outlier to Calibrate Nodal Water Demands in Water Distribution Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfei, A.; Menapace, A.; Brentan, B.M.; Righetti, M. How Does Missing Data Imputation Affect the Forecasting of Urban Water Demand. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, D.; Suribabu, C.R.; Filion, Y. Method for Extended Period Simulation of Water Distribution Networks with Pressure Driven Demands. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, R.; Gorev, N.B.; Kodzhespirova, I.F.; Kovalenko, Y.; Negrete, S.; Ramos, A.; Rivera, J.J. Pseudotransient Continuation Method in Extended Period Simulation of Water Distribution Systems. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Jin, Y.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Z.; Butler, D. The Role of Deep Learning in Urban Water Management: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scozzari, A.; Mounce, S.; Han, D.; Soldovieri, F.; Solomatine, D. (Eds.) ICT for Smart Water Systems: Measurements and Data Science; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 102, ISBN 978-3-030-61972-5. [Google Scholar]
- Aral, M.M.; Guan, J.; Maslia, M.L. Optimal Design of Sensor Placement in Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 136, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wan, X.; Liu, S.; Su, K.; Wang, W.; Farmani, R. An All-Purpose Method for Optimal Pressure Sensor Placement in Water Distribution Networks Based on Graph Signal Analysis. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X. A Review of Graph and Complex Network Theory in Water Distribution Networks: Mathematical Foundation, Application and Prospects. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, M.; Alvisi, S.; Simani, S.; Manservigi, L. Energy Production by Means of Pumps As Turbines in Water Distribution Networks. Energies 2017, 10, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; Del Giudice, G.; Fecarotta, O.; Ramos, H. PAT Design Strategy for Energy Recovery in Water Distribution Networks by Electrical Regulation. Energies 2013, 6, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, R.; Ortiz-Caraballo, C.; Preciado, J.C.; Conejero, J.M.; Sánchez Figueroa, F.; Rubio-Largo, A. A Short-Term Data Based Water Consumption Prediction Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).